hose DODGE NEON 2000 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 1100 of 1285
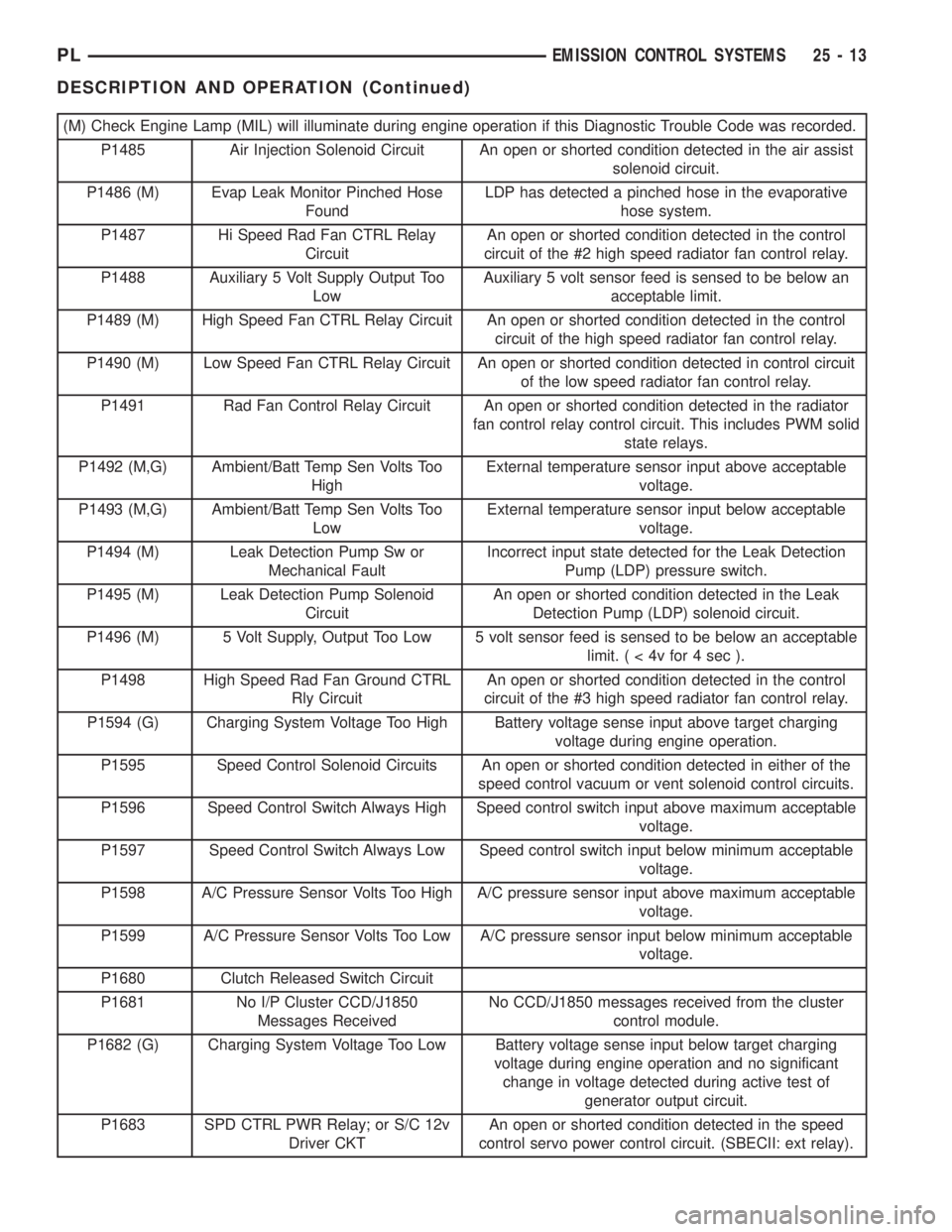
(M) Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
P1485 Air Injection Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the air assist
solenoid circuit.
P1486 (M) Evap Leak Monitor Pinched Hose
FoundLDP has detected a pinched hose in the evaporative
hose system.
P1487 Hi Speed Rad Fan CTRL Relay
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the control
circuit of the #2 high speed radiator fan control relay.
P1488 Auxiliary 5 Volt Supply Output Too
LowAuxiliary 5 volt sensor feed is sensed to be below an
acceptable limit.
P1489 (M) High Speed Fan CTRL Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the control
circuit of the high speed radiator fan control relay.
P1490 (M) Low Speed Fan CTRL Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in control circuit
of the low speed radiator fan control relay.
P1491 Rad Fan Control Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the radiator
fan control relay control circuit. This includes PWM solid
state relays.
P1492 (M,G) Ambient/Batt Temp Sen Volts Too
HighExternal temperature sensor input above acceptable
voltage.
P1493 (M,G) Ambient/Batt Temp Sen Volts Too
LowExternal temperature sensor input below acceptable
voltage.
P1494 (M) Leak Detection Pump Sw or
Mechanical FaultIncorrect input state detected for the Leak Detection
Pump (LDP) pressure switch.
P1495 (M) Leak Detection Pump Solenoid
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the Leak
Detection Pump (LDP) solenoid circuit.
P1496 (M) 5 Volt Supply, Output Too Low 5 volt sensor feed is sensed to be below an acceptable
limit.(<4vfor4sec).
P1498 High Speed Rad Fan Ground CTRL
Rly CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the control
circuit of the #3 high speed radiator fan control relay.
P1594 (G) Charging System Voltage Too High Battery voltage sense input above target charging
voltage during engine operation.
P1595 Speed Control Solenoid Circuits An open or shorted condition detected in either of the
speed control vacuum or vent solenoid control circuits.
P1596 Speed Control Switch Always High Speed control switch input above maximum acceptable
voltage.
P1597 Speed Control Switch Always Low Speed control switch input below minimum acceptable
voltage.
P1598 A/C Pressure Sensor Volts Too High A/C pressure sensor input above maximum acceptable
voltage.
P1599 A/C Pressure Sensor Volts Too Low A/C pressure sensor input below minimum acceptable
voltage.
P1680 Clutch Released Switch Circuit
P1681 No I/P Cluster CCD/J1850
Messages ReceivedNo CCD/J1850 messages received from the cluster
control module.
P1682 (G) Charging System Voltage Too Low Battery voltage sense input below target charging
voltage during engine operation and no significant
change in voltage detected during active test of
generator output circuit.
P1683 SPD CTRL PWR Relay; or S/C 12v
Driver CKTAn open or shorted condition detected in the speed
control servo power control circuit. (SBECII: ext relay).
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 13
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1106 of 1285

when the MIL is illuminated due to any of the fol-
lowing faults:
²Misfire
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Fuel System Rich
²Fuel System Lean
²EGR Monitor
²MAP
²TPS
²ECT
²DCP Solenoid
Conflict Conditions-With or Without LDPÐ
The EVAP Monitor does not run if any of the follow-
ing tests are in progress:
²Catalyst
²EGR
²Fuel System
²Misfire
TRIP DEFINITION
OPERATION
A ªTripº means vehicle operation (following an
engine-off period) of duration and driving mode such
that all components and systems are monitored at
least once by the diagnostic system. The monitors
must successfully pass before the PCM can verify
that a previously malfunctioning component is meet-
ing the normal operating conditions of that compo-
nent. For misfire or fuel system malfunction, the
MIL may be extinguished if the fault does not recur
when monitored during three subsequent sequential
driving cycles in which conditions are similar to
those under which the malfunction was first deter-
mined.
Anytime the MIL is illuminated, a DTC is stored.
The DTC can self erase only when the MIL has been
extinguished. Once the MIL is extinguished, the
PCM must pass the diagnostic test for the most
recent DTC for 40 warm-up cycles (80 warm-up
cycles for the Fuel System Monitor and the Misfire
Monitor). A warm-up cycle can best be described by
the following:
²The engine must be running
²A rise of 40ÉF in engine temperature must occur
from the time when the engine was started
²Engine coolant temperature must reach at least
160ÉF
²A ªdriving cycleº that consists of engine start up
and engine shut off.
Once the above conditions occur, the PCM is con-
sidered to have passed a warm-up cycle. Due to the
conditions required to extinguish the MIL and erase
the DTC, it is most important that after a repair has
been made, all DTC's be erased and the repair veri-
fied.
MONITORED COMPONENT
DESCRIPTION
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (Check Engine) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of a
greater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum
and 1600 rpm.
Any component that has an associated limp in will
set a fault after 1 trip with the malfunction present.
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Description
Charts in this section and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Procedure Manual for diagnostic
procedures.
The following is a list of the monitored compo-
nents:
²Comprehensive Components
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Catalyst Monitor
COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENTS
Along with the major monitors, OBD II requires
that the diagnostic system monitor any component
that could affect emissions levels. In many cases,
these components were being tested under OBD I.
The OBD I requirements focused mainly on testing
emissions-related components for electrical opens and
shorts.
However, OBD II also requires that inputs from
powertrain components to the PCM be tested for
rationality, and that outputs to powertrain compo-
nents from the PCM be tested forfunctionality.
Methods for monitoring the various Comprehensive
Component monitoring include:
(1) Circuit Continuity
²Open
²Shorted high
²Shorted to ground
(2) Rationality or Proper Functioning
²Inputs tested for rationality
²Outputs tested for functionality
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 19
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1112 of 1285

EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROLS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
EVAPORATION CONTROL SYSTEM..........25
EVAP CANISTER.........................25
PROPORTIONAL PURGE SOLENOIDÐPCM
OUTPUT..............................25
LEAK DETECTION PUMP..................26
LEAK DETECTION PUMP PRESSURE
SWITCH..............................27
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION (PCV)
SYSTEMS.............................28POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION VALVE. . . 28
VEHICLE EMISSION CONTROL
INFORMATION LABEL...................29
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
EVAP CANISTER.........................29
LEAK DETECTION PUMP..................30
PROPORTIONAL PURGE SOLENOID VALVE....30
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
EVAPORATION CONTROL SYSTEM
OPERATION
The evaporation control system prevents the emis-
sion of fuel tank vapors into the atmosphere. When
fuel evaporates in the fuel tank, the vapors pass
through vent hoses or tubes to an activated carbon
filled evaporative canister. The canister temporarily
holds the vapors. The Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) allows intake manifold vacuum to draw
vapors into the combustion chambers during certain
operating conditions.
All engines use a proportional purge solenoid sys-
tem. The PCM controls vapor flow by operating the
purge solenoid. Refer to Proportional Purge Solenoid
in this section.
NOTE: The evaporative system uses specially man-
ufactured hoses. If they need replacement, only use
fuel resistant hose. Also the hoses must be able to
pass an Ozone compliance test.
NOTE: For more information on Onboard Refueling
Vapor Recovery (ORVR), refer to the Fuel Delivery
section.
EVAP CANISTER
DESCRIPTION
The vacuum and vapor tubes connect to the top of
the canister (Fig. 1).
OPERATION
All vehicles use a, maintenance free, evaporative
(EVAP) canister. Fuel tank vapors vent into the can-
ister. The canister temporarily holds the fuel vapors
until intake manifold vacuum draws them into the
combustion chamber. The Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) purges the canister through the proportional
purge solenoid. The PCM purges the canister at pre-
determined intervals and engine conditions.
Purge Free Cells
Purge-free memory cells are used to identify the
fuel vapor content of the evaporative canister. Since
the evaporative canister is not purged 100% of the
time, the PCM stores information about the evapora-
tive canister's vapor content in a memory cell.
The purge-free cells are constructed similar to cer-
tain purge-normal cells. The purge-free cells can be
monitored by the DRB III Scan Tool. The only differ-
ence between the purge-free cells and normal adap-
tive cells is that in purge-free, the purge is
completely turned off. This gives the PCM the ability
to compare purge and purge-free operation.
PROPORTIONAL PURGE SOLENOIDÐPCM
OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION
OPERATION
All vehicles use a proportional purge solenoid. The
solenoid regulates the rate of vapor flow from the
EVAP canister to the throttle body. The PCM oper-
ates the solenoid.
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged.
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 25
Page 1115 of 1285

The check valves are one-way valves. The first
check valve is used to draw outside air into the lower
chamber of the LDP (the space that is below the
pump diaphragm). The second check valve is used to
vent this outside air, which has become pressurized
from the fall of the pump diaphragm, into the evap-
orative system.
The spring loaded vent seal valve, inside the LDP
is used to seal off the evaporative system. When the
pump diaphragm is in the ªupº position the spring
pushes the vent seal valve closed. The vent seal valve
opens only when the pump diaphragm is in its ªfull
downº position. When the pump assembly is in its
pump mode the pump diaphragm is not allowed to
descend (fall) so far as to allow the vent seal valve to
open. This allows the leak detection pump to develop
the required pressure within the evaporative system
for system leak testing.
A pressure build up within the evaporative system
may cause pressure on the lower side of the LDP dia-
phragm. This will cause the LDP diaphragm to
remain in its ªupº position (stuck in the up position).
This condition can occur even when the solenoid
valve is deenergized. This condition can be caused by
previous cycling (pumping) of the LDP by the techni-
cian (dealer test). Another way that this condition is
created is immediately following the running of the
vehicle evaporative system monitor. In this case, the
PCM has not yet opened the proportional purge sole-
noid in order to vent the pressure that has been built
up in the evaporative system to the engine combus-
tion system. The technician will need to vent the
evaporative system pressure via the vehicle fuel filler
cap and its fuel filler secondary seal (if so equipped
in the fuel filler neck). This will allow the technician
to cycle the LDP and to watch switch state changes.
After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained until the purge sys-
tem is activated, in effect creating a leak. If the dia-
phragm falls (as is expected), causing the reed switch
to change state, then the diagnostic test is completed.
When of the evaporative system leak monitor
begins its various tests, a test is performed to deter-
mine that no part of the evaporative system is
blocked. In this test, the LDP is cycled (pumped) a
calibrated (few) number of times. Pressure should not
build up in the evaporative system. If pressure is
present, then LDP diaphragm is forced to stay in its
ªupº position. The reed switch now stays open and
the PCM senses this open (incorrect) state. The evap-
orative system monitor will fail the test because of a
detected obstruction within the system.
Possible causes:
²Open or shorted LDP switch sense circuit
²Leak Detection Pump switch failure²Open fused ignition switch output
²Restricted, disconnected, or blocked manifold
vacuum source
²Obstruction of hoses or lines
²PCM failure
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION (PCV)
SYSTEMS
DESCRIPTION
OPERATION
Intake manifold vacuum removes crankcase vapors
and piston blow-by from the engine. The emissions
pass through the PCV valve into the intake manifold
where they become part of the calibrated air-fuel
mixture. They are burned and expelled with the
exhaust gases. The air cleaner supplies make up air
when the engine does not have enough vapor or
blow-by gases. In this system, fresh air does not
enter the crankcase.
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION VALVE
OPERATION
The PCV valve contains a spring loaded plunger.
The plunger meters the amount of crankcase vapors
routed into the combustion chamber based on intake
manifold vacuum.
When the engine is not operating or during an
engine backfire, the spring forces the plunger back
against the seat. This prevents vapors from flowing
through the valve (Fig. 4).
When the engine is at idle or cruising, high mani-
fold vacuum is present. At these times manifold vac-
uum is able to completely compress the spring and
Fig. 3 PCV System
25 - 28 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1116 of 1285

pull the plunger to the top of the valve (Fig. 5). In
this position there is minimal vapor flow through the
valve.
During periods of moderate intake manifold vac-
uum the plunger is only pulled part way back from
the inlet. This results in maximum vapor flow
through the valve (Fig. 6).
VEHICLE EMISSION CONTROL INFORMATION
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
All models have a Vehicle Emission Control Infor-
mation (VECI) Label. DaimlerChrysler permanently
attaches the label in the engine compartment. It can-
not be removed without defacing information and
destroying the label.
The label contains the vehicle's emission specifica-
tions and vacuum hose routings. All hoses must be
connected and routed according to the label.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
EVAP CANISTER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Raise vehicle and support.
(3) Disconnect the hoses from the EVAP canister
(Fig. 7).
(4) Remove 1 nuts from the bracket of the EVAP
canister (Fig. 8).
(5) Remove EVAP canister from bracket.
Fig. 4 Engine Off or Engine BackfireÐNo Vapor
Flow
Fig. 5 High Intake Manifold VacuumÐMinimal Vapor
Flow
Fig. 6 Moderate Intake Manifold VacuumÐMaximum
Vapor Flow
Fig. 7 EVAP Canister
Fig. 8 EVAP Bracket and Bracket
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 29
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1117 of 1285

INSTALLATION
(1) Install EVAP canister to Bracket (Fig. 8).
(2) Install 2 nuts to EVAP canister and bracket
and tighten nuts to 6.7 N´m (60 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect hoses.
(4) Install EVAP canister and bracket to vehicle
and tighten nut 22.4 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Connect negative battery cable.
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle on a hoist.
(2) Push locking tab on electrical connector to
unlock and remove connector.
(3) loosen the sway bar bracket to remove the
pump bracket.
(4) Remove pump and bracket as an assembly.
(5) Disconnect lines from LDP.
(6) Remove filter.
(7) Remove pump from bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install pump to bracket and tighten bolts to 1.2
N´m (10.6 in. lbs.).
(2) Install filter and tighten to 2.8 N´m (25 in.
lbs.).
(3)Before installing hoses to LDP, make sure
they are not cracked or split. If a hose leaks, it
will cause the Check Engine Lamp to illumi-
nate.Connect lines to the LDP.
NOTE: The LDP bracket must be between the rail
and sway bar bracket.
(4) Install pump and bracket assembly to body and
tighten bolts to 5.0 N´m (45 in. lbs.).
(5) Install sway bar bracket bolt and tighten bolts
to 33.8 N´m (25 ft. lbs.).
(6) Install electrical connector to pump and push
locking tab to lock.
(7) Lower vehicle(8) Use the DRB scan tool, verify proper operation
of LDP.
PROPORTIONAL PURGE SOLENOID VALVE
The solenoid attaches to a bracket near the steer-
ing gear (Fig. 9). The solenoid will not operate unless
it is installed correctly.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and support.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from solenoid.
(3) Disconnect vacuum tubes from solenoid.
(4) Remove solenoid from bracket.
INSTALLATION
The top of the solenoid has TOP printed on it. The
solenoid will not operate unless it is installed cor-
rectly.
(1) Install solenoid on bracket.
(2) Connect vacuum tube to solenoid.
(3) Connect electrical connector to solenoid.
(4) Lower vehicle.
Fig. 9 Proportional Purge Solenoid Valve
25 - 30 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1135 of 1285

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WATER LEAKS
Water leaks can be caused by poor sealing,
improper body component alignment, body seam
porosity, missing plugs, or blocked drain holes. Cen-
trifugal and gravitational force can cause water to
drip from a location away from the actual leak point,
making leak detection difficult. All body sealing
points should be water tight in normal wet-driving
conditions. Water flowing downward from the front of
the vehicle should not enter the passenger or luggage
compartment. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal water tight under all conditions. At
times, side glass or door seals will allow water to
enter the passenger compartment during high pres-
sure washing or hard driving rain (severe) condi-
tions. Overcompensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop a water leak that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After completing
a repair, water-test vehicle to verify leak has stopped
before returning vehicle to use.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE WATER LEAK TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place, body
drains are clear, and body components are properly
aligned and sealed. If component alignment or seal-
ing is necessary, refer to the appropriate section of
this group for proper procedures.
WATER LEAK TESTS
WARNING: DO NOT USE ELECTRIC SHOP LIGHTS
OR TOOLS IN WATER TEST AREA. PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT.
When the conditions causing a water leak have
been determined, simulate the conditions as closely
as possible.
²If a leak occurs with the vehicle parked in a
steady light rain, flood the leak area with an open-
ended garden hose.
²If a leak occurs while driving at highway speeds
in a steady rain, test the leak area with a reasonable
velocity stream or fan spray of water. Direct the
spray in a direction comparable to actual conditions.
²If a leak occurs when the vehicle is parked on an
incline, hoist the end or side of the vehicle to simu-
late this condition. This method can be used when
the leak occurs when the vehicle accelerates, stops or
turns. If the leak occurs on acceleration, hoist the
front of the vehicle. If the leak occurs when braking,
hoist the back of the vehicle. If the leak occurs on left
turns, hoist the left side of the vehicle. If the leak
occurs on right turns, hoist the right side of the vehi-cle. For hoisting recommendations refer to Group 0,
Lubrication and Maintenance, General Information
section.
WATER LEAK DETECTION
To detect a water leak point-of-entry, do a water
test and watch for water tracks or droplets forming
on the inside of the vehicle. If necessary, remove inte-
rior trim covers or panels to gain visual access to the
leak area. If the hose cannot be positioned without
being held, have someone help do the water test.
Some water leaks must be tested for a considerable
length of time to become apparent. When a leak
appears, find the lowest point of the water track or
drop. After leak point has been found, repair the leak
and water test to verify that the leak has stopped.
Locating the entry point of water that is leaking
into a cavity between panels can be difficult. The
trapped water may splash or run from the cavity,
often at a distance from the entry point. Most water
leaks of this type become apparent after accelerating,
stopping, turning, or when on an incline.
MIRROR INSPECTION METHOD
When a leak point area is visually obstructed, use
a suitable mirror to gain visual access. A mirror can
also be used to deflect light to a limited-access area
to assist in locating a leak point.
BRIGHT LIGHT LEAK TEST METHOD
Some water leaks in the luggage compartment can
be detected without water testing. Position the vehi-
cle in a brightly lit area. From inside the darkened
luggage compartment inspect around seals and body
seams. If necessary, have a helper direct a drop light
over the suspected leak areas around the luggage
compartment. If light is visible through a normally
sealed location, water could enter through the open-
ing.
PRESSURIZED LEAK TEST METHOD
When a water leak into the passenger compart-
ment cannot be detected by water testing, pressurize
the passenger compartment and soap test exterior of
the vehicle. To pressurize the passenger compart-
ment, close all doors and windows, start engine, and
set heater control to high blower in HEAT position. If
engine can not be started, connect a charger to the
battery to ensure adequate voltage to the blower.
With interior pressurized, apply dish detergent solu-
tion to suspected leak area on the exterior of the
vehicle. Apply detergent solution with spray device or
soft bristle brush. If soap bubbles occur at a body
seam, joint, seal or gasket, the leak entry point could
be at that location.
23 - 18 BODYPL
Page 1232 of 1285
HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
A/C APPLICATION TABLE...................2
HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING CONTROL...2
HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING............2
INTRODUCTION..........................3
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS......4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
A/C REFRIGERANT LINES..................4
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR................5
COMPRESSOR...........................5
COMPRESSOR FRONT SHAFT SEAL..........6
CONDENSATION DRAIN TUBE...............6
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS...6
EVAPORATOR PROBE......................6
HANDLING TUBING AND FITTINGS...........6
HIGH PRESSURE CUT OUT SWITCH..........6
LOW PRESSURE CUT OFF SWITCH..........6
SIDE WINDOW DEMISTERS................7
SYSTEM AIRFLOW........................7
SYSTEM OIL LEVEL.......................7
VACUUM CONTROL SYSTEM................8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
A/C PERFORMANCE TEST..................9
BLOWER MOTOR ELECTRICAL DIAGNOSIS....9
BLOWER MOTOR VIBRATION AND/OR
NOISE DIAGNOSIS.....................11
COMPRESSOR NOISE DIAGNOSIS..........11
EVAPORATOR PROBE TEST................11
EXPANSION VALVE.......................11
HEATER PERFORMANCE TEST.............13
LOW PRESSURE CUT OFF SWITCH.........14
SYSTEM CHARGE LEVEL TEST.............14
VACUUM CONTROL SYSTEM...............15
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CHARGING A/C SYSTEM..................17EVACUATING REFRIGERANT SYSTEM........18
R-134a REFRIGERANT....................19
SERVICING REFRIGERANT OIL LEVEL.......19
SYSTEM LEAK CHECKING.................20
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
A/C FILTER/DRIER.......................20
A/C SERVICE PORT VALVE CORES..........21
BLOWER MOTOR AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY....21
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR...............22
BLOWER MOTOR WHEEL.................22
COMPRESSOR..........................22
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL ASSEMBLY.....23
CONDENSATION DRAIN TUBE..............25
CONDENSER............................25
DISCHARGE LINE........................26
EVAPORATOR...........................26
EVAPORATOR PROBE.....................26
EXPANSION VALVE.......................27
HEATER CORE..........................28
HEATER HOSES.........................28
HIGH PRESSURE CUT OUT SWITCH.........29
HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE............29
LIQUID LINE............................29
LOW PRESSURE CUT OFF SWITCH.........29
MODE CONTROL CABLE..................30
RECIRCULATION DOOR ACTUATOR.........31
SUCTION LINE..........................31
TEMPERATURE CONTROL CABLE...........32
UNIT HOUSING..........................32
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
HEATER-A/C HOUSING....................34
ADJUSTMENTS
MODE CONTROL CABLE..................34
TEMPERATURE CONTROL CABLE...........34
PLHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 1
Page 1237 of 1285

COMPRESSOR FRONT SHAFT SEAL
The compressor front shaft seal is not serviceable.
If a leak is detected at the shaft seal, the compressor
must be replaced as a unit.
CONDENSATION DRAIN TUBE
Condensation that accumulates in the evaporator
housing is drained from a tube through the dash and
on to the ground. This tube must be kept open to
prevent condensate water from collecting in the bot-
tom of the housing.
The tapered end of the drain tube is designed to
keep contaminants from entering the heater A/C unit
housing. If the tube is pinched or blocked, condensate
cannot drain, causing water to back up and spill into
the passenger compartment. It is normal to see con-
densate drainage below the vehicle. If the tube is
damaged, it should be replaced.
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
To maintain ample temperature levels from the
heating-A/C system, the cooling system must be in
proper working order. Refer to Group 0, Lubrication
and Maintenance or Group 7, Cooling System of this
manual.
The use of a bug screen is not recommended. Any
obstructions forward of the condenser can reduce the
effectiveness of the air conditioning system.
EVAPORATOR PROBE
The evaporator probe can be replaced without hav-
ing to remove the unit housing from the vehicle.
The evaporator probe is located in the unit housing
and placed in the evaporator fins. The probe prevents
evaporator freeze-up. This is done by cycling the com-
pressor clutch OFF when evaporator temperature
drops below freeze point. It cycles ON when the
evaporator temperature rises above freeze point. The
evaporator probe uses a thermistor probe in a capil-
lary tube. The tube is inserted between the evapora-
tor fins in the heater-A/C unit housing.
HANDLING TUBING AND FITTINGS
Kinks in the refrigerant tubing or sharp bends in
the refrigerant hose lines will greatly reduce the
capacity of the entire system. High pressures are pro-
duced in the system when it is operating. Extreme
care must be exercised to make sure that all connec-
tions are pressure tight. Dirt and moisture can enter
the system when it is opened for repair or replace-
ment of lines or components. The refrigerant oil will
absorb moisture readily out of the air. This moisture
will convert into acids within a closed system.CAUTION: The system must be completely empty
before opening any fitting or connection in the
refrigeration system. Open fittings with caution
even after the system has been emptied. If any
pressure is noticed as a fitting is loosened,
retighten fitting and evacuate the system again.
A good rule for the flexible hose lines is to keep
the radius of all bends at least 10 times the diame-
ter of the hose. Sharper bends will reduce the flow
of refrigerant. The flexible hose lines should be
routed so they are at least 3 inches (80 mm) from
the exhaust manifold. Inspect all flexible hose lines
to make sure they are in good condition and prop-
erly routed.
The use of correct wrenches when making con-
nections is very important. Improper wrenches or
improper use of wrenches can damage the fittings.
The internal parts of the A/C system will remain
stable as long as moisture-free refrigerant and
refrigerant oil is used. Abnormal amounts of dirt,
moisture or air can upset the chemical stability.
This may cause operational troubles or even seri-
ous damage if present in more than very small
quantities.
When opening a refrigeration system, have every-
thing you will need to repair the system ready. This
will minimize the amount of time the system must
be opened. Cap or plug all lines and fittings as
soon as they are opened. This will help prevent the
entrance of dirt and moisture. All new lines and
components should be capped or sealed until they
are ready to be used.
All tools, including the refrigerant dispensing
manifold, the manifold gauge set, and test hoses
should be kept clean and dry.
HIGH PRESSURE CUT OUT SWITCH
The high pressure cut out switch is located on the
rear of the compressor (Fig. 7). It turns off the com-
pressor if the system pressure exceeds 3240 kPa (470
psi).
LOW PRESSURE CUT OFF SWITCH
The Low Pressure Cut Off Switch (Fig. 8) monitors
the refrigerant gas pressure on the suction side of
the system. The low pressure cut off switch is located
on the expansion valve. The low pressure cut off
switch turns off voltage to the compressor clutch coil
when refrigerant gas pressure drops to levels that
could damage the compressor. The low pressure cut
out switch is a sealed factory calibrated unit. It must
be replaced if defective.
24 - 6 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONINGPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1244 of 1285

WARNING: PROTECT SKIN AND EYES FROM CON-
TACTING CO2 PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
(7) If suction side low pressure is within specified
range, freeze the expansion valve control head (Fig.
13) for 30 seconds. Use a super cold substance (liquid
CO2).Do not spray refrigerant on the expansion
valve for this test.Suction side low pressure should
drop to 34.5 kPa (5 psi) If not, replace expansion
valve.(8) Allow expansion valve to thaw. The low pres-
sure gauge reading should stabilize at 103 to 241
kPa (15 to 35 psi). If not, replace expansion valve.
(9) When expansion valve test is complete, test
A/C overall performance. Refer to the Heater and A/C
Performance Test in this section. Remove all test
equipment before returning vehicle to use.
HEATER PERFORMANCE TEST
PRE-DIAGNOSTIC PREPARATIONS
Review Safety Precautions and Warnings in this
group before performing the following procedures.
Check the coolant level, drive belt tension, vacuum
line connections, radiator air flow and fan operation.
Start engine and allow to warm up to normal tem-
perature.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE RADIATOR CAP
WHEN ENGINE IS HOT, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
If vehicle has been run recently, wait 15 minutes
before removing cap. Place a rag over the cap and
turn it to the first safety stop. Allow pressure to
escape through the overflow tube. When the system
stabilizes, remove the cap completely.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT: TEST AND ACTION
Engine coolant is provided to the heater system by
two 16 mm (5/8 inch inside diameter) heater hoses.
With engine idling at normal running temperature,
set the control to maximum heat, floor, and high
blower setting. Using a test thermometer, check the
air temperature coming from the floor outlets, refer
to Temperature Reference chart.
If the floor outlet air temperature is insufficient,
refer to Group 7, Cooling Systems for specifications.
Both heater hoses should be HOT to the touch (cool-
ant return hose should be slightly cooler than the
supply hose). If coolant return hose is much cooler
than the supply hose, locate and repair engine cool-
ant flow obstruction in heater system.
Fig. 12 Evaporator Probe Harness Connector
1 ± PIN #3
2 ± PIN #2
3 ± PIN #1
Fig. 13 Expansion Valve & Low Pressure Cut-Off
Switch - Typical
1 ± EXPANSION VALVE
2 ± LOW PRESSURE CUT OFF SWITCH
3 ± SUCTION LINE
4 ± CONTROL HEAD
TEMPERATURE REFERENCE CHART
Ambient Temp. Minimum
FloorOutlet
Temp.
Celsius Fahrenheit Celsius Fahrenheit
15.5É 60É 62.2É 144É
21.1É 70É 63.8É 147É
26.6É 80É 65.5É 150É
32.2É 90É 67.2É 153É
PLHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 13
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)