service DATSUN B110 1973 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1973, Model line: B110, Model: DATSUN B110 1973Pages: 513, PDF Size: 28.74 MB
Page 440 of 513

ENGINE
Stator
core
EE044
Fig
EE
41
Testing
stator
for
ground
Inspection
of
diode
Perform
a
conduction
test
on
diodes
in
both
directions
using
an
ohmmeter
A
total
of
six
diodes
are
used
three
are
mounted
on
the
positive
EB
plate
and
other
three
are
on
the
negative
3
plate
The
conduction
test
should
be
performed
on
each
diode
between
the
terminal
and
plate
The
diode
installed
on
the
G
l
plate
is
a
positive
diode
which
allows
current
flowing
from
the
terminal
to
G
l
plate
only
In
other
words
current
does
not
flow
from
the
G
l
plate
to
the
terminal
EE046
Fig
EE
42
Inspecting
positive
diode
The
diode
installed
on
the
8
plate
is
a
negative
diode
which
allows
current
flowing
from
the
8
plate
to
the
terminal
only
In
other
words
current
does
not
flow
from
the
terminal
t08
plate
EE
20
8
Plate
EE047
Fig
EE
43
Inspecting
negative
diode
If
current
flows
in
both
positive
and
negative
diree
tions
the
diode
is
short
circuited
If
current
does
not
flow
in
any
direction
the
diode
is
open
These
diodes
are
unserviceable
If
there
is
a
defective
diode
replace
all
diodes
six
diodes
as
an
assembly
See
the
Figure
EE44
I
Test
probe
of
a
circuit
tester
I
8
E8
I
terminal
E8
plate
I
@
plate
terminal
I
terminal
8
plate
18
plate
te
rminal
18
plate
@
plate
18
plate
8
plate
Conduction
x
x
x
Fig
EE
44
lnspection
of
diodes
Inspection
of
brush
Check
the
movement
of
brush
and
if
the
movement
is
unsmooth
check
brush
holder
and
deJn
it
If
th
bmsh
is
worn
and
the
length
is
7
mm
0
2756
in
or
less
replace
the
brush
with
a
new
one
Check
the
brush
pig
tail
and
if
it
is
about
to
break
replace
Page 442 of 513
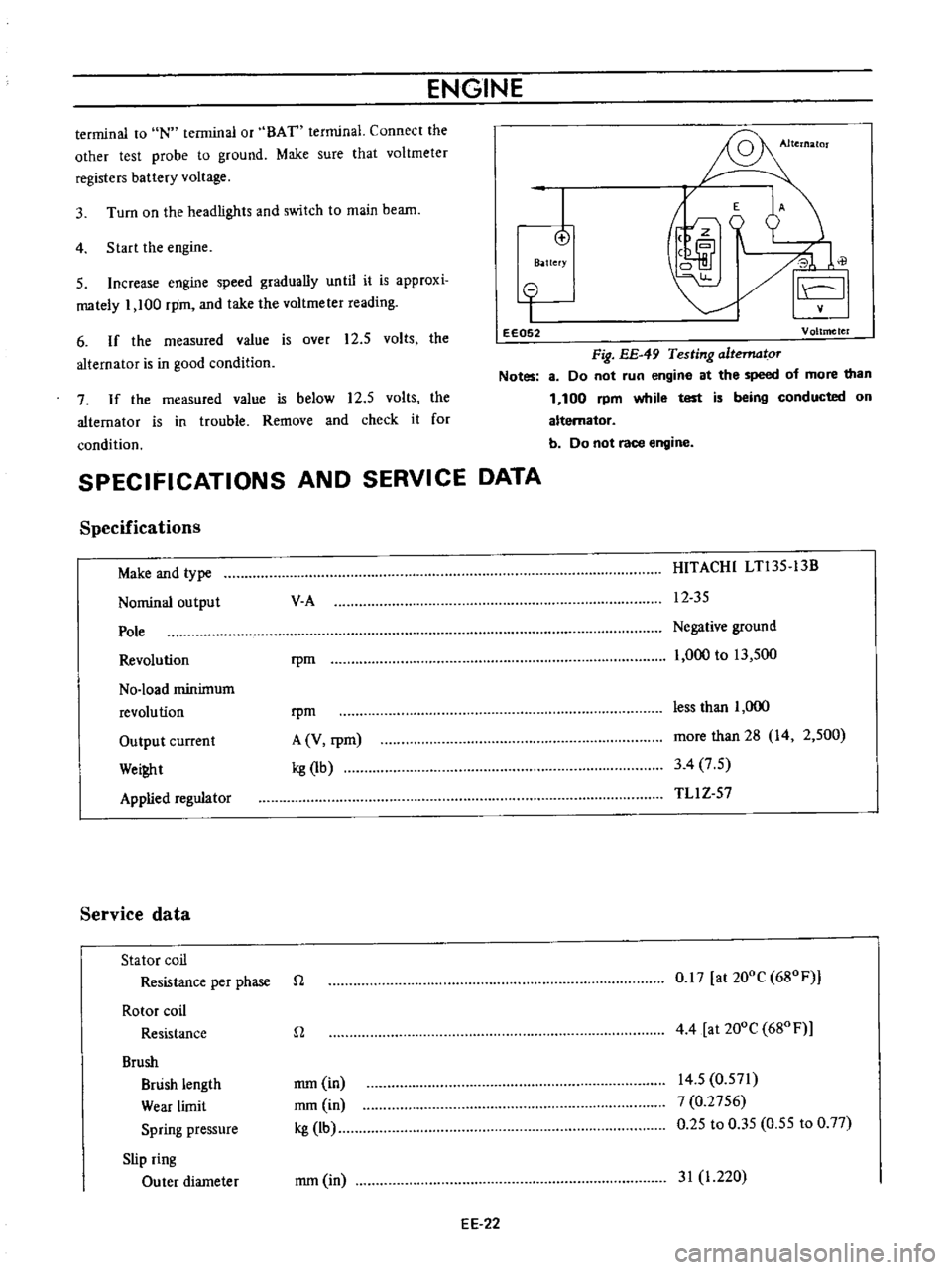
ENGINE
terminal
to
IN
terminal
or
BAT
terminal
Connect
the
other
test
probe
to
ground
Make
sure
that
voltmeter
registers
battery
voltage
4
Start
the
engine
3
Turn
on
the
headlights
and
switch
to
main
beam
I
o
B
ttefY
E
A
J
0
il
I
5
Increase
engine
speed
gradually
until
it
is
approxi
mately
1
100
rpm
and
take
the
voltmeter
reading
6
If
the
measured
value
is
over
12
5
volts
the
alternator
is
in
good
condition
o
I
eE052
Voltmeter
Fig
EE
49
Testing
altematoT
Notes
8
Do
not
run
engine
at
the
speed
of
more
than
1
100
rpm
while
test
is
being
conducted
on
alternator
b
Do
not
race
engine
7
If
the
measured
value
is
below
12
5
volts
the
alternator
is
in
trouble
Remove
and
check
it
for
condition
SPECIFICATIONS
AND
SERVICE
DATA
Specifications
Make
and
type
Nominal
output
Pole
Revolution
No
load
minimum
revolution
Output
current
Wei
t
Applied
regulator
Service
data
Stator
coil
Resistance
per
phase
Rotor
coil
Resistance
Brush
Brush
length
Wear
limit
Spring
pressure
Slip
ring
Outer
diameter
V
A
HITACHI
LTl35
13B
12
35
rpm
Negative
ground
1
000
to
13
500
rpm
A
V
rpm
kg
1b
less
than
1
000
more
than
28
14
2
500
3
4
7
5
TLl
Z
57
n
0
17
at
200C
680F
n
4
4
at
200e
680
F
mm
in
mm
in
kg
lb
14
5
0
571
7
0
2756
0
25
to
0
35
0
55
to
0
77
mm
in
31
1
220
EE
22
Page 443 of 513
Charge
relay
SPECIFICATIONS
AND
SERVICE
DATA
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
Reduction
limit
Repair
limit
Repair
accuracy
mm
in
mm
in
mm
in
REGULATOR
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTiON
MEASUREMENT
OF
REGULATING
VOLTAGE
ADJUSTMENT
Voltage
regu
lator
EE
23
EE
24
EE
25
EE
25
DESCRIPTION
I
0
0394
0
3
0
0118
0
05
0
0197
EE
26
EE
26
EE
27
1
I
T
r
@
V
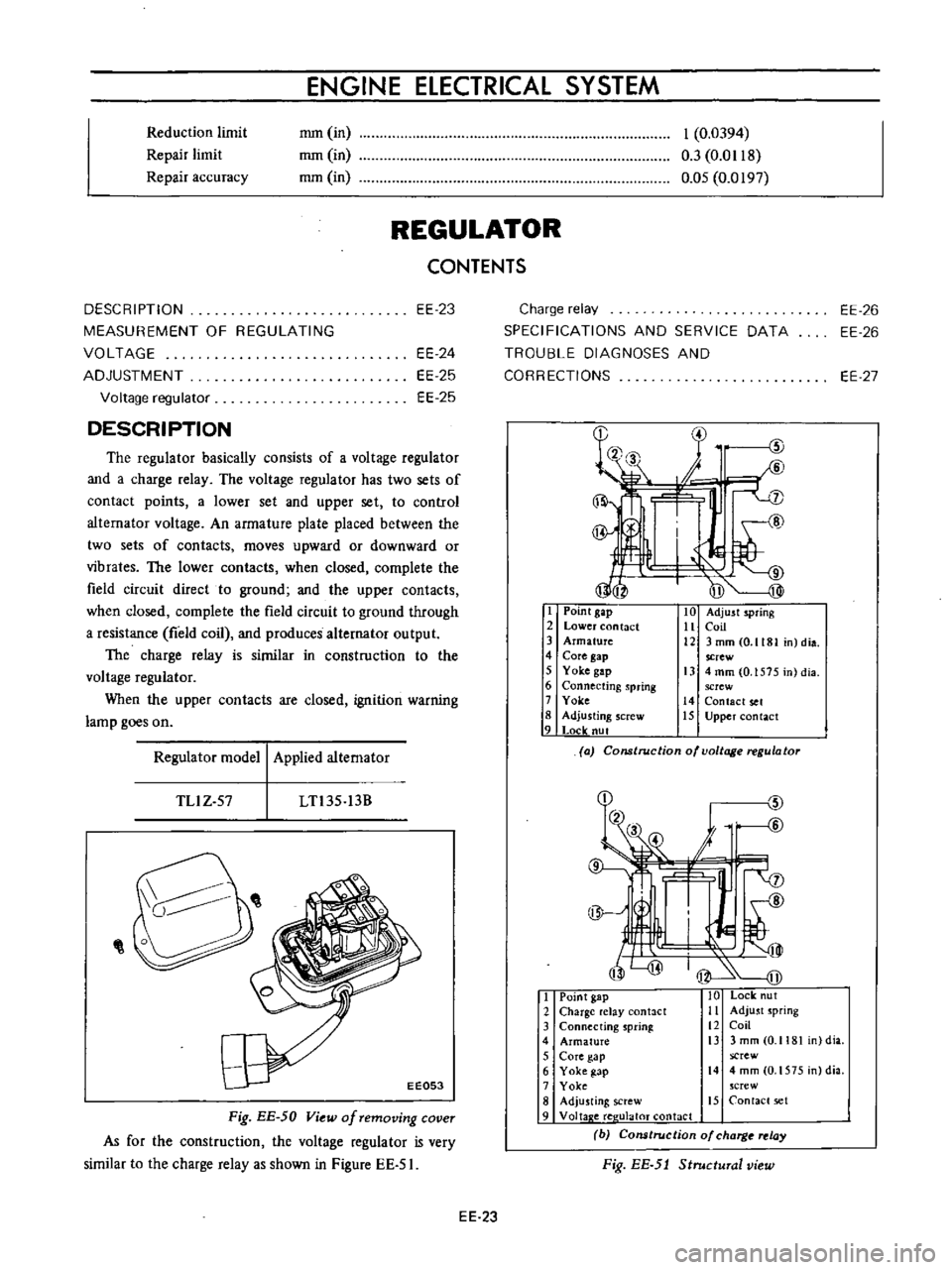
The
regulator
basically
consists
of
a
voltage
regulator
and
a
charge
relay
The
voltage
regulator
has
two
sets
of
contact
points
a
lower
set
and
upper
set
to
control
altemator
voltage
An
armature
plate
placed
between
the
two
sets
of
contacts
moves
upward
or
downward
or
vibrates
The
lower
contacts
when
closed
complete
the
field
circuit
direct
to
ground
and
the
upper
contacts
when
closed
complete
the
field
circuit
to
ground
through
a
resistance
field
coil
and
produces
alternator
output
The
charge
relay
is
similar
in
construction
to
the
voltage
regulator
When
the
upper
contacts
are
closed
ignition
warning
lamp
goes
on
I
Point
gap
2
Lower
contact
3
Armature
4
Core
gap
5
Yoke
gap
6
Connecting
spring
7
Yoke
8
Adjusting
screw
9
Locle
nut
10
Adjust
spring
11
Coil
12
3mmCO
1181
n
dia
screw
13
4
mm
0
1575
in
dia
screw
14
Contact
set
15
Upper
contact
Regulator
model
Applied
alternator
a
Construction
of
voltage
regulator
TLlZ
57
LTl35
13B
I
Point
gap
10
Lock
ut
2
Charge
elay
antact
Ii
Adjust
spring
3
Connecting
sprinl
12
Coil
4
Armature
i3
3
mm
0
1181
dia
5
Core
gap
screw
6
Yoke
gap
14
4mm
O
1575
n
dia
7
Yoke
crew
8
Adju
ting
screw
15
Contact
set
9
Voltap
e
ree
ulaloT
contact
b
Cons
rue
ion
of
charg
relay
Fig
EE
5J
Structural
view
Fig
EE
50
View
of
removing
cover
As
for
the
construction
the
voltage
regulator
is
very
similar
to
the
charge
relay
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
51
EE
23
Page 446 of 513
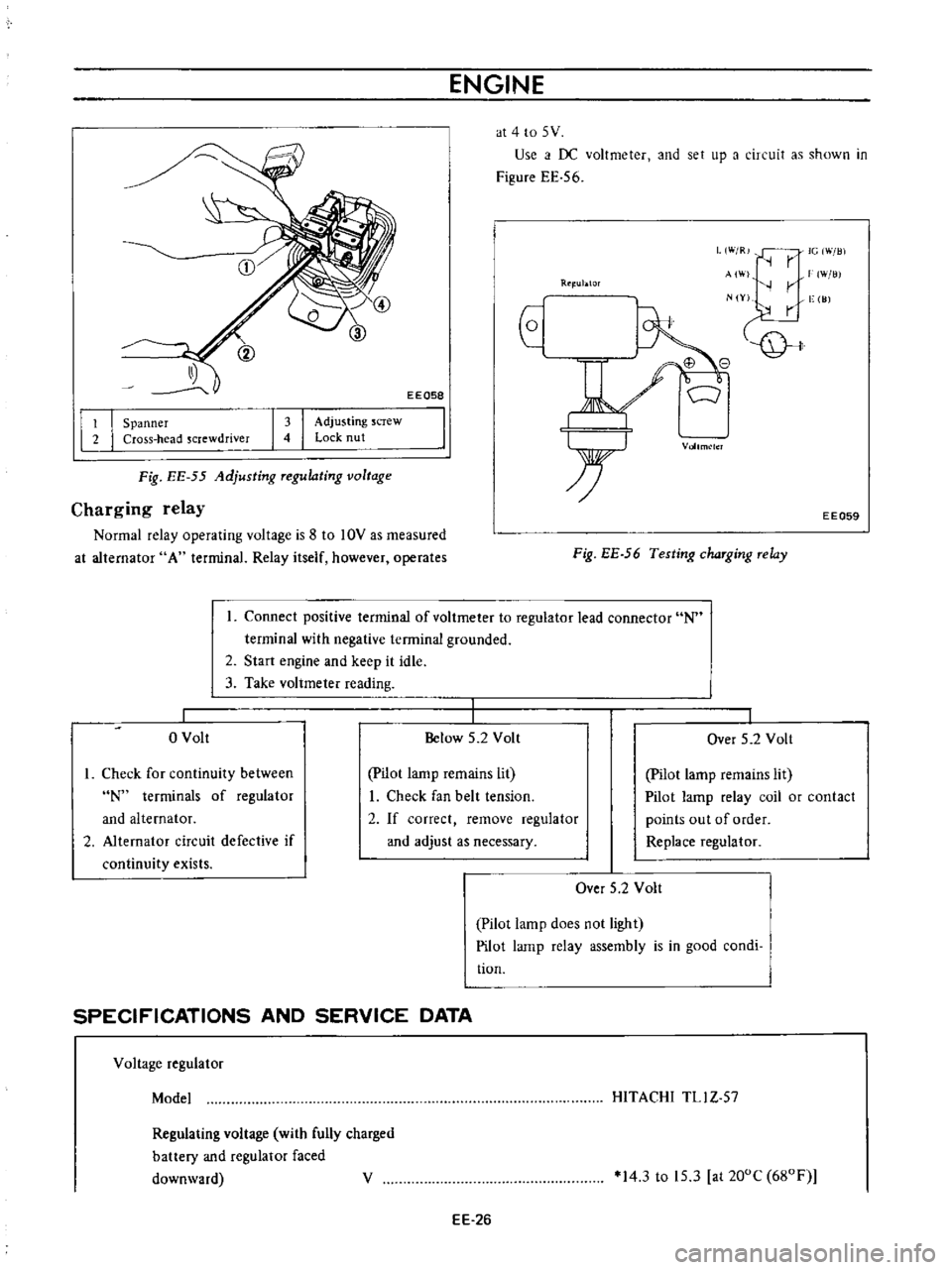
ENGINE
at
4
to
5
V
Use
i
f
DC
voltmeter
and
set
up
a
circuit
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
56
EEQ58
L
W
R
IG
Will
r
AI
W
lli
r
N
Y
vge
I
JJ
Rtl
ublOr
I
I
Spanner
Cross
head
screwdriver
I
I
Adjusting
screw
Lock
nut
Vollm
lcl
Fig
EE
55
Adjusting
Tegulating
voltage
Charging
relay
Normal
relay
operating
voltage
is
8
to
10V
as
measured
at
alternator
A
terminal
Relay
itself
however
operates
EE059
Fig
EE
56
Testing
chaTging
Telay
Connect
positive
terminal
of
voltmeter
to
regulator
lead
connector
N
terminal
with
negative
terminal
grounded
2
Start
engine
and
keep
it
idle
3
Take
voltmeter
reading
o
Volt
Below
5
2
Volt
I
Over
5
2
Volt
I
Check
for
continuity
between
N
terminals
of
regulator
and
alternator
2
Alternator
circuit
defective
if
continuity
exists
pilot
lamp
remains
lit
I
Check
fan
belt
tension
2
If
correct
remove
regulator
and
adjust
as
necessary
Pilot
lamp
remains
lit
Pilot
lamp
relay
coil
or
contact
points
out
of
order
Replace
regulator
Over
5
2
Volt
Pilot
lamp
does
not
light
Pilot
lamp
relay
assembly
is
in
good
condi
tion
SPECIFICATIONS
AND
SERVICE
DATA
Voltage
regulator
Model
HITACHI
TLl
Z
57
Regulating
voltage
with
fully
charged
battery
and
regulator
faced
downward
V
14
3
to
15
3
at
200C
680F
EE
26
Page 449 of 513
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
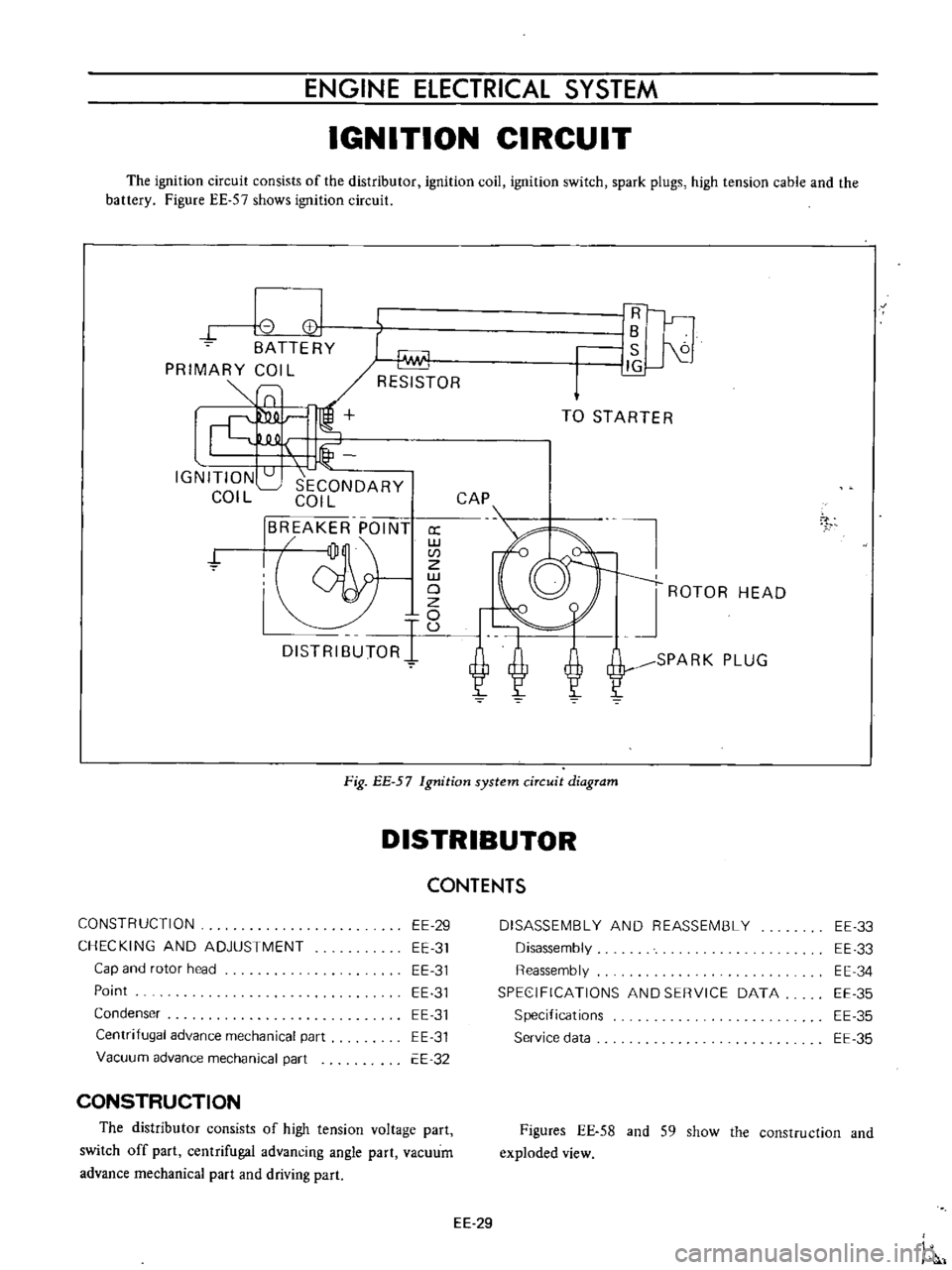
IGNITION
CIRCUIT
The
ignition
circuit
consists
of
the
distributor
ignition
coil
ignition
switch
spark
plugs
high
tension
cable
and
the
battery
Figure
EE
57
shows
ignition
circuit
8
I
CC
BATTERY
PRIMARY
COIL
SlO
Lf
IGNITION
SECONDARY
COIL
COIL
BREAKER
POINT
jJ
a
w
CI
Z
w
19
DISTRIBUTORI
U
1Fl
r
lB
S
J1G
TO
STARTER
CAP
ROTOR
HEAD
SPARK
PLUG
7
Fig
EE
57
Ignition
system
circuit
diagram
DISTRIBUTOR
CONSTRUCTION
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTMENT
Cap
and
rotor
head
Point
Condenser
Centrifugal
advance
mechanical
part
Vacuum
advance
mechanical
part
EE
29
EE
31
EE
31
EE
31
EE
31
EE
31
EE
32
CONSTRUCTION
The
distributor
consists
of
high
tension
voltage
part
switch
off
part
centrifugal
advancing
angle
part
vacuum
advance
mechanical
part
and
driving
part
CONTENTS
DISASSEMBLY
AND
REASSEMBLY
Disassembly
Reassembly
SPEC
IFICATIONS
AND
SERVICE
DATA
Specifications
Service
data
EE
33
EE
33
EE
34
EE
35
EE
35
EE
35
Figures
EE
58
and
S9
show
the
construction
and
exploded
view
EE
29
Page 455 of 513

ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
SPECIFICATIONS
AND
SERVICE
DATA
Specifications
Make
and
type
0412
80
0412
89
for
Manual
for
Automatic
Transmission
Transmission
Firing
order
1
3
4
2
I
3
4
2
Rotating
direction
Counterclockwise
Counterclockwise
Dwell
angle
49
550
49
550
Condenser
capacity
J
lF
0
20
to
0
24
0
20
to
0
24
Service
data
Point
gap
mm
in
0
45
to
0
55
0
0177
to
0
0217
0
50
to
0
65
1
1
to
1
4
Point
pressure
kg
lb
Condenser
capacity
p
F
Micro
Farad
0
20
to
0
24
Condenser
isolate
resistance
M
1
Mega
Ohms
5
Cap
carbon
point
mm
in
rom
in
Housing
inner
diameter
mm
in
12
0
472
0
010
D
0004
12
45
0
020
0
4902
D
0008
12
45
018
0
4902
0007
Shaft
diameter
lower
part
Clearance
between
shaft
and
housing
mm
in
Amendment
limit
of
clearance
mm
in
0
010
to
0
Q38
0
0004
to
0
0015
0
08
0
0031
8
0
005
0
3150
0
0002
D
O
14
D
0006
8
O
15
0
3150
0006
0
005
to
0
029
0
0002
to
0
00
II
Shaft
diameter
upper
part
mm
in
earn
inner
diameter
rom
in
Clearance
between
shaft
and
cam
mm
in
EE
35
Page 457 of 513
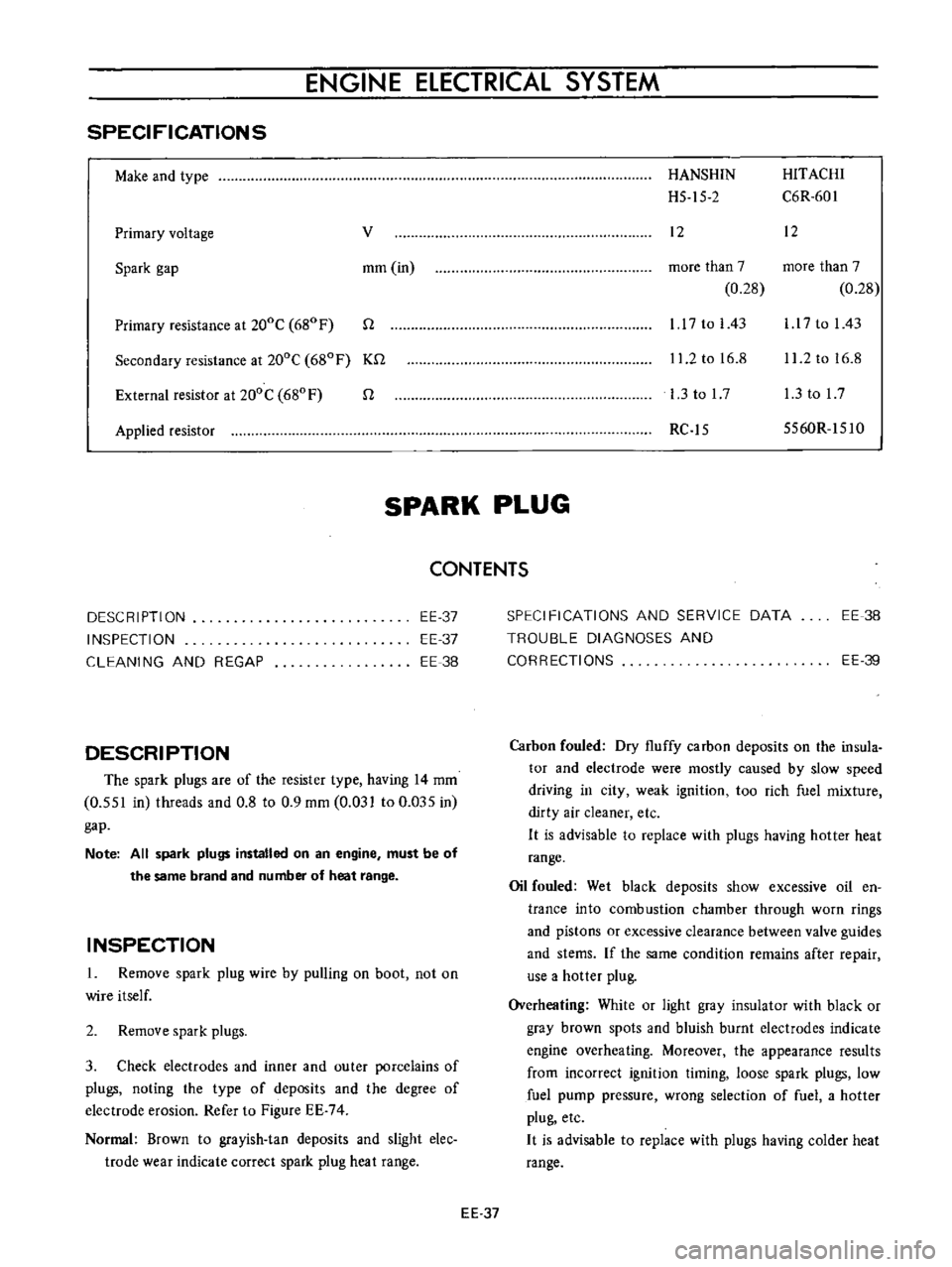
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
SPECIFICATIONS
Make
and
type
Primary
voltage
v
Spark
gap
mm
in
Primary
resistance
at
200C
680
F
n
Secondary
resistance
at
200C
680F
Kn
External
resistor
at
200C
680
F
n
Applied
resistor
HANSHIN
HITACHI
H5
15
2
C6R
601
12
12
more
than
7
more
than
7
0
28
0
28
1
17
to
I
43
l
l
7
to
I
43
11
2
to
16
8
11
2
to
16
8
l
3tol7
l
3tol7
RC
15
5560R
151O
SPARK
PLUG
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION
INSPECTION
CLEANING
AND
REGAP
EE
37
EE
37
EE
38
DESCRIPTION
The
spark
plugs
are
of
the
resister
type
having
14
mm
0
551
in
threads
and
0
8
to
0
9
mm
0
031
to
0
Q35
in
gap
Note
All
spark
plugs
installed
on
an
engine
must
be
of
the
same
brand
and
number
of
heat
range
INSPECTION
1
Remove
spark
plug
wire
by
pulling
on
boot
not
on
wire
itself
2
Remove
spark
plugs
3
Check
electrodes
and
inner
and
outer
porcelains
of
plugs
noting
the
type
of
deposits
and
the
degree
of
electrode
erosion
Refer
to
Figure
EE
74
Normal
Brown
to
grayish
tan
deposits
and
slight
elec
trode
wear
indicate
correct
spark
plug
heat
range
SPECIFICATIONS
AND
SERVICE
DATA
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
EE
38
EE
39
Carbon
fouled
Dry
fluffy
carbon
deposits
on
the
insula
tor
and
electrode
were
mostly
caused
by
slow
speed
driving
in
city
weak
ignition
too
rich
fuel
mixture
dirty
air
cleaner
etc
H
is
advisable
to
replace
with
plugs
having
hotter
heat
range
Oil
fouled
Wet
black
deposits
show
excessive
oil
en
trance
into
combustion
chamber
through
worn
rings
and
pistons
or
excessive
clearance
between
valve
guides
and
stems
If
the
same
condition
remains
after
repair
use
a
hotter
plug
Overheating
White
or
light
gray
insulator
with
black
or
gray
brown
spots
and
bluish
burnt
electrodes
indicate
engine
overheating
Moreover
the
appearance
results
from
incorrect
ignition
timing
loose
spark
plugs
low
fuel
pump
pressure
wrong
selection
of
fuel
a
hotter
plug
etc
H
is
advisable
to
replace
with
plugs
having
colder
heat
range
EE
37
Page 458 of 513

ENGINE
Overheating
Normal
Carbon
fould
Fig
EE
74
SpaTk
plug
Life
4
After
cleaning
dress
electrodes
with
a
small
fine
fIle
to
flatten
the
surfaces
of
both
center
and
side
electrodes
in
parallel
Set
spark
plug
gap
to
specification
5
Install
spark
plugs
and
torque
each
plug
to
1
5
to
2
0
kg
m
ll
to
15
ft
lb
6
Connect
spark
plug
wires
CLEANING
AND
REGAP
Clean
spark
plugs
in
a
sand
blast
type
cleaner
Avoid
excessive
blasting
Clean
and
remove
carbon
or
oxide
deposits
but
do
not
wear
away
porcelain
If
deposits
are
too
stubborn
discard
plugs
Mter
cleaning
spark
plugs
renew
firing
surface
of
electrodes
with
me
mentioned
above
Then
gap
spark
plugs
to
0
8
to
0
9
mm
0
030
to
0
035
in
using
a
round
SPECIFICATIONS
AND
SERVICE
DATA
Make
Model
Size
Screw
dia
x
Reach
mm
in
Plug
gap
mm
in
Tightening
torque
kg
m
ft
b
EE
38
wire
feeler
gauge
All
spark
plugs
new
or
used
should
have
the
gap
checked
and
reset
by
bending
ground
electrode
Fig
EE
75
Setting
spaTk
plug
gap
NGK
HITACHI
BP5ES
1A6PW
14
x
19
0
55
x
0
75
0
8
to
0
9
0
031
to
0
035
1
5
to
2
5
11
0
to
15
0
Page 461 of 513
DATE
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
SERVICE
JOURNAL
OR
BUl
LETIN
REFE
RENCE
JOURNAL
or
BULLETIN
No
PAGE
No
SUBJECT
EE
41
Page 469 of 513

15
Lift
up
the
engine
toward
the
front
INSTALLATION
Install
the
engine
in
reverse
sequence
of
removal
CHASSIS
Fig
ER
14
Lifting
up
engine
SERVICE
JOURNAL
OR
BULLETIN
REFERENCE
DATE
JOURNAL
or
BULLETIN
No
PAGE
No
ER
6
SUBJECT