steering wheel DATSUN 610 1969 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1969, Model line: 610, Model: DATSUN 610 1969Pages: 171, PDF Size: 10.63 MB
Page 97 of 171

I
Fig
K
16
Removing
the
column
sheD
covers
inter
i
mj
rD
1
f
1
A
iJI1i
j
j
r
I
I
s
Ii
i
FIg
K
15
Removing
the
steering
wheel
Fig
K
l7
Removing
the
rubber
coupling
securing
bolt
1
bclttt
ube
2
Column
clamp
Fig
K
19
Steering
lock
installation
Fig
K
18
The
standard
dimension
between
coluDDl
clamp
and
lower
jacket
J
A
6
c
V
1
Rubbt
r
coupling
2
Steen
column
3
Worm
1
4
Dash
ptmd
5
ColUmrl
3hDf
6
Colli
clamp
7
Lowt
r
jacket
flangt
FIg
K
20
Installing
tbe
steering
column
assembly
96
f
ftb
Fig
K
21
The
outer
tie
rod
ball
joint
I
I
t
I
Fig
K
22
The
centre
tie
rod
ball
joint
Page 98 of 171

3
Free
the
ball
studs
from
the
knuckle
arms
by
placing
a
hammer
behind
the
boss
and
striking
the
opposite
side
with
another
hammer
4
Remove
the
centre
tie
rod
ball
studs
in
a
similar
manner
to
that
described
above
and
remove
the
centre
tie
rod
and
outer
tie
rods
as
an
assembly
5
Remove
the
idler
assembly
from
the
side
member
by
with
drawing
the
retaining
bolts
SfEERING
LINKAGE
Dismantling
Disconnect
the
tie
rods
from
the
centre
rod
Loosen
the
clamp
bolts
unscrew
the
socket
assembly
and
remove
the
socket
from
the
tie
rods
Remove
the
idler
arm
nut
and
dismantle
the
idler
assembly
Check
the
idler
arm
rubber
bushing
for
signs
of
damage
wear
or
play
and
replace
the
bushing
if
necessary
Oteck
the
centre
and
outer
tie
rod
for
damage
or
bending
Inspect
the
ball
joints
and
replace
them
i
the
amount
of
play
is
excessive
or
if
the
dust
cover
is
cracked
Further
infor
mation
can
be
found
in
the
section
FRONT
SUSPENSION
See
also
Figs
K
21
and
K
22
STEERING
LINKAGE
Assembly
and
Installation
Assembly
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
procedure
noting
the
following
points
To
assembly
the
idler
arm
assembly
coat
the
outer
dia
meter
of
the
bushing
with
soapy
water
and
press
the
bushing
into
the
idler
arm
until
the
bushing
protrudes
equally
at
both
sides
Fit
the
idler
arm
body
in
the
rubber
bushing
Ensure
that
the
centre
line
of
the
idler
arm
is
parallel
with
the
centre
line
of
the
chassis
Installation
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
procedure
The
outer
tie
rods
must
be
set
so
that
the
lengths
between
the
ball
stud
centres
are
309
5
mm
12
18
in
for
the
1400
and
1600cc
models
and
313
2
mm
12
33
in
for
the
1800cc
models
Tighten
the
ball
stud
nut
to
a
torque
reading
of
5
5
7
6
kgm
39
8
55Ib
ft
the
idler
ann
nut
to
5
5
7
6
kgm
39
8
55Ib
ft
and
the
pitman
arm
nut
to
14
kgm
lOllb
ft
The
front
wheel
alignment
toe
in
and
steering
angle
should
be
checked
and
adjusted
as
described
in
the
section
FRONT
SUSPENSION
TechnIcal
Data
Steering
type
Gear
ratio
Steering
angle
Inner
wheel
l800cc
Outer
wheel
1800
cc
Inner
wheel
1400
and
1600cc
Saloon
1400
and
1600cc
Estate
Outer
wheel
1400
and
1600cc
Saloon
1400
and
1600cc
Estate
Steering
wheel
play
1400
and
1600cc
Steering
wheel
play
1800cc
Standard
total
thickness
of
worm
bearing
shims
End
play
between
sector
shaft
and
adjusting
screw
Initial
turning
torque
of
worm
bearing
l800cc
models
1400
and
1600cc
models
Worm
and
recirculating
ball
15
0
I
370
380
30040
32040
380
380
30
31020
330
25
30mm
0
98
1
18
in
less
than
35mm
1
378
in
at
outer
rim
of
steering
wheel
1
5
mm
0
059
in
0
0
I
0
03mm
0
0004
0
0012
in
4
0
6
0
kg
cm
55
6
83
4
in
oz
4
0
8
0
kg
cm
55
6
112
in
oz
97
Page 110 of 171

ElectrIcal
EquIpment
DESCRIPTION
BATTERY
Maintenance
STARTER
MOTOR
Removal
and
Dismantling
STARTER
MOTOR
Testing
STARTER
MOTOR
Assembly
and
Installation
ALTERNATOR
Removal
Dismantling
and
Inspection
DESCRIPTION
A
12
volt
negative
earth
electrical
system
is
used
in
which
the
battery
is
charged
by
an
alternator
In
the
alternator
a
magnetic
field
is
produced
by
the
rotor
which
consists
of
the
alternator
shaft
field
coil
p
le
pieces
and
slip
rings
Output
current
is
generated
in
the
armature
coils
located
in
the
stator
Six
silicon
diodes
are
incorporated
in
the
alternator
caSing
to
rectify
the
alternating
current
supply
A
voltage
regulator
and
pilot
lamp
relay
are
built
in
the
regulator
box
which
nonnally
does
not
give
trouble
or
require
attention
The
starter
motor
is
a
brush
type
series
wound
motor
in
which
positive
meshing
of
the
pinion
and
ring
gear
teeth
are
secured
by
means
of
an
overrunning
clutch
BATTERY
Maintenance
The
battery
should
be
maintained
in
a
clean
and
dry
condition
at
all
times
or
a
current
leakage
may
occur
between
the
terminals
If
frequent
topping
up
is
required
it
is
an
indication
of
overcharging
or
deterioration
of
the
battery
When
refitting
the
cables
clean
them
thoroughly
and
coat
their
terminals
and
the
terminal
posts
with
petroleum
jelly
Check
the
level
of
the
electrolyte
in
the
battery
at
frequent
intervals
and
top
up
if
necessary
to
the
level
mark
on
the
battery
case
with
distilled
water
A
hydrometer
test
should
be
carried
out
to
determine
the
state
of
charge
of
the
battery
by
measuring
the
specific
gravity
of
the
electrolyte
It
should
be
pointed
out
that
the
addition
of
sulphuric
acid
will
not
normally
be
necessary
and
should
only
be
carried
out
by
an
expert
when
required
The
specific
gravity
of
the
electrolyte
should
be
ascertained
with
the
battery
fully
charged
at
an
electrolyte
temperature
of
200C
680F
The
specific
gravity
of
the
electrolyte
decreases
or
increases
by
0
0007
when
its
temperature
rises
or
falls
by
10C
1
80F
respectively
The
temperature
referred
to
is
that
of
the
electrolyte
and
not
the
ambient
temperature
to
correct
a
reading
for
an
air
temperature
it
will
be
necessary
to
add
0
0035
to
the
reading
for
every
50C
above
200C
Conversely
0
0035
must
be
deducted
for
every
SOC
below
200C
Test
each
cell
separately
and
draw
the
liquid
into
the
hydrometer
several
times
if
a
built
in
thermometer
type
is
used
The
correct
specific
gravity
readings
should
be
as
follows
ALTERNATOR
Assembly
and
Installation
HEAD
LAMPS
Replacing
HORN
INSTRUMENT
PANEL
Removal
WINDSCREEN
WIPERS
WINDSCREEN
WASHERS
IGNITION
SWITCH
AND
STEERING
LOCK
Cold
climates
Temperature
climates
Tropical
climates
Permissible
value
Over
1
22
Over
1
20
Over
1
18
Fully
charged
at
200C
680F
1
28
1
26
1
23
The
battery
should
be
recharged
if
a
low
specific
gravity
reading
is
indicated
Always
disconnect
both
terminals
of
the
battery
when
charging
and
clean
the
terminal
posts
with
a
soda
solution
Remove
the
vent
plugs
and
keep
the
electrolyte
temperature
below
450C
l130F
during
charging
Check
the
specific
gravity
after
charging
and
if
it
is
above
1
260
at
200C
680C
add
distilled
water
STARTER
MOTOR
Removal
and
Dismantling
As
previously
stated
the
starter
motor
is
brush
type
series
wound
motor
in
which
the
positive
meshing
of
the
pinion
and
ring
gear
teeth
are
secured
by
an
overrunning
clutch
The
over
running
clutch
employs
a
shift
lever
to
slide
the
pinion
into
mesh
with
the
flywheel
ring
gear
teeth
when
the
starter
is
operated
When
the
engine
starts
the
pL
lion
is
permitted
to
overrun
the
clutch
and
armature
but
is
held
in
mesh
until
the
shift
lever
is
released
An
exploded
view
of
the
starter
is
shown
in
Fig
M
2
To
remove
the
starter
motor
proceed
as
follows
Disconnect
the
battery
earth
cable
2
Disconnect
the
black
and
yellow
wire
from
the
solenoid
terminal
and
the
black
cable
from
the
battery
terminal
3
Remove
the
two
bolts
securing
the
starter
motor
to
the
clutch
housing
Pull
the
starter
motor
assembly
forwards
and
withdraw
it
from
the
v
hicle
To
dismantle
the
starter
motor
ftrst
remove
the
brush
cover
and
lift
out
the
brushes
as
shown
in
Fig
M
3
Loosen
the
nut
securing
the
connecting
plate
to
the
solenoid
M
terminal
Remove
the
solenoid
retaining
screws
take
out
the
cotter
pin
and
withdraw
the
shift
lever
pin
Remove
the
solenoid
assembly
as
shown
in
Fig
M
4
Remove
the
two
through
bolts
and
rear
cover
assembly
then
remove
the
yoke
assembly
by
lightly
tapping
it
with
a
wooden
mallet
Fig
M
S
Withdraw
the
armature
and
shift
lever
Fig
M
6
Remove
the
pinion
stopper
from
the
armature
shaft
by
removing
the
stopper
washer
pushing
the
109
Page 118 of 171

4
Remove
the
shell
covers
from
the
steering
column
slacken
the
screws
securing
the
meter
housing
and
withdraw
the
panel
from
the
facia
Fig
M
33
5
Pull
out
the
12
pole
round
shaped
connector
and
remove
the
speedometer
cable
union
nut
then
remove
the
instru
ment
panel
completely
WINDSCREEN
WIPERS
A
two
speed
wiper
motor
is
fitted
The
motor
has
an
auto
stop
mechanism
and
drives
the
wiper
arms
through
a
link
mechanism
located
behind
the
instrument
panel
If
the
wiper
system
does
not
operate
check
the
fuses
connectors
control
switch
and
motor
If
the
wiper
speed
does
not
change
the
switch
must
be
repaired
or
replaced
If
the
wiper
motor
becomes
unserviceable
it
can
be
removed
from
the
vehicle
in
the
fOllowing
manner
I
Remove
the
connector
plug
from
the
motor
See
Fig
M
34
2
Working
from
the
passenger
compartment
side
of
the
dash
panel
remove
the
nut
connecting
the
wiper
motor
worm
wheel
shaft
to
the
connecting
rod
3
Remove
the
three
bolts
securing
the
wiper
motor
to
the
cowl
and
lift
out
the
motor
Battery
Starter
motor
Type
Output
No
load
Terminal
voltage
Current
Revolution
Load
Terminal
voltage
Current
Torque
Brushes
Brush
length
Wear
limit
Spring
tension
Commutator
Standard
outer
diameter
Wear
limit
Depth
of
nuca
Repair
limit
Repair
accuracy
Qearance
between
armature
shaft
and
bushing
Repair
liinit
Repair
accuracy
Armature
shaft
ou
ter
diameter
Pinion
side
Rear
end
Wear
limit
Bend
limit
The
wiper
arms
can
be
removed
quite
easily
by
taking
off
the
attachment
bolt
as
shown
in
Fig
M
J
5
and
then
pullin
the
wiper
arm
from
the
pivot
shaft
When
installing
the
wiper
arm
make
sure
that
the
blade
is
positioned
approximately
27mm
1
06
in
away
from
the
bottom
of
the
windscreen
and
tighten
the
wiper
arm
attachment
bolt
WINDSCREEN
WASHERS
The
windscreen
washer
SWItch
and
wiper
switch
are
com
bined
in
a
single
unit
See
Fig
M
36
the
washers
can
be
operated
by
turning
the
switch
in
the
appropriate
direction
It
should
be
pointed
out
that
it
is
inadvisable
to
operate
the
washers
for
more
than
30
seconds
at
a
time
If
the
washers
are
operated
in
short
spells
of
approximately
10
seconds
duration
their
working
efficiency
will
remain
unimpaired
for
a
considerable
length
of
time
IGNITION
SWITCH
AND
STEERING
LOCK
The
steering
lock
is
built
in
to
the
goition
switch
When
the
key
is
turned
to
the
LOCK
position
and
then
removed
the
steering
system
is
automatically
locked
by
the
steering
lock
spindle
which
engages
in
a
notch
in
the
collar
on
the
steering
shaft
See
Fig
M
37
The
heads
of
the
screws
are
sheared
off
on
installation
so
that
the
steering
lock
system
cannot
be
tampered
with
If
the
steering
lock
is
to
be
replaced
it
will
be
necessary
to
remove
the
two
securing
screws
8
and
then
drill
out
the
self
shearing
screws
7
When
installing
a
new
steering
lock
tighten
the
new
self
shearing
screws
until
the
heads
shear
TechnICal
Data
12
volt
HITACHI
S114
87M
1
0KW
12
volts
Less
than
60
amperes
More
than
7000
r
p
m
6
3
volts
Less
than
420
amperes
More
than
0
9
mkg
6
5
lb
ft
16
mm
0
630
in
6
5mm
0
256
in
0
8
kg
1
8
lb
33mm
1
299
in
2mm
0
078
in
0
2mm
0
008
in
0
5
0
8mm
0
0197
0
0315
in
0
2mm
0
008
in
0
03
O
lmm
0
0012
0
0039
in
13mm
0
512
in
11
5
mm
0
453
in
O
lmm
0
0039
in
0
08
mm
0
0031
in
Oearance
between
pinion
and
stopper
0
3
1
5mm
0
0118
0
0591
in
ALTERNATOR
Type
HITACHI
LTl25
06
HITACHI
LTl33
05
USA
Canada
More
than
18
amps
at
14
volts
2500
r
p
m
More
than
25
amps
at
14
volts
5000
r
p
m
Output
current
LTl25
06
Output
current
LT
133
05
More
than
24
amps
at
14
volts
2500
r
p
m
More
than
33
amps
at
14
volts
5000
r
p
m
Brushes
Lengtb
Wear
limit
Spring
pressure
14
5mm
0
571
In
7mm
0
2756
in
0
25
0
35
kg
0
55
0
771b
Slip
ring
Outer
diameter
Reduction
limit
Repair
limit
Repair
accuracy
31
mm
1
220
in
I
mm
0
039
in
O
3mm
0
0118
in
0
05
mm
0
0197
in
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
Type
Regulating
voltage
HITACHI
TL
lZ
37
14
3
15
3
volts
at
200C
680F
117
Page 128 of 171

Clutch
MIPTOOlS
Trouble
Shootmg
Steering
IYMmlMS
mDING
S1
1FFNESS
ITIBJJNG
IIl
ACJt
STEEIUNG
WANDER
WHEEL
SHIIlOlY
CAR
PUl
U
TO
ONE
IIDE
POOR
RECa
Dy
OF
STEERING
WHEEL
10
CENl1tE
EXCESSIVE
01
ABNORMAL
TYKE
WEAR
It
d
e
f
I
II
J
e
It
b
I
J
k1
D
0
P
41
r
nUTCH
SI
IPPING
WIu
NOT
ENGAGE
PROPERLY
CLUfCHDRAG
WILLNOT
DISENGAGE
PROf
ERL
Yl
a
1JTCH
JUDDE
a
tn
CII
eRA
fON
ENCAGEMDIT
CLIJfCH
NOISE
SQUEAL
DEl
ltESSlNG
nlE
PEDAL
nUTCH
NOISE
RATTLE
WHEN
IDI
ING
CLUTCH
NOISE
CHATTER
ON
a
GAGEMENI
I
I
j
ILlm
ROUBLE
CAUSE
I
hllUtrident
f
lay
In
RIM
link
Ia
CllIlclldilC
facbllWl
lmorlludlned
t
Gt
dM
01
oil
cluu
h
d
ana
d
Wellk
or
brotell
pralure
plate
coilsprinp
or
diapht
m
IprIzlf
to
Alrinhydr
lIlie
tma
r
l
ffid
n
r
I
tc
hltcbped
Elc
c
frw
plly
kft
Iink
h
MlIali
DIIleruofdutdabOUJ
i
a
L
ctutcb
dlx
hllb
blndinl
011
of
FctJoz
laput
matt
J
Clutch
dilc
faclnf
10
or
brot
II
Pn
n
pllte
malin
Nrflet
w
d
L
ClukIl
CO
Ierdl
lorl
d
m
Lo
nttl
It
tnlllmblllon
or
rlIkm
Ii
Clutch
d
4i1torWd
LoC
drift
plate
hub
p
Relr
a
ba
tIn
d
rcc
q
Reina
UlIl
Mnt
r
l
o
b
Vau1lcf
luld
l
I
b
OE
1
R08A1LE
CAUSE
I
Adj
t
IinbF
tI
Replace
elutchdlK
c
CIUlllnd
l
eIlIedy
CIII
d
ae
prln
lInSl
llem
f
AdJ
t
tnweL
Niju
st
gII
It
Irom
put
lLaealipll
ReIl
CIU
gfbUadiJll
j
aepllC
t1utdl
dK
11
Pit
ne
puta
1
lI
epla
c
m
TIk
lIp
pia
ae
dK
aepl
cellub
p
Reiin
b
4
Strlilhtenor
f
To
I
p
hy4rw1k
ftuid
Tyre
pnlUUI1IIlncoo
ct
or
un
no
b
Lec1l
oIJ
l
brk
l
ltlnltlt
r
Co
uck
oflubric
t1on
t
t
lU
IliDt
p
ball
Joillta
4
Inc
t
Mil
a1
aNM
nt
laeomctl
adj
ma
tccriaI
pr
f
StMrbtloobuMb
IrtJlptooaptorcohuMbcalor
aUalllipMd
I
na
UU
JobltJ
u1I
or
Joe
b
Proal
lrbtd
artap
or
116
4
L
sacu
1Il
frollt
lUlptlllioa
J
d
boolnallloo
t
It
Ill
wb
100II
L
StMdn
plr
mountiJl
both
100
m
ltleerina
I
U
om
II
SIlock
IblOl
WI
defoc
or
ItlOUfttinp
IGolC
0
ll
oIId
wbedJ
lmbllancedor
t
tu
l
lIImitltr
x
D
p
S
IIPIUioa
IPrInp
e
Ik
01
blOt
CII
IrUd
paDiq
Oft
Oft
r
aa
frllJlt
or
AlIPfaaoa
mbaIlpcd
llllproperobtriftJ
II
I
ma
P
l
f
Il
i
I
II
I
m
JtE
lIED1D
I
Inn
te
Ind
balln
t
ra
b
Inject
lIItln
nl
C
Lubnclte
4
Check
1
rifla
tOll
t
ry
e
djUlt
QOlTectly
I
djuttrelll
defe
t
pIrtI
Ti
ht
n
r
pllCe
joints
h
t
ilDtor
renc
bannp
i
Ttchtentoco
cttorqu
j
Tiaht
n
correct
torque
t
fiahten
con
ttO
lIe
I
Tiahtcn
correct
torque
m
Jlepl
c
om
putl
II
aepl
c
ith
nC
Ballonce
h
p
Rene
prinp
q
laJan
bnltct
r
lI
eaJian
Ull
Ielllllion
drio
Page 131 of 171

REAR
AXLE
AND
REAR
SUSPENSION
Rear
wheel
bearing
nut
Brake
backplate
25
33
kgm
181
239
IbJt
7
3
7
kgm
19
5
26
8
lb
ft
1400
1600
Shock
absorber
upper
mounting
3
kgm
l6
61b
ft
Shock
absorber
lower
mounting
3
kgm
16
6
Ih
ft
1800cc
Shock
absorber
mountings
1
6
2
2
kgm
12
161b
ft
Drive
shaft
to
differential
nuts
5
6
kgm
36
2
4341b
ft
Drive
shaft
to
rear
axle
flange
5
6
kgm
36
2
43
4lb
ft
Bump
rubber
nuts
2
8
4
0
kgm
20
29
Ib
ft
Bump
rubber
nuts
180Occ
1
6
2
2
kgm
12
16
Ib
ft
Wheel
nuts
Rear
suspension
member
mounting
nuts
8
9
kgm
58
651b
ft
10
kgm
72
Ib
ft
Differential
member
mounting
nuts
8
5
kgm
61
5Ib
ft
Suspension
arm
to
suspension
member
nuts
10
kgm
58
72
Ib
ft
Differential
to
differential
member
6
8
kgm
43
581b
fl
Propeller
shaft
flange
nuts
4
0
8
5
kgm
29
62
Ib
ft
Propeller
shaft
flange
nuts
I
800cc
2
0
2
7
kgm
14
201b
fl
Differential
to
suspension
member
6
8
kgm
43
58Ib
ft
1800cc
Estate
car
and
Van
610
Body
Shock
absorber
upper
mounting
0
9
1
2
kgm
6
5
8
7Ih
fl
Shock
absorber
lower
mounting
3
5
4
5
kgm
25
33Ib
ft
Rear
spring
U
bolt
clip
6
0
6
5
kgm
43
47
Ib
ft
Shackle
spring
6
0
6
5
kgm
43
47Ib
ft
Spring
front
pin
6
0
6
5
kgm
43
47Ib
ft
Brake
back
plate
Estate
car
Van
Differential
gear
carrier
to
axle
case
Propeller
shaft
flange
Bump
rubber
Wheel
nut
Drain
and
filler
plug
2
2
2
7
kgm
16
20IbJt
L5
2
0
kgm
II
14
Ib
ft
2
0
2
5
kgm
14
18Ib
ft
2
0
2
7kgm
14
20Ib
ft
0
9
1
2
kgm
6
5
8
7Ib
ft
9
kgm
58
65Ib
ft
4
2
6
9
kgm
30
4
49
9
lb
ft
FRONT
SUSPENSION
Front
hub
nut
3
0
3
5
kgm
21
7
25
3
Ib
ft
Disc
brake
backplate
to
strut
2
7
3
7
kgm
19
5
26
7
Ib
ft
Brake
ca1liper
bolts
7
3
9
9
kgm
52
8
71
6
Ib
ft
Brake
disc
bolts
3
9
5
3
kgm
28
381b
ft
Stabilizer
bolts
suspension
arm
side
1
2
I
7kgm
8
7
12
3
Ib
ft
130
Tension
rod
to
frame
Tension
rod
to
transverse
link
Strut
assembly
upper
nuts
Steering
lever
to
strut
Ball
joint
to
transverse
link
Ball
joint
to
knuckle
ann
Piston
rod
nut
Gland
packing
1400
and
1600
CC
models
Flange
mounting
bolts
Bali
stud
nut
Gear
ann
nut
Idler
ann
nut
Adjusting
screw
nut
Steering
gear
mounting
bolts
Idler
arm
bolts
1800cc
models
610
Body
Gear
ann
nut
Rear
cover
bolts
Sector
shaft
cover
Sector
shaft
adjusting
screw
locknut
Steering
gear
mounting
bolts
Steering
linkage
Idler
arm
to
frame
Ball
stud
nuts
Side
rod
locknuts
Column
shaft
Steering
wheel
nut
Column
clamp
COll
piing
worm
shaft
Coupling
mounting
bolts
Brake
pedal
pivot
Brake
pipe
connection
Brake
disc
bolts
Bridge
pipe
Brake
hose
to
cylinder
Brake
calliper
bolts
Wheel
cylinder
bolts
Stud
side
Hexagon
side
4
5
5
5
kgm
33
40Ib
ft
4
9
6
3
kgm
35
4
45
6
Ib
ft
3
9
5
2
kgm
28
2
37
6
Ib
fr
6
8
kgm
43
581b
ft
1
9
5
kgm
14
18Ib
fL
5
5
7
6
kgm
40
55Ib
ft
6
7
5
kgm
43
54Ib
ft
7
13
kgm
51
94Ib
ft
STEERING
1
8
2
5
kgm
13
18Ib
ft
5
5
7
6
kgm
40
55Ib
ft
12
5
14
0
kgm
90
101
lb
ft
5
5
7
6
kgm
40
55Ib
ft
1
8
2
5
kgm
13
18Ib
ft
10
kgm
72
Ib
ft
4
4
6
1
kgm
32
44Ib
ft
14
kgm
lOllb
ft
L5
2
5
kgm
II
18Ib
ft
1
5
2
5
kgm
II
18Ib
ft
2
0
2
5
kgm
14
5
18Ib
ft
6
8
kgm
43
4
57
8Ib
ft
4
4
6
1
kgm
32
44Ib
ft
5
5
7
6
kgm
40
55Ib
ft
4
4
6
1
kgm
32
44lb
ft
4
5
kgm
29
36
Ib
ft
1
3
1
8
kgm
9
4
13
0
lb
ft
4
5
kgm
29
36Ib
ft
L5
2
2
kgm
II
16Ib
ft
BRAKES
3
5
4
0
kgm
25
3
28
9
Ib
ft
1
5
1
8
kgm
10
8
13
0
lb
ft
3
9
5
3
kgm
28
2
38
3
IbJt
1
7
2
0
kgm
12
3
14
51b
fl
1
7
2
0
kgm
12
3
14
5lb
ft
7
3
9
0
kgm
52
8
65
llb
ft
0
5
0
7
kgm
3
6
5
llb
ft
1
4
1
8
kgm
10
13
Ib
ft
Page 153 of 171
inter
M
j
@W
J
1
i
I
r
p
@
2
1
Strut
mounting
inzulDtor
Thruu
b
aring
J
Coil
prins
4
rubber
j
Sl1ut
mbly
6
Compression
rod
Z
Bal
joint
8
T
1ink
9
Stabi
iur
10
ODS
rnt
r
i
L
St
Ting
wheel
2
Steering
column
maft
J
Rubb
rCOfl
linK
4
Sturing
lower
joint
5
St
rinuotlr
IwusUr8
6
Sid
rod
XlI
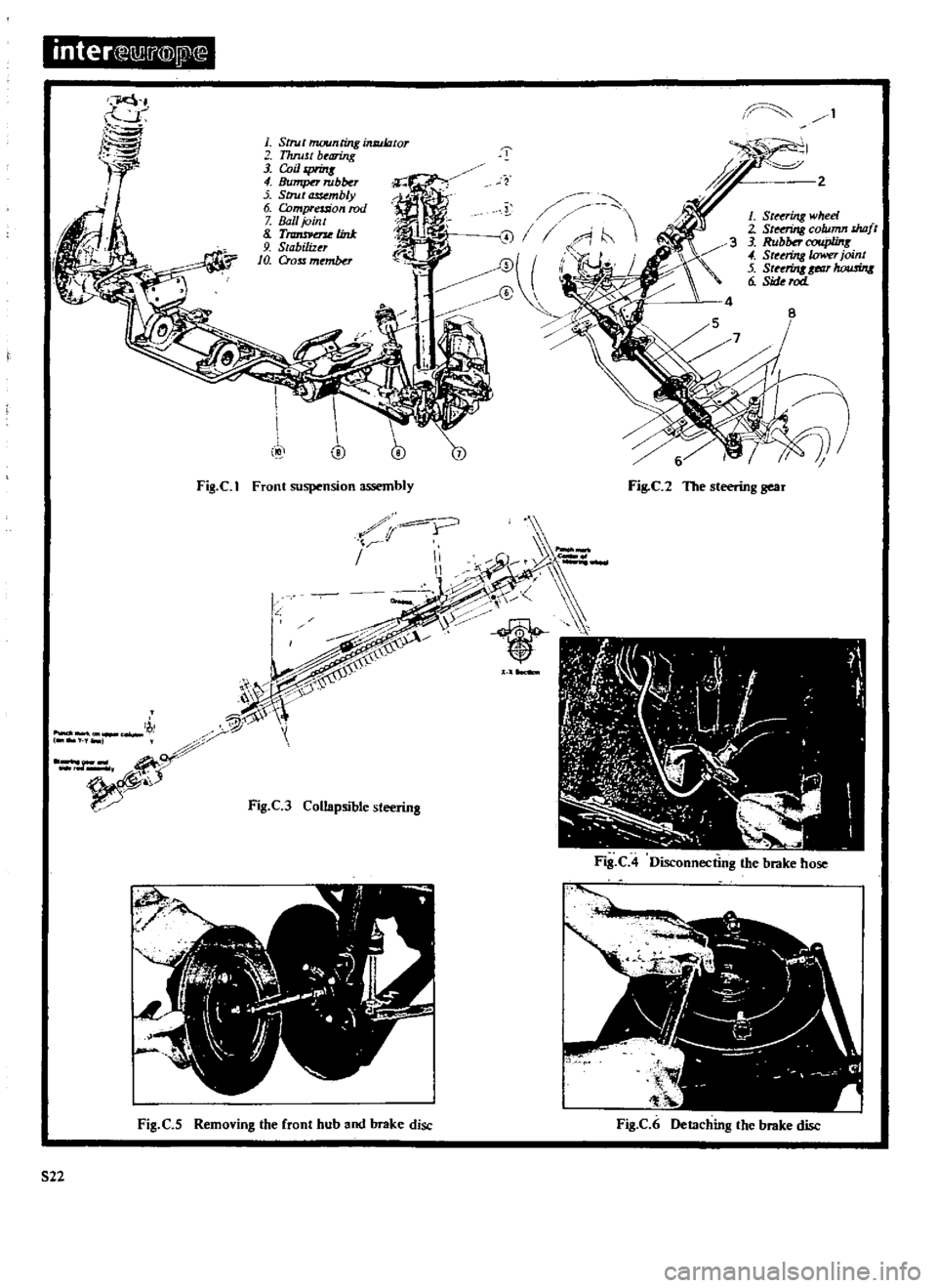
Fig
C
1
Front
suspension
assembly
Fig
C
2
The
steering
gear
iQ
r
y
y
v
I
Ii
1
1
Fig
C
3
Collapsible
steering
Fig
C
4
Disconnecting
the
brake
hose
I
f41
I
I
t
h
I
t
t
Il
t
k
I
Fig
C
5
Removing
the
front
hub
and
brake
disc
Fig
C
6
Detaching
the
brake
disc
522
Page 154 of 171

Accelerator
pump
Piston
diameter
Pump
discharge
Outer
hole
position
Middle
hole
position
Inner
hole
position
Pump
nozzle
diameter
Main
nozzle
diameter
Primary
Secondary
14
0
mm
0
551
in
0
2
cc
per
stroke
0
4
cc
per
stroke
0
6
cc
per
stroke
0
5
mm
0
020
in
2
3
mm
0
0906
in
2
8
mm
0
110
in
Throttle
valve
fully
closed
angle
Primary
10
degrees
Secondary
20
degrees
Idling
opening
5
degrees
approx
Choke
valve
fully
closed
angle
10
degrees
Throttle
opening
at
full
choke
13
5
degrees
FUEL
PUMP
Type
Delivery
Electric
1400
cc
in
one
minute
Emission
control
system
Air
pump
bracket
to
cylinder
head
nut
Adjusting
bar
to
bracket
bolt
Air
pump
to
bracket
bolt
Air
pump
to
adjusting
bar
nut
Anti
backfrre
bracket
to
rocker
cover
0
4Q
0
65
kgm
2
94
7
lb
ft
Anti
backfire
valve
to
bracket
0
4Q
O
65
kgm
2
94
7
lb
ft
Sensing
hose
clamp
to
rocker
cover
0
4Q
0
65
kgm
2
M
7
Ib
ft
Air
gallery
to
exhaust
manifold
plug
5
Q
6
0
kgm
36
243
4lb
ft
Check
valve
to
air
gallery
9
0
10
5
kgm
65
1
75
9Ib
ft
1
6
2
4
kgm
I
1
6
17
4Ib
ft
1
6
2
4
kgm
I
1
6
17
4Ib
ft
1
6
2
4
kgm
I
1
6
17
4
lb
ft
1
6
2
4
kgm
11
6
17
4Ib
ft
Front
SuspensIon
SteerIng
Description
Steering
Maintenance
Wheel
hub
and
bearing
Stabilizer
Spring
and
strut
assembly
Transverse
link
and
lower
ball
joint
Suspension
member
Front
wheel
alignment
Steering
wheel
and
column
Rack
and
pinion
and
tie
rod
Collapsible
steering
DESCRIPTION
The
front
suspension
is
of
the
strut
type
with
the
coil
spring
and
hydraulic
damper
units
mounted
on
the
crossmember
and
transverse
link
assembly
See
Fig
C
I
Vertical
movement
of
the
suspension
is
controlled
by
the
strut
assembly
Forward
and
rearward
movement
is
absorbed
by
compression
rods
6
and
side
movement
controlled
by
the
transverse
links
Front
suspension
servicing
procedures
are
similar
to
those
given
for
vehicle
fitted
with
L14
Ll6
and
LIB
engines
and
can
be
carried
out
by
reference
to
the
instructions
given
in
the
appropriate
section
Camber
and
castor
angles
are
preset
and
cannot
be
adjusted
and
a
check
must
be
made
for
signs
of
damage
to
the
suspension
system
if
the
angles
do
not
confonn
to
the
figures
given
in
Technical
Data
The
steering
is
of
the
direct
acting
rack
and
pinion
type
See
Fig
C
2
A
rubber
coupling
which
absorbs
vibration
and
two
universal
join
ts
are
incorpora
ted
between
the
steering
wheel
and
gear
assembly
The
collapsible
type
of
steering
column
assembly
Fig
C3
is
an
optional
fitting
A
full
description
of
this
type
of
assembly
i
given
in
the
Steering
section
for
L14
L16
and
L18
engines
STEERING
Maintenance
The
steering
system
should
be
lubricated
every
two
years
or
50
000
km
30
000
miles
whichever
comes
fIrst
A
lithium
base
multipurpose
grease
must
be
used
for
the
rack
and
pinion
and
rack
and
tie
rod
joints
The
plug
on
the
steering
gear
housing
should
be
removed
and
a
grease
nipple
fitted
so
that
the
recommended
quantity
of
10
to
15
gram
0
35
to
0
53
oz
of
grease
can
be
injected
Remove
the
grease
nipple
and
replace
the
plug
when
lubrication
is
completed
The
grease
reservoir
on
the
tube
side
should
be
replenished
when
the
level
of
grease
falls
to
approximately
one
third
ofits
capacity
WHEEL
HUB
AND
BEARING
Removal
and
Installation
Wheel
hub
and
bearing
servicing
procedures
are
similar
to
those
previously
given
for
vehicles
fitted
with
L14
LI6
and
LIB
engines
S23
Page 156 of 171

Remove
the
road
wheel
and
disconnect
the
brake
hose
at
the
connector
as
shown
in
Fig
C
4
of
this
section
Remove
the
brake
calliper
assembly
and
hub
cap
Withdraw
the
cotter
pin
and
remove
the
wheel
bearing
locknut
Remove
the
wheel
bearing
washer
and
take
off
the
hub
and
brake
disc
Fig
C
5
Remove
the
bearing
collar
take
out
the
outer
bearing
cage
and
prise
out
the
hub
grease
seal
Remove
the
inner
bearing
cage
and
drive
out
the
outer
races
of
the
inner
and
outer
bearings
using
the
special
drift
ST49120000
if
avail
able
Separate
the
brake
disc
from
the
hub
by
taking
out
the
retaining
bolts
as
shown
in
Fig
C
6
Installation
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
procedure
Adjust
the
wheel
bearings
as
previously
described
taking
care
to
tighten
the
wheel
bearing
locknut
to
the
specified
torque
read
ing
of
3
0
to
3
5
kgm
21
7
to
25
3lb
ft
Turn
the
hub
several
times
to
settle
the
bearing
then
retighten
the
nut
to
the
same
figure
Slacken
the
locknut
by
a
quarter
turn
900
and
insert
the
cotter
pin
when
the
hole
in
the
spindle
is
aligned
with
the
hole
in
the
nut
Check
that
the
force
required
to
turn
the
hub
is
less
than
7
0
kg
cm
97
2
in
oz
STABILIZER
Removal
and
Installation
Remove
the
splash
board
and
take
off
the
bolts
I
in
Fig
C
7
which
attach
the
stabilizer
at
the
transverse
link
sides
Remove
the
bolts
attaching
the
stabilizer
bracket
2
to
the
frame
then
withdraw
the
stabilizer
Check
the
bar
and
rubber
components
for
signs
of
deforma
tion
or
damage
and
renew
as
necessary
Installation
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
procedures
Tighten
the
fixing
bolts
to
a
torque
reading
of
1
2
to
I
7
kgm
8
7
to
12
3
lb
ft
at
the
transverse
link
side
and
1
9
to
2
5
kgm
13
7
to
18
llb
ft
at
the
frame
bracket
SPRING
AND
STRUT
ASSEMBLY
The
spring
and
strut
assembly
can
be
serviced
by
following
the
instructions
previously
given
for
the
assemblies
on
vehicles
fitted
with
the
L14
L16
and
Ll8engines
When
reassembling
make
sure
that
the
parts
shown
in
Fig
C
8
are
thomughly
greased
Installation
of
the
assembly
will
be
accomplished
more
easily
if
the
dust
cover
on
the
bonnet
ledge
is
removed
Tighten
the
nuts
and
bolts
to
a
torque
figures
given
in
TIGHTENING
TORQUES
TRANSVERSE
LINK
AND
LOWER
BALL
JOINT
The
transverse
link
and
lower
ball
joint
can
be
removed
in
a
similar
manner
to
the
parts
on
vehicles
fitted
with
L
14
L
16
and
L
18
engines
Renew
the
link
if
cracked
or
damaged
in
any
way
Check
the
measurement
A
in
Fig
C
9
The
measurement
between
front
and
rear
transverse
link
bushes
should
be
less
than
1
0
mm
0
039
in
Replace
the
bushes
if
necessary
The
lower
ball
joint
should
be
replaced
if
the
axial
play
of
the
joint
exceeds
0
03
to
0
6
mm
0
0012
to
0
0136
in
A
grease
nipple
must
be
installed
in
place
of
the
ball
joint
plug
so
that
the
joint
can
be
lubricated
with
multi
purpose
grease
as
previously
described
SUSPENSION
MEMBER
Removing
and
Installing
Jack
up
the
vehicle
and
support
it
on
stands
2
Remove
the
splash
board
Refer
to
Fig
C
I
0
and
detach
the
compression
rod
I
the
stabilizer
2
from
the
trans
verse
link
3
Detach
the
steering
linkage
from
the
suspen
sion
crossmember
4
3
Take
out
the
nuts
attaching
the
transverse
links
and
remove
the
links
at
both
sides
of
the
vehicle
4
Support
the
engine
with
a
hoist
as
shown
in
Fig
C
II
taking
care
not
to
damage
the
throttle
and
remote
control
linkages
and
then
remove
the
engine
mounting
bolts
at
both
sides
5
Remove
the
bolts
shown
arrowed
in
Fig
C
12
and
lift
the
suspension
member
away
Renew
the
suspension
member
if
it
is
cracked
or
deformed
in
any
way
Installation
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
procedure
FRONT
WHEEL
ALIGNMENT
As
previously
stated
the
castor
and
camber
angles
are
preset
and
cannot
be
adjusted
A
thorough
check
should
be
made
of
the
steering
and
suspension
system
and
all
defective
parts
renewed
if
the
angles
are
incorrect
See
Technical
Data
The
front
wheels
should
toe
in
12
to
15
mm
0
4
7
to
0
59
in
Adjustment
can
be
carried
out
by
slackening
the
locknuts
1
in
Fig
C
13
and
then
turning
the
tie
rods
by
an
equal
amount
until
the
correct
toe
in
is
achieved
A
toe
in
gauge
will
of
course
be
required
for
this
operation
STEERING
WHEEL
AND
COLUMN
Removal
Disconnect
the
horn
wire
and
remove
the
horn
bar
Remove
the
steering
wheel
nut
and
pull
off
the
steering
wheel
2
Remove
the
turn
signal
and
lighting
switch
assembly
followed
by
the
steering
column
shell
covers
3
Remove
the
bolts
from
the
rubber
coupling
to
disconnect
the
lower
joint
See
Figs
C
14
and
C
I
5
if
the
car
is
fitted
with
right
hand
drive
The
lower
joint
upper
bolt
should
be
removed
to
disconnect
the
joint
if
the
car
is
fitted
with
left
hand
drive
4
Remove
the
cotter
pin
from
the
trunnion
and
disconnect
the
gearchange
rod
and
selector
rod
5
Remove
the
steering
column
upper
clamp
and
take
out
the
bolts
securing
the
lower
plate
STEERING
COLUMN
Dismantling
and
Assembling
Remove
the
C
washer
socket
screw
and
upper
bracket
bolt
Remove
the
lower
bracket
bolts
and
detach
the
remote
control
linkage
from
the
column
assembly
Remove
the
snap
ring
at
the
top
of
the
column
and
extract
the
column
shaft
from
the
jacket
Disconnect
the
rubber
coupling
from
the
lower
joint
then
remove
the
snap
ring
and
dismantle
the
lower
joint
S25
Page 158 of 171

Gean
all
parts
thoroughly
and
renew
if
damaged
If
the
column
shaft
or
jacket
is
excessively
damaged
the
steering
gear
housing
must
be
checked
A
damaged
bearing
must
be
replaced
together
with
the
column
jacket
assembly
Assembly
is
a
reversal
of
the
dismantling
procedures
The
column
shaft
journal
should
be
lubricated
with
multipurpose
grease
which
can
also
be
used
to
fill
up
the
dust
cover
Grease
the
needle
bearing
when
assembling
the
universal
joint
Use
the
tightest
snap
ring
available
when
fitting
the
needle
bearing
Snap
rings
are
supplied
in
oversizes
of
0
95
mm
05
mm
and
1
5
mm
0
0374
0
0413
and
0
0453
in
Installation
of
the
column
assembly
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
procedures
Tighten
the
rubber
coupling
bolts
to
a
torque
reading
of
I
S
to
1
8
kgm
I
0
8
to
13
0
Ib
ft
Refit
the
steering
wheel
and
tighten
the
nut
to
a
reading
of
4
0
to
5
0
kgm
28
9
to
36
2Ib
ft
RACK
AND
PINION
AND
TIE
ROD
Removing
and
Dismantling
1
Jack
up
the
vehicle
and
support
it
on
stands
Remove
the
road
wheels
2
Slacken
the
bolts
connecting
the
pinion
to
the
steering
lower
joint
See
Figs
C
16
3
Remove
the
bolts
from
the
steering
column
rubber
coupl
ing
See
Fig
C
15
and
remove
the
splash
board
Fig
C
17
4
Remove
the
tie
rod
ball
stud
nut
and
disconnect
the
tie
rod
from
the
knuckle
arm
Fig
C
I8
5
Lift
the
engine
slightly
with
suitable
tackle
but
take
care
not
to
damage
the
accelerator
or
remote
control
linkage
Remove
the
bolts
securing
the
steering
gear
housing
to
the
suspension
member
Withdraw
the
rack
and
pinion
assem
bly
Dismantle
as
follows
Detach
the
steering
lower
joint
from
the
rack
and
pinion
assembly
Clamp
the
unit
in
a
vice
taking
care
not
to
damage
the
steering
gear
housing
Refer
to
Fig
C
16
and
take
off
the
dust
cover
and
boot
clamps
at
both
sides
Slacken
the
stopper
nut
remove
the
tie
rod
inner
socket
and
disconnect
the
tie
rods
from
the
rack
Withdraw
the
spring
seat
and
tie
rod
spring
Take
off
the
steering
gear
boots
at
both
sides
Slacken
the
locknut
and
disconnect
the
tie
rod
outer
socket
from
the
ball
Slacken
the
locknut
remove
the
retainer
adjusting
screw
and
withdraw
the
steering
gear
retainer
See
Fig
C
19
Take
off
the
oil
seal
remove
the
snap
ring
and
withdraw
the
pinion
Remove
the
snap
ring
and
withdraw
the
bearing
from
the
pinion
Remove
the
filler
plug
and
take
out
the
rack
Remove
the
grease
reservoir
Clcan
all
parts
thoroughly
and
replace
any
which
show
signs
of
wear
or
damage
Check
the
axial
play
of
the
inner
and
outer
ball
joints
The
play
should
be
0
06
mm
0
0024
in
for
the
inner
ball
joint
and
from
0
1
to
0
5
mm
0
0039
to
0
0197
in
for
the
outer
joints
Use
a
spring
balance
to
check
the
force
required
to
swing
the
ball
joints
this
should
be
between
0
8
to
LS
kgm
5
8
to
10
8Ib
ft
Renew
the
oil
seal
Examine
the
retainer
and
tie
rod
springs
and
compare
them
with
the
values
given
in
Figs
C
20
and
c
n
RACK
AND
PINION
AND
TIE
ROD
Assembling
and
Adjusting
Press
the
bearing
on
to
the
pinion
gear
and
fi
t
the
tigh
test
snap
ring
available
Snap
rings
are
supplied
in
the
following
over
sizes
Snap
Ring
Thicknesses
1
04
to
1
09
mm
0
0409
to
0
0429
in
1
09
to
I
14
mm
0
0429
to
0
0449
in
1
14toI19mm
0
0449toO
0469in
Ll9
to
1
24
mm
0
0469
to
0
0488
in
1
24
to
1
29
mm
0
0488
to
0
0502
in
Clamp
the
steering
gear
housing
in
a
vice
Grease
the
teeth
and
friction
surfaces
of
the
rack
with
multipurpose
grease
Lubricate
the
gear
housing
from
the
pinion
housing
side
Ensure
that
the
rack
projects
by
an
equal
amount
of
96
mm
3
8
in
in
both
ends
of
the
housing
with
the
rack
teeth
directed
towards
the
pinion
shaft
Grease
the
pinion
teeth
end
bushing
and
pinion
bearing
Engage
the
tccth
of
the
pinion
with
the
rack
and
insert
the
pinion
Make
sure
that
the
bushing
does
not
become
damaged
The
rack
must
project
from
the
housing
by
an
equal
amount
at
each
side
with
the
groove
on
the
pinion
serration
facing
upwards
Fit
the
snap
ring
into
the
housing
groove
to
hold
the
bearing
outer
race
in
position
The
snap
ring
must
fit
tightly
and
can
be
selected
from
the
following
oversizes
Snap
Ring
Thicknesses
LS5
to
1
60
mm
0
0610
to
0
0630
in
1
60
to
1
65
mm
0
0630
to
0
0650
in
1
65
to
I
70
mm
0
0650
to
0
0669
in
1
70
to
I
75
mm
0
0669
to
0
0689
in
Fit
the
oil
seal
Use
a
dial
gauge
as
shown
in
Fig
C
22
to
check
the
thrust
play
of
the
pinion
The
play
should
be
less
than
0
09mm
0
0035
in
Grease
the
retainer
and
insert
it
with
the
spring
Tighten
the
retainer
adjusting
screw
fully
then
back
it
off
by
20
to
25
degrees
Tighten
the
locknut
to
a
torque
reading
of
4
0
to
6
0
kgm
28
9
to
43
4lb
ft
Coat
the
locknut
with
liquid
pack
ing
Three
Bond
When
the
rack
and
pinion
is
assembled
measure
the
force
required
to
rotate
the
pinion
and
also
the
preload
of
the
rack
Use
a
spring
balance
as
shown
in
Figs
C
23
and
C
24
and
check
that
the
pinion
torque
is
8
to
20
kg
cm
7
to
17
Ib
in
and
the
rack
preload
is
from
8
to
18
kg
17
6
to
39
7Ibs
Take
care
to
slide
the
assembly
over
the
complete
range
of
the
stroke
Fit
a
dust
cover
clamp
at
each
end
of
the
housing
Install
the
stop
nut
on
the
threads
of
the
rack
Liberally
grease
the
ball
joint
friction
area
of
the
tie
rod
assembly
Assemble
the
spring
and
ball
seat
and
fit
the
inner
socket
part
of
the
tie
rod
assembly
to
the
rack
Make
sure
the
boot
is
positioned
at
the
ball
stud
end
Note
that
the
left
hand
tie
rod
is
marked
with
an
L
the
right
hand
rod
is
not
marked
527