spark plugs replace DODGE NEON 1999 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 5 of 1200

²Replace air cleaner element.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transmission fluid.
37,500 Miles (60 000 km) or at 30 months
²Change engine oil.
45,000 Miles (72 000 km) or at 36 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Flush and replace engine coolant at 36 months,
regardless of mileage.
52,500 Miles (84 000 km) or at 42 months
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if not done at
36 months.
60,000 Miles (96 000 km) or at 48 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Check and replace, if necessary***, the PCV
valve.**
²Lubricate front suspension upper ball joints.
²Replace drive belts.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Replace ignition cables.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transmission fluid.
67,500 Miles (108 000 km) or at 54 months
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
75,000 Miles (120 000 km) or at 60 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
82,500 Miles (132 000 km) or at 66 months
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
90,000 Miles (144 000 km) or at 72 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Check and replace, if necessary***, the PCV
valve.**
²Lubricate front suspension upper ball joints.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Replace air cleaner air cleaner element.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transmission fluid.
97,500 Miles (156 000 km) or at 78 months
²Change engine oil.
105,000 Miles (168 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace engine timing belt
²Adjust drive belt tension.
SCHEDULE ± B
NOTE: * Follow this schedule if you usually operate
your vehicle under one or more of the following
conditions. Change the automatic transmission
fluid and filter every 15,000 miles (24 000 km) if you
usually operate your vehicle under one of the con-
ditions marked with an *.
3,000 Miles (5 000 km)
²Change engine oil
6,000 Miles (10 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
9,000 Miles (14 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake lining.
12,000 Miles (19 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
15,000 Miles (24 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Inspect and replace, if required, the air
cleaner element.
²Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
18,000 Miles (29 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
21,000 Miles (34 000 km)
²Change engine oil
0 - 4 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 6 of 1200

24,000 Miles (38 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
27,000 Miles (43 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
30,000 Miles (48 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Check and replace, if necessary, the PCV
valve.**
²Lubricate front suspension upper ball joints.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transmission fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
33,000 Miles (53 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
36,000 Miles (58 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Flush and replace engine coolant.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
39,000 Miles (62 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
42,000 Miles (67 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
45,000 Miles (72 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
²Inspect and replace, if necessary, the air
cleaner element.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
48,000 Miles (77 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
51,000 Miles (82 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant.
54,000 Miles (86 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
57,000 Miles (91 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
60,000 Miles (96 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Check and replace, if necessary***, the PCV
valve.**
²Lubricate front suspension upper ball joints.
²Replace drive belts.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Replace ignition cables.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
63,000 Miles (101 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
66,000 Miles (106 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
69,000 Miles (110 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
72,000 Miles (115 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
75,000 Miles (120 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Inspect and replace, if necessary, the air
cleaner element.
²Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
78,000 Miles (125 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
81,000 Miles (130 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace the engine coolant.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
84,000 Miles (134 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
87,000 Miles (139 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
PLLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 5
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 7 of 1200

90,000 Miles (144 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
²Check and replace, if necessary***, the PCV
valve.**
²Lubricate front suspension upper ball joints.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Replace spark plugs.
²Change automatic transaxle fluid and filter.
Adjust the bands.*
93,000 Miles (149 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
96,000 Miles (154 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
99,000 Miles (158 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings.
102,000 Miles (163 000km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
105,000 Miles (168 000km)
²Replace the engine timing belt
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Adjust drive belt tension.
²Inspect and replace, if necessary, the air
cleaner element.
NOTE: **This maintenance is recommended by
Chrysler to the owner but is not required to main-
tain the warranty on the PCV valve.
NOTE: ***This maintenance is not required if the
PCV valve was previously replaced.
0 - 6 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 251 of 1200

The major difference between the two engines is
component location which affects the ignition system
service procedures. There are various sensors that
are in different locations due to a different cylinder
head and intake manifold.
The 2.0L engines use a fixed ignition timing sys-
tem. The distributorless electronic ignition system is
referred to as the Direct Ignition System (DIS).
Basic ignition timing is not adjustable.The
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) determines spark
advance. The system's three main components are
the coil pack, crankshaft position sensor, and cam-
shaft position sensor.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) controls the
ignition system (Fig. 1). The PCM supplies battery
voltage to the ignition coil through the Auto Shut-
down (ASD) Relay. The PCM also controls the ground
circuit for the ignition coil. By switching the ground
path for the coil on and off, the PCM adjusts ignition
timing to meet changing engine operating conditions.
During the crank-start period the PCM maintains
spark advance at 9É BTDC. During engine operation
the following inputs determine the amount of spark
advance provided by the PCM.
²Intake air temperature
²Coolant temperature
²Engine RPM
²Intake manifold vacuum
²Knock sensor
The PCM also regulates the fuel injection system.
Refer to the Fuel Injection sections of Group 14.
SPARK PLUGS
The 2.0L engines uses resistor spark plugs. For
spark plug identification and specifications, Refer to
the Specifications section at the end of this group.Remove the spark plugs and examine them for
burned electrodes and fouled, cracked or broken por-
celain insulators. Keep plugs arranged in the order
in which they were removed from the engine. An iso-
lated plug displaying an abnormal condition indicates
that a problem exists in the corresponding cylinder.
Replace spark plugs at the intervals recommended in
Group 0.
Spark plugs that have low mileage may be cleaned
and reused if not otherwise defective. Refer to the
Spark Plug Condition section of this group. After
cleaning, file the center electrode flat with a small
point file or jewelers file. Adjust the gap between the
electrodes (Fig. 2) to the dimensions specified in the
chart at the end of this section.
Always tighten spark plugs to the specified torque.
Over tightening can cause distortion and damage.
Tighten spark plugs to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
SPARK PLUG CABLES
Spark plug cables are sometimes referred to as sec-
ondary ignition wires. The wires transfer electrical
current from the coil pack to individual spark plugs
at each cylinder. The resistor type, nonmetallic spark
plug cables provide suppression of radio frequency
emissions from the ignition system.
Check the spark plug cable connections for good
contact at the coil and spark plugs. Terminals should
be fully seated. The nipples and spark plug covers
should be in good condition. Nipples should fit tightly
on the coil. Spark plug boot should completely cover
the spark plug hole in the cylinder head cover. Install
the boot until the terminal snaps over the spark
plug. A snap must be felt to ensure the spark plug
cable terminal engaged the spark plug.
Loose cable connections will corrode, increase resis-
tance and permit water to enter the coil towers.
These conditions can cause ignition malfunction.
Fig. 1 Powertrain Control Module
Fig. 2 Setting Spark Plug Electrode Gap
8D - 2 IGNITION SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 252 of 1200

Plastic clips in various locations protect the cables
from damage. When the cables are replaced the clips
must be used to prevent damage to the cables. The
#1 cable must be routed under the PCV hose and
clipped to the #2 cable.
ELECTRONIC IGNITION COILS
WARNING: THE DIRECT IGNITION SYSTEM GEN-
ERATES APPROXIMATELY 40,000 VOLTS. PER-
SONAL INJURY COULD RESULT FROM CONTACT
WITH THIS SYSTEM.
The coil pack consists of 2 coils molded together.
The coil pack is mounted on the valve cover (Fig. 3)
or (Fig. 4). High tension leads route to each cylinder
from the coil. The coil fires two spark plugs every
power stroke. One plug is the cylinder under com-
pression, the other cylinder fires on the exhaust
stroke. Coil number one fires cylinders 1 and 4. Coil
number two fires cylinders 2 and 3. The PCM deter-
mines which of the coils to charge and fire at the cor-
rect time.
The Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay provides battery
voltage to the ignition coil. The PCM provides a
ground contact (circuit) for energizing the coil. When
the PCM breaks the contact, the energy in the coil
primary transfers to the secondary causing the
spark. The PCM will de-energize the ASD relay if it
does not receive the crankshaft position sensor and
camshaft position sensor inputs. Refer to Auto Shut-
down (ASD) RelayÐPCM Output, in this section for
relay operation.
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAY
The Automatic Shutdown (ASD) relay supplies bat-
tery voltage to the fuel injectors, electronic ignition
coil and the heating elements in the oxygen sensors.
A buss bar in the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
supplies voltage to the solenoid side and contact sideof the relay. The ASD relay power circuit contains a
20 amp fuse between the buss bar in the PDC and
the relay. The fuse also protects the power circuit for
the fuel pump relay and pump. The fuse is located in
the PDC. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams for
circuit information.
The PCM controls the ASD relay by switching the
ground path for the solenoid side of the relay on and
off. The PCM turns the ground path off when the
ignition switch is in the Off position. When the igni-
tion switch is in On or Start, the PCM monitors the
crankshaft and camshaft position sensor signals to
determine engine speed and ignition timing (coil
dwell). If the PCM does not receive crankshaft and
camshaft position sensor signals when the ignition
switch is in the Run position, it will de-energize the
ASD relay.
The ASD relay is located in the PDC (Fig. 5). The
inside top of the PDC cover has label showing relay
and fuse identification.
Fig. 3 Ignition Coil PackÐSOHC
Fig. 4 Ignition Coil PackÐDOHC
Fig. 5 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
PLIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 259 of 1200

Connect the DVM between the center and sensor
ground terminal. Refer to Group 8W - Wiring Dia-
grams for correct pinout.
With the ignition switch in the ON position, check
the output voltage at the center terminal wire of the
connector. Check the output voltage at idle and at
Wide-Open-Throttle (WOT). At idle, TPS output volt-
age should be approximately 0.38 volts to 1.2 volts.
At wide open throttle, TPS output voltage should be
approximately 3.1 volts to 4.4 volts. The output volt-
age should gradually increase as the throttle plate
moves slowly from idle to WOT.
Check for spread terminals at the sensor and PCM
connections before replacing the TPS.
SPARK PLUG CONDITION
NORMAL OPERATING CONDITIONS
The few deposits present will be probably light tan
or slightly gray in color with most grades of commer-
cial gasoline (Fig. 21). There will not be evidence of
electrode burning. Gap growth will not average more
than approximately 0.025 mm (.001 in) per 1600 km
(1000 miles) of operation for non platinum spark
plugs. Non-platnium spark plugs that have normal
wear can usually be cleaned, have the electrodes filed
and regapped, and then reinstalled.
CAUTION: Never attempt to file the electrodes or
use a wire brush for cleaning platinum spark plugs.
This would damage the platinum pads which would
shorten spark plug life.Some fuel refiners in several areas of the United
States have introduced a manganese additive (MMT)
for unleaded fuel. During combustion, fuel with MMT
may coat the entire tip of the spark plug with a rust
colored deposit. The rust color deposits can be misdi-
agnosed as being caused by coolant in the combustion
chamber. Spark plug performance is not affected by
MMT deposits.
COLD FOULING (CARBON FOULING)
Cold fouling is sometimes referred to as carbon
fouling because the deposits that cause cold fouling
are basically carbon (Fig. 21). A dry, black deposit on
one or two plugs in a set may be caused by sticking
valves or misfire conditions. Cold (carbon) fouling of
the entire set may be caused by a clogged air cleaner.
Cold fouling is normal after short operating peri-
ods. The spark plugs do not reach a high enough
operating temperature during short operating peri-
ods.Replace carbon fouled plugs with new
spark plugs.
FUEL FOULING
A spark plug that is coated with excessive wet fuel
is called fuel fouled. This condition is normally
observed during hard start periods.Clean fuel
fouled spark plugs with compressed air and
reinstall them in the engine.
OIL FOULING
A spark plug that is coated with excessive wet oil
is oil fouled. In older engines, wet fouling can be
caused by worn rings or excessive cylinder wear.
Break-in fouling of new engines may occur before
normal oil control is achieved.Replace oil fouled
spark plugs with new ones.
OIL OR ASH ENCRUSTED
If one or more plugs are oil or ash encrusted, eval-
uate the engine for the cause of oil entering the com-
bustion chambers (Fig. 22). Sometimes fuel additives
can cause ash encrustation on an entire set of spark
plugs.Ash encrusted spark plugs can be cleaned
and reused.
HIGH SPEED MISS
When replacing spark plugs because of a high
speed miss condition;wide open throttle opera-
tion should be avoided for approximately 80 km
(50 miles) after installation of new plugs.This
will allow deposit shifting in the combustion chamber
to take place gradually and avoid plug destroying
splash fouling shortly after the plug change.
Fig. 21 Normal Operation and Cold (Carbon) Fouling
8D - 10 IGNITION SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 260 of 1200

ELECTRODE GAP BRIDGING
Loose deposits in the combustion chamber can
cause electrode gap bridging. The deposits accumu-
late on the spark plugs during continuous stop-
and-go driving. When the engine is suddenly
subjected to a high torque load, the deposits partially
liquefy and bridge the gap between the electrodes
(Fig. 23). This short circuits the electrodes.Spark
plugs with electrode gap bridging can be
cleaned and reused.
SCAVENGER DEPOSITS
Fuel scavenger deposits may be either white or yel-
low (Fig. 24). They may appear to be harmful, but
are a normal condition caused by chemical additives
in certain fuels. These additives are designed tochange the chemical nature of deposits and decrease
spark plug misfire tendencies. Notice that accumula-
tion on the ground electrode and shell area may be
heavy but the deposits are easily removed.Spark
plugs with scavenger deposits can be consid-
ered normal in condition, cleaned and reused.
CHIPPED ELECTRODE INSULATOR
A chipped electrode insulator usually results from
bending the center electrode while adjusting the
spark plug electrode gap. Under certain conditions,
severe detonation also can separate the insulator
from the center electrode (Fig. 25).Spark plugs
with chipped electrode insulators must be
replaced.
PREIGNITION DAMAGE
Excessive combustion chamber temperature can
cause preignition damage. First, the center electrode
dissolves and the ground electrode dissolves some-
what later (Fig. 26). Insulators appear relatively
deposit free. Determine if the spark plugs are the
correct type, as specified on the VECI label, or if
Fig. 22 Oil or Ash Encrusted
Fig. 23 Electrode Gap Bridging
Fig. 24 Scavenger Deposits
Fig. 25 Chipped Electrode Insulator
PLIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 715 of 1200

assure gasket rails are flat. Flatten rails with a ham-
mer on a heavy steel plate if required. Gasket sur-
faces must be free of oil and dirt. Make sure old
gasket material is removed from blind attaching
holes.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier then using precut gas-
kets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 inch.) diameter or less of seal-
ant to one gasket surface. Be certain the material
surrounds each mounting hole. Excess material can
easily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
The MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant gas-
ket material or equivalent should be applied in a con-
tinuous bead approximately 3 mm (0.120 inch) in
diameter. All mounting holes must be circled. For
corner sealing, a 3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 inch.)
drop is placed in the center of the gasket contact
area. Uncured sealant may be removed with a shop
towel. Components should be torqued in place while
the sealant is still wet to the touch (within 10 min-
utes). The usage of a locating dowel is recommended
during assembly to prevent smearing material off the
location.
CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET BOLT ACCESS PLUG
An Access plug is located in the right inner fender
shield. Remove the plug and insert the proper size
socket, extension and ratchet, when crankshaft rota-
tion is necessary.
ENGINE CORE PLUGS
REMOVAL
Using a blunt tool such as a drift or a screwdriver
and a hammer, strike the bottom edge of the cup
plug (Fig. 1). With the cup plug rotated, grasp firmly
with pliers or other suitable tool and remove plug
(Fig. 1).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting
as restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
INSTALLATION
Thoroughly remove all rust and clean inside of cup
plug hole in cylinder block or head. Be sure to
remove old sealer. Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole
with sealer. Make certain the new plug is cleaned of
all oil or grease. Using proper drive plug, drive plug
into hole so that the sharp edge of the plug is atleast 0.5 mm (0.020 inch.) inside the lead in chamfer
(Fig. 1).
It is in not necessary to wait for curing of the seal-
ant. The cooling system can be refilled and the vehi-
cle placed in service immediately.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
If a loss of performance is noticed, timing belt or
chain may have skipped one or two teeth. Camshaft
and crankshaft timing should be checked. Refer to
Group 9, Engine Timing belt or chain installation.
It is important that the vehicle is operating to its
optimum performance level to maintain fuel economy
and lowest vehicle emissions. If vehicle is not operat-
ing to these standards, refer to Engine Diagnosis out-
lined is this section. The following procedures can
assist in achieving the proper engine diagnosis.
(1) Test cranking amperage draw. Refer to Group
8B, Starting.
(2) Check intake manifold for vacuum leaks.
(3) Perform cylinder compression pressure test.
Refer to Engine Diagnosis, outlined in this section.
(4) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary and
adjust gap as specified in Group 8D, Ignition System.
Tighten to specifications.
(5) Test resistance of spark plug cables. Refer to
Group 8D, Ignition System.
(6) Test ignition coils primary and secondary resis-
tance. Replace parts as necessary. Refer to Group 8D,
Ignition System.
(7) Check fuel pump pressure at idle and different
RPM ranges. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System for
Specifications.
(8) The air filter elements should be replaced as
specified in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance.
(9) Inspect crankcase ventilation system as out-
lined in Group 25, Emission Control Systems.
(10) Road test vehicle as a final test.
Fig. 1 Core Hole Plug Removal
9 - 2 ENGINEPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 721 of 1200

cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
(11) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary
and adjust gap as specified in Group 8, Electrical.
Tighten to specifications.
(12) Test resistance of spark plug cables. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical Ignition System Secondary Cir-
cuit Inspection.
(13) Test coil output voltage, primary and second-
ary resistance. Replace parts as necessary. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical Ignition System.
(14) Check fuel pump pressure at idle and differ-
ent RPM ranges. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System for
Specifications.
(15) The air filter elements should be replaced as
specified in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance,.
(16) Inspect crankcase ventilation system as out
lined in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance. For
emission controls see Group 25, Emission Controls
for service procedures.
(17) Inspect and adjust accessory belt drives refer-
ring to Group 7, Cooling System, Accessory Drive
Belts for proper adjustments.
(18) Road test vehicle as a final test.
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1 379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
LASH ADJUSTER (TAPPET) NOISE DIAGNOSIS
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) During this time, turn engine off and let set for
a few minutes before restarting. Repeat this several
times after engine has reached normal operating
temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor pressed into the vertical oil
passage to the cylinder head is plugged with debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Faulty lash adjuster.
a. Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head. Depress part of rocker
arm over adjuster. Normal adjusters should feel very
firm. Spongy adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected rocker arms (sohc) or lash
adjuster (dohc) and replace.
INSPECTION (ENGINE OIL LEAKS IN GENERAL)
Begin with a through visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
9 - 8 ENGINEPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 723 of 1200
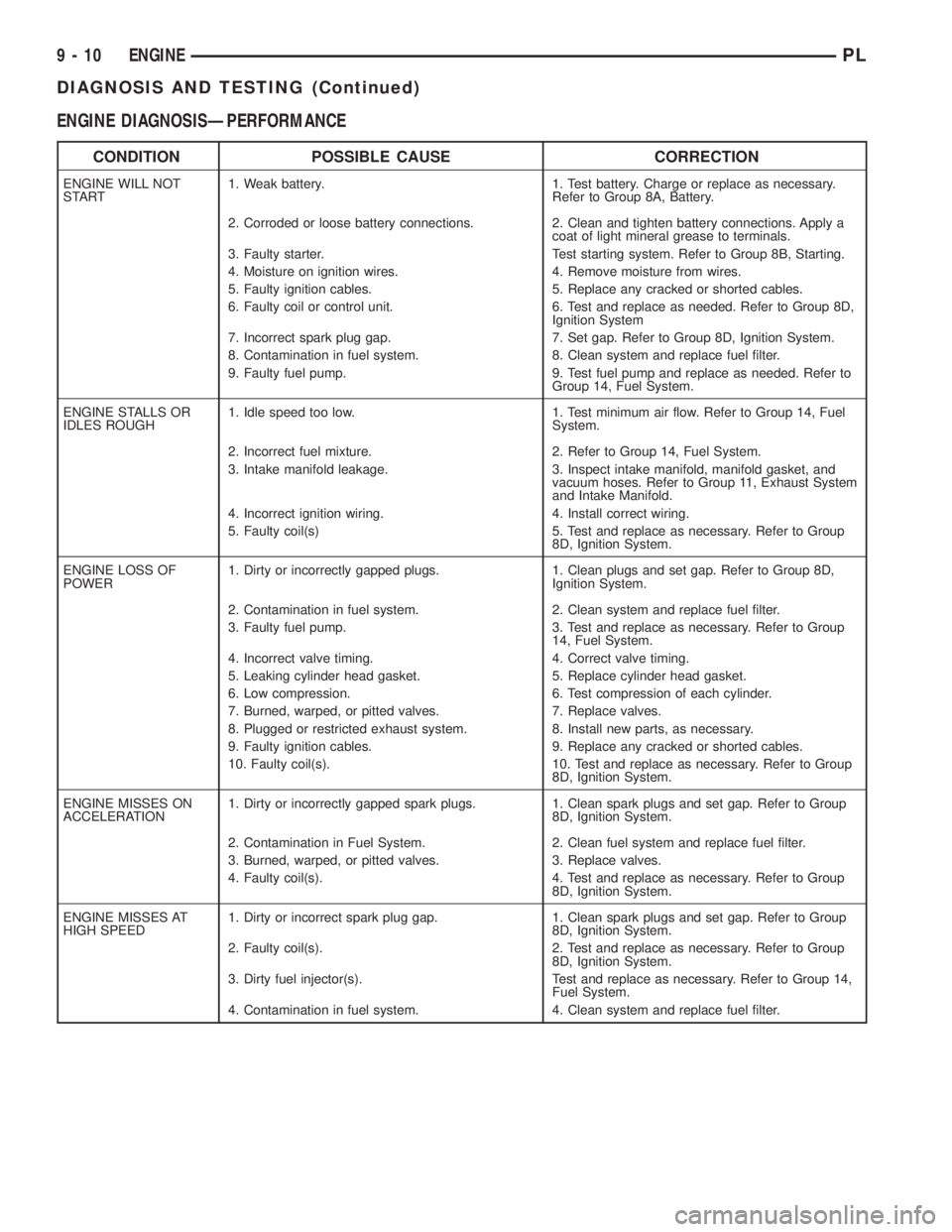
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐPERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT
START1. Weak battery. 1. Test battery. Charge or replace as necessary.
Refer to Group 8A, Battery.
2. Corroded or loose battery connections. 2. Clean and tighten battery connections. Apply a
coat of light mineral grease to terminals.
3. Faulty starter. Test starting system. Refer to Group 8B, Starting.
4. Moisture on ignition wires. 4. Remove moisture from wires.
5. Faulty ignition cables. 5. Replace any cracked or shorted cables.
6. Faulty coil or control unit. 6. Test and replace as needed. Refer to Group 8D,
Ignition System
7. Incorrect spark plug gap. 7. Set gap. Refer to Group 8D, Ignition System.
8. Contamination in fuel system. 8. Clean system and replace fuel filter.
9. Faulty fuel pump. 9. Test fuel pump and replace as needed. Refer to
Group 14, Fuel System.
ENGINE STALLS OR
IDLES ROUGH1. Idle speed too low. 1. Test minimum air flow. Refer to Group 14, Fuel
System.
2. Incorrect fuel mixture. 2. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System.
3. Intake manifold leakage. 3. Inspect intake manifold, manifold gasket, and
vacuum hoses. Refer to Group 11, Exhaust System
and Intake Manifold.
4. Incorrect ignition wiring. 4. Install correct wiring.
5. Faulty coil(s) 5. Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
ENGINE LOSS OF
POWER1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped plugs. 1. Clean plugs and set gap. Refer to Group 8D,
Ignition System.
2. Contamination in fuel system. 2. Clean system and replace fuel filter.
3. Faulty fuel pump. 3. Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group
14, Fuel System.
4. Incorrect valve timing. 4. Correct valve timing.
5. Leaking cylinder head gasket. 5. Replace cylinder head gasket.
6. Low compression. 6. Test compression of each cylinder.
7. Burned, warped, or pitted valves. 7. Replace valves.
8. Plugged or restricted exhaust system. 8. Install new parts, as necessary.
9. Faulty ignition cables. 9. Replace any cracked or shorted cables.
10. Faulty coil(s). 10. Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark plugs. 1. Clean spark plugs and set gap. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
2. Contamination in Fuel System. 2. Clean fuel system and replace fuel filter.
3. Burned, warped, or pitted valves. 3. Replace valves.
4. Faulty coil(s). 4. Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
ENGINE MISSES AT
HIGH SPEED1. Dirty or incorrect spark plug gap. 1. Clean spark plugs and set gap. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
2. Faulty coil(s). 2. Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group
8D, Ignition System.
3. Dirty fuel injector(s). Test and replace as necessary. Refer to Group 14,
Fuel System.
4. Contamination in fuel system. 4. Clean system and replace fuel filter.
9 - 10 ENGINEPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)