tra DODGE NEON 2000 Service Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 174 of 1285

(d) Remove mounting bolt and nut (Fig. 10) and
partially remove air cleaner assembly.
(e) Disconnect accelerator and speed control (if
equipped) cables after the assy. is removed from
position. Remove air cleaner assembly from vehi-
cle.
(4) Remove battery tray from bracket.
(5) Disconnect ground cable at battery tray
bracket.
(6) Disconnect back-up lamp switch connector.
(7) Remove bellhousing cap (Fig. 11).
(8) Disconnect clutch cable from release lever and
remove from transaxle (Fig. 11).
(9) Remove shift cable-to-bracket clips (Fig. 12).
(10) Disconnect shift selector and crossover cable
from levers (Fig. 12). Remove cables and secure out
of the way.
(11) Disconnect the vehicle speed sensor connector
(Fig. 13).
(12) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(13) Remove transaxle oil drain plug and drain oil
into a suitable container.
(14) Remove both axle shafts. Refer to Group 3,
Differential and Driveline for the correct procedures.
(15) Remove structural collar (Fig. 14).
(16) Remove the left engine-to-transaxle lateral
bending brace (Fig. 14).
(17) Remove bellhousing dust cover (Fig. 14).
(18) Remove the right engine-to-transaxle lateral
bending brace (Fig. 15).(19) Remove starter motor (Fig. 16).
(20) Remove drive plate-to-clutch module bolts.
(21) Support engine at oil pan with screw jack and
wood block.
(22) Remove transaxle upper mount thru-bolt.
Gain access to this bolt through the driver's side
wheel house (Fig. 17).
(23) Carefully lower engine and transaxle on screw
jack until proper removal clearance is obtained.
Fig. 10 Air Cleaner Assembly Removal/Installation
1 ± AIR CLEANER ASSY.
2 ± THROTTLE BODY DUCTFWD
Fig. 11 Clutch Cable at Transaxle
1 ± CLUTCH CABLE
2 ± TRANSAXLE
3 ± BELLHOUSING CAP
Fig. 12 Shift Cables at Transaxle
1 ± SHIFT CABLES
2 ± CLIPS
3 ± BRACKET
PLCLUTCH 6 - 9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 175 of 1285
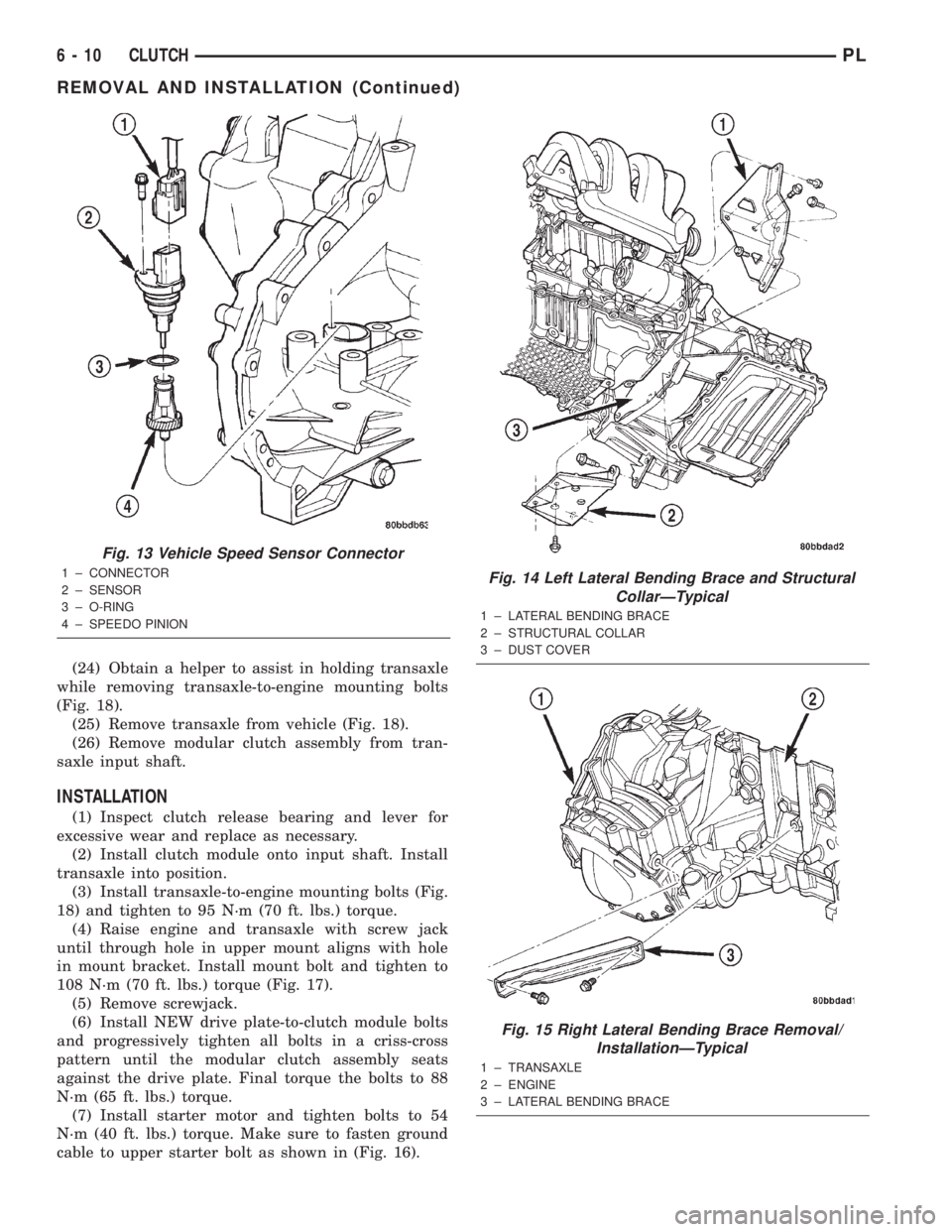
(24) Obtain a helper to assist in holding transaxle
while removing transaxle-to-engine mounting bolts
(Fig. 18).
(25) Remove transaxle from vehicle (Fig. 18).
(26) Remove modular clutch assembly from tran-
saxle input shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Inspect clutch release bearing and lever for
excessive wear and replace as necessary.
(2) Install clutch module onto input shaft. Install
transaxle into position.
(3) Install transaxle-to-engine mounting bolts (Fig.
18) and tighten to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Raise engine and transaxle with screw jack
until through hole in upper mount aligns with hole
in mount bracket. Install mount bolt and tighten to
108 N´m (70 ft. lbs.) torque (Fig. 17).
(5) Remove screwjack.
(6) Install NEW drive plate-to-clutch module bolts
and progressively tighten all bolts in a criss-cross
pattern until the modular clutch assembly seats
against the drive plate. Final torque the bolts to 88
N´m (65 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Install starter motor and tighten bolts to 54
N´m (40 ft. lbs.) torque. Make sure to fasten ground
cable to upper starter bolt as shown in (Fig. 16).
Fig. 13 Vehicle Speed Sensor Connector
1 ± CONNECTOR
2 ± SENSOR
3 ± O-RING
4 ± SPEEDO PINIONFig. 14 Left Lateral Bending Brace and Structural
CollarÐTypical
1 ± LATERAL BENDING BRACE
2 ± STRUCTURAL COLLAR
3 ± DUST COVER
Fig. 15 Right Lateral Bending Brace Removal/
InstallationÐTypical
1 ± TRANSAXLE
2 ± ENGINE
3 ± LATERAL BENDING BRACE
6 - 10 CLUTCHPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 176 of 1285

(8) Connect starter electrical harness and tighten
positive cable nut to 10 N´m (90 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install bellhousing dust cover (Fig. 14).
(10) Install left engine-to-transaxle bending brace
(Fig. 14).(11) Install structural collar (Fig. 14) as follows:
(a) Position collar and install all bolts finger
tight.
(b) Tighten the collar-to-oil pan bolts to 3 N´m
(30 in. lbs.) torque.
(c) Tighten the collar-to-transaxle bolts to 108
N´m (80 ft. lbs.) torque.
(d) Final torque the collar-to-oil pan bolts to 54
N´m (40 ft. lbs.) torque.
(12) Install the right lateral bending brace and
tighten bolts to 81 N´m (60 ft. lbs.) torque (Fig. 15).
(13) Install both front axle driveshafts. Refer to
Group 3, Differential and Driveline for the correct
procedures.
(14) Fill transaxle with suitable amount of Mopart
Manual Transaxle Lubricant (PN 04874465).
(15) Lower vehicle.
(16) Connect vehicle speed sensor connector (Fig.
13).
(17) Connect shift crossover and selector cables to
shift lever. Install cables to bracket and install
retaining clips (Fig. 12).
(18) Connect clutch cable to fork and secure to
transaxle (Fig. 11).
(19) Install bellhousing cap (Fig. 11).
(20) Connect back-up lamp switch connector.
(21) Connect ground strap to transaxle upper
mount bracket.
(22) Install battery lower tray and battery, and
tighten battery hold down clamp to secure battery.
(23) Install the air cleaner/throttle body assy. as
follows:
(a) Connect the accelerator and speed control (if
equipped) cables to the air cleaner/throttle body
assy.
(b) Install assy into position, making sure the
air cleaner locating slot is engaged to the battery
bracket tab, and tighten fasteners to 14 N´m (120
in. lbs.) torque.
(c) Verify throttle body duct is fully seated to
intake manifold and tighten clamp to 5 N´m (40 in.
lbs.) torque.
(d) Connect the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
and Idle Air Control (IAC) connectors.
(e) Connect proportional purge solenoid (PPS)
and crankcase vent hose from throttle body.
(24) Connect the battery cables.
(25) Road test vehicle and inspect for leaks.
Fig. 16 Starter Motor Removal/InstallationÐTypical
1 ± BOLT
2 ± GROUND
3±STARTER
4 ± BOLT
Fig. 17 Transaxle Upper Mount Thru-BoltÐTypical
1 ± MOUNT BRACKET
2 ± BOLT
3 ± MOUNT
PLCLUTCH 6 - 11
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 177 of 1285

RELEASE BEARING AND FORK
Remove the transaxle from the vehicle. See Group
21, Transaxle for removal and installation proce-
dures.
REMOVAL
(1) Move the lever and bearing assembly to a ver-
tical in-line position. Grasp the release lever with
two hands in the pivot stud socket area. Pull with
even pressure and the lever will pop off the pivot±
stud. Do not use a screwdriver or pry bar to pop off
the lever. This may damage the spring clip on the
lever.
(2) As a unit, remove the fork from the bearing
thrust plate. Be careful not to damage retention tabs
on bearing.
(3) Examine the condition of the bearing.It is
pre-lubricated and sealed and should not be
immersed in oil or solvent.
(4) The bearing should turn smoothly when held in
the hand under a light thrust load. A light drag
caused by the lubricant fill is normal. If the bearing
is noisy, rough, or dry, replace the complete bearing
assembly with a new bearing.
(5) Check the condition of the pivot stud spring
clips on back side of clutch fork. If the clips are bro-
ken or distorted, replace the clutch fork.
INSTALLATION
(1) The pivot ball pocket in the fork, as well as the
fork arms should be lubricated with grease prior to
installation.
(2) Assemble the fork to the bearing. The small
pegs on the bearing must go over the fork arms.
(3) Slide the bearing and fork assembly onto the
input shaft bearing retainer, as a unit.
(4) Snap the clutch fork onto the pivot ball.
(5) Reinstall transaxle assembly. Refer to Group
21, Transaxle for further information.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CLUTCH CONTAMINATION
Fluid contamination is a frequent cause of clutch
malfunctions. Oil, grease, water, or other fluids on
the clutch contact surfaces will cause faulty opera-
tion.
During inspection, note if any components are con-
taminated. Look for evidence of oil, grease, or water/
road splash on clutch components.
OIL CONTAMINATION
Oil contamination indicates a leak at the rear main
seal and/or transaxle input shaft. Oil leaks produce a
residue of oil on the transaxle housing interior, clutch
Fig. 18 Transaxle Removal/Installation
1 ± MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
2 ± CLIP3 ± TRANSAXLE
4 ± CLUTCH MODULE BOLT (4)
VIEW A
6 - 12 CLUTCHPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 178 of 1285

cover and flywheel. Heat buildup caused by slippage
can bake the oil residue onto the components. This
glaze-like residue ranges in color from amber to
black.
GREASE CONTAMINATION
Grease contamination is usually a product of over-
lubrication. During clutch service, apply only a small
amount of grease to the input shaft splines. Excess
grease may be thrown off during operation, contami-
nating the disc.
ROAD SPLASH/WATER CONTAMINATION
Road splash contamination is usually caused by
driving the vehicle through deep water puddles.
Water can be forced into the clutch housing, causing
clutch components to become contaminated. Facing of
disc will absorb moisture and bond to the flywheel
and/or, pressure plate, if vehicle is allowed to stand
for some time before use. If this condition occurs,
replacement of clutch assembly may be required.
Drive the vehicle until normal clutch operating tem-
perature has been obtained. This will dry off disc
assembly, pressure plate, and flywheel.
CLEANING PRECAUTIONS
Condensation from steam vapors tend to accumu-
late on the internal clutch mechanism when the vehi-
cle is steam cleaned. Facing of disc will absorb
moisture and will bond to flywheel and/or pressure
plate, if vehicle is allowed to stand for some time
before use. If this condition occurs, it may require
replacement of clutch assembly. After cleaning, drive
the vehicle to its normal clutch operating tempera-
ture. This will dry off disc assembly, pressure plate,
and flywheel.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Modular Clutch-to-Drive Plate Bolts..... 88N´m
(65 ft. lbs.)
Transaxle-to-Engine Mounting Bolts...... 95N´m
(70 ft. lbs.)
PLCLUTCH 6 - 13
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 180 of 1285
COOLING SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COOLING SYSTEM........................1
COOLANT...............................2
COOLANT PERFORMANCE..................2
COOLANT RECOVERY SYSTEM..............3
ENGINE THERMOSTAT.....................3
RADIATOR..............................3
RADIATOR COOLING FAN MODULE...........3
COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE CAP..........4
RADIATOR HOSES AND CLAMPS............5
WATER PUMP...........................5
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION OIL COOLER.....6
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS.................6
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER...................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS..............7
ENGINE THERMOSTAT TESTING............14
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT DIAGNOSIS........14
WATER PUMP DIAGNOSIS................15
COOLING SYSTEM FLOW CHECK...........15
ELECTRIC FAN MOTOR TEST...............15
COOLANT CONCENTRATION TESTING........15
TESTING COOLING SYSTEM FOR LEAKS.....15
PRESSURE CAP TO FILLER NECK SEAL
PRESSURE RELIEF CHECK...............16
PRESSURE TESTING COOLING SYSTEM
PRESSURE CAP.......................16
LOW COOLANT LEVEL AERATION...........17
DEAERATION...........................17
TEMPERATURE GAUGE INDICATION.........17
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER..................17
SERVICE PROCEDURES
COOLANT LEVEL CHECKÐROUTINE.........17COOLANTÐADDING ADDITIONAL...........18
COOLANT LEVELÐSERVICING.............18
COOLING SYSTEMÐDRAINING.............19
COOLING SYSTEMÐREFILLING............19
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
WATER PUMP..........................19
WATER PUMP INLET TUBE................20
ENGINE THERMOSTAT....................20
RADIATOR.............................21
RADIATOR DRAINCOCK...................22
COOLING FAN MODULE...................22
COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER..........23
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER..................24
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS................24
AUTOMATIC BELT TENSIONER & PULLEY....26
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
COOLING FAN MODULE...................26
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
WATER PUMP..........................28
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT INSPECTION.......28
COOLING SYSTEM CAP...................28
COOLING SYSTEM CLEANING..............28
RADIATOR FLUSHING....................28
REVERSE FLUSHING.....................29
CHEMICAL CLEANING....................29
ADJUSTMENTS
BELT TENSION..........................29
SPECIFICATIONS
COOLING SYSTEM CAPACITY..............30
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS.................30
SPECIAL TOOLS
COOLING..............................30
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system consists of an engine cooling
module, thermostat, coolant, and a water pump to
circulate the coolant. The engine cooling module may
consist of a radiator, electric fan motor, fan, shroud,
coolant reserve system, transmission oil cooler, hoses,clamps, air conditioning condenser and transmission
oil lines.
²When the Engine is cold: The thermostat is
closed and the cooling system has no flow through
the radiator. The coolant flows through the engine,
heater system and bypass.
²When the Engine is warm: Thermostat is open
and the cooling system has flow through the radiator,
engine, heater system, and bypass.
PLCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 1
Page 181 of 1285

Coolant flow circuit for the 2.0L engine is shown in
(Fig. 1).
During any reassembly procedures all pipe fittings
in water jacket, and water box require cleaning and
application of thread sealant for entire length of
threads.
COOLANT
The cooling system is designed around the coolant.
The coolant must accept heat from engine block
metal and in the cylinder head area near the exhaust
valves. Then coolant carries this heat to the radiator
where the tube/fin assemblies can give off the heat to
the air.
MopartAntifreeze or the equivalent is recom-
mended for optimum cooling performance and corro-
sion protection when mixed to a freeze point of -37É C
(-35É F).
COOLANT REPLACEMENT
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
schedule.
COOLANT PERFORMANCE
Performance is measurable. For heat transfer pure
water excels (Formula = 1 btu per minute for eachdegree of temperature rise for each pound of water).
This formula is altered when necessary additives to
control boiling, freezing, and corrosion are added as
follows:
²Pure Water (1 btu) boils at 100ÉC (212ÉF) and
freezes at 0ÉC (32ÉF).
²100 Percent Glycol (.7 btu) can cause a hot
engine and detonation and will raise the freeze point
to 22ÉC (-8ÉF).
²50/50 Glycol and Water (0.82 btu) is the recom-
mended combination that provides a freeze point of
-37ÉC (-35ÉF). The radiator, water pump, engine
water jacket, radiator pressure cap, thermostat, tem-
perature gauge, sending unit and heater are all
designed for 50/50 glycol.
Where required, a 56 percent glycol and 44 percent
water mixture will provide a freeze point of -59ÉC
(-50ÉF).
CAUTION: Richer mixtures cannot be measured
with field equipment which can lead to problems
associated with 100 percent glycol.SELECTION AND ADDITIVES
The use of aluminum cylinder heads, intake mani-
folds, and water pumps requires special corrosion
Fig. 1 Cooling System Operation
1 ± HEATER
2 ± HEAT UP
3 ± COOL DOWN
4 ± PRESSURE CAP
5 ± THERMOSTAT HOUSING6 ± WATER PUMP
7 ± ENGINE
8 ± COOLANT RECOVERY SYSTEM TANK
9 ± RADIATOR
7 - 2 COOLING SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 182 of 1285

protection. MopartAntifreeze or the equivalent is
recommended for best engine cooling without corro-
sion. When mixed only to a freeze point of -37ÉC
(-35ÉF) to -59ÉC (-50ÉF). If it looses color or becomes
contaminated, drain, flush, and replace with fresh
properly mixed solution.
COOLANT RECOVERY SYSTEM
This system works in conjunction with the radiator
pressure cap to utilize thermal expansion and con-
traction of the coolant to keep the coolant free of
trapped air. The system provides space for expansion
and contraction. Also, the system provides a conve-
nient and safe method for checking and adjusting the
coolant level at atmospheric pressure without remov-
ing the pressure cap. It also provides some reserve
coolant to compensate for minor leaks and evapora-
tion or boiling losses. All vehicles are equipped with
this system (Fig. 2).
Refer to Coolant Level Check, Deaeration, and
Pressure Cap sections for operation and service.
ENGINE THERMOSTAT
The engine thermostat is located on the front of
the engine (radiator side) in the thermostat housing/
engine outlet connector. The thermostat has an air
bleed (vent) located in the flange and a O-ring for
sealing incorporate on it. There is a relief in the ther-
mostat housing/outlet connector for the O-ring.
The engine thermostat is a wax pellet driven,
reverse poppet choke type. It is designed to provide
the fastest warm up possible by preventing leakage
through it and to guarantee a minimum engine oper-
ating temperature of 88 to 93ÉC (192 to 199ÉF). Also,
the thermostat will automatically reach wide open, to
accommodate unrestricted flow to the radiator astemperature of the coolant rises in hot weather to
around 104ÉC (220ÉF). Above this temperature the
coolant temperature is controlled by the radiator, fan,
and ambient temperatureÐnot the thermostat.
A thermostats primary purpose is to maintain
engine temperature in a range that will provide sat-
isfactory engine performance and emission levels
under all expected driving conditions. It also provides
hot water (coolant) for heater performance. It does
this by transferring heat from engine metal and
automatic transmission oil cooler (if equipped) to
coolant, moving this heated coolant to the heater core
and radiator, and then transferring this heat to the
ambient air.
RADIATOR
The radiator is a down-flow type (vertical tubes)
with design features that provide greater strength,
as well as sufficient heat transfer capabilities to keep
the engine coolant within operating temperatures.
The radiator functions as a heat exchanger, using
air flow across the exterior of the radiator tubes. This
heat is then transferred from the coolant and into
the passing air.
The radiator has an aluminum core with plastic
tanks. Although stronger than brass, plastic tanks
are subject to damage by impact. Always handle radi-
ator with care.
RADIATOR COOLING FAN MODULE
The radiator cooling fan is a single speed electric
motor driven fan. The fan module includes an electric
motor, fan blade, and a support shroud that is
attached to the radiator (Fig. 3).
Fig. 2 Coolant Recovery System
1 ± RECOVERY HOSE
2 ± ENGINE COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
3 ± PRESSURE CAP
Fig. 3 Radiator Fan
1 ± SCREWS
2 ± LOWER MOUNTS
3 ± FAN MOTOR ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
PLCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 183 of 1285

Radiator cooling fan control operation is accomplished
two ways. The fan always runs when the air condition-
ing compressor clutch is engaged. In addition to this
control, the fan is turned on by the temperature of the
coolant which is sensed by the coolant temperature sen-
sor which sends the message to the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM). The PCM turns on the fan through a
fan relay by grounding the relay's coil. The fan relay is
located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC) (Fig. 4).
Refer to the label beneath the PDC cover for location of
fan relay.
The PCM will actuate the fan relay whenever the A/C
clutch is engaged regardless of coolant temperature and
vehicle speed. If the A/C clutch is not engaged, the PCM
will actuate the fan relay when the coolant temperature
reaches approximately (97É C) 207É F and turns off the
fan relay when the coolant temperature drops to
approximately (94ÉC) 201É F. The fan relay is also
turned off when the vehicle speed is above approxi-
mately 100 Km/h (62 MPH). Refer to Group 8W, Wiring
Diagrams for circuity provided.
If the cooling fan is inoperative or a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) related to fan control has been
set, refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic
Manual for complete diagnostic procedures.
COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE CAP
The cooling system pressure cap is located on the cool-
ant outlet housing near the front of the cylinder head.
The cooling system will operate at higher than atmo-
spheric pressure. The higher pressure raises the coolant
boiling point, allowing increased radiator cooling capac-
ity. The pressure cap will release cooling system pres-
sure in a range of 97±124 kPa (14±18 psi).
A vent valve located in the center of the cap allows
a small amount of coolant flow from the coolant
reserve system (CRS) tank. This valve is spring
loaded in the closed position. However, it must be
free to open during system cool-down.If the valve is
stuck shut, the radiator hoses will collapse on
cool-down. Clean the vent valve (Fig. 5) to
ensure proper sealing function.
There is a gasket in the cap that seals to the top of
the filler neck so that vacuum is maintained to draw
coolant back into the system from the coolant reserve
system (CRS) tank.
Fig. 4 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
RADIATOR COOLING FAN OPERATION CHART
Cooling Fan Control
A/C Off
Fan On: 97É C (207É F)
Fan Off: 94É C (201É F)Vehicle Speed >
100 Km/h (62
MPH)
A/C On
Fan OnÐregardless of coolant temperature or vehicle
speed.
Fig. 5 Cooling System Pressure Cap
1 ± PRESSURE RATING
2 ± FILLER NECK SEAL
3 ± PRESSURE VALVE
4 ± VACUUM VENT VALVE (SHOWN IN SEALING POSITION)
7 - 4 COOLING SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 185 of 1285
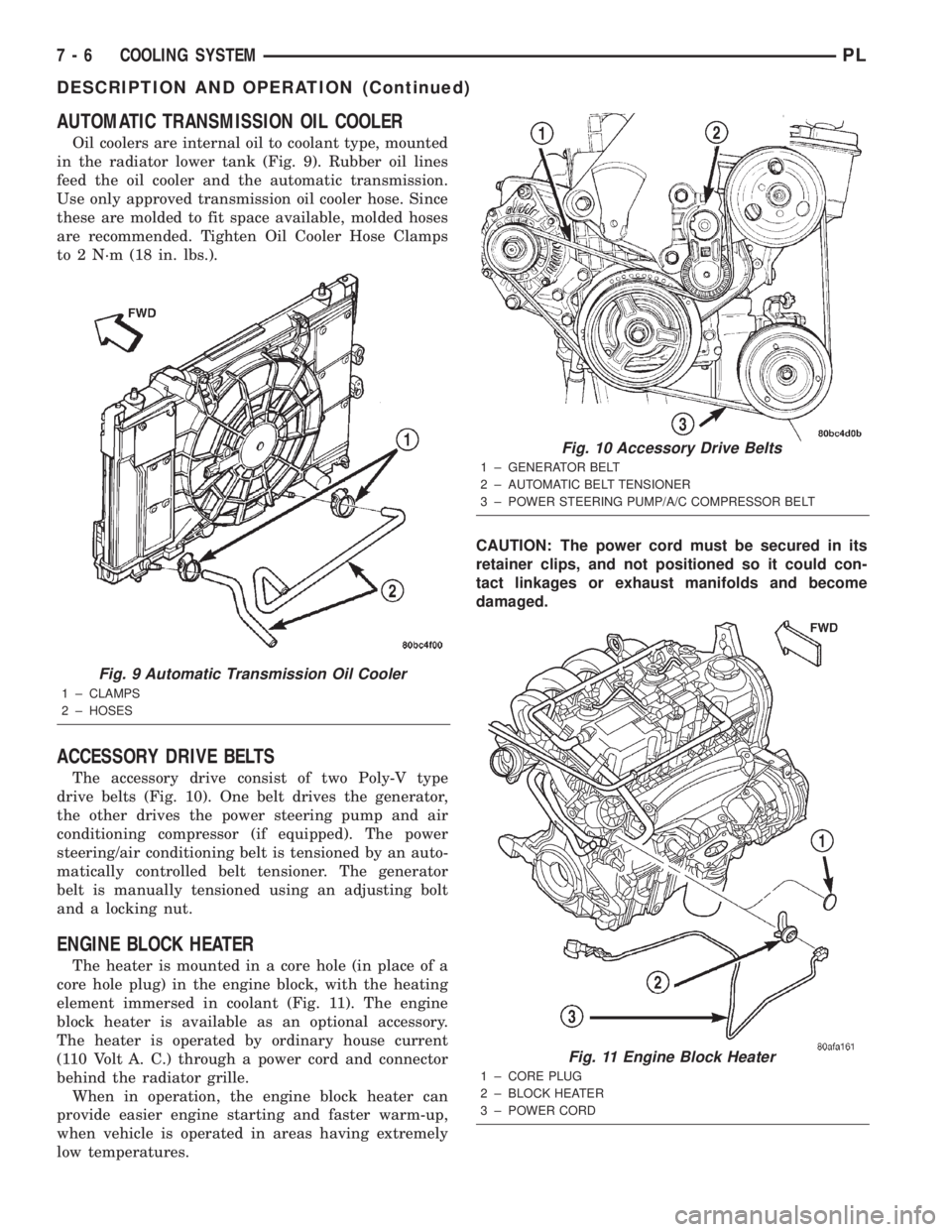
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION OIL COOLER
Oil coolers are internal oil to coolant type, mounted
in the radiator lower tank (Fig. 9). Rubber oil lines
feed the oil cooler and the automatic transmission.
Use only approved transmission oil cooler hose. Since
these are molded to fit space available, molded hoses
are recommended. Tighten Oil Cooler Hose Clamps
to 2 N´m (18 in. lbs.).
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS
The accessory drive consist of two Poly-V type
drive belts (Fig. 10). One belt drives the generator,
the other drives the power steering pump and air
conditioning compressor (if equipped). The power
steering/air conditioning belt is tensioned by an auto-
matically controlled belt tensioner. The generator
belt is manually tensioned using an adjusting bolt
and a locking nut.
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
The heater is mounted in a core hole (in place of a
core hole plug) in the engine block, with the heating
element immersed in coolant (Fig. 11). The engine
block heater is available as an optional accessory.
The heater is operated by ordinary house current
(110 Volt A. C.) through a power cord and connector
behind the radiator grille.
When in operation, the engine block heater can
provide easier engine starting and faster warm-up,
when vehicle is operated in areas having extremely
low temperatures.CAUTION: The power cord must be secured in its
retainer clips, and not positioned so it could con-
tact linkages or exhaust manifolds and become
damaged.
Fig. 9 Automatic Transmission Oil Cooler
1 ± CLAMPS
2 ± HOSES
Fig. 10 Accessory Drive Belts
1 ± GENERATOR BELT
2 ± AUTOMATIC BELT TENSIONER
3 ± POWER STEERING PUMP/A/C COMPRESSOR BELT
Fig. 11 Engine Block Heater
1 ± CORE PLUG
2 ± BLOCK HEATER
3 ± POWER CORD
7 - 6 COOLING SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)