hose DODGE NEON 2000 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 968 of 1285

GENERAL INFORMATION
IN VEHICLE SERVICE
The following components are serviceable in the
vehicle without transaxle removal:
²Valve Body Assembly
²Converter Clutch Solenoid
²Governor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor & Pinion
²Park/Neutral & Back-up Lamp Switch
²Transfer Gears and Transfer Shaft
²Low/Reverse Servo
²Kickdown Servo
²Accumulator
FLUID REQUIREMENTS
NOTE: The transmission and differential have a
common oil sump with an opening between the
two.
TRANSMISSION/DIFFERENTIAL
MopartATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid
Type 9602) is required in this transaxle. Substitute
fluids must meet fluid specification MS-9602.
FLUID ADDITIVES
Chrysler Corporation strongly recommends against
the addition of any fluids to the transmission, other
than those automatic transmission fluids listed
above. Exceptions to this policy are the use of special
dyes to aid in detecting fluid leaks.
Various ªspecialº additives and supplements exist
that claim to improve shift feel/quality and converter
clutch operation, inhibit overheating, oxidation, var-
nish and sludge. These claims have not been sup-
ported to Chrysler's satisfaction and these additives
must not be used. The use of transmission ªsealersº
should also be avoided, since they may adversely
affect the integrity of tranmission seals.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
31TH GENERAL INFORMATION
NOTE: Safety goggles should be worn at all times
when working on these transaxles.
This transaxle combines torque converter, three
speed transmission, final drive gearing, and differen-
tial into a front wheel drive system.
NOTE: Transaxle operation requirements are differ-
ent for each vehicle and engine combination. Some
internal parts will be different to provide for this.Therefore, when replacing parts, refer to the seven
digit part number stamped on rear of the transaxle
oil pan flange.
Within this transaxle, there are three primary
areas:
(1) Main center line plus valve body.
(2) Transfer shaft center line (includes governor
and parking sprag).
(3) Differential center line.
Center distances between the main rotating parts
in these three areas are held precise to maintain a
low noise level.
The torque converter, transaxle area, and differen-
tial are housed in an integral aluminum die casting.
The differential oil sump is common with the
transaxle sump. Separate filling of the differen-
tial is NOT necessary.
The torque converter is attached to the crankshaft
through a flexible driving plate. Cooling of the con-
verter is accomplished by circulating the transaxle
fluid through a remote cooler. There are two types of
coolers used. An oil-to-water type cooler located in
the radiator side tank and/or an oil-to-air heat
exchanger. The torque converter assembly is a sealed
unit that cannot be disassembled.
The transaxle fluid is filtered by an internal filter
attached to the lower side of the valve body assembly.
Engine torque is transmitted to the torque con-
verter and then through the input shaft to multiple-
disc clutches in the transaxle. The power flow
depends on the application of the clutches and bands.
Refer to Elements in Use Chart in Diagnosis and
Tests section.
The transaxle consists of:
²Two multiple-disc clutches
²An overrunning clutch
²Two servos
²A hydraulic accumulator
²Two bands
²Two planetary gear sets
This provides three forward ratios and a reverse
ratio. The common sun gear of the planetary gear
sets is connected to the front clutch by a driving
shell. The driving shell is splined to the sun gear and
front clutch retainer. The hydraulic system consists
of an oil pump and a single valve body which con-
tains all of the valves except the governor valves.
The transaxle sump and differential sump are both
vented through the dipstick. Output torque from the
main center line is delivered through helical gears to
the transfer shaft. This gear set is a factor in the
transaxle final drive (axle) ratio. The shaft also car-
ries the governor and parking sprag. An integral heli-
cal gear on the transfer shaft drives the differential
ring gear.
PLTRANSAXLE 21 - 55
Page 978 of 1285

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NO REVERSE (OR SLIPS
IN REVERSE)1. Direct Clutch Pack (front clutch)
Worn.1. Disassemble unit and rebuild clutch
pack.
2. Rear Band Misadjusted. 2. Adjust band.
3. Front Clutch Malfunctioned/Burnt. 3. Air pressure test clutch operation.
Remove and rebuild if necessary.
OIL LEAKS (ITEMS
LISTED REPRESENT
POSSIBLE LEAK POINTS
AND SHOULD ALL BE
CHECKED.1. Fluid Lines and Fittings Loose/
Leaks/Damaged.1. Tighten fittings. If leaks persist, replace
fittings and lines if necessary.
2. Filler Tube (where tube enters
case) Leaks/Damaged.2. Replace tube seal. Inspect tube for
cracks in tube.
3. Pressure Port Plug Loose
Loose/Damaged.3. Tighten to correct torque. Replace plug
or reseal if leak persists.
4. Pan Gasket Leaks. 4. Tighten pan screws to 150 inch pounds.
If leaks persist, replace gasket. Do no over
tighten screws.
5. Valve Body Manual Lever Shaft
Seal Leaks/Worn.5. Replace shaft seal.
6. Rear Bearing Access Plate Leaks. 6. Replace gasket. Tighten screws.
7. Gasket Damaged or Bolts are
Loose.7. Replace bolts or gasket or tighten both.
8. Adapter/Extension Gasket
Damaged Leaks/Damaged.8. Replace gasket.
9. Neutral Switch Leaks/Damaged. 9. Replace switch and gasket.
10. Converter Housing Area Leaks. 10. Check for leaks at seal caused by worn
seal or burr on converter hub (cutting seal),
worn bushing, missing oil return, oil in front
pump housing or hole plugged. Check for
leaks past O-ring seal on pump or past
pump-to-case bolts; pump housing porous,
oil coming out vent due to overfill or leak
past front band shaft access plug.
11. Pump Seal Leaks/Worn/
Damaged.11. Replace seal.
12. Torque Converter Weld
Leak/Cracked Hub.12. Replace converter.
13. Case Porosity Leaks. 13. Replace case.
ROAD TEST
Prior to performing a road test, check the fluid
level and throttle valve cable adjustments.
During the road test, the transaxle should be oper-
ated in each position to check for slipping and any
variation in shifting.
If vehicle operates at high speeds, but has poor
acceleration, the converter's overrunning clutch may
be slipping. If acceleration is normal, but high throt-
tle opening is needed for high speeds, the stator
clutch may have seized.Observe closely for slipping or engine speed flare-
up. Slipping or flare-up in any gear usually indicates
clutch, band, or overrunning clutch problems. If the
condition is far advanced, an overhaul will probably
be necessary to restore normal operation.
In most cases, the clutch or band that is slipping
can be determined by noting the transaxle operation
in all selector positions and then comparing which
internal units are applied in those positions. The Ele-
ments±in±Use Chart provides a basis for road test
analysis.
PLTRANSAXLE 21 - 65
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 979 of 1285
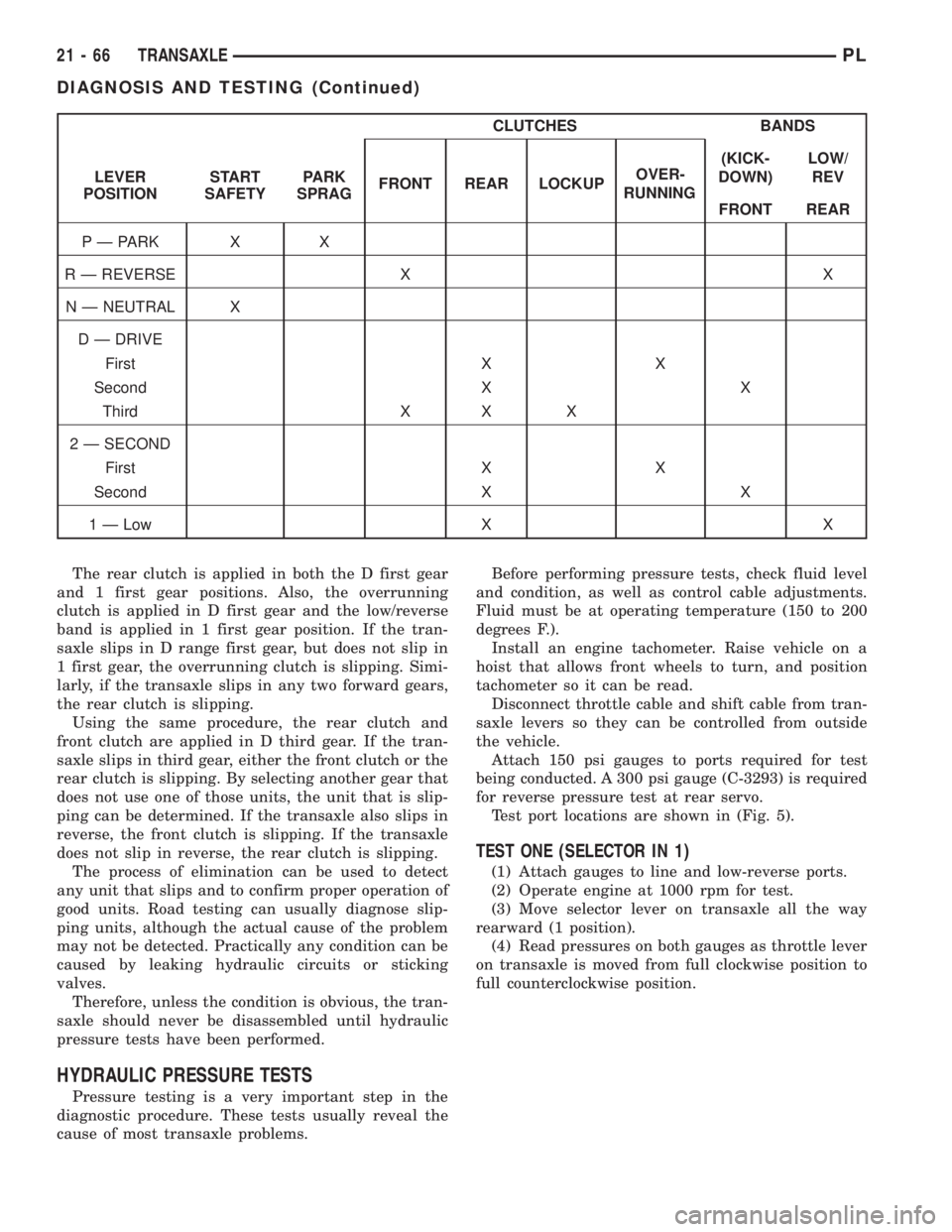
CLUTCHES BANDS
LEVER START PARK
FRONT REAR LOCKUPOVER-
RUNNING(KICK-
DOWN)LOW/
REV
POSITION SAFETY SPRAG
FRONT REAR
P Ð PARK X X
R Ð REVERSE X X
N Ð NEUTRAL X
D Ð DRIVE
First X X
Second X X
Third X X X
2 Ð SECOND
First X X
Second X X
1 Ð Low X X
The rear clutch is applied in both the D first gear
and 1 first gear positions. Also, the overrunning
clutch is applied in D first gear and the low/reverse
band is applied in 1 first gear position. If the tran-
saxle slips in D range first gear, but does not slip in
1 first gear, the overrunning clutch is slipping. Simi-
larly, if the transaxle slips in any two forward gears,
the rear clutch is slipping.
Using the same procedure, the rear clutch and
front clutch are applied in D third gear. If the tran-
saxle slips in third gear, either the front clutch or the
rear clutch is slipping. By selecting another gear that
does not use one of those units, the unit that is slip-
ping can be determined. If the transaxle also slips in
reverse, the front clutch is slipping. If the transaxle
does not slip in reverse, the rear clutch is slipping.
The process of elimination can be used to detect
any unit that slips and to confirm proper operation of
good units. Road testing can usually diagnose slip-
ping units, although the actual cause of the problem
may not be detected. Practically any condition can be
caused by leaking hydraulic circuits or sticking
valves.
Therefore, unless the condition is obvious, the tran-
saxle should never be disassembled until hydraulic
pressure tests have been performed.
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TESTS
Pressure testing is a very important step in the
diagnostic procedure. These tests usually reveal the
cause of most transaxle problems.Before performing pressure tests, check fluid level
and condition, as well as control cable adjustments.
Fluid must be at operating temperature (150 to 200
degrees F.).
Install an engine tachometer. Raise vehicle on a
hoist that allows front wheels to turn, and position
tachometer so it can be read.
Disconnect throttle cable and shift cable from tran-
saxle levers so they can be controlled from outside
the vehicle.
Attach 150 psi gauges to ports required for test
being conducted. A 300 psi gauge (C-3293) is required
for reverse pressure test at rear servo.
Test port locations are shown in (Fig. 5).
TEST ONE (SELECTOR IN 1)
(1) Attach gauges to line and low-reverse ports.
(2) Operate engine at 1000 rpm for test.
(3) Move selector lever on transaxle all the way
rearward (1 position).
(4) Read pressures on both gauges as throttle lever
on transaxle is moved from full clockwise position to
full counterclockwise position.
21 - 66 TRANSAXLEPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 987 of 1285

(6) Disconnect both battery cables, remove battery
hold down clamp and bolt, and remove battery.
(7) Remove air cleaner/throttle body assy. (Fig. 13)
as follows:
(a) Disconnect proportional purge solenoid (PPS)
and crankcase vent hose from throttle body.
(b) Disconnect the Throttle Position Sensor
(TPS) and Idle Air Control (IAC) connectors.
(c) Remove mounting bolt and nut (Fig. 13) and
partially remove air cleaner assembly.
(d) Disconnect accelerator and speed control (if
equipped) cables after the assy. is removed from
position. Remove air cleaner assembly from vehi-
cle.
(8) Remove battery tray from bracket.
(9) Disconnect shifter cable from shift lever and
remove from bracket (Fig. 14).
(10) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(11) Remove catalytic converter heat shield (Fig.
15).
(12) Remove intermediate pipe heat shield front
bolts.
(13) Remove remaining grommet plate screw and
remove cable assembly from vehicle (Fig. 16).
Fig. 13 Air Cleaner Assembly Removal/Installation
1 ± AIR CLEANER ASSY.
2 ± THROTTLE BODY DUCT
Fig. 14 Gear Shift Cable at Transaxle
1 ± SHIFT LEVER
2 ± SHIFT CABLE
Fig. 15 Catalytic Converter Heat Shield
1 ± CONVERTER HEAT SHIELD
21 - 74 TRANSAXLEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 988 of 1285
INSTALLATION
(1) Install cable assembly through floor pan open-
ing and secure to floor pan with grommet plate and
one screw (Fig. 16). Make sure the three grommet
plate studs protrude through cable assembly and
floor pan and tighten screw to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.).
(2) Route transaxle end of cable assembly into
engine compartment and over transaxle assembly.
(3) Install and tighten intermediate pipe heat
shield front screws.
(4) Install catalytic converter heat shield (Fig. 15).
(5) Install gear shift cable to bracket and connect
to shift lever (Fig. 14).
(6) Install and tighten the three grommet plate-to-
floor pan nuts. Tighten to 6 N´m (50 in. lbs.) torque.
(7) Connect gearshift cable to shifter assembly as
shown in (Fig. 12).
(8) Install shifter bezel (Fig. 11).
(9)Adjust gearshift cable as follows:
(a) Place gearshift lever in the PARK (P) posi-
tion.
(b) Loosen shift cable adjustment screw (Fig.
17).
(c) Verify transaxle is in the PARK (P) position
and the shifter lever is in gated PARK..
(d) Tighten shift cable adjustment screw to 8
N´m (70 in. lbs.) torque.
(10) Install battery tray.
(11) Install battery and hold down clamp.
(12) Install the air cleaner/throttle body assy. (Fig.
13) as follows:(a) Connect the accelerator and speed control (if
equipped) cables to the air cleaner/throttle body
assy.
(b) Install assy into position, making sure the
air cleaner locating slot is engaged to the battery
bracket tab, and tighten fasteners to 14 N´m (120
in. lbs.) torque.
(c) Verify throttle body duct is fully seated to
intake manifold and tighten clamp to 5 N´m (40 in.
lbs.) torque.
(d) Connect the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
and Idle Air Control (IAC) connectors.
(e) Connect proportional purge solenoid (PPS)
and crankcase vent hose from throttle body.
(13) Install center console assembly (Fig. 10).
(14) Install gearshift knob and tighten set screw to
2 N´m (15 in. lbs.) torque (Fig. 9).
(15) Connect battery cables.
(16) Verify that engine starter operates in both
PARK (P) and NEUTRAL (N). Starter should not
operate in any other gear position.
Fig. 16 Grommet Plate/Shift Cable at Floor Pan
1 ± GROMMET PLATE
2 ± SHIFT CABLE
Fig. 17 Gearshift Cable Adjustment Screw
1 ± GEARSHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT SCREW
PLTRANSAXLE 21 - 75
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 990 of 1285
(6) Disconnect the shifter/ignition interlock cable
from the shifter lever and bracket as shown in (Fig.
22).
(7) Remove the four shifter assembly-to-floor pan
nuts and remove shifter assembly from vehicle (Fig.
23).INSTALLATION
(1) Install gearshift mechanism and tighten the
four nuts to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install gearshift cable as shown in (Fig. 21).
(3) Install shifter/ignition interlock cable as shown
in (Fig. 22).
(4) Install shifter bezel (Fig. 20).
(5) Install center console assembly (Fig. 19).
(6) Install gearshift knob and tighten set screw to
2 N´m (15 in. lbs.) torque (Fig. 18).
THROTTLE VALVE (KICKDOWN) CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove air cleaner/throttle body assy. (Fig. 24)
as follows:
(a) Disconnect proportional purge solenoid (PPS)
and crankcase vent hose from throttle body.
(b) Disconnect the Throttle Position Sensor
(TPS) and Idle Air Control (IAC) connectors.
(c) Disconnect throttle body air duct at intake
manifold.
(d) Remove mounting bolt and nut (Fig. 24) and
partially remove air cleaner assembly (leave cables
attached).
NOTE: Pay attention to throttle valve cable routing
before removal so it can be re-installed in the same
manner. For proper transaxle operation, the cable
must not bind.
Fig. 22 Shifter Ignition Interlock Cable
1 ± INTERLOCK CABLE
2 ± SHIFTER ASSEMBLY
Fig. 23 Gearshift Mechanism Removal/Installation
1 ± SHIFTER ASSEMBLY
2 ± NUT (4)Fig. 24 Air Cleaner Assembly Removal/Installation
1 ± AIR CLEANER ASSY.
2 ± THROTTLE BODY DUCT
PLTRANSAXLE 21 - 77
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 991 of 1285

(2) Disconnect throttle valve cable from air clean-
er/throttle body assembly as shown in (Fig. 25).
(3) Disconnect throttle valve cable from lever on
transaxle and remove from bracket (Fig. 26).INSTALLATION
NOTE: Route throttle valve cable in a manner that
allows free, unobstructed travel. For proper tran-
saxle operation, the cable must not bind.
(1) Install transaxle throttle valve cable to bracket
and lever as shown in (Fig. 26). Make sure the cable
snapsonto the lever.
(2) Install the throttle valve cable to the air clean-
er/throttle body as shown in (Fig. 25).
(3) Install the air cleaner/throttle body assy. as fol-
lows:
(a) Install assy into position, making sure the
air cleaner locating slot is engaged to the battery
bracket tab, and tighten fasteners to 14 N´m (120
in. lbs.) torque.
(b) Verify throttle body duct is fully seated to
intake manifold and tighten clamp to 5 N´m (40 in.
lbs.) torque.
(c) Connect the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
and Idle Air Control (IAC) connectors.
(d) Connect proportional purge solenoid (PPS)
and crankcase vent hose from throttle body.
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
(5) Perform the Throttle Valve Cable Adjustment
Procedure found in this group.
(6) Road test vehicle and verify proper transaxle
operation.
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE ADJUSTMENT
PROCEDURE
The transmission throttle valve is operated by a
cam on the valve body throttle lever. The throttle
lever is actuated by a cable connected to the engine
throttle body lever.
The throttle valve is located within the transaxle
valve body and is responsible for transaxle shift
speed, shift quality, and part-throttle downshift sen-
sitivity. Proper cable adjustment is essential for
proper transaxle operation.
NOTE: The air cleaner/throttle body assembly must
be installed into position before making this adjust-
ment.
Fig. 25 Throttle Valve Cable at Air Cleaner/Throttle
Body
1 ± KICKDOWN CABLE
2 ± AIR CLEANER/THROTTLE BODY ASSY.
Fig. 26 Throttle Valve Cable at Transaxle
1 ± LEVER
2 ± BRACKET
3 ± KICKDOWN CABLE
21 - 78 TRANSAXLEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 997 of 1285

PARK/NEUTRAL STARTING AND BACK-UP
LAMP SWITCH
TEST
The park/neutral starting switch is the center ter-
minal of the three terminal switch. It provides
ground for the starter solenoid circuit through the
selector lever in PARK and NEUTRAL positions only.
(1) To test switch, remove wiring connector from
switch and test for continuity between center pin of
switch and transaxle case. Continuity should exist
only when transaxle is in PARK or NEUTRAL.
(2) Check gearshift cable adjustment before replac-
ing a switch that tests bad.
REMOVAL
(1) Unscrew switch from transaxle case allowing
fluid to drain into a container. Move selector lever to
PARK, then to NEUTRAL position, and inspect to see
the switch operating lever fingers are centered in
switch opening.
INSTALLATION
(1) Screw the switch with a new seal into tran-
saxle case and tighten to 33 N´m (24 ft. lbs.). Retest
switch with the test lamp.
(2) Add fluid to transaxle to bring up to proper
level.
(3) The back-up lamp switch circuit is through the
two outside terminals of the three terminal switch.
(4) To test switch, remove wiring connector from
switch and test for continuity between the two out-
side pins.
(5) Continuity should exist only with transaxle in
REVERSE position.
(6) No continuity should exist from either pin to
the case.
TRANSAXLE AND TORQUE CONVERTER
REMOVAL
(1) Raise hood.
(2) Disconnect both battery cables, remove battery
hold down clamp and bolt, and remove battery.
(3) Remove air cleaner/throttle body assy. (Fig. 45)
as follows:
(a) Disconnect proportional purge solenoid (PPS)
and crankcase vent hose from throttle body.
(b) Disconnect the Throttle Position Sensor
(TPS) and Idle Air Control (IAC) connectors.
(c) Remove mounting bolt and nut (Fig. 45) and
partially remove air cleaner assembly.
(d) Disconnect accelerator, transaxle kickdown,
and speed control (if equipped) cables after the
assy. is removed from position. Remove air cleaner
assembly from vehicle.(4) Remove battery tray from bracket.
(5) Disconnect torque converter clutch solenoid and
neutral safety/back-up lamp switch connectors.
(6) Disconnect and plug transaxle oil cooler lines
(Fig. 46).
(7) Disconnect shifter cable from shift lever and
remove from bracket (Fig. 47). Secure cable out of the
way.
Fig. 45 Air Cleaner Assembly Removal/Installation
1 ± AIR CLEANER ASSY.
2 ± THROTTLE BODY DUCT
Fig. 46 Transaxle Oil Cooler Lines
1 ± RETURN
2 ± CLAMPS
3 ± PRESSURE
21 - 84 TRANSAXLEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1001 of 1285

(c) Tighten the collar-to-transaxle bolts to 108
N´m (80 ft. lbs.) torque.
(d) Final torque the collar-to-oil pan bolts to 54
N´m (40 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Install both front axle driveshafts. Refer to
Group 3, Differential and Driveline for the correct
procedures.
(12) Connect vehicle speed sensor connector (Fig.
50).
(13) Install right lateral bending brace and tighten
bolts to 81 N´m (60 ft. lbs.) torque.
(14) Lower vehicle.
(15) Connect transaxle cooler lines and tighten
clamps (Fig. 46).
(16) Connect torque converter clutch solenoid and
neutral safety/back-up lamp switch connectors.
(17) Install transaxle dipstick tube.
(18) Install gear shift cable to bracket and connect
to shift lever (Fig. 47).
(19) Install transaxle kickdown cable to bracket
and lever as shown in (Fig. 48).
(20) Install battery lower tray and battery, and
tighten battery hold down clamp to secure battery.
(21) Install the air cleaner/throttle body assy. as
follows:
(a) Connect the accelerator, transaxle kickdown,
and speed control (if equipped) cables to the air
cleaner/throttle body assy.
(b) Install assy into position and tighten fasten-
ers to 14 N´m (120 in. lbs.) torque.
(c) Connect the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
and Idle Air Control (IAC) connectors.
(d) Connect proportional purge solenoid (PPS)
and crankcase vent hose from throttle body.
(22) Fill transaxle with a suitable amount of
ATF+4.
(23) Road test vehicle.
(24) Check for leaks, inspect fluid level, and adjust
as necessary.
PUMP OIL SEAL
The pump oil seal can be replaced without remov-
ing the pump and reaction shaft support assembly
from the transaxle case.
REMOVAL
(1) Screw seal remover Tool C-3981-B into seal
(Fig. 56), then tighten screw portion of tool to with-
draw the seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) To install a new seal, place seal in opening of
the pump housing (lip side facing inward). Using Tool
C-4193 and Handle Tool C-4171, drive new seal into
housing until tool bottoms (Fig. 57).
Fig. 56 Remove Pump Oil Seal
1 ± PUMP OIL SEAL
2 ± OIL SEAL REMOVER TOOL C-3981-B
3 ± OIL PUMP
Fig. 57 Install Pump Oil Seal
1 ± OIL PUMP
2 ± OIL SEAL INSTALLER TOOL C-4193
3 ± SPECIAL TOOL HANDLE C-4171
21 - 88 TRANSAXLEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1075 of 1285
SERVICE PROCEDURES
PRESSURE GAUGES
A quality air pressure gauge is recommended to
check tire pressure. After checking the air pressure,
replace valve cap finger tight.
TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES
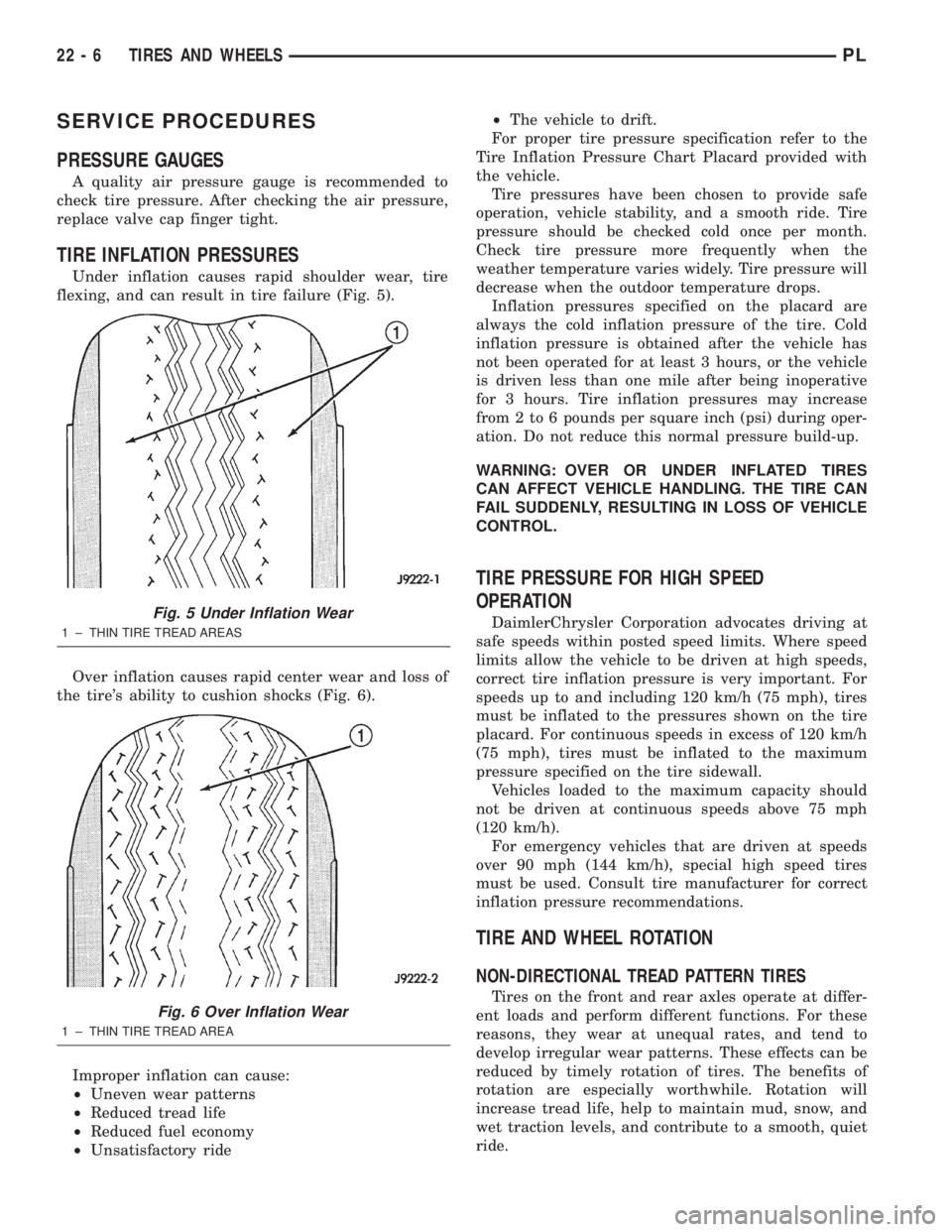
Under inflation causes rapid shoulder wear, tire
flexing, and can result in tire failure (Fig. 5).
Over inflation causes rapid center wear and loss of
the tire's ability to cushion shocks (Fig. 6).
Improper inflation can cause:
²Uneven wear patterns
²Reduced tread life
²Reduced fuel economy
²Unsatisfactory ride²The vehicle to drift.
For proper tire pressure specification refer to the
Tire Inflation Pressure Chart Placard provided with
the vehicle.
Tire pressures have been chosen to provide safe
operation, vehicle stability, and a smooth ride. Tire
pressure should be checked cold once per month.
Check tire pressure more frequently when the
weather temperature varies widely. Tire pressure will
decrease when the outdoor temperature drops.
Inflation pressures specified on the placard are
always the cold inflation pressure of the tire. Cold
inflation pressure is obtained after the vehicle has
not been operated for at least 3 hours, or the vehicle
is driven less than one mile after being inoperative
for 3 hours. Tire inflation pressures may increase
from 2 to 6 pounds per square inch (psi) during oper-
ation. Do not reduce this normal pressure build-up.
WARNING: OVER OR UNDER INFLATED TIRES
CAN AFFECT VEHICLE HANDLING. THE TIRE CAN
FAIL SUDDENLY, RESULTING IN LOSS OF VEHICLE
CONTROL.
TIRE PRESSURE FOR HIGH SPEED
OPERATION
DaimlerChrysler Corporation advocates driving at
safe speeds within posted speed limits. Where speed
limits allow the vehicle to be driven at high speeds,
correct tire inflation pressure is very important. For
speeds up to and including 120 km/h (75 mph), tires
must be inflated to the pressures shown on the tire
placard. For continuous speeds in excess of 120 km/h
(75 mph), tires must be inflated to the maximum
pressure specified on the tire sidewall.
Vehicles loaded to the maximum capacity should
not be driven at continuous speeds above 75 mph
(120 km/h).
For emergency vehicles that are driven at speeds
over 90 mph (144 km/h), special high speed tires
must be used. Consult tire manufacturer for correct
inflation pressure recommendations.
TIRE AND WHEEL ROTATION
NON-DIRECTIONAL TREAD PATTERN TIRES
Tires on the front and rear axles operate at differ-
ent loads and perform different functions. For these
reasons, they wear at unequal rates, and tend to
develop irregular wear patterns. These effects can be
reduced by timely rotation of tires. The benefits of
rotation are especially worthwhile. Rotation will
increase tread life, help to maintain mud, snow, and
wet traction levels, and contribute to a smooth, quiet
ride.
Fig. 5 Under Inflation Wear
1 ± THIN TIRE TREAD AREAS
Fig. 6 Over Inflation Wear
1 ± THIN TIRE TREAD AREA
22 - 6 TIRES AND WHEELSPL