width DODGE NEON 2000 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 861 of 1285
DATA LINK CONNECTOR
DESCRIPTION
The data link connector is located inside the vehi-
cle, under the instrument panel, left of the steering
column (Fig. 25).
OPERATION
The data link connector (diagnostic connector)
links the DRB scan tool with the powertrain control
module (PCM). Refer to On-Board Diagnostics in the
General Diagnosis section of this group.
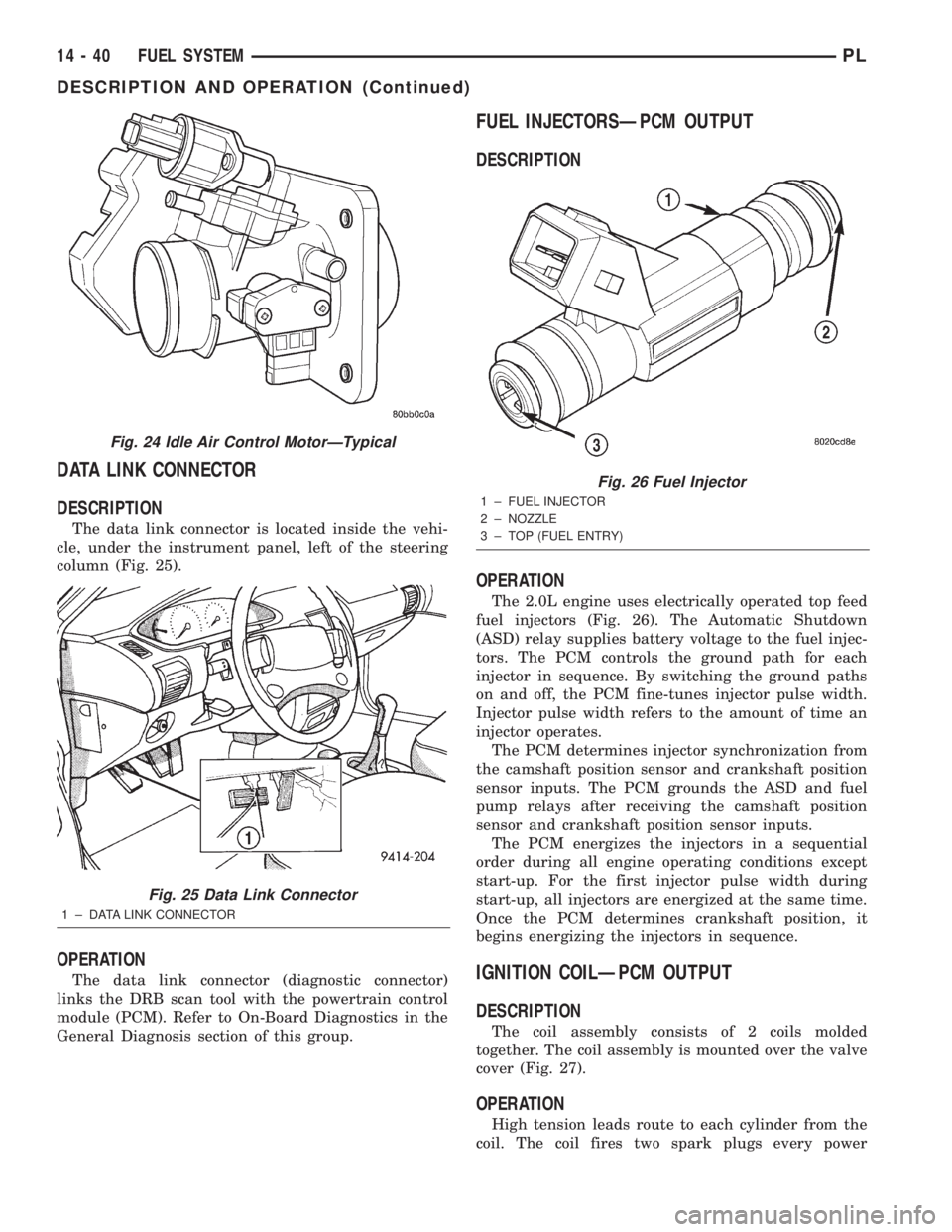
FUEL INJECTORSÐPCM OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION
OPERATION
The 2.0L engine uses electrically operated top feed
fuel injectors (Fig. 26). The Automatic Shutdown
(ASD) relay supplies battery voltage to the fuel injec-
tors. The PCM controls the ground path for each
injector in sequence. By switching the ground paths
on and off, the PCM fine-tunes injector pulse width.
Injector pulse width refers to the amount of time an
injector operates.
The PCM determines injector synchronization from
the camshaft position sensor and crankshaft position
sensor inputs. The PCM grounds the ASD and fuel
pump relays after receiving the camshaft position
sensor and crankshaft position sensor inputs.
The PCM energizes the injectors in a sequential
order during all engine operating conditions except
start-up. For the first injector pulse width during
start-up, all injectors are energized at the same time.
Once the PCM determines crankshaft position, it
begins energizing the injectors in sequence.
IGNITION COILÐPCM OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION
The coil assembly consists of 2 coils molded
together. The coil assembly is mounted over the valve
cover (Fig. 27).
OPERATION
High tension leads route to each cylinder from the
coil. The coil fires two spark plugs every power
Fig. 24 Idle Air Control MotorÐTypical
Fig. 25 Data Link Connector
1 ± DATA LINK CONNECTOR
Fig. 26 Fuel Injector
1 ± FUEL INJECTOR
2 ± NOZZLE
3 ± TOP (FUEL ENTRY)
14 - 40 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1078 of 1285

CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CLEANING TIRES
Remove the protective coating on the tires before
delivery of a vehicle. This coating may cause deteri-
oration of the tires.
To remove the protective coating, apply warm
water and let it soak for a few minutes. Afterwards,
scrub the coating away with a soft bristle brush.Steam cleaning may also be used to remove the coat-
ing.
NOTE: DO NOT use gasoline, mineral oil, oil-based
solvent or a wire brush for cleaning.
SPECIFICATIONS
TIRE SPECIFICATIONS
The following guide should help you understand the tire designations:
P Passenger car tire (or ªTº for temporary-use tire).
185 Nominal width of tire in millimeters.
70 Tire height-to-width ratio.
R Radial-ply tire (or ªDº for bias-ply tire).
14 Nominal rim diameter in inches.
Do not install smaller than minimum size tires shown on the tire inflation placard on the vehicle.
PLTIRES AND WHEELS 22 - 9
Page 1080 of 1285

sections help hold the tire in position on the wheel
until the vehicle can be brought to a safe stop.
Cast aluminum wheels require special balance
weights to fit on the thicker flange of the rim and
special wheel clamps for the alignment equipment.
The wheel studs and nuts are designed for specific
wheel applications and must be replaced with equiv-
alent parts. Do not use replacement parts of lesser
quality or of a substitute design. All aluminum
wheels use wheel nuts with an enlarged nose. This
enlarged nose is necessary to ensure proper retention
of the wheels.
Vehicles that are equipped with lock-on wheel cov-
ers use large nose wheel nuts. The wheel nuts are
externally threaded so that the wheel covers can be
attached to the wheel nuts.
WHEEL COVER (LOCK-ON)
This vehicle uses a lock-on type wheel cover (Fig.
3) on certain models.
The wheel cover is attached to the wheel using the
5 nuts located in the wheel cover (Fig. 3). The nuts in
the wheel cover thread onto a special externally
threaded wheel nut (Fig. 4) to retain the wheel cover
to the wheel.
The wheel cover retaining nut (Fig. 3) is retained
in the wheel cover and will stay on the wheel cover
when un-threaded from the wheel nut. If required,
the retaining nut can be removed from the wheel
cover and replaced as a separate part of the wheel
cover.
The lock-on wheel cover can not be removed from
the wheel until all 5 wheel cover retaining nuts areun-threaded from the wheel nuts. Then the lock-on
wheel cover can be removed by hand from the wheel.DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WHEEL INSPECTION
Inspect wheels for:
²Excessive run out
²Dents or cracks
²Damaged wheel lug nut holes
²Air Leaks from any area or surface of the rim
NOTE: Do not attempt to repair a wheel by ham-
mering, heating or welding.
If a wheel is damaged an original equipment
replacement wheel should be used. When obtaining
replacement wheels, they should be equivalent in
load carrying capacity. The diameter, width, offset,
Fig. 2 Safety Rim
1 ± TIRE
2 ± WELL
3 ± SAFETY HUMPS
4 ± FLANGE
Fig. 3 Wheel Cover And Retaining Nut
1 ± WHEEL COVER RETAINING NUTS
2 ± TIRE
3 ± WHEEL
4 ± LOCK-ON WHEEL COVER
Fig. 4 Wheel Nut And Wheel Cover Retaining Nut
1 ± WHEEL NUT
2 ± EXTERNAL THREADS
3 ± LOCK-ON WHEEL COVER RETAINING NUT
PLTIRES AND WHEELS 22 - 11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1102 of 1285

MONITORED SYSTEMS
DESCRIPTION
There are new electronic circuit monitors that
check fuel, emission, engine and ignition perfor-
mance. These monitors use information from various
sensor circuits to indicate the overall operation of the
fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems and thus
the emissions performance of the vehicle.
The fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems
monitors do not indicate a specific component prob-
lem. They do indicate that there is an implied prob-
lem within one of the systems and that a specific
problem must be diagnosed.
If any of these monitors detect a problem affecting
vehicle emissions, the Malfunction Indicator (Check
Engine) Lamp will be illuminated. These monitors
generate Diagnostic Trouble Codes that can be dis-
played with the check engine lamp or a scan tool.
The following is a list of the monitored systems:
²EGR Monitor
²Misfire Monitor
²Fuel System Monitor
²Evaporative Emissions Monitor
Following is a description of each system monitor,
and its DTC.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnos-
tics Procedures manual for diagnostic proce-
dures.
EGR MONITOR
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) performs
an on-board diagnostic check of the EGR system.
The EGR system consists of two main components:
a vacuum solenoid back pressure transducer and a
vacuum operated valve. The EGR monitor is used to
test whether the EGR system is operating within
specifications. The diagnostic check activates only
during selected engine/driving conditions. When the
conditions are met, the EGR is turned off (solenoid
energized) and the O2S compensation control is mon-
itored. Turning off the EGR shifts the air fuel (A/F)
ratio in the lean direction. Oxygen sensor voltage
then indicates increased oxygen in the exhaust. Con-
sequently, Short Term Compensation shifts to rich
(increased injector pulse width). By monitoring the
shift, the PCM can indirectly monitor the EGR sys-
tem. While this test does not directly measure the
operation of the EGR system, it can be inferred from
the shift in the O2S data whether the EGR system is
operating correctly. Because the O2S is being used,
the O2S test must pass its test before the EGR test.
Enabling ConditionsÐ
²Engine Temperature
²Engine Run Time
²Engine RPM²MAP Sensor
²TPS
²Vehicle Speed
²Short Term Compensation
Pending ConditionsÐThe EGR Monitor does
not run when any of the following example faults
have illuminated the MIL:
²Misfire
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Fuel System Rich/Lean
²Limp in for MAP, TPS or ECT
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Cam or Crank Sensor
²EGR Electrical
²EVAP Electrical
²Fuel Injector
²Ignition Coil
²Idle Speed
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
²MAP Sensor
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT)
Conflict ConditionsÐThe EGR Monitor typi-
cally does not run if any of the following conditions
are present:
²Fuel System Monitor
²Purge Monitor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Low Fuel Level
²High Altitude
²Low Ambient Air Temperature
The EGR Monitor does not run if any of the follow-
ing example DTCs are present:
²Misfire Monitor, Priority 2
²Upstream Oxygen Sensor Heater, Priority 1
²Fuel System Monitor, Priority 2
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Priority 1
MISFIRE MONITOR
Excessive engine misfire results in increased cata-
lyst temperature and causes an increase in HC emis-
sions. Severe misfires could cause catalyst damage.
To prevent catalytic convertor damage, the PCM
monitors engine misfire.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
for misfire during most engine operating conditions
(positive torque) by looking at changes in the crank-
shaft speed. If a misfire occurs the speed of the
crankshaft will vary more than normal.
OBD II regulations for misfire monitoring require
two different tests for misfire. The first is a Catalyst
Damage level of misfire test. The second is for emis-
sions greater than 1.5 times the Federal Tailpipe
(FTP) standards. The tests are monitored by two dif-
ferent counters. These counters are:
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 15
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1104 of 1285

The PCM is programmed to maintain the optimum
air/fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1. This is done by making
short term corrections in the fuel injector pulse width
based on the O2S output. The programmed memory
acts as a self calibration tool that the engine control-
ler uses to compensate for variations in engine spec-
ifications, sensor tolerances and engine fatigue over
the life span of the engine. By monitoring the actual
air-fuel ratio with the O2S (short term) and multiply-
ing that with the program long-term (adaptive) mem-
ory and comparing that to the limit, it can be
determined whether it will pass an emissions test. If
a malfunction occurs such that the PCM cannot
maintain the optimum A/F ratio, then the MIL will
be illuminated.
Monitor OperationÐFuel systems monitors do
not have a pre-test because they are continuously
running monitors. Therefore, the PCM constantly
monitors Short Term Compensation and Long Term
Adaptive memory.
Lean: If at anytime during a lean engine operation,
short term compensation multiplied by long term
adaptive exceeds a certain percentage for an
extended period, the PCM sets a Fuel System Lean
Fault for that trip and a Freeze Frame is entered.
Rich: If at anytime during a rich operation, Short
Term Compensation multiplied by Long Term Adap-
tive is less than a predetermined value, the PCM
checks the Purge Free Cells.
Purge Free Cells are values placed in Adaptive
Memory cells when the EVAP Purge Solenoid is OFF.
Two, three or four Purge Free cells are used. One cor-
responds to an Adaptive Memory cell at idle, the
other to a cell that is off-idle. For example, if a Purge
Free cell is labeled PFC1, it would hold the value for
Adaptive Memory cell C1 under non-purge condi-
tions.
If all Purge Free Cells are less than a certain per-
centage, and the Adaptive Memory factor is less than
a certain percentage, the PCM sets a Fuel System
Rich fault for that trip and a Freeze Frame is
entered.
The Fuel Monitor is a two trip monitor. The PCM
records engine data in Freeze Frame upon setting of
the first fault, or maturing code. When the fuel mon-
itor fails on a second consecutive trip, the code is
matured and the MIL is illuminated. The stored
Freeze Frame data is still from the first fault.
In order for the PCM to extinguish the MIL, the
Fuel Monitor must pass in a Similar Condition Win-
dow. The similar conditions relate to RPM and load.
The engine must be within a predetermined percent-
age of both RPM and load when the monitor runs to
count a good trip. As with all DTCs, three good tripsare required to extinguish the MIL and 40 warm up
cycles are required to erase the DTC. If the engine
does not run in a Similar Conditions Window, the
Task Manager extinguishes the MIL after 80 good
trips.
Enabling ConditionsÐThe following conditions
must be met to operate the fuel control monitor:
²PCM not in fuel crank mode (engine running)
²PCM in Closed Loop fuel control
²Fuel system updating Long Term Adaptive
²Fuel level above 15% of capacity
²Fuel level below 85% of capacity
Pending ConditionsÐThe Fuel Control Monitor
does not operate if the MIL is illuminated for any of
the following:
²Misfire Monitor
²Upstream O2S
²EVAP Purge Solenoid Electrical PCM Self Test
Fault
²Camshaft or Crankshaft Position Sensor
²Fuel Injectors
²Ignition Coil Primary
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Idle Air Control (IAC)
²5V Output Too Low
²EGR Monitor
²EGR Solenoid Circuit
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Electrical
²Idle Speed Rationality
²Intake Air Temperature
SuspendÐThe Task Manager will suspend
maturing a Fuel System fault if any of the following
are present:
²Oxygen Sensor Response, Priority 1
²O2 Heater, Priority 1
²Misfire Monitor, Priority 2
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS MONITOR
LEAK DETECTION PUMP MONITORÐThe
leak detection assembly incorporates two primary
functions: it must detect a leak in the evaporative
system and seal the evaporative system so the leak
detection test can be run.
The primary components within the assembly are:
A three port solenoid that activates both of the func-
tions listed above; a pump which contains a switch,
two check valves and a spring/diaphragm, a canister
vent valve (CVV) seal which contains a spring loaded
vent seal valve.
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 17
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1107 of 1285

NOTE: Comprehensive component monitors are
continuous. Therefore, enabling conditions do not
apply.
Input RationalityÐWhile input signals to the
PCM are constantly being monitored for electrical
opens and shorts, they are also tested for rationality.
This means that the input signal is compared against
other inputs and information to see if it makes sense
under the current conditions.
PCM sensor inputs that are checked for rationality
include:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Oxygen Sensor (O2S)
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Ambient/Battery Temperature Sensors
²Power Steering Switch
²Oxygen Sensor Heater
²Engine Controller
²Brake Switch
²Leak Detection Pump Switch
²P/N Switch
²Trans Controls
Output FunctionalityÐPCM outputs are tested
for functionality in addition to testing for opens and
shorts. When the PCM provides a voltage to an out-
put component, it can verify that the command was
carried out by monitoring specific input signals for
expected changes. For example, when the PCM com-
mands the Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor to a specific
position under certain operating conditions, it expects
to see a specific (target) idle speed (RPM). If it does
not, it stores a DTC.
PCM outputs monitored for functionality include:
²Fuel Injectors
²Ignition Coils
²Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
²Idle Air Control
²Purge Solenoid
²EGR Solenoid
²LDP Solenoid
²Radiator Fan Control
²Trans Controls
OXYGEN SENSOR (O2S) MONITOR
DESCRIPTIONÐEffective control of exhaust
emissions is achieved by an oxygen feedback system.
The most important element of the feedback system
is the O2S. The O2S is located in the exhaust path.
Once it reaches operating temperature 300É to 350ÉC
(572É to 662ÉF), the sensor generates a voltage that
is inversely proportional to the amount of oxygen inthe exhaust. When there is a large amount of oxygen
in the exhaust caused by a lean condition, the sensor
produces a low voltage, below 450 mV. When the oxy-
gen content is lower, caused by a rich condition, the
sensor produces a higher voltage, above 450mV.
The information obtained by the sensor is used to
calculate the fuel injector pulse width. This main-
tains a 14.7 to 1 air fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture
ratio, the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons
(HC), carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrous oxide (NOx)
from the exhaust.
The O2S is also the main sensing element for the
EGR, Catalyst and Fuel Monitors.
The O2S may fail in any or all of the following
manners:
²Slow response rate (Big Slope)
²Reduced output voltage (Half Cycle)
²Heater Performance
Slow Response Rate (Big Slope)ÐResponse
rate is the time required for the sensor to switch
from lean to rich signal output once it is exposed to a
richer than optimum A/F mixture or vice versa. As
the PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio, the sensor must
be able to rapidly detect the change. As the sensor
ages, it could take longer to detect the changes in the
oxygen content of the exhaust gas. The rate of
change that an oxygen sensor experiences is called
'Big Slope'. The PCM checks the oxygen sensor volt-
age in increments of a few milliseconds.
Reduced Output Voltage (Half Cycle)ÐThe
output voltage of the O2S ranges from 0 to 1 volt. A
good sensor can easily generate any output voltage in
this range as it is exposed to different concentrations
of oxygen. To detect a shift in the A/F mixture (lean
or rich), the output voltage has to change beyond a
threshold value. A malfunctioning sensor could have
difficulty changing beyond the threshold value. Each
time the voltage signal surpasses the threshold, a
counter is incremented by one. This is called the Half
Cycle Counter.
Heater PerformanceÐThe heater is tested by a
separate monitor. Refer to the Oxygen Sensor Heater
Monitor.
OPERATIONÐAs the Oxygen Sensor signal
switches, the PCM monitors the half cycle and big
slope signals from the oxygen sensor. If during the
test neither counter reaches a predetermined value, a
malfunction is entered and a Freeze Frame is stored.
Only one counter reaching its predetermined value is
needed for the monitor to pass.
The Oxygen Sensor Monitor is a two trip monitor
that is tested only once per trip. When the Oxygen
Sensor fails the test in two consecutive trips, the
MIL is illuminated and a DTC is set. The MIL is
extinguished when the Oxygen Sensor monitor
passes in three consecutive trips. The DTC is erased
25 - 20 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1139 of 1285
from was and oil. Scuff surfaces around repair area
with 360 grit wet/dry sand paper, or equivalent, to
assure adhesion of epoxy repair materials.
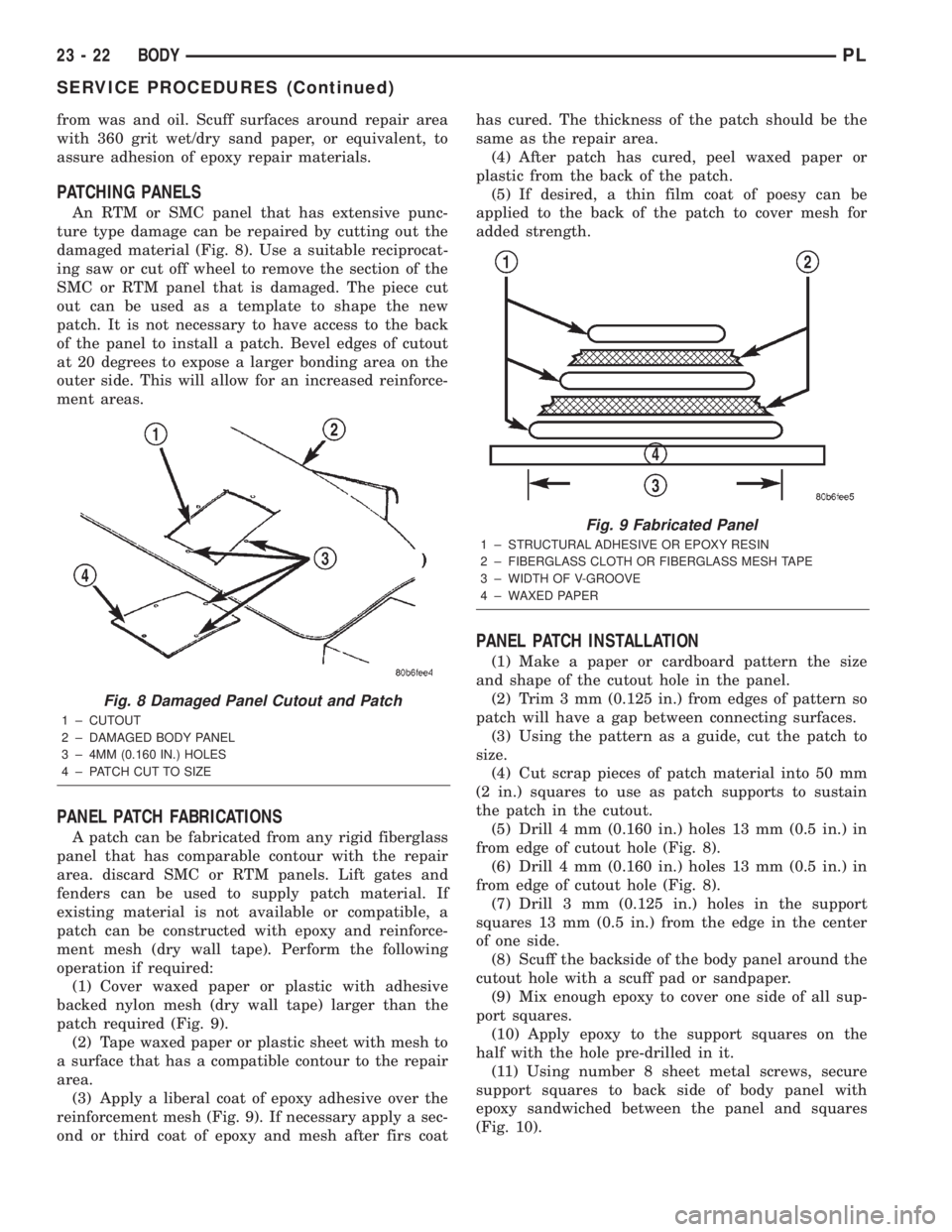
PATCHING PANELS
An RTM or SMC panel that has extensive punc-
ture type damage can be repaired by cutting out the
damaged material (Fig. 8). Use a suitable reciprocat-
ing saw or cut off wheel to remove the section of the
SMC or RTM panel that is damaged. The piece cut
out can be used as a template to shape the new
patch. It is not necessary to have access to the back
of the panel to install a patch. Bevel edges of cutout
at 20 degrees to expose a larger bonding area on the
outer side. This will allow for an increased reinforce-
ment areas.
PANEL PATCH FABRICATIONS
A patch can be fabricated from any rigid fiberglass
panel that has comparable contour with the repair
area. discard SMC or RTM panels. Lift gates and
fenders can be used to supply patch material. If
existing material is not available or compatible, a
patch can be constructed with epoxy and reinforce-
ment mesh (dry wall tape). Perform the following
operation if required:
(1) Cover waxed paper or plastic with adhesive
backed nylon mesh (dry wall tape) larger than the
patch required (Fig. 9).
(2) Tape waxed paper or plastic sheet with mesh to
a surface that has a compatible contour to the repair
area.
(3) Apply a liberal coat of epoxy adhesive over the
reinforcement mesh (Fig. 9). If necessary apply a sec-
ond or third coat of epoxy and mesh after firs coathas cured. The thickness of the patch should be the
same as the repair area.
(4) After patch has cured, peel waxed paper or
plastic from the back of the patch.
(5) If desired, a thin film coat of poesy can be
applied to the back of the patch to cover mesh for
added strength.
PANEL PATCH INSTALLATION
(1) Make a paper or cardboard pattern the size
and shape of the cutout hole in the panel.
(2) Trim 3 mm (0.125 in.) from edges of pattern so
patch will have a gap between connecting surfaces.
(3) Using the pattern as a guide, cut the patch to
size.
(4) Cut scrap pieces of patch material into 50 mm
(2 in.) squares to use as patch supports to sustain
the patch in the cutout.
(5) Drill 4 mm (0.160 in.) holes 13 mm (0.5 in.) in
from edge of cutout hole (Fig. 8).
(6) Drill 4 mm (0.160 in.) holes 13 mm (0.5 in.) in
from edge of cutout hole (Fig. 8).
(7) Drill 3 mm (0.125 in.) holes in the support
squares 13 mm (0.5 in.) from the edge in the center
of one side.
(8) Scuff the backside of the body panel around the
cutout hole with a scuff pad or sandpaper.
(9) Mix enough epoxy to cover one side of all sup-
port squares.
(10) Apply epoxy to the support squares on the
half with the hole pre-drilled in it.
(11) Using number 8 sheet metal screws, secure
support squares to back side of body panel with
epoxy sandwiched between the panel and squares
(Fig. 10).
Fig. 8 Damaged Panel Cutout and Patch
1 ± CUTOUT
2 ± DAMAGED BODY PANEL
3 ± 4MM (0.160 IN.) HOLES
4 ± PATCH CUT TO SIZE
Fig. 9 Fabricated Panel
1 ± STRUCTURAL ADHESIVE OR EPOXY RESIN
2 ± FIBERGLASS CLOTH OR FIBERGLASS MESH TAPE
3 ± WIDTH OF V-GROOVE
4 ± WAXED PAPER
23 - 22 BODYPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)