acc DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 326 of 2643
1F – 80IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
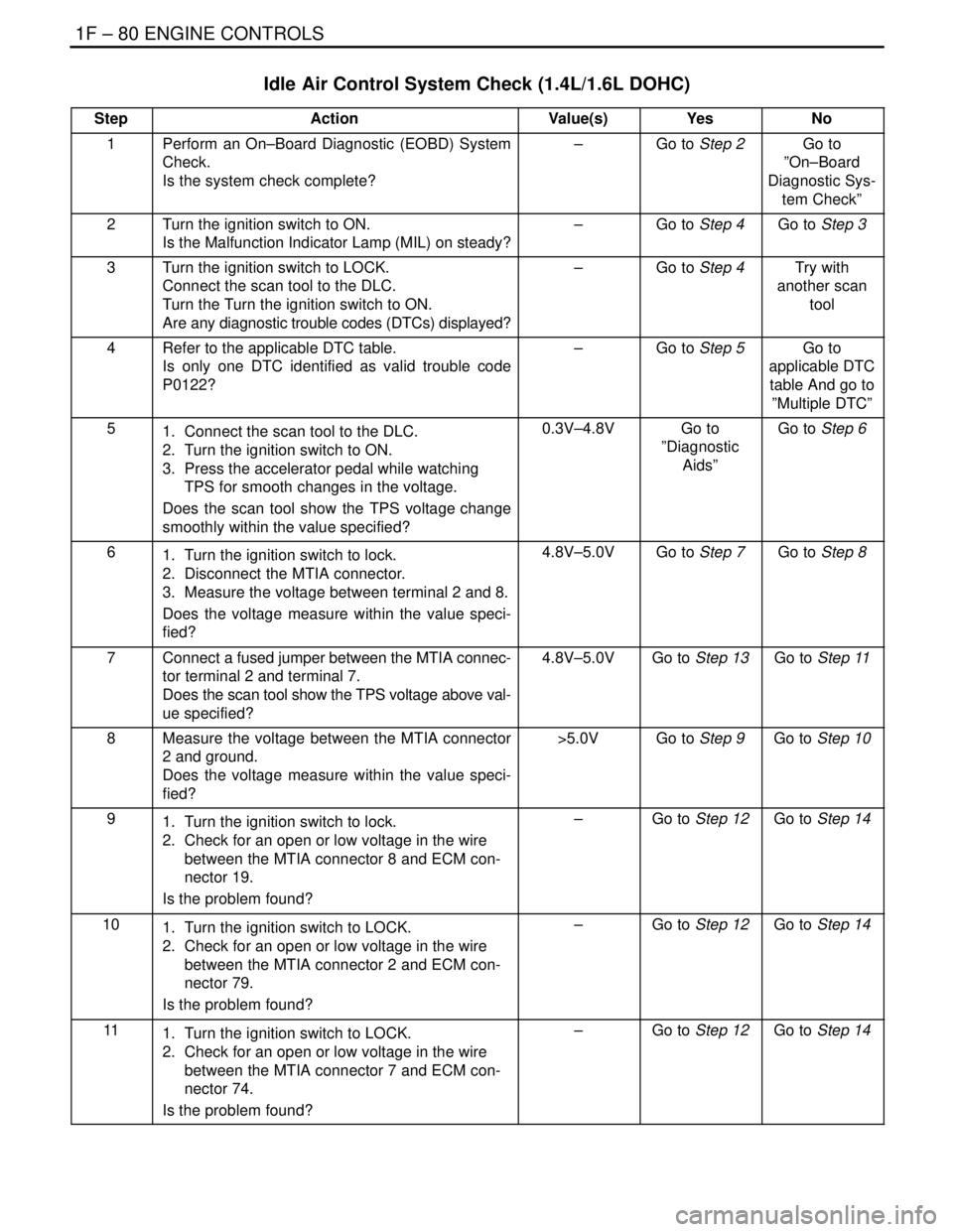
Idle Air Control System Check (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
2Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Is the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) on steady?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 3
3Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
Connect the scan tool to the DLC.
Turn the Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Are any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) displayed?–Go to Step 4Try with
another scan
tool
4Refer to the applicable DTC table.
Is only one DTC identified as valid trouble code
P0122?–Go to Step 5Go to
applicable DTC
table And go to
”Multiple DTC”
51. Connect the scan tool to the DLC.
2. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
3. Press the accelerator pedal while watching
TPS for smooth changes in the voltage.
Does the scan tool show the TPS voltage change
smoothly within the value specified?0.3V–4.8VGo to
”Diagnostic
Aids”Go to Step 6
61. Turn the ignition switch to lock.
2. Disconnect the MTIA connector.
3. Measure the voltage between terminal 2 and 8.
Does the voltage measure within the value speci-
fied?4.8V–5.0VGo to Step 7Go to Step 8
7Connect a fused jumper between the MTIA connec-
tor terminal 2 and terminal 7.
Does the scan tool show the TPS voltage above val-
ue specified?4.8V–5.0VGo to Step 13Go to Step 11
8Measure the voltage between the MTIA connector
2 and ground.
Does the voltage measure within the value speci-
fied?>5.0VGo to Step 9Go to Step 10
91. Turn the ignition switch to lock.
2. Check for an open or low voltage in the wire
between the MTIA connector 8 and ECM con-
nector 19.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 14
101. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Check for an open or low voltage in the wire
between the MTIA connector 2 and ECM con-
nector 79.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 14
111. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Check for an open or low voltage in the wire
between the MTIA connector 7 and ECM con-
nector 74.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 14
Page 361 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 115
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
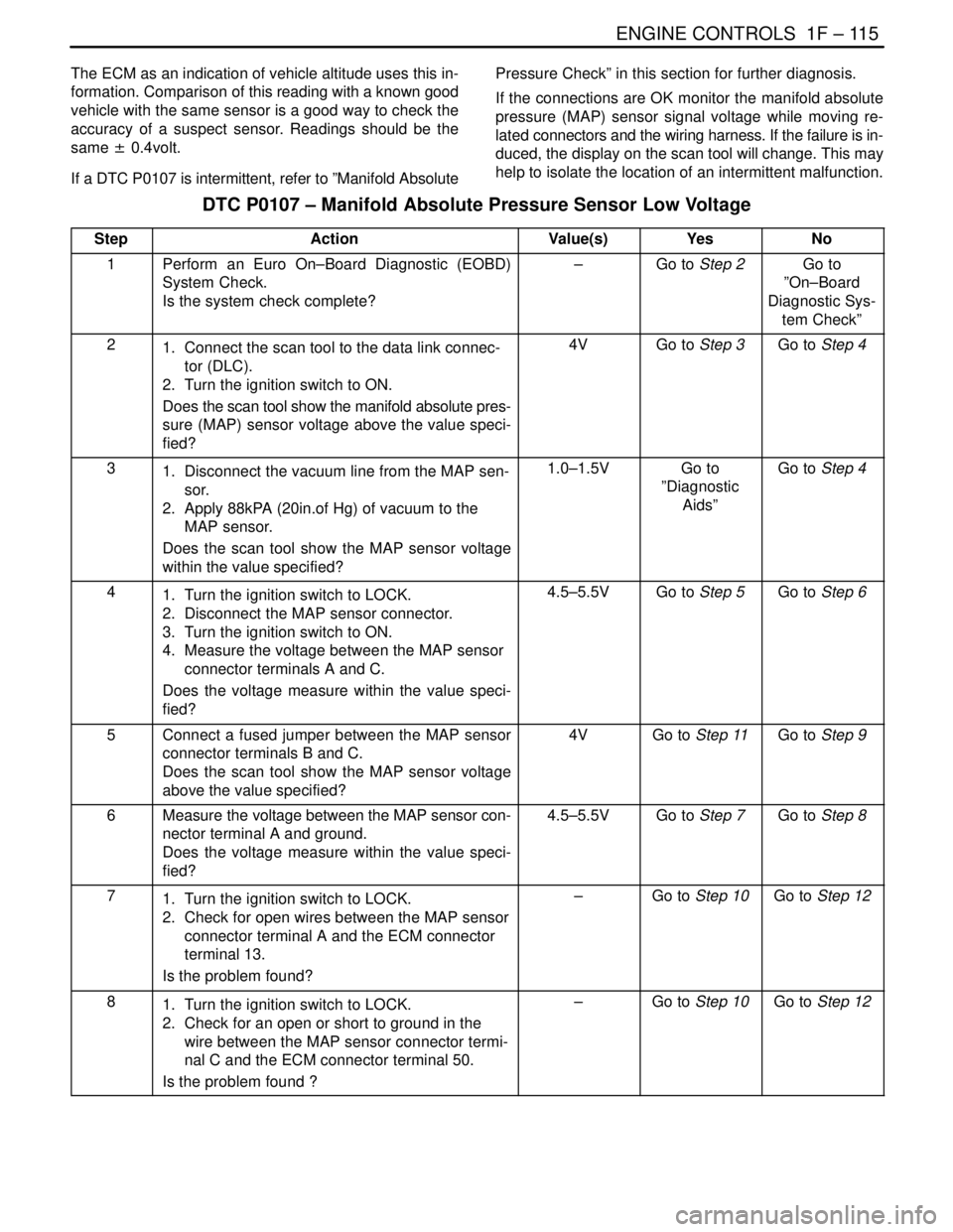
The ECM as an indication of vehicle altitude uses this in-
formation. Comparison of this reading with a known good
vehicle with the same sensor is a good way to check the
accuracy of a suspect sensor. Readings should be the
same ± 0.4volt.
If a DTC P0107 is intermittent, refer to ”Manifold AbsolutePressure Check” in this section for further diagnosis.
If the connections are OK monitor the manifold absolute
pressure (MAP) sensor signal voltage while moving re-
lated connectors and the wiring harness. If the failure is in-
duced, the display on the scan tool will change. This may
help to isolate the location of an intermittent malfunction.
DTC P0107 – Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Low Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Connect the scan tool to the data link connec-
tor (DLC).
2. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Does the scan tool show the manifold absolute pres-
sure (MAP) sensor voltage above the value speci-
fied?4VGo to Step 3Go to Step 4
31. Disconnect the vacuum line from the MAP sen-
sor.
2. Apply 88kPA (20in.of Hg) of vacuum to the
MAP sensor.
Does the scan tool show the MAP sensor voltage
within the value specified?1.0–1.5VGo to
”Diagnostic
Aids”Go to Step 4
41. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the MAP sensor connector.
3. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
4. Measure the voltage between the MAP sensor
connector terminals A and C.
Does the voltage measure within the value speci-
fied?4.5–5.5VGo to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Connect a fused jumper between the MAP sensor
connector terminals B and C.
Does the scan tool show the MAP sensor voltage
above the value specified?4VGo to Step 11Go to Step 9
6Measure the voltage between the MAP sensor con-
nector terminal A and ground.
Does the voltage measure within the value speci-
fied?4.5–5.5VGo to Step 7Go to Step 8
71. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Check for open wires between the MAP sensor
connector terminal A and the ECM connector
terminal 13.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 10Go to Step 12
81. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Check for an open or short to ground in the
wire between the MAP sensor connector termi-
nal C and the ECM connector terminal 50.
Is the problem found ?–Go to Step 10Go to Step 12
Page 363 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 117
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0108
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR HIGH
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) uses the Manifold Ab-
solute Pressure (MAP) sensor to control the fuel delivery
and the ignition timing. The MAP sensor measures the
changes in the intake manifold pressure, which results
from engine load (intake manifold vacuum) and the rpm
changes; and converts these into voltage outputs. The
ECM sends a 5 volt–reference voltage to the MAP sensor.
As the manifold pressure changes, the output voltage of
the MAP sensor also changes. By monitoring the MAP
sensor output voltage, the ECM knows the manifold pres-
sure. A low–pressure (low voltage) output voltage will be
about 1.0 to 1.5 volts at idle, while higher pressure (high
voltage) output voltage will be about 4.5 to 4.8 at wide
open throttle (WOT). The MAP sensor is metric pressure,
allowing the ECM to make adjustments for different alti-
tudes.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S This DTC can be stored in ”key–on” status.
S When the engine idling.
S Engine speed is greater than 700rpm.
S No throttle position sensor (TPS) fail conditions
present.
S The MAP is greater than 95kPA.
S A high voltage condition exists.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
S The ECM will substitutes a fixed MAP value and
use TP to control the fuel delivery (the scan tool will
not show defaulted)
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
With the ignition ON and the engine stopped, the manifold
pressure is equal to atmosphere pressure and the signal
voltage will be high.
The ECM as an indication of vehicle altitude uses this in-
formation. Comparison of this reading with a known good
vehicle with the same sensor is a good way to check the
accuracy of a suspect sensor. Readings should be the
same ±0.4volt.
If a DTC P0108 is intermittent, refer to ”Manifold Absolute
Pressure Check” in this section for further diagnosis.
If the connections are OK monitor the manifold absolute
pressure(MAP) sensor signal voltage while moving re-
lated connectors and the wiring harness. If the failure is in-
duced, the display on the scan tool will change. This may
help to isolate the location of an intermittent malfunction.
Page 377 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 131
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0122
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR LOW VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The aim of the MTIA (Main Throttle Idle Actuator) is to con-
trol the idle speed with the throttle body itself. The throttle
is motorized for low opening angle (05, 195). The charac-
teristics of the airflow are not the same for low and high
opening angles. As a matter of fact, the gradient of the
mass air flow function of TPS is lower for small angles that
permits to be more precise during the idle speed control.
Out of idle speed the throttle is actuated mechanically by
a classical bowdencable.
The throttle position sensor (TPS) provides a voltage sig-
nal that changes in relation to the throttle plate angle. The
signal voltage will vary from about nearly 5.0 V at idles to
about 0.2V to 0.4 V at wide–open throttle. The TPS is one
of the most important inputs used by the ECM for fuel con-
trol and other functions such as idle, wide open throttle,
deceleration enleanment, and acceleration enrichment.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S TPS voltage is less than 0.3V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The coolant fan turns ON.
S The ECM will default to 20°C (68°F) for the first 60
seconds of the engine run time, and then 92 °C
(198 °F).
S The scan tool will not show the defaulted value.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
If the DTC P0122 cannot be duplicated, the information in-
cluded in the Freeze Frame data can be useful. Use the
scan tool DTC information data to determine the status of
the DTC. If the DTC occurs intermittently, using the DTC
P0121 diagnostic table may help isolate the problem.
Page 378 of 2643
1F – 132IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
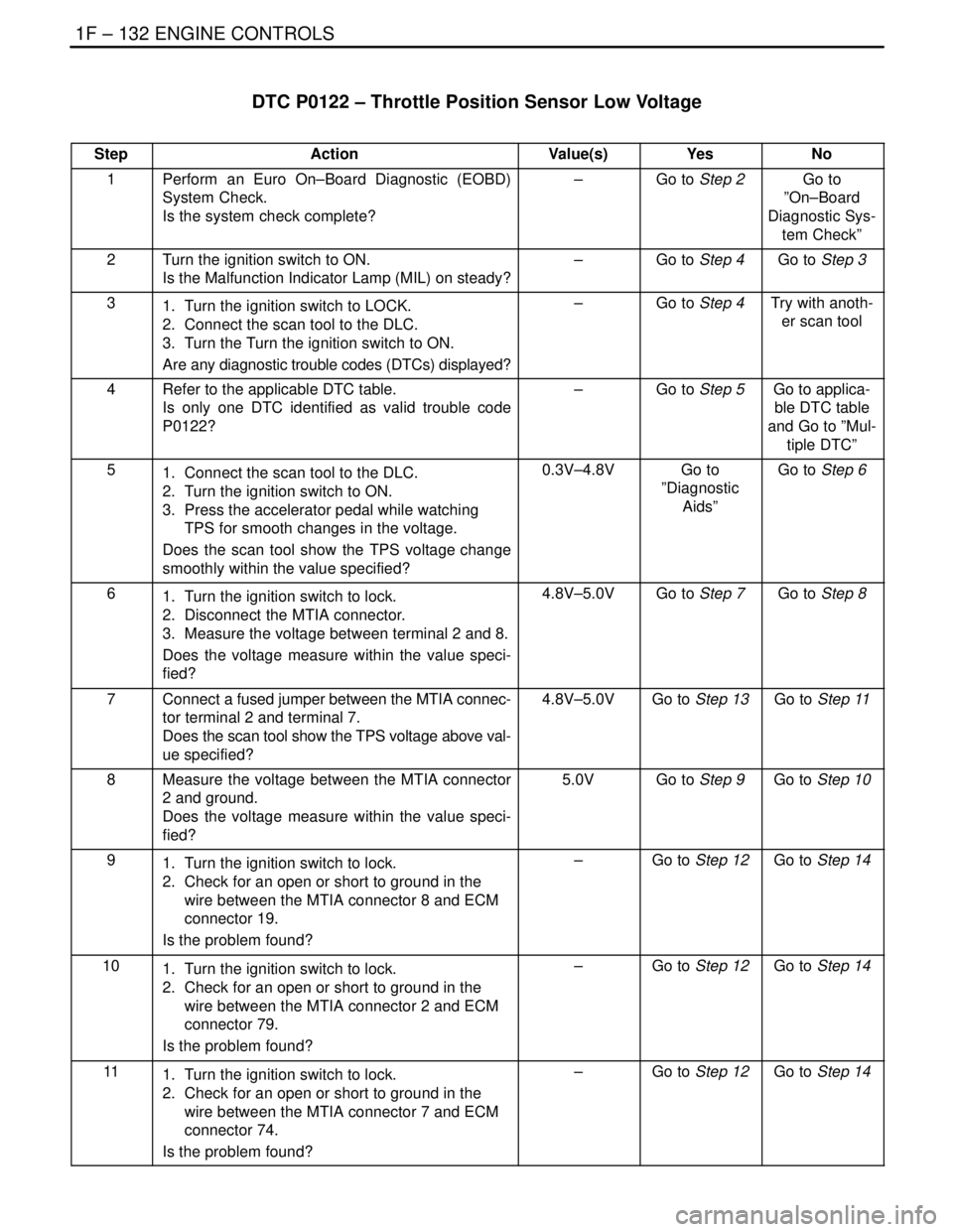
DTC P0122 – Throttle Position Sensor Low Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
2Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Is the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) on steady?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Connect the scan tool to the DLC.
3. Turn the Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Are any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) displayed?–Go to Step 4Try with anoth-
er scan tool
4Refer to the applicable DTC table.
Is only one DTC identified as valid trouble code
P0122?–Go to Step 5Go to applica-
ble DTC table
and Go to ”Mul-
tiple DTC”
51. Connect the scan tool to the DLC.
2. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
3. Press the accelerator pedal while watching
TPS for smooth changes in the voltage.
Does the scan tool show the TPS voltage change
smoothly within the value specified?0.3V–4.8VGo to
”Diagnostic
Aids”Go to Step 6
61. Turn the ignition switch to lock.
2. Disconnect the MTIA connector.
3. Measure the voltage between terminal 2 and 8.
Does the voltage measure within the value speci-
fied?4.8V–5.0VGo to Step 7Go to Step 8
7Connect a fused jumper between the MTIA connec-
tor terminal 2 and terminal 7.
Does the scan tool show the TPS voltage above val-
ue specified?4.8V–5.0VGo to Step 13Go to Step 11
8Measure the voltage between the MTIA connector
2 and ground.
Does the voltage measure within the value speci-
fied?5.0VGo to Step 9Go to Step 10
91. Turn the ignition switch to lock.
2. Check for an open or short to ground in the
wire between the MTIA connector 8 and ECM
connector 19.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 14
101. Turn the ignition switch to lock.
2. Check for an open or short to ground in the
wire between the MTIA connector 2 and ECM
connector 79.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 14
111. Turn the ignition switch to lock.
2. Check for an open or short to ground in the
wire between the MTIA connector 7 and ECM
connector 74.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 14
Page 380 of 2643

1F – 134IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0123
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR HIGH VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The aim of the MTIA (Main Throttle Idle Actuator) is to con-
trol the idle speed with the throttle body itself. The throttle
is motorized for low opening angle (05, 195). The charac-
teristics of the airflow are not the same for low and high
opening angles. As a matter of fact, the gradient of the
mass air flow function of TPS is lower for small angles that
permits to be more precise during the idle speed control.
Out of idle speed the throttle is actuated mechanically by
a classical bowdencable.
The throttle position sensor (TPS) provides a voltage sig-
nal that changes in relation to the throttle plate angle. The
signal voltage will vary from about nearly 5.0 V at idles to
about 0.2V to 0.4 V at wide–open throttle. The TPS is one
of the most important inputs used by the ECM for fuel con-
trol and other functions such as idle, wide open throttle,
deceleration enleanment, and acceleration enrichment.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S TPS voltage is greater than 4.8V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
S The coolant fan turns ON.
S The ECM will default to 20°C (68°F) for the first 60
seconds of the engine run time, and then 92 °C
(198 °F).
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
If the DTC P0123 cannot be duplicated, the information in-
cluded in the Freeze Frame data can be useful. Use the
scan tool DTC information data to determine the status of
the DTC. If the DTC occurs intermittently, using the DTC
P0121 diagnostic table may help isolate the problem.
With the ignition ON and the throttle at closed position the
voltage should read between 0.20 V and 0.90V and in-
crease steadily to over 4.5V at WOT.
DTCs P0123 and P0113 stored at the same time could be
the result of an open sensor ground circuit.
Page 381 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 135
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
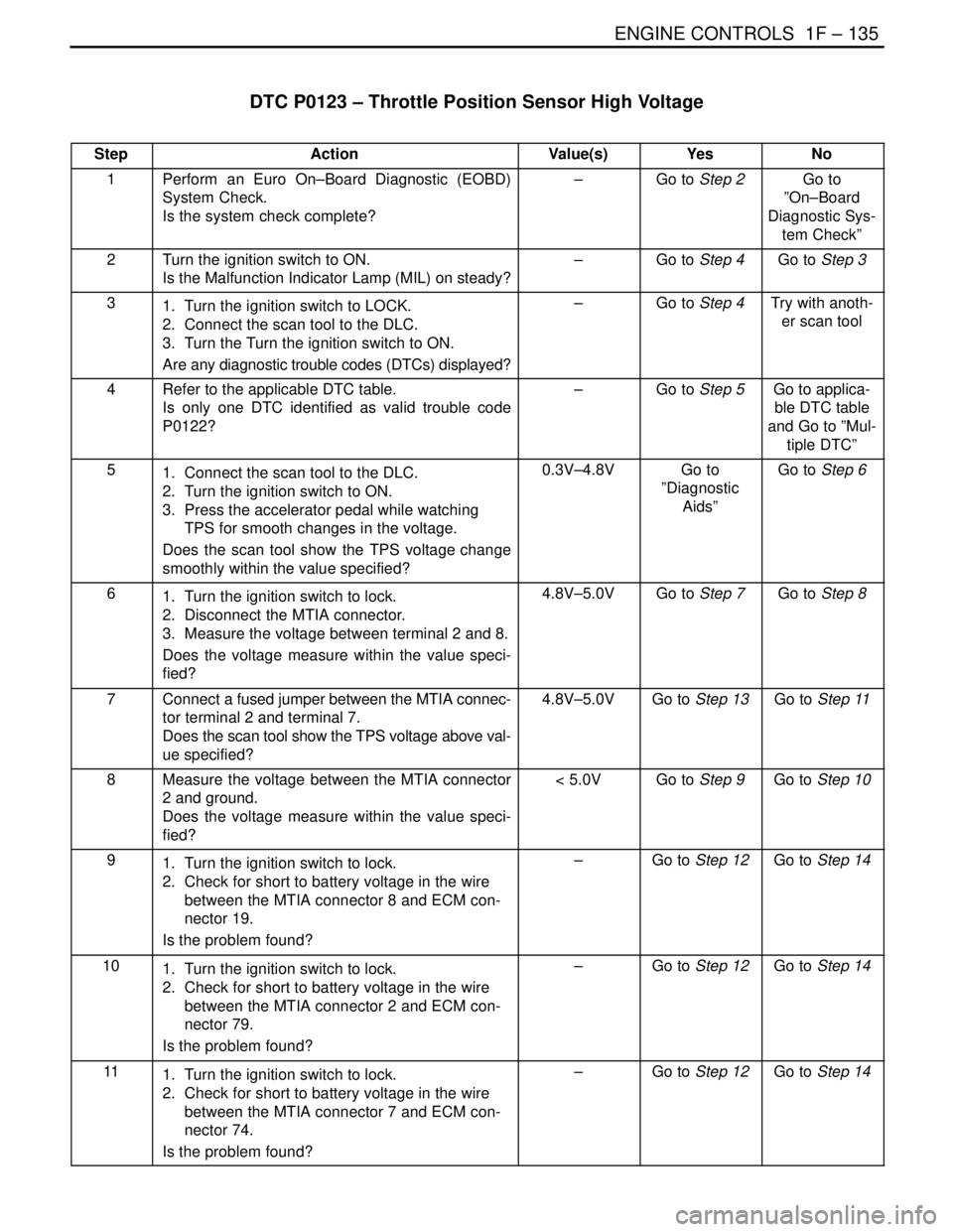
DTC P0123 – Throttle Position Sensor High Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
2Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Is the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) on steady?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Connect the scan tool to the DLC.
3. Turn the Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Are any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) displayed?–Go to Step 4Try with anoth-
er scan tool
4Refer to the applicable DTC table.
Is only one DTC identified as valid trouble code
P0122?–Go to Step 5Go to applica-
ble DTC table
and Go to ”Mul-
tiple DTC”
51. Connect the scan tool to the DLC.
2. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
3. Press the accelerator pedal while watching
TPS for smooth changes in the voltage.
Does the scan tool show the TPS voltage change
smoothly within the value specified?0.3V–4.8VGo to
”Diagnostic
Aids”Go to Step 6
61. Turn the ignition switch to lock.
2. Disconnect the MTIA connector.
3. Measure the voltage between terminal 2 and 8.
Does the voltage measure within the value speci-
fied?4.8V–5.0VGo to Step 7Go to Step 8
7Connect a fused jumper between the MTIA connec-
tor terminal 2 and terminal 7.
Does the scan tool show the TPS voltage above val-
ue specified?4.8V–5.0VGo to Step 13Go to Step 11
8Measure the voltage between the MTIA connector
2 and ground.
Does the voltage measure within the value speci-
fied?< 5.0VGo to Step 9Go to Step 10
91. Turn the ignition switch to lock.
2. Check for short to battery voltage in the wire
between the MTIA connector 8 and ECM con-
nector 19.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 14
101. Turn the ignition switch to lock.
2. Check for short to battery voltage in the wire
between the MTIA connector 2 and ECM con-
nector 79.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 14
111. Turn the ignition switch to lock.
2. Check for short to battery voltage in the wire
between the MTIA connector 7 and ECM con-
nector 74.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 14
Page 391 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 145
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0135
FRONT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER CIRCUIT
NOT FUNCTIONING
Circuit Description
Heated oxygen sensors (HO2S) are used for fuel control
and post catalyst monitoring. Each HO2S compares the
oxygen content of the surrounding air with the oxygen con-
tent in the exhaust stream. The HO2S must reach operat-
ing temperature to provide an accurate voltage signal. A
heating element inside the HO2S minmizes the time re-
quired for the sensor to reach operating temperature. Volt-
age is provided to the heater by the ignition 1 voltage cir-
cuit through a fuse. With the engine running, ground is
provided to the heater by the HO2S heater low control cir-
cuit, through a low side driver within the engine control
module (ECM). The ECM monitors the current flow
through the heater for diagnosis.
If the ECM detects that the HO2S heater current is above
or blelow a specified range, DTC P0135 seats.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S DTCs P0106, P0117, P0118, P1017 are not set.
S Engine run time is greater than 30 seconds.
S Filtered O2 heater current is less than 0.1 amps.
Action Taken When the DTC SetsS The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after three consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by rubbed through wire in-
sulation or a wire contacting the exhaust.
Check for poor connection or damaged harness – inspect
harness connectors for the following conditions:
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
Page 410 of 2643
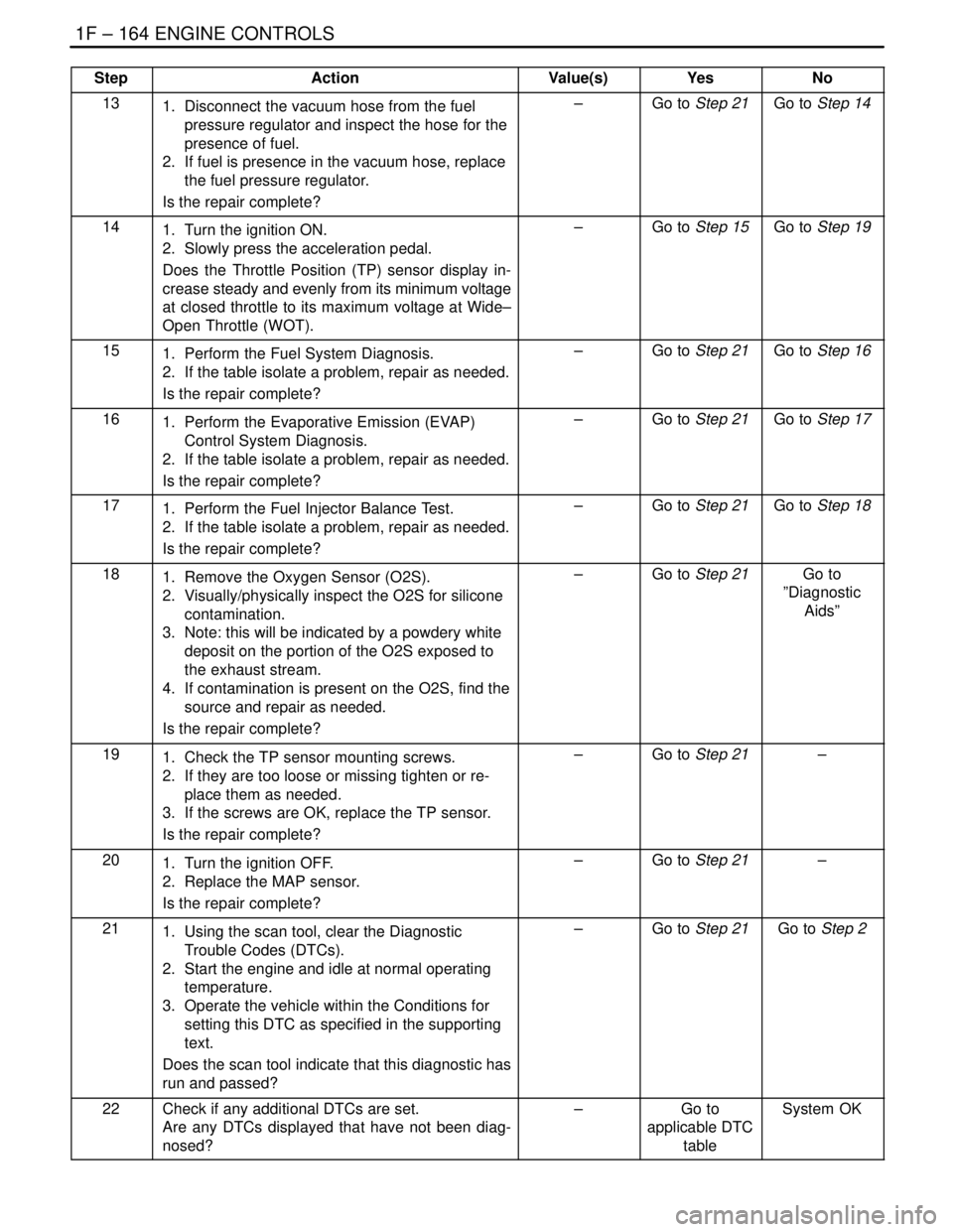
1F – 164IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
131. Disconnect the vacuum hose from the fuel
pressure regulator and inspect the hose for the
presence of fuel.
2. If fuel is presence in the vacuum hose, replace
the fuel pressure regulator.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 21Go to Step 14
141. Turn the ignition ON.
2. Slowly press the acceleration pedal.
Does the Throttle Position (TP) sensor display in-
crease steady and evenly from its minimum voltage
at closed throttle to its maximum voltage at Wide–
Open Throttle (WOT).–Go to Step 15Go to Step 19
151. Perform the Fuel System Diagnosis.
2. If the table isolate a problem, repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 21Go to Step 16
161. Perform the Evaporative Emission (EVAP)
Control System Diagnosis.
2. If the table isolate a problem, repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 21Go to Step 17
171. Perform the Fuel Injector Balance Test.
2. If the table isolate a problem, repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 21Go to Step 18
181. Remove the Oxygen Sensor (O2S).
2. Visually/physically inspect the O2S for silicone
contamination.
3. Note: this will be indicated by a powdery white
deposit on the portion of the O2S exposed to
the exhaust stream.
4. If contamination is present on the O2S, find the
source and repair as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 21Go to
”Diagnostic
Aids”
191. Check the TP sensor mounting screws.
2. If they are too loose or missing tighten or re-
place them as needed.
3. If the screws are OK, replace the TP sensor.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 21–
201. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the MAP sensor.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 21–
211. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 21Go to Step 2
22Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 411 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 165
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0222
MAIN THROTTLE IDLE ACTUATOR (MTIA) LOW VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The aim of the MTIA (Main Throttle Idle Actuator) is to con-
trol the idle speed with the throttle body itself. The throttle
is motorized for low opening angle (05, 22.55). The char-
acteristics of the air flow are not the same for low and high
opening angles. As a matter of fact, the gradient of the
mass air flow function of TPS is lower for small angles that
permits to be more precise during the idle speed control.
Out of idle speed the throttle is actuated mechanically by
a classical bowdencable.
The throttle position sensor (TPS) provides a voltage sig-
nal that changes in relation to the throttle plate angle. The
signal voltage will vary from about nearly 5.0 V at idle to
about 0.2 V to 0.4 V at wide open throttle. The TPS is one
of the most important inputs used by the ECM for fuel con-
trol and other functions such as idle, wide open throttle,
deceleration enleanment, and acceleration enrichment.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S MTIA voltage is less than 0.275V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Records buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for 10 sec-
onds.
Diagnostic Aids
An Intermittent problem may be caused by a poor connec-
tion, rubbed through wire insulation, or wire that is broken
inside the insulation.
Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the complaint,
should be thoroughly checked for the following conditions.
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminals to wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness