Lamp DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 456 of 2643

1F – 210IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0341
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR RATIONALITY
Circuit Description
The Camshaft Position Sensor is used to detect Camshaft
position and to have correlation with Crankshaft position
so that the ECM can determine which cylinder is ready to
be fueled by the injector. The polarity of camshaft sensor
signal must be changed only once per crankshaft position.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S No traction of CMP signal between teeth 25 and 33
but change in polarity.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTCS The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check and correct any abnormal engine noise before us-
ing the diagnostic table.
Any circuitry that is suspected as causing engine noise
complaint should be thoroughly checked for the following
conditions :
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness
Page 458 of 2643

1F – 212IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0342
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR SIGNAL
Circuit Description
The Camshaft Position Sensor is used to detect Camshaft
position and to have correlation with Crankshaft position
so that the ECM can determine which cylinder is ready to
be fueled by the injector. The polarity of camshaft sensor
signal must be changed only once per crankshaft position.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S No traction of CMP signal between teeth 25 and 33
but change in polarity.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTCS The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check and correct any abnormal engine noise before us-
ing the diagnostic table.
Any circuitry that is suspected as causing engine noise
complaint should be thoroughly checked for the following
conditions :
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness
Page 460 of 2643

1F – 214IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0351
IGNITION SIGNAL COIL A FAULT
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) provides a ground for
the electronic spark timing 1 circuit. When the ECM re-
moves the ground path of the ignition primary coil, the
magnetic field produced by the coil collapses. The collaps-
ing magnetic field produces a voltage in the secondary coil
which fires the spark plug. The circuit between the ECM
and the electronic ignition system is monitored for an open
circuit, short to voltage, and low voltage. When the ECM
detects a problem in the spark timing 1 circuit, it will set
DTC P0351.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The ignition signal coil A circuit is an open or a
short to ground or short to battery condition exists.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check and correct any abnormal engine noise before us-
ing the diagnostic table.
Any circuitry that is suspected as causing engine noise
complaint should be thoroughly checked for the following
conditions :
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness
Page 462 of 2643

1F – 216IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0352
IGNITION SIGNAL COIL B FAULT
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) provides a ground for
the electronic spark timing 3 circuit. When the ECM re-
moves the ground path of the ignition primary coil, the
magnetic field produced by the coil collapses. The collaps-
ing magnetic field produces a voltage in the secondary
coil, which fires the spark plug. The circuit between the
ECM and the electronic ignition system is monitored for an
open circuit, short to voltage, and low voltage. When the
ECM detects a problem in the spark timing 3 circuit, it will
set DTC P0352.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The ignition signal coil B circuit is an open or a
short ground or short to battery condition exists.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.S The ECM will default to 6 degree timing.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S Using the scan tool can clear DTC(s).
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for 10 sec-
onds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check and correct any abnormal engine noise before us-
ing the diagnostic table.
Any circuitry that is suspected as causing engine noise
complaint should be thoroughly checked for the following
conditions :
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness
Page 465 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 219
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
S DTCs P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117,
P0118, P0122, P0123, P0131, P0300, P0335,
P0336, P0341, P0342, P1671, P1672, P1673 are
NOT SET.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Recordsbuffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
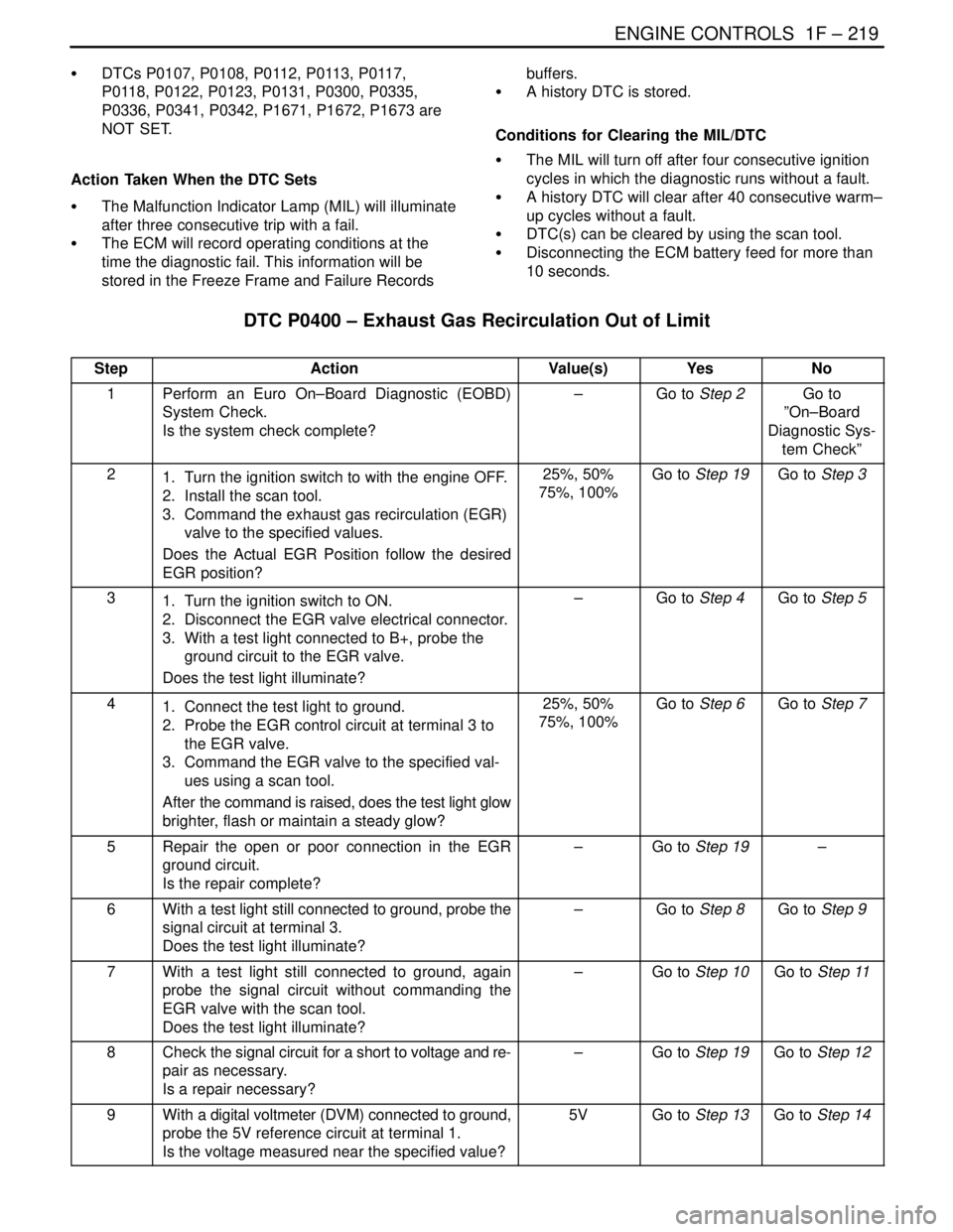
DTC P0400 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Out of Limit
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition switch to with the engine OFF.
2. Install the scan tool.
3. Command the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)
valve to the specified values.
Does the Actual EGR Position follow the desired
EGR position?25%, 50%
75%, 100%Go to Step 19Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
2. Disconnect the EGR valve electrical connector.
3. With a test light connected to B+, probe the
ground circuit to the EGR valve.
Does the test light illuminate?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
41. Connect the test light to ground.
2. Probe the EGR control circuit at terminal 3 to
the EGR valve.
3. Command the EGR valve to the specified val-
ues using a scan tool.
After the command is raised, does the test light glow
brighter, flash or maintain a steady glow?25%, 50%
75%, 100%Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
5Repair the open or poor connection in the EGR
ground circuit.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 19–
6With a test light still connected to ground, probe the
signal circuit at terminal 3.
Does the test light illuminate?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 9
7With a test light still connected to ground, again
probe the signal circuit without commanding the
EGR valve with the scan tool.
Does the test light illuminate?–Go to Step 10Go to Step 11
8Check the signal circuit for a short to voltage and re-
pair as necessary.
Is a repair necessary?–Go to Step 19Go to Step 12
9With a digital voltmeter (DVM) connected to ground,
probe the 5V reference circuit at terminal 1.
Is the voltage measured near the specified value?5VGo to Step 13Go to Step 14
Page 467 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 221
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0404
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION OPENED
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Re–circulation (EGR) system is used to
lower oxides of nitrogen (NOx) emission levels caused by
high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this by
feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the
combustion chamber. When the air/fuel mixture is diluted
with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are re-
duced.
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear EGR
valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust gases to
the engine without the use of intake manifold vacuum. The
valve controls exhaust flow going into the intake manifold
from the exhaust manifold through an orifice with a engine
control module(ECM) controlled pintle. The ECM controls
the pintle position using inputs from the Throttle Position
(TP) and the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor.
The ECM then commands the EGR valve to operate when
necessary by controlling an ignition signal through the
ECM. This can be monitored on a scan tool as the Desired
EGR position.
The ECM monitors the results of its command through a
feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a
ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing the
EGR valve pintle position is sent to the ECM. This feed-back signal can also be monitored on a scan tool and is the
actual position of the EGR pintle. The actual EGR position
should always be near the commanded or Desired EGR
position.
This Diagnostic Trouble Code(DTC) will detect an open or
short circuit.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S EGR circuit is a short to ground or an open condi-
tion exist.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
Page 470 of 2643

1F – 224IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0405
EGR PINTLE POSITION SENSOR LOW VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Re–circulation (EGR) system is used to
lower oxides of nitrogen (NOx) emission levels caused by
high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this by
feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the
combustion chamber. When the air/fuel mixture is diluted
with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are re-
duced.
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear EGR
valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust gases to
the engine without the use of intake manifold vacuum. The
valve controls exhaust flow going into the intake manifold
from the exhaust manifold through an orifice with a engine
control module(ECM) controlled pintle. The ECM controls
the pintle position using inputs from the Throttle Position
(TP) and the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor.
The ECM then commands the EGR valve to operate when
necessary by controlling an ignition signal through the
ECM. This can be monitored on a scan tool as the Desired
EGR position.
The ECM monitors the results of its command through a
feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a
ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing the
EGR valve pintle position is sent to the ECM. This feed-back signal can also be monitored on a scan tool and is the
actual position of the EGR pintle. The actual EGR position
should always be near the commanded or Desired EGR
position.
This Diagnostic Trouble Code(DTC) will detect an open or
short circuit.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S EGR voltage is less than 0.01V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Page 473 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 227
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0406
EGR PINTLE POSITION SENSOR HIGH VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Re–circulation (EGR) system is used to
lower oxides of nitrogen (NOx) emission levels caused by
high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this by
feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the
combustion chamber. When the air/fuel mixture is diluted
with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are re-
duced.
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear EGR
valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust gases to
the engine without the use of intake manifold vacuum. The
valve controls exhaust flow going into the intake manifold
from the exhaust manifold through an orifice with a engine
control module(ECM) controlled pintle. The ECM controls
the pintle position using inputs from the Throttle Position
(TP) and the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor.
The ECM then commands the EGR valve to operate when
necessary by controlling an ignition signal through the
ECM. This can be monitored on a scan tool as the Desired
EGR position.
The ECM monitors the results of its command through a
feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a
ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing the
EGR valve pintle position is sent to the ECM. This feed-back signal can also be monitored on a scan tool and is the
actual position of the EGR pintle. The actual EGR position
should always be near the commanded or Desired EGR
position.
This Diagnostic Trouble Code(DTC) will detect an open or
short circuit.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S EGR voltage is higher than 4.99V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Page 476 of 2643

1F – 230IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0420
CATALYST LOW EFFICIENCY
Circuit Description
In order to control exhaust emissions of Hydrocarbons
(HC), Carbon Monoxide (CO) and Nitrogen Oxide (NOx),
a Three–Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) is used. The cat-
alyst within the converter promotes a chemical reaction
which oxidizes the HC and CO present in the exhaust gas,
converting them into harmless water vapor and carbon
dioxide, it also reduces NOx, converting it into nitrogen.
The catalytic converter also has the ability to store oxygen.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) has the capability to
monitor this process using a Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S) located in the exhaust stream past the TWC. The
HO2S produces an output signal which indicates the oxy-
gen storage capacity of the catalyst; this in turn indicates
the catalyst’s ability to convert exhaust emissions effec-
tively. The ECM monitors the catalyst efficiency by first al-
lowing the catalyst to heat up, waiting for a stabilization pe-
riod while the engine is idling, and then adding and
removing fuel while monitoring the reaction of the HO2S.
When the catalyst is functioning properly, the HO2S re-
sponse to the extra fuel is slow compared to the Oxygen
Sensor (O2S). When the HO2S response is close to that
of the O2S, the Oxygen storage capability or efficiency of
the catalyst is considered to be bad, and the Malfunction
Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Closed loop stoichiometry.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is more than
75°C (167°F) . (1.4L DOHC)
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is more than
70°C (158°F) . (1.6L DOHC)
S Engine speed between 1,766rpm and 2,368rpm.
(1.4L DOHC)
S Engine speed between 1,760rpm and 2,530rpm.
(1.6L DOHC)
S Vehicle speed is between 47km/h (29.2mph) and
80km/h (49.7mph). (1.4L DOHC)
S Vehicle speed is between 60km/h (37.3mph) and
76km/h (47.2mph). (1.6L DOHC)
S The manifold absolute pressure is greater than 70
kpa. (1.4L DOHC)S The manifold absolute pressure is greater than 76
kpa. (1.6L DOHC)
S Activity of the heated oxygen sensor excited by
lambda controller stimuli higher than a threshold.
S DTC(s) P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118, P0122,
P0123, P0131, P0132, P0133, P0137, P0138,
P0140, P0141, P0171, P0172, P0300, P0336,
P0337, P0341, P0342, P0351, P0352, P0404,
P0405, P0405 and P0562 are not sets.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
The catalyst test may abort due to a change in the engine
load. Do not change the engine load (i.e. A/C, coolant fan,
heater motor) while a catalyst test is in progress.
An intermittent problem may be caused by a poor connec-
tion, rubbed–through wire insulation, or a wire that is bro-
ken inside the insulation.
Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the intermittent
complaint, should be thoroughly checked for the following
conditions:
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection.
Page 479 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 233
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Although this DTC is considered a type. A diagnostic, it
acts like a type B diagnostic under certain conditions.
Whenever this diagnostic reports the system has passed,
or if the battery is disconnected, the diagnostic must fail
twice before setting a DTC. The initial failure is not re-ported to the diagnostic executive or displayed on a scan
tool. A passing system always reports to the diagnostic
executive immediately.
Check for the following conditions :
S Missing or damaged fuel cap.
S Missing or damaged O–rings at fuel vapor and
EVAP purge line canister fittings.
S Cracked or punctured EVAP canister.
S Damaged source vacuum line, EVAP purge line,
EVAP vent hose or fuel tank vapor line.
S Poor connection at the ECM. Inspect the harness
connectors for the following conditions.
S Backed–out terminals.
S Improper mating.
S Broken locks.
S Improperly formed.
S Damaged terminals.
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection.
S Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness to
the EVAP vent solenoid, EVAP canister purge
valve, and the fuel tank pressure sensor for an in-
termittent open or short circuit.
S Kinked, pinched or plugged vacuum source, EVAP
purge, or fuel tank vapor line. Verify that the lines
are not restricted.
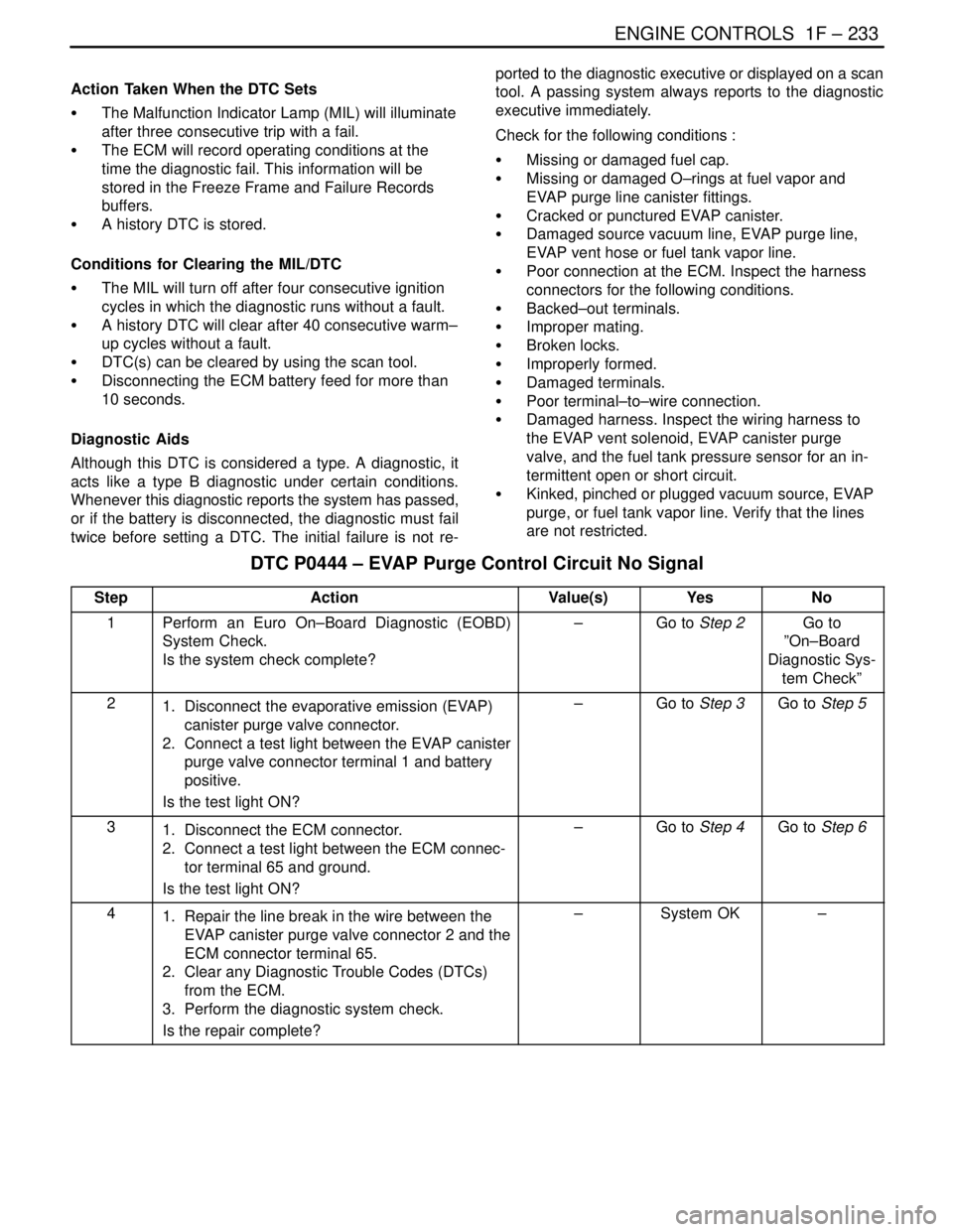
DTC P0444 – EVAP Purge Control Circuit No Signal
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Disconnect the evaporative emission (EVAP)
canister purge valve connector.
2. Connect a test light between the EVAP canister
purge valve connector terminal 1 and battery
positive.
Is the test light ON?–Go to Step 3Go to Step 5
31. Disconnect the ECM connector.
2. Connect a test light between the ECM connec-
tor terminal 65 and ground.
Is the test light ON?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 6
41. Repair the line break in the wire between the
EVAP canister purge valve connector 2 and the
ECM connector terminal 65.
2. Clear any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
from the ECM.
3. Perform the diagnostic system check.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–