tra DODGE NEON 2000 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 35 of 1285

(5) Remove the upper mount from the strut shaft
(Fig. 27).
(6) Remove the upper spring seat and bearing,
along with the upper spring isolator as an assembly
from the top of the coil spring by pulling them
straight up (Fig. 27). The upper spring isolator can
be separated from the spring seat and bearing once
removed from vehicle.
(7) Remove the dust shield, then the jounce
bumper from the strut shaft by pulling each straight
up (Fig. 27).
(8) Remove the clamp from the bottom of the coil
spring and remove the strut out through the bottom
of the coil spring.
(9) Remove the lower spring isolator from the
lower spring seat on the strut.
NOTE: If the coil spring needs to be serviced, pro-
ceed with the next step, otherwise, proceed with
step 11.(10) Release the tension from the coil spring by
backing off the compressor drive completely. Push
back the compressor hooks and remove the coil
spring.
(11) Inspect the strut assembly components for the
following and replace as necessary:
²Inspect the strut for any condition of shaft bind-
ing over the full stroke of the shaft.
²Inspect the jounce bumper for cracks and signs
of deterioration.
²Check the upper mount for cracks and distortion
and its retaining studs for any sign of damage.
²Check the upper spring seat and bearing for
cracks and distortion.
²Check for binding of the upper spring seat and
bearing pivot bearing.
²Inspect the dust shield for rips and deteriora-
tion.
²Inspect the upper and lower spring isolators for
material deterioration and distortion.
²Inspect the coil spring for any sign of damage to
the coating.
ASSEMBLY
NOTE: If the coil spring has been removed from the
spring compressor, proceed with the next step, oth-
erwise, proceed with step 3.
(1) Place the coil spring in the compressor follow-
ing the manufacturers instructions. Before compress-
ing the spring, rotate the spring so the end of the top
coil is directly in the back as shown (Fig. 28).
(2) Slowly compress the coil spring until enough
room is available for strut assembly reassembly.
(3) Install the lower spring isolator on the lower
spring seat of the strut.
(4) Install the strut through the bottom of the coil
spring until the lower spring seat contacts the lower
end of the coil spring. Rotate the strut as necessary
until the clevis bracket is positioned straight outward
away from the compressor (Fig. 24). Install the clamp
on the lower end of the coil spring and strut, so the
strut is held in place.
(5) Install the jounce bumper on the strut shaft.
The jounce bumper is to be installed with the smaller
end pointing downward toward the lower seat (Fig.
27).
(6) Install the dust shield on the strut shaft (Fig.
27). The bottom of the dust shield will snap past the
retainer on top of the strut housing.
(7) If disassembled, reinstall the upper spring iso-
lator on the upper spring seat and bearing.
(8) Install the upper spring seat and bearing on
top of the coil spring. Position the notch formed into
the edge of the upper seat straight out away from the
compressor (Fig. 25).
Fig. 27 Strut Assembly Components
1 ± NUT
2 ± STRUT ASSEMBLY
3 ± STRUT
4 ± LOWER SPRING ISOLATOR
5 ± COIL SPRING
6 ± JOUNCE BUMPER
7 ± DUST SHIELD
8 ± SPRING SEAT AND BEARING (WITH SPRING ISOLATOR)
9 ± UPPER MOUNT
2 - 24 SUSPENSIONPL
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 46 of 1285

REAR SUSPENSION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
REAR SUSPENSION SYSTEM.............35
STRUT ASSEMBLY (REAR)................37
KNUCKLE (REAR).......................37
HUB AND BEARING (REAR)...............37
LATERAL ARMS........................37
TENSION STRUT.......................38
STABILIZER BAR (REAR).................38
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
STRUT ASSEMBLY (REAR)................38
KNUCKLE (REAR).......................39
HUB AND BEARING (REAR)...............39
LATERAL ARMS........................39
TENSION STRUT.......................39
STABILIZER BAR (REAR).................39REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS........40
STRUT ASSEMBLY (REAR).................40
KNUCKLE (REAR)........................42
HUB AND BEARING (REAR)................44
LATERAL ARMS..........................45
TENSION STRUT.........................46
STABILIZER BAR (REAR)...................47
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
STRUT ASSEMBLY (REAR).................47
SPECIFICATIONS
REAR SUSPENSION FASTENER TORQUE
SPECIFICATIONS........................50
SPECIAL TOOLS
REAR SUSPENSION......................50
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
REAR SUSPENSION SYSTEM
The rear suspension system used on this vehicle is
a fully independent type rear suspension system (Fig.
1). This means that each side of the rear suspension
acts independently from the other.
The rear suspension is supported by a strut assem-
bly. The strut assembly also controls ride quality.When the vehicle strikes a bump, the force is trans-
ferred through the hub, bearing, and knuckle, into
the strut assembly to absorb the force and dampen it.
Lateral movement of the rear knuckle is controlled
by lateral arms going from the front and rear of the
knuckle to the rear crossmember. Fore and aft move-
ment of the knuckle is controlled by a tension strut.
PLSUSPENSION 2 - 35
Page 49 of 1285

The lateral arms are made of stamped steel and
have rubber isolator bushings at each end. The lat-
eral arms are attached to the rear crossmember and
knuckle using a unique bolt and nut assembly at
each end. The lateral arm-to-rear crossmember
attaching bolts are longer than the lateral arm-to-
knuckle attaching bolts. Each lateral arm to knuckle
attaching bolt and nut assembly uses two flat wash-
ers. Each lateral arm to rear crossmember attaching
bolt uses one flat washer and one adjustment cam to
provide a means for rear wheel alignment toe adjust-
ment.
TENSION STRUT
The tension strut controls the fore-and-aft move-
ment of the rear knuckle (Fig. 1).
There is one tension strut per side of the rear sus-
pension. The leading end of the tension strut
attaches to the frame rail while the trailing end of
the strut attaches to the lower end of the rear
knuckle. The tension strut is isolated from the rest of
the rear suspension through the use of rubber bush-
ings located at each end. The rear bushings (bayonet
type) can be serviced separately, the front bushings
(spool type) cannot.
STABILIZER BAR (REAR)
The stabilizer bar interconnects both rear strut
assemblies and is attached to the rear frame rails of
the vehicle (Fig. 3).
The rear stabilizer bar allows jounce and rebound
movements affecting one wheel to be partially trans-
mitted to the opposite wheel of the vehicle to stabi-
lize body roll.Attachment of the stabilizer bar to the rear frame
rails of the vehicle is through two rubber-isolator
cushions and retainers (Fig. 1). The stabilizer bar
attachment to each strut assembly is done utilizing a
rubber isolated stabilizer bar link. All parts of the
stabilizer bar are serviceable, and the stabilizer bar
to frame rail isolator cushions are split for easy
removal and installation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
STRUT ASSEMBLY (REAR)
Inspect the strut assembly for the following condi-
tions (Fig. 4):
²Inspect for a damaged or broken coil spring.
²Inspect for a torn or damaged strut assembly
dust shield.
²Lift the dust shield and inspect the strut assem-
bly for evidence of fluid running from the upper end
of the strut fluid reservoir. (Actual leakage will be a
stream of fluid running down the side and dripping
off lower end of unit.) A slight amount of seepage
between the strut shaft and strut shaft seal is not
unusual and does not affect performance of the strut
assembly.
²Lift the dust shield and inspect the jounce
bumper for signs of damage or deterioration.
Fig. 2 Lateral Arms
1 ± REAR STABILIZER BAR
2 ± REAR LATERAL ARMS
3 ± RIGHT FRONT LATERAL ARM
4 ± LEFT FRONT LATERAL ARM
Fig. 3 Rear Stabilizer Bar
1 ± REAR STABILIZER BAR
2 ± REAR LATERAL ARMS
3 ± RIGHT FRONT LATERAL ARM
4 ± LEFT FRONT LATERAL ARM
2 - 38 SUSPENSIONPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 50 of 1285

KNUCKLE (REAR)
The rear knuckle is not a repairable component of
the rear suspension. Upon visual inspection, if it is
determined that the knuckle is cracked, bent or bro-
ken, no attempt is to be made to repair or to
straighten the knuckle. The knuckle must be
replaced if found to be damaged in any way.
HUB AND BEARING (REAR)
The hub and bearing is designed for the life of the
vehicle and requires no type of periodic maintenance
(Fig. 1). The following procedure may be used for
diagnosing the condition of the hub and bearing.
With the wheel, disc brake rotor or brake drum
removed, rotate the hub. Any roughness or resistance
to rotation may indicate dirt intrusion or a failed hub
bearing. If the bearing exhibits any of these condi-
tions during diagnosis, the hub and bearing will
require replacement. The bearing is not serviceable
alone.
Damaged bearing seals and the resulting excessive
grease loss may also require hub and bearing
replacement. Moderate grease weapage from thebearing is considered normal and should not require
replacement of the wheel bearing.
To diagnose a bent hub, refer to BRAKE ROTOR in
the DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING section in the
BRAKES service manual group for the procedure on
measuring hub runout.
LATERAL ARMS
Inspect each lateral arm (Fig. 1). Look for signs of
contact with an object that has caused damage to the
lateral arm. If the lateral arm is bent or damaged,
the lateral arm will require replacement. Do not
attempt to repair or straighten a lateral arm.
Inspect the lateral arm isolator bushings and their
sleeves for signs of damage or deterioration. If dam-
age or deterioration is present, replacement of the
entire lateral arm will be required. The isolator
bushings cannot be serviced separately from the lat-
eral arms.
TENSION STRUT
Inspect the tension strut (Fig. 1). Look for signs of
contact with any object that has bent or caused other
damage to the tension strut. If the tension strut is
bent or damaged, the tension strut will require
replacement. Do not attempt to repair or straighten a
tension strut.
Inspect the tension strut front (spool type) bushing,
and rear (bayonet type) bushings and retainers for
signs of deterioration or damage. If the front bushing
is damaged or shows signs of deteriation, the tension
strut must be replaced. The front bushing cannot be
replaced separately. If the rear bushings are deterio-
rated or damaged, or the retainers are damaged,
replacement is necessary. The bushings and retainers
can be replaced separately from the tension strut.
STABILIZER BAR (REAR)
Inspect the stabilizer bar (Fig. 1). Look for damage
or bending. If damage is evident, the bar must be
replaced.
Inspect for broken, cracked or distorted stabilizer
bar cushions and cushion retainers. The horizontal
slit at the front of each cushion is supposed to be
there. If damage is evident, the cushions can be
replaced separately from the stabilizer bar utilizing
the horizontal slit.
Inspect the stabilizer bar links that attach the sta-
bilizer bar to each rear strut. Look for damage or
deterioration of the bushings on the ends of each
link. Inspect the stabilizer bar link to ensure it is not
bent or broken. If any of these conditions are present,
the stabilizer bar link must be replaced. The links
can be replaced separately from the stabilizer bar.
Fig. 4 Strut Assembly
1 ± STRUT ASSEMBLY
2 ± STRUT
3 ± LOWER SPRING ISOLATOR
4 ± COIL SPRING
5 ± JOUNCE BUMPER
6 ± DUST SHIELD
7 ± UPPER MOUNT
PLSUSPENSION 2 - 39
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 51 of 1285

REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE STRUT SHAFT
NUT WHILE STRUT ASSEMBLY IS INSTALLED IN
VEHICLE, OR BEFORE THE COIL SPRING IS COM-
PRESSED WITH A COMPRESSION TOOL. THE
SPRING IS HELD UNDER HIGH PRESSURE.
CAUTION: Only frame contact or wheel lift hoisting
equipment can be used on vehicles having a fully
independent rear suspension. Vehicles with inde-
pendent rear suspension can not be hoisted using
equipment designed to lift a vehicle by the rear
axle. If this type of hoisting equipment is used dam-
age to rear suspension components will occur.
NOTE: If a rear suspension component becomes
bent, damaged or fails, no attempt should be made
to straighten or repair it. Always replace it with a
new component.
STRUT ASSEMBLY (REAR)
NOTE: Before proceeding with this procedure,
review SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS at the
beginning of REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION in this
section.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle. Refer to HOISTING in the
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE group for the
proper lifting procedure.
(2) Remove the rear wheel and tire assembly from
the vehicle.
(3) If the vehicle is equipped with rear drum
brakes, remove the screw securing the brake hose
bracket to the rear of the strut assembly (Fig. 5).
(4) If the vehicle is equipped with the antilock
brake system (ABS), remove the screw securing the
ABS wheel speed sensor bracket to the rear of the
strut assembly (Fig. 6).
(5) Remove the nut from the end of the rear stabi-
lizer bar link bolt (Fig. 5). Pull the bolt out through
the top of the link and remove the link.
(6) If the vehicle is equipped with rear disc brakes
(Fig. 7), perform the following:
²Remove the two guide pin bolts securing the
front disc brake caliper to the steering knuckle.
²Remove the disc brake caliper from the knuckle
and brake rotor.²Hang the caliper out of the way using a wire
hanger or cord. Do not support the caliper by letting
it hang by the hydraulic hose.
Fig. 5 Rear of Strut Assembly
1 ± BRAKE HOSE BRACKET SCREW
2 ± STABILIZER BAR LINK
3 ± NUT
4 ± STRUT ASSEMBLY
Fig. 6 Rear of Strut Assembly with ABS
1 ± ABS WHEEL SPEED SENSOR BRACKET SCREW
2 ± STABILIZER BAR LINK
3 ± NUT
4 ± STRUT ASSEMBLY
2 - 40 SUSPENSIONPL
Page 56 of 1285

LATERAL ARMS
NOTE: Before proceeding with this procedure,
review SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS at the
beginning of REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION in this
section.
Use the following procedure for removal and instal-
lation of one or both lateral arms on one side of the
vehicle's rear suspension.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle. Refer to HOISTING in the
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE group for the
proper lifting procedure.
(2) Remove the rear tire and wheel assembly.
(3) Remove the nut, bolt and washers attaching
both lateral arms to the knuckle (Fig. 1).
(4) Remove nut, washer, bolt and wheel alignment
cam attaching the lateral arms to the rear crossmem-
ber (Fig. 1).
(5) Remove the lateral arms from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Both lateral arms when being installed,
must be specifically positioned and orientated on
the vehicle. The lateral arm that has the same size
bushing sleeves on both ends must be mounted on
the forward side of the crossmember and knuckle
with the trimmed outer edge facing rearward. This
front arm is also marked with the word ªFOR-
WARDº. The side of the arm displaying this must
face forward.
The lateral arm with two different size bushing
sleeves must be mounted on the rearward side of
the crossmember and knuckle. Position the smaller
bushing sleeve end at the knuckle and the larger
bushing sleeve end at the rear crossmember (the
larger bushing sleeve is necessary to accommodate
the rear wheel alignment adjustment cam). If the
rear arm is to be mounted on the right side, the
trimmed outer edge must face rearward. If the rear
arm is to be mounted on the left side, the trimmed
outer edge must face forward.
(1) Following the note above, place the forward lat-
eral arm against the leading end of the knuckle, and
then install the short lateral arm mounting bolt with
a washer through the lateral arm and knuckle and
out the trailing end of the knuckle (Fig. 1).
(2) Following the note above, install the small
bushing sleeved end of the rear lateral arm onto the
end of the bolt just installed through the knuckle
(Fig. 1). Install a washer and nut onto the end of the
mounting bolt, but do not completely tighten the bolt
at this time.(3) Install a wheel alignment adjustment cam on
the long arm mounting bolt.
(4) Hold the rear lateral arm up against the cross-
member and install the long mounting bolt with the
adjustment cam through the lateral arm bushing and
rear crossmember (Fig. 1). The bolt must be installed
with the notch in the adjustment cam pointing
straight up.
(5) Position the forward lateral arm against the
rear crossmember hole. Pass the long mounting bolt
through the lateral arm bushing sleeve.
(6) Install a washer and nut onto the end of lateral
arm mounting bolt at the rear crossmember, but do
not completely tighten the bolt at this time.
NOTE: Once installed, each lateral arm should have
the bow in its length facing downward. Both right
side arms should have the trimmed outer edge fac-
ing toward the rear of the car. Left side arms should
have the trimmed outer edge facing each other. The
mounting bolt at the knuckle should have the nut at
the rear and the mounting bolt at the crossmember
should have the nut at the front (Fig. 13).
(7) Install tire and wheel assembly on the vehicle.
Tighten the wheel mounting nuts in proper sequence
until all nuts are torqued to half specification.
Repeat the tightening sequence to the full specified
torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(8) Lower the vehicle to the ground.
(9) With suspension at curb height, tighten the lat-
eral arm mounting bolt nut at the knuckle to 95 N´m
(70 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 13 Lateral Arms
1 ± REAR STABILIZER BAR
2 ± REAR LATERAL ARMS
3 ± RIGHT FRONT LATERAL ARM
4 ± LEFT FRONT LATERAL ARM
PLSUSPENSION 2 - 45
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 57 of 1285

(10) With suspension at curb height, tighten the
lateral arm mounting bolt nut at the crossmember to
88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.).
(11) Set the rear toe on the vehicle to the required
specification as necessary. Refer to WHEEL ALIGN-
MENT in this service manual group.
TENSION STRUT
NOTE: Before proceeding with this procedure,
review SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS at the
beginning of REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION in this
section.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle. Refer to HOISTING in the
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE group for the
proper lifting procedure.
(2) Remove the rear wheel and tire assembly from
the vehicle.
(3) Disconnect the tension strut from the knuckle.
To do this, first hold the tension strut from turning
by using a wrench on the flat on the tension strut
and then remove the nut from the rear of the tension
strut (Fig. 14). Next, remove the tension strut
retainer, then the rear tension strut bayonet bushing
from the tension strut.
(4) Remove the nut attaching the parking brake
cable to the stud on the inboard tension strut mount-
ing bolt at the frame (Fig. 15). Remove the parking
brake cable from the stud.
(5) Remove the two mounting bolts holding the
tension bolts to the frame, then remove the tension
strut from the vehicle.(6) Remove the forward bayonet bushing and
retainer from the tension strut.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the forward retainer and a bayonet
bushing on the tension strut trailing end. Be sure the
stepped area of the bushing is installed to face the
knuckle.
(2) To install the knuckle on the tension, first stick
the trailing end through the hole in the lower end of
the knuckle, seating the bayonet bushing squarely
against the hole. Next, raise the end of the tension
strut with the spool bushing into its mounting posi-
tion on the frame (Fig. 15). Install the mounting
bolts securing the tension strut to the frame.
Remember, the mounting bolt with the stud on the
head is installed on the inboard side.
(3) Tighten the two mounting bolts at the frame to
a torque of 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(4) Place the parking brake cable routing bracket
on the stud of the inboard mounting bolt and install
the nut securing it in place (Fig. 15). Tighten the nut
to a torque of 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(5) Install the rear bayonet bushing on the tension
strut. Be sure the stepped area of the bushing is
squarely seated into the hole in the knuckle.
(6) Install the rear tension strut retainer, then the
nut. To completely install the nut, place a wrench on
the flat formed into the tension strut and tighten the
nut (Fig. 14). Tighten the nut to a torque of 95 N´m
(70 ft. lbs.).
(7) Install the tire and wheel assembly. Tighten
the wheel mounting nuts in proper sequence until all
Fig. 14 Tension Strut Nut Removal/Installation
1 ± KNUCKLE
2 ± TENSION STRUT
3 ± FLAT
Fig. 15 Tension Strut Mounting At Frame
1 ± TENSION STRUT MOUNTING BOLTS
2 ± TENSION STRUT
3 ± SPOOL BUSHING
4 ± NUT
5 ± PARKING BRAKE CABLE
2 - 46 SUSPENSIONPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 59 of 1285
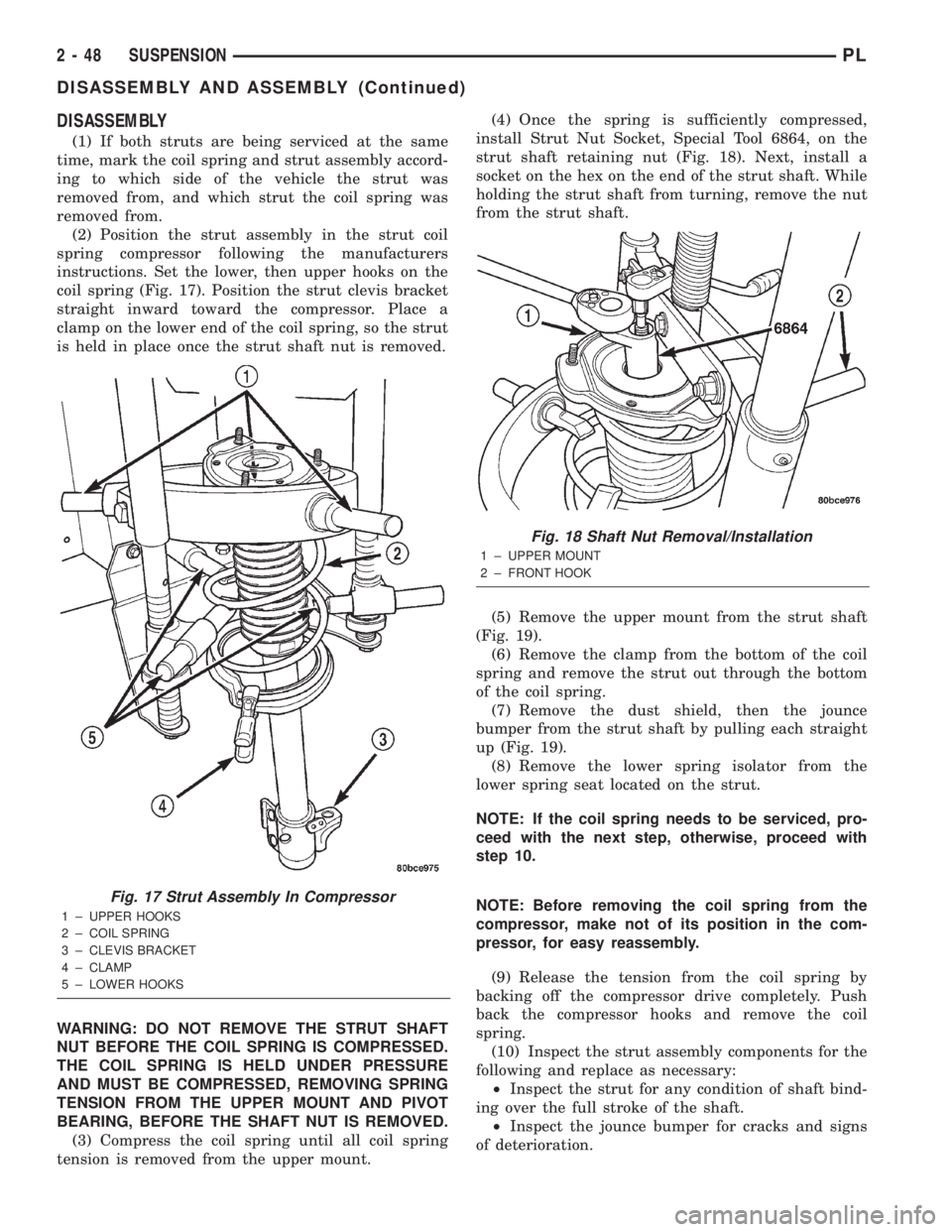
DISASSEMBLY
(1) If both struts are being serviced at the same
time, mark the coil spring and strut assembly accord-
ing to which side of the vehicle the strut was
removed from, and which strut the coil spring was
removed from.
(2) Position the strut assembly in the strut coil
spring compressor following the manufacturers
instructions. Set the lower, then upper hooks on the
coil spring (Fig. 17). Position the strut clevis bracket
straight inward toward the compressor. Place a
clamp on the lower end of the coil spring, so the strut
is held in place once the strut shaft nut is removed.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE STRUT SHAFT
NUT BEFORE THE COIL SPRING IS COMPRESSED.
THE COIL SPRING IS HELD UNDER PRESSURE
AND MUST BE COMPRESSED, REMOVING SPRING
TENSION FROM THE UPPER MOUNT AND PIVOT
BEARING, BEFORE THE SHAFT NUT IS REMOVED.
(3) Compress the coil spring until all coil spring
tension is removed from the upper mount.(4) Once the spring is sufficiently compressed,
install Strut Nut Socket, Special Tool 6864, on the
strut shaft retaining nut (Fig. 18). Next, install a
socket on the hex on the end of the strut shaft. While
holding the strut shaft from turning, remove the nut
from the strut shaft.
(5) Remove the upper mount from the strut shaft
(Fig. 19).
(6) Remove the clamp from the bottom of the coil
spring and remove the strut out through the bottom
of the coil spring.
(7) Remove the dust shield, then the jounce
bumper from the strut shaft by pulling each straight
up (Fig. 19).
(8) Remove the lower spring isolator from the
lower spring seat located on the strut.
NOTE: If the coil spring needs to be serviced, pro-
ceed with the next step, otherwise, proceed with
step 10.
NOTE: Before removing the coil spring from the
compressor, make not of its position in the com-
pressor, for easy reassembly.
(9) Release the tension from the coil spring by
backing off the compressor drive completely. Push
back the compressor hooks and remove the coil
spring.
(10) Inspect the strut assembly components for the
following and replace as necessary:
²Inspect the strut for any condition of shaft bind-
ing over the full stroke of the shaft.
²Inspect the jounce bumper for cracks and signs
of deterioration.
Fig. 17 Strut Assembly In Compressor
1 ± UPPER HOOKS
2 ± COIL SPRING
3 ± CLEVIS BRACKET
4 ± CLAMP
5 ± LOWER HOOKS
Fig. 18 Shaft Nut Removal/Installation
1 ± UPPER MOUNT
2 ± FRONT HOOK
2 - 48 SUSPENSIONPL
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 60 of 1285
²Check the upper mount for cracks and distortion
and its retaining studs for any sign of damage.
²Inspect the dust shield for rips and deteriora-
tion.
²Inspect the upper and lower spring isolators for
material deterioration and distortion.
²Inspect the coil spring for any sign of damage to
the coating.
ASSEMBLY
NOTE: If the coil spring has been removed from the
spring compressor, proceed with the next step, oth-
erwise, proceed with step 3.
(1) Place the coil spring in the compressor follow-
ing the manufacturers instructions. Before compress-
ing the spring, rotate the spring to the position
determined in the note prior to step 9 in disassembly.
(2) Slowly compress the coil spring until enough
room is available for strut assembly reassembly.
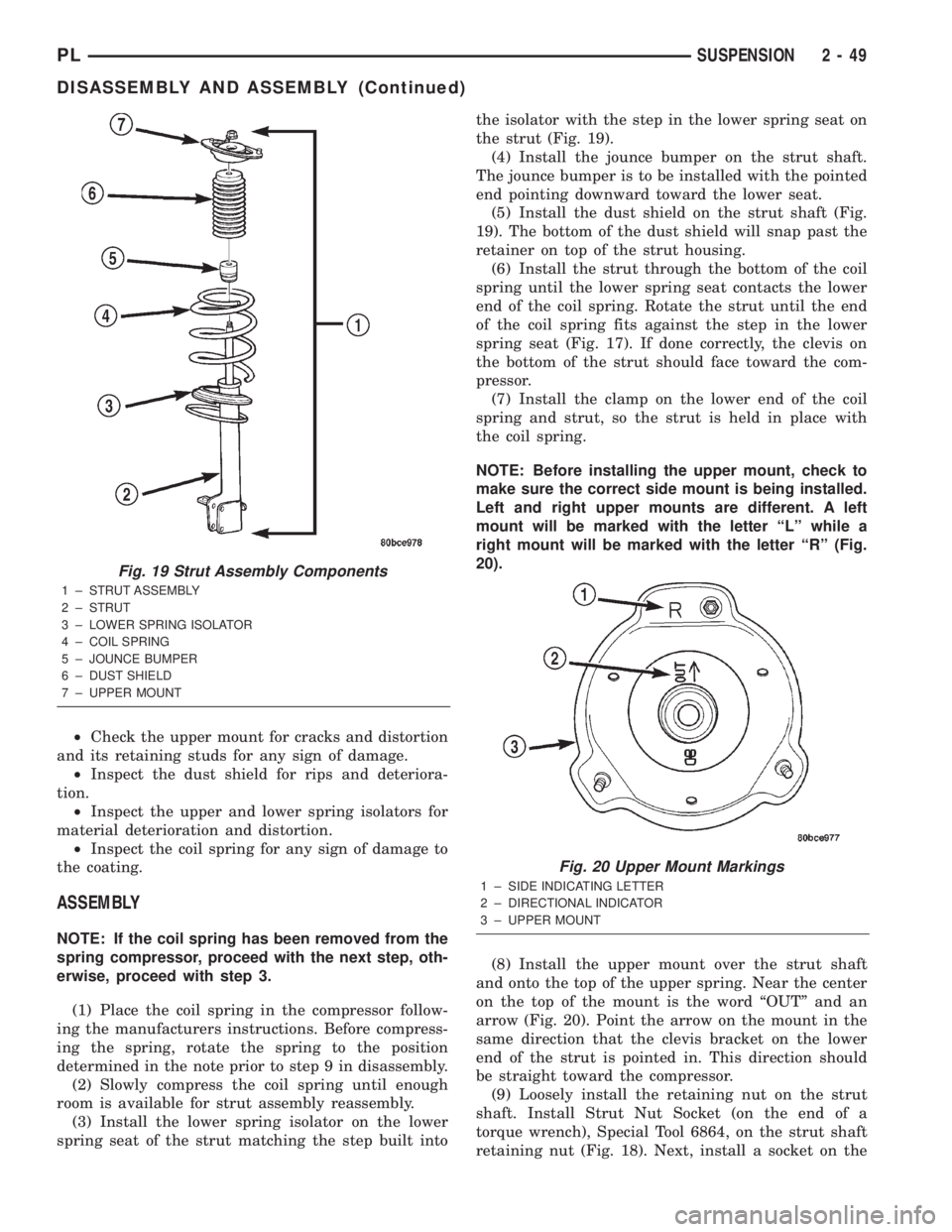
(3) Install the lower spring isolator on the lower
spring seat of the strut matching the step built intothe isolator with the step in the lower spring seat on
the strut (Fig. 19).
(4) Install the jounce bumper on the strut shaft.
The jounce bumper is to be installed with the pointed
end pointing downward toward the lower seat.
(5) Install the dust shield on the strut shaft (Fig.
19). The bottom of the dust shield will snap past the
retainer on top of the strut housing.
(6) Install the strut through the bottom of the coil
spring until the lower spring seat contacts the lower
end of the coil spring. Rotate the strut until the end
of the coil spring fits against the step in the lower
spring seat (Fig. 17). If done correctly, the clevis on
the bottom of the strut should face toward the com-
pressor.
(7) Install the clamp on the lower end of the coil
spring and strut, so the strut is held in place with
the coil spring.
NOTE: Before installing the upper mount, check to
make sure the correct side mount is being installed.
Left and right upper mounts are different. A left
mount will be marked with the letter ªLº while a
right mount will be marked with the letter ªRº (Fig.
20).
(8) Install the upper mount over the strut shaft
and onto the top of the upper spring. Near the center
on the top of the mount is the word ªOUTº and an
arrow (Fig. 20). Point the arrow on the mount in the
same direction that the clevis bracket on the lower
end of the strut is pointed in. This direction should
be straight toward the compressor.
(9) Loosely install the retaining nut on the strut
shaft. Install Strut Nut Socket (on the end of a
torque wrench), Special Tool 6864, on the strut shaft
retaining nut (Fig. 18). Next, install a socket on the
Fig. 19 Strut Assembly Components
1 ± STRUT ASSEMBLY
2 ± STRUT
3 ± LOWER SPRING ISOLATOR
4 ± COIL SPRING
5 ± JOUNCE BUMPER
6 ± DUST SHIELD
7 ± UPPER MOUNT
Fig. 20 Upper Mount Markings
1 ± SIDE INDICATING LETTER
2 ± DIRECTIONAL INDICATOR
3 ± UPPER MOUNT
PLSUSPENSION 2 - 49
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 62 of 1285
DIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
FRONT DRIVESHAFTS.....................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DRIVESHAFT DIAGNOSIS...................2
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
DRIVESHAFTS...........................3
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
DRIVESHAFT RECONDITION................7INNER TRIPOD JOINT SEAL BOOT...........7
OUTER C/V JOINT SEAL BOOT.............13
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE...............................17
SPECIAL TOOLS
DRIVESHAFT............................17
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
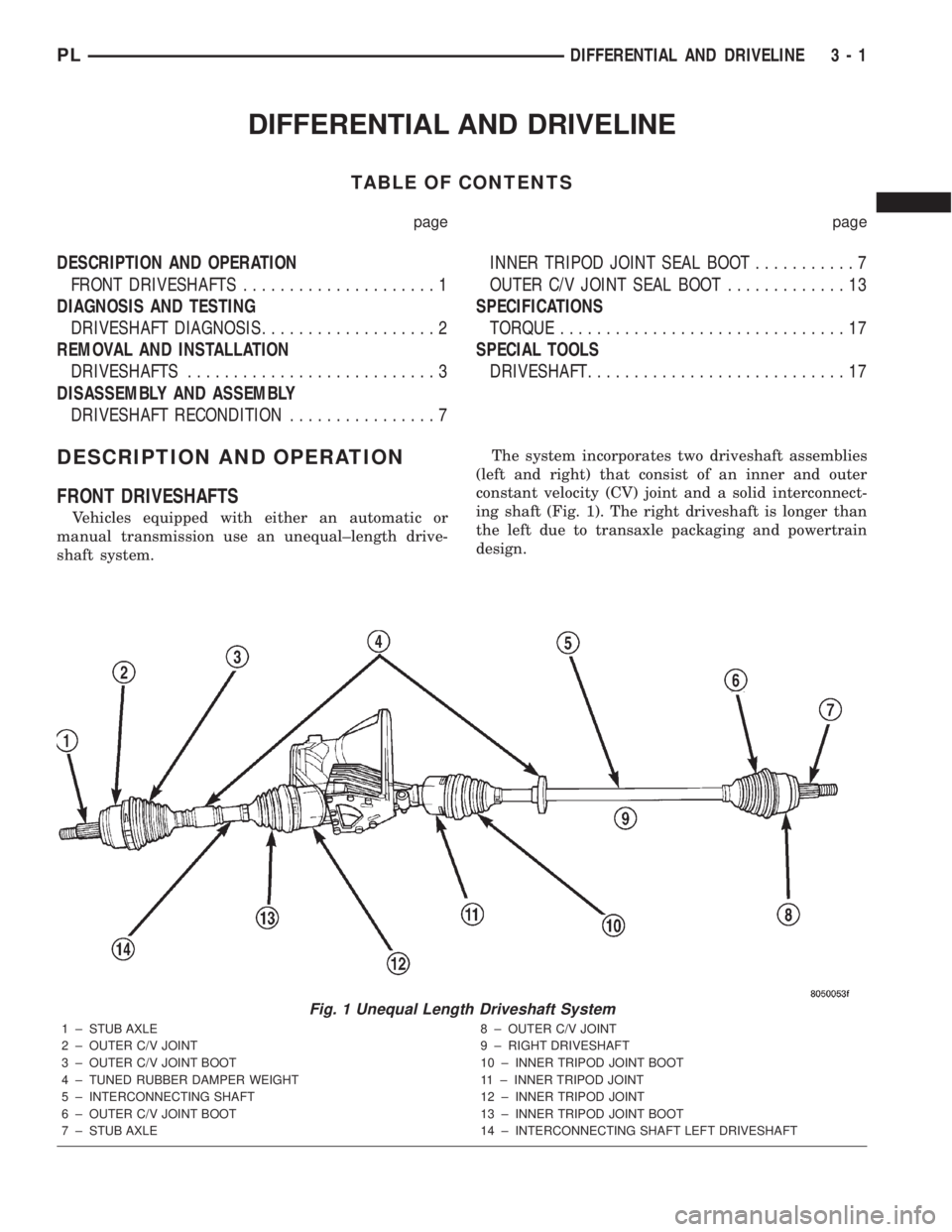
FRONT DRIVESHAFTS
Vehicles equipped with either an automatic or
manual transmission use an unequal±length drive-
shaft system.The system incorporates two driveshaft assemblies
(left and right) that consist of an inner and outer
constant velocity (CV) joint and a solid interconnect-
ing shaft (Fig. 1). The right driveshaft is longer than
the left due to transaxle packaging and powertrain
design.
Fig. 1 Unequal Length Driveshaft System
1 ± STUB AXLE
2 ± OUTER C/V JOINT
3 ± OUTER C/V JOINT BOOT
4 ± TUNED RUBBER DAMPER WEIGHT
5 ± INTERCONNECTING SHAFT
6 ± OUTER C/V JOINT BOOT
7 ± STUB AXLE8 ± OUTER C/V JOINT
9 ± RIGHT DRIVESHAFT
10 ± INNER TRIPOD JOINT BOOT
11 ± INNER TRIPOD JOINT
12 ± INNER TRIPOD JOINT
13 ± INNER TRIPOD JOINT BOOT
14 ± INTERCONNECTING SHAFT LEFT DRIVESHAFT
PLDIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINE 3 - 1