lock DODGE NEON 1999 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 704 of 1200
SPLICE LOCATIONS (RHD)
The following index covers all splices shown in the
wiring diagrams. If a splice is not shown in this sec-
tion, a N/S will be in the Fig. column.
Spllice Location Fig.
S101 Near Dat Link T/O 1
S104 Right Strut Tower 1
S105 Left Strut Tower N/S
S106 Near PCM T/O 1
S107 Before T/O for Left Headlamp
Leveling2
S108 Near T/O for Left Headlamp
Leveling2
S109 Before T/O for Left Headlamp
Leveling2
S110 In PCM T/O 1
S111 Near T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S112 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S113 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S114 Near T/O for Left Headlamp 2
S115 Near T/O for Radiator Fan
Motor2
S116 Near T/O for Left Fog Lamp 2
S117 Near EVAP/Purge Sol T/O 2
S118 Between VSS and Crank
Sensor T/O3
S119 Between Crank Sensor and
VSS T/O3
S120 Near INJ #4 3
S121 Between INJ #2 and #3 T/O 3
S122 Near T/O for VSS and Engine
Oil Pressure Switch3
S123 Near T/O for O2S 3
S124 Near Cam Sensor and Coil
T/O's3
S125 Near Starter N/S
S126 In PCM T/O N/S
S127 Near Left Headlamp T/O 2
S131 Near T/O for PCM 1
S133 In Left Headlamp Leveling T/O N/S
S139 In Ignition Coil 3
S201 Near T/O for Center Console N/S
S202 Near T/O for PAB 5
Spllice Location Fig.
S203 Near T/O for HVAC 5
S204 Near HVAC Connector 5
S205 Near Center Stack T/O 5
S206 Near Center Stack T/O 5
S207 Top Center of I.P. 4
S208 Top Center of I.P. 4
S209 Top Center of I.P. 4
S210 Top Center of I.P. 4
S211 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's4
S212 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's4
S213 Near T/O for Left Fuseblock 4
S214 Right Cluster and Right Panel
speaker4
S217 Near T/O for FuseBlock 4
S218 Between RT and LT Cluster
T/O's4
S221 Top Right of I.P. 4
S222 Near T/O for FuseBlock 4
S223 Top Center of I/P 5
S224 In T/O for Headlamp Switch 4
S301 Near RT B-Pillar T/O 7
S302 Near RT B-Pillar T/O 7
S303 Near RT B-Pillar T/O 7
S304 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S306 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S307 Near Rear Fog Lamp T/O 7
S308 Near LR Body Ground 6
S309 Near Top of A-Pillar, Left Side 9
S310 Near DR/LK SW and PWR
Mirror T/O8
S313 Near T/O for Sunroof Slide
SW9
S314 Near T/O for Sunroof Slide
Switch9
S315 Near Rear Fog Lamp T/O 6
S316 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S317 Near Fuel Tank T/O 7
S318 Near DR/LK Switch T/O 8
PL8W - 95 SPLICE LOCATIONS 8W - 95 - 11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 714 of 1200

ENGINE
CONTENTS
page page
2.0L DOHC ENGINE...................... 58
2.0L SOHC ENGINE...................... 12ENGINE DIAGNOSIS....................... 7
STANDARD SERVICE PROCEDURES.......... 1
STANDARD SERVICE PROCEDURES
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
CHECKING ENGINE OIL LEVEL.............. 5
CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET BOLT ACCESS
PLUG................................ 2
ENGINE CORE PLUGS.................... 2
ENGINE OIL SERVICE..................... 5
ENGINE PERFORMANCE.................. 2FORM-IN-PLACE GASKETS................. 1
HONING CYLINDER BORES................ 3
HYDROSTATIC LOCKED ENGINE............ 4
MEASURING MAIN BEARING AND
CONNECTING ROD BEARING CLEARANCES . 3
REPAIR OF DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS . . . 4
GENERAL INFORMATION
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKETS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Silicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant and MopartGas-
ket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtSILICONE RUBBER ADHESIVE
SEALANT
MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant or equiv-
alent, normally black in color, is available in three
ounce tubes. Moisture in the air causes the Mopart
Silicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant material to cure.
This material is normally used on flexible metal
flanges. It has a shelf life of one year and will not
properly cure if over age. Always inspect the package
for the expiration date before use.MOPARtGASKET MAKER
MopartGasket Maker is an anaerobic type gasket
material. The material cures in the absence of air
when squeezed between two metallic surfaces. It will
not cure if left in the uncovered tube. The anaerobic
material is for use between two machined surfaces.
Do not use on flexible metal flanges.
MOPARtTORQUE CURE GASKET MAKER
MopartTorque Cure Gasket Maker is a unique
anaerobic type gasket material to be usedONLY
between the bedplate and engine block. The material
cures in the absence of air when torqued between
two metallic surfaces. It will not cure if left in the
uncovered tube. This anaerobic material is specially
made to seal the area between the bedplate and cyl-
inder block without disturbing the bearing clearance
or alignment of these components.
GASKET DISASSEMBLY
Parts assembled with form-in-place gaskets may be
disassembled without unusual effort. In some
instances, it may be necessary to lightly tap the part
with a mallet or other suitable tool to break the seal
between the mating surfaces. A flat gasket scraper
may also be lightly tapped into the joint but care
must be taken not to damage the mating surfaces.
SURFACE PREPARATION
Scrape clean or wire brush all gasket surfaces
removing all loose material. Inspect stamped parts to
PLENGINE 9 - 1
Page 715 of 1200

assure gasket rails are flat. Flatten rails with a ham-
mer on a heavy steel plate if required. Gasket sur-
faces must be free of oil and dirt. Make sure old
gasket material is removed from blind attaching
holes.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier then using precut gas-
kets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 inch.) diameter or less of seal-
ant to one gasket surface. Be certain the material
surrounds each mounting hole. Excess material can
easily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
The MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant gas-
ket material or equivalent should be applied in a con-
tinuous bead approximately 3 mm (0.120 inch) in
diameter. All mounting holes must be circled. For
corner sealing, a 3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 inch.)
drop is placed in the center of the gasket contact
area. Uncured sealant may be removed with a shop
towel. Components should be torqued in place while
the sealant is still wet to the touch (within 10 min-
utes). The usage of a locating dowel is recommended
during assembly to prevent smearing material off the
location.
CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET BOLT ACCESS PLUG
An Access plug is located in the right inner fender
shield. Remove the plug and insert the proper size
socket, extension and ratchet, when crankshaft rota-
tion is necessary.
ENGINE CORE PLUGS
REMOVAL
Using a blunt tool such as a drift or a screwdriver
and a hammer, strike the bottom edge of the cup
plug (Fig. 1). With the cup plug rotated, grasp firmly
with pliers or other suitable tool and remove plug
(Fig. 1).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting
as restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
INSTALLATION
Thoroughly remove all rust and clean inside of cup
plug hole in cylinder block or head. Be sure to
remove old sealer. Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole
with sealer. Make certain the new plug is cleaned of
all oil or grease. Using proper drive plug, drive plug
into hole so that the sharp edge of the plug is atleast 0.5 mm (0.020 inch.) inside the lead in chamfer
(Fig. 1).
It is in not necessary to wait for curing of the seal-
ant. The cooling system can be refilled and the vehi-
cle placed in service immediately.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
If a loss of performance is noticed, timing belt or
chain may have skipped one or two teeth. Camshaft
and crankshaft timing should be checked. Refer to
Group 9, Engine Timing belt or chain installation.
It is important that the vehicle is operating to its
optimum performance level to maintain fuel economy
and lowest vehicle emissions. If vehicle is not operat-
ing to these standards, refer to Engine Diagnosis out-
lined is this section. The following procedures can
assist in achieving the proper engine diagnosis.
(1) Test cranking amperage draw. Refer to Group
8B, Starting.
(2) Check intake manifold for vacuum leaks.
(3) Perform cylinder compression pressure test.
Refer to Engine Diagnosis, outlined in this section.
(4) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary and
adjust gap as specified in Group 8D, Ignition System.
Tighten to specifications.
(5) Test resistance of spark plug cables. Refer to
Group 8D, Ignition System.
(6) Test ignition coils primary and secondary resis-
tance. Replace parts as necessary. Refer to Group 8D,
Ignition System.
(7) Check fuel pump pressure at idle and different
RPM ranges. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System for
Specifications.
(8) The air filter elements should be replaced as
specified in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance.
(9) Inspect crankcase ventilation system as out-
lined in Group 25, Emission Control Systems.
(10) Road test vehicle as a final test.
Fig. 1 Core Hole Plug Removal
9 - 2 ENGINEPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 716 of 1200

HONING CYLINDER BORES
(1) Used carefully, the cylinder bore resizing hone
C-823 equipped with 220 grit stones, is the best tool
for this job. In addition to deglazing, it will reduce
taper and out-of-round as well as removing light
scuffing, scoring or scratches. Usually a few strokes
will clean up a bore and maintain the required lim-
its.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done
using a cylinder surfacing hone, Tool C-3501,
equipped with 280 grit stones, if the cylinder bore is
straight and round. 20-60 strokes depending on the
bore condition, will be sufficient to provide a satisfac-
tory surface. Inspect cylinder walls after each 20
strokes, using a light honing oil.Do not use engine
or transmission oil, mineral spirits or kerosene.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a cross-hatch pattern.
When hone marksintersectat 50-60 degrees, the
cross hatch angle is most satisfactory for proper seat-
ing of rings (Fig. 2).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between
200-300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 50-60
degree angle. Faster up and down strokes increase
the cross-hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned again to remove all traces of abrasive.
CAUTION: Ensure all abrasives are removed from
engine parts after honing. It is recommended that a
solution of soap and hot water be used with a
brush and the parts then thoroughly dried. The bore
can be considered clean when it can be wiped
clean with a white cloth and cloth remains clean.
Oil the bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
MEASURING MAIN BEARING AND CONNECTING
ROD BEARING CLEARANCES
PLASTIGAGE METHOD
Engine crankshaft bearing clearances can be deter-
mined by use of Plastigage or equivalent. The follow-
ing is the recommended procedure for the use of
Plastigage:
NOTE: The total clearance of the main bearings
can only be determined by removing the weight of
the crankshaft. This can be accomplished by either
of two methods:
PREFERRED METHOD
Shimming the bearings adjacent to the bearing to
be checked in order to remove the clearance between
upper bearing shell and the crankshaft. This can be
accomplished by placing a minimum of 0.254 mm
(0.010 in.) shim (e. g. cardboard, matchbook cover,
etc.) between the bearing shell and the bearing cap
on the adjacent bearings and tightening bolts to
14-20 N´m (10-15 ft. lbs.). The number of main bear-
ing will vary from engine to engine.
ENGINE WITH 5 MAIN BEARINGS
²When checking #1 main bearing shim #2 main
bearing.
²When checking #2 main bearing shim #1 & 3
main bearing.
²When checking #3 main bearing shim #2 & 4
main bearing.
²When checking #4 main bearing shim #3 & 5
main bearing.
²When checking #5 main bearing shim #4 main
bearing.
ENGINE WITH 4 MAIN BEARING
²When checking #1 main bearing shim # 2 main
bearing.
²When checking #2 main bearing shim #1 & #3
main bearing.
Fig. 2 Cylinder Bore Cross-Hatch Pattern
Fig. 3 Plastigage Placed in Lower Shell
PLENGINE 9 - 3
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 717 of 1200

²When checking #3 main bearing shim #2 & #4
main bearing.
²When checking #4 main bearing shim #3 main
bearing.
NOTE: REMOVE ALL SHIMS BEFORE REASSEM-
BLING ENGINE
ALTERNATIVE METHOD
The weight of the crankshaft can be supported by a
jack under the counterweight adjacent to the bearing
being checked.
PLASTIGAGE PROCEDURE
(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(2) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the cap approximately
6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from the oil
holes (Fig. 3). (In addition, suspected areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspected
area). Torque the bearing cap bolts of the bearing
being checked to the proper specifications.
(3) Remove the bearing cap and compare the
width of the flattened Plastigage (Fig. 4) with the
metric scale provided on the package. Locate the
band closest to the same width. This band shows the
amount of clearance in thousandths of a millimeter.
Differences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken.
Refer to Engine Specifications.Plastigage gener-
ally is accompanied by two scales. One scale is
in inches, the other is a metric scale.
NOTE: Plastigage is available in a variety of clear-
ance ranges. Use the most appropriate range for
the specifications you are checking.
CONNECTING ROD BEARING CLEARANCE
Engine connecting rod bearing clearances can be
determined by use of Plastigage or equivalent. The
following is the recommended procedure for the use
of Plastigage:(1) Rotate the crankshaft until the connecting rod
to be checked is at the bottom of its stroke.
(2) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(3) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the bearing cap approx-
imately 6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from
the oil hole (Fig. 3). In addition, suspect areas can be
checked by placing plastigage in the suspect area.
(4) Assemble the rod cap with Plastigage in place.
Tighten the rod cap to the specified torque.Do not
rotate the crankshaft while assembling the cap
or the Plastigage may be smeared, giving inac-
curate results.
(5) Remove the bearing cap and compare the
width of the flattened Plastigage (Fig. 4) with the
scale provided on the package. Locate the band clos-
est to the same width. This band indicates the
amount of oil clearance. Differences in readings
between the ends indicate the amount of taper
present. Record all readings taken. Refer to Engine
Specifications.Plastigage generally is accompa-
nied by two scales. One scale is in inches, the
other is a metric scale. If the bearing clearance
exceeds 0.076 mm (0.003 in.) replace bearing.
NOTE: Plastigage is available in a variety of clear-
ance ranges. Use the most appropriate range for
the specifications you are checking.
REPAIR OF DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
Damaged or worn threads (including aluminum
head spark plug threads) can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of drilling out worn or
damaged threads, tapping the hole with a special
Heli-Coil Tap, (or equivalent) and installing an insert
into the tapped hole. This brings the hole back to its
original thread size.
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original centerline.
Heli-Coil tools and inserts are readily available
from automotive parts jobbers.
HYDROSTATIC LOCKED ENGINE
When an engine is suspected to be hydrostatically
locked, regardless of what caused the problem, these
steps should be used.
CAUTION: Do Not Use Starter Motor To Rotate
Engine, severe damage may occur.
(1) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and
intake manifold to insure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
Fig. 4 Clearance Measurement
9 - 4 ENGINEPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 722 of 1200

(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.
(5)If the oil leak source is not positively
identified at this time, proceed with the air leak
detection test method as follows:
(6) Disconnect the fresh air hose (makeup air) at
the cylinder head cover and plug or cap the nipple on
the cover.
(7) Remove the PCV valve hose from the cylinder
head cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve nipple on the
cover.
(8) Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and
regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
(9) Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provide the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
(10) If the leakage occurs at the rear oil seal area,
refer to the section, Inspection for Rear Seal Area
Leak.
(11) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air sup-
ply and remove the air hose and all plugs and caps.
Install the PCV valve and breather cap hose. Proceed
to next step.
(12) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area
using a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. Thefollowing steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak. If a leak is
present in this area remove transmission for further
inspection.
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, oil galley cup
plug, bedplate to cylinder block mating surfaces
and seal bore. See proper repair procedures for
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurized the crank-
case as outlined in the, Inspection (Engine oil Leaks
in general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified. Refer to Rear
Crankshaft Seals, for proper replacement procedures.
PLENGINE 9 - 9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 725 of 1200

2.0L SOHC ENGINE
INDEX
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE COMPONENTS.................. 14
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION................. 12
ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM............ 13
GENERAL SPECIFICATION................ 12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE......... 14
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY................. 16
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON SIZING....... 14
FITTING CONNECTING RODS.............. 16
FITTING CRANKSHAFT BEARINGS.......... 16
FITTING PISTON RINGS.................. 16
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL.................... 28
CAMSHAFT............................ 22
CRANKSHAFT DAMPER.................. 46
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEALÐFRONT........... 37
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEALÐREAR............ 38
CRANKSHAFT.......................... 39
CYLINDER HEAD COVER................. 21
CYLINDER HEAD........................ 25
ENGINE ASSEMBLY...................... 19
ENGINE MOUNTÐFRONT................. 18
ENGINE MOUNTÐLEFT................... 18
ENGINE MOUNTÐRIGHT................. 18
OIL FILTER ADAPTER.................... 42OILFILTER ............................ 42
OILPAN ............................... 36
OIL PUMP............................. 42
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD........... 44
POWER HOP DAMPER................... 18
ROCKER ARM/HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER . . 23
SPARK PLUG TUBE...................... 21
STRUCTURAL COLLARÐ2.0L.............. 19
TIMING BELT COVER.................... 27
TIMING BELT TENSIONERÐMECHANICAL.... 36
TIMING BELTÐWITH HYDRAULIC TENSIONER . 28
TIMING BELTÐWITH MECHANICAL
TENSIONER.......................... 33
VALVE SEALS AND SPRINGS IN VEHICLE.... 24
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
OIL PUMP............................. 47
VALVE SERVICE WITH THE CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVED........................... 47
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BORE............. 51
CYLINDER HEAD AND CAMSHAFT JOURNALS . 50
OIL PUMP............................. 50
SPECIFICATIONS
2.0L SOHC............................. 52
TORQUE CHART 2.0L SOHC............... 54
SPECIAL TOOLS
2.0L SOHC............................. 55
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION
The engine identification number is located on the
left rear of the cylinder block behind starter (Fig. 1).
GENERAL SPECIFICATION
Type ..............In-Line OHV, DOHC & SOHC
Bore......................87.5mm (3.445 Inch)
Stroke.....................83.0mm (3.268 inch)
Compression Ratio.....DOHC - 9.6:1 SOHC - 9.8:1
Displacement..........2.0 Liters (122 Cubic Inch)
Firing Order.........................1,3,4,2
Compression Pressure............1172-1551 kPa
(170 - 225 psi)
Maximum Variation Between Cylinders.......25%
Lubrication. . . .Pressure Feed - Full Flow Filtration
(Crankshaft Driven Pump)
Engine Oil Capacity............Refer to Group 0,
Lubrication and Maintenance
Fig. 1 Engine Identification SOHC
9 - 12 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
Page 726 of 1200
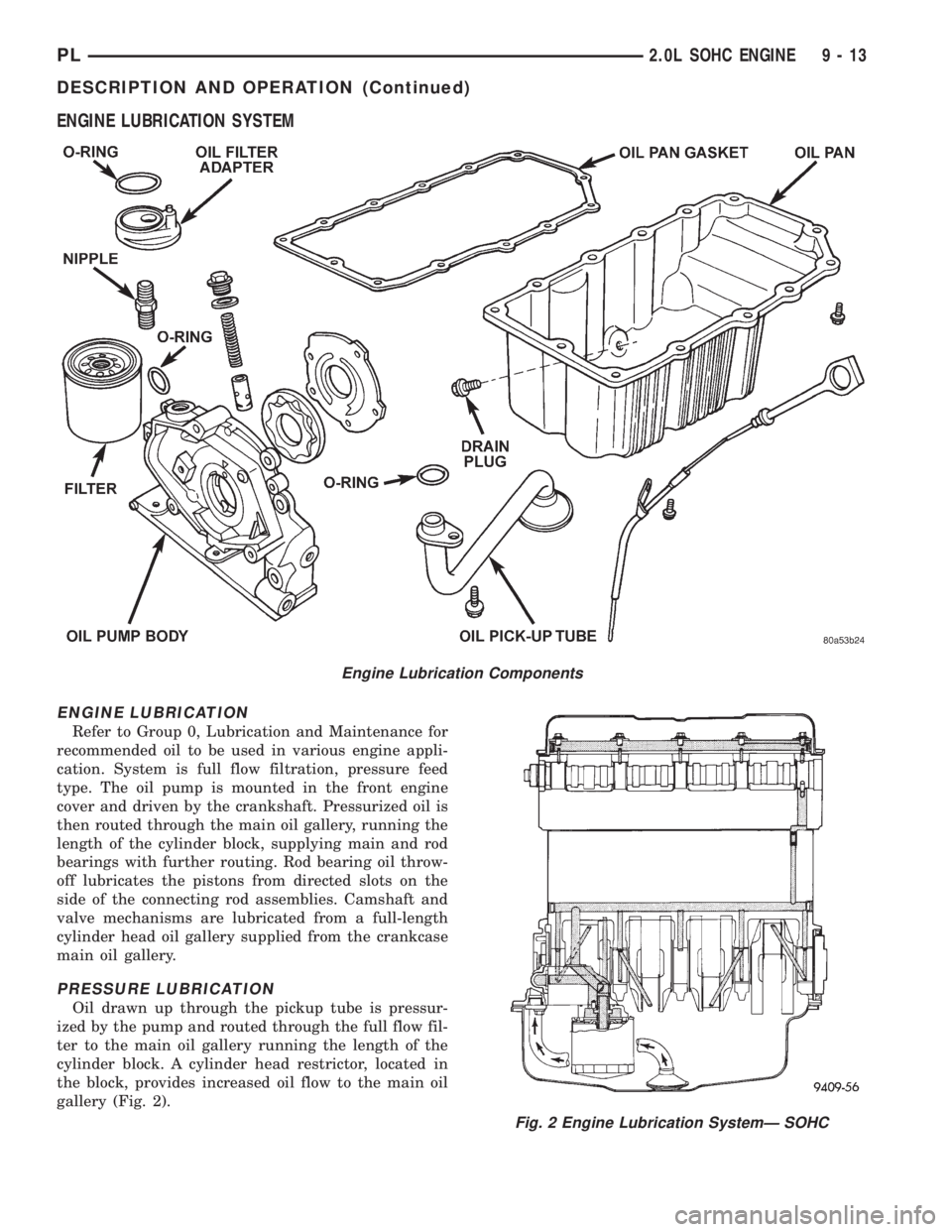
ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM
ENGINE LUBRICATION
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
recommended oil to be used in various engine appli-
cation. System is full flow filtration, pressure feed
type. The oil pump is mounted in the front engine
cover and driven by the crankshaft. Pressurized oil is
then routed through the main oil gallery, running the
length of the cylinder block, supplying main and rod
bearings with further routing. Rod bearing oil throw-
off lubricates the pistons from directed slots on the
side of the connecting rod assemblies. Camshaft and
valve mechanisms are lubricated from a full-length
cylinder head oil gallery supplied from the crankcase
main oil gallery.
PRESSURE LUBRICATION
Oil drawn up through the pickup tube is pressur-
ized by the pump and routed through the full flow fil-
ter to the main oil gallery running the length of the
cylinder block. A cylinder head restrictor, located in
the block, provides increased oil flow to the main oil
gallery (Fig. 2).
Engine Lubrication Components
Fig. 2 Engine Lubrication SystemÐ SOHC
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 13
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 727 of 1200

MAIN/ROD BEARINGS
A diagonal hole in each bulkhead feeds oil to each
main bearing. Drilled passages within the crankshaft
route oil from main bearing journals to connecting
rod journals.
CAMSHAFT/HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTERS
A vertical hole at the number five bulkhead routes
pressurized oil through a restrictor up into the cylin-
der head. The rocker shafts route oil to the rocker
arms/hydraulic lash adjuster assemblies.
SPLASH LUBRICATION
Oil returning to the pan from pressurized compo-
nents supplies lubrication to the valve stems. Cylin-
der bores and wrist pins are splash lubricated from
directed slots on the connecting rod thrust collars.
ENGINE COMPONENTS
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BEDPLATE ASSEM-
B LY:A partial open deck is used for cooling and
weight reduction with water pump molded into the
block. Nominal wall thickness is 4 mm. The bedplate
incorporates main bearing caps. Rear seal retainer is
integral with the block.
CRANKSHAFT:A nodular cast iron crankshaft is
used. The engine has 5 main bearings, with number
3 flanged to control thrust. The 52 mm diameter
main and 48 mm diameter crank pin journals (all)
have undercut fillet radiuses that are deep rolled for
added strength. To optimize bearing loading 8 coun-
terweights are used. Hydrodynamic seals provide end
sealing, where the crankshaft exits the block.
Anaerobic gasket material is used for parting line
sealing. A sintered iron timing belt sprocket is
mounted on the crankshaft nose. This sprocket trans-
mits crankshaft movement, via timing belt to the
camshaft sprocket providing timed valve actuation.
PISTONS:The SOHC EngineDOES NOThave
provision for a free wheeling valve train. Non free
wheeling valve train means, in the event of a broken
timing belt Pistons will contact the Valves. All
engines use pressed-in piston pins to attach forged
powdered metal connecting rods. The connecting rods
are a cracked cap design and are not repairable. Hex
head cap screw are used to provide alignment and
durability in the assembly. Pistons And Connecting
rods are serviced as an assembly.
PISTON RINGS:The piston rings include a
molybdenum faced top ring for reliable compression
sealing and a taper faced intermediate ring for addi-
tional cylinder pressure control. Oil Control Ring
Package consist of 2 steel rails and a expander
spacer.
CYLINDER HEADÐSOHC:It features a Single
Over Head Camshaft, four-valves per cylinder cross
flow design. The valves are arranged in two inlinebanks, with the two intake per cylinder facing
toward the radiator. The exhaust valves facing
toward the dash panel. Rocker arm shafts mount
directly to the cylinder head. It incorporates powder
metal valve guides and seats. The hollow rocker arm
shafts supplies oil to the hydraulic lash adjusters,
camshaft and valve mechanisms.
CAMSHAFTÐSOHC:The nodular iron camshaft
has five bearing journals and 3 cam lobes per cylin-
der. Provision for cam position sensor on the cam at
the rear of cylinder head which also acts as thrust
plate. A hydrodynamic oil seal is used for oil control
at the front of the camshaft.
VALVESÐSOHC:Four valves per cylinder are
actuated by roller rocker arms/hydraulic lash adjust-
ers assemblies which pivot on rocker arm shafts. All
valves have 6 mm diameter chrome plated valve
stems. The valve train has 33 mm (1.299 inch) diam-
eter intake valves and 28 mm (1.10 inch) diameter
exhaust valves. Viton rubber valve stem seals are
integral with spring seats. Valve springs, spring
retainers, and locks are conventional design.
INTAKE MANIFOLD:The intake manifold is a
molded plastic composition, attached to the cylinder
head with ten fasteners. This long branch design
enhances low and mid-range torque.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD:The exhaust manifold is
made of nodular cast iron for strength and high tem-
peratures. Exhaust gasses exit through a machined,
articulated joint connection to the exhaust pipe.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure switch and install gauge
assembly C-3292 with adaptor.
(2) Run engine until thermostat opens.
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, Do Not per-
form the 3000 RPM test in the next step.
(3) Oil Pressure:Curb Idle25 kPa (4 psi) mini-
mum3000 RPM170-550 kPa (25-80 psi).
(4) If oil pressure is 0 at idle. Shut off engine,
check for pressure relief valve stuck open, a clogged
oil pick-up screen or a damaged oil pick-up tube
O-ring.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON SIZING
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with Tool C-119 (Fig. 3). The cylin-
der bore out-of-round is 0.050 mm (.002 inch)
maximum and cylinder bore taper is 0.051 mm (0.002
9 - 14 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 728 of 1200

inch) maximum. If the cylinder walls are badly
scuffed or scored, the cylinder block should be
rebored and honed, and new pistons and rings fitted.
Whatever type of boring equipment is used, boring
and honing operation should be closely coordinated
with the fitting of pistons and rings in order that
specified clearances may be maintained.Refer to
Honing Cylinder Bores outlined in the Stan-
dard Service Procedures for specification and
procedures.
Measure the cylinder bore at three levels in direc-
tions A and B (Fig. 3). Top measurement should be
10 mm (3/8 inch) down and bottom measurement
should be 10 mm (3/8 inch.) up from bottom of bore.
Refer to Cylinder Bore and Piston Specifications
Chart.
SIZING PISTONS
Piston and cylinder wall must be clean and dry.
Piston diameter should be measured 90 degrees to
piston pin about 17.5 mm (11/16 inch) from the bot-
tom of the skirt as shown in (Fig. 4). Cylinder boresshould be measured halfway down the cylinder bore
and transverse to the engine crankshaft center line
shown in (Fig. 3). Refer to Cylinder Bore and Speci-
fications Table. Correct piston to bore clearance must
be established in order to assure quiet and economi-
cal operation.
Chrysler engines use pistons designed specifically
for each engine model. Clearance and sizing locations
vary with respect to engine model.
NOTE: Pistons and cylinder bores should be mea-
sured at normal room temperature, 21ÉC (70ÉF).
Fig. 3 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON
SPECIFICATION CHART
Standard Bore Maximum
Out-of-RoundMaximum Taper
87.5 mm
(3.445 in.)0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)
Standard Piston Size
Federal Emission: 87.463 - 87.481 mm
(3.4434 - 3.4441 in.)
Low Emission
Vehicle (LEV):87.456 - 87.474 mm
(3.4432 - 3.4439 in.)
Piston to Bore Clearance
Federal Emission: 0.012 - 0.044 mm (0.0004 - 0.0017 in.)
Low Emission
Vehicle (LEV):0.18 - 0.050 mm (0.0008 - 0.0020 in.)
Measurements Taken at Piston Size Location
Fig. 4 Piston Measurements
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 15
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)