fuse DODGE NEON 1999 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 694 of 1200
8W-95 SPLICE LOCATIONS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
INTRODUCTION
This section provides illustrations identifying the
general location of the splices in this vehicle. A splice
index is provided. Use the wiring diagrams in each
section for splice number identification. Refer to the
index for proper splice number.
SPLICE LOCATIONS (LHD)
The following index covers all splices shown in the
wiring diagrams. If a splice is not shown in this sec-
tion, a N/S will be in the Fig. column.
Spllice Location Fig.
S101 Near Dat Link T/O 1
S104 Left Strut Tower 1
S105 Left Strut Tower 1
S106 Near PCM T/O 1
S107 Before T/O for Left
Headlamp2
S108 Before T/O for Left
Headlamp2
S109 Before T/O for Left
Headlamp2
S110 In PCM T/O 1
S111 Near T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S112 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S113 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S114 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S115 Neat T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S116 Near T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S117 Near EVAP/Purge Sol T/O 2
S118 Between VSS and Crank
Sensor T/O3
S119 Between Crank Sensor and
VSS T/O3
S120 Near INJ #4 3
S121 Between INJ #2 and #3 T/O 3
S122 Near T/O for VSS and
Engine Oil Pressure Switch3
S123 Near T/O for O2S 3
S124
SOHCNear Cam Sensor and Coil
T/O'sN/S
S124
DOHCNear TP Sensor T/O 3Spllice Location Fig.
S125 Near Starter N/S
S126 In PCM T/O N/S
S127 Near Left Headlamp T/O 2
S131 Near T/O for PCM 1
S133 In Left Headlamp Leveling
T/ON/S
S139 In Ignition Coil 3
S201 Near T/O for Center Console 5
S202 Near T/O for PAB 4
S203 Near T/O for Passenger Air
Bag4
S204 Near HVAC Connector 4
S205 Near Center Stack T/O 4
S206 Near Center Stack T/O 4
S207 Top Center of I.P. 5
S208 Top Center of I.P. 5
S209 Top Center of I.P. 5
S210 Top Center of I.P. 5
S211 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's5
S212 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's5
S213 Near T/O for Left Cluster 4
S214 Near T/O for Fuseblock 4
S216 Near STRG Column T/O 4
S217 Near T/O for Fuse Block 4
S218 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's4
S219 In T/O for RKE Module 5
S221 In T/O for Body Wiring 4
S222 Near T/O for Fuse Block 4
S223 Top Center of I/P 4
PL8W - 95 SPLICE LOCATIONS 8W - 95 - 1
Page 704 of 1200
SPLICE LOCATIONS (RHD)
The following index covers all splices shown in the
wiring diagrams. If a splice is not shown in this sec-
tion, a N/S will be in the Fig. column.
Spllice Location Fig.
S101 Near Dat Link T/O 1
S104 Right Strut Tower 1
S105 Left Strut Tower N/S
S106 Near PCM T/O 1
S107 Before T/O for Left Headlamp
Leveling2
S108 Near T/O for Left Headlamp
Leveling2
S109 Before T/O for Left Headlamp
Leveling2
S110 In PCM T/O 1
S111 Near T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S112 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S113 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S114 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S115 Near T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S116 Near T/O for Left Fog Lamp 2
S117 Near EVAP/Purge Sol T/O 2
S118 Between VSS and Crank
Sensor T/O3
S119 Between Crank Sensor and
VSS T/O3
S120 Near INJ #4 3
S121 Between INJ #2 and #3 T/O 3
S122 Near T/O for VSS and Engine
Oil Pressure Switch3
S123 Near T/O for O2S 3
S124 Near Cam Sensor and Coil
T/O's3
S125 Near Starter N/S
S126 In PCM T/O N/S
S127 Near Left Headlamp T/O 2
S131 Near T/O for PCM 1
S133 In Left Headlamp Leveling T/O N/S
S139 In Ignition Coil 3
S201 Near T/O for Center Console N/S
S202 Near T/O for PAB 5
Spllice Location Fig.
S203 Near T/O for HVAC 5
S204 Near HVAC Connector 5
S205 Near Center Stack T/O 5
S206 Near Center Stack T/O 5
S207 Top Center of I.P. 4
S208 Top Center of I.P. 4
S209 Top Center of I.P. 4
S210 Top Center of I.P. 4
S211 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's4
S212 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's4
S213 Near T/O for Left Fuseblock 4
S214 Right Cluster and Right Panel
speaker4
S217 Near T/O for FuseBlock 4
S218 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's4
S221 Top Right of I.P. 4
S222 Near T/O for FuseBlock 4
S223 Top Center of I/P 5
S224 In T/O for Headlamp Switch 4
S301 Near RT B-Pillar T/O 7
S302 Near RT B-Pillar T/O 7
S303 Near RT B-Pillar T/O 7
S304 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S306 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S307 Near Rear Fog Lamp T/O 7
S308 Near LR Body Ground 6
S309 Near Top of A-Pillar, Left Side 9
S310 Near DR/LK SW and PWR
Mirror T/O8
S313 Near T/O for Sunroof Slide
SW9
S314 Near T/O for Sunroof Slide
Switch9
S315 Near Rear Fog Lamp T/O 6
S316 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S317 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S318 Near DR/LK Switch T/O 8
PL8W - 95 SPLICE LOCATIONS 8W - 95 - 11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 852 of 1200

The hose clamps have rolled edges to prevent the
clamp from cutting into the hose. Only use clamps
that are original equipment or equivalent. Other
types of clamps may cut into the hoses and cause
high pressure fuel leaks. Tighten hose clamps to 1
N´m (10 in. lbs.) torque.
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
REMOVAL
When disconnecting a quick-connect fitting, the
retainer will remain on the fuel tube nipple.
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE DISCONNECTING A QUICK-CONNECT FIT-
TINGS. REFER TO THE FUEL PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDURE.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Perform Fuel Pressure Release Procedure.
Refer to the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this
section.
(3) Squeeze retainer tabs together and pull fuel
tube/quick-connect fitting assembly off of fuel tube
nipple. The retainer will remain on fuel tube.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Never install a quick-connect fitting
without the retainer being either on the fuel tube or
already in the quick-connect fitting. In either case,
ensure the retainer locks securely into the quick-
connect fitting by firmly pulling on fuel tube and fit-
ting to ensure it is secured.
(1) Using a clean lint free cloth, clean the fuel tube
nipple and retainer.
(2) Prior to connecting the fitting to the fuel tube,
coat the fuel tube nipple with clean 30 weight engine
oil.
(3) Push the quick-connect fitting over the fuel
tube until theretainer seats and a click is heard.
(4) The plastic quick-connect fitting has windows
in the sides of the casing. When the fitting com-
pletely attaches to the fuel tube, the retainer locking
ears and the fuel tube shoulder are visible in the
windows. If they are not visible, the retainer was not
properly installed (Fig. 14).Do not rely upon the
audible click to confirm a secure connection.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or
until the ignition switch is turned to the Off posi-
tion.
(5) Use the DRB scan tool ASD Fuel System Test
to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAY
The relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC) (Fig. 15). The PDC is located next to the
battery in the engine compartment. For the location
of the relay within the PDC, refer to the PDC cover
for location. Check electrical terminals for corrosion
and repair as necessary.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
The fuel pump relay is located in the PDC. The
inside top of the PDC cover has a label showing relay
and fuse location.
FUEL PUMP MODULE
REMOVAL
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
SERVICE VEHICLES IN WELL VENTILATED AREAS
AND AVOID IGNITION SOURCES. NEVER SMOKE
WHILE SERVICING THE VEHICLE.
(1) Drain the fuel. Refer to Draining Fuel Tank in
the Fuel Tank section of this group.
Fig. 14 Plastic Quick-Connect Fitting/Fuel Tube
Connection
Fig. 15 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 11
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 864 of 1200

below the minimum acceptable percentage, the PCM
stores a diagnostic trouble code in memory.
During certain idle conditions, the PCM may enter
a variable idle speed strategy. During variable idle
speed strategy the PCM adjusts engine speed based
on the following inputs.
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Battery temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine run time
²Power steering pressure switch
²Vehicle mileage
ACCELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. The PCM recog-
nizes an abrupt increase in Throttle Position sensor
output voltage or MAP sensor output voltage as a
demand for increased engine output and vehicle
acceleration. The PCM increases injector pulse width
in response to increased fuel demand.
DECELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During decelera-
tion the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²A/C pressure transducer
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Exhaust gas oxygen content (upstream heated
oxygen sensor)
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Power steering pressure switch
²Throttle position
²IAC motor control changes in respones to MAP
sensor feedback
The PCM may receive a closed throttle input from
the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) when it senses an
abrupt decrease in manifold pressure. This indicates
a hard deceleration. In response, the PCM may
momentarily turn off the injectors. This helps
improve fuel economy, emissions and engine braking.
If decel fuel shutoff is detected, downstream oxy-
gen sensor diagnostics is performed.
WIDE-OPEN-THROTTLE MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. During wide-open-
throttle operation, the following inputs are received
by the PCM:
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine speed
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure²Throttle position
When the PCM senses a wide-open-throttle condi-
tion through the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) it de-
energizes the A/C compressor clutch relay. This
disables the air conditioning system.
The PCM does not monitor the heated oxygen sen-
sor inputs during wide-open-throttle operation except
for downstream heated oxygen sensor and both
shorted diagnostics. The PCM adjusts injector pulse
width to supply a predetermined amount of addi-
tional fuel.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
When the operator turns the ignition switch to the
OFF position, the following occurs:
²All outputs are turned off, unless 02 Heater
Monitor test is being run. Refer to Group 25,
On-Board Diagnostics.
²No inputs are monitored except for the heated
oxygen sensors. The PCM monitors the heating ele-
ments in the oxygen sensors and then shuts down.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
The PCM can test many of its own input and out-
put circuits. If the PCM senses a fault in a major
system, the PCM stores a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) in memory.
For DTC information, refer to Group 25, Emission
Control Systems. See On-Board Diagnostics.
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
The power distribution center (PDC) is located next
to the battery (Fig. 1). The PDC contains the starter
relay, radiator fan relay, A/C compressor clutch relay,
auto shutdown relay, fuel pump relay and several
fuses.
Fig. 1 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 23
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 872 of 1200
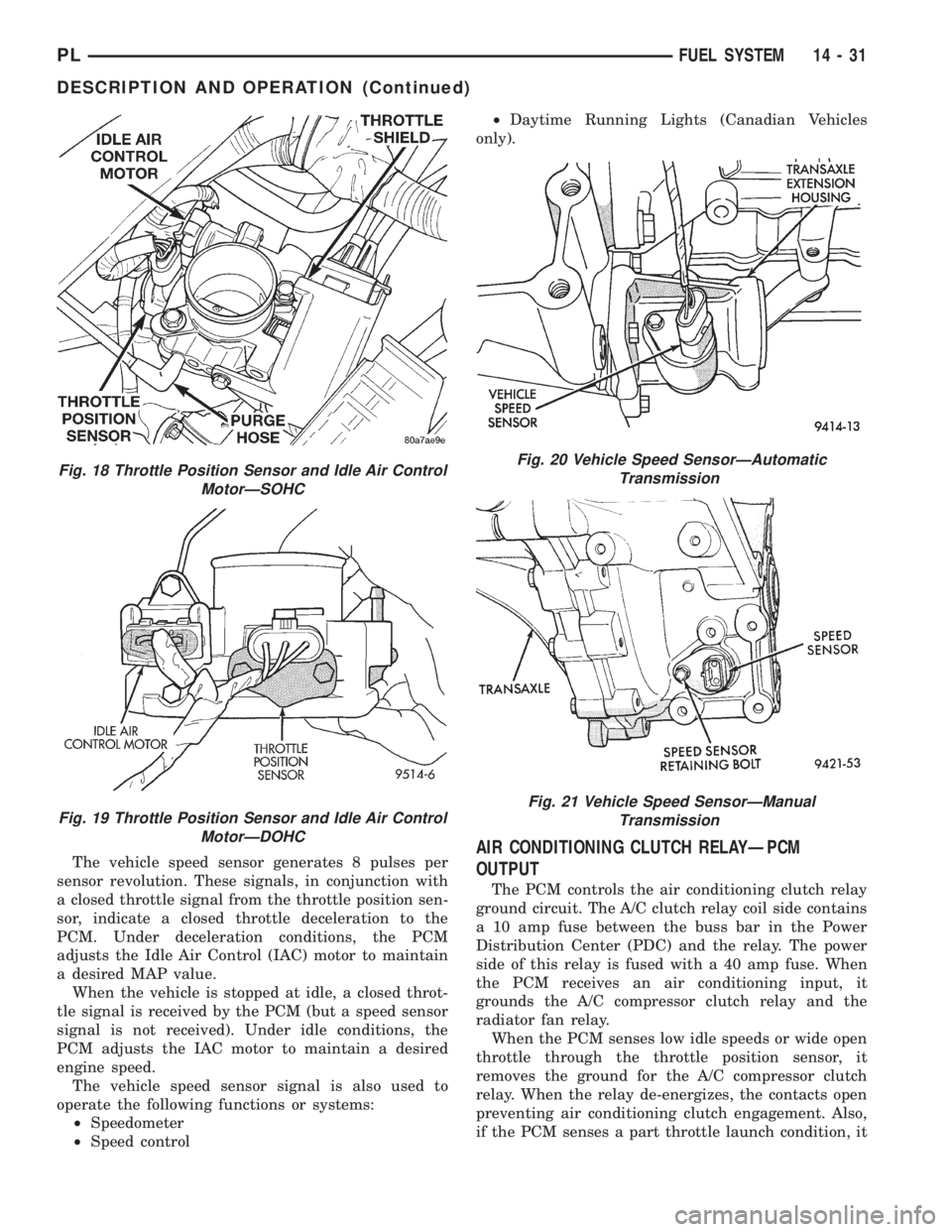
The vehicle speed sensor generates 8 pulses per
sensor revolution. These signals, in conjunction with
a closed throttle signal from the throttle position sen-
sor, indicate a closed throttle deceleration to the
PCM. Under deceleration conditions, the PCM
adjusts the Idle Air Control (IAC) motor to maintain
a desired MAP value.
When the vehicle is stopped at idle, a closed throt-
tle signal is received by the PCM (but a speed sensor
signal is not received). Under idle conditions, the
PCM adjusts the IAC motor to maintain a desired
engine speed.
The vehicle speed sensor signal is also used to
operate the following functions or systems:
²Speedometer
²Speed control²Daytime Running Lights (Canadian Vehicles
only).AIR CONDITIONING CLUTCH RELAYÐPCM
OUTPUT
The PCM controls the air conditioning clutch relay
ground circuit. The A/C clutch relay coil side contains
a 10 amp fuse between the buss bar in the Power
Distribution Center (PDC) and the relay. The power
side of this relay is fused with a 40 amp fuse. When
the PCM receives an air conditioning input, it
grounds the A/C compressor clutch relay and the
radiator fan relay.
When the PCM senses low idle speeds or wide open
throttle through the throttle position sensor, it
removes the ground for the A/C compressor clutch
relay. When the relay de-energizes, the contacts open
preventing air conditioning clutch engagement. Also,
if the PCM senses a part throttle launch condition, it
Fig. 18 Throttle Position Sensor and Idle Air Control
MotorÐSOHC
Fig. 19 Throttle Position Sensor and Idle Air Control
MotorÐDOHC
Fig. 20 Vehicle Speed SensorÐAutomatic
Transmission
Fig. 21 Vehicle Speed SensorÐManual
Transmission
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 31
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 873 of 1200

disables the A/C compressor clutch for several sec-
onds.
The air conditioning clutch relay is located in the
PDC. The inside top of the PDC cover has a label
showing relay and fuse location.
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The automatic shutdown (ASD) relay supplies bat-
tery voltage to the fuel injectors, electronic ignition
coil and the heating elements in the oxygen sensors.
A buss bar in the power distribution center (PDC)
supplies voltage to the solenoid side and contact side
of the relay. The ASD relay power circuit contains a
20 amp fuse between the buss bar in the PDC and
the relay. The fuse also protects the power circuit for
the fuel pump relay and pump. The fuse is located in
the PDC. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams for
circuit information.
The PCM controls the relay by switching the
ground path for the solenoid side of the relay on and
off. The PCM turns the ground path off when the
ignition switch is in the Off position unless the 02
Heater Monitor test is being run. Refer to Group 25,
On-Board Diagnostics. When the ignition switch is in
the On or Crank position, the PCM monitors the
crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sen-
sor signals to determine engine speed and ignition
timing (coil dwell). If the PCM does not receive the
crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sen-
sor signals when the ignition switch is in the Run
position, it will de- energize the ASD relay.
The ASD relay is located in the PDC. The inside
top of the PDC cover has a label showing relay and
fuse location.
CHARGING SYSTEM INDICATOR LAMPÐPCM
OUTPUT
The PCM turns the instrument panel Charging
System Lamp on. Refer to Group 8C for charging sys-
tem information.
FUEL PUMP RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The fuel pump relay supplies battery voltage to the
fuel pump. A buss bar in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC) supplies voltage to the solenoid side and
contact side of the relay. The fuel pump relay power
circuit contains a 20 amp fuse between the buss bar
in the PDC and the relay. The fuse also protects the
power circuit for the Automatic Shutdown (ASD)
relay. The fuse is located in the PDC. Refer to Group
8W, Wiring Diagrams for circuit information.
The PCM controls the fuel pump relay by switch-
ing the ground path for the solenoid side of the relay
on and off. The PCM turns the ground path off when
the ignition switch is in the Off position. When the
ignition switch is in the On position, the PCM ener-gizes the fuel pump. If the crankshaft position sensor
does not detect engine rotation, the PCM de-ener-
gizes the relay after approximately one second.
The fuel pump relay is located in the PDC. The
inside top of the PDC cover has a label showing relay
and fuse location.
DUTY CYCLE EVAP PURGE SOLENOIDÐPCM
OUTPUT
The duty cycle EVAP purge solenoid regulates the
rate of vapor flow from the EVAP canister to the
throttle body. The powertrain control module oper-
ates the solenoid.
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged.
The engine enters closed loop operation after it
reaches a specified temperature and the programmed
time delay ends. During closed loop operation, the
PCM energizes and de-energizes the solenoid 5 to 10
times per second, depending upon operating condi-
tions. The PCM varies the vapor flow rate by chang-
ing solenoid pulse width. Pulse width is the amount
of time the solenoid is energized.
The solenoid attaches to a bracket near the front
engine mount (Fig. 22). To operate correctly, the sole-
noid must be installed with the electrical connector
on top.
ELECTRIC EGR TRANSDUCERÐPCM OUTPUT
The Electric EGR Transducer contains an electri-
cally operated solenoid and a back-pressure con-
trolled vacuum transducer (Fig. 23). The PCM
Fig. 22 Duty Cycle EVAP Purge Solenoid
14 - 32 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 877 of 1200

(3) Open the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
Check for blown fuses. Ensure the relays and fuses
are fully seated in the PDC (Fig. 32). A label on the
underside of the PDC cover shows the locations of
each relay and fuse.
(4) Verify the throttle cable operates freely (Fig.
33).
(5) Check the electrical connections at the idle air
control motor and throttle position sensor (Fig. 34).
(6) Check hose connections between the PCV
valve, vacuum port - intake manifold and the oil sep-
arator (Fig. 35).
(7) Inspect the electrical connections at the MAP
sensor/intake air temperature sensor and the (Fig.
36).
(8) Inspect the fuel injector electrical connections
(Fig. 37).
(9) Inspect the ignition coil electrical connector.
Ensure the spark plug insulators are firmly seated
over the spark plugs (Fig. 38).
Fig. 30 2.0L SOHC Engine Compartment
Fig. 31 Battery, PCM, and PDC
Fig. 32 Power Distribution Center
Fig. 33 Throttle CableÐAutomatic Transmission
Fig. 34 Idle Air Control Motor and Throttle Position
SensorÐTypical
14 - 36 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 882 of 1200
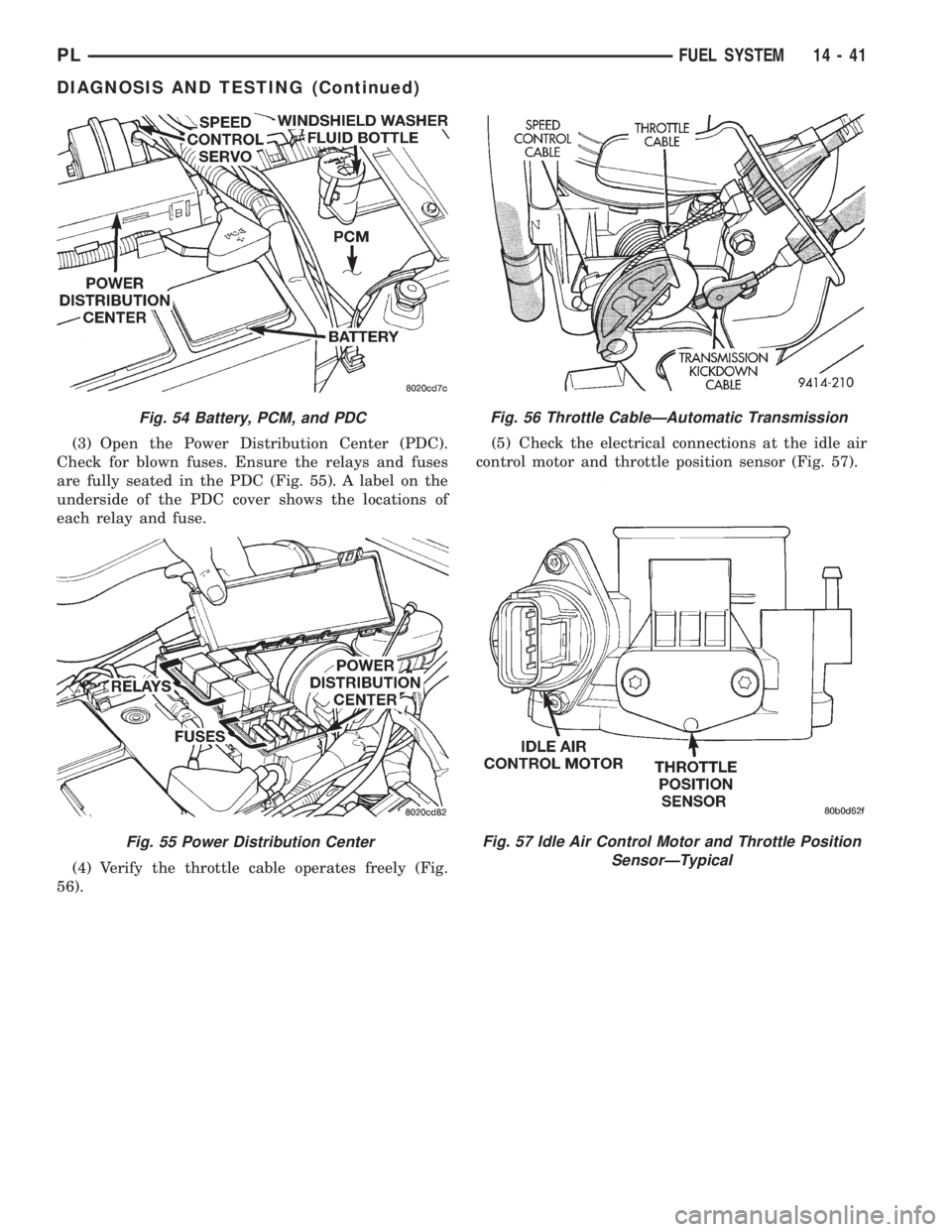
(3) Open the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
Check for blown fuses. Ensure the relays and fuses
are fully seated in the PDC (Fig. 55). A label on the
underside of the PDC cover shows the locations of
each relay and fuse.
(4) Verify the throttle cable operates freely (Fig.
56).(5) Check the electrical connections at the idle air
control motor and throttle position sensor (Fig. 57).
Fig. 54 Battery, PCM, and PDC
Fig. 55 Power Distribution Center
Fig. 56 Throttle CableÐAutomatic Transmission
Fig. 57 Idle Air Control Motor and Throttle Position
SensorÐTypical
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 41
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1128 of 1200

SUNROOF
INDEX
page page
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES............... 47
SUNROOF DIAGNOSIS................... 47
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SUNROOF CABLES...................... 48
SUNROOF COMPONENTS................ 49
SUNROOF DRIVE MOTOR................. 49
SUNROOF GLASS PANEL................. 49SUNROOF GUIDE AND MECHANISM
ASSEMBLY........................... 49
SUNROOF MODULE..................... 50
SUNROOF PROCEDURE INFORMATION...... 48
SUNROOF SUNSHADE................... 50
SUNROOF WIND DEFLECTOR............. 51
ADJUSTMENTS
SUNROOF GLASS HEIGHT ADJUSTMENT.... 51
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
Before beginning sunroof diagnostics verify that all
other power accessories are in proper operating con-
dition. If not, a common electrical problem may exist.
Refer to the Wiring Diagrams section of this publica-tion for circuit, splice and component descriptions.
Check the condition of the circuit protection (fuses,
circuit breakers or fuse links). Inspect all wiring con-
nector pins for proper engagement and continuity.
Check for battery voltage at the power sunroof con-
trol switches. If battery voltage is detected at the
control switches, proceed with the following tests.
SUNROOF DIAGNOSIS
SYMPTOM POSSIBLE CAUSE
Sunroof motor inoperative.²Contaminated or corroded slides and channels.
²Binding cable or linkage.
²Faulty circuit ground.
²Faulty power circuit to sunroof drive motor.
²Faulty sunroof drive motor.
²Faulty sunroof motor connector.
Audible whine when switch is depressed,
sunroof does not operate.²Faulty motor drive clutch.
²Binding linkage.
²Faulty sunroof motor connections.
Sunroof opens, but does not close.²Binding linkage.
²Faulty circuit.
²Faulty switch.
Sunroof vents, but does not open.²Binding linkage.
²Faulty circuit.
²Faulty switch.
Sunroof does not vent²Binding cable.
²Faulty circuit.
²Faulty switch.
Sunroof vents and opens but does not
close²Binding linkage.
²Faulty circuit.
²Faulty switch.
Sunroof water leak.²Drain tubes clogged or kinked.
²Glass panel improperly adjusted.
²Faulty glass panel seal.
PLBODY 23 - 47
Page 1141 of 1200

(3) Close all doors, windows and vents to the pas-
senger compartment.
(4) Set Heater-A/C control to A/C, full heat, floor,
RECIRC. and high blower.
(5) Start the engine and hold the idle speed (1000
rpm). After the engine has reached running temper-
ature, allow the passenger compartment to heat up.
This will create the need for maximum refrigerant
flow into the evaporator.
(6) If the refrigerant charge is sufficient, discharge
(high pressure) gauge should read 965 to 2620 kPa
(140 to 380 psi). Suction (low pressure) gauge should
read 103 to 2417 kPa (15 to 35 psi). If system cannot
achieve proper pressure readings, replace the expan-
sion valve. If pressure is correct, proceed with test.
WARNING: PROTECT SKIN AND EYES FROM CON-
TACTING CO2 PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
(7) If suction side low pressure is within specified
range, freeze the expansion valve control head (Fig.
10) for 30 seconds. Use a super cold substance (liquid
CO2).Do not spray refrigerant on the expansion
valve for this test.Suction side low pressure should
drop to 34.5 kPa (5 psi) If not, replace expansion
valve.
(8) Allow expansion valve to thaw. The low pres-
sure gauge reading should stabilize at 103 to 241
kPa (15 to 35 psi). If not, replace expansion valve.
(9) When expansion valve test is complete, test
A/C overall performance. Refer to the Heater and A/C
Performance Test in this section. Remove all test
equipment before returning vehicle to use.
BLOWER MOTOR ELECTRICAL DIAGNOSIS
Refer to the Blower Motor Electrical System Diag-
nosis chart in this section. Also refer to Group 8W,
Wiring Diagrams for more information.
BLOWER MOTOR VIBRATION AND/OR NOISE
DIAGNOSIS
The resistor block supplies the blower motor with
varied voltage (low and middle speeds) or battery
voltage (high speed).
CAUTION: Stay clear of the blower motor and resis-
tor block (Hot). Do not operate the blower motor
with the resistor block removed from the heater-A/C
housing.
Refer to the Blower Motor Vibration/Noise chart
for diagnosis.
EVAPORATOR PROBE TEST
The work area and vehicle must be between 16É C
(60É F) and 32É C (90É F) when testing the switch.(1) Disconnect the three wire connector from the
evaporator probe lead located behind the glove box.
(2) Start engine and set A/C to low blower motor
speed, panel, full cool, and RECIRC.
(3) Using a voltmeter, check for battery voltage
between Pin 1 and 2. If no voltage is detected, there
is no power to the switch. Check wiring and fuses.
Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams for circuit diag-
nosis.
(4) Using a voltmeter, check for battery voltage
between Pin 1 and Pin 3. If no voltage is detected,
there is no voltage from the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams. If voltage
is OK, connect a jumper wire between Pin 1 and Pin
3. The compressor clutch should engage. If the clutch
engages, remove the jumper wire immediately and go
to Step 5. If the compressor clutch does not engage,
check the operation of the clutch and repair as nec-
essary.
(5) If compressor clutch engages, connect the evap-
orator probe 3-way connector. The compressor clutch
should engage or cycle depending on evaporator tem-
perature. If OK, go to Step 6. If not OK, replace the
clutch cycling switch.
(6) The engine running and the A/C set to:
²Blower motor on low speed
²Panel position
²Full cool
²RECIRC.
Close all doors and windows. Place a thermometer
in the center discharge vent.
(7) If the clutch does not begin to cycle off between
2É C to 7É C (35É F to 45É F), verify that the evapo-
rator probe is fully installed and not loose in evapo-
rator. If it is not properly installed, install probe and
retest outlet temperature. If the evaporator probe is
properly installed, replace the clutch cycling switch.
HEATER PERFORMANCE TEST
PRE-DIAGNOSTIC PREPARATIONS
Review Safety Precautions and Warnings in this
group before performing the following procedures.
Check the coolant level, drive belt tension, vacuum
line connections, radiator air flow and fan operation.
Start engine and allow to warm up to normal tem-
perature.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE RADIATOR CAP
WHEN ENGINE IS HOT, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
If vehicle has been run recently, wait 15 minutes
before removing cap. Place a rag over the cap and
turn it to the first safety stop. Allow pressure to
escape through the overflow tube. When the system
stabilizes, remove the cap completely.
24 - 8 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONINGPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)