air filter DODGE NEON 1999 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 5 of 1200

²Replace air cleaner element.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transmission fluid.
37,500 Miles (60 000 km) or at 30 months
²Change engine oil.
45,000 Miles (72 000 km) or at 36 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Flush and replace engine coolant at 36 months,
regardless of mileage.
52,500 Miles (84 000 km) or at 42 months
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if not done at
36 months.
60,000 Miles (96 000 km) or at 48 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Check and replace, if necessary***, the PCV
valve.**
²Lubricate front suspension upper ball joints.
²Replace drive belts.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Replace ignition cables.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transmission fluid.
67,500 Miles (108 000 km) or at 54 months
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
75,000 Miles (120 000 km) or at 60 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
82,500 Miles (132 000 km) or at 66 months
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
90,000 Miles (144 000 km) or at 72 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Check and replace, if necessary***, the PCV
valve.**
²Lubricate front suspension upper ball joints.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Replace air cleaner air cleaner element.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transmission fluid.
97,500 Miles (156 000 km) or at 78 months
²Change engine oil.
105,000 Miles (168 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace engine timing belt
²Adjust drive belt tension.
SCHEDULE ± B
NOTE: * Follow this schedule if you usually operate
your vehicle under one or more of the following
conditions. Change the automatic transmission
fluid and filter every 15,000 miles (24 000 km) if you
usually operate your vehicle under one of the con-
ditions marked with an *.
3,000 Miles (5 000 km)
²Change engine oil
6,000 Miles (10 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
9,000 Miles (14 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake lining.
12,000 Miles (19 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
15,000 Miles (24 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Inspect and replace, if required, the air
cleaner element.
²Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
18,000 Miles (29 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
21,000 Miles (34 000 km)
²Change engine oil
0 - 4 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 6 of 1200

24,000 Miles (38 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
27,000 Miles (43 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
30,000 Miles (48 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Check and replace, if necessary, the PCV
valve.**
²Lubricate front suspension upper ball joints.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transmission fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
33,000 Miles (53 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
36,000 Miles (58 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Flush and replace engine coolant.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
39,000 Miles (62 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
42,000 Miles (67 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
45,000 Miles (72 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
²Inspect and replace, if necessary, the air
cleaner element.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
48,000 Miles (77 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
51,000 Miles (82 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant.
54,000 Miles (86 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
57,000 Miles (91 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
60,000 Miles (96 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Check and replace, if necessary***, the PCV
valve.**
²Lubricate front suspension upper ball joints.
²Replace drive belts.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Replace ignition cables.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
63,000 Miles (101 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
66,000 Miles (106 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
69,000 Miles (110 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
72,000 Miles (115 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
75,000 Miles (120 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Inspect and replace, if necessary, the air
cleaner element.
²Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
78,000 Miles (125 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
81,000 Miles (130 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace the engine coolant.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
84,000 Miles (134 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
87,000 Miles (139 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
PLLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 5
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 7 of 1200

90,000 Miles (144 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
²Check and replace, if necessary***, the PCV
valve.**
²Lubricate front suspension upper ball joints.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
93,000 Miles (149 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
96,000 Miles (154 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
99,000 Miles (158 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
102,000 Miles (163 000km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
105,000 Miles (168 000km)
²Replace the engine timing belt
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Inspect and replace, if necessary, the air
cleaner element.
NOTE: **This maintenance is recommended by
Chrysler to the owner but is not required to main-
tain the warranty on the PCV valve.
NOTE: ***This maintenance is not required if the
PCV valve was previously replaced.
0 - 6 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 262 of 1200

SPARK PLUG CABLE SERVICE
Failure to route the cables properly could cause the
radio to reproduce ignition noise, cross ignition of the
spark plugs or short circuit the cables to ground.
REMOVAL
Remove spark plug cable from coil frist.
Always remove the spark plug cable by grasping
the top of the spark plug insulator, turning the boot
1/2 turn and pulling straight up in a steady motion.
INSTALLATION
Install spark plug insulators over spark plugs.
Ensure the top of the spark plug insulator covers the
upper end of the spark plug tube.The connect the
other end to coil pack. OnSOHCengines, be sure
that dual plastic clip holds #1,#2 cables off of valve
cover and that PCV hose plastic clip holds #3 cable
away from metal PCV clamp and edge of air duct. On
DOHC, be sure that the plastic clip on PCV hose is
positioned so that cable clip is beneath hose, and that
#1 cable is snapped into this clip to protect it from
metal PCV clamp.
SPARK PLUG TUBES
The spark plugs tubes are pressed into the cylinder
head. Sealant is applied to the end of the tube before
installation. For engine information, refer to Group
9, Engines.
IGNITION COIL
SOHC/DOHC
The electronic ignition coil pack attaches directly
to the valve cover (Fig. 29) or (Fig. 30).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from coil pack.
(2) Remove coil pack mounting nuts.
(3) Remove coil pack.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install coil pack on valve cover.
(2) Transfer spark plug cables to new coil pack.
The coil pack towers are numbered with the cylinder
identification. Be sure the ignition cables snap onto
the towers.
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAY
The relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC) (Fig. 31). The PDC is located next to the
battery in the engine compartment. For the location
of the relay within the PDC, refer to the PDC cover
for location. Check electrical terminals for corrosion
and repair as necessary.CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐSOHC
The camshaft position sensor is mounted to the
rear of the cylinder head (Fig. 32).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the filtered air tube from the throt-
tle body and air cleaner housing. Remove filtered air
tube.
Fig. 29 Electronic Ignition Coil PackÐSOHC
Fig. 30 Electronic Ignition Coil PackÐDOHC
Fig. 31 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
PLIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 13
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 263 of 1200
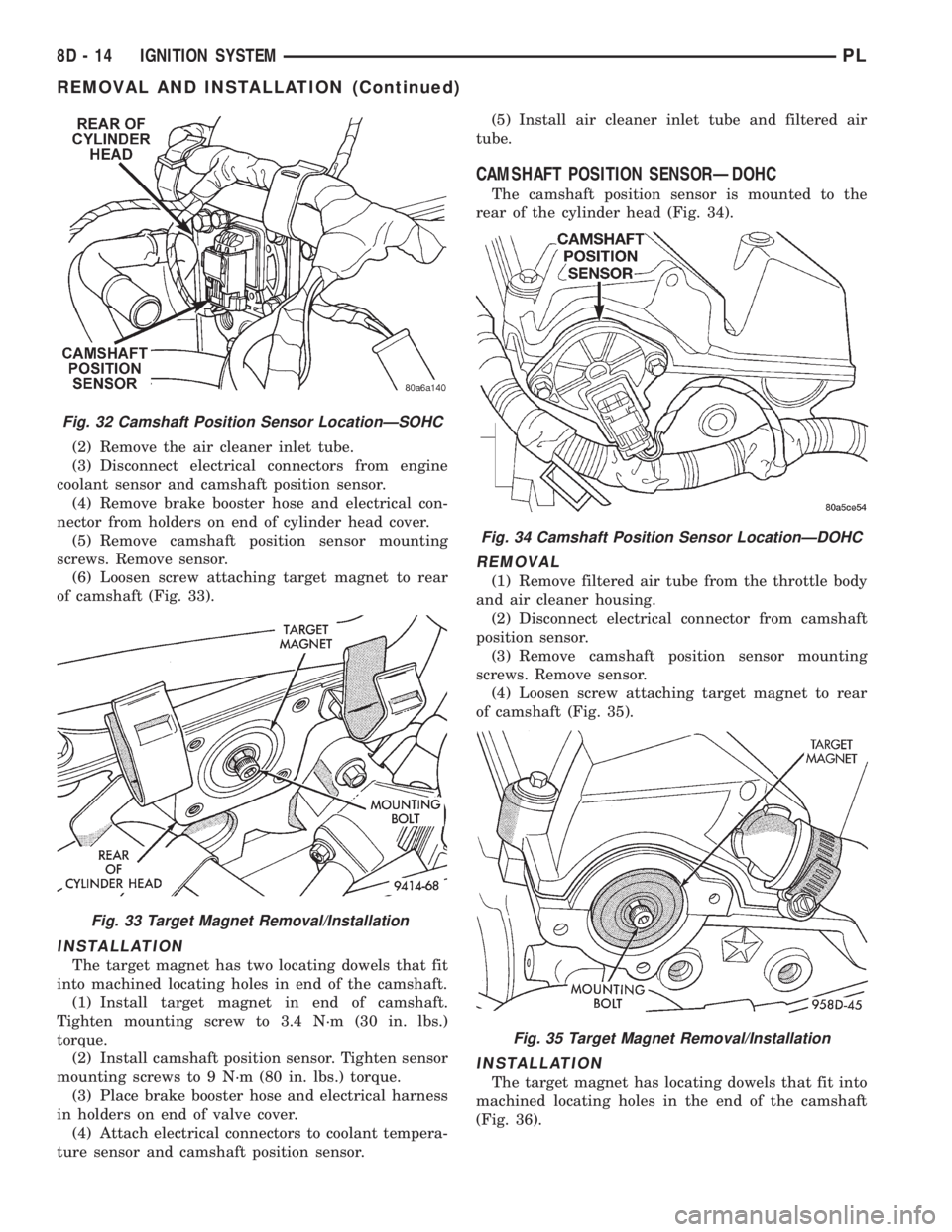
(2) Remove the air cleaner inlet tube.
(3) Disconnect electrical connectors from engine
coolant sensor and camshaft position sensor.
(4) Remove brake booster hose and electrical con-
nector from holders on end of cylinder head cover.
(5) Remove camshaft position sensor mounting
screws. Remove sensor.
(6) Loosen screw attaching target magnet to rear
of camshaft (Fig. 33).
INSTALLATION
The target magnet has two locating dowels that fit
into machined locating holes in end of the camshaft.
(1) Install target magnet in end of camshaft.
Tighten mounting screw to 3.4 N´m (30 in. lbs.)
torque.
(2) Install camshaft position sensor. Tighten sensor
mounting screws to 9 N´m (80 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Place brake booster hose and electrical harness
in holders on end of valve cover.
(4) Attach electrical connectors to coolant tempera-
ture sensor and camshaft position sensor.(5) Install air cleaner inlet tube and filtered air
tube.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐDOHC
The camshaft position sensor is mounted to the
rear of the cylinder head (Fig. 34).
REMOVAL
(1) Remove filtered air tube from the throttle body
and air cleaner housing.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from camshaft
position sensor.
(3) Remove camshaft position sensor mounting
screws. Remove sensor.
(4) Loosen screw attaching target magnet to rear
of camshaft (Fig. 35).
INSTALLATION
The target magnet has locating dowels that fit into
machined locating holes in the end of the camshaft
(Fig. 36).
Fig. 32 Camshaft Position Sensor LocationÐSOHC
Fig. 33 Target Magnet Removal/Installation
Fig. 34 Camshaft Position Sensor LocationÐDOHC
Fig. 35 Target Magnet Removal/Installation
8D - 14 IGNITION SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 264 of 1200

(1) Install target magnet in end of camshaft.
Tighten mounting screw to 3 N´m (30 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install camshaft position sensor. Tighten sensor
mounting screws to 9 N´m (80 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Carefully attach electrical connector to cam-
shaft position sensor. Installation at an angle may
damage the sensor pins.
(4) Install filtered air tube. Tighten clamps to 3
N´m61 (25 in. lbs.65) torque.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The crankshaft position sensor mounts to the
engine block behind the generator, just above the oil
filter (Fig. 37).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from crankshaft
position sensor.
(2) Remove sensor mounting screw. Remove sensor.
INSTALLATION
Reverse procedure for installation.
COMBINATION ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSORÐSOHC
The combination engine coolant sensor is located at
the rear of the cylinder head next to the camshaft
position sensor (Fig. 38). New sensors have sealant
applied to the threads.
REMOVAL
(1) With the engine cold, drain the cooling system
until coolant level drops below sensor. Refer to Group
7, Cooling System.
(2) Disconnect coolant sensor electrical connector.
(3) Remove coolant sensor
INSTALLATION
(1) Install coolant sensor. Tighten sensor to 18.6
N´m (165 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Attach electrical connector to sensor.
(3) Fill cooling system. Refer to Group 7, Cooling
System.
COMBINATION ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSORÐDOHC
The coolant sensor threads into the intake mani-
fold next to the thermostat housing (Fig. 39). New
sensors have sealant applied to the threads.
REMOVAL
(1) With the engine cold, drain coolant until level
drops below cylinder head. Refer to Group 7, Cooling
System.
(2) Disconnect coolant sensor electrical connector.
(3) Remove coolant sensor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install coolant sensor. Tighten sensor to 18.6
N´m (165 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Attach electrical connector to sensor.
(3) Fill cooling system. Refer to Group 7, Cooling
System.
Fig. 36 Target Magnet Installation
Fig. 37 Crankshaft Position Sensor
Fig. 38 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
PLIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 15
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 715 of 1200

assure gasket rails are flat. Flatten rails with a ham-
mer on a heavy steel plate if required. Gasket sur-
faces must be free of oil and dirt. Make sure old
gasket material is removed from blind attaching
holes.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier then using precut gas-
kets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 inch.) diameter or less of seal-
ant to one gasket surface. Be certain the material
surrounds each mounting hole. Excess material can
easily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
The MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant gas-
ket material or equivalent should be applied in a con-
tinuous bead approximately 3 mm (0.120 inch) in
diameter. All mounting holes must be circled. For
corner sealing, a 3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 inch.)
drop is placed in the center of the gasket contact
area. Uncured sealant may be removed with a shop
towel. Components should be torqued in place while
the sealant is still wet to the touch (within 10 min-
utes). The usage of a locating dowel is recommended
during assembly to prevent smearing material off the
location.
CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET BOLT ACCESS PLUG
An Access plug is located in the right inner fender
shield. Remove the plug and insert the proper size
socket, extension and ratchet, when crankshaft rota-
tion is necessary.
ENGINE CORE PLUGS
REMOVAL
Using a blunt tool such as a drift or a screwdriver
and a hammer, strike the bottom edge of the cup
plug (Fig. 1). With the cup plug rotated, grasp firmly
with pliers or other suitable tool and remove plug
(Fig. 1).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting
as restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
INSTALLATION
Thoroughly remove all rust and clean inside of cup
plug hole in cylinder block or head. Be sure to
remove old sealer. Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole
with sealer. Make certain the new plug is cleaned of
all oil or grease. Using proper drive plug, drive plug
into hole so that the sharp edge of the plug is atleast 0.5 mm (0.020 inch.) inside the lead in chamfer
(Fig. 1).
It is in not necessary to wait for curing of the seal-
ant. The cooling system can be refilled and the vehi-
cle placed in service immediately.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
If a loss of performance is noticed, timing belt or
chain may have skipped one or two teeth. Camshaft
and crankshaft timing should be checked. Refer to
Group 9, Engine Timing belt or chain installation.
It is important that the vehicle is operating to its
optimum performance level to maintain fuel economy
and lowest vehicle emissions. If vehicle is not operat-
ing to these standards, refer to Engine Diagnosis out-
lined is this section. The following procedures can
assist in achieving the proper engine diagnosis.
(1) Test cranking amperage draw. Refer to Group
8B, Starting.
(2) Check intake manifold for vacuum leaks.
(3) Perform cylinder compression pressure test.
Refer to Engine Diagnosis, outlined in this section.
(4) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary and
adjust gap as specified in Group 8D, Ignition System.
Tighten to specifications.
(5) Test resistance of spark plug cables. Refer to
Group 8D, Ignition System.
(6) Test ignition coils primary and secondary resis-
tance. Replace parts as necessary. Refer to Group 8D,
Ignition System.
(7) Check fuel pump pressure at idle and different
RPM ranges. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System for
Specifications.
(8) The air filter elements should be replaced as
specified in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance.
(9) Inspect crankcase ventilation system as out-
lined in Group 25, Emission Control Systems.
(10) Road test vehicle as a final test.
Fig. 1 Core Hole Plug Removal
9 - 2 ENGINEPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 718 of 1200

(2) Remove negative battery cable.
(3) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs
when removing them from the engine. This will catch
any fluid that may possibly be in the cylinder under
pressure.
(4) With all spark plugs removed, rotate engine
crankshaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(5) Identify the fluid in the cylinder(s) (i.e., cool-
ant, fuel, oil or other).
(6) Make sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders. Inspect engine for damage (i.e., Connecting
Rods, Pistons, Valves etc.)
(7) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
CAUTION: Squirt approximately 1 teaspoon of oil
into cylinders, rotate engine to lubricate the cylin-
der walls to prevent damage on restart.
(8) Install new spark plugs.
(9) Drain engine oil and remove oil filter.
(10) Fill engine with specified amount of approved
oil and install new oil filter.
(11) Connect negative battery cable.
(12) Start engine and check for any leaks.
CHECKING ENGINE OIL LEVEL
The best time to check engine oil level is after it
has sat overnight, or if the engine has been running,
allow the engine to be shut off for at least 5 minutes
before checking oil level.
Checking the oil while the vehicle is on level
ground will improve the accuracy of the oil level
reading. Add only when the level is at or below the
ADD mark (Fig. 5).
ENGINE OIL SERVICE
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY. CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR GOVERN-MENT AGENCY FOR LOCATION OF COLLECTION
CENTER IN YOUR AREA.
ENGINE OIL SPECIFICATION
CAUTION: Do not use non-detergent or straight
mineral oil when adding or changing crankcase
lubricant. Engine failure can result.
API SERVICE GRADE CERTIFIED
Use an engine oil that is API Service Grade Certi-
fied. MOPARtprovides engine oils that conforms to
this service grade.
SAE VISCOSITY
An SAE viscosity grade is used to specify the vis-
cosity of engine oil. Use only, engine oils with multi-
ple viscosities such as 5W-30 or 10W-30. These are
specified with a dual SAE viscosity grade which indi-
cates the cold-to-hot temperature viscosity range.
Select an engine oil that is best suited to your par-
ticular temperature range and variation (Fig. 6).
ENERGY CONSERVING OIL
An Energy Conserving type oil is recommended for
gasoline engines. They are designated as either
ENERGY CONSERVING or ENERGY CONSERV-
ING II.
CONTAINER IDENTIFICATION
Standard engine oil identification notations have
been adopted to aid in the proper selection of engine
oil. The identifying notations are located on the label
of engine oil plastic bottles and the top of engine oil
cans (Fig. 7).
ENGINE OIL CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in the Maintenance Schedule.
TO CHANGE ENGINE OIL
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
Fig. 5 Oil Level
Fig. 6 Temperature/Engine Oil Viscosity
PLENGINE 9 - 5
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 721 of 1200

cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
(11) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary
and adjust gap as specified in Group 8, Electrical.
Tighten to specifications.
(12) Test resistance of spark plug cables. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical Ignition System Secondary Cir-
cuit Inspection.
(13) Test coil output voltage, primary and second-
ary resistance. Replace parts as necessary. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical Ignition System.
(14) Check fuel pump pressure at idle and differ-
ent RPM ranges. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System for
Specifications.
(15) The air filter elements should be replaced as
specified in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance,.
(16) Inspect crankcase ventilation system as out
lined in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance. For
emission controls see Group 25, Emission Controls
for service procedures.
(17) Inspect and adjust accessory belt drives refer-
ring to Group 7, Cooling System, Accessory Drive
Belts for proper adjustments.
(18) Road test vehicle as a final test.
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1 379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
LASH ADJUSTER (TAPPET) NOISE DIAGNOSIS
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) During this time, turn engine off and let set for
a few minutes before restarting. Repeat this several
times after engine has reached normal operating
temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor pressed into the vertical oil
passage to the cylinder head is plugged with debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Faulty lash adjuster.
a. Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head. Depress part of rocker
arm over adjuster. Normal adjusters should feel very
firm. Spongy adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected rocker arms (sohc) or lash
adjuster (dohc) and replace.
INSPECTION (ENGINE OIL LEAKS IN GENERAL)
Begin with a through visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
9 - 8 ENGINEPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 723 of 1200
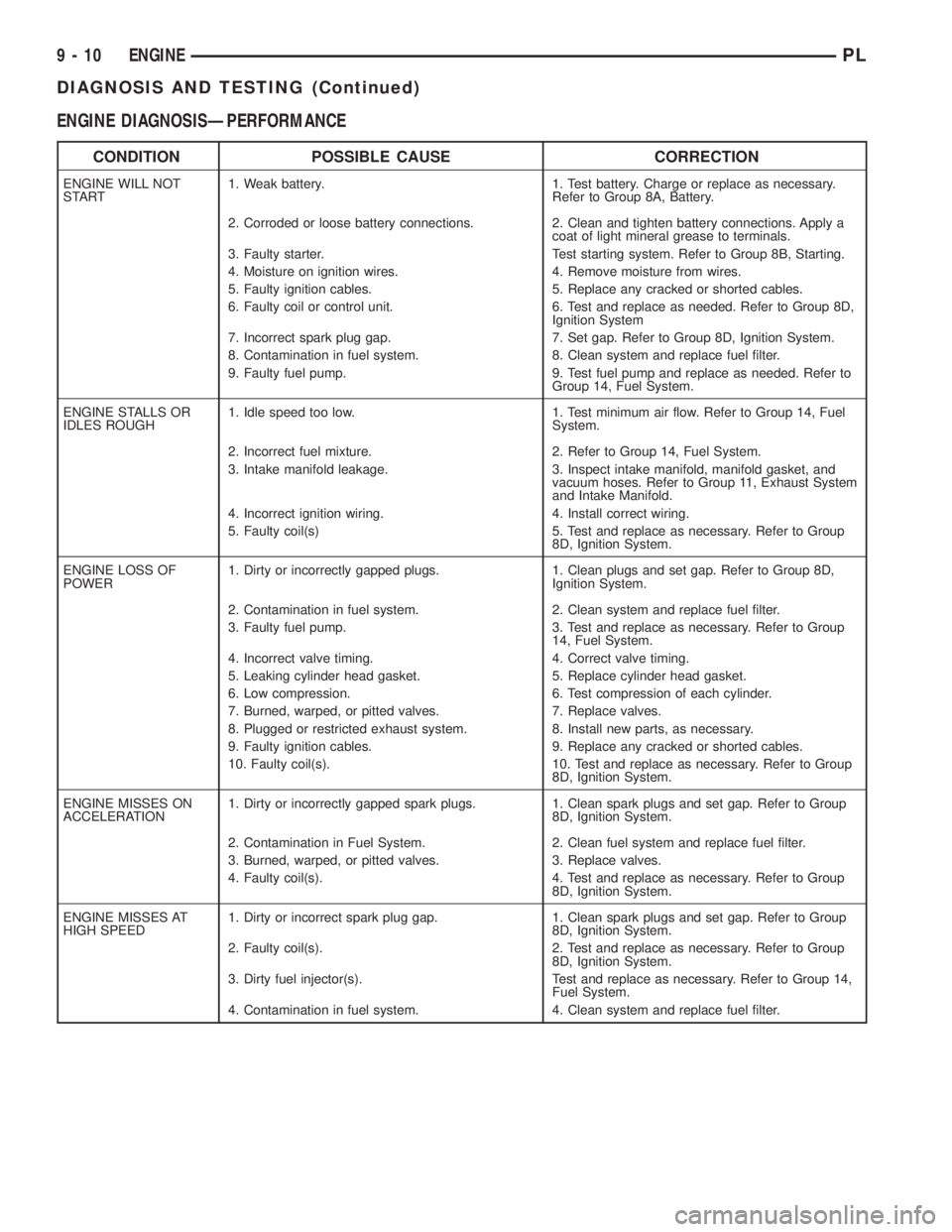
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐPERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT
START1. Weak battery. 1. Test battery. Charge or replace as necessary.
Refer to Group 8A, Battery.
2. Corroded or loose battery connections. 2. Clean and tighten battery connections. Apply a
coat of light mineral grease to terminals.
3. Faulty starter. Test starting system. Refer to Group 8B, Starting.
4. Moisture on ignition wires. 4. Remove moisture from wires.
5. Faulty ignition cables. 5. Replace any cracked or shorted cables.
6. Faulty coil or control unit. 6. Test and replace as needed. Refer to Group 8D,
Ignition System
7. Incorrect spark plug gap. 7. Set gap. Refer to Group 8D, Ignition System.
8. Contamination in fuel system. 8. Clean system and replace fuel filter.
9. Faulty fuel pump. 9. Test fuel pump and replace as needed. Refer to
Group 14, Fuel System.
ENGINE STALLS OR
IDLES ROUGH1. Idle speed too low. 1. Test minimum air flow. Refer to Group 14, Fuel
System.
2. Incorrect fuel mixture. 2. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System.
3. Intake manifold leakage. 3. Inspect intake manifold, manifold gasket, and
vacuum hoses. Refer to Group 11, Exhaust System
and Intake Manifold.
4. Incorrect ignition wiring. 4. Install correct wiring.
5. Faulty coil(s) 5. Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
ENGINE LOSS OF
POWER1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped plugs. 1. Clean plugs and set gap. Refer to Group 8D,
Ignition System.
2. Contamination in fuel system. 2. Clean system and replace fuel filter.
3. Faulty fuel pump. 3. Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group
14, Fuel System.
4. Incorrect valve timing. 4. Correct valve timing.
5. Leaking cylinder head gasket. 5. Replace cylinder head gasket.
6. Low compression. 6. Test compression of each cylinder.
7. Burned, warped, or pitted valves. 7. Replace valves.
8. Plugged or restricted exhaust system. 8. Install new parts, as necessary.
9. Faulty ignition cables. 9. Replace any cracked or shorted cables.
10. Faulty coil(s). 10. Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark plugs. 1. Clean spark plugs and set gap. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
2. Contamination in Fuel System. 2. Clean fuel system and replace fuel filter.
3. Burned, warped, or pitted valves. 3. Replace valves.
4. Faulty coil(s). 4. Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
ENGINE MISSES AT
HIGH SPEED1. Dirty or incorrect spark plug gap. 1. Clean spark plugs and set gap. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
2. Faulty coil(s). 2. Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
3. Dirty fuel injector(s). Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group 14,
Fuel System.
4. Contamination in fuel system. 4. Clean system and replace fuel filter.
9 - 10 ENGINEPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)