wheel bolt torque DATSUN PICK-UP 1977 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1977, Model line: PICK-UP, Model: DATSUN PICK-UP 1977Pages: 537, PDF Size: 35.48 MB
Page 372 of 537

RA148
Fig
RA
16
Remvoing
spring
pin
6
Remove
rubber
bush
in
spring
if
necessary
and
install
new
bush
Coat
rubber
hush
with
a
soapy
solution
prior
to
assembly
InstaH
rear
spring
in
the
reverse
order
of
removal
noting
the
following
poinc
Vehicle
weight
must
be
on
rear
wheels
when
tightening
front
pin
shackle
and
shock
absorber
lower
end
nut
in
order
to
clamp
rubber
bush
in
a
neutral
or
unloaded
position
Tightening
torque
Spring
fTont
pin
nut
11
5
to
13
0
kg
m
83
to
94
ft
Ib
Spring
shackle
nut
11
5
to
13
0
kg
m
83
t094
ft
b
U
bolt
7
3
to
9
9
kg
m
S3
to
72
ft
lb
Shock
absorber
lower
end
nut
1
6
to
2
2
kg
m
12
to
16
ft
lb
Rear
Axle
Rear
Suspension
SHOCK
ABSORBER
Raise
rear
of
vehicle
and
support
under
axle
case
on
stands
It
is
recom
mended
that
a
hydraulic
hoist
or
open
pit
be
utilized
if
available
2
Disconnect
lower
end
of
shock
absorber
by
removing
nuts
Q
at
spring
seat
3
Disconnect
upper
end
of
shock
absorber
by
removing
nut
2
at
frame
RA146
Fig
RA
J
7
Removing
shock
absorber
Installation
of
shock
absorber
in
the
reverse
order
of
removal
Note
Vehicle
weight
must
be
on
Tear
wheels
when
tigtrtening
shock
ab
sorber
upper
and
lower
ends
in
order
to
clamp
rubber
bushings
in
a
neutral
or
unloaded
position
INSPECTION
REAR
AXLE
SHAFT
AND
WHEEL
BEARING
Inspect
the
following
parts
for
faults
and
replace
as
required
RA
6
I
Check
axle
shaft
for
straightness
cracks
damage
wear
and
distortion
2
Check
the
lip
of
oil
seal
for
damage
deformation
and
wear
3
Check
bearing
for
wear
and
damage
REAR
AXLE
CASE
Check
axle
case
for
yield
deforma
tion
cracks
or
oil
leakage
and
replace
if
necessary
REAR
SPRING
Clean
all
rust
and
dirt
from
spring
leaves
using
a
wire
brush
if
necessary
1
Examine
spring
leaves
for
frae
tures
or
cracks
2
Check
front
bracket
and
pin
shackle
U
bolts
and
spring
seat
for
wear
cracks
straightness
and
damaged
threads
If
faulty
parts
are
found
replace
with
new
ones
3
Inspect
all
rubber
parts
for
wear
damage
separation
and
deformation
Replace
them
if
necessary
SHOCK
ABSORBER
I
Test
shock
absorber
and
compare
with
the
specifications
given
in
Service
Data
and
Specifications
Replace
if
necessary
2
Check
for
oil
leakage
and
cracks
Also
check
shaft
for
straightness
3
Inspect
rubber
bushings
for
dam
age
cracl
s
and
deformation
Replace
parts
if
necessary
Page 374 of 537
Rear
Axle
Rear
Suspension
Spring
front
pin
Spring
shackle
Bearing
cage
fIXing
bolt
Wheel
bearing
lock
nut
Air
breather
Differential
gear
carrier
to
axle
case
nut
Propeller
shaft
flange
bolt
Drain
and
filler
plug
Bumper
rubber
fixing
bolt
Wheel
nut
kg
m
ft
lb
kg
m
ft
Ib
kg
en
ft
lb
kg
m
ft
Ib
kg
m
ft
Ib
kg
m
ft
Ib
kg
en
ft
Ib
kg
m
ft
Ib
kg
m
ft
Ib
kg
m
ft
lb
11
5
to
13
0
83
to
94
11
5
to
13
0
83
to
94
S
4
to
6
4
39
to
46
IS
to
20
108
to
l4S
0
7
to
0
9
S
I
to
6
S
17
to
2
7
12
to
20
2
0
to
2
7
14
to
20
6
to
10
43
to
72
1
6
to
2
2
12
to
16
8
to
9
S8
to
6S
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
When
rear
axle
and
suspension
is
suspected
of
being
noisy
it
is
advisable
to
make
a
thorough
test
to
determine
whether
the
noise
originates
in
the
tires
road
surface
exhaust
propeller
shaft
engine
transmission
universal
joint
wheel
bearings
or
suspension
Noise
which
originates
in
other
places
can
not
be
corrected
by
adjust
ment
or
replacement
of
parts
in
the
rear
axle
and
rear
suspension
In
case
of
oil
leak
first
check
if
there
is
any
damage
or
restriction
in
breather
Condition
Probable
cause
Noise
Loose
wheel
nuts
Loose
one
or
more
securing
bolts
Lack
of
lubricating
oil
or
grease
Faulty
shock
absorber
Incorrect
adjustment
of
rear
axle
shaft
end
play
Damaged
or
worn
wheel
bearing
Worn
spline
portion
of
rear
axle
shaft
Broken
leaf
spring
Loose
journal
connections
or
so
no
Wheel
and
tire
unbalance
Damaged
rubber
parts
such
as
leaf
spring
bush
shock
absorber
moun
ting
bush
Faulty
universal
joints
Instability
in
driving
Loose
wheel
nuts
Worn
shock
absorber
Worn
or
broken
leaf
spring
Oil
leakage
Damaged
or
restricted
air
breather
Damaged
oil
seal
in
rear
axle
case
or
differ
ential
carrier
Oil
leakage
from
between
the
differential
carrier
and
axle
case
RA
8
Corrective
action
Tighten
the
wheel
nuts
Tighten
the
bolts
to
the
specified
torque
Lubricate
as
required
Replace
the
shock
absorber
Adjust
the
rear
axle
shaft
end
play
Replace
wheel
bearing
Replace
if
necessary
Replace
leaf
spring
Tighten
to
the
given
torque
Balance
wheel
and
tire
Replace
the
required
parts
Adjust
or
replace
Tighten
to
the
given
torque
Replace
faulty
shock
absorber
Replace
leaf
spring
Clean
or
replace
air
breather
Replace
the
damaged
oil
seal
Tighten
to
the
specified
torque
or
replace
gasket
Page 384 of 537
After
connecting
brake
tube
be
sure
to
check
the
clearance
to
prevent
from
damage
The
clearance
at
the
following
portions
must
be
specified
distance
or
more
Tube
to
body
panel
and
frame
Over
5
mm
0
20
in
Tube
to
edge
of
each
panel
Over
10
mm
0
39
in
Tube
to
tube
Loop
pitch
OVer
5
mm
0
20
in
Between
front
tube
and
rear
tube
Over
9
mOl
0
35
in
Tube
to
moving
parts
Over
10
mm
0
39
in
Loop
tube
to
hood
ledge
panel
Over
10
mm
0
39
in
Notes
a
Brake
tubes
are
shaped
at
factory
to
secure
specified
clearance
and
may
not
require
reshaping
Discard
if
they
call
for
excessive
reshaping
b
In
reshaping
a
brake
tube
take
care
to
avoid
damaging
galvanization
or
collapsing
section
Mter
brake
lines
have
been
asssem
bled
check
to
make
sure
that
all
fittings
and
flare
nu
Is
ale
lightened
to
correct
torques
Tightenint
torque
Brake
tube
to
connector
I
Ston
kg
m
II
to
13
ft
Ib
Brake
tube
to
brake
hose
1
7
to
2
0
kg
m
12
to
14
ft
lb
Connector
and
clip
fixing
bolt
O
3S
to
O
4S
kg
m
2
5
to
3
3
ft
lb
3
way
connector
fixing
bolt
on
rear
axle
case
0
8
to
1
1
kg
m
6
to
8
ft
lb
N
L
S
V
DESCRIPTION
The
Nissan
Load
Sensing
Valve
N
L
S
V
serves
to
change
braking
power
of
the
rear
wheels
in
response
to
changes
in
the
load
and
fluid
pressure
improving
braking
stability
and
shortening
stopping
distances
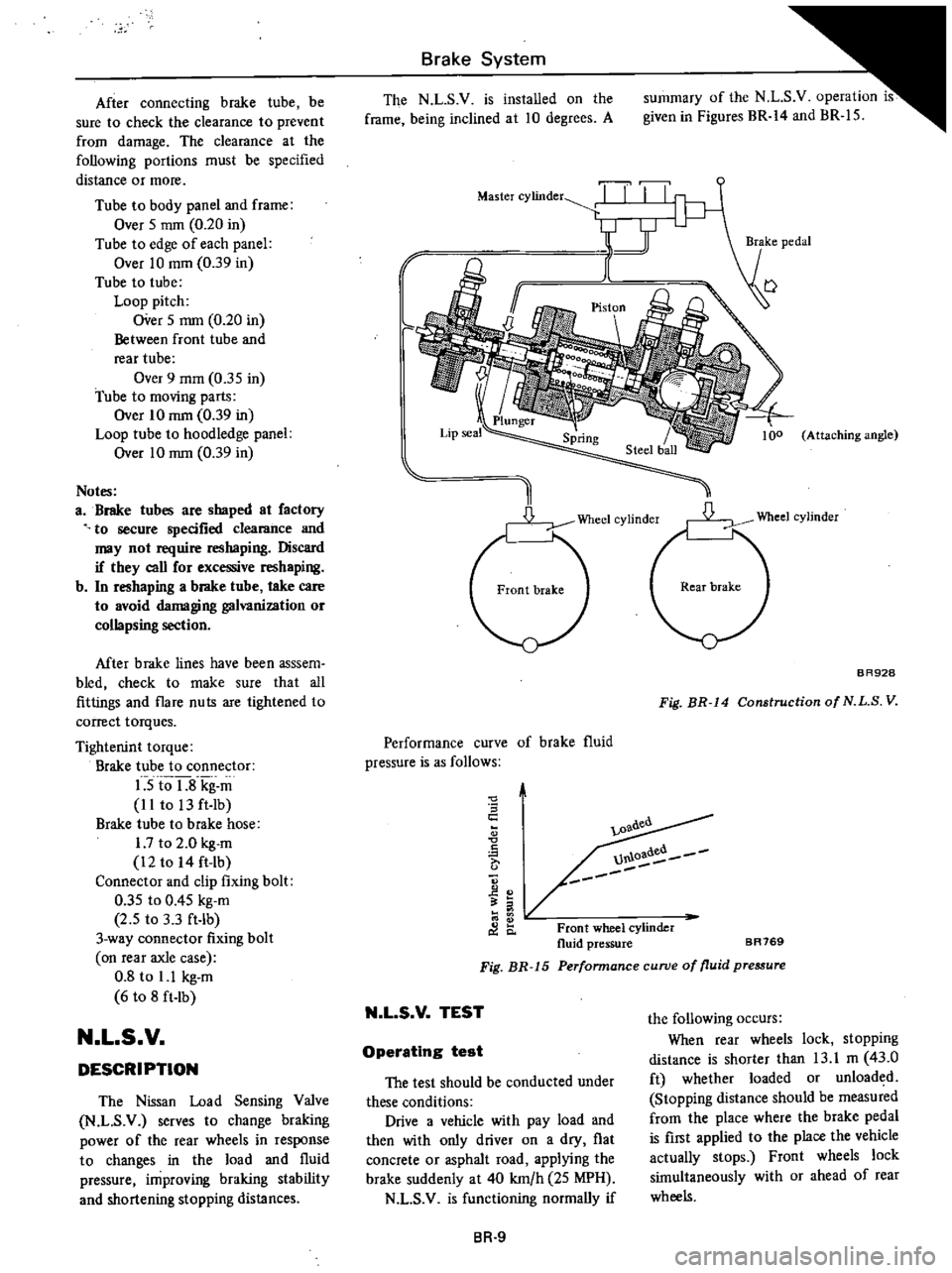
Brake
System
The
N
L
S
V
is
installed
on
the
frame
being
inclined
at
10
degrees
A
summary
of
the
N
L
S
v
operation
is
given
in
Figures
BR
14
and
BR
15
r
Master
cylinder
TI
II
I
y
1
J
I
l
Attaching
angle
D
Wheel
cylinder
BR928
Fig
BR
14
Construction
of
N
L
S
V
Performance
curve
of
brake
fluid
pressure
is
as
follows
0
S
c
A
0
C
o
l
0
oadea
U1U
Front
wheel
cylinder
fluid
pressure
BR769
Perfonnance
curve
of
fluid
pressure
Fig
BR
15
N
L
S
V
TEST
the
following
occurs
When
rear
wheels
lock
stopping
distance
is
shorter
than
13
1
m
43
0
ft
whether
loaded
or
unloaded
Stopping
distance
should
be
measured
from
the
place
where
the
brake
pedal
is
first
applied
to
the
place
the
vehicle
actually
stops
Front
wheels
lock
simultaneously
with
or
ahead
of
rear
wheels
Operating
test
The
test
should
be
conducted
under
these
conditions
Drive
a
vehicle
with
pay
load
and
then
with
only
driver
on
a
dry
flat
concrete
or
asphalt
road
applying
the
brake
suddenly
at
40
km
h
25
MPH
N
L
S
V
is
functioning
normally
if
BR
9
Page 386 of 537

2
The
allowable
maximum
out
of
round
of
brake
drum
is
0
02
mm
0
0008
in
Re
condition
or
replace
brake
drum
if
specified
limit
is
exceeded
3
Measure
for
tapered
brake
drum
If
specified
limit
of
0
02
mm
0
0008
in
is
exceeded
as
measured
at
a
position
where
the
distance
of
4S
mm
177
in
is
kept
away
from
inlet
re
condition
or
replace
brake
drum
4
Contact
surface
with
which
linings
come
into
contact
should
be
finished
to
such
an
extent
that
it
is
ground
by
a
No
120
to
150
sand
paper
S
Using
a
drum
racer
finish
brake
drum
by
machining
if
it
shows
any
sign
of
score
marks
partial
wear
or
stepped
wear
on
its
contact
surface
Note
After
brake
drum
is
completely
re
conditioned
or
renewed
check
drum
and
shoes
for
proper
contact
pattern
Brake
assembly
I
When
brake
shoe
linings
are
cracked
incompletely
seated
uneven
Iy
worn
andlor
deteriorated
due
to
excessive
heating
or
soiled
with
oil
grease
and
brake
fluid
replace
2
Replace
linings
if
the
thickness
is
worn
down
to
less
than
1
0
mm
0
039
in
Note
When
brake
shoe
lining
is
in
stalled
grind
brake
shoe
lining
face
to
diameter
equal
to
that
of
brake
drum
lining
dimension
Width
x
Thickness
x
Length
4S
x
4
S
x
244
mm
1
77
x
0
177
x
9
61
in
3
Check
adjuster
for
smooth
oper
ation
4
Replace
shoe
return
springs
which
are
broken
or
fatigued
Brake
System
Standard
dimensions
of
shoe
springs
Free
length
Dia
of
spring
No
of
Installed
Item
lengthlload
mOl
in
mOl
in
coils
mm
kg
in
lb
Upper
136
5
2
0
0
079
37
IS9
S
14
to
16
S
37
6
28
31
to
3S
Lower
134
S
2
3
0
091
35
IS9
5
21
to
23
5
30
6
28
46
to
Sl
After
shoe
83
2
1
4
O
OSS
27
S
99
4
to
S
3
28
3
90
9
to
II
Wheel
cylinder
I
Replace
any
cylinder
or
piston
which
is
scratched
scored
or
worn
on
its
sliding
contact
surface
2
Replace
worn
parts
if
piston
to
cylinder
clearance
is
beyond
O
IS
mm
0
OOS9
in
Wheel
cylinder
inner
diameter
19
0S
mOl
Y
in
3
Replace
piston
cup
which
is
worn
or
otherwise
damaged
4
Replace
if
contacting
face
of
cyl
inder
and
shoe
is
worn
locally
or
in
step
S
Replace
damaged
dust
cover
fatigued
piston
spring
or
faulty
threaded
parts
6
Replace
tube
connector
which
is
worn
on
its
threaded
portion
INSTALLATION
Install
front
brake
in
the
reverse
sequence
of
removal
paying
particular
attention
to
the
following
instructions
I
When
assembling
adjuster
assem
bly
apply
brake
grease
to
adjuster
housing
bore
adjuster
wheel
and
ad
juster
screw
When
installing
adjuster
assembly
to
brake
disc
apply
brake
grease
to
disc
adjuster
and
retaining
spring
slid
ing
surfaces
to
slide
adjuster
smoothly
Measure
adjuster
sliding
resistance
Adjust
by
adjuster
shim
when
sliding
resistance
is
in
rrect
BR
ll
Adjuster
sliding
resistance
S
to
12
kg
II
to
261b
2
When
installing
wheel
cylinder
be
sure
to
secure
the
cylinder
with
R
mark
to
right
hand
disc
and
the
one
with
L
mark
to
left
hand
disc
Otherwise
brake
hoses
may
interfere
with
other
adjacent
parts
As
to
the
connecting
instructions
of
brake
hose
no
twist
or
contact
is
existed
on
brake
hose
referring
the
related
topic
Brake
line
Tightening
torque
Wheel
cylinder
SA
to
6
6
kg
m
39
to
48
ft
lb
Connector
bolt
1
9
to
2
5
kg
m
14
to
18
ft
Ib
Brake
hose
1
7
to
2
0
kg
m
12
to
14
ft
lb
Air
bleeder
0
7
to
0
9
kg
m
5
to
7
ft
Ib
Brake
disc
4
2
to
S
O
kg
m
30
to
36
ft
lb
3
Before
installing
brake
shoe
as
semblies
apply
brake
grease
to
wheel
cylinder
and
adjuster
brake
shoe
in
stalling
grooves
and
brake
disc
and
brake
shoe
assembly
contact
faces
two
places
Exercise
care
not
to
allow
grease
to
come
into
contact
with
linings
and
adjuster
Page 389 of 537
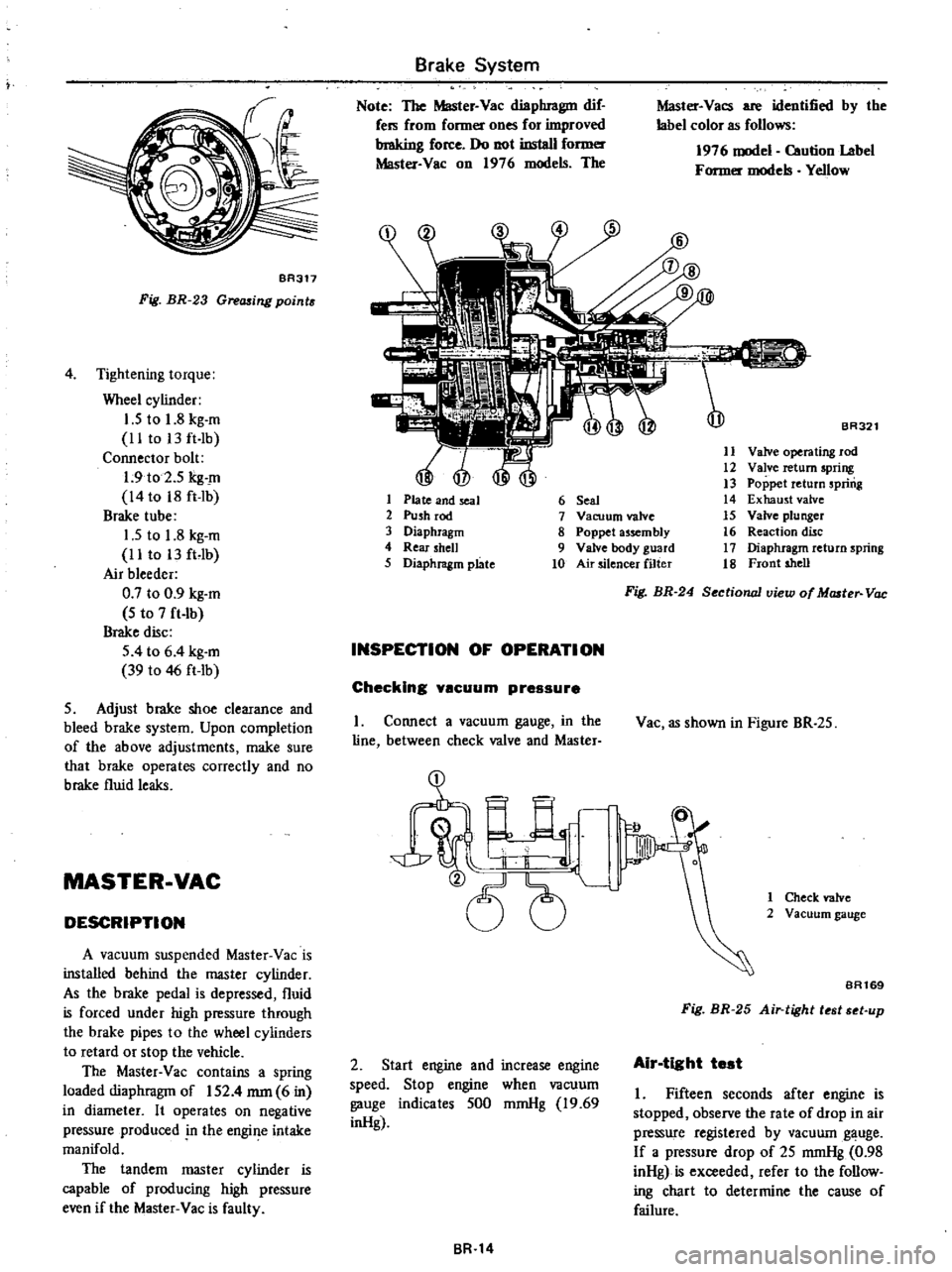
f
BR317
Fig
BR
23
Gre
ing
point
4
Tightening
torque
Wheel
cylinder
J
S
to
1
8
kg
m
II
to
13ft
Ib
Connector
bolt
1
9
to
2
5
kg
m
14
to
18
ft
Ib
Brake
tube
1
5
to
1
8
kg
m
II
to
13
ft
Ib
Air
bleeder
0
7
to
0
9
kg
m
S
to
7
ft
Ib
Brake
disc
5
4
to
6
4
kg
m
39
to
46
ft
Ib
S
Adjust
brake
shoe
clearance
and
bleed
brake
system
Upon
completion
of
the
above
adjustments
make
sure
that
brake
operates
correctly
and
no
brake
fluid
leaks
MASTER
VAC
DESCRIPTION
A
vacuum
suspended
Master
Vac
is
installed
behind
the
master
cylinder
As
the
brake
pedal
is
depressed
fluid
is
forced
under
high
pressure
through
the
brake
pipes
to
the
wheel
cylinders
to
retard
or
stop
the
vehicle
The
Master
Vac
contains
a
spring
loaded
diaphragm
of
IS2
4
mm
6
in
in
diameter
It
operates
on
negative
pressure
produced
n
the
engine
intake
manifold
The
tandem
master
cylinder
is
capable
of
producing
high
pressure
even
if
the
Master
Vac
is
faulty
Brake
System
Note
The
Master
Vac
diaphragm
dif
fers
from
fonner
ones
for
improved
braking
force
Do
not
install
fonner
Master
Vac
on
1976
models
The
1
Plate
and
seal
2
Push
rod
3
Diaphragm
4
Rear
shell
5
Diaphragm
plate
Master
Vacs
are
identified
by
the
label
color
as
follows
1976
model
Caution
Label
Former
models
YeJlow
BR321
11
Valve
operating
rod
12
Valve
return
spring
13
Poppet
return
spring
14
Exhaust
valve
15
Valve
plunger
16
Reaction
disc
17
Diaphragm
return
spring
18
Front
shell
6
Seal
7
Vacuum
valve
8
Poppet
assembly
9
Valve
body
guard
10
Air
silencer
filter
INSPECTION
OF
OPERATION
Checking
yscuum
pressure
I
Connect
a
vacuum
gauge
in
the
line
between
check
valve
and
Master
2
Start
engine
and
increase
engine
speed
Stop
engine
when
vacuum
gauge
indicates
SOO
mmHg
19
69
inHg
BR
14
Fig
BR
24
Sectionall1iew
of
Master
Vac
Vac
as
shown
in
Figure
BR
25
1
Check
valve
2
Vacuum
gauge
BA169
Fig
BR
25
Air
tight
t
t
t
up
Air
tight
test
I
Fifteen
seconds
after
engine
is
stopped
observe
the
rate
of
drop
in
air
pressure
registered
by
vacuum
gauge
If
a
pressure
drop
of
25
mmHg
0
98
inHg
is
exceeded
refer
to
the
follow
ing
chart
to
determine
the
cause
of
failure
Page 396 of 537

Brake
System
Tightening
torque
Master
cylinder
to
Master
Vac
kg
m
ft
Ib
0
8
to
l
l
6
to
8
Brake
tube
flare
nut
kg
m
ft
Ib
I
S
to
1
8
II
to
13
Brake
hose
connector
kg
m
ft
lb
1
8
to
2
1
13
to
IS
Air
bleeder
valve
kg
m
ft
lb
0
7
to
0
9
S
to
7
Fulcrum
pin
of
brake
pedal
kg
m
ft
Ib
1
2
to
1
5
9
to
II
Connector
and
clip
fIXing
bolt
kg
m
ft
lb
0
35
to
O
4S
2
5
to
3
3
3
way
connector
fIXing
bolt
kg
m
ft
Ib
0
8
to
l
l
6
to
8
on
rear
axle
case
Brake
pedal
stopper
lock
nut
kg
m
ft
Ib
1
2
to
1
5
9
to
II
N
L
S
V
to
body
kg
m
ft
Ib
0
8
to
l
l
6
to
8
Wheel
cylinder
mounting
nut
Front
kg
m
ft
Ib
S
4
to
6
6
39
to
48
Rear
kg
m
ft
Ib
1
5
to
1
8
II
to
13
Wheel
cylinder
connector
bolt
kg
m
ft
lb
1
9
to
2
5
14
to
18
Brake
disc
Back
plate
nut
Front
kg
m
ft
Ib
4
2
to
S
O
30
to
36
Rear
kg
m
ft
Ib
S
4
to
6
4
39
to
46
Master
Vac
Master
Vac
to
body
nut
kg
m
ft
lb
0
8
to
l
l
6
to
8
Flange
to
shell
cover
nut
kg
m
ft
lb
0
8
to
1
1
6
to
8
Operating
rod
lock
nut
kg
m
ft
Ib
1
6
to
2
2
12
to
16
Push
rod
adjusting
nut
kg
m
ft
Ib
1
9
to
2
4
14
to
17
BR
21
Page 398 of 537

Condition
Brake
chatters
Brake
squeals
Pedal
pulsates
Brakes
fade
Brakes
drag
Unbalanced
brakes
Brake
System
Probable
cause
Groove
or
out
of
round
brake
drum
Loose
or
bent
brake
disc
Distorted
brake
shoes
or
pads
Grease
or
brake
fluid
on
linings
Dirty
or
scored
brake
drums
Distorted
brake
shoes
or
bent
support
plate
Weak
or
broken
brake
shoe
retaining
spring
or
return
spring
Glazed
or
contaminated
brake
lining
Out
of
round
or
off
center
drum
Brake
fluid
has
too
low
boiling
point
Use
of
improper
linings
or
brake
linings
are
contaminated
Brake
drums
are
out
of
round
Hydraulic
connections
master
cylinder
and
wheel
cylinders
are
corroded
or
damaged
Bleed
screw
is
open
Pedal
linkage
is
binding
or
push
rod
adjust
ment
is
too
long
Master
cylinder
compensator
part
is
ob
structed
Seized
master
cylinder
piston
Poor
shoe
condition
Poor
wheel
cylinder
condition
Deformation
of
piston
cups
Hand
brake
will
not
return
Clogged
master
cylinder
return
port
Improper
tire
inflation
Improper
adjustment
of
shoe
to
drum
clear
anee
Grease
oil
mud
or
water
on
linings
or
pads
Mud
in
brake
drum
Deterioration
of
linings
or
pads
Excessive
wear
of
linings
or
pads
BR
23
Corrective
action
Grind
or
replace
as
required
Tighten
support
plate
bolts
to
specified
torque
or
replace
plate
Replace
as
necessary
Replace
linings
Blowout
assembly
with
compressed
air
or
refinish
drum
Replace
faulty
unit
Replace
if
faulty
Cam
ground
lining
to
eliminate
glaze
If
it
doesn
t
replace
linings
Turn
drum
or
replace
as
necessary
Drain
and
fill
system
with
approved
fluid
Replace
linings
Repair
or
replace
as
necessary
Repair
as
necessary
Close
screw
and
bleed
system
Lubricate
linkage
check
pedal
return
spring
for
condition
and
adjust
push
rod
as
neces
sary
Blowout
foreign
matter
with
compressed
air
Disassemble
master
cylinder
and
replace
piston
Bleed
system
Clean
and
repair
Repair
or
replace
Replace
Check
and
repair
Clean
Inflate
to
correct
pressure
Readjust
Clean
brake
mechanism
and
check
for
cause
of
problem
Replace
linings
or
pads
Clean
Replace
Replace
Page 409 of 537

ST202
Fig
ST
6
Withdrawing
gear
ann
Note
Before
removing
steering
gear
arm
scribe
match
marks
on
arm
and
housing
so
that
they
can
easily
be
replaced
in
their
original
posi
tions
at
assembly
9
Remove
three
bolts
securing
steering
gear
housing
to
frame
10
Withdraw
steering
gear
assembly
toward
engine
compartment
Installation
Install
steering
gear
assembly
in
the
reverse
order
of
removal
observing
the
following
instructions
I
When
installing
steering
gear
housing
securing
bolts
insert
two
bolts
through
gear
housing
to
frame
2
When
installing
steering
gear
arm
align
four
grooves
of
gear
arm
serra
tions
with
four
projections
of
sector
shaft
serrations
3
Tightening
torque
Steering
gear
housing
4
6
to
S
3
kg
m
33
to
38
ft
lb
Gear
arm
13
to
IS
kg
m
94
to
108
ft
lb
Steering
wheel
7
0
to
7
S
kg
m
51
to
54
ft
Ib
4
With
front
wheels
set
in
a
straight
ahead
position
make
sure
that
punch
mark
on
the
upper
end
surface
of
steering
column
shaft
is
at
the
center
of
the
upper
side
in
its
installing
portion
S
When
installing
steering
wheel
apply
grease
to
sliding
parts
6
After
installing
make
sure
that
steering
wheel
turns
smoothly
STEERING
SYSTEM
Disassembly
and
assembly
Disassembly
I
Drain
oil
in
steering
gear
housing
by
unscrewing
fIller
plug
2
Place
steering
gear
assembly
in
a
vise
securely
3
Loosen
lock
nut
and
turn
sector
shaft
adjusting
screw
a
few
turns
coun
terclockwise
Remove
sector
shaft
cover
by
un
screwing
four
fixing
bolts
rn
ST203
Fig
ST
7
Remouing
sector
haft
couer
4
Turn
sector
shaft
adjusting
screw
a
few
turns
clockwise
and
pull
sector
shaft
cover
together
with
sector
shaft
from
gear
housing
ST204
Fig
ST
B
PuUing
out
ector
haft
S
Separate
sector
shaft
adjusting
screw
and
shim
from
cover
6
Remove
jacket
tube
by
unscrew
ing
three
fixing
bolts
7
Remove
steering
worm
assembly
from
gear
housing
8
Detach
worm
bearings
and
worm
bearing
adjusting
shims
from
worm
gear
assembly
and
column
jacket
Note
Be
careful
not
to
allow
ball
nut
to
run
down
to
the
worm
end
If
ball
nut
rotates
suddenly
to
the
worm
end
the
ends
of
ball
guides
may
be
damaged
ST
4
9
Pry
out
sector
shaft
oil
seal
from
gear
housing
and
discard
it
10
Remove
O
ring
from
the
rear
cover
of
column
jacket
and
discard
it
11
Remove
column
jacket
bushing
Notes
a
Do
not
remove
sector
shaft
bushing
from
housing
If
necessary
replace
as
a
gea2
nousing
assembly
b
Do
not
disassemble
ball
nut
and
worm
geir
If
necessary
replace
them
with
new
ones
as
a
worm
gear
assembly
Fig
ST
9
Removing
steering
worm
assem
bly
Assembly
and
adjustment
Apply
recommended
gear
oil
to
all
disassembled
parts
1
Fit
column
jacket
bushing
to
column
jacket
in
place
Note
When
fitting
apply
adhesive
to
bushing
exterior
and
grease
to
in
terior
2
Fill
the
space
between
new
sector
shaft
oil
seal
lips
with
grease
and
fit
it
to
gear
housing
3
Place
steering
worm
assembly
in
position
in
gear
housing
together
with
worm
bearings
4
Install
column
jacket
on
gear
housing
with
O
ring
and
worm
bearing
shims
Be
sure
to
install
thicker
shims
to
the
gear
housing
side
Standard
shim
thickness
1
5
mOl
0
OS9
in
Tightening
torque
1
5
to
2
S
kg
m
11
to
18
ft
Ib
Page 411 of 537
STEERING
LINKAGE
Removal
and
installation
Removal
I
Jack
up
the
front
of
vehicle
and
support
it
on
the
safety
stands
2
Remove
cotter
pins
and
nuts
fas
tening
side
rod
ball
stud
to
knuckle
arms
3
To
detach
side
rod
ball
studs
from
knuckle
arms
insert
Ball
Joint
Remover
HT72520000
between
them
and
separate
them
by
striking
the
top
of
this
tool
with
a
hammer
If
this
operation
must
be
done
without
this
tool
strike
the
knuckle
arm
boss
with
a
hammer
backing
up
the
opposite
side
of
it
with
a
large
hammer
and
bail
stud
is
freed
from
knuckle
arm
Must
not
strike
the
baIl
stud
head
the
ball
socket
of
side
rod
and
side
rod
with
a
hammer
and
so
on
in
this
operation
Fig
ST
11
Ball
joints
Ic
ann
side
4
Remove
riut
securing
gear
armOD
sector
shaft
and
remove
gear
arm
with
the
use
of
Pitman
Arm
Puller
ST29020001
See
Figure
ST
6
S
Remove
idler
arm
assembly
from
frame
by
backing
off
fixing
bolt
and
nut
Ffa
ST
12
Removing
idler
ann
STEERING
SYSTEM
6
Cross
rod
both
side
rods
and
the
adjacent
parts
can
then
be
freed
from
the
vehicle
as
an
assembly
7
Then
separate
the
ball
joints
of
steering
linkage
assembly
following
the
procedure
for
removal
of
the
side
rods
ball
joints
at
knuckle
arm
sides
Assembly
Install
steering
linkage
in
the
reo
verse
sequence
of
removal
observing
the
following
notes
Tightening
torque
Ball
stud
S
S
to
10
0
kg
m
40
to
72
ft
lb
Idler
arm
assembly
3
2
to
3
7
kg
m
23
to
27
ft
lb
Cross
rod
adjust
bar
lock
nut
8
to
10
kg
m
72
fL
2
f
2
When
cross
rod
sockets
and
cross
rod
are
separated
adjust
cross
rod
length
correctly
Adjustment
should
be
done
be
tween
the
centers
of
ball
joints
at
the
both
end
of
cross
rod
assembly
Standard
cross
rod
length
516
rom
20
31
in
3
Adjust
toe
in
and
steering
angle
The
procedures
of
toe
in
and
steer
ing
angle
adjustments
Ie
described
in
Section
F
A
Toe
in
1
to
5
mm
0
04
to
0
20
in
Steering
angle
Inner
wheel
3S030
to
36030
Outer
wheel
30030
to
31030
5t6
mm
20
31
in
1
Cro
s
rod
2
Side
rod
3
Cross
rod
socket
4
Idler
arm
assembly
5
Gear
housing
assembly
Mter
adjustment
of
toe
in
be
sure
that
dimension
A
at
both
ends
of
cross
rod
is
not
less
than
20
nun
0
79
in
Idler
ann
assembly
ST210
Fig
ST
13
Adjusting
cross
rod
assembly
@
1
Idler
body
2
Collar
welded
to
idler
body
A
3
Plain
bushing
4
Screw
bushing
T529
ST
6
Fig
ST
14
Sectional
W
of
idler
arm
as
sembly
Page 412 of 537
I
J
L6
3
4
5
1
Apply
recommended
grease
to
screw
bushing
interior
plain
bushing
interior
dust
seal
inside
and
bushing
sliding
surface
of
idler
ann
Screw
bushing
tightening
torque
12
kg
m
87
ft
lb
2
Before
installing
idler
arm
assem
bly
replace
f
iller
plug
with
grease
nipple
and
apply
recommended
grease
to
idler
ann
through
this
grease
nipple
until
grease
is
forced
out
at
the
lower
end
of
the
dust
seal
lip
Remove
grease
I
8
I
II
I
I
FIODt
Inspection
and
repair
Ball
joint
1
When
ball
stud
is
worn
or
axial
play
is
too
excessive
replace
cross
rod
socket
or
side
rod
with
a
new
one
2
When
dust
cover
is
broken
or
defonned
be
sure
to
replace
with
a
new
one
Axial
end
play
0
1
to
0
5
mm
0
004
to
0
020
in
Initial
swing
torque
S
to
15
kg
cm
70
to
209
in
oz
STEERING
SYSTEM
nipple
and
reinstall
filler
plug
3
In
installing
idler
arm
assembly
make
sure
that
the
standard
dimension
A
is
adjusted
correctly
Standard
dimension
A
137
8
to
139
8
mm
S
42S
to
S
504
in
See
Figure
ST
14
Furthermore
be
sure
to
install
washers
correctly
See
Figure
ST
IS
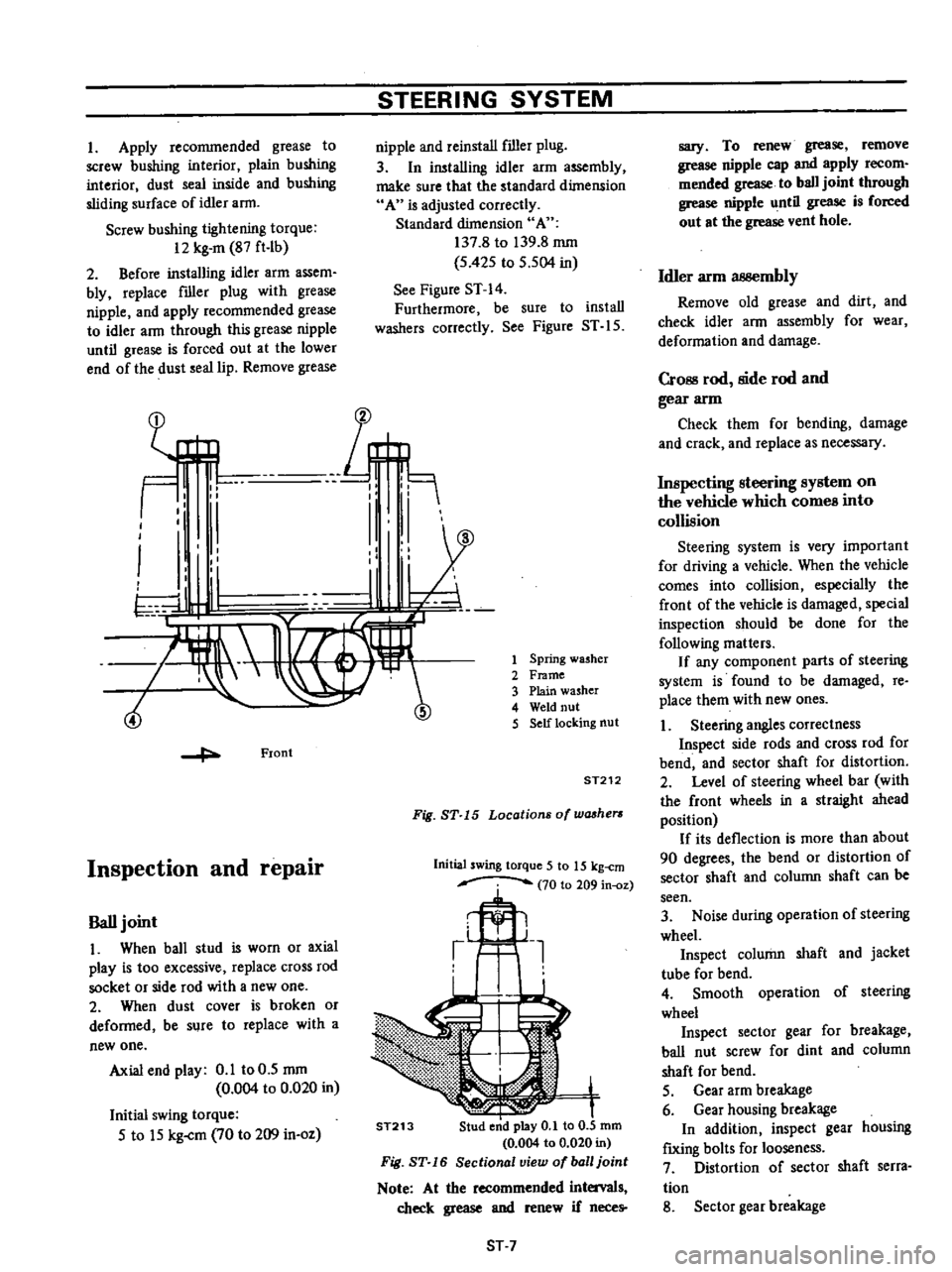
Spring
washer
Frame
Plain
washer
Weld
nut
Self
locking
nut
ST212
Fig
ST
15
Locations
of
washers
Initial
swing
torque
5
to
15
kg
cm
70
to
209
in
oz
ST213
ST
7
sary
To
renew
grease
remove
grease
nipple
cap
and
apply
recom
mended
grease
to
ball
joint
through
grease
nipple
until
grease
is
forced
out
at
the
grease
vent
hole
Idler
arm
3B8embly
Remove
old
grease
and
dirt
and
check
idler
ann
assembly
for
wear
deformation
and
damage
CrOBS
rod
side
rod
and
gear
arm
Check
them
for
bending
damage
and
crack
and
replace
as
necessary
Inspecting
steering
system
on
the
vehicle
which
comes
into
collision
Steering
system
is
very
important
for
driving
a
vehicle
When
the
vehicle
comes
into
collision
especially
the
front
of
the
vehicle
is
damaged
special
inspection
should
be
done
for
the
following
matters
If
any
component
parts
of
steering
system
is
found
to
be
damaged
re
place
them
with
new
ones
1
Steering
angles
correctness
Inspect
side
rods
and
cross
rod
for
bend
and
sector
shaft
for
distortion
2
Level
of
steering
wheel
bar
with
the
front
wheels
in
a
straight
ahead
position
If
its
deflection
is
more
than
about
90
degrees
the
bend
or
distortion
of
sector
shaft
and
column
shaft
can
be
seen
3
Noise
during
operation
of
steering
wheel
Inspect
column
shaft
and
jacket
tube
for
bend
4
Smooth
operation
of
steering
wheel
Inspect
sector
gear
for
breakage
ball
nut
screw
for
dint
and
column
shaft
for
bend
S
Gear
arm
breakage
6
Gear
housing
breakage
In
addition
inspect
gear
housing
f
IXing
bolts
for
looseness
7
Distortion
of
sector
shaft
serra
tion
8
Sector
gear
breakage