steering rack CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 371 of 2339

INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Install coil over studs on bracket.
(2) Install 2 nuts to the ignition coil studs. Tighten
nuts and bolts.
(3) Connect the electrical connector to the ignition
coil.
(4) Install the ignition cables to the ignition coil.
(5) Reposition the Power steering reservoir. Slide
bracket over the mounting stud (Fig. 11).
(6) Install 2 bolts to the Power steering reservoir
to intake manifold.
(7) Tighten the lower nut to stud on ignition coil
bracket.
(8) Install the throttle and speed control cables to
clip.
(9) Connect the negative battery cable.
KNOCK SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The knock sensor threads into the cylinder block.
The knock sensor is designed to detect engine vibra-
tion that is caused by detonation.
OPERATION
When the knock sensor detects a knock in one of
the cylinders, it sends an input signal to the PCM. In
response, the PCM retards ignition timing for all cyl-
inders by a scheduled amount.
Knock sensors contain a piezoelectric material
which constantly vibrates and sends an input voltage
(signal) to the PCM while the engine operates. As the
intensity of the crystal's vibration increases, the
knock sensor output voltage also increases.
The voltage signal produced by the knock sensor
increases with the amplitude of vibration. The PCM
receives as an input the knock sensor voltage signal.
If the signal rises above a predetermined level, the
PCM will store that value in memory and retard
ignition timing to reduce engine knock. If the knock
sensor voltage exceeds a preset value, the PCM
retards ignition timing for all cylinders. It is not a
selective cylinder retard.
The PCM ignores knock sensor input during engine
idle conditions. Once the engine speed exceeds a
specified value, knock retard is allowed.
Knock retard uses its own short term and long
term memory program.
Long term memory stores previous detonation
information in its battery-backed RAM. The maxi-
mum authority that long term memory has over tim-
ing retard can be calibrated.
Short term memory is allowed to retard timing up
to a preset amount under all operating conditions (as
long as rpm is above the minimum rpm) except WOT.The PCM, using short term memory, can respond
quickly to retard timing when engine knock is
detected. Short term memory is lost any time the
ignition key is turned off.
NOTE: Over or under tightening affects knock sen-
sor performance, possibly causing improper spark
control.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L
The knock sensor threads into the side of the cyl-
inder block in front of the starter (Fig. 12).
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from knock sen-
sor.
(2) Use a crow foot socket to remove the knock
sensors.
REMOVAL - 3.8L
The knock sensor threads into the side of the cyl-
inder block in the rear.
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Raise vehicle and support.
(3) On All Wheel Drive vehicles remove the PTU
(Power Transfer Unit), refer to the Transmission sec-
tion for more information.
(4) Disconnect electrical connector from knock sen-
sor.
(5) Use a crow foot socket to remove the knock
sensor.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
The knock sensor threads into the side of the cyl-
inder block in front of the starter (Fig. 12).
(1) Install knock sensor. Tighten knock sensor to
10 N´m (7 ft. lbs.) torque.Over or under tighten-
ing effects knock sensor performance, possibly
causing improper spark control.
(2) Attach electrical connector to knock sensor.
INSTALLATION - 3.8L
The knock sensor threads into the side of the cyl-
inder block in the rear.
(1) Install knock sensor. Tighten knock sensor to
10 N´m (7 ft. lbs.) torque.Over or under tighten-
ing effects knock sensor performance, possibly
causing improper spark control.
(2) Attach electrical connector to knock sensor.
(3) On All Wheel Drive vehicles install the PTU
(Power Transfer Unit) for the rear wheels, refer to
the Transmission section for more information.
8I - 8 IGNITION CONTROLRS
IGNITION COIL (Continued)
Page 390 of 2339

(3) Gently push the plunger on the brake lamp
switch in until it stops.
(4) With the switch in this depressed position
(plunger pushed in), use an ohmmeter to test each of
the three internal switches as shown (Fig. 2). You
should achieve the results as listed in the figure.
If you do not achieve the results as listed in both
figures, the switch is faulty and must be replaced.
Refer to Removal And Installation in this section.
If the switch is found to be operating properly, it
may be misadjusted. Do not reinstall the switch,
replace it. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/
LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/BRAKE LAMP SWITCH -
INSTALLATION)
CAUTION: The switch can only be adjusted once.
That is during initial installation of the switch. If the
switch is not adjusted properly or has beenremoved for any reason, a new switch must be
installed and adjusted.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable from its post on the battery.
(2) Remove silencer panel below steering column
and knee blocker.
(3) Remove the brake lamp switch by rotating the
switch in a counterclockwise direction approximately
30 degrees and pulling it out of the bracket (Fig. 3).
(4) Release the locking tab and disconnect the wir-
ing connector from the switch.
(5) Discard the brake lamp switch. It must not be
reused.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Do not reuse the original brake lamp
switch. The switch can only be adjusted once. That
is during initial installation of the switch. If the
switch is not adjusted properly or has been
removed for some service, a new switch must be
installed and adjusted.
(1) Mount and adjust the NEW brake lamp switch
using the following procedure:
(a) Connect the wiring connector to the switch
and latch the locking tab.
Fig. 1 SWITCH TEST - RELEASED POSITION
Fig. 2 SWITCH TEST - DEPRESSED POSITION
Fig. 3 Brake Lamp Switch And Pedal With Bracket
1 - BRAKE LAMP SWITCH
2 - WIRING CONNECTOR
3 - PEDAL AND BRACKET
RSLAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR8L-5
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH (Continued)
Page 391 of 2339
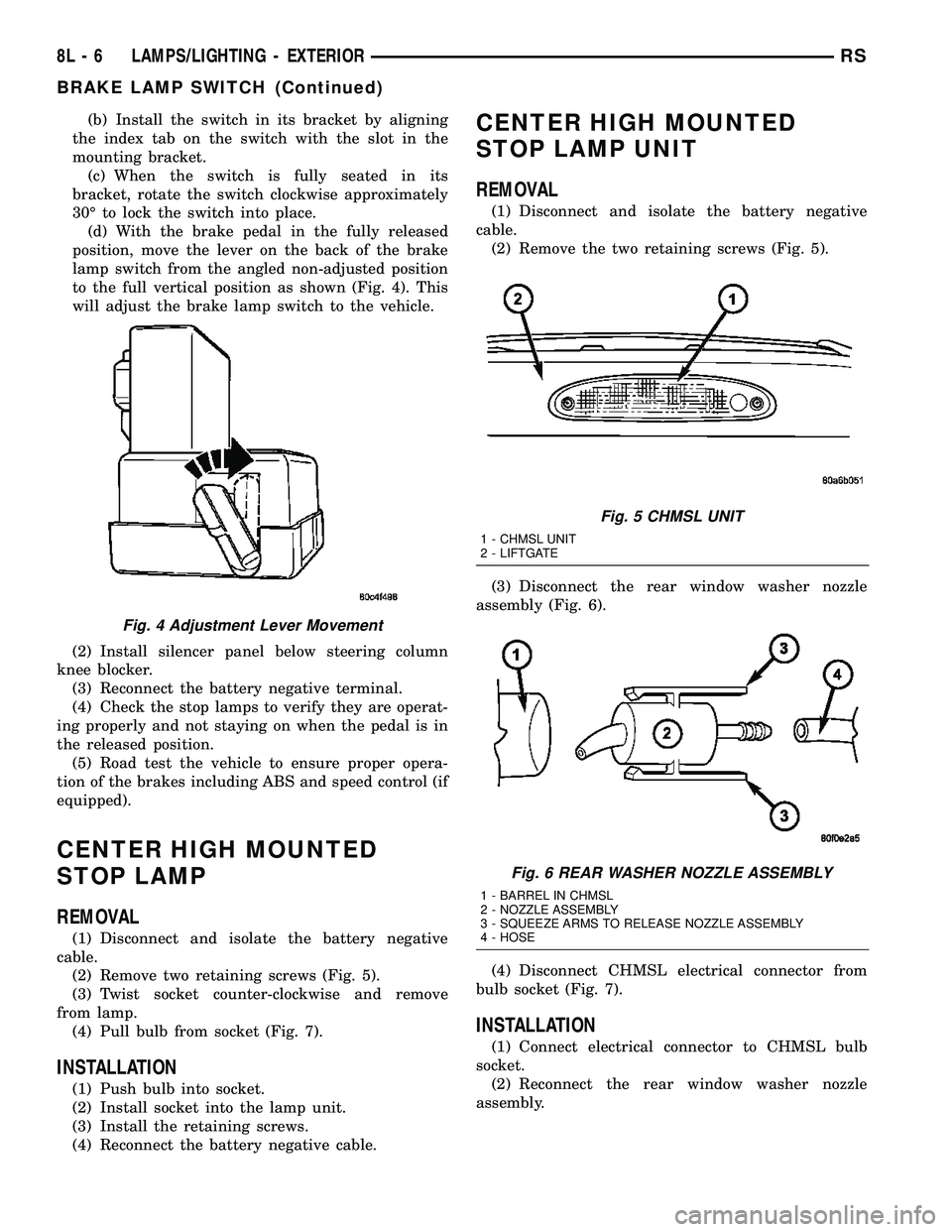
(b) Install the switch in its bracket by aligning
the index tab on the switch with the slot in the
mounting bracket.
(c) When the switch is fully seated in its
bracket, rotate the switch clockwise approximately
30É to lock the switch into place.
(d) With the brake pedal in the fully released
position, move the lever on the back of the brake
lamp switch from the angled non-adjusted position
to the full vertical position as shown (Fig. 4). This
will adjust the brake lamp switch to the vehicle.
(2) Install silencer panel below steering column
knee blocker.
(3) Reconnect the battery negative terminal.
(4) Check the stop lamps to verify they are operat-
ing properly and not staying on when the pedal is in
the released position.
(5) Road test the vehicle to ensure proper opera-
tion of the brakes including ABS and speed control (if
equipped).
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED
STOP LAMP
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove two retaining screws (Fig. 5).
(3) Twist socket counter-clockwise and remove
from lamp.
(4) Pull bulb from socket (Fig. 7).
INSTALLATION
(1) Push bulb into socket.
(2) Install socket into the lamp unit.
(3) Install the retaining screws.
(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED
STOP LAMP UNIT
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the two retaining screws (Fig. 5).
(3) Disconnect the rear window washer nozzle
assembly (Fig. 6).
(4) Disconnect CHMSL electrical connector from
bulb socket (Fig. 7).
INSTALLATION
(1) Connect electrical connector to CHMSL bulb
socket.
(2) Reconnect the rear window washer nozzle
assembly.
Fig. 4 Adjustment Lever Movement
Fig. 5 CHMSL UNIT
1 - CHMSL UNIT
2 - LIFTGATE
Fig. 6 REAR WASHER NOZZLE ASSEMBLY
1 - BARREL IN CHMSL
2 - NOZZLE ASSEMBLY
3 - SQUEEZE ARMS TO RELEASE NOZZLE ASSEMBLY
4 - HOSE
8L - 6 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORRS
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH (Continued)
Page 503 of 2339

INSTALLATION
(1) Position curtain airbag over retaining holes in
roof rail and firmly snap into place (Fig. 17).
(2) Install the curtain airbag retaining bolts (Fig.
17).
(3) Engage the side curtain airbag front tether in
the A-pillar and install retaining bolt (Fig. 16).
(4) Install the bolt in the curtain airbag inflator
mounting bracket (Fig. 18).
(5) Install the retaining bolts at the d-pillar (Fig.
19).
(6) Connect the curtain airbag squib connector
(Fig. 15).
(7) Install the headliner into the vehicle (Refer to
23 - BODY/INTERIOR/HEADLINER - INSTALLA-
TION).
WARNING: Do not connect the battery negative
cable (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM). Per-
sonal injury or death may result if the system test
is not performed first.
(8) Verify vehicle and system operation.
(9) Close hood.
DRIVER AIRBAG
DESCRIPTION
The injection molded, thermoplastic driver airbag
protective trim cover is the most visible part of the
driver airbag. The driver airbag is located in the cen-
ter of the steering wheel, where it is secured to the
steering wheel armature. Concealed beneath the
driver airbag trim cover are the horn switch, thefolded airbag cushion, the airbag cushion retainer,
the airbag housing, the airbag inflator, and the
retainers that secure the inflator to the airbag hous-
ing. The airbag cushion, housing, and inflator are
secured within an integral receptacle molded into the
back of the trim cover.
The resistive membrane-type horn switch is
secured with heat stakes to the inside surface of the
driver airbag trim cover, between the trim cover and
the folded airbag cushion. The horn switch ground
pigtail wire has a female spade terminal connector
that receives a path to ground through a male spade
terminal that is integral to the driver airbag housing
stamping and is located near the upper right corner
on the back of the housing. The horn switch feed pig-
tail wire has a white, molded plastic insulator that is
secured by an integral retainer to a mounting hole
located near the lower left corner on the back of the
housing, and is connected to the vehicle electrical
system through a take out and connector of the steer-
ing wheel wire harness.
The airbag is a multistage unit that deploys with
less force than those previously used. The airbag
inflator is a dual-initiator, non-azide, pyrotechnic-
type unit with four mounting studs and is secured to
the stamped metal airbag housing using four hex
nuts with washers. Two keyed and color-coded con-
nector receptacles on the driver airbag inflator con-
nect the two inflator initiators to the vehicle
electrical system through two yellow or black-jack-
eted, two-wire pigtail harnesses of the clockspring.
The driver airbag, trim cover, and horn switch unit
cannot be repaired, and must be replaced if deployed
or in any way damaged.
OPERATION
The Driver Airbag Trim Cover contains the horn
switch, inflator device, and a fabric bag. The driver
airbag trim cover/horn switch is not serviced sepa-
rately from the driver airbag components.
When the front airbag system is deployed, the fol-
lowingMUSTbe replaced:
²Complete Steering Column Assembly
²Lower Steering Column Coupler
²Steering Wheel.
²Clockspring.
²Driver Airbag
²Passenger Airbag
²Knee Blocker Airbag
²Upper Instrument Panel with Pad
²Front Seat Belt Buckles, both driver and passen-
ger with integral tensioners.
Fig. 19 CURTAIN AIRBAG D-PILLAR ATTACHMENT
1 - CURTAIN AIRBAG D-PILLAR ATTACHMENT LOCATIONS
2 - D-PILLAR
3 - ROOF RAIL AT REAR QUARTER GLASS
8O - 16 RESTRAINTSRS
CURTAIN AIRBAG (Continued)
Page 505 of 2339

INSTALLATION
DEPLOYED AIRBAG
(1) Perform clean up procedure (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/RESTRAINTS - STANDARD PROCEDURE
- SERVICE AFTER AN AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT).
(2) Install a new steering column assembly and
lower steering column coupler (Refer to 19 - STEER-
ING/COLUMN - INSTALLATION).
(3) Install the new clockspring.
(4) Connect the 4-way and 6-way connectors
between the clockspring and the instrument panel
wiring harness.
(5) Install the steering column shrouds and con-
nect traction control wire connector (if equipped)
(Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/LOWER
SHROUD - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install the steering wheel (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/COLUMN/STEERING WHEEL -
INSTALLATION).
(7) Connect the 4±way harness connector to the
speed control/horn harness to the clockspring.
(8) Connect the 2±way connector to the remote
radio control harness.
(9) Install the driver airbag and the two screws
retaining the airbag. Tighten screws to 10 N´m (90
in. lbs.)
WARNING: Do not connect the battery negative
cable (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM). Per-
sonal injury or death may result if the system test
is not performed first.
UNDEPLOYED AIRBAG
(1) Connect the harness connector on the driver
airbag trim cover (horn, speed controls) to the clock-
spring.
(2) Connect the squib connectors to the driver air-
bag.
(3) Position the driver airbag into the steering
wheel.
(4) Install the two screws retaining the airbag.
Tighten screws to 10 N´m (90 in. lbs.)
WARNING: Do not connect the battery negative
cable (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM). Per-
sonal injury or death may result if the system test
is not performed first.
IMPACT SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
FRONT IMPACT SENSORS
There are two front impact sensors (Fig. 21), one
on the left, and one on the right front sides of the
vehicle. These sensors are mounted remotely from
the impact sensor that is internal to the Occupant
Restraint Controller (ORC). The right and left front
and side impact sensors are identical in construction
and calibration and each front impact sensor is
secured with two screws. The front impact sensors
are secured with two screws to the outboard sides of
the right and left front rail tips.
The impact sensor housing has an integral connec-
tor and two mounting ears, each with a metal sleeve
to provide crush protection. A cavity in the center of
the molded black plastic impact sensor housing con-
tains the electronic circuitry of the sensor which
includes an electronic communication chip and an
electronic impact sensor. Potting material fills the
cavity to seal and protect the internal electronic cir-
cuitry and components. The front impact sensors are
each connected to the vehicle electrical system
through the headlamp to dash wire harness.
The front impact sensors cannot be repaired or
adjusted and, if damaged or faulty, they must be
replaced. If a front impact sensor is faulty, only the
sensor needs to be replaced. If the sensor is damaged
or faulty, or if proper tightening torque of the screws
that secure the sensor to the bracket cannot be
achieved, the sensor and bracket must be replaced.
Refer to the proper body diagnostic information for
diagnosis and testing.
Fig. 21 FRONT IMPACT SENSOR
8O - 18 RESTRAINTSRS
DRIVER AIRBAG (Continued)
Page 517 of 2339

WARNING: Never replace both the Occupant
Restraint Controller (ORC) and the Occupant Clas-
sification Module (OCM) at the same time. If both
require replacement, replace one, then perform the
Airbag System test (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RE-
STRAINTS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG
SYSTEM) before replacing the other. Both the ORC
and the OCM store Occupant Classification System
(OCS) calibration data, which they transfer to one
another when one of them is replaced. If both are
replaced at the same time, an irreversible fault will
be set in both modules and the OCS may malfunc-
tion and result in personal injury or death.
(1) Install the ORC into vehicle (Fig. 39).
(2) Connect the wire connector to the ORC (Fig.
39).
(3) Install three bolts holding ORC to floor bracket
(Fig. 39). Torque bolts to 7.3 - 9.6 N´m (65 to 85 in.
lbs.)
(4) Install the storage bin onto the instrument
panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
STORAGE BIN - INSTALLATION).
WARNING: Do not connect the battery negative
cable (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM). Per-
sonal injury or death may result if the system test
is not performed first.
(5) Verify vehicle and system operation.
(6) Close hood.
PASSENGER AIRBAG
DESCRIPTION
WARNING: Never disassemble the passenger air-
bag. The passenger airbag has no serviceable
parts. If tampered with internally, the airbag could
deploy and result in personal injury or death.
The Passenger Airbag is located beneath the
instrument panel and pad assembly. The airbag is
mounted to the back side of the instrument panel
reinforcement.
The instrument panel top pad is the most visible
part of the passenger airbag system. Located under
the instrument panel top pad are the airbag door, the
passenger airbag cushion and the airbag cushion
supporting components.
The passenger airbag includes a magnesium hous-
ing within which the cushion and inflator are
mounted and sealed.
Following a passenger airbag deployment, the pas-
senger airbag and the instrument panel must bereplaced. The passenger airbag cannot be repaired,
and must be replaced if deployed or damaged in any
way.
OPERATION
The passenger airbag is equipped with two infla-
tors, each with three levels of pressure output. The
inflators seal the hole in the airbag cushion so it can
discharge the gas it produces directly into the cush-
ion when supplied with the proper electrical signal.
Following an airbag deployment, the airbag cushion
quickly deflates by venting this gas through the
cushion material towards the instrument panel.
The passenger airbag is secured with screws to the
instrument panel beneath the instrument panel top
pad and above the glove box opening. The instrument
panel top pad above the glove box opening conceals
the airbag door and a predetermined hinge line
beneath its decorative cover. Upon airbag deploy-
ment, the top pad will bend at the hinge line and the
door will fold back out of the way onto the top of the
instrument panel.
When the front airbag system is deployed, the fol-
lowingMUSTbe replaced:
²Complete Steering Column Assembly.
²Lower Steering Column Coupler.
²Steering Wheel.
²Clock Spring.
²Driver Airbag.
²Passenger Airbag.
²Upper Instrument Panel with Pad.
CARE OF UNDEPLOYED AIRBAGS
Airbags must be stored in their original special
container until used for service. At no time should a
source of electricity be permitted near the inflator on
the back of an airbag. When carrying or handling an
undeployed airbag, the trim side of the airbag should
be pointing away from the body to minimize possibil-
ity of injury if accidental deployment occurs. Do not
place undeployed airbag face down on a solid surface,
the airbag will propel into the air if accidental
deployment occurs.
REMOVAL
DEPLOYED AIRBAG
(1) Open hood.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(3)
8O - 30 RESTRAINTSRS
OCCUPANT RESTRAINT CONTROLLER (Continued)
Page 518 of 2339

WARNING: Wait two minutes for the airbag system
reserve capacitor to discharge before beginning
any airbag system or component service. Failure to
do so may result in accidental airbag deployment,
personal injury or death.
(4) Clean powder residue from interior of vehicle
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE - SERVICE AFTER AN AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT).
(5) Remove instrument panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INSTRUMENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT PANEL
ASSEMBLY - REMOVAL).
(6) Remove all reusable components from the
upper instrument panel and transfer to the new
instrument panel.
UNDEPLOYED AIRBAG
(1) Open hood.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(3)
WARNING: Wait two minutes for the airbag system
reserve capacitor to discharge before beginning
any airbag system or component service. Failure to
do so may result in accidental airbag deployment,
personal injury or death.
(4) Remove center console bin between front seats.
(5) Remove left front door sill plate using a trim
stick (special tool #C-4755) or equivalent, and gently
prying up on sill plate.
(6) Remove left cowl panel using a trim stick or
equivalent, and gently prying out on cowl panel.
(7) Remove four screws to lower steering column
cover and remove cover.
(8) Unsnap parking brake lever from knee blocker
reinforcement.
(9) Remove Data Link Connector (DLC) from knee
blocker.
(10) Remove screws to knee blocker.
(11) Unsnap left A-pillar lower extension trim
using a trim stick or equivalent.
(12) Remove three left side instrument panel A-pil-
lar retaining bolts and loosen the instrument panel
roll down bolt.
(13) Remove four nuts at brake pedal support
bracket to instrument panel.
(14) Using a trim stick or equivalent, gently pry
off left side upper A-pillar trim.
(15) Remove six screws and two wiring connectors
to lower instrument panel cubby bin at bottom of
center stack.
(16) Remove two left side nuts at instrument panel
center stack support to floor.(17) Remove two right side nuts at instrument
panel center stack support to floor.
(18) Remove right front door sill plate using a trim
stick or equivalent, and gently prying up on sill
plate.
(19) Remove right cowl panel using a trim stick or
equivalent, and gently prying out on cowl panel.
(20) Using a trim stick or equivalent, gently pry
out on right instrument panel end cap.
(21) Unsnap right A-pillar lower extension trim
using a trim stick or equivalent.
(22) Remove three right side instrument panel
A-pillar retaining bolts and loosen the instrument
panel roll down bolt.
(23) Using a trim stick or equivalent, gently pry
off right side upper A-pillar trim.
(24) Open glove box, pinch in sides and roll down
towards floor. With a firm pull, snap glove box door
off hinges and remove.
(25) Using a trim stick or equivalent, gently pry
up on rear of instrument panel top cover and then
pull rearward and out.
(26) Using a trim stick or equivalent, gently pry
off the filler bezel just above the cup holder to expose
the lower screws to center bezel.
(27) Remove two screws and then using a trim
stick or equivalent, gently pry off instrument panel
center bezel.
(28) Remove center bezel wiring connectors to
HVAC control and switch assembly (hazard, rear
wiper/washer, heated seats) and remove bezel.
(29) Slide cup holder assembly from instrument
panel.
(30) Remove nineteen screws to right lower instru-
ment panel trim (glove box surround), unplug glove
box lamp wire connector, and remove panel.
(31) Remove four screws and wiring connectors to
radio and remove radio.
(32) Remove one far left instrument panel speaker
retaining screw.
(33) Remove four screws along top front edge of
instrument panel cover/pad.
(34) Remove seven lower instrument panel cover/
pad retaining screws starting from right of vehicle
and only removing these seven, not all of them.
(35) Remove six upper fence line instrument panel
retaining bolts.
(36) Roll back instrument panel just enough to
increase access to the passenger airbag retaining
bolts at the reinforcement. Lift the instrument panel
up slightly so as not to damage the air distribution to
HVAC unit seal.
(37) Disconnect the passenger airbag electrical
connector. Using a trim stick or equivalent, gently
pry electrical connector off of instrument panel rein-
forcement.
RSRESTRAINTS8O-31
PASSENGER AIRBAG (Continued)
Page 520 of 2339

(28) Install two right side nuts at instrument
panel center stack support to floor.
(29) Install two left side nuts at instrument panel
center stack support to floor.
(30) Connect the two wiring connectors to lower
instrument panel cubby bin at bottom of center stack
and install six screws.
(31) Align left side upper A-pillar trim over retain-
ing slots and firmly snap into place.
(32) Install four nuts at brake pedal support
bracket to instrument panel.
(33) Align left A-pillar lower extension trim over
retaining slots and firmly snap into place.
(34) Install knee blocker and retaining screws.
(35) Install Data Link Connector (DLC) into bot-
tom of knee blocker.
(36) Align parking brake lever and snap into place
on knee blocker reinforcement.
(37) Install lower steering column cover and four
retaining screws
(38) Align left cowl panel over retaining slots and
firmly snap into place.
(39) Align left front door sill plate over retaining
slots and firmly snap into place.
(40) Install center console bin between front seats.
WARNING: Do not connect the battery negative
cable (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM). Per-
sonal injury or death may result if the system test
is not performed first.
(41) Close hood.
(42) Verify system and vehicle operation.
PASSENGER AIRBAG
DISABLED INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with the Occupant Classification
System (OCS) include a Passenger Airbag Disabled
(PAD) indicator (Fig. 40) which is located in the
instrument panel center stack, above the radio. The
PAD indicator is present only in vehicles equipped
with the OCS.The PAD indicator consists of a molded plastic
housing with an integral connector at the back. An
amber Light Emitting Diode (LED) behind the lens
causes the ªPASS AIR BAG OFFº text and icon to
appear silhouetted against an amber field through
the translucent lens when the indicator is illumi-
nated from behind by the LED. The PAD indicator is
available for separate service replacement.
OPERATION
In vehicles equipped with the Occupant Classifica-
tion System (OCS), the Passenger Airbag Disabled
(PAD) indicator gives an indication when the passen-
ger airbag and seat belt tensioner deployment cir-
cuits are disabled by the Occupant Restraint
Controller (ORC). The PAD indicator is controlled by
a transistor within the ORC through a hard wired
output based upon ORC programming and electronic
occupant classification messages received by the ORC
over the Programmable Communications Interface
(PCI) data bus from the Occupant Classification
Module (OCM). The PAD indicator Light Emitting
Diode (LED) is completely controlled by the ORC.
The LED receives a battery current input on the
fused ignition switch output (RUN/START) circuit.
Therefore, the LED will always be OFF when the
ignition switch is in any position except ON or
START. The LED only illuminates when it is pro-
vided a path to ground by the ORC transistor. The
ORC will turn on the PAD indicator for the following
reasons:
²Bulb Test- Each time the ignition switch is
turned to the ON position the PAD indicator is illu-
minated for about six seconds.
²Child Seat Detected Occupant Classifica-
tion Message- Each time the ORC receives a mes-
sage from the OCM indicating a child seat has been
detected in the passenger front seat, the passenger
airbag and seat belt tensioner deployment circuits
are deactivated and the PAD indicator will be illumi-
nated. The indicator remains illuminated until the
ORC receives an occupant classification message
indicating that:
²The passenger front seat is empty.
²The seat is occupied by a load equal to or
greater than a fifth percentile female.
²OR,Until the ignition switch is turned to the
OFF position, whichever of these three occurs first.
²Load Less Than Fifth Percentile Female
Occupant Classification Message- Each time the
ORC receives a message from the OCM indicating
that a load less than a fifth percentile female has
been detected in the passenger front seat, the pas-
senger airbag and seat belt tensioner deployment cir-
cuits are deactivated and the PAD indicator will be
illuminated. The indicator remains illuminated until:
Fig. 40 PASSENGER AIRBAG DISABLED (PAD)
INDICATOR
RSRESTRAINTS8O-33
PASSENGER AIRBAG (Continued)
Page 530 of 2339
SEAT BELT TENSIONER
DESCRIPTION
The seat belt system incorporates Seat Belt Ten-
sioners. The tensioner is designed to hold the occu-
pant in their respective seat by retracting the seat
belt up to four inches. They are integral to the front
seat belt buckles and cannot be serviced. If found
defective they must be replaced. After an airbag
deployment, the tensioner must be replaced.
Seat Belt Tensioners supplement the dual front air-
bag system. The seat belt tensioners are integral to
the front seat belt buckles, which are secured to the
seat cushion frame on the inboard side. The seat belt
tensioners are controlled by the Occupant Restraint
Controller (ORC) and are connected to the vehicle
electrical system through the body wire harness.
The seat belt tensioners cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, the entire front seat belt buckle
must be replaced. The seat belt tensioners are not
intended for reuse and must be replaced following
any front airbag deployment.
OPERATION
WARNING: When the front airbag is deployed, the
tensioner will have deployed also and should be
replaced. Failure to do so could result in occupant
personal injury or death.
The seat belt tensioners are deployed by a signal
generated by the Occupant Restraint Controller
(ORC) through the driver or passenger seat belt ten-
sioner line 1 and line 2 (or squib) circuits. When the
ORC sends the proper electrical signal to the tension-
ers, the electrical energy generates enough heat to
initiate a small pyrotechnic gas generator.
Removing excess slack from the front seat belts not
only keeps the occupants properly positioned for an
airbag deployment following a frontal impact of the
vehicle, but also helps to reduce injuries that the
occupants of the front seat might experience in these
situations as a result of a harmful contact with the
steering wheel, steering column, instrument panel
and/or windshield.
The ORC monitors the condition of the seat belt
tensioners through circuit resistance, and will illumi-
nate the airbag indicator in the ElectroMechanical
Instrument Cluster (EMIC) and store a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) for any fault that is detected.
For proper diagnosis of the seat belt tensioners, use a
scan tool and the appropriate diagnostic information.
SEAT WEIGHT BLADDER &
PRESSURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
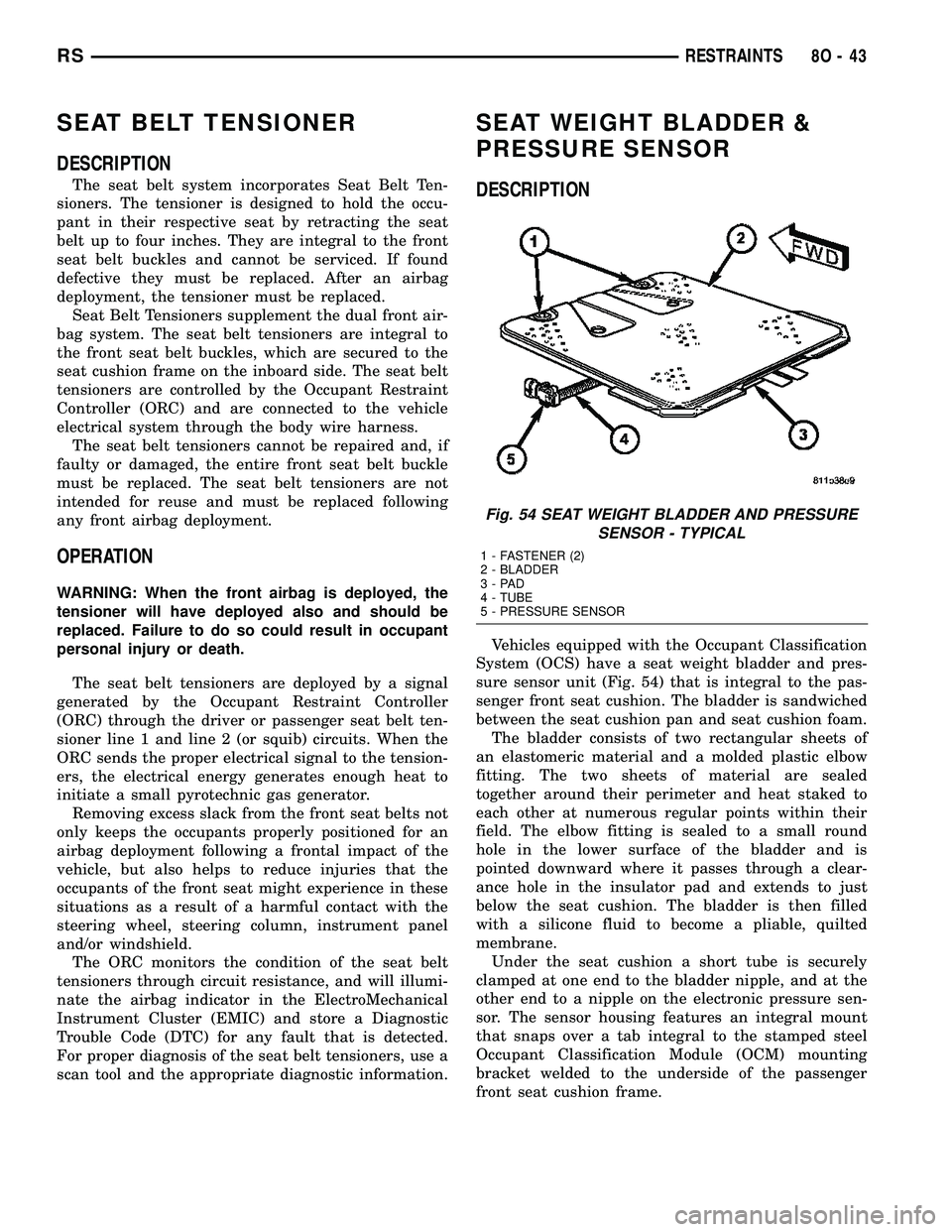
Vehicles equipped with the Occupant Classification
System (OCS) have a seat weight bladder and pres-
sure sensor unit (Fig. 54) that is integral to the pas-
senger front seat cushion. The bladder is sandwiched
between the seat cushion pan and seat cushion foam.
The bladder consists of two rectangular sheets of
an elastomeric material and a molded plastic elbow
fitting. The two sheets of material are sealed
together around their perimeter and heat staked to
each other at numerous regular points within their
field. The elbow fitting is sealed to a small round
hole in the lower surface of the bladder and is
pointed downward where it passes through a clear-
ance hole in the insulator pad and extends to just
below the seat cushion. The bladder is then filled
with a silicone fluid to become a pliable, quilted
membrane.
Under the seat cushion a short tube is securely
clamped at one end to the bladder nipple, and at the
other end to a nipple on the electronic pressure sen-
sor. The sensor housing features an integral mount
that snaps over a tab integral to the stamped steel
Occupant Classification Module (OCM) mounting
bracket welded to the underside of the passenger
front seat cushion frame.
Fig. 54 SEAT WEIGHT BLADDER AND PRESSURE
SENSOR - TYPICAL
1 - FASTENER (2)
2 - BLADDER
3-PAD
4 - TUBE
5 - PRESSURE SENSOR
RSRESTRAINTS8O-43
Page 536 of 2339
(4) Connect vacuum line to speed control servo
that leads to the battery tray/vacuum reservoir.
(5) Install speed control servo and bracket.
(6) Install battery tray/vacuum reservoir, refer to
the Battery section for more information.
(7) Install speed control and throttle cable casing
to cable mount bracket.
(8) Connect the throttle and speed control cable
ends to throttle body.
(9) Connect the negative battery cable.
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
There are two separate switch pods that operate
the speed control system and are located on the
steering wheel.
OPERATION
The speed control system has five separate resis-
tive switches that provide a single multiplexed
(MUX) voltage inputs to the PCM.The switch names
are: ON, OFF, SET, COAST, RESUME, ACCEL, TAP-
UP, COAST, and CANCEL. Based on conditions when
the buttons are pushed (and released), the five volt-
age ranges provided to the PCM result in the follow-
ing functions: ON, OFF, SET, COAST, RESUME,
ACCEL, TAP-UP, TAP-DOWN, COAST, and CAN-
CEL. Refer to the Speed Control Section for more
information
Also the PCM receives an input from the brake
switch to sense whether the brake pedal has been
depressed. When the PCM receives the brake
depressed input, it turns off power to the speed con-
trol servo and disengages speed control. Also the
power to the servo is supplied through the brake
switch, which opens the circuit when the brake pedal
is depressed.
The individual switches cannot be repaired. If one
switch fails, the entire switch module must be
replaced.
REMOVAL
The speed control switches are mounted in the
steering wheel and wired through the clock spring
device under the airbag module.
Fig. 2 Speed Control Cable End
1 - SPEED CONTROL VACUUM HOSE
2 - THROTTLE BODY
3 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
Fig. 3 BATTERY TRAY/VACUUM RESERVOIR
Fig. 4 SPEED CONTROL SERVO
RSSPEED CONTROL8P-5
SERVO (Continued)