Vacuum DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 308 of 2643
1F – 62IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
FUEL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
Circuit Description
The fuel pump is an in–tank type mounted to a fuel sender
assembly. The fuel pump will remain on as long as the en-
gine is cranking or running and the Engine Control Module
(ECM) is receiving reference pulses from the crankshaft
position (CKP) sensor. If there are no reference pulses,
the ECM will turn off the fuel pump two seconds after the
ignition switch is turned ON or two seconds after the en-
gine stops running. The fuel pump delivers fuel to the fuel
rail and the fuel injectors, where the fuel system pressure
is controlled from 284 to 325 kPa (41 to 47 psi) by the fuel
pressure regulator. The excess fuel is returned to the fuel
tank.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
2. When the engine is idling, the intake manifold vacu-
um is high. This vacuum is applied to the fuel pres-
sure regulator diaphragm, offsetting the spring
pressure inside the fuel pressure regulator and low-
ering the fuel pressure.10. If there is fuel bleeding back through the fuel return
outlet, this is due to a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
14. Another symptom often present when the fuel injec-
tors are leaking is hard starting. Leaking fuel injec-
tors can cause a flooding condition.
23. Fuel leaking from the fuel pump inlet is due to a
faulty one–way check valve in the fuel pump.
CAUTION : The fuel system is under pressure. To
avoid fuel spillage and the risk of personal injury or
fire, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system pressure
before disconnecting the fuel lines.
CAUTION : Do not pinch or restrict nylon fuel lines to
avoid damage that could cause a fuel leak, resulting
in possible fire or personal injury.
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
1. Remove the fuel cap.
2. Remove the fuel pump fuse EF18 from the engine
fuse box.
3. Start the engine and allow the engine to stall.
4. Crank the engine for an additional 10 seconds.
Fuel System Diagnosis
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Relieve the fuel system pressure.
2. Install a fuel pressure gauge.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
Is the fuel pressure within the values specified and
holding steady?284~325 kPa
(41~47psi)Go to Step 2Go to Step 4
21. Allow the engine to idle.
2. Disconnect the vacuum hose from the fuel
pressure regulator.
3. Connect a vacuum pump with a gauge to the
fuel pressure regulator vacuum port.
4. Apply 41~47 kPa (12~14 in. Hg) of vacuum to
the fuel pressure regulator.
Does the fuel pressure decrease?–Go to Step 3Go to Step 15
31. Locate and correct the cause of the vacuum
restriction to the fuel pressure regulator.
2. Confirm the operation of the fuel pressure reg-
ulator.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
41. Relieve the fuel system pressure.
2. Install a fuel pressure gauge.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
Is the fuel pressure within the values specified but
not holding steady?284~325 kPa
(41~47psi)Go to Step 5Go to Step 16
5Inspect the fuel lines for a leak.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
Page 309 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 63
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
61. Replace the fuel line(s) as needed.
2. Install a fuel pressure gauge.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
Is the fuel pressure within the values specified but
not holding steady?284~325 kPa
(41~47psi)System OK–
71. Remove the fuel pump assembly.
2. With the fuel pump under pressure, inspect the
fuel pump coupling hoses for leaking.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 9
81. Tighten or replace the fuel pump coupling
hoses as needed.
2. Install a fuel pressure gauge.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
Is the fuel pressure within the values specified but
not holding steady?41–47 psi
(284–325 kPa)System OK–
9With the fuel system under pressure, inspect the fuel
return outlet for leaking.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 10Go to Step 11
101. Replace the fuel pressure regulator.
2. Install a fuel pressure gauge.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
Is the fuel pressure within the values specified but
not holding steady?284~325 kPa
(41~47psi)System OK–
11With the fuel system under pressure, inspect the fuel
inlet for leaking.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 13
121. Replace the fuel pump assembly.
2. Install a fuel pressure gauge.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
Is the fuel pressure within the values specified but
not holding steady?284~325 kPa
(41~47psi)System OK–
131. Remove the fuel rail and the fuel injectors as
an assembly.
2. With the fuel system under pressure, inspect
all of the fuel injectors for leaking.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 14–
141. Replace the leaking fuel injector(s).
2. Install a fuel pressure gauge.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
Is the fuel pressure within the values specified but
not holding steady?284~325 kPa
(41~47psi)System OK–
151. Replace the fuel pressure regulator.
2. Disconnect the fuel pressure regulator vacuum
hose.
3. Start the engine.
4. Allow the engine to idle.
5. Connect the fuel pressure regulator vacuum
hose.
Does the fuel pressure decrease?–System OK–
Page 321 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 75
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE CHECK
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor measures
the changes in the intake manifold pressure which result
from engine load (intake manifold vacuum) and rpm
changes. The MAP sensor converts these changes into a
voltage output. The engine control module (ECM) sends
a 5–volt reference voltage to the MAP sensor. As the in-
take manifold pressure changes, the output voltage of the
MAP sensor also changes. A low voltage (high vacuum)
output of 1 to 2 volts is present at idle. A high voltage (low
vacuum) output of 4.0 to 4.8 volts is present at wide open
throttle. The MAP sensor is also used under certain condi-
tions to measure baro–metric pressure. This allows the
ECM to make adjustments for altitude changes. The ECMuses the MAP sensor for fuel delivery and ignition timing
changes.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
2. Applying 34 kPa (10 inches Hg) of vacuum to the
MAP sensor should cause the voltage to change.
Subtract the second voltage reading from the first.
That voltage value should be more than 1.5 volts.
When applying vacuum to the MAP sensor, the
change in the voltage should happen instantly. A
slow voltage change indicates a faulty MAP sensor.
3. Disconnect the MAP sensor from the bracket and
twist the MAP sensor. Output changes more than
0.1 volt indicate a faulty connector or connection.
Page 322 of 2643
1F – 76IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Manifold Absolute Pressure Check (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Connect a scan tool to the Data Link Connec-
tor (DLC).
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. Compare the Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) sensor voltage reading from the scan-
ner with that from a known good vehicle.
Is the difference in the two voltage readings less
than the value specified?0.4 vGo to Step 2Go to Step 5
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Connect a scan tool to the DLC.
3. Disconnect the MAP sensor vacuum line.
4. Connect a hand vacuum pump to the MAP
sensor.
5. Turn the ignition ON.
6. Note the MAP sensor voltage.
7. Apply 10 in. Hg (34 kPa) of vacuum to the
MAP sensor and note the voltage change.
Is the difference in voltage readings more than the
value specified?1.5 vSystem OKGo to Step 3
3Inspect the MAP sensor connector terminals.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
4Repair the MAP sensor connector terminals as
needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
5Replace the MAP sensor.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 323 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 77
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE CHECK (1.8L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor measures
the changes in the intake manifold pressure which result
from engine load (intake manifold vacuum) and rpm
changes. The MAP sensor converts these changes into a
voltage output. The engine control module (ECM) sends
a 5–volt reference voltage to the MAP sensor. As the in-
take manifold pressure changes, the output voltage of the
MAP sensor also changes. A low voltage (high vacuum)
output of 1 to 2 volts is present at idle. A high voltage (low
vacuum) output of 4.0 to 4.8 volts is present at wide open
throttle. The MAP sensor is also used under certain condi-
tions to measure baro–metric pressure. This allows the
ECM to make adjustments for altitude changes. The ECMuses the MAP sensor for fuel delivery and ignition timing
changes.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
2. Applying 34 kPa (10 inches Hg) of vacuum to the
MAP sensor should cause the voltage to change.
Subtract the second voltage reading from the first.
That voltage value should be more than 1.5 volts.
When applying vacuum to the MAP sensor, the
change in the voltage should happen instantly. A
slow voltage change indicates a faulty MAP sensor.
3. Disconnect the MAP sensor from the bracket and
twist the MAP sensor. Output changes more than
0.1 volt indicate a faulty connector or connection.
Page 324 of 2643
1F – 78IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Manifold Absolute Pressure Check (1.8L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Connect a scan tool to the Data Link Connec-
tor (DLC).
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. Compare the Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) sensor voltage reading from the scan-
ner with that from a known good vehicle.
Is the difference in the two voltage readings less
than the value specified?0.4 vGo to Step 2Go to Step 5
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Connect a scan tool to the DLC.
3. Disconnect the MAP sensor vacuum line.
4. Connect a hand vacuum pump to the MAP
sensor.
5. Turn the ignition ON.
6. Note the MAP sensor voltage.
7. Apply 10 in. Hg (34 kPa) of vacuum to the
MAP sensor and note the voltage change.
Is the difference in voltage readings more than the
value specified?1.5 vSystem OKGo to Step 3
3Inspect the MAP sensor connector terminals.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
4Repair the MAP sensor connector terminals as
needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
5Replace the MAP sensor.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 325 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 79
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
IDLE AIR CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The aim of the MTIA (Main Throttle Idle Actuator) is to con-
trol the idle speed with the throttle body itself. The throttle
is motorized for low opening angle (0°C, 19°C). The char-
acteristics of the airflow are not the same for low and high
opening angles. As a matter of fact, the gradient of the
mass air flow function of TPS is lower for small angles that
permits to be more precise during the idle speed control.
Out of idle speed the throttle is actuated mechanically by
a classical bowdencable.
The main throttle idle actuator (MTIA) provides a voltagesignal that changes in relation to the throttle plate angle.
The signal voltage will vary from about nearly 5.0 V at idles
to about 0.2V to 0.4 V at wide–open throttle. The TPS is
one of the most important inputs used by the ECM for fuel
control and other functions such as idle, wide open
throttle, deceleration enleanment, and acceleration en-
richment.
Diagnostic Aids
If the idle is too high, stop the engine. Fully extend the main
throttle idle actuator (MTIA) with a IAC driver. Start the en-
gine. If the idle speed is above 800 rpm, locate and repair
the vacuum leak. Also, check for a binding throttle plate or
throttle linkage or an incorrect base idle setting.
Page 328 of 2643

1F – 82IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
IDLE AIR CONTROL SYSTEM CHECK (1.8L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) controls the engine idle
speed with the Idle Air Control (IAC) valve. To increase the
idle speed, the ECM pulls the IAC pintle away from its seat,
allowing more air to pass by the throttle body. To decrease
the idle speed, it extends the IAC valve pintle toward its
seat, reducing bypass air flow. A scan tool will read the
ECM commands to the IAC valve in counts. The higher
counts indicate more air bypass (higher idle). The lower
counts indicate less air is allowed to bypass (lower idle).
Diagnostic Aids
If the idle is too high, stop the engine. Fully extend the Idle
Air Control (IAC) valve with a IAC driver. Start the engine.
If the idle speed is above 800 rpm, locate and repair the
vacuum leak. Also, check for a binding throttle plate or
throttle linkage or an incorrect base idle setting.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
2. The IAC valve is extended and retracted by the IAC
driver. IAC valve movement is verified by an engine
speed change. If no change in engine speed oc-
curs, the valve can be removed from the throttle
body and tested. Connect the IAC driver to the re-
moved IAC valve and turn the ignition ON. Do not
start the engine.5. This step checks the quality of the IAC valve move-
ment in Step 2. Fully extending the IAC valve may
cause an engine stall. This may be normal.
6. Steps 2 and 5 verify proper IAC valve operation.
This step checks the IAC circuit for a wiring or ECM
fault.
Idle Air Control Valve Reset Procedure
Whenever the battery cable or the Engine Control Module
(ECM) connector or the ECM fuse Ef11 is disconnected or
replaced, the following idle learn procedure must be per-
formed:
1. Turn the ignition ON for 5 seconds.
2. Turn the ignition OFF for 10 seconds.
3. Turn the ignition ON for 5 seconds.
4. Start the engine in park/neutral.
5. Allow the engine to run until the engine coolant is
above 185°F (85°C).
6. Turn the A/C ON for 10 seconds, if equipped.
7. Turn the A/C OFF for 10 seconds, if equipped.
8. If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic trans-
axle, apply the parking brake. While pressing the
brake pedal, place the transaxle in D (drive).
9. Turn the A/C ON for 10 seconds, if equipped.
10. Turn the A/C OFF for 10 seconds, if equipped.
11. Turn the ignition OFF. The idle learn procedure is
complete.
Page 360 of 2643

1F – 114IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0107
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR LOW
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) uses the Manifold Ab-
solute Pressure (MAP) sensor to control the fuel delivery
and the ignition timing. The MAP sensor measures the
changes in the intake manifold pressure, which results
from engine load (intake manifold vacuum) and the rpm
changes; and converts these into voltage outputs. The
ECM sends a 5 volt–reference voltage to the MAP sensor.
As the manifold pressure changes, the output voltage of
the MAP sensor also changes. By monitoring the MAP
sensor output voltage, the ECM knows the manifold pres-
sure. A low–pressure (low voltage) output voltage will be
about 1.0 to 1.5 volts at idle, while higher pressure (high
voltage) output voltage will be about 4.5 to 4.8 at wide
open throttle (WOT). The MAP sensor is metric pressure,
allowing the ECM to make adjustments for different alti-
tudes.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S This DTC can be stored in ”key–on” status.
(Case A)
S When the engine idling.
S No throttle position(TP) sensor MTIA fail conditions
present.
S Engine speed(rpm) is less than 2,500rpm.
S The MAP is less than 12.0 kPa.
(Case A)
S When the engine part load.
S The engine revolution speed is less than 4,000rpm.S No Throttle Position (TP) Sensor fails conditions
present.
S The Throttle Position (TP) angle greather than
30.0°.
S The MAP is less than 11.5 kPa.
S An open or low voltage condition exists.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The coolant fan turns ON.
S The ECM will substitutes a fixed MAP value and
use TP to control the fuel delivery (the scan tool will
not show defaulted)
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
With the ignition ON and the engine stopped, the manifold
pressure is equal to atmosphere pressure and the signal
voltage will be high.
Page 361 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 115
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
The ECM as an indication of vehicle altitude uses this in-
formation. Comparison of this reading with a known good
vehicle with the same sensor is a good way to check the
accuracy of a suspect sensor. Readings should be the
same ± 0.4volt.
If a DTC P0107 is intermittent, refer to ”Manifold AbsolutePressure Check” in this section for further diagnosis.
If the connections are OK monitor the manifold absolute
pressure (MAP) sensor signal voltage while moving re-
lated connectors and the wiring harness. If the failure is in-
duced, the display on the scan tool will change. This may
help to isolate the location of an intermittent malfunction.
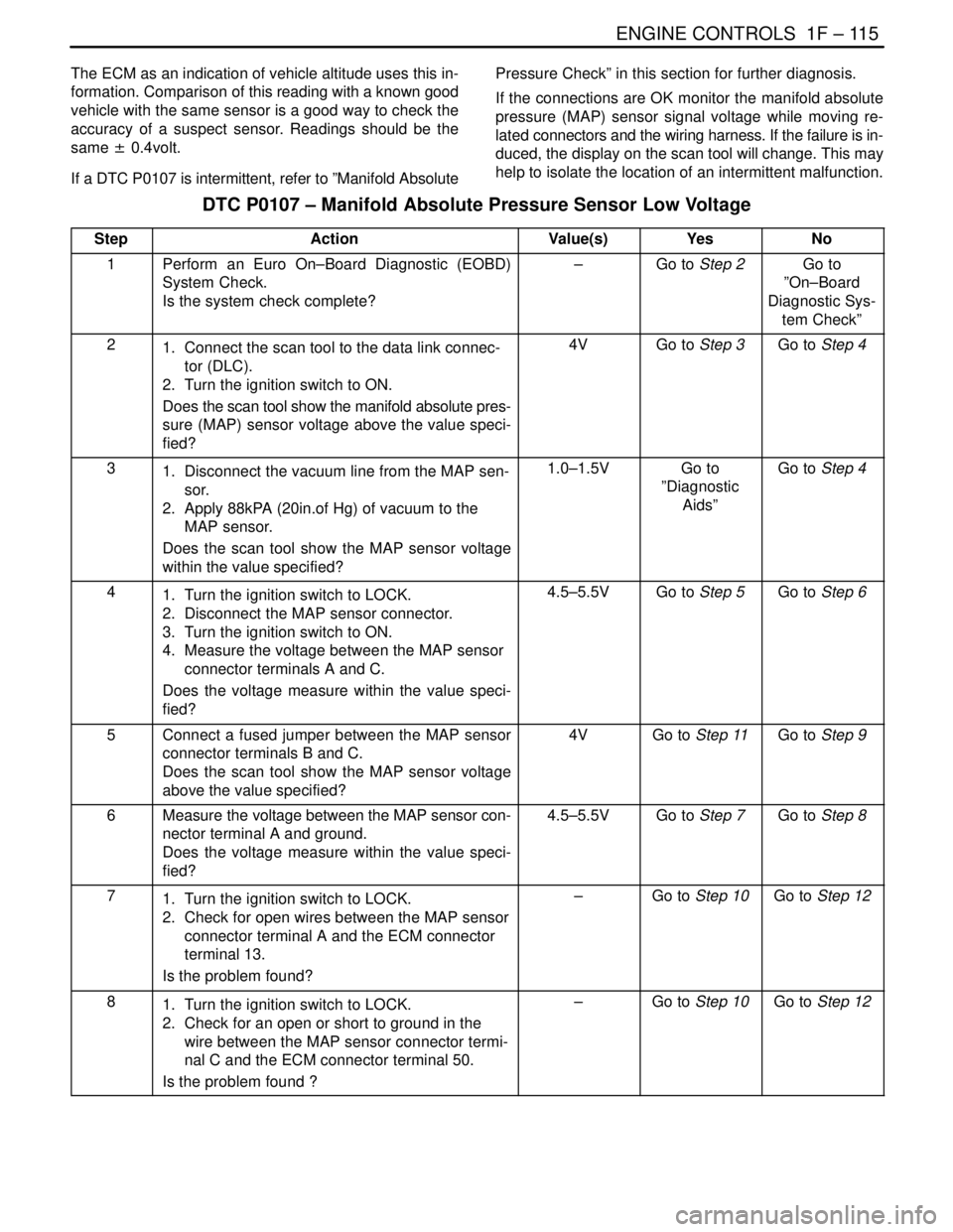
DTC P0107 – Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Low Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Connect the scan tool to the data link connec-
tor (DLC).
2. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Does the scan tool show the manifold absolute pres-
sure (MAP) sensor voltage above the value speci-
fied?4VGo to Step 3Go to Step 4
31. Disconnect the vacuum line from the MAP sen-
sor.
2. Apply 88kPA (20in.of Hg) of vacuum to the
MAP sensor.
Does the scan tool show the MAP sensor voltage
within the value specified?1.0–1.5VGo to
”Diagnostic
Aids”Go to Step 4
41. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the MAP sensor connector.
3. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
4. Measure the voltage between the MAP sensor
connector terminals A and C.
Does the voltage measure within the value speci-
fied?4.5–5.5VGo to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Connect a fused jumper between the MAP sensor
connector terminals B and C.
Does the scan tool show the MAP sensor voltage
above the value specified?4VGo to Step 11Go to Step 9
6Measure the voltage between the MAP sensor con-
nector terminal A and ground.
Does the voltage measure within the value speci-
fied?4.5–5.5VGo to Step 7Go to Step 8
71. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Check for open wires between the MAP sensor
connector terminal A and the ECM connector
terminal 13.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 10Go to Step 12
81. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Check for an open or short to ground in the
wire between the MAP sensor connector termi-
nal C and the ECM connector terminal 50.
Is the problem found ?–Go to Step 10Go to Step 12