Steering CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 88 of 2339

WHEEL ALIGNMENT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
DESCRIPTION - WHEEL ALIGNMENT.......47
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SUSPENSION
AND STEERING......................50
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WHEEL
ALIGNMENT.........................52STANDARD PROCEDURE - CURB HEIGHT
MEASUREMENT......................55
SPECIFICATIONS
WHEEL ALIGNMENT...................56
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
DESCRIPTION - WHEEL ALIGNMENT
Vehicle wheel alignment is the positioning of all
interrelated front and rear suspension angles. These
angles affect the handling and steering of the vehicle
when it is in motion. Proper wheel alignment is
essential for efficient steering, good directional stabil-
ity, and proper tire wear.
The method of checking a vehicle's front and rear
wheel alignment varies depending on the manufac-
turer and type of equipment used. The manufactur-
er's instructions should always be followed to ensure
accuracy of the alignment, except when
DaimlerChrysler Corporation's wheel alignment spec-
ifications differ.
On this vehicle, the suspension angles that can be
adjusted are as follows:
²Front Camber (with camber bolt package and
standard procedure)
²Front Toe
Check the wheel alignment and make all wheel
alignment adjustments with the vehicle standing at
its proper curb height specification. Curb height is
the normal riding height of the vehicle. It is mea-
sured from a certain point on the vehicle to the
ground or a designated area while the vehicle is sit-
ting on a flat, level surface. Refer to Curb Height
Measurement in this section for additional informa-
tion.
Typical wheel alignment angles and measurements
are described in the following paragraphs.
CAMBER
Camber is the inward or outward tilt of the top of
the tire and wheel assembly (Fig. 1). Camber is mea-
sured in degrees of angle relative to a true vertical
line. Camber is a tire wearing angle.
²Excessive negative camber will cause tread wear
at the inside of the tire.²Excessive positive camber will cause tread wear
on the outside of the tire.
Fig. 1 Camber
1 - WHEELS TILTED OUT AT TOP
2 - WHEELS TILTED IN AT TOP
RSWHEEL ALIGNMENT2-47
Page 90 of 2339

TOE-OUT ON TURNS
Toe-out on turns is the relative positioning of the
front wheels while steering through a turn (Fig. 4).
This compensates for each front wheel's turning
radius. As the vehicle encounters a turn, the out-
board wheel must travel in a larger radius circle
than the inboard wheel. The steering system is
designed to make each wheel follow its particular
radius circle. To accomplish this, the front wheels
must progressively toe outward as the steering is
turned from center. This eliminates tire scrubbing
and undue tire wear when steering a vehicle through
a turn.
DYNAMIC TOE PATTERN
Dynamic toe pattern is the inward and outward toe
movement of the front and rear tires through the
suspension's jounce and rebound travel. As the vehi-
cle's suspension moves up and down, the toe pattern
varies. Toe pattern is critical in controlling the direc-
tional stability of the vehicle while in motion. Front
and rear dynamic toe pattern is preset by the factory
at the time the vehicle is assembled.
It is not necessary to check or adjust front or rear
dynamic toe pattern when doing a normal wheel
alignment. The only time dynamic toe pattern needs
to be checked or adjusted is if the frame of the vehi-
cle has been damaged.
STEERING AXIS INCLINATION (S. A. I.)
Steering axis inclination is the angle between a
true vertical line starting at the center of the tire at
the road contact point and a line drawn through the
center of the upper ball joint (or strut) and the lower
ball joint (Fig. 5). S.A.I. is built into the vehicle and
is not an adjustable angle. If S.A.I. is not within
specifications, a bent or damaged suspension compo-
nent may be the cause.
INCLUDED ANGLE (I. A.)
Included angle is the sum of the S.A.I. angle plus
or minus the camber angle, depending on whether or
not the wheel has positive or negative camber (Fig.
5). If camber is positive, add the camber angle to the
S.A.I. angle. If camber is negative, subtract the cam-
ber angle from the S.A.I. angle. Included angle is not
adjustable, but can be used to diagnose a frame mis-
alignment or bent suspension component (spindle,
strut).
Fig. 4 Toe-Out On Turns
1 - TOE-OUT ON TURNS
Fig. 5 S.A.I. and I.A.
1 - S.A.I.
2 - CAMBER
3 - I.A.
RSWHEEL ALIGNMENT2-49
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 91 of 2339
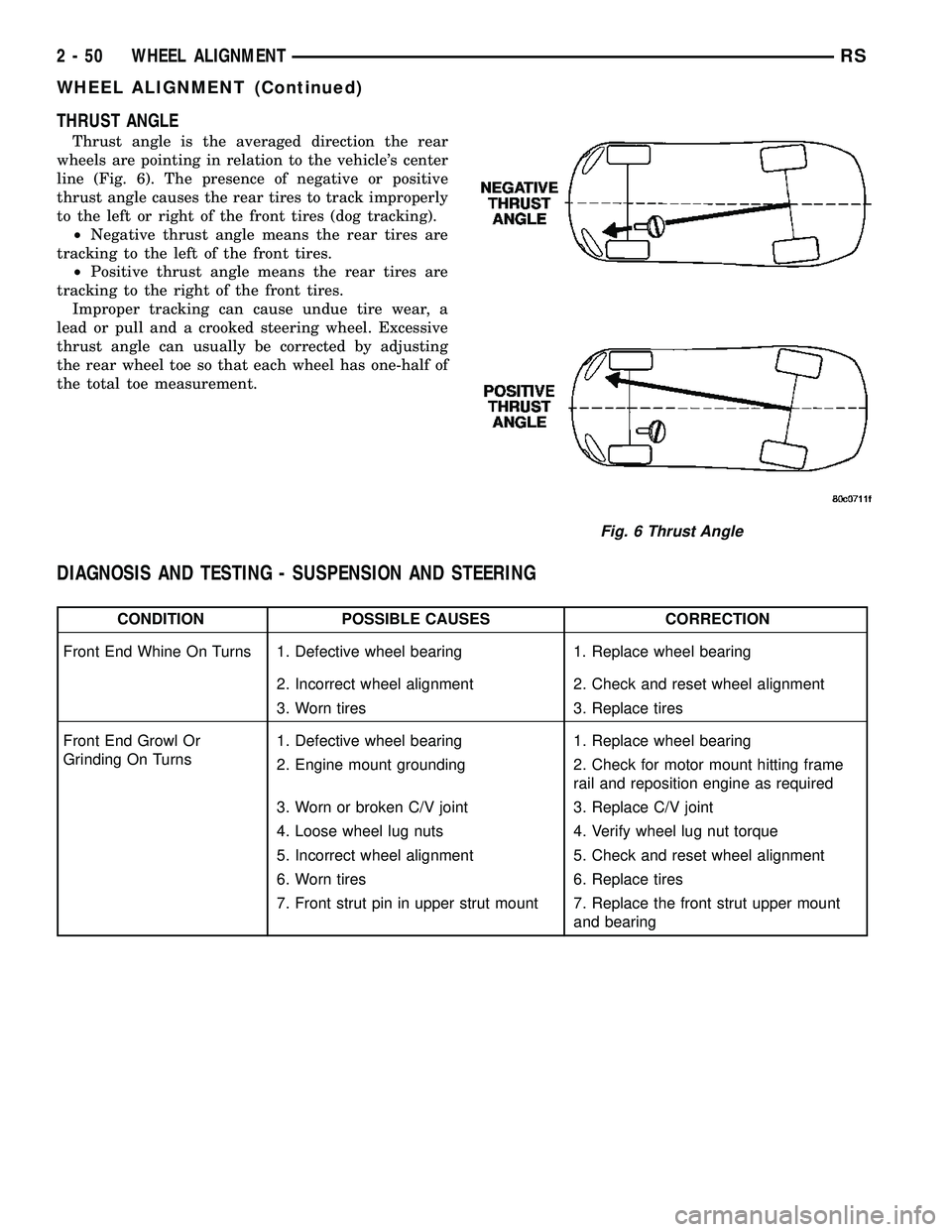
THRUST ANGLE
Thrust angle is the averaged direction the rear
wheels are pointing in relation to the vehicle's center
line (Fig. 6). The presence of negative or positive
thrust angle causes the rear tires to track improperly
to the left or right of the front tires (dog tracking).
²Negative thrust angle means the rear tires are
tracking to the left of the front tires.
²Positive thrust angle means the rear tires are
tracking to the right of the front tires.
Improper tracking can cause undue tire wear, a
lead or pull and a crooked steering wheel. Excessive
thrust angle can usually be corrected by adjusting
the rear wheel toe so that each wheel has one-half of
the total toe measurement.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SUSPENSION AND STEERING
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Front End Whine On Turns 1. Defective wheel bearing 1. Replace wheel bearing
2. Incorrect wheel alignment 2. Check and reset wheel alignment
3. Worn tires 3. Replace tires
Front End Growl Or
Grinding On Turns1. Defective wheel bearing 1. Replace wheel bearing
2. Engine mount grounding 2. Check for motor mount hitting frame
rail and reposition engine as required
3. Worn or broken C/V joint 3. Replace C/V joint
4. Loose wheel lug nuts 4. Verify wheel lug nut torque
5. Incorrect wheel alignment 5. Check and reset wheel alignment
6. Worn tires 6. Replace tires
7. Front strut pin in upper strut mount 7. Replace the front strut upper mount
and bearing
Fig. 6 Thrust Angle
2 - 50 WHEEL ALIGNMENTRS
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 92 of 2339
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Front End Clunk Or Snap
On Turns1. Loose lug nuts 1. Verify wheel lug nut torque
2. Worn or broken C/V joint 2. Replace C/V joint
3. Worn or loose tie rod 3. Tighten or replace tie rod end
4. Worn or loose ball joint 4. Tighten or replace ball joint
5. Worn/loose control arm bushing 5. Replace control arm bushing
6. Loose stabilizer bar. 6. Tighten stabilizer bar to specified
torque
7. Loose strut mount to body
attachment7. Tighten strut attachment to specified
torque
8. Loose crossmember bolts 8. Tighten crossmember bolts to
specified torque
Front End Whine With
Vehicle Going Straight At A
Constant Speed1. Defective wheel bearing 1. Replace wheel bearing
2. Incorrect wheel alignment 2. Check and reset wheel alignment
3. Worn tires 3. Replace tires
4. Worn or defective transaxle gears or
bearings4. Replace transaxle gears or bearings
Front End Growl Or
Grinding With Vehicle
Going Straight At A
Constant Speed1. Engine mount grounding 1. Reposition engine as required
2. Worn or broken C/V joint 2. Replace C/V joint
Front End Whine When
Accelerating Or
Decelerating1. Worn or defective transaxle gears or
bearings1. Replace transaxle gears or bearings
Front End Clunk When
Accelerating Or
Decelerating1. Worn or broken engine mount 1. Replace engine mount
2. Worn or defective transaxle gears or
bearings2. Replace transaxle gears or bearings
3. Loose lug nuts 3. Verify wheel lug nut torque
4. Worn or broken C/V joint 4. Replace C/V joint
5. Worn or loose ball joint 5. Tighten or replace ball joint
6. Worn or loose control arm bushing 6. Replace control arm bushing
7. Loose crossmember bolts 7. Tighten crossmember bolts to
specified torque
8. Worn tie rod end 8. Replace tie rod end
Road Wander 1. Incorrect tire pressure 1. Inflate tires to recommended pressure
2. Incorrect front or rear wheel toe 2. Check and reset wheel toe
3. Worn wheel bearings 3. Replace wheel bearing
4. Worn control arm bushings 4. Replace control arm bushing
5. Excessive friction in steering gear 5. Replace steering gear
6. Excessive friction in steering shaft
coupling6. Replace steering coupler
7. Excessive friction in strut upper
bearing7. Replace strut bearing
RSWHEEL ALIGNMENT2-51
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 93 of 2339
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Lateral Pull 1. Unequal tire pressure 1. Inflate all tires to recommended
pressure
2. Radial tire lead 2. Perform lead correction procedure
3. Incorrect front wheel camber 3. Check and reset front wheel camber
4. Power steering gear imbalance 4. Replace power steering gear
5. Wheel braking 5. Correct braking condition causing
lateral pull
Excessive Steering Free
Play1. Incorrect Steering Gear Adjustment 1. Adjust Or Replace Steering Gear
2. Worn or loose tie rod ends 2. Replace or tighten tie rod ends
3. Loose steering gear mounting bolts 3. Tighten steering gear bolts to specified
torque
4. Loose or worn steering shaft coupler 4. Replace steering shaft coupler
Excessive Steering Effort 1. Low tire pressure 1. Inflate all tires to recommended
pressure
2. Lack of lubricant in steering gear 2. Replace steering gear
3. Low power steering fluid level 3. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
correct level
4. Loose power steering pump drive
belt4. Correctly adjust power steering pump
drive belt
5. Lack of lubricant in ball joints 5. Lubricate or replace ball joints
6. Steering gear malfunction 6. Replace steering gear
7. Lack of lubricant in steering coupler 7. Replace steering coupler
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WHEEL ALIGNMENT
PRE-WHEEL ALIGNMENT INSPECTION
Before any attempt is made to change or correct
the wheel alignment, the following inspection and
necessary corrections must be made to ensure proper
alignment.
(1) Verify that the fuel tank is full of fuel. If the
tank is not full, the reduction in weight will affect
the curb height of the vehicle and the alignment
angles.
(2) The passenger and luggage compartments of
the vehicle should be free of any load that is not fac-
tory equipment.
(3) Check the tires on the vehicle. All tires must be
the same size and in good condition with approxi-
mately the same amount of tread wear. Inflate all
the tires to the recommended air pressure.
(4) Check the front wheel and tire assemblies for
excessive radial runout.(5) Inspect lower ball joints and all steering link-
age for looseness, binding, wear or damage. Repair as
necessary.
(6) Check suspension fasteners for proper torque
and retighten as necessary.
(7) Inspect all suspension component rubber bush-
ings for signs of wear or deterioration. Replace any
faulty bushings or components before aligning the
vehicle.
(8) Check the vehicle's curb height to verify it is
within specifications. Refer to Curb Height Measure-
ment.
WHEEL ALIGNMENT SETUP
(1) Position the vehicle on an alignment rack.
(2) Install all required alignment equipment on
the vehicle per the alignment equipment manufactur-
er's instructions. On this vehicle, a four-wheel align-
ment is recommended.
2 - 52 WHEEL ALIGNMENTRS
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 94 of 2339

NOTE: Prior to reading the vehicle's alignment
readouts, the front and rear of vehicle should be
jounced. Induce jounce (rear first, then front) by
grasping the center of the bumper and jouncing
each end of vehicle an equal number of times. The
bumper should always be released when vehicle is
at the bottom of the jounce cycle.
(3) Read the vehicle's current front and rear align-
ment settings. Compare the vehicle's current align-
ment settings to the vehicle specifications for camber,
caster and toe-in. (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/
WHEEL ALIGNMENT - SPECIFICATIONS)
(4) If front camber and caster are not within spec-
ifications, proceed to CAMBER AND CASTER below.
If caster and camber are within specifications, pro-
ceed to TOE which can be found following CAMBER
AND CASTER. Rear camber, caster and toe are not
adjustable. If found not to be within specifications,
reinspect for damaged suspension or body compo-
nents and replace as necessary.
CAMBER AND CASTER
Camber and caster settings on this vehicle are
determined at the time the vehicle is designed, by
the location of the vehicle's suspension components.
This is referred to as NET BUILD. The result is no
required adjustment of camber and caster after the
vehicle is built or when servicing the suspension
components. Thus, when performing a wheel align-
ment, caster and camber are not normally considered
adjustable angles. Camber and caster should be
checked to ensure they meet vehicle specifications.
If front camber is found not to meet alignment
specifications, it can be adjusted using an available
camber adjustment bolt package. Before installing a
camber adjustment bolt package on a vehicle found
to be outside the specifications, inspect the suspen-
sion components for any signs of damage or bending.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to adjust the vehicles
wheel alignment by heating, bending or by perform-
ing any other modification to the vehicle's front
suspension components or body.
If camber readings are not within specifications,
use the following procedure to install the front cam-
ber adjustment bolt package and then adjust front
camber.
CAMBER ADJUSTMENT BOLT PACKAGE INSTALLATION
The camber adjustment bolt package contains 2
flange bolts, 2 cam bolts, 2 dog bone washers, and 4
nuts. This package services both sides of the vehicle.
Use the package to attach the strut clevis bracket to
the steering knuckle after the strut clevis brackethas been modified. To install and adjust the camber
adjustment bolt package, follow the procedure below.
(1) Raise the vehicle until its tires are not support-
ing the weight of the vehicle.
(2) Remove the front tire and wheel assemblies.
CAUTION: When removing the steering knuckle
from the strut clevis bracket, do not put a strain on
the brake flex hose. Also, do not let the weight of
the steering knuckle assembly be supported by the
brake flex hose when removed from the strut
assembly. If necessary use a wire hanger to sup-
port the steering knuckle assembly or if required
remove the brake flex hose from the caliper assem-
bly.
CAUTION: The knuckle to strut assembly attaching
bolt shanks are serrated and must not be turned
during removal. Remove the nuts while holding the
bolts stationary.
(3) Remove the top and bottom, strut clevis
bracket to steering knuckle attaching bolts (Fig.
7)and discard. Separate the steering knuckle from
the strut clevis bracket and position steering knuckle
so it is out of the way of the strut.
CAUTION: When slotting the bottom mounting hole
on the strut clevis bracket, do not enlarge the hole
beyond the indentations on the sides of the strut
clevis bracket (Fig. 8).
Fig. 7 Clevis Bracket To Steering Knuckle Attaching
Bolts
1 - STRUT CLEVIS BRACKET
2 - ATTACHING BOLTS
3 - TIE ROD END
4 - ROTOR
5 - STEERING KNUCKLE
RSWHEEL ALIGNMENT2-53
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 95 of 2339
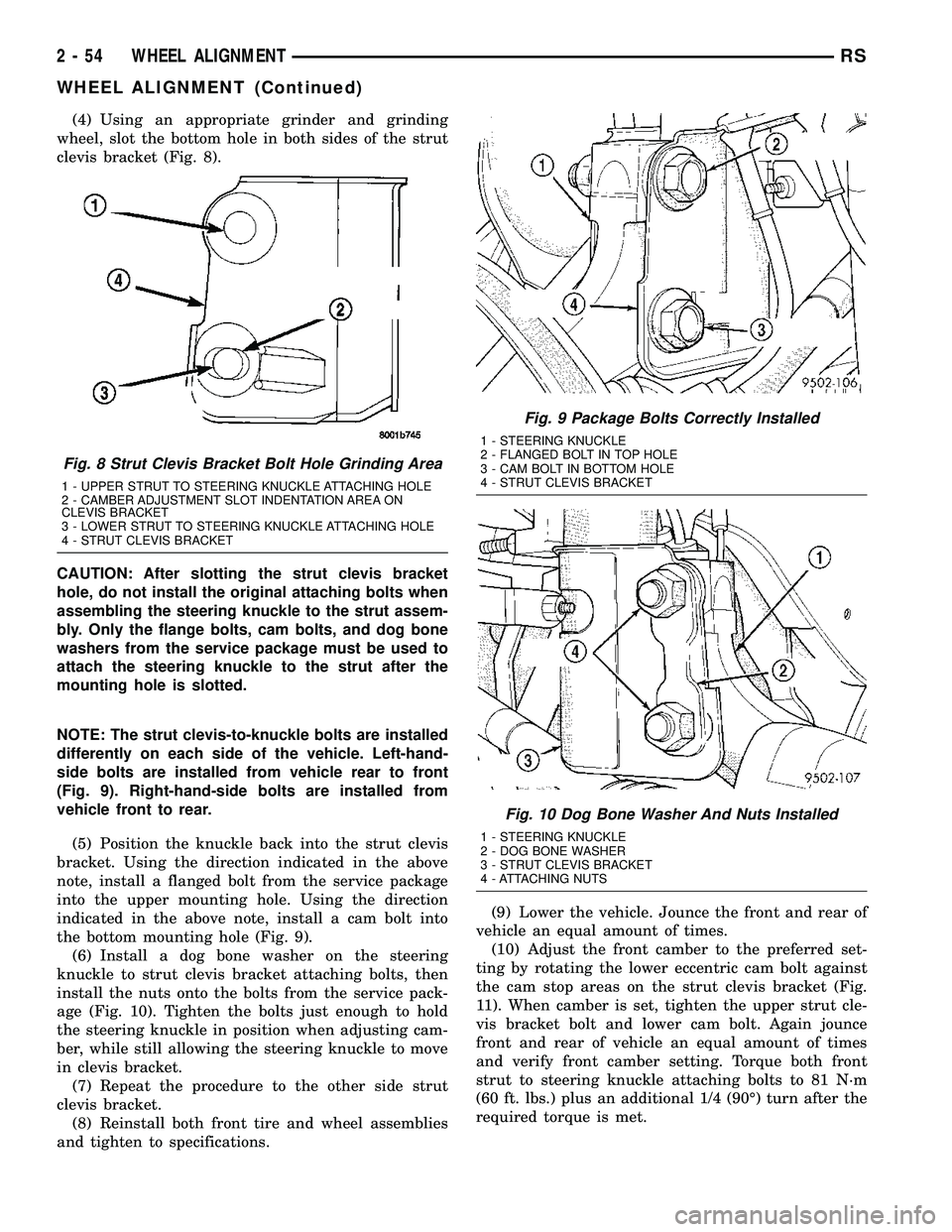
(4) Using an appropriate grinder and grinding
wheel, slot the bottom hole in both sides of the strut
clevis bracket (Fig. 8).
CAUTION: After slotting the strut clevis bracket
hole, do not install the original attaching bolts when
assembling the steering knuckle to the strut assem-
bly. Only the flange bolts, cam bolts, and dog bone
washers from the service package must be used to
attach the steering knuckle to the strut after the
mounting hole is slotted.
NOTE: The strut clevis-to-knuckle bolts are installed
differently on each side of the vehicle. Left-hand-
side bolts are installed from vehicle rear to front
(Fig. 9). Right-hand-side bolts are installed from
vehicle front to rear.
(5) Position the knuckle back into the strut clevis
bracket. Using the direction indicated in the above
note, install a flanged bolt from the service package
into the upper mounting hole. Using the direction
indicated in the above note, install a cam bolt into
the bottom mounting hole (Fig. 9).
(6) Install a dog bone washer on the steering
knuckle to strut clevis bracket attaching bolts, then
install the nuts onto the bolts from the service pack-
age (Fig. 10). Tighten the bolts just enough to hold
the steering knuckle in position when adjusting cam-
ber, while still allowing the steering knuckle to move
in clevis bracket.
(7) Repeat the procedure to the other side strut
clevis bracket.
(8) Reinstall both front tire and wheel assemblies
and tighten to specifications.(9) Lower the vehicle. Jounce the front and rear of
vehicle an equal amount of times.
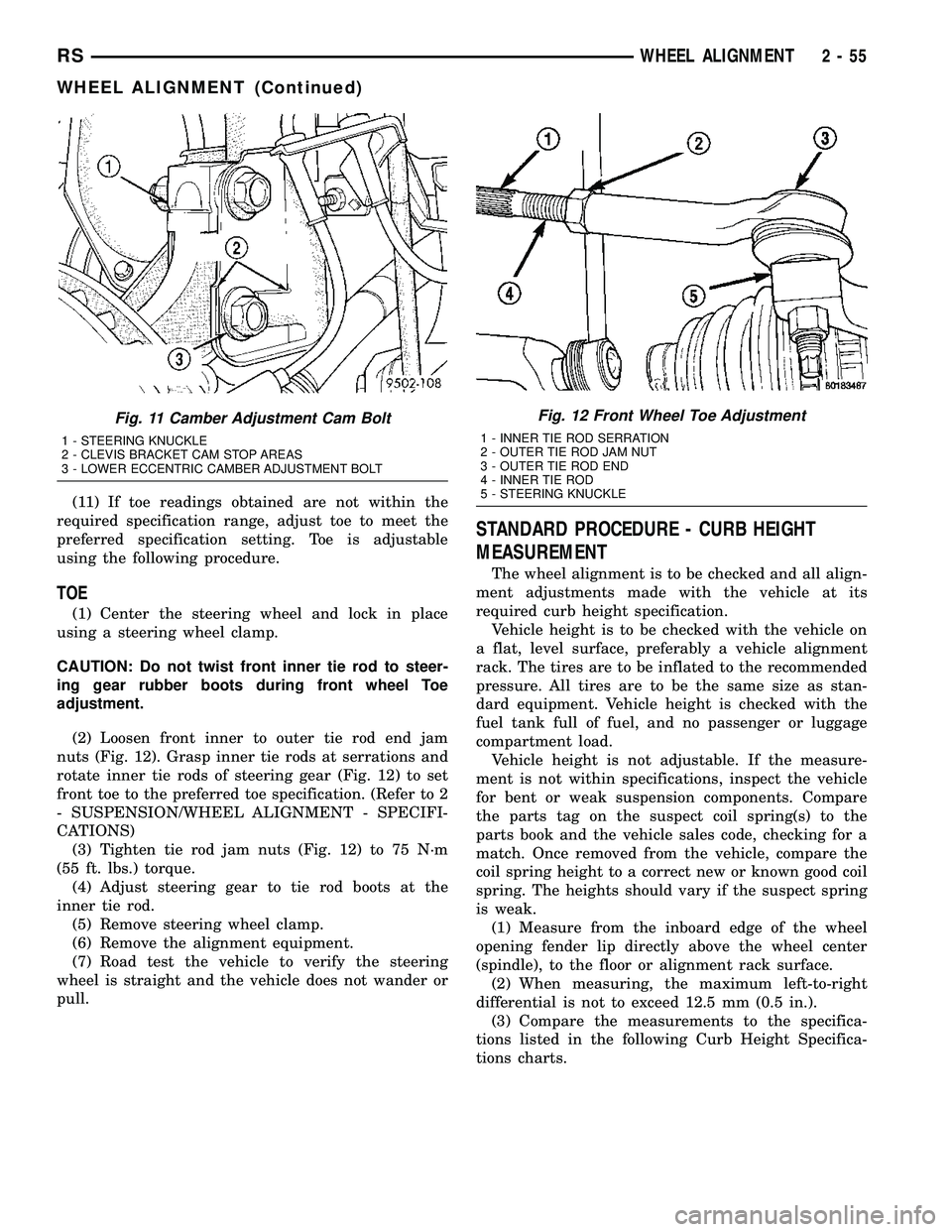
(10) Adjust the front camber to the preferred set-
ting by rotating the lower eccentric cam bolt against
the cam stop areas on the strut clevis bracket (Fig.
11). When camber is set, tighten the upper strut cle-
vis bracket bolt and lower cam bolt. Again jounce
front and rear of vehicle an equal amount of times
and verify front camber setting. Torque both front
strut to steering knuckle attaching bolts to 81 N´m
(60 ft. lbs.) plus an additional 1/4 (90É) turn after the
required torque is met.
Fig. 8 Strut Clevis Bracket Bolt Hole Grinding Area
1 - UPPER STRUT TO STEERING KNUCKLE ATTACHING HOLE
2 - CAMBER ADJUSTMENT SLOT INDENTATION AREA ON
CLEVIS BRACKET
3 - LOWER STRUT TO STEERING KNUCKLE ATTACHING HOLE
4 - STRUT CLEVIS BRACKET
Fig. 9 Package Bolts Correctly Installed
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - FLANGED BOLT IN TOP HOLE
3 - CAM BOLT IN BOTTOM HOLE
4 - STRUT CLEVIS BRACKET
Fig. 10 Dog Bone Washer And Nuts Installed
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - DOG BONE WASHER
3 - STRUT CLEVIS BRACKET
4 - ATTACHING NUTS
2 - 54 WHEEL ALIGNMENTRS
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 96 of 2339
(11) If toe readings obtained are not within the
required specification range, adjust toe to meet the
preferred specification setting. Toe is adjustable
using the following procedure.
TOE
(1) Center the steering wheel and lock in place
using a steering wheel clamp.
CAUTION: Do not twist front inner tie rod to steer-
ing gear rubber boots during front wheel Toe
adjustment.
(2) Loosen front inner to outer tie rod end jam
nuts (Fig. 12). Grasp inner tie rods at serrations and
rotate inner tie rods of steering gear (Fig. 12) to set
front toe to the preferred toe specification. (Refer to 2
- SUSPENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - SPECIFI-
CATIONS)
(3) Tighten tie rod jam nuts (Fig. 12) to 75 N´m
(55 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Adjust steering gear to tie rod boots at the
inner tie rod.
(5) Remove steering wheel clamp.
(6) Remove the alignment equipment.
(7) Road test the vehicle to verify the steering
wheel is straight and the vehicle does not wander or
pull.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CURB HEIGHT
MEASUREMENT
The wheel alignment is to be checked and all align-
ment adjustments made with the vehicle at its
required curb height specification.
Vehicle height is to be checked with the vehicle on
a flat, level surface, preferably a vehicle alignment
rack. The tires are to be inflated to the recommended
pressure. All tires are to be the same size as stan-
dard equipment. Vehicle height is checked with the
fuel tank full of fuel, and no passenger or luggage
compartment load.
Vehicle height is not adjustable. If the measure-
ment is not within specifications, inspect the vehicle
for bent or weak suspension components. Compare
the parts tag on the suspect coil spring(s) to the
parts book and the vehicle sales code, checking for a
match. Once removed from the vehicle, compare the
coil spring height to a correct new or known good coil
spring. The heights should vary if the suspect spring
is weak.
(1) Measure from the inboard edge of the wheel
opening fender lip directly above the wheel center
(spindle), to the floor or alignment rack surface.
(2) When measuring, the maximum left-to-right
differential is not to exceed 12.5 mm (0.5 in.).
(3) Compare the measurements to the specifica-
tions listed in the following Curb Height Specifica-
tions charts.
Fig. 11 Camber Adjustment Cam Bolt
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - CLEVIS BRACKET CAM STOP AREAS
3 - LOWER ECCENTRIC CAMBER ADJUSTMENT BOLT
Fig. 12 Front Wheel Toe Adjustment
1 - INNER TIE ROD SERRATION
2 - OUTER TIE ROD JAM NUT
3 - OUTER TIE ROD END
4 - INNER TIE ROD
5 - STEERING KNUCKLE
RSWHEEL ALIGNMENT2-55
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 97 of 2339

CURB HEIGHT SPECIFICATIONS
VEHICLE FRONT REAR
CARGO VAN755mm 11mm
29.72 in. 0.43 in795mm 11mm
31.30 in. 0.43 in.
ALL OTHERS755mm 11mm
29.72 in. 0.43 in770mm 11mm
30.31 in. 0.43 in.
SPECIFICATIONS
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
NOTE: All specifications are given in degrees.NOTE: All wheel alignments are to be set at curb
height. (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/WHEEL ALIGN-
MENT - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT PREFERRED SETTING ACCEPTABLE RANGE
CAMBER +0.10É -0.30É to +0.50É
Cross-Camber (Maximum side-to-side
difference)0.0É 0.50É
CASTER* +2.31É +1.31É to +3.31É
Cross-Caster (Maximum side-to-side difference) 0.0É 1.00É
TOTAL TOE** +0.10É20.10É to +0.30É
Maximum side-to-side difference 0.0É 0.06É
REAR WHEEL ALIGNMENT PREFERRED SETTING ACCEPTABLE RANGE
CAMBER* 0.0É -0.25É to +0.25É
TOTAL TOE* ** 0.0É20.20É to +0.20É
THRUST ANGLE* 0.0É -0.30É to +0.30É
Notes:
* For reference only. These are non-adjustable angles.
** TOTAL TOE is the sum of both left and right wheel toe settings. TOTAL TOE must be equally split between
each front wheel to ensure the steering wheel is centered after setting toe. Positive toe is toe-in and negative toe
is toe-out
2 - 56 WHEEL ALIGNMENTRS
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 100 of 2339

(4) With the vehicle's brakes applied to keep hub
from turning,loosen and removethe half shaft
nut.
(5) Remove the two front disc brake caliper
adapter to steering knuckle attaching bolts (Fig. 4).
(6) Remove the disc brake caliper assembly from
the steering knuckle. Caliper assembly is removed by
first rotating top of caliper assembly away from
steering knuckle and then removing bottom of assem-
bly out from under machined abutment on steering
knuckle.(7) Support disc brake caliper assembly by using a
wire hook and suspending it from the strut assembly
(Fig. 5).Do not allow the brake caliper assembly
to hang by the brake flex hose.
(8) Remove the brake rotor from the hub and bear-
ing assembly.
(9) Remove the steering knuckle-to-strut attach-
ment bolts (Fig. 6) from the steering knuckle.
(10) Pull the steering knuckle from the strut clevis
bracket.
Fig. 3 Wave Washer
1 - HUB/BEARING ASSEMBLY
2 - WAVE WASHER
3 - STUB AXLE
Fig. 4 Front Brake Mounting
1 - BRAKE ROTOR
2 - HUB AND BEARING
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
4 - ADAPTER MOUNTING BOLTS
5 - BRAKE CALIPER
6 - ADAPTER
7 - CLIP
Fig. 5 Properly Supported Disc Brake Caliper -
Typical
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - BRAKE FLEX HOSE
3 - CALIPER ASSEMBLY
4 - WIRE HANGER
5 - STRUT ASSEMBLY
Fig. 6 Strut To Steering Knuckle Attaching Bolts
1 - STRUT CLEVIS BRACKET
2 - NUTS AND BOLTS
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
RSHALF SHAFT - FRONT3-3
HALF SHAFT - FRONT (Continued)