heating DODGE NEON 1999 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 12 of 1200

SUSPENSION
CONTENTS
page page
FRONT SUSPENSION..................... 10
REAR SUSPENSION...................... 39WHEEL ALIGNMENT....................... 1
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
INDEX
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COMPETITION PACKAGE ALIGNMENT........ 2
WHEEL ALIGNMENT GENERAL
INFORMATION......................... 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
PRE-ALIGNMENT VEHICLE INSPECTION...... 5
SUSPENSION AND STEERING DIAGNOSIS.... 3SERVICE PROCEDURES
WHEEL ALIGNMENT CHECK AND
ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE.............. 5
SPECIFICATIONS
VEHICLE ALIGNMENT SPECIFICATIONS AT
CURB HEIGHT......................... 9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
WHEEL ALIGNMENT GENERAL INFORMATION
Proper vehicle wheel alignment is the proper
adjustment of all interrelated front and rear suspen-
sion angles (Fig. 1). These angles are what affects
the handling and steering of the vehicle when it is in
motion.
The method of checking a vehicle's front and rear
wheel alignment will vary depending on the type and
manufacturer of the equipment being used. Instruc-
tions furnished by the manufacturer of the equip-
ment being used should always be followed to ensure
accuracy of the alignment, except alignment specifi-
cations recommended by Chrysler Corporation
MUST ALWAYSbe used.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to modify any suspen-
sion or steering components by heating or bending
of the component.Wheel alignment adjustments should be made in
the following sequence, to ensure that an accurate
alignment is performed.
(1) Rear Wheel Toe Adjustment within specifica-
tions for both total toe and thrust angle.
(2) Front Wheel Toe Adjustment within specifica-
tions for total toe.
(3)To eis measured in degrees or inches and is
the distance that the front edges of the tires are
closer (or farther apart) than the rear edges (Fig. 1).
See Front Wheel Drive Specifications for correct front
and rear wheel Toe specifications.
(4)Thrust Angleis defined as the average of the
Toe settings on each rear wheel. If this measurement
is out of specification, re-adjust rear wheel Toe so
that each wheel has 1/2 of the total Toe measure-
ment. When re-adjusting, do not exceed the total Toe
specification.
PLSUSPENSION 2 - 1
Page 16 of 1200

PRE-ALIGNMENT VEHICLE INSPECTION
CAUTION: If the front suspension crossmember
shows any sign of impact damage, the steering col-
umn to steering gear coupling must be inspected.
Refer to Group 19 Steering in this service manual
for the inspection procedure.
Before any attempt is made to change or correct
the wheel alignment factors, the following inspection
and necessary corrections must be made on those
parts which influence the steering of the vehicle.
(1) Be sure the fuel tank is full when the wheel
alignment specifications are checked and or adjusted.
A full tank of fuel weighs approximately 75 pounds,
if the fuel tank is not full this reduction in weight
will affect the curb height of the vehicle and the
alignment specifications.
(2) Alignment specifications of a vehicle can be the
most accurately checked and set when the passenger
compartment and trunk of the vehicle are vacant
with the exception of the spare tire. People, luggage,
and any other appreciable weight will adversely
affect the checking and setting of the camber specifi-
cation.
(3) Check and if required, inflate all of the tires to
the recommended air pressure. All tires must be of
the same size and in good condition and have approx-
imately the same tread wear.Note the type of
tread wear on the tire, this will aid in diagnos-
ing problems. Refer to Group 22 Tires And
Wheels in this service manual for the tire wear
diagnosis.
(4) Check the front tire and wheel assemblies for
radial runout.
(5) Before beginning the alignment process,
inspect all suspension component fasteners for loose-
ness and/or loss of specified torque.
(6) Inspect the lower front ball joints and all steer-
ing linkage for looseness and any signs of wear and
or damage.
(7) Inspect the tie rod ends for looseness and any
signs of wear and or damage.
(8) Inspect the rubber bushings on all suspension
components for signs of wear or deterioration. If any
bushings show signs of wear or deterioration they
should be replaced prior to aligning the vehicle.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
WHEEL ALIGNMENT CHECK AND ADJUSTMENT
PROCEDURE
CASTER CAMBER
Front and rear Caster and Camber settings on this
vehicle are determined at the time the vehicle isdesigned, by the location of the vehicle's suspension
components. This is called a Net Build vehicle and
results in no required adjustment of Caster and
Camber after vehicle is built or when servicing the
suspension components. Thus Caster and Camber are
not normally considered an adjustable specification
when performing an alignment on this vehicle.
Though Caster and Camber are not adjustable they
must be checked to ensure they meet vehicle specifi-
cations.
If front and or rear camber is found not to meet
the vehicle alignment specifications, it can be
adjusted using a Mopar Service Kit developed to
allow for camber adjustment. If a vehicle's front or
rear camber is found to be outside the specifications,
the vehicles suspension components should be
inspected for any signs of damage on bending.This
must be done before using the Mopar Service
Kit for setting camber to meet required specifi-
cation.
If a vehicles caster is not within manufacturers
alignment specifications, check for damaged suspen-
sion components or body parts. This type of damage
can cause component locations to move affecting
vehicle alignment.No adjustment can be made
for the Caster setting on this vehicle.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to adjust the vehicles
Caster or Camber by heating, bending or any other
modification of the suspension components.
(1) Correctly position vehicle on alignment rack
and install all required equipment on vehicle, per the
alignment equipment manufacturers specifications.
(2) Center the steering wheel and lock in place
using a steering wheel clamp.
NOTE: Prior to reading each alignment specifica-
tion, jounce the front and rear of the vehicle an
equal number of times. Induce jounce (rear first
then front) by grasping center of bumper and jounc-
ing each end of vehicle an equal number of times.
Bumper should always be released when vehicle is
at the bottom of the jounce cycle.
(3) Correctly jounce vehicle and read front and
rear alignment settings and compare to vehicle spec-
ifications for Camber, Caster and Toe. See Alignment
Specifications in this group of the service manual for
required specifications.If front and rear camber
readings are within required specifications pro-
ceed to step Step 3 in the Front And Rear Toe
Setting procedure. If Camber readings are not
within specifications refer to step Step 1 in the
following camber adjustment bolt package
installation procedure, for the front and rear
Camber adjustment procedure.
PLSUSPENSION 2 - 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 117 of 1200

(8) Remove lower brake shoe to anchor plate
return spring (Fig. 86).
(9) Remove the park brake lever pin to rear brake
shoe retaining clip (Fig. 87).
(10) Remove the leading and trailing brake shoe,
upper return spring and automatic adjuster screw
from the brake support plate as an assembly (Fig.
88).
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
Clean metal portion of brake shoes. Check to see if
shoes are bent.
Lining should show contact across entire width and
from heel to toe, otherwise replace.
Shoes with lack of contact at toe or heel may be
improperly ground.
Clean and inspect support and adjusting screws.
Apply a thin coat of Mopar Multi-Purpose Lubricant
or equivalent to the threads of the self adjuster (Fig.
89). Replace adjusting screw if corroded.If old springs have overheated or are damaged,
replace. Overheating indications are paint discolora-
tion or distorted end coils.
INSTALL
(1) Lubricate the eight shoe contact areas on the
support plate and anchor using Mopar Multi-Purpose
Lubricant or equivalent (Fig. 90).
Fig. 85 Brake Shoe Hold Down Clips And Pins
Fig. 86 Brake Shoe To Anchor Plate Return Spring
Fig. 87 Park Brake Lever Pin To Brake Shoe
Retaining Clip
Fig. 88 Remove /Install Brake Shoes
Fig. 89 Adjuster Screw and Lever (Typical)
5 - 36 BRAKESPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 146 of 1200

If old brake shoe return or hold down springs have
overheated or are damaged, replace. Overheating
indications are paint discoloration or distorted end
coils.
REAR DRUM BRAKE WHEEL CYLINDER
With brake drums removed, inspect the wheel cyl-
inder boots for evidence of a brake fluid leak. Visu-
ally check the boots for cuts, tears, or heat cracks. If
any of these conditions exist, the wheel cylinders
should be completely cleaned, inspected and new
parts installed.
If a wheel cylinder is leaking and the brake lining
material is saturated with brake fluid, the brake
shoes must be replaced.
CHASSIS TUBES AND HOSES
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front and rear
brakes. Inspection of brake hoses should be per-
formed whenever the brake system is serviced and
every 7,500 miles or 12 months, whichever comes
first (every engine oil change). Inspect hydraulic
brake hoses for severe surface cracking, scuffing,
worn spots or physical damage. If the fabric casing of
the rubber hose becomes exposed due to cracks or
abrasions in the rubber hose cover, the hose should
be replaced immediately. Eventual deterioration of
the hose can take place with possible burst failure.
Faulty installation can cause twisting, resulting in
wheel, tire, or chassis interference.
The steel brake tubing should be inspected periodi-
cally for evidence of corrosion, physical damage or con-
tact with moving or hot components of the vehicle.
REAR WHEEL HUB AND BEARING ASSEMBLY
The rear hub and bearing assembly is designed for
the life of the vehicle and should require no mainte-
nance. The following procedure may be used for eval-
uation of bearing condition.
With wheel and brake drum removed, rotate
flanged outer ring of hub. Excessive roughness, lat-
eral play or resistance to rotation may indicate dirt
intrusion or bearing failure. If the rear wheel bear-
ings exhibit these conditions during inspection, the
hub and bearing assembly should be replaced.Damaged bearing seals and resulting excessive
grease loss may also require bearing replacement.
Moderate grease loss from bearing is considered nor-
mal and should not require replacement of the hub
and bearing assembly.
ADJUSTMENTS
STOP LAMP SWITCH
(1) Remove stop lamp switch from its bracket by
rotating it approximately 30É in a counter-clockwise
direction.
(2) Disconnect wiring harness connector from stop
lamp switch.
(3) Hold stop lamp switch firmly in one hand.
Then using other hand, pull outward on the plunger
of the stop lamp switch until it has ratcheted out to
its fully extended position.
(4) Install the stop lamp switch into the bracket
using the following procedure. Depress the brake
pedal as far down as possible. Then while keeping
the brake pedal depressed, install the stop lamp
switch into the bracket by aligning index key on
switch with slot at top of square hole in mounting
bracket. When switch is fully installed in the square
hole of the bracket, rotate switch clockwise approxi-
mately 30É to lock the switch into the bracket.
CAUTION: Do not use excessive force when pulling
back on brake pedal to adjust the stop lamp switch.
If too much force is used, damage to the vacuum
booster, stop lamp switch or striker (Fig. 185) can
result.
(5) Connect the wiring harness connector to the
stop lamp switch.
(6) Gently pull back on brake pedal until the pedal
stops moving. This will cause the switch plunger
(Fig. 185) to ratchet backward to the correct position.
REAR DRUM BRAKE SHOE ADJUSTMENT
NOTE: Normally, self adjusting drum brakes will
not require manual brake shoe adjustment.
Although in the event of a brake reline it is advis-
able to make the initial adjustment manually to
speed up the adjusting time.
(1) Raise the vehicle so all wheels are free to turn.
See Hoisting Recommendations in the Lubrication
And Maintenance Section at the front of this service
manual.
(2) Remove rear brake adjusting hole rubber plug
(Fig. 186) from the rear brake shoe support plate.
Fig. 184 Adjuster Screw And Lever (Typical)
PLBRAKES 5 - 65
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 175 of 1200
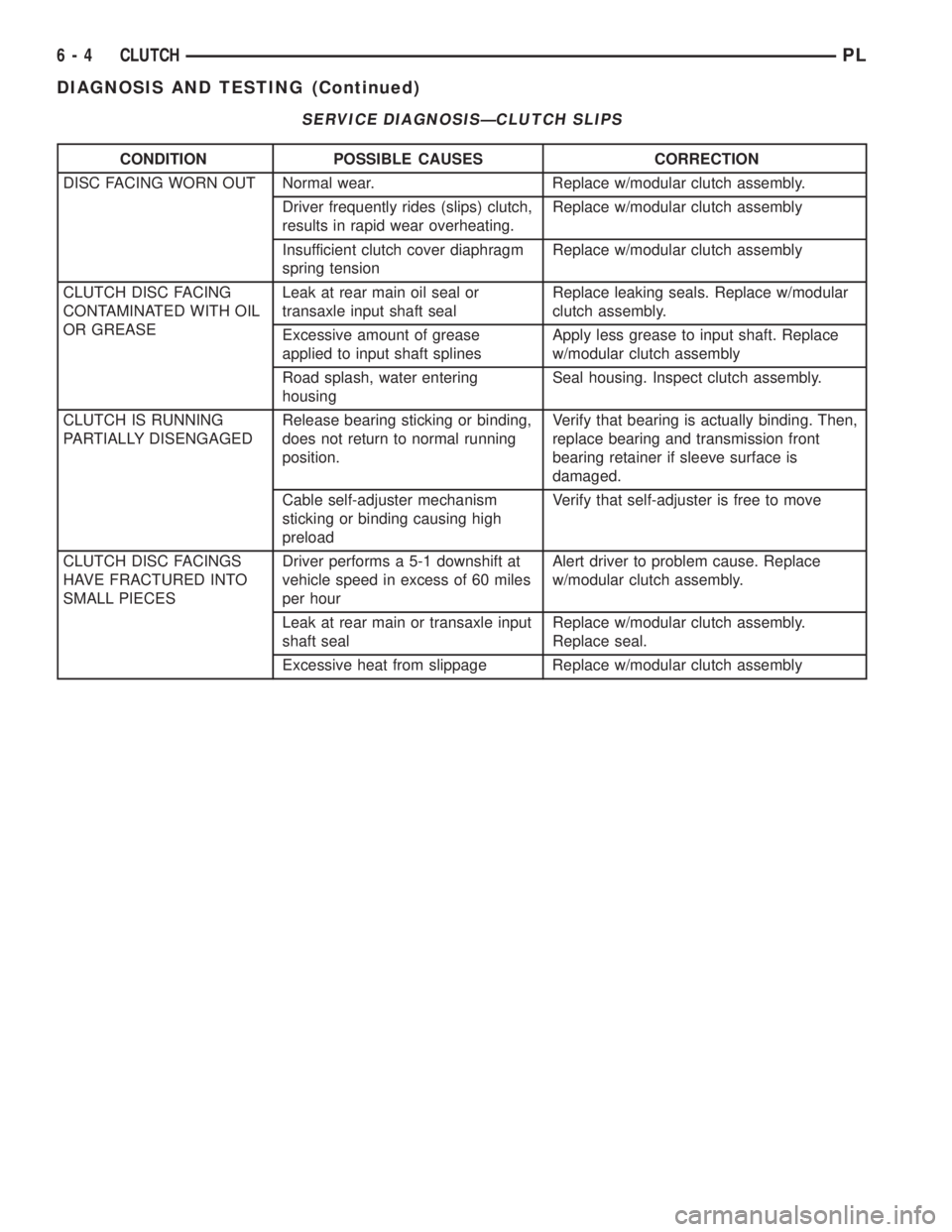
SERVICE DIAGNOSISÐCLUTCH SLIPS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
DISC FACING WORN OUT Normal wear. Replace w/modular clutch assembly.
Driver frequently rides (slips) clutch,
results in rapid wear overheating.Replace w/modular clutch assembly
Insufficient clutch cover diaphragm
spring tensionReplace w/modular clutch assembly
CLUTCH DISC FACING
CONTAMINATED WITH OIL
OR GREASELeak at rear main oil seal or
transaxle input shaft sealReplace leaking seals. Replace w/modular
clutch assembly.
Excessive amount of grease
applied to input shaft splinesApply less grease to input shaft. Replace
w/modular clutch assembly
Road splash, water entering
housingSeal housing. Inspect clutch assembly.
CLUTCH IS RUNNING
PARTIALLY DISENGAGEDRelease bearing sticking or binding,
does not return to normal running
position.Verify that bearing is actually binding. Then,
replace bearing and transmission front
bearing retainer if sleeve surface is
damaged.
Cable self-adjuster mechanism
sticking or binding causing high
preloadVerify that self-adjuster is free to move
CLUTCH DISC FACINGS
HAVE FRACTURED INTO
SMALL PIECESDriver performs a 5-1 downshift at
vehicle speed in excess of 60 miles
per hourAlert driver to problem cause. Replace
w/modular clutch assembly.
Leak at rear main or transaxle input
shaft sealReplace w/modular clutch assembly.
Replace seal.
Excessive heat from slippage Replace w/modular clutch assembly
6 - 4 CLUTCHPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 187 of 1200

SERVICE DIAGNOSISÐCLUTCH SLIPS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
DISC FACING WORN OUT Normal wear. Replace w/modular clutch assembly.
Driver frequently rides (slips) clutch,
results in rapid wear and
overheating.Replace w/modular clutch assembly
Insufficient clutch cover diaphragm
spring tensionReplace w/modular clutch assembly
CLUTCH DISC FACING
CONTAMINATED WITH OIL OR
GREASELeak at rear main oil seal or
transaxle input shaft sealReplace leaking seals. Replace
w/modular clutch assembly.
Excessive amount of grease applied
to input shaft splinesApply less grease to input shaft.
Replace w/modular clutch assembly
Road splash, water entering housing Seal housing. Inspect clutch
assembly.
CLUTCH IS RUNNING
PARTIALLY DISENGAGEDRelease bearing sticking or binding,
does not return to normal running
position.Verify that bearing is actually
binding. Then, replace bearing and
transmission front bearing retainer if
sleeve surface is damaged.
Hydraulic clutch mechanism sticking
or binding causing high preloadVerify that clutch slave cylinder and
fork are free to move
CLUTCH DISC FACINGS HAVE
FRACTURED INTO SMALL
PIECESDriver performs a 5-1 downshift at
vehicle speed in excess of 60 miles
per hourAlert driver to problem cause.
Replace w/modular clutch assembly.
Leak at rear main or transaxle input
shaft sealReplace w/modular clutch assembly.
Replace seal.
Excessive heat from slippage Replace w/modular clutch assembly
6 - 4 CLUTCHPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 198 of 1200

SELECTION AND ADDITIVES
The use of aluminum cylinder heads, intake mani-
folds DOHC, and water pumps requires special corro-
sion protection. MopartAntifreeze or the equivalent
is recommended for best engine cooling without cor-
rosion. When mixed only to a freeze point of -37ÉC
(-35ÉF) to -59ÉC (-50ÉF). If it looses color or becomes
contaminated, drain, flush, and replace with fresh
properly mixed solution.
COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE CAP
The cooling system is equipped with a pressure cap
that releases built up pressure, maintaining a range
of 97-124 kPa (14-18 psi).
The cooling system will operate at higher than
atmospheric pressure. The higher pressure raises the
coolant boiling point thus, allowing increased radia-
tor cooling capacity.
There is a vent valve in the center of the cap that
allows a small coolant flow from the coolant reserve
system (CRS) tank. This valve is spring loaded in the
closed position. However it must be free to open dur-
ing system cool-down.If the valve is stuck shut,
the radiator hoses will collapse on cool-down.
Clean the vent valve (Fig. 7) to ensure proper
sealing function.
There is a gasket in the cap that seals to the top of
the filler neck so that vacuum is maintained to draw
coolant back into the system from the coolant reserve
system (CRS) tank.
RADIATOR HOSES AND CLAMPS
WARNING: IF VEHICLE HAS BEEN RUN
RECENTLY, WAIT 15 MINUTES BEFORE WORKING
ON VEHICLE. RELIEVE PRESSURE BY PLACING A
SHOP TOWEL OVER THE CAP AND WITHOUT
PUSHING DOWN ROTATE IT COUNTERCLOCKWISE
TO THE FIRST STOP. ALLOW FLUIDS TO ESCAPE
THROUGH THE OVERFLOW TUBE AND WHEN THE
SYSTEM STOPS PUSHING OUT COOLANT AND
STEAM AND THE PRESSURE DROPS CONTINUE
SERVICE.
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAM. ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN
SERVICING CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only a original equipment clamp
with matching number or letter.The hose clamps are removed by using Special Tool
6094 or equivalent constant tension clamp pliers
(Fig. 8) to compress hose clamp.
A hardened, cracked, swollen or restricted hose
should be replaced. Do not damage radiator inlet and
outlet when loosening hoses.
Radiator hoses should be routed without any kinks
and indexed as designed. The use of molded hoses is
recommended.
Spring type hose clamps are used in all applica-
tions. If replacement is necessary replace with the
original Mopartequipment spring type clamp.
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
The heater is mounted in a core hole (in place of a
core hole plug) in the engine block, with the heating
element immersed in coolant.The power cord
must be secured in its retainer clips, and not
positioned so it could contact linkages or
exhaust manifolds and become damaged.
If unit does not operate, trouble can be in either
the power cord or the heater element. Test power
cord for continuity with a 110-volt voltmeter or 110-
volt test light; test heater element continuity with an
ohmmeter or 12-volt test light.
Fig. 7 Cooling System Pressure Cap
PLCOOLING 7 - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 200 of 1200

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READS
LOW1. Has a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) been set indicating a stuck
open engine thermostat?1. Refer to On Board Diagnostic in
Group 25. Replace thermostat if
necessary. If a (DTC) has not been
set, the problem may be with the
temperature gauge.
2. Is the temperature gauge (if
equipped) connected to the
temperature gauge coolant sensor
on the engine?2. Check the connector at the
engine coolant sensor. Refer to
Group 8E. Repair as necessary.
3. Is the temperature gauge (if
equipped) operating OK?3. Check Gauge operation. Refer to
Group 8E. Repair as necessary.
4. Coolant level low during cold
ambient temperature, accompanied
by poor heater performance.4. Check coolant level in the coolant
overflow/reserve tank and the
radiator. Inspect the system for
leaks. Repair as necessary. Refer to
WARNINGS outlined in this section
before removing pressure cap.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READS
HIGH OR ENGINE COOLANT
WARNING LAMP ILLUMINATES.
COOLANT MAY OR MAY NOT BE
LOST FROM SYSTEM.1. Trailer being towed, a steep hill
being climbed, vehicle being
operated in slow moving traffic, or
engine idling during high ambient
(outside) temperatures with air
conditioning on. High altitudes
Could aggravate these conditions.1. This may be a temporary
condition and repair is not
necessary. Turn off the air
conditioning and drive the vehicle
without any of the previous
conditions. Observe the temperature
gauge the gauge should return to
the normal range. If the gauge does
not return to the normal range,
determine the cause of the
overheating and repair. Refer to
POSSIBLE CAUSES in this section.
2. Is temperature gauge (if
equipped) reading correctly?2. Check gauge. Refer to Group 8E.
Repair as necessary.
3. Is temperature warning lamp (if
equipped) illuminating
unnecessarily?3. Check warning lamp operation.
Refer to Group 8E. Repair as
necessary.
4. Coolant low in overflow/reserve
tank and radiator?4. Check for coolant leaks and
repair as necessary. Refer to
checking cooling system for leaks in
this group.
5. Pressure cap not installed tightly.
If cap is loose, boiling point of
coolant will be lowered. Also refer
to the following step 6.5. Tighten cap.
6. Poor seals at radiator cap. 6. (a) Check condition of cap and
cap seals. Refer to Radiator cap
Inspection. Replace cap if
necessary.
6. (b) Check condition of filler neck.
If neck is bent or damaged, replace
neck.
PLCOOLING 7 - 7
Page 201 of 1200

COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CONT.
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READS
HIGH OR ENGINE COOLANT
WARNING LAMP ILLUMINATES.
COOLANT MAY OR MAY NOT BE
LOST FROM SYSTEM.7. Coolant level low in radiator but
not in coolant overflow/reserve
tank. This means the radiator is not
drawing coolant from the coolant
overflow/reserve tank as the engine
cools.
As the engine cools, a vacuum is
formed inside the cooling system. If
the radiator cap seals are defective,
or the cooling system has a leak, a
vacuum can not be formed.7. (a) Check condition of radiator
cap and cap seals. Replace cap if
necessary.
(b) Check condition of filler neck. If
neck is damaged, replace filler
neck.
(c) Check condition of hoses from
filler neck to coolant tank. It should
be tight at both ends without any
kinks or tears. Replace hose if
necessary.
(d) Check coolant overflow/reserve
tank and tank hoses for blockage.
Repair as necessary.
8. Freeze point of coolant not
correct. Mixture may be to rich.8. Check coolant. Refer to coolant
section in this group. Adjust glycol
to water ratio as required.
9. Coolant not flowing through
system.9. Check for coolant flow at filler
neck with some coolant removed,
engine warm and thermostat open.
Coolant should be observed flowing
through filler neck. If flow is not
observed determine reason for lack
of flow and repair as necessary.
10. Radiator or A/C condenser fins
are dirty or clogged.10. Clean insects or debris.
11. Radiator core is plugged or
corroded.11. Replace or re-core radiator.
12. Fuel or ignition system
problems.12. Refer to Fuel and Ignition
System group for diagnosis. Also
refer to the appropriate Powertrain
Diagnosis Procedures manual for
operation of the DRB scan tool.
13. Dragging brakes. 13. Inspect brake system and repair
as necessary. Refer to Group 5,
Brakes for diagnosis.
14. Bug screen is being used
causing reduced air flow.14. Remove bug screen.
15. Thermostat partially or
completely shut. This is more
prevalent on high mileage vehicles.15. Check thermostat operation and
replace as necessary. Refer to
thermostats in this group.
16. Electric cooling fan not
operating properly.16. Check electric fan operation and
repair as necessary.
17. Cylinder head gasket leaking. 17. Check cylinder head gasket for
leaks. Refer to testing cooling
system for leaks. For repairs, refer
to group 9, Engines.
18. Heater core leaking. 18. Check heater core for leaks.
Refer to Group 24, Heating and Air
Conditioning. Repair as necessary.
7 - 8 COOLINGPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 204 of 1200
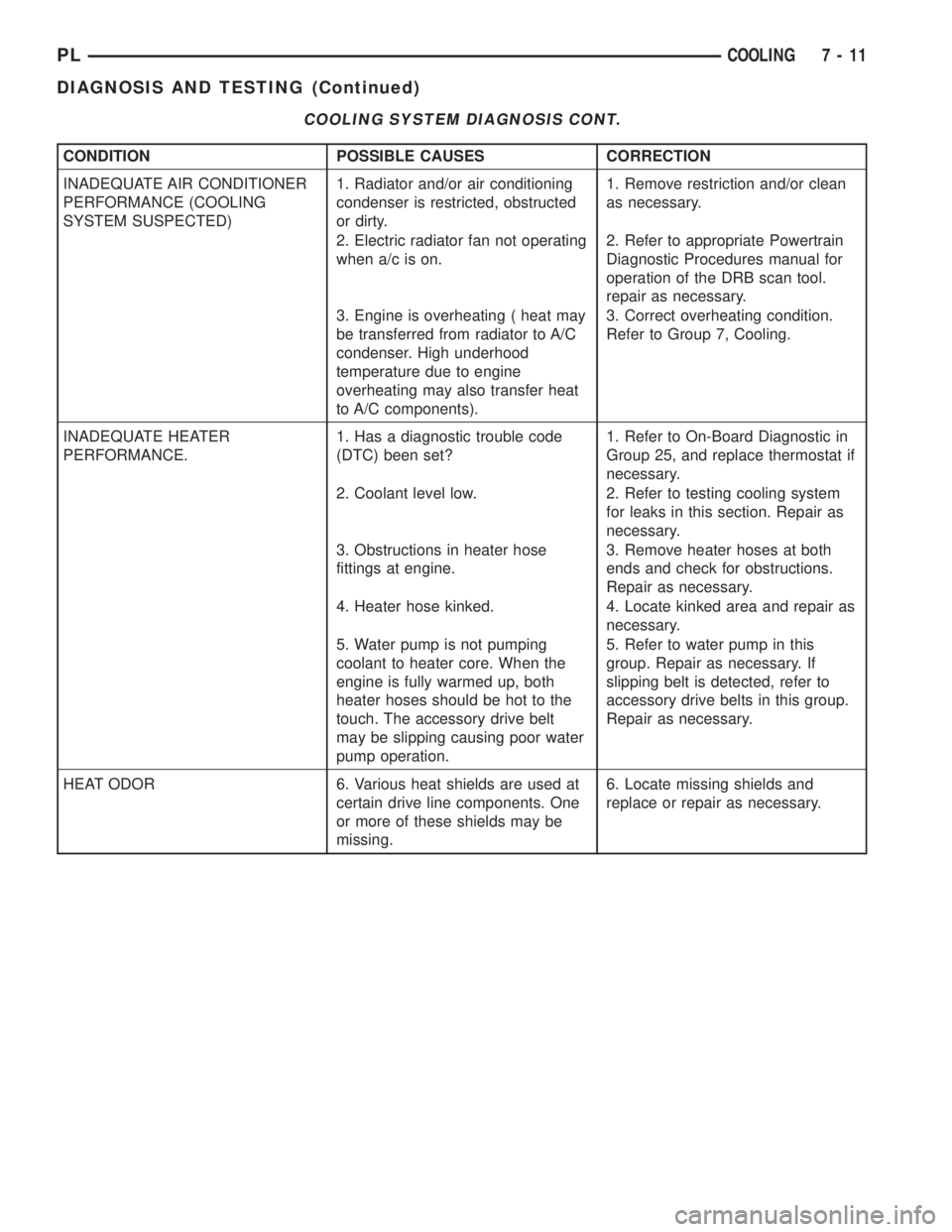
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CONT.
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
INADEQUATE AIR CONDITIONER
PERFORMANCE (COOLING
SYSTEM SUSPECTED)1. Radiator and/or air conditioning
condenser is restricted, obstructed
or dirty.1. Remove restriction and/or clean
as necessary.
2. Electric radiator fan not operating
when a/c is on.2. Refer to appropriate Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures manual for
operation of the DRB scan tool.
repair as necessary.
3. Engine is overheating ( heat may
be transferred from radiator to A/C
condenser. High underhood
temperature due to engine
overheating may also transfer heat
to A/C components).3. Correct overheating condition.
Refer to Group 7, Cooling.
INADEQUATE HEATER
PERFORMANCE.1. Has a diagnostic trouble code
(DTC) been set?1. Refer to On-Board Diagnostic in
Group 25, and replace thermostat if
necessary.
2. Coolant level low. 2. Refer to testing cooling system
for leaks in this section. Repair as
necessary.
3. Obstructions in heater hose
fittings at engine.3. Remove heater hoses at both
ends and check for obstructions.
Repair as necessary.
4. Heater hose kinked. 4. Locate kinked area and repair as
necessary.
5. Water pump is not pumping
coolant to heater core. When the
engine is fully warmed up, both
heater hoses should be hot to the
touch. The accessory drive belt
may be slipping causing poor water
pump operation.5. Refer to water pump in this
group. Repair as necessary. If
slipping belt is detected, refer to
accessory drive belts in this group.
Repair as necessary.
HEAT ODOR 6. Various heat shields are used at
certain drive line components. One
or more of these shields may be
missing.6. Locate missing shields and
replace or repair as necessary.
PLCOOLING 7 - 11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)