engine coolant CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 249 of 2339

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RADIATOR FAN MOTOR
RADIATOR FAN DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY RADIATOR FAN 1. Fan blade loose. 1. Replace fan assembly. (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR
FAN - REMOVAL)
2. Fan blade striking a surrounding
object.2. Locate point of fan blade contact
and repair as necessary.
3. Air obstructions at radiator or A/C
condenser.3. Remove obstructions and/or
clean debris.
4. Electric fan motor defective. 4. Replace fan assembly. (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR
FAN - REMOVAL)
ELECTRIC FAN MOTOR DOES
NOT OPERATE1. Fan relay, powertrain control
module (PCM), coolant temperature
sensor, or wiring defective.1. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information) Repair as necessary.
2. Defective A/C pressure
transducer.2. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information) Repair as necessary.
ELECTRIC RADIATOR FAN
OPERATES ALL THE TIME1. Fan relay, powertrain control
module (PCM), coolant temperature
sensor or wiring defective.1. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information) Repair as necessary.
2. Check for low coolant level. 2. Add coolant as necessary.
3. Defective A/C pressure
transducer.3. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information) Repair as necessary.
REMOVAL
There are no repairs to be made to the fan or
shroud assembly. If the fan is warped, cracked, or
otherwise damaged, it must be replaced as an assem-
bly (Fig. 20).
(1) Remove the radiator upper crossmember. (Refer
to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/GRILLE OPENING REIN-
FORCEMENT - REMOVAL)
(2) Disconnect the radiator fan electrical connec-
tors.
(3) Remove radiator fan(s) retaining screw (Fig.
20).
(4) Remove the radiator fan(s) by lifting upward to
release from mounts.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the radiator fan(s) into mounts and
attaching clips on the radiator.
(2) Install radiator fan(s) attaching screws (Fig.
20). Tighten to 5 N´m (45 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the radiator fan(s) electrical connec-
tors.(4) Install the radiator upper support crossmem-
ber. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/GRILLE OPEN-
ING REINFORCEMENT - INSTALLATION)
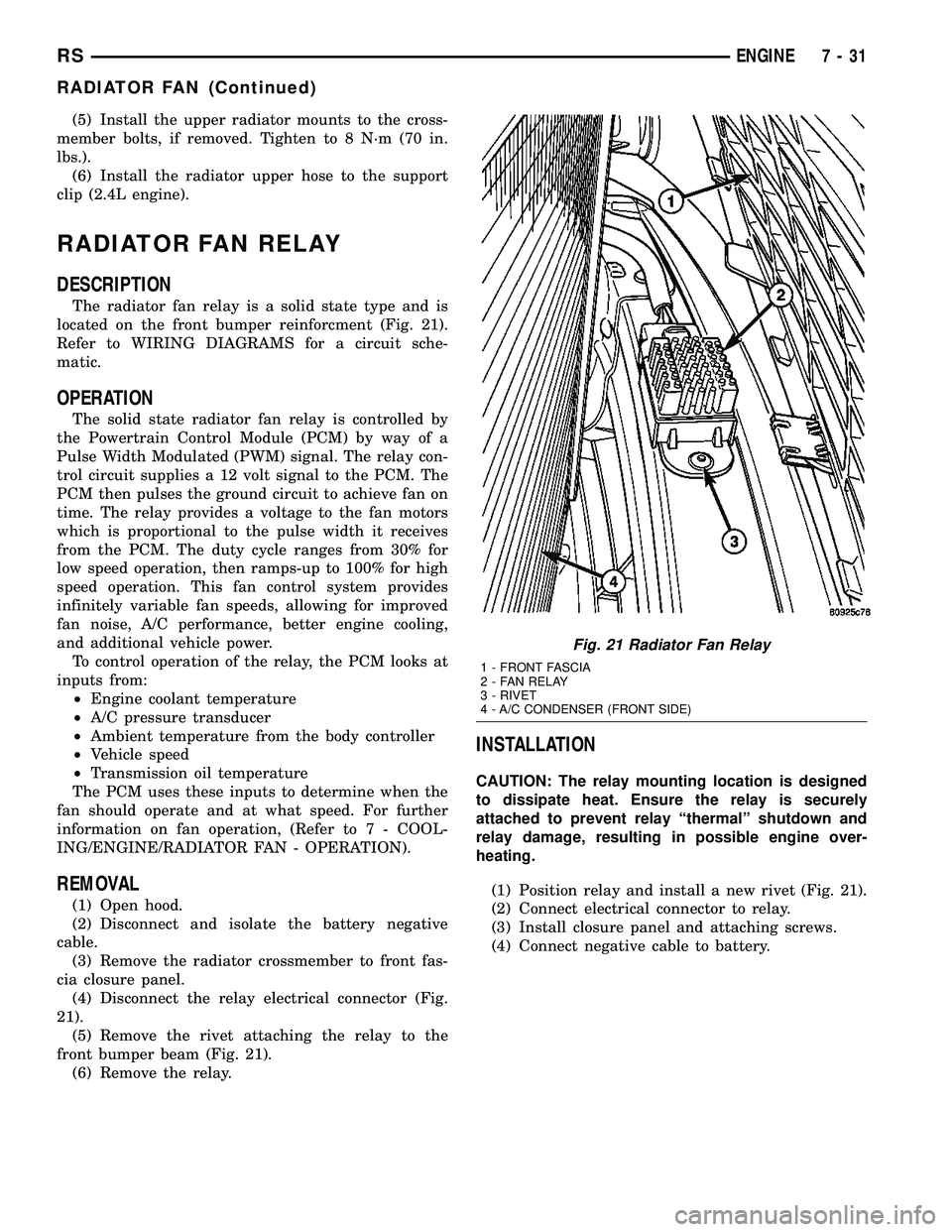
Fig. 20 Radiator Fans
1 - SCREWS - RADIATOR FAN ATTACHING
2 - RADIATOR FAN - RIGHT
3 - MOUNT - RIGHT RADIATOR FAN
4 - CLIPS - RADIATOR FAN LOWER
5 - MOUNT - LEFT RADIATOR FAN
6 - RADIATOR FAN - LEFT
7 - 30 ENGINERS
RADIATOR FAN (Continued)
Page 250 of 2339
(5) Install the upper radiator mounts to the cross-
member bolts, if removed. Tighten to 8 N´m (70 in.
lbs.).
(6) Install the radiator upper hose to the support
clip (2.4L engine).
RADIATOR FAN RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The radiator fan relay is a solid state type and is
located on the front bumper reinforcment (Fig. 21).
Refer to WIRING DIAGRAMS for a circuit sche-
matic.
OPERATION
The solid state radiator fan relay is controlled by
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) by way of a
Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) signal. The relay con-
trol circuit supplies a 12 volt signal to the PCM. The
PCM then pulses the ground circuit to achieve fan on
time. The relay provides a voltage to the fan motors
which is proportional to the pulse width it receives
from the PCM. The duty cycle ranges from 30% for
low speed operation, then ramps-up to 100% for high
speed operation. This fan control system provides
infinitely variable fan speeds, allowing for improved
fan noise, A/C performance, better engine cooling,
and additional vehicle power.
To control operation of the relay, the PCM looks at
inputs from:
²Engine coolant temperature
²A/C pressure transducer
²Ambient temperature from the body controller
²Vehicle speed
²Transmission oil temperature
The PCM uses these inputs to determine when the
fan should operate and at what speed. For further
information on fan operation, (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - OPERATION).
REMOVAL
(1) Open hood.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(3) Remove the radiator crossmember to front fas-
cia closure panel.
(4) Disconnect the relay electrical connector (Fig.
21).
(5) Remove the rivet attaching the relay to the
front bumper beam (Fig. 21).
(6) Remove the relay.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The relay mounting location is designed
to dissipate heat. Ensure the relay is securely
attached to prevent relay ªthermalº shutdown and
relay damage, resulting in possible engine over-
heating.
(1) Position relay and install a new rivet (Fig. 21).
(2) Connect electrical connector to relay.
(3) Install closure panel and attaching screws.
(4) Connect negative cable to battery.
Fig. 21 Radiator Fan Relay
1 - FRONT FASCIA
2 - FAN RELAY
3 - RIVET
4 - A/C CONDENSER (FRONT SIDE)
RSENGINE7-31
RADIATOR FAN (Continued)
Page 251 of 2339
WATER PUMP - 2.4L
DESCRIPTION
The water pump has a cast aluminum body and
housing with a stamped steel impeller. The water
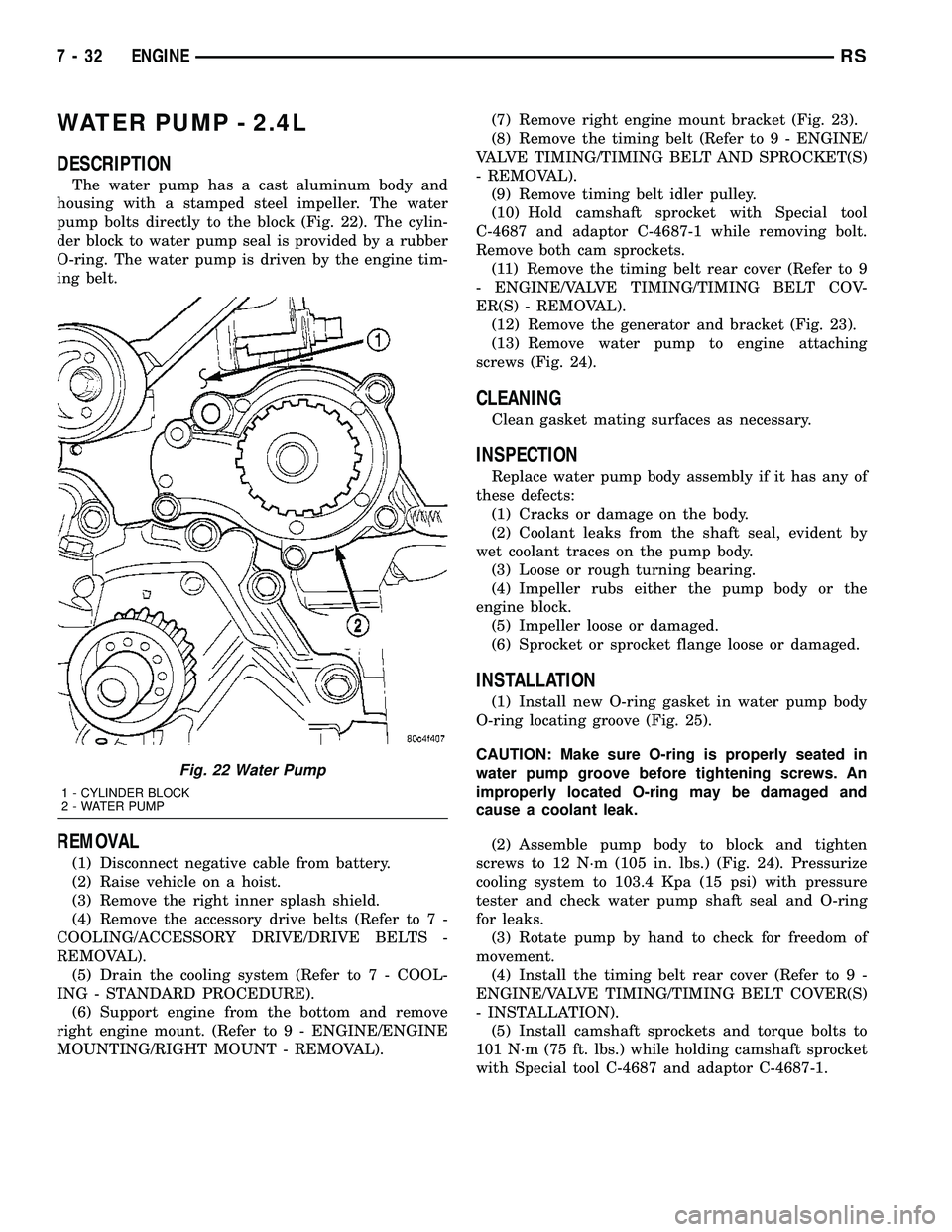
pump bolts directly to the block (Fig. 22). The cylin-
der block to water pump seal is provided by a rubber
O-ring. The water pump is driven by the engine tim-
ing belt.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Raise vehicle on a hoist.
(3) Remove the right inner splash shield.
(4) Remove the accessory drive belts (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(5) Drain the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(6) Support engine from the bottom and remove
right engine mount. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE
MOUNTING/RIGHT MOUNT - REMOVAL).(7) Remove right engine mount bracket (Fig. 23).
(8) Remove the timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT AND SPROCKET(S)
- REMOVAL).
(9) Remove timing belt idler pulley.
(10) Hold camshaft sprocket with Special tool
C-4687 and adaptor C-4687-1 while removing bolt.
Remove both cam sprockets.
(11) Remove the timing belt rear cover (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT COV-
ER(S) - REMOVAL).
(12) Remove the generator and bracket (Fig. 23).
(13) Remove water pump to engine attaching
screws (Fig. 24).
CLEANING
Clean gasket mating surfaces as necessary.
INSPECTION
Replace water pump body assembly if it has any of
these defects:
(1) Cracks or damage on the body.
(2) Coolant leaks from the shaft seal, evident by
wet coolant traces on the pump body.
(3) Loose or rough turning bearing.
(4) Impeller rubs either the pump body or the
engine block.
(5) Impeller loose or damaged.
(6) Sprocket or sprocket flange loose or damaged.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install new O-ring gasket in water pump body
O-ring locating groove (Fig. 25).
CAUTION: Make sure O-ring is properly seated in
water pump groove before tightening screws. An
improperly located O-ring may be damaged and
cause a coolant leak.
(2) Assemble pump body to block and tighten
screws to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) (Fig. 24). Pressurize
cooling system to 103.4 Kpa (15 psi) with pressure
tester and check water pump shaft seal and O-ring
for leaks.
(3) Rotate pump by hand to check for freedom of
movement.
(4) Install the timing belt rear cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT COVER(S)
- INSTALLATION).
(5) Install camshaft sprockets and torque bolts to
101 N´m (75 ft. lbs.) while holding camshaft sprocket
with Special tool C-4687 and adaptor C-4687-1.
Fig. 22 Water Pump
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - WATER PUMP
7 - 32 ENGINERS
Page 254 of 2339
(8) Remove and discard the seal.
(9) Clean seal groove and sealing surfaces on
pump and timing chain case cover. Take care not to
scratch or gouge sealing surfaces.
CLEANING
Clean gasket mating surfaces as necessary.
INSPECTION
Replace the water pump if it has any of the follow-
ing defects.
(1) Damage or cracks on the pump body.
(2) Coolant leaks; this will be evident by a wet
stream of coolant running down the pump body and
components below. A thin stain below the weep hole
reservoir slot (Fig. 29) is considered normal opera-
tion.(3) Impeller rubs inside of chain case cover.
(4) Excessively loose or rough turning bearing.
NOTE: A weepage stain that is black, brown, or grey
is considered normal, if it is dry. If the weep
appears wet; pressure test the cooling system at
15±18 psi and observe the weep area. If weep area
remains unchanged, do not replace the water pump
for this condition. Replace the water pump, if a
steady flow of engine coolant is evident from the
weep hole/reservoir slot (Fig. 29) (shaft seal failure).
Be sure to perform a thorough analysis before
replacing water pump.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install new seal into water pump housing
groove (Fig. 30).
NOTE: The water pump pulley MUST be positioned
loosely between the pump housing and drive hub
BEFORE water pump installation.
(2) Position the water pump pulley loosely between
pump housing and drive hub (Fig. 27).
(3) Install water pump and pulley to the timing
chain case cover (Fig. 26). Tighten water pump bolts
to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(4) Position pulley on water pump hub. Install
bolts and tighten to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.) (Fig. 26).
(5) Rotate pump by hand to check for freedom of
movement.
(6) Install the accessory drive belt. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION)
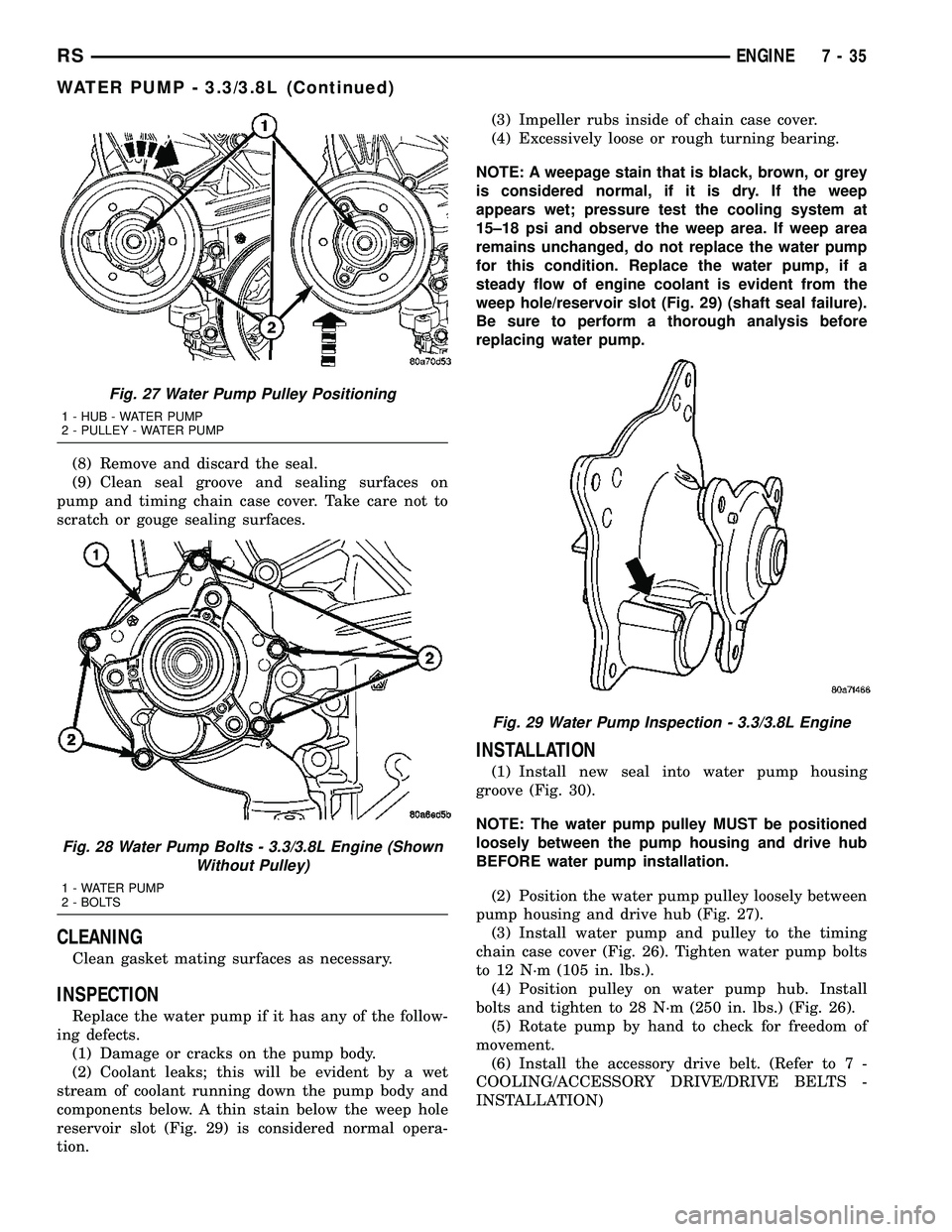
Fig. 27 Water Pump Pulley Positioning
1 - HUB - WATER PUMP
2 - PULLEY - WATER PUMP
Fig. 28 Water Pump Bolts - 3.3/3.8L Engine (Shown
Without Pulley)
1 - WATER PUMP
2 - BOLTS
Fig. 29 Water Pump Inspection - 3.3/3.8L Engine
RSENGINE7-35
WATER PUMP - 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 255 of 2339
(7) Install drive belt shield.
(8) Fill the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING
- STANDARD PROCEDURE)
WATER PUMP INLET TUBE -
2.4L
DESCRIPTION
The 2.4L engine uses a metal tube to connect the
engine block to the lower radiator hose and heater
return (Fig. 31). The tube has an O-ring for block to
tube sealing and bolts attach the tube to the engine
block.
REMOVAL
(1) Drain the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(2) Remove radiator upper hose to access the hose
connections at the inlet tube.
(3) Remove radiator lower (Fig. 7) and heater
hoses from the inlet tube (Fig. 32).
(4) Remove the two fasteners that hold the inlet
tube to the block.
(5) Rotate tube while removing the tube from the
engine block.
INSTALLATION
(1) Inspect the O-ring for damage before installing
the tube into the cylinder block (Fig. 31).
(2) Lube O-ring with coolant and install inlet tube
into the cylinder block opening (Fig. 31).(3) Install the two inlet tube fasteners and tighten
to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(4) Connect the radiator lower hose (Fig. 7) and
heater hose to inlet tube (Fig. 32).
(5) Install the radiator upper hose.
(6) Fill the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING
- STANDARD PROCEDURE)
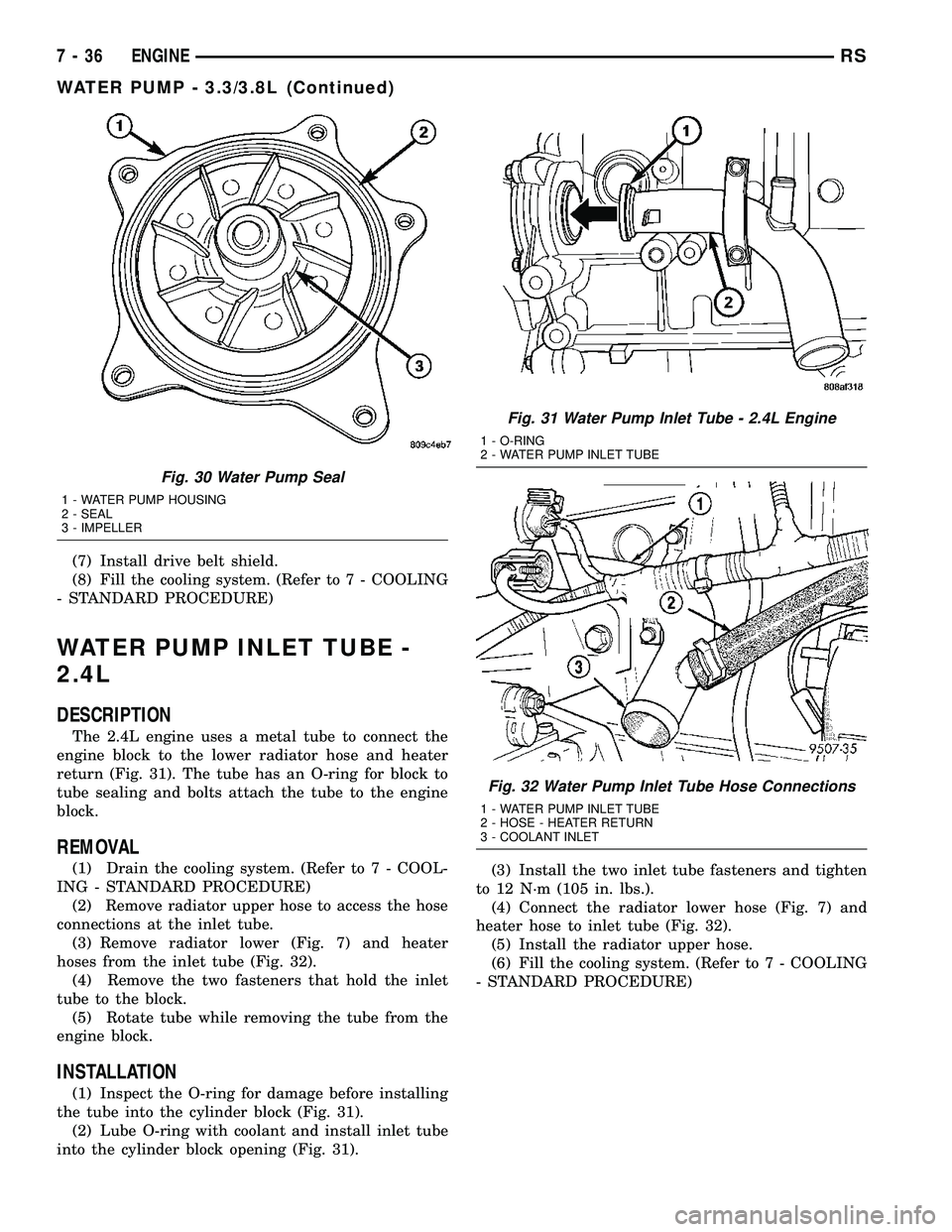
Fig. 30 Water Pump Seal
1 - WATER PUMP HOUSING
2 - SEAL
3 - IMPELLER
Fig. 31 Water Pump Inlet Tube - 2.4L Engine
1 - O-RING
2 - WATER PUMP INLET TUBE
Fig. 32 Water Pump Inlet Tube Hose Connections
1 - WATER PUMP INLET TUBE
2 - HOSE - HEATER RETURN
3 - COOLANT INLET
7 - 36 ENGINERS
WATER PUMP - 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 296 of 2339
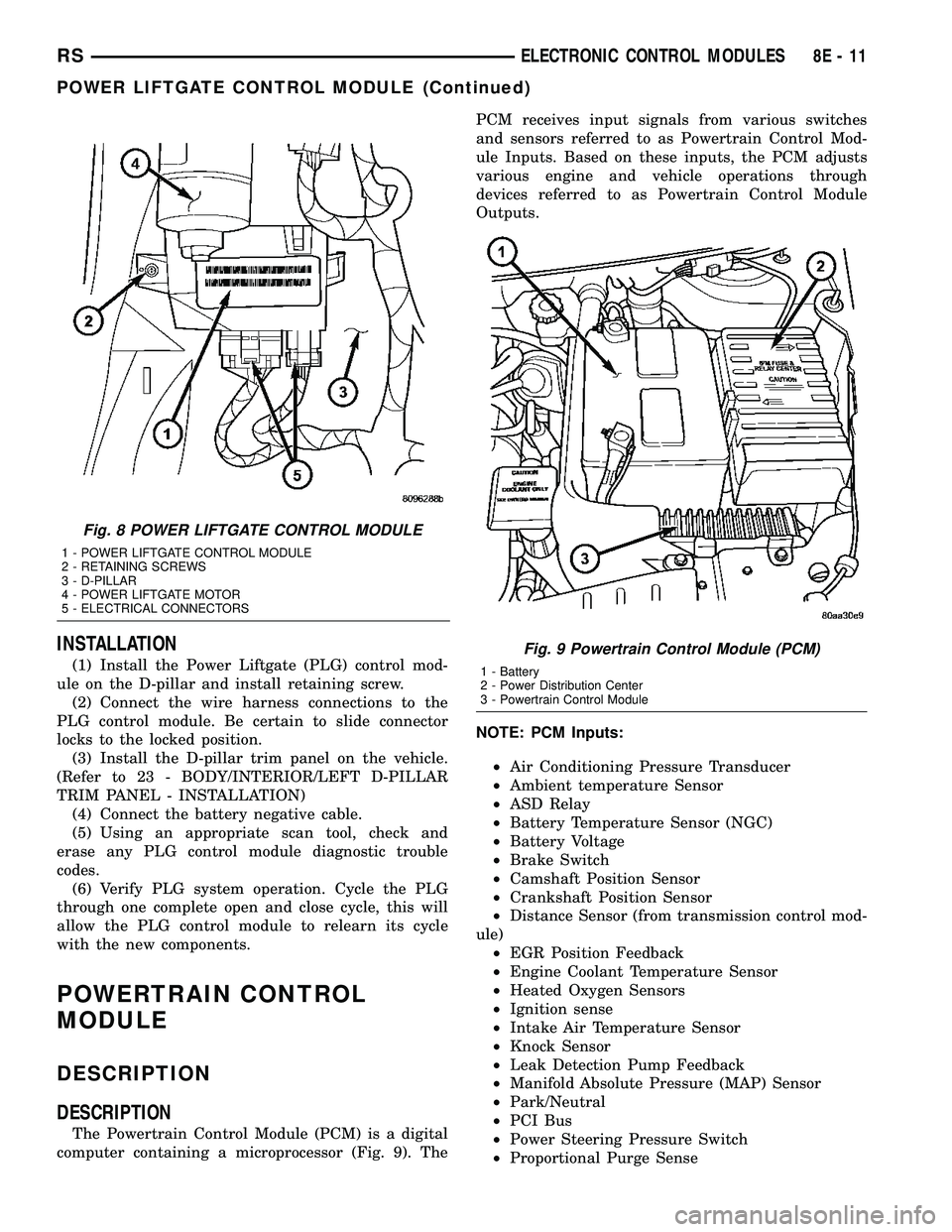
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the Power Liftgate (PLG) control mod-
ule on the D-pillar and install retaining screw.
(2) Connect the wire harness connections to the
PLG control module. Be certain to slide connector
locks to the locked position.
(3) Install the D-pillar trim panel on the vehicle.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/LEFT D-PILLAR
TRIM PANEL - INSTALLATION)
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
(5) Using an appropriate scan tool, check and
erase any PLG control module diagnostic trouble
codes.
(6) Verify PLG system operation. Cycle the PLG
through one complete open and close cycle, this will
allow the PLG control module to relearn its cycle
with the new components.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is a digital
computer containing a microprocessor (Fig. 9). ThePCM receives input signals from various switches
and sensors referred to as Powertrain Control Mod-
ule Inputs. Based on these inputs, the PCM adjusts
various engine and vehicle operations through
devices referred to as Powertrain Control Module
Outputs.
NOTE: PCM Inputs:
²Air Conditioning Pressure Transducer
²Ambient temperature Sensor
²ASD Relay
²Battery Temperature Sensor (NGC)
²Battery Voltage
²Brake Switch
²Camshaft Position Sensor
²Crankshaft Position Sensor
²Distance Sensor (from transmission control mod-
ule)
²EGR Position Feedback
²Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
²Heated Oxygen Sensors
²Ignition sense
²Intake Air Temperature Sensor
²Knock Sensor
²Leak Detection Pump Feedback
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Park/Neutral
²PCI Bus
²Power Steering Pressure Switch
²Proportional Purge Sense
Fig. 8 POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE
1 - POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE
2 - RETAINING SCREWS
3 - D-PILLAR
4 - POWER LIFTGATE MOTOR
5 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
Fig. 9 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
1 - Battery
2 - Power Distribution Center
3 - Powertrain Control Module
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-11
POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 297 of 2339

²SCI Receive
²Speed Control
²Throttle Position Sensor
²Transmission Control Relay (Switched B+)
²Transmission Pressure Switches
²Transmission Temperature Sensor
²Transmission Input Shaft Speed Sensor
²Transmission Output Shaft Speed Sensor
²Transaxle Gear Engagement
²Vehicle Speed
NOTE: PCM Outputs:
²Air Conditioning Clutch Relay
²Automatic Shut Down (ASD) and Fuel Pump
Relays
²Data Link Connector (PCI and SCI Transmit)
²Double Start Override
²EGR Solenoid
²Fuel Injectors
²Generator Field
²High Speed Fan Relay
²Idle Air Control Motor
²Ignition Coils
²Leak Detection Pump
²Low Speed Fan Relay
²MTV Actuator
²Proportional Purge Solenoid
²SRV Valve
²Speed Control Relay
²Speed Control Vent Relay
²Speed Control Vacuum Relay
²8 Volt Output
²5 Volt Output
²Torque Reduction Request
²Transmission Control Relay
²Transmission Solenoids
²Vehicle Speed
Based on inputs it receives, the powertrain control
module (PCM) adjusts fuel injector pulse width, idle
speed, ignition timing, and canister purge operation.
The PCM regulates the cooling fans, air conditioning
and speed control systems. The PCM changes gener-
ator charge rate by adjusting the generator field.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width (air-fuel
ratio) based on the following inputs.
²Battery Voltage
²Intake Air Temperature Sensor
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Engine Speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Exhaust Gas Oxygen Content (heated oxygen
sensors)
²Manifold Absolute Pressure
²Throttle Position
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the
idle air control motor based on the following inputs.
²Brake Switch²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Engine Speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Park/Neutral
²Transaxle Gear Engagement
²Throttle Position
²Vehicle Speed
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based on the fol-
lowing inputs.
²Intake Air Temperature
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Engine Speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Knock Sensor
²Manifold Absolute Pressure
²Park/Neutral
²Transaxle Gear Engagement
²Throttle Position
The automatic shut down (ASD) and fuel pump
relays are mounted externally, but turned on and off
by the powertrain control module through the same
circuit.
The camshaft and crankshaft signals are sent to
the powertrain control module. If the PCM does not
receive both signals within approximately one second
of engine cranking, it deactivates the ASD and fuel
pump relays. When these relays are deactivated,
power is shut off to the fuel injectors, ignition coils,
fuel pump and the heating element in each oxygen
sensor.
The PCM contains a voltage converter that
changes battery voltage to a regulated 8.0 volts. The
8.0 volts power the camshaft position sensor, crank-
shaft position sensor and vehicle speed sensor. The
PCM also provides a 5.0 volts supply for the engine
coolant temperature sensor, intake air temperature
sensor, manifold absolute pressure sensor and throt-
tle position sensor.
The PCM engine control strategy prevents reduced
idle speeds until after the engine operates for 320 km
(200 miles). If the PCM is replaced after 320 km (200
miles) of usage, update the mileage in new PCM. Use
the DRBIIItscan tool to change the mileage in the
PCM. Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic
Manual and the DRBIIItscan tool.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL
CLUTCH VOLUME INDEX (CVI)
An important function of the PCM is to monitor
Clutch Volume Index (CVI). CVIs represent the vol-
ume of fluid needed to compress a clutch pack.
The PCM monitors gear ratio changes by monitor-
ing the Input and Output Speed Sensors. The Input,
or Turbine Speed Sensor sends an electrical signal to
the PCM that represents input shaft rpm. The Out-
put Speed Sensor provides the PCM with output
shaft speed information.
8E - 12 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 299 of 2339
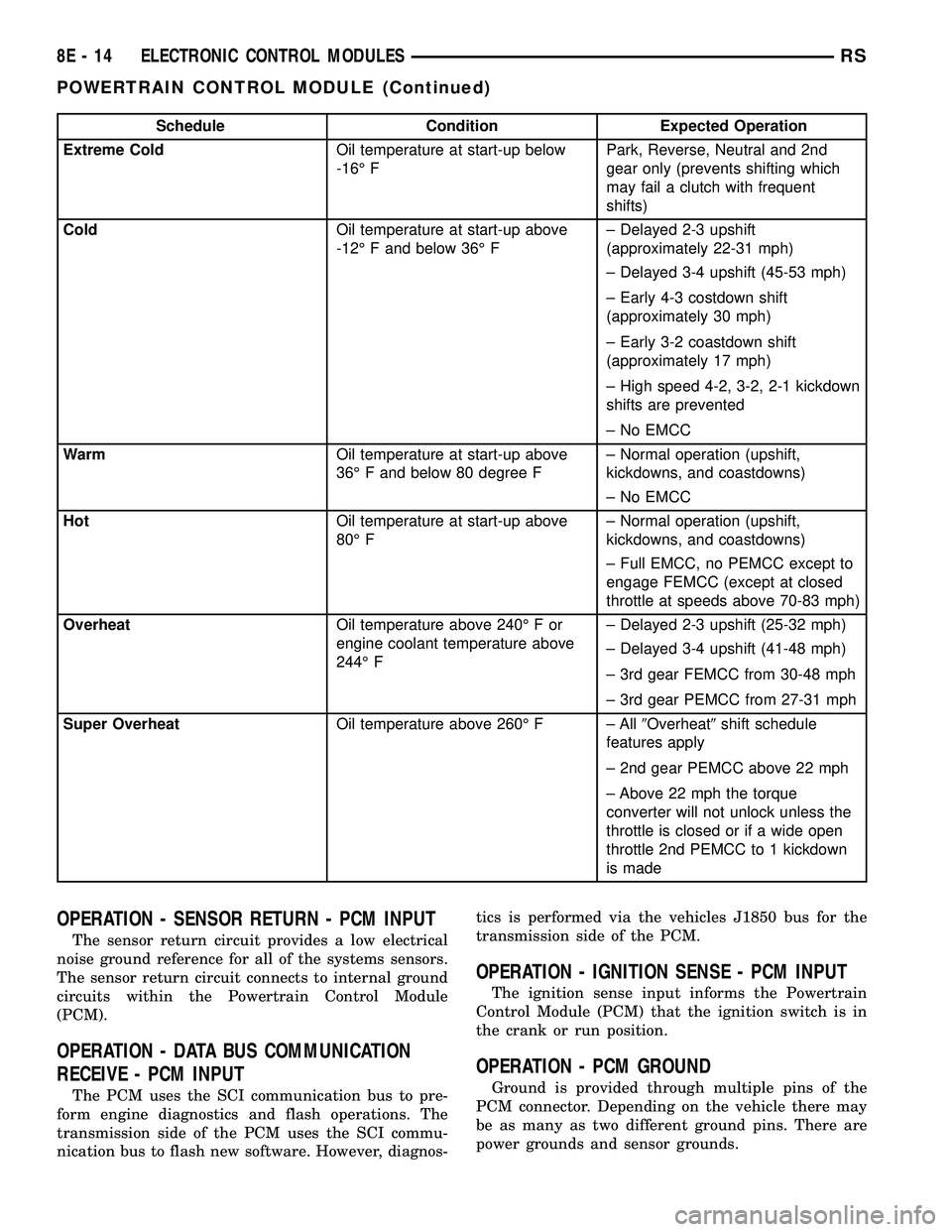
Schedule Condition Expected Operation
Extreme ColdOil temperature at start-up below
-16É FPark, Reverse, Neutral and 2nd
gear only (prevents shifting which
may fail a clutch with frequent
shifts)
ColdOil temperature at start-up above
-12É F and below 36É F± Delayed 2-3 upshift
(approximately 22-31 mph)
± Delayed 3-4 upshift (45-53 mph)
± Early 4-3 costdown shift
(approximately 30 mph)
± Early 3-2 coastdown shift
(approximately 17 mph)
± High speed 4-2, 3-2, 2-1 kickdown
shifts are prevented
± No EMCC
WarmOil temperature at start-up above
36É F and below 80 degree F± Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns)
± No EMCC
HotOil temperature at start-up above
80É F± Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns)
± Full EMCC, no PEMCC except to
engage FEMCC (except at closed
throttle at speeds above 70-83 mph)
OverheatOil temperature above 240É F or
engine coolant temperature above
244É F± Delayed 2-3 upshift (25-32 mph)
± Delayed 3-4 upshift (41-48 mph)
± 3rd gear FEMCC from 30-48 mph
± 3rd gear PEMCC from 27-31 mph
Super OverheatOil temperature above 260É F ± All9Overheat9shift schedule
features apply
± 2nd gear PEMCC above 22 mph
± Above 22 mph the torque
converter will not unlock unless the
throttle is closed or if a wide open
throttle 2nd PEMCC to 1 kickdown
is made
OPERATION - SENSOR RETURN - PCM INPUT
The sensor return circuit provides a low electrical
noise ground reference for all of the systems sensors.
The sensor return circuit connects to internal ground
circuits within the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM).
OPERATION - DATA BUS COMMUNICATION
RECEIVE - PCM INPUT
The PCM uses the SCI communication bus to pre-
form engine diagnostics and flash operations. The
transmission side of the PCM uses the SCI commu-
nication bus to flash new software. However, diagnos-tics is performed via the vehicles J1850 bus for the
transmission side of the PCM.
OPERATION - IGNITION SENSE - PCM INPUT
The ignition sense input informs the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) that the ignition switch is in
the crank or run position.
OPERATION - PCM GROUND
Ground is provided through multiple pins of the
PCM connector. Depending on the vehicle there may
be as many as two different ground pins. There are
power grounds and sensor grounds.
8E - 14 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 300 of 2339

The power grounds are used to control the ground
side relays, solenoids, ignition coil or injectors. The
signal ground is used for any input that uses sensor
return for ground, and the ground side of any inter-
nal processing component.
The PCM case is shielded to prevent RFI and EMI.
The PCM case is grounded and must be firmly
attached to a good, clean body ground.
Internally all grounds are connected together, how-
ever there is noise suppression on the sensor ground.
For EMI and RFI protection the housing and cover
are also grounded separately from the ground pins.
OPERATION - 5 VOLT SUPPLY - PCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies 5 volts to the following sensors:
²A/C pressure transducer
²Ambient Temperature sensor
²Battery temperature
²Camshaft Position Sensor (NGC)
²Crankshaft Position Sensor (NGC)
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Inlet Air Temperature Sensor
²Knock sensor
²Linear EGR solenoid (if equipped)
²Manifold absolute pressure sensor
²Oil Pressure Switch
²Throttle position sensor
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OBTAINING
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
BULB CHECK
Key on: Bulb illuminated until vehicle starts, as
long as all once per trip (readiness) monitors com-
pleted. If monitors havenotbeen completed, then:
Key on: bulb check for about 5 to 8 seconds, lamp
then flashes if once per trip (readiness) monitors
havenotbeen completed until vehicle is started,
then MIL is extinguished.
OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
(4) To erase DTC's, use the ªErase Trouble Codeº
data screen on the DRB scan tool.Do not erase any
DTC's until problems have been investigated
and repairs have been performed.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PINION FACTOR
SETTING
NOTE: This procedure must be performed if the
PCM has been replaced with a NEW or replacement
unit. Failure to perform this procedure will result in
an inoperative or improperly calibrated speedome-
ter.
The vehicle speed readings for the speedometer are
taken from the output speed sensor. The PCM must
be calibrated to the different combinations of equip-
ment (final drive and tires) available. Pinion Factor
allows the technician to set the Powertrain Control
Module initial setting so that the speedometer read-
ings will be correct. To properly read and/or reset the
Pinion Factor, it is necessary to use a DRBIIItscan
tool.
(1) Plug the DRBIIItscan tool into the diagnostic
connector located under the instrument panel.
(2) Select the Transmission menu.
(3) Select the Miscellaneous menu.
(4) Select Pinion Factor. Then follow the instruc-
tions on the DRBIIItscan tool screen.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - QUICK LEARN
PROCEDURE
The quick learn procedure requires the use of the
DRBIIItscan tool. This program allows the PCM to
recalibrate itself. This will provide the best possible
transaxle operation.
NOTE: The quick learn procedure should be per-
formed if any of the following procedures are per-
formed:
²Transaxle Assembly Replacement
²Powertrain Control Module Replacement
²Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly Replacement
²Clutch Plate and/or Seal Replacement
²Valve Body Replacement or Recondition
To perform the Quick Learn Procedure, the follow-
ing conditions must be met:
²The brakes must be applied
²The engine speed must be above 500 rpm
²The throttle angle (TPS) must be less than 3
degrees
²The shift lever position must stay until
prompted to shift to overdrive
²The shift lever position must stay in overdrive
after the Shift to Overdrive prompt until the
DRBIIItindicates the procedure is complete
²The calculated oil temperature must be above
60É and below 200É
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-15
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 329 of 2339

SPECIAL TOOLS
BATTERY TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
(NGC Vehicles) The PCM incorporates a Battery
Temperature Sensor (BTS) on its circuit board.
OPERATION
The PCM uses the temperature of the battery area
to control the charge system voltage. This tempera-
ture, along with data from monitored line voltage, is
used by the PCM to vary the battery charging rate.
The system voltage is higher at cold temperatures
and is gradually reduced as temperature around the
battery increases.
For vehicles with 1.6L engine, there is no physical
battery temp sensor in place to detect battery temp.
Rather, an algorithm buit in PCM is employed to pre-
dict battery temp using inlet air temp, vehicle speed,
and coolant temp, among other signals. The PCM
maintains the optimal output of the generator by
monitoring battery voltage and controlling it to a
range of 13.5 - 14.7 volts based on battery tempera-
ture. The system target voltage is 13.5 ± 14.7 volts.
However the actual voltage go below this during
heavy electrical loads and generator speeds. Also the
actual voltage can be lower than the target voltage
between the battery and the battery voltage sense
circuit, approximately 0.2 Ð 0.3 volts.
The battery temperature sensor is also used for
OBD II diagnostics. Certain faults and OBD II mon-
itors are either enabled or disabled depending upon
the battery temperature sensor input (example: dis-
able purge and EGR, enable LDP). Most OBD II
monitors are disabled below 20ÉF.
REMOVAL
The battery temperature sensor is not serviced sep-
arately. If replacement is necessary, the PCM must
be replaced.
GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION
The generator is belt-driven by the engine. The
generator produces DC voltage at the B+ terminal. If
the generator is failed, the generator assembly sub-
components (generator and decoupler pulley) must be
inspected for individual failure and replaced accord-
ingly.
OPERATION
As the energized rotor begins to rotate within the
generator, the spinning magnetic field induces a cur-
rent into the windings of the stator coil. Once the
generator begins producing sufficient current, it also
provides the current needed to energize the rotor.
The Y type stator winding connections deliver the
induced AC current to 3 positive and 3 negative
diodes for rectification. From the diodes, rectified DC
current is delivered to the vehicles electrical system
through the generator, battery, and ground terminals.
Excessive or abnormal noise emitting from the gen-
erator may be caused by:
²Worn, loose or defective bearings
²Loose or defective drive pulley (2.4L) or decou-
pler (3.3/3.8L)
²Incorrect, worn, damaged or misadjusted drive
belt
²Loose mounting bolts
²Misaligned drive pulley
²Defective stator or diode
²Damaged internal fins
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L
(1) Release hood latch and open hood.
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(3) Disconnect the Inlet Air Temperature sensor.
(4) Remove the Air Box, refer to the Engine/Air
Cleaner for more information.
(5) Remove the EVAP Purge solenoid from its
bracket and reposition.
(6) Disconnect the push-in field wire connector
from back of generator.
(7) Remove nut holding B+ wire terminal to back
of generator.
(8) Separate B+ terminal from generator.
GENERATOR DECOUPLER 8433
8F - 24 CHARGINGRS
CHARGING (Continued)