air filter DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 715 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 469
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
2. Commanding the EGR valve open determines
whether the EGR system is totally restricted or par-
tially restricted.
3. Visually and physically inspect the EGR passages
and valve for excessive carbon deposits or dam-
age.
4. Be sure all gasket material is removed from the
EGR mounting surface. Even a small amount of
material may cause a DTC P0401 to set.
5. This step verifies if the fault is present and also ver-
ifies if a repair corrected the problem. If the EGR
Deceleration Filter value stays near 0 or a positivenumber after several tests have been run, then a
small restriction may still exist. Be sure to check the
EGR pipe for damage or dents and the EGR valve
for any excessive carbon build up. Only 1 test per
ignition cycle will run unless a DTC P0401 has
been cleared or the battery has been disconnected.
6. Clearing DTCs is a very important step for this
diagnostic. The clearing function allows the EGR
valve to relearn a new pintle position as the old
pintle position was inaccurate due to the failure that
caused the DTC. The DTC must be cleared with
the ignition ON, engine OFF or when the engine is
idling. If the ECM sees a EGR command, the new
pintle will not be learned.
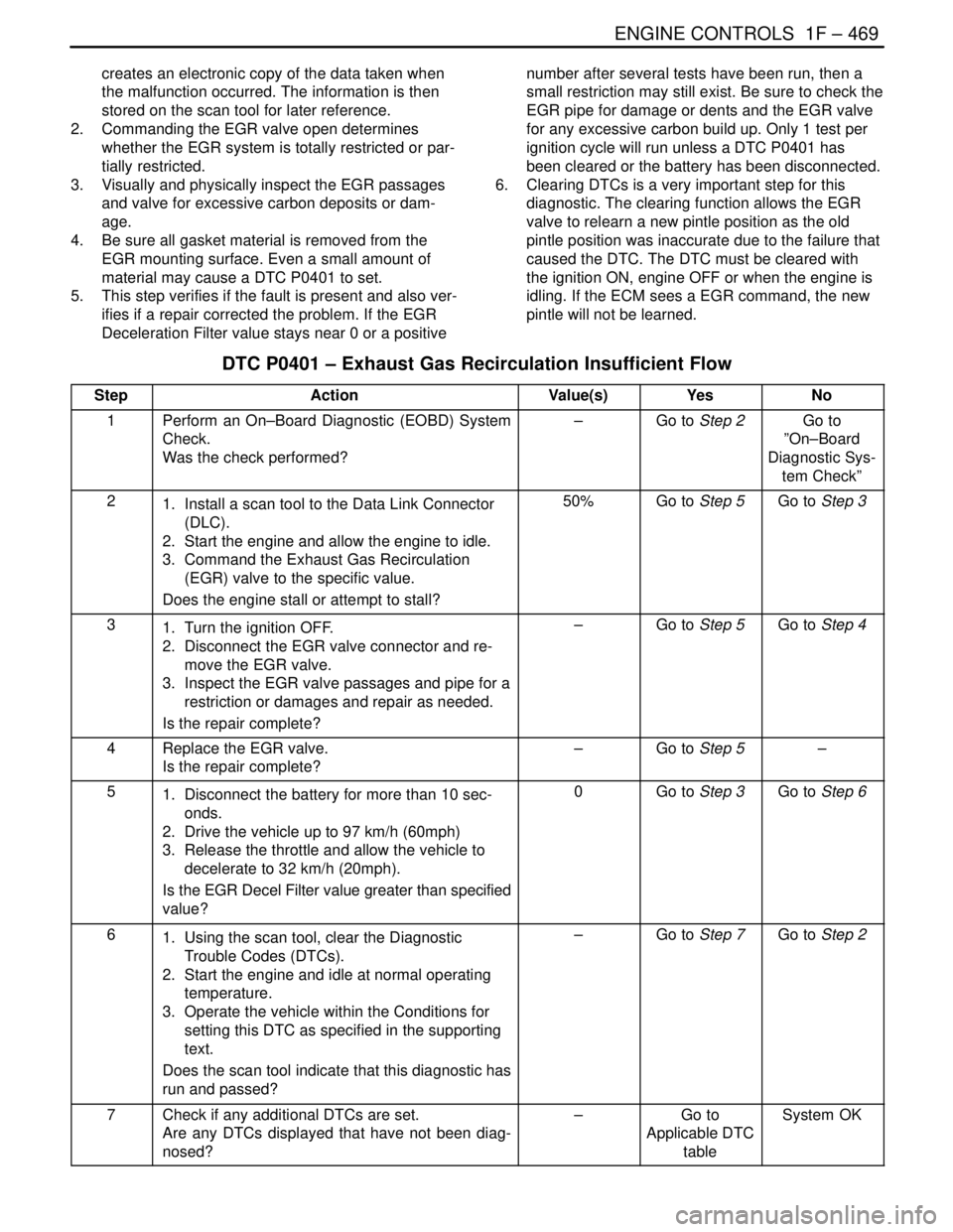
DTC P0401 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Insufficient Flow
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Start the engine and allow the engine to idle.
3. Command the Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) valve to the specific value.
Does the engine stall or attempt to stall?50%Go to Step 5Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the EGR valve connector and re-
move the EGR valve.
3. Inspect the EGR valve passages and pipe for a
restriction or damages and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 4
4Replace the EGR valve.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 5–
51. Disconnect the battery for more than 10 sec-
onds.
2. Drive the vehicle up to 97 km/h (60mph)
3. Release the throttle and allow the vehicle to
decelerate to 32 km/h (20mph).
Is the EGR Decel Filter value greater than specified
value?0Go to Step 3Go to Step 6
61. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 2
7Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 794 of 2643

1F – 548IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1171
FUEL TRIM SYSTEM LEAN DURING POWER
ENRICHMENT
System Description
The internal circuitry of the Engine control Module (ECM)
can identify if the vehicle fuel system is capable of supply-
ing adequate amounts of fuel during heavy acceleration(
power enrichment). When a Power Enrichment (PE)
mode of operation is requested by heavy acceleration dur-
ing Closed Loop operation, the ECM will provide more fuel
to the engine. Under these conditions the ECM should de-
tect a rich condition. If this reich condition is nor detected
at this time, Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1171 will set.
A plugged fuel filter or restricted fuel line can prevent ade-
quate amount of fuel from being supplied during Power
Enrichment mode.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S HO2S1 voltage is less than 0.35 volts in Power En-
richment (PE) mode.
S Engine is operating in Closed Loop and in PE
mode.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is greater than
60°C (140°F).
S System voltage is greater than 10 volts.
S Air/Fuel ration is less than 13.5:1.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0171, P0172, P0201, P0202,
P0203, P0204, P0300, P0336, P0337, P0351,
P0352, P0402, P0404, P0405, P0406, P0506,
P0507, P1404, and P0443 are not set.
S 3 second delay after in PE mode.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after two consecutive ignition cycle with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The vehicle will operate in Open Loop.Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after three consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.v
Diagnostic Aids
A restricted fuel filter can supply adequate amounts of fuel
at idle, but may not be able to supply enough fuel during
heavy acceleration.
Water or alcohol n fuel may cause low HO2S1 voltage dur-
ing acceleration.
Check for adequate amount of fuel in the Tank.
When the engine is idling or at steady cruise, the HO2S1
voltage should vary from between approximately a00 to
900 millivolts. During power enrichment mode, more fuel
is needed, and the HO2S1 should rise above 444 milli-
volts.
Check for faulty or plugged injector(s).
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
4. This step checks to see if the HO2S1 is operating
properly.
6. If no faults have been found at this point and no
additional DTCs were set, refer to ”Diagnostic Aids”
in this section for additional checks and informa-
tion.
Page 825 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 579
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
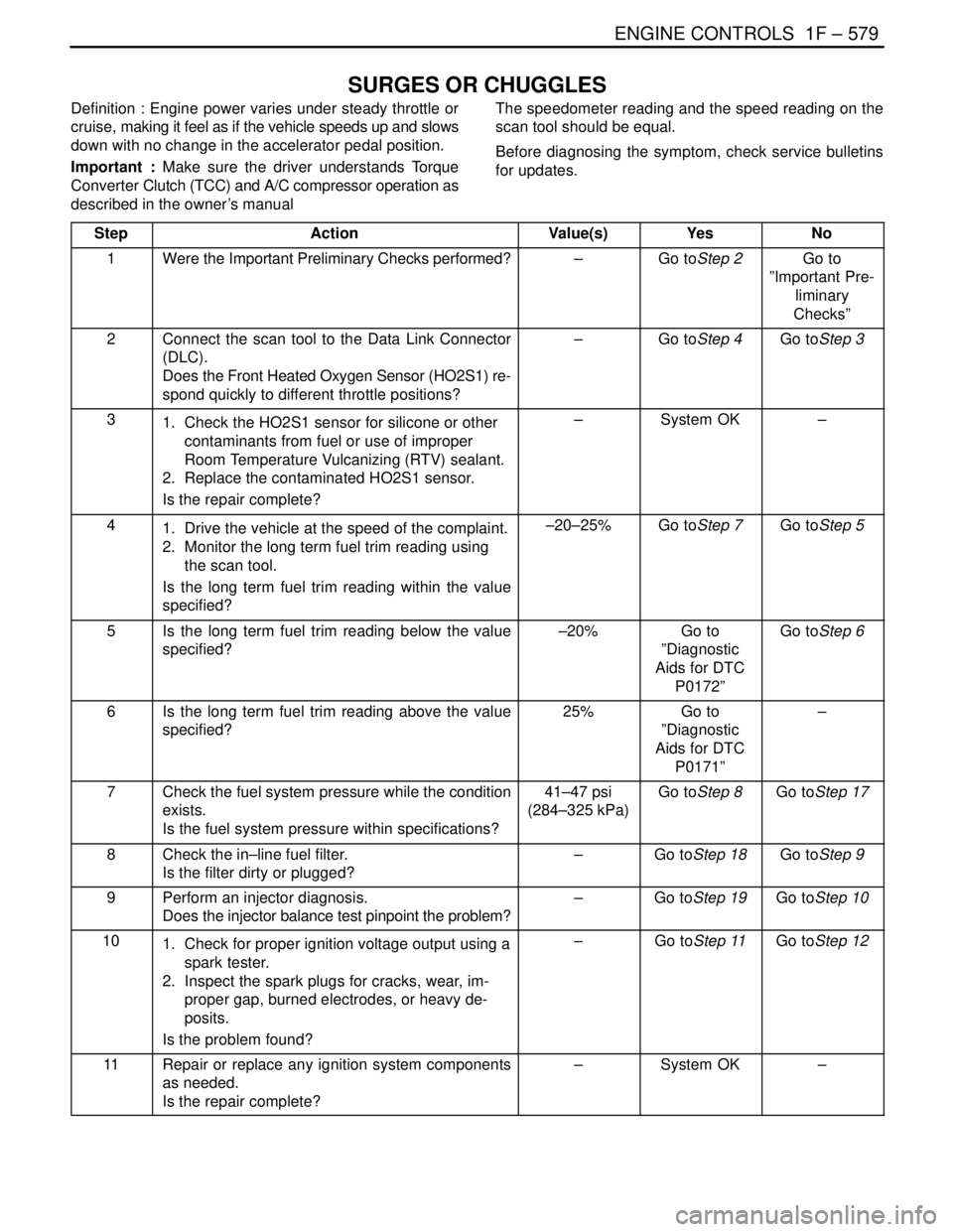
SURGES OR CHUGGLES
Definition : Engine power varies under steady throttle or
cruise, making it feel as if the vehicle speeds up and slows
down with no change in the accelerator pedal position.
Important : Make sure the driver understands Torque
Converter Clutch (TCC) and A/C compressor operation as
described in the owner’s manualThe speedometer reading and the speed reading on the
scan tool should be equal.
Before diagnosing the symptom, check service bulletins
for updates.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
1Were the Important Preliminary Checks performed?–Go toStep 2Go to
”Important Pre-
liminary
Checks”
2Connect the scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
Does the Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) re-
spond quickly to different throttle positions?–Go toStep 4Go toStep 3
31. Check the HO2S1 sensor for silicone or other
contaminants from fuel or use of improper
Room Temperature Vulcanizing (RTV) sealant.
2. Replace the contaminated HO2S1 sensor.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
41. Drive the vehicle at the speed of the complaint.
2. Monitor the long term fuel trim reading using
the scan tool.
Is the long term fuel trim reading within the value
specified?–20–25%Go toStep 7Go toStep 5
5Is the long term fuel trim reading below the value
specified?–20%Go to
”Diagnostic
Aids for DTC
P0172”Go toStep 6
6Is the long term fuel trim reading above the value
specified?25%Go to
”Diagnostic
Aids for DTC
P0171”–
7Check the fuel system pressure while the condition
exists.
Is the fuel system pressure within specifications?41–47 psi
(284–325 kPa)Go toStep 8Go toStep 17
8Check the in–line fuel filter.
Is the filter dirty or plugged?–Go toStep 18Go toStep 9
9Perform an injector diagnosis.
Does the injector balance test pinpoint the problem?–Go toStep 19Go toStep 10
101. Check for proper ignition voltage output using a
spark tester.
2. Inspect the spark plugs for cracks, wear, im-
proper gap, burned electrodes, or heavy de-
posits.
Is the problem found?–Go toStep 11Go toStep 12
11Repair or replace any ignition system components
as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 826 of 2643
1F – 580IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
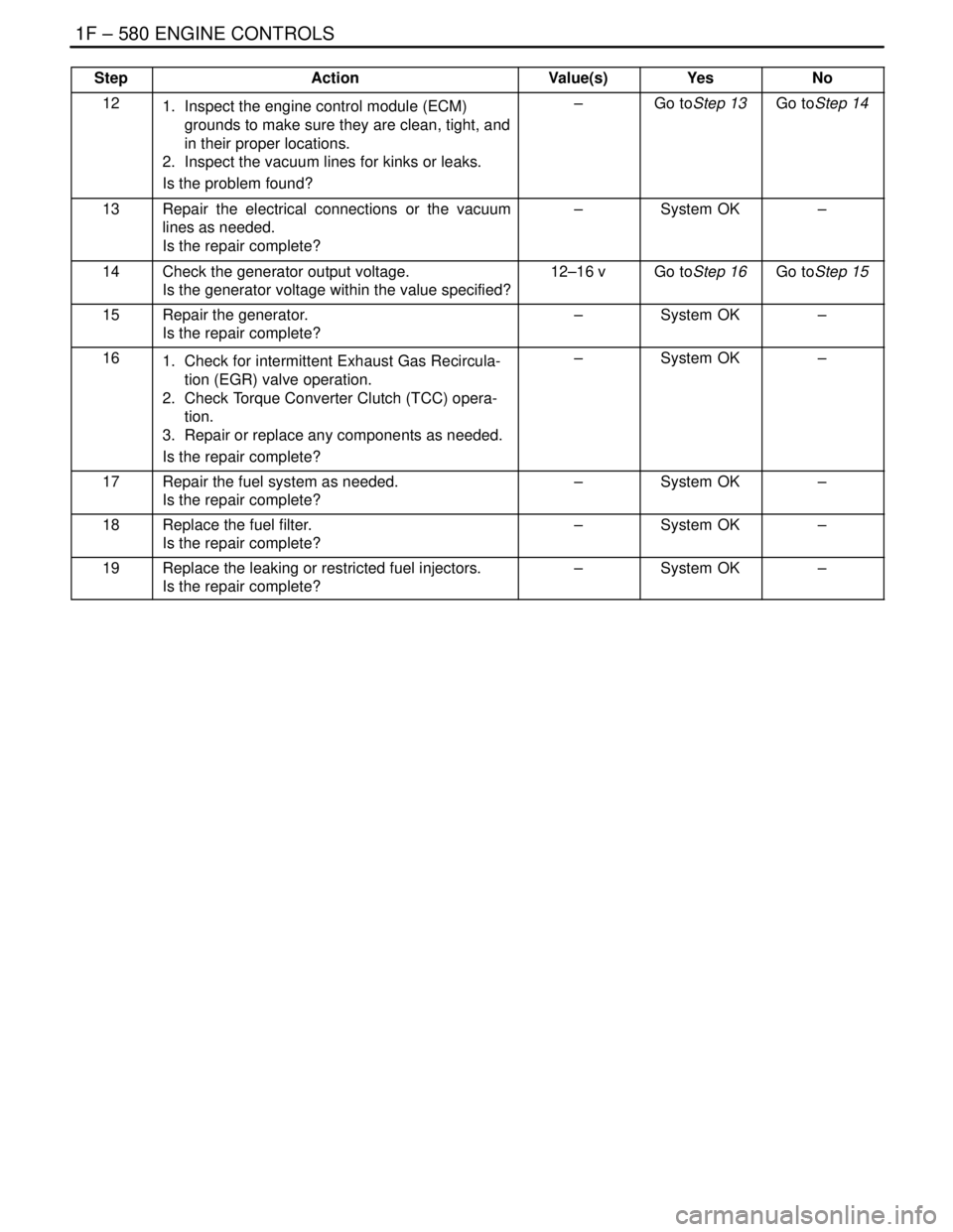
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
121. Inspect the engine control module (ECM)
grounds to make sure they are clean, tight, and
in their proper locations.
2. Inspect the vacuum lines for kinks or leaks.
Is the problem found?–Go toStep 13Go toStep 14
13Repair the electrical connections or the vacuum
lines as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
14Check the generator output voltage.
Is the generator voltage within the value specified?12–16 vGo toStep 16Go toStep 15
15Repair the generator.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
161. Check for intermittent Exhaust Gas Recircula-
tion (EGR) valve operation.
2. Check Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) opera-
tion.
3. Repair or replace any components as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
17Repair the fuel system as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
18Replace the fuel filter.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
19Replace the leaking or restricted fuel injectors.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 827 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 581
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
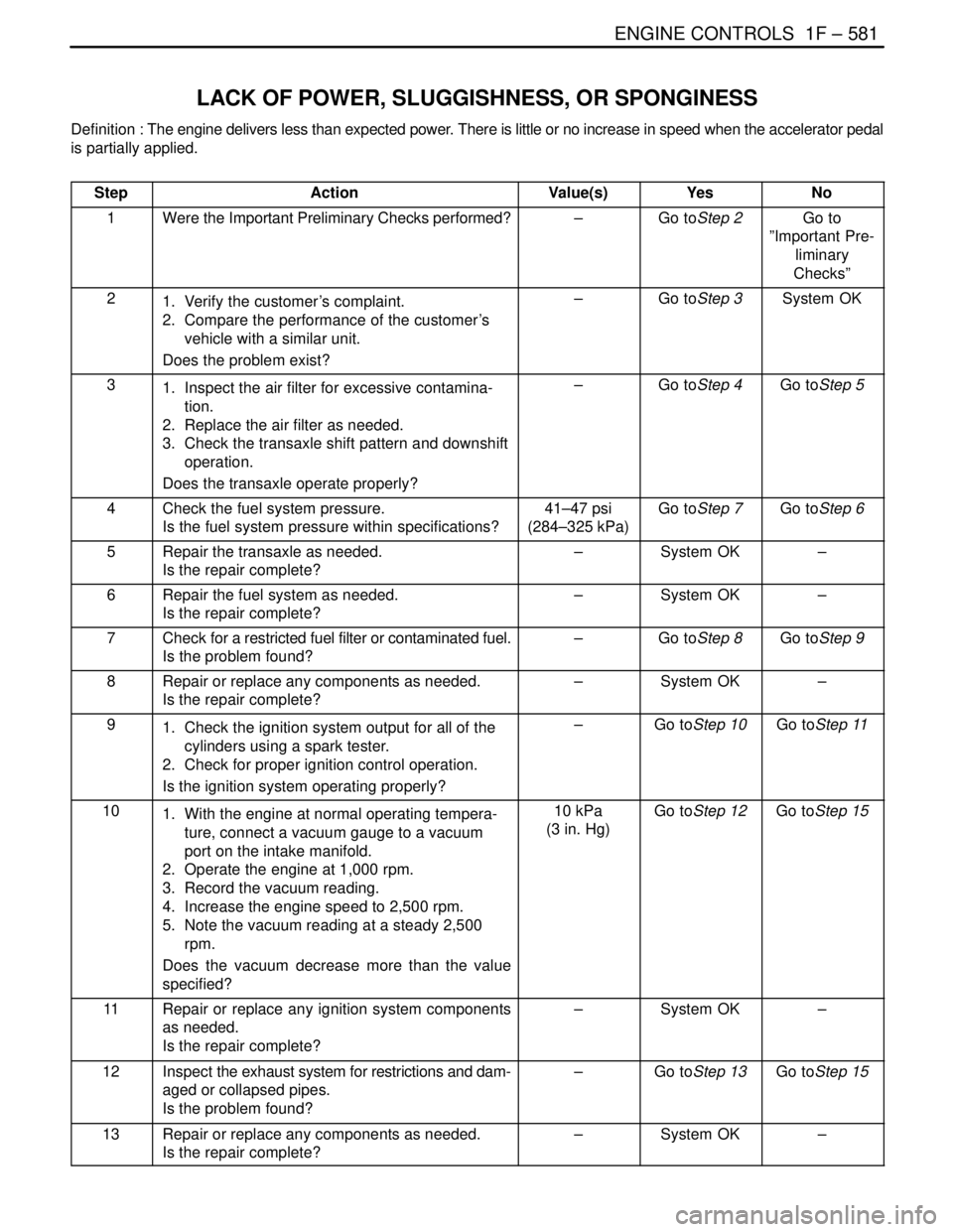
LACK OF POWER, SLUGGISHNESS, OR SPONGINESS
Definition : The engine delivers less than expected power. There is little or no increase in speed when the accelerator pedal
is partially applied.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
1Were the Important Preliminary Checks performed?–Go toStep 2Go to
”Important Pre-
liminary
Checks”
21. Verify the customer’s complaint.
2. Compare the performance of the customer’s
vehicle with a similar unit.
Does the problem exist?–Go toStep 3System OK
31. Inspect the air filter for excessive contamina-
tion.
2. Replace the air filter as needed.
3. Check the transaxle shift pattern and downshift
operation.
Does the transaxle operate properly?–Go toStep 4Go toStep 5
4Check the fuel system pressure.
Is the fuel system pressure within specifications?41–47 psi
(284–325 kPa)Go toStep 7Go toStep 6
5Repair the transaxle as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
6Repair the fuel system as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
7Check for a restricted fuel filter or contaminated fuel.
Is the problem found?–Go toStep 8Go toStep 9
8Repair or replace any components as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
91. Check the ignition system output for all of the
cylinders using a spark tester.
2. Check for proper ignition control operation.
Is the ignition system operating properly?–Go toStep 10Go toStep 11
101. With the engine at normal operating tempera-
ture, connect a vacuum gauge to a vacuum
port on the intake manifold.
2. Operate the engine at 1,000 rpm.
3. Record the vacuum reading.
4. Increase the engine speed to 2,500 rpm.
5. Note the vacuum reading at a steady 2,500
rpm.
Does the vacuum decrease more than the value
specified?10 kPa
(3 in. Hg)Go toStep 12Go toStep 15
11Repair or replace any ignition system components
as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
12Inspect the exhaust system for restrictions and dam-
aged or collapsed pipes.
Is the problem found?–Go toStep 13Go toStep 15
13Repair or replace any components as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 831 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 585
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
71. Perform a cylinder compression test.
2. If the compression is low, repair the engine as
needed.
3. Inspect for proper valve timing, bent pushrods,
worn rocker arms, broken or weak valve
springs, and worn camshaft lobes.
4. Inspect the intake manifold and the exhaust
manifold passages for casting flash.
Is the problem found?–Go toStep 8Go toStep 9
8Repair or replace any components as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
91. Check the fuel system for a plugged in–line fuel
filter.
2. Check the fuel system for low fuel pressure. If
the fuel pressure is below the value specified,
service the fuel system as needed.
3. Inspect for contaminated fuel.
Is the problem found?41–47 psi
(284–325 kPa)Go toStep 10Go toStep 11
10Repair or replace any components as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
111. Disconnect all of the fuel injector harness con-
nectors at the fuel injectors.
2. Connect an injector test light to the harness
terminals of each fuel injector connector.
3. Note the test light while cranking the engine for
each fuel injector.
Does the test light blink for all of the fuel injectors?–Go toStep 13Go toStep 12
121. Repair or replace the faulty injector drive circuit
harness, the connector, or the connector termi-
nal.
2. If the harness, the connectors, and the termi-
nals are OK, replace the engine control module
(ECM).
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
13Measure the resistance of each fuel injector. The re-
sistance will increase slightly at higher tempera-
tures.
Is the injector resistance within the value specified?11.6–12.4 ΩGo toStep 15Go toStep 14
14Replace any fuel injectors with a resistance that is
out of specifications.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
15Perform an injector balance test.
Is the problem found?–Go toStep 16Go toStep 17
16Replace any restricted or leaking fuel injectors.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 833 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 587
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
POOR FUEL ECONOMY
Definition : Fuel economy, as measured by an actual road
test, is noticeably lower than expected. Also, fuel econo-
my is noticeably lower than it was on this vehicle at one
time, as previously shown by an actual road test.
Important : Driving habits affect fuel economy. Check the
owner’s driving habits by asking the following questions:1. Is the A/C system (i.e. defroster mode) turned on
all the time?
2. Are the tires at the correct air pressure?
3. Have excessively heavy loads been carried?
4. Does the driver accelerate too much and too often?
Suggest the driver read the section in the owner’s
manual about fuel economy.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
1Were the Important Preliminary Checks performed?–Go toStep 2Go to
”Important Pre-
liminary
Checks”
21. Inspect the air filter for excessive contamina-
tion.
2. Inspect for fuel system leaks.
Are all needed checks complete?–Go toStep 3–
31. Inspect the spark plugs for excessive wear,
insulation cracks, improper gap, or heavy de-
posits.
2. Replace any faulty spark plugs.
3. Inspect the ignition wires for cracking, hard-
ness, and proper connections.
Are all needed checks and repairs complete?–Go toStep 4–
41. Inspect the engine coolant level.
2. Check the thermostat for being always open or
for an incorrect heat range.
3. Replace the thermostat as needed.
Are all needed checks and repairs complete?–Go toStep 5–
51. Check the transaxle shift pattern. Ensure all
transaxle gears are functioning.
2. Check the Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) op-
eration with a scan tool. The scan tool should
indicate rpm drop when the TCC is command-
ed on.
3. Check for proper calibration of the speedome-
ter.
4. Check the brakes for dragging.
5. Check the cylinder compression.
6. Repair, replace, or adjust any components as
needed.
Are all checks and needed repairs complete?–System OK–
Page 865 of 2643
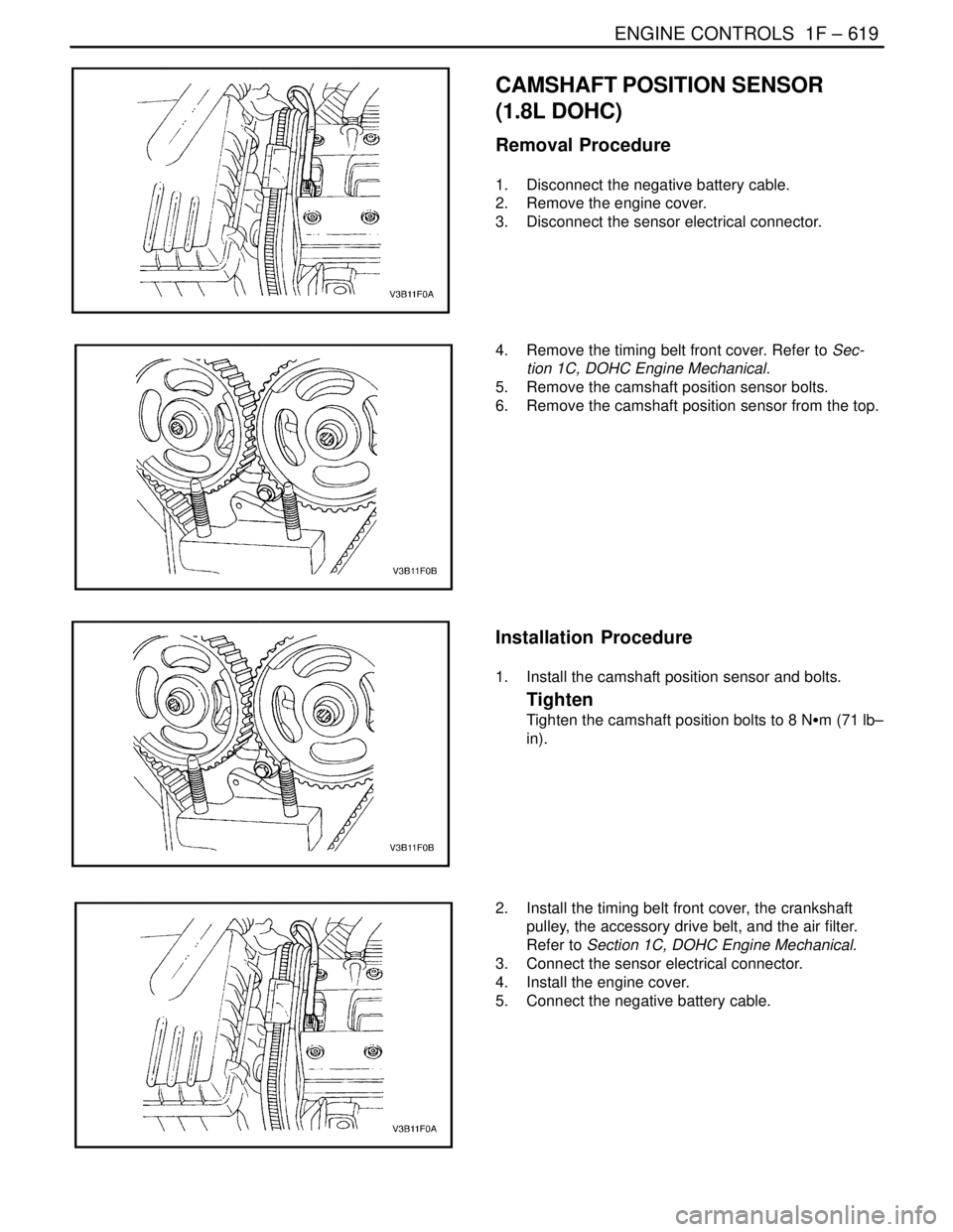
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 619
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
(1.8L DOHC)
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the engine cover.
3. Disconnect the sensor electrical connector.
4. Remove the timing belt front cover. Refer to Sec-
tion 1C, DOHC Engine Mechanical.
5. Remove the camshaft position sensor bolts.
6. Remove the camshaft position sensor from the top.
Installation Procedure
1. Install the camshaft position sensor and bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the camshaft position bolts to 8 NSm (71 lb–
in).
2. Install the timing belt front cover, the crankshaft
pulley, the accessory drive belt, and the air filter.
Refer to Section 1C, DOHC Engine Mechanical.
3. Connect the sensor electrical connector.
4. Install the engine cover.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
Page 875 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 629
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
tentially interfere with the operation of the Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) valve and thereby turn on the MIL.
Small leaks in the exhaust system near the post catalyst
oxygen sensor can also cause the MIL to turn on.
Aftermarket electronics, such as cellular phones, stereos,
and anti–theft devices, may radiate electromagnetic inter-
ference (EMI) into the control system if they are improperly
installed. This may cause a false sensor reading and turn
on the MIL.
Environment
Temporary environmental conditions, such as localized
flooding, will have an effect on the vehicle ignition system.
If the ignition system is rain–soaked, it can temporarily
cause engine misfire and turn on the MIL.
Refueling
A new EOBD diagnostic checks the integrity of the entire
Evaporative (EVAP) Emission system. If the vehicle is re-
started after refueling and the fuel cap is not secured cor-
rectly, the on–board diagnostic system will sense this as
a system fault, turn on the MIL, and set DTC P0440.
Vehicle Marshaling
The transportation of new vehicles from the assembly
plant to the dealership can involve as many as 60 key
cycles within 2 to 3 miles of driving. This type of operation
contributes to the fuel fouling of the spark plugs and will
turn on the MIL with a set DTC P0300.
Poor Vehicle Maintenance
The sensitivity of EOBD diagnostics will cause the MIL to
turn on if the vehicle is not maintained properly. Restricted
air filters, fuel filters, and crankcase deposits due to lack
of oil changes or improper oil viscosity can trigger actual
vehicle faults that were not previously monitored prior to
EOBD. Poor vehicle maintenance can not be classified as
a ”non–vehicle fault,” but with the sensitivity of EOBD
diagnostics, vehicle maintenance schedules must be
more closely followed.
Severe Vibration
The Misfire diagnostic measures small changes in the
rotational speed of the crankshaft. Severe driveline vibra-
tions in the vehicle, such as caused by an excessive
amount of mud on the wheels, can have the same effect
on crankshaft speed as misfire and, therefore, may set
DTC P0300.
Related System Faults
Many of the EOBD system diagnostics will not run if the
engine controlmodule (ECM) detects a fault on a related
system or component. One example would be that if the
ECM detected a Misfire fault, the diagnostics on the cata-
lytic converter would be suspended until the Misfire fault
was repaired. If the Misfire fault is severe enough, the cat-
alytic converter can be damaged due to overheating andwill never set a Catalyst DTC until the Misfire fault is re-
paired and the Catalyst diagnostic is allowed to run to
completion. If this happens, the customer may have to
make two trips to the dealership in order to repair the ve-
hicle.
SERIAL DATA COMMUNICATIONS
Class II Serial Data Communications
Government regulations require that all vehicle manufac-
turers establish a common communication system. This
vehicle utilizes the ”Class II” communication system. Each
bit of information can have one of two lengths: long or
short. This allows vehicle wiring to be reduced by transmit-
ting and receiving multiple signals over a single wire. The
messages carried on Class II data streams are also priori-
tized. If two messages attempt to establish communica-
tions on the data line at the same time, only the message
with higher priority will continue. The device with the lower
priority message must wait. Themost significant result of
this regulation is that it provides scan tool manufacturers
with the capability to access data from any make or model
vehicle that is sold.
The data displayed on the other scan tool will appear the
same, with some exceptions. Some scan tools will only be
able to display certain vehicle parameters as values that
are a coded representation of the true or actual value. On
this vehicle the scan tool displays the actual values for ve-
hicle parameters. It will not be necessary to perform any
conversions from coded values to actual values.
ON–BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (EOBD)
On–Board Diagnostic Tests
A diagnostic test is a series of steps, the result of which is
a pass or fail reported to the diagnostic executive. When
a diagnostic test reports a pass result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
S The diagnostic test has been completed since the
last ignition cycle.
S The diagnostic test has passed during the current
ignition cycle.
S The fault identified by the diagnostic test is not cur-
rently active.
When a diagnostic test reports a fail result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
S The diagnostic test has been completed since the
last ignition cycle.
S The fault identified by the diagnostic test is current-
ly active.
S The fault has been active during this ignition cycle.
S The operating conditions at the time of the failure.
Remember, a fuel trim Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
may be triggered by a list of vehicle faults. Make use of all
information available (other DTCs stored, rich or lean con-
dition, etc.) when diagnosing a fuel trim fault.
Page 1394 of 2643

ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A1 – 45
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
CLUTCH PLATE DIAGNOSIS
Composition Plates
Dry the plate and inspect the plates for the following condi-
tions :
S Pitting
S Flaking
S Wear
S Glazing
S Cracking
S Charring
Chips or metal particles embedded in the lining
Replace a composition plate which shows any of these
conditions.
Steel Plates
Wipe the plates dry and check the plates for heat discolor-
ation. If the surfaces are smooth, even if colorsmear is in-
dicated, you can reuse the plate. If the plate is discolored
with hot spots or if the surface is scuffed, replace the plate.
Important : If the clutch shows evidence or extreme heat
or burning, replace the springs.
Causes of Burned Clutch Plates
The following conditions can result in a burned clutch
plate:
S Incorrect usage of clutch plates.
S Engine coolant in the transaxle fluid.
S A cracked clutch piston.
S Damaged or missing seals.
S Low line pressure.
S Valve problems.
– The valve body face is not flat
– Porosity between channels
– The valve bushing clips are improperly installed.
– The check balls are misplaced.
S The seal rings are worn or damaged
Engine Coolant in Transaxle
Notice : Antifreeze will deteriorate the O–ring seals and
the glue used to bond the clutch material to the pressure
plate. Both conditions may cause transaxle damage.
Perform the following steps if the transaxle oil cooler has
developed a leak, allowing engine coolant to enter the
transaxle:
1. Because the coolant will attach to the seal material
causing leakage, disassemble the transaxle and
replace all rubber type seals.
2. Because the facing material may become sepa-
rated from the steel center portion, replace the
composition faced clutch plate assemblies.
3. Replace all nylon parts including washers.
4. Replace the torque converter.
5. Thoroughly clean and rebuild the transaxle, using
new gaskets and oil filter.6. Flush the cooler lines after you have properly re-
paired or replaced the transaxle.
COOLER FLUSHING AND FLOW
TEST
Notice : You must flush the cooler whenever you receive
a transaxle for service. Cooler flushing is essential for
SRTA installation, major overhaul, whenever you replace
a pump or torque converter, or whenever you suspect that
the fluid has been contaminated.
After filling the transaxle with fluid, start the engine and run
for 30 seconds. This will remove any residual moisture
from the oil cooler. Disconnect the return line at the trans-
axle and observe the flow with the engine running. If the
fluid flow is insufficient, check the fluid flow by disconnect-
ing the feed line at the cooler. Observe the flow with the
engine running.
S If the flow from the cooler return line at the trans-
axle is insufficient, check the flow rate from the feed
line to the cooler. BLockage exists in the transaxle
or the cooler.
S If the flow from the transaxle feed line to the cooler
is insufficient, the transaxle is the cause of the fluid
flow problem.
S If the flow the transaxle feed line to the cooler is
insufficient, but flow from the cooler return line to
the transaxle is insufficient, inspect the cooler pipes
and fittings. Then repeat the cooler flushing proce-
dure. If the flow is still insufficient, replace the cool-
er.
TRANSAXLE FLUID LEVEL SERVICE
PROCEDURE
This procedure is to be used when checking a concern
with the fluid level in a vehicle. A low fluid level will result
in slipping and loss of drive/ reverse or delay on engage-
ment of drive/ reverse when the vehicle is cold.
The vehicle is first checked for transaxle diagnostic mes-
sages on the scan tool. If the oil level is low, it is possible
to register a vehicle speed signal fault.
The vehicle is to be test driven to determine if there is an
abnormal delay when selecting drive or reverse, or loss of
drive. One symptom of low fluid level is a momentary loss
of drive when driving the vehicle around a corner. Also
when the transaxle fluid level is low, a loss of drive may oc-
cur when the transaxle fluid temperature is low.
When adding or changing transaxle fluid use only ESSO
LT 71141 automatic transaxle fluid or other approved
fluids. The use of incorrect fluid will cause the performance
and durability of the transaxle to be severely degraded.
Fluid Level Diagnosis Procedure
1. If the vehicle is at operating temperature allow the
vehicle to cool down for two hours, but no greater
than four hours. Or if the vehicle is at cool status,
start the engine and allow the engine to idle for
approximately 5 minutes (825~875 rpm), if pos-