ABS DODGE NEON 2000 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 162 of 1285
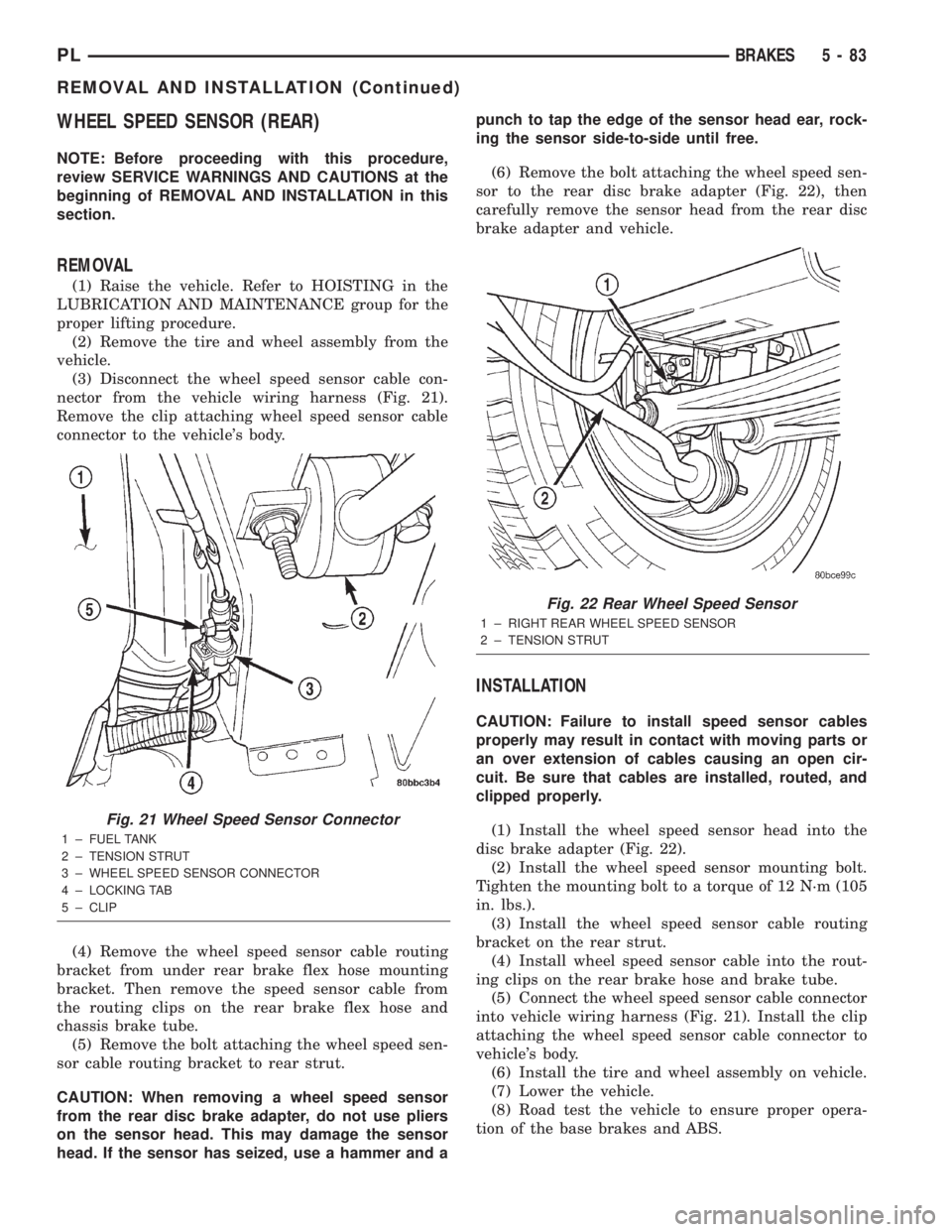
WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (REAR)
NOTE: Before proceeding with this procedure,
review SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS at the
beginning of REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION in this
section.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle. Refer to HOISTING in the
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE group for the
proper lifting procedure.
(2) Remove the tire and wheel assembly from the
vehicle.
(3) Disconnect the wheel speed sensor cable con-
nector from the vehicle wiring harness (Fig. 21).
Remove the clip attaching wheel speed sensor cable
connector to the vehicle's body.
(4) Remove the wheel speed sensor cable routing
bracket from under rear brake flex hose mounting
bracket. Then remove the speed sensor cable from
the routing clips on the rear brake flex hose and
chassis brake tube.
(5) Remove the bolt attaching the wheel speed sen-
sor cable routing bracket to rear strut.
CAUTION: When removing a wheel speed sensor
from the rear disc brake adapter, do not use pliers
on the sensor head. This may damage the sensor
head. If the sensor has seized, use a hammer and apunch to tap the edge of the sensor head ear, rock-
ing the sensor side-to-side until free.
(6) Remove the bolt attaching the wheel speed sen-
sor to the rear disc brake adapter (Fig. 22), then
carefully remove the sensor head from the rear disc
brake adapter and vehicle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Failure to install speed sensor cables
properly may result in contact with moving parts or
an over extension of cables causing an open cir-
cuit. Be sure that cables are installed, routed, and
clipped properly.
(1) Install the wheel speed sensor head into the
disc brake adapter (Fig. 22).
(2) Install the wheel speed sensor mounting bolt.
Tighten the mounting bolt to a torque of 12 N´m (105
in. lbs.).
(3) Install the wheel speed sensor cable routing
bracket on the rear strut.
(4) Install wheel speed sensor cable into the rout-
ing clips on the rear brake hose and brake tube.
(5) Connect the wheel speed sensor cable connector
into vehicle wiring harness (Fig. 21). Install the clip
attaching the wheel speed sensor cable connector to
vehicle's body.
(6) Install the tire and wheel assembly on vehicle.
(7) Lower the vehicle.
(8) Road test the vehicle to ensure proper opera-
tion of the base brakes and ABS.
Fig. 21 Wheel Speed Sensor Connector
1 ± FUEL TANK
2 ± TENSION STRUT
3 ± WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 ± LOCKING TAB
5 ± CLIP
Fig. 22 Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
1 ± RIGHT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
2 ± TENSION STRUT
PLBRAKES 5 - 83
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 163 of 1285
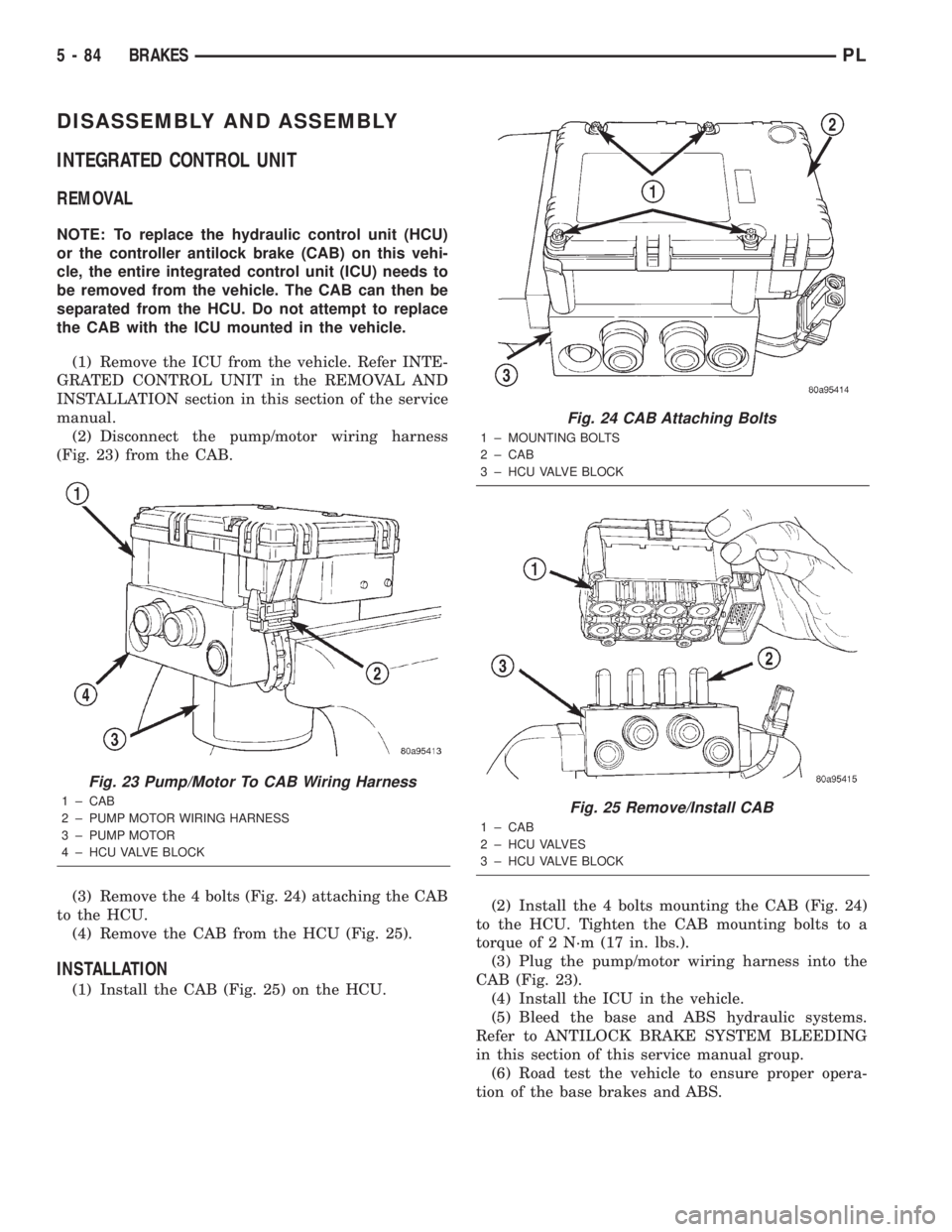
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
INTEGRATED CONTROL UNIT
REMOVAL
NOTE: To replace the hydraulic control unit (HCU)
or the controller antilock brake (CAB) on this vehi-
cle, the entire integrated control unit (ICU) needs to
be removed from the vehicle. The CAB can then be
separated from the HCU. Do not attempt to replace
the CAB with the ICU mounted in the vehicle.
(1) Remove the ICU from the vehicle. Refer INTE-
GRATED CONTROL UNIT in the REMOVAL AND
INSTALLATION section in this section of the service
manual.
(2) Disconnect the pump/motor wiring harness
(Fig. 23) from the CAB.
(3) Remove the 4 bolts (Fig. 24) attaching the CAB
to the HCU.
(4) Remove the CAB from the HCU (Fig. 25).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the CAB (Fig. 25) on the HCU.(2) Install the 4 bolts mounting the CAB (Fig. 24)
to the HCU. Tighten the CAB mounting bolts to a
torque of 2 N´m (17 in. lbs.).
(3) Plug the pump/motor wiring harness into the
CAB (Fig. 23).
(4) Install the ICU in the vehicle.
(5) Bleed the base and ABS hydraulic systems.
Refer to ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM BLEEDING
in this section of this service manual group.
(6) Road test the vehicle to ensure proper opera-
tion of the base brakes and ABS.
Fig. 23 Pump/Motor To CAB Wiring Harness
1 ± CAB
2 ± PUMP MOTOR WIRING HARNESS
3 ± PUMP MOTOR
4 ± HCU VALVE BLOCK
Fig. 24 CAB Attaching Bolts
1 ± MOUNTING BOLTS
2 ± CAB
3 ± HCU VALVE BLOCK
Fig. 25 Remove/Install CAB
1 ± CAB
2 ± HCU VALVES
3 ± HCU VALVE BLOCK
5 - 84 BRAKESPL
Page 166 of 1285

CLUTCH
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY..............1
CLUTCH CABLE..........................1
CLUTCH INTERLOCK/UPSTOP SWITCH........1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CLUTCH SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS...............2
DRIVE PLATE MISALIGNMENT..............5
CLUTCH CHATTER COMPLAINTS............5
CLASH±INTO±REVERSE COMPLAINTS........5
CLUTCH INTERLOCK/UPSTOP SWITCH........5REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CLUTCH CABLE..........................7
CLUTCH INTERLOCK/UPSTOP SWITCH........8
MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY..............8
RELEASE BEARING AND FORK.............12
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CLUTCH CONTAMINATION.................12
CLEANING PRECAUTIONS.................13
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE...............................13
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
All 2.0L SOHC engines equipped with the A578
5-speed transaxle use a modular clutch assembly
(Fig. 1). The transaxle must be removed to gain
access to and replace the modular clutch, drive plate,
and/or clutch release bearing and lever.
The modular clutch assembly used in this vehicle
consists of a single, dry-type clutch disc, a diaphragm
style clutch cover, and an integrated flywheel. The
clutch cover is riveted to the flywheel, containing theclutch disc within. The modular clutch can only be
serviced as an assembly.
The clutch disc has cushion springs riveted to the
disc hub assembly. The clutch disc facings are riveted
to the cushion springs. The facings are made from a
non-asbestos material.
The clutch cover pressure plate assembly is a dia-
phragm type unit with a one-piece diaphragm spring
with multiple release fingers. The pressure plate
release fingers are preset during manufacture and
are not adjustable.
CLUTCH CABLE
The clutch cable assembly (Fig. 2) carries the
movement of the clutch pedal to the clutch release
bearing. The cable is designed to maintain tension
against the clutch fork, or lever, and has a built in
self-adjusting mechanism, which compensates for
clutch disc wear.
CLUTCH INTERLOCK/UPSTOP SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The clutch interlock/upstop switch is an assembly
consisting of two switches: an engine starter inhibit
switch (interlock) and a clutch pedal upstop switch
(Fig. 3). The switch assembly is located in the clutch/
brake pedal bracket assembly (Fig. 4), each switch
being fastened by four plastic wing tabs.
OPERATION
Clutch Interlock Switch
The clutch interlock switch prevents engine starter
operation and inadvertent vehicle movement with the
clutch engaged and the transaxle in gear.
Fig. 1 Modular Clutch Assembly
1 ± MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
PLCLUTCH 6 - 1
Page 170 of 1285

DRIVE PLATE MISALIGNMENT
Common causes of misalignment are:
²Heat warping
²Mounting drive plate on a dirty crankshaft
flange
²Incorrect bolt tightening
²Improper seating on the crankshaft shoulder
²Loose crankshaft bolts
Clean the crankshaft flange before mounting the
drive plate. Dirt and grease on the flange surface
may misalign the flywheel, causing excessive runout.
Use new bolts when mounting drive plate to crank-
shaft. Tighten drive plate bolts to specified torque
only. Over-tightening can distort the drive plate hub
causing excessive runout.
CLUTCH CHATTER COMPLAINTS
For all clutch chatter complaints, do the following:
(1) Check for loose, misaligned, or broken engine
and transmission mounts. If present, they should be
corrected at this time. Test vehicle for chatter. If
chatter is gone, there is no need to go any further. If
chatter persists:
(2) Check to see if clutch cable routing is correct
and operates smoothly.
(3) Check for loose connections in drive train. Cor-
rect any problems and determine if clutch chatter
complaints have been satisfied. If not:
(4) Remove transaxle. See Group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle for procedure.
(5) Check to see if the release bearing is sticky or
binding. Replace bearing, if needed.
(6) Check linkage for excessive wear on the pivot
stud and fork fingers. Replace all worn parts.
(7) Check clutch assembly for contamination (dirt,
oil). Replace clutch assembly, if required.
(8) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines are
damaged. Replace with new clutch assembly, if nec-
essary.
(9) Check input shaft splines for damage. Replace,
if necessary.
(10) Check for uneven wear on clutch fingers.
(11) Check for broken clutch cover diaphragm
spring fingers. Replace with new clutch assembly, if
necessary.
CLASH±INTO±REVERSE COMPLAINTS
Certain NV T350 (A-578) manual transaxles are
equipped with a reverse brake. It prevents clash
when shifting into reverse, but only if the vehicle is
not moving. See Group 21, Transaxle for further
diagnosis.
(1) Depress clutch pedal to floor and hold. After
three seconds, shift to reverse. If clash is present,
clutch has excessive spin time, and the reverse brake
may not be functioning.(2) Remove transaxle. See Group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle for procedure.
(3) Check the input shaft spline, clutch disc
splines, and release bearing for dry rust. If present,
clean rust off and apply a light coat of bearing grease
to the input shaft splines. Apply grease on the input
shaft splines only where the clutch disc slides. Verify
that the clutch disc slides freely along the input shaft
spline.
(4) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines are
damaged, and replace with new clutch assembly if
required.
(5) Check the input shaft for damaged splines.
Replace as necessary.
(6) Check for broken clutch cover diaphragm
spring fingers.
(7) Install clutch assembly and transaxle.
CLUTCH INTERLOCK/UPSTOP SWITCH
The clutch interlock/upstop switch is an assembly
consisting of two switches: an engine starter inhibit
switch (clutch interlock) and a clutch pedal upstop
switch (Fig. 5). The switch assembly is located in the
clutch/brake pedal bracket assembly (Fig. 6), each
switch being fastened by four plastic wing tabs.
CLUTCH INTERLOCK SWITCH
Mechanical Test
(1) With the park brake set and the transaxleIN
NEUTRAL,turn the ignition key to the start posi-
tion. The engine starter should not crank with the
clutch pedal at rest (not depressed). If the starter
cranks, proceed to the electrical test to determine
whether the switch is defective or the circuit is
shorted. If the vehicle does not crank, proceed to the
next step.
(2) With the park brake set and the transaxleIN
NEUTRAL,fully depress the clutch pedal and turn
Fig. 5 Clutch Interlock/Upstop Switch
1 ± UPSTOP SWITCH
2 ± INTERLOCK SWITCH
3 ± CONNECTOR
PLCLUTCH 6 - 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 173 of 1285
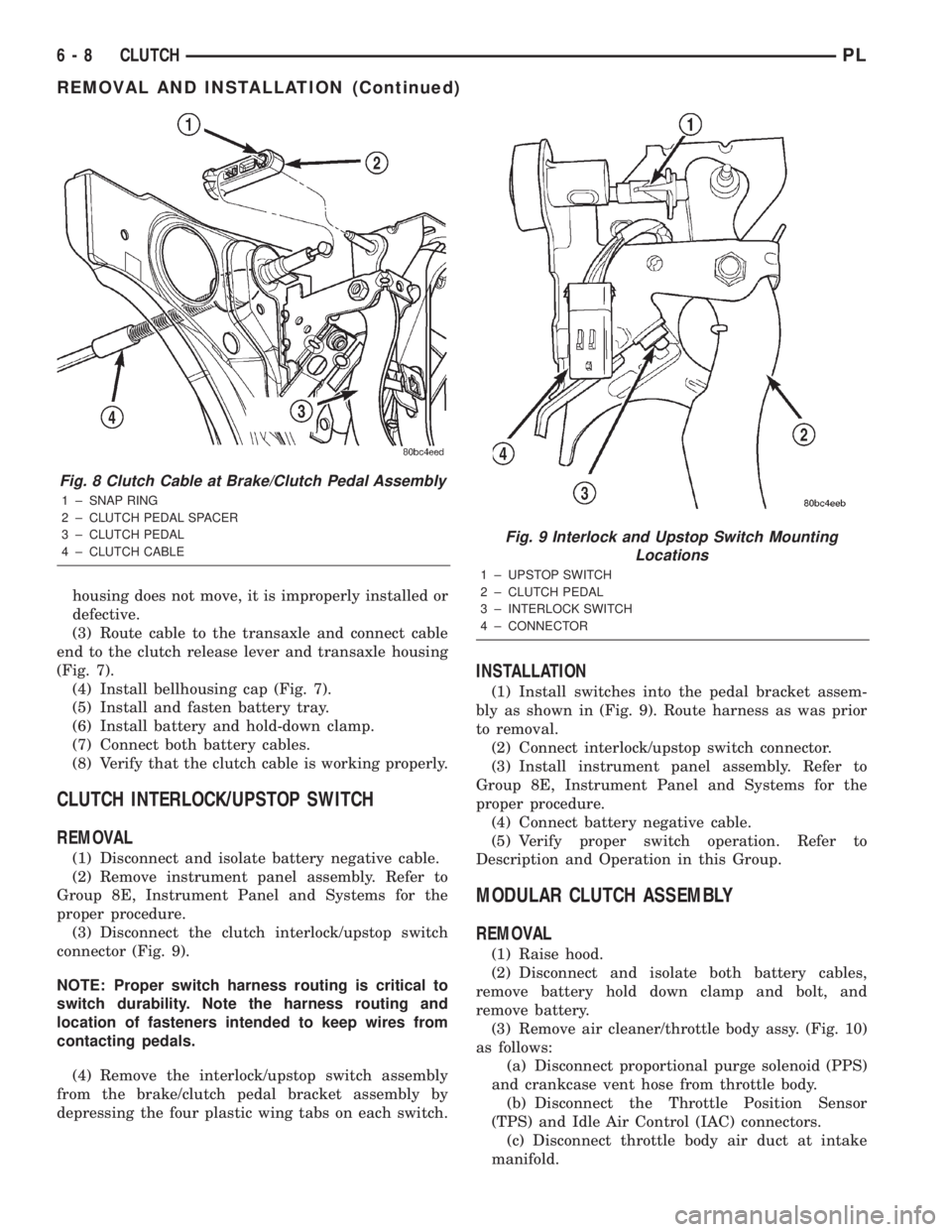
housing does not move, it is improperly installed or
defective.
(3) Route cable to the transaxle and connect cable
end to the clutch release lever and transaxle housing
(Fig. 7).
(4) Install bellhousing cap (Fig. 7).
(5) Install and fasten battery tray.
(6) Install battery and hold-down clamp.
(7) Connect both battery cables.
(8) Verify that the clutch cable is working properly.
CLUTCH INTERLOCK/UPSTOP SWITCH
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate battery negative cable.
(2) Remove instrument panel assembly. Refer to
Group 8E, Instrument Panel and Systems for the
proper procedure.
(3) Disconnect the clutch interlock/upstop switch
connector (Fig. 9).
NOTE: Proper switch harness routing is critical to
switch durability. Note the harness routing and
location of fasteners intended to keep wires from
contacting pedals.
(4) Remove the interlock/upstop switch assembly
from the brake/clutch pedal bracket assembly by
depressing the four plastic wing tabs on each switch.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install switches into the pedal bracket assem-
bly as shown in (Fig. 9). Route harness as was prior
to removal.
(2) Connect interlock/upstop switch connector.
(3) Install instrument panel assembly. Refer to
Group 8E, Instrument Panel and Systems for the
proper procedure.
(4) Connect battery negative cable.
(5) Verify proper switch operation. Refer to
Description and Operation in this Group.
MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
(1) Raise hood.
(2) Disconnect and isolate both battery cables,
remove battery hold down clamp and bolt, and
remove battery.
(3) Remove air cleaner/throttle body assy. (Fig. 10)
as follows:
(a) Disconnect proportional purge solenoid (PPS)
and crankcase vent hose from throttle body.
(b) Disconnect the Throttle Position Sensor
(TPS) and Idle Air Control (IAC) connectors.
(c) Disconnect throttle body air duct at intake
manifold.
Fig. 8 Clutch Cable at Brake/Clutch Pedal Assembly
1 ± SNAP RING
2 ± CLUTCH PEDAL SPACER
3 ± CLUTCH PEDAL
4 ± CLUTCH CABLE
Fig. 9 Interlock and Upstop Switch Mounting
Locations
1 ± UPSTOP SWITCH
2 ± CLUTCH PEDAL
3 ± INTERLOCK SWITCH
4 ± CONNECTOR
6 - 8 CLUTCHPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 177 of 1285

RELEASE BEARING AND FORK
Remove the transaxle from the vehicle. See Group
21, Transaxle for removal and installation proce-
dures.
REMOVAL
(1) Move the lever and bearing assembly to a ver-
tical in-line position. Grasp the release lever with
two hands in the pivot stud socket area. Pull with
even pressure and the lever will pop off the pivot±
stud. Do not use a screwdriver or pry bar to pop off
the lever. This may damage the spring clip on the
lever.
(2) As a unit, remove the fork from the bearing
thrust plate. Be careful not to damage retention tabs
on bearing.
(3) Examine the condition of the bearing.It is
pre-lubricated and sealed and should not be
immersed in oil or solvent.
(4) The bearing should turn smoothly when held in
the hand under a light thrust load. A light drag
caused by the lubricant fill is normal. If the bearing
is noisy, rough, or dry, replace the complete bearing
assembly with a new bearing.
(5) Check the condition of the pivot stud spring
clips on back side of clutch fork. If the clips are bro-
ken or distorted, replace the clutch fork.
INSTALLATION
(1) The pivot ball pocket in the fork, as well as the
fork arms should be lubricated with grease prior to
installation.
(2) Assemble the fork to the bearing. The small
pegs on the bearing must go over the fork arms.
(3) Slide the bearing and fork assembly onto the
input shaft bearing retainer, as a unit.
(4) Snap the clutch fork onto the pivot ball.
(5) Reinstall transaxle assembly. Refer to Group
21, Transaxle for further information.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CLUTCH CONTAMINATION
Fluid contamination is a frequent cause of clutch
malfunctions. Oil, grease, water, or other fluids on
the clutch contact surfaces will cause faulty opera-
tion.
During inspection, note if any components are con-
taminated. Look for evidence of oil, grease, or water/
road splash on clutch components.
OIL CONTAMINATION
Oil contamination indicates a leak at the rear main
seal and/or transaxle input shaft. Oil leaks produce a
residue of oil on the transaxle housing interior, clutch
Fig. 18 Transaxle Removal/Installation
1 ± MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
2 ± CLIP3 ± TRANSAXLE
4 ± CLUTCH MODULE BOLT (4)
VIEW A
6 - 12 CLUTCHPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 178 of 1285

cover and flywheel. Heat buildup caused by slippage
can bake the oil residue onto the components. This
glaze-like residue ranges in color from amber to
black.
GREASE CONTAMINATION
Grease contamination is usually a product of over-
lubrication. During clutch service, apply only a small
amount of grease to the input shaft splines. Excess
grease may be thrown off during operation, contami-
nating the disc.
ROAD SPLASH/WATER CONTAMINATION
Road splash contamination is usually caused by
driving the vehicle through deep water puddles.
Water can be forced into the clutch housing, causing
clutch components to become contaminated. Facing of
disc will absorb moisture and bond to the flywheel
and/or, pressure plate, if vehicle is allowed to stand
for some time before use. If this condition occurs,
replacement of clutch assembly may be required.
Drive the vehicle until normal clutch operating tem-
perature has been obtained. This will dry off disc
assembly, pressure plate, and flywheel.
CLEANING PRECAUTIONS
Condensation from steam vapors tend to accumu-
late on the internal clutch mechanism when the vehi-
cle is steam cleaned. Facing of disc will absorb
moisture and will bond to flywheel and/or pressure
plate, if vehicle is allowed to stand for some time
before use. If this condition occurs, it may require
replacement of clutch assembly. After cleaning, drive
the vehicle to its normal clutch operating tempera-
ture. This will dry off disc assembly, pressure plate,
and flywheel.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Modular Clutch-to-Drive Plate Bolts..... 88N´m
(65 ft. lbs.)
Transaxle-to-Engine Mounting Bolts...... 95N´m
(70 ft. lbs.)
PLCLUTCH 6 - 13
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 240 of 1285
KNOCK SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The knock sensor threads into the cylinder block.
OPERATION
When the knock sensor detects a knock in one of
the cylinders, it sends an input signal to the PCM. In
response, the PCM retards ignition timing for all cyl-
inders by a scheduled amount.Knock sensors contain a piezoelectric material
which constantly vibrates and sends an input voltage
(signal) to the PCM while the engine operates. As the
intensity of the crystal's vibration increases, the
knock sensor output voltage also increases.
NOTE: Over or under tightening affects knock sen-
sor performance, possibly causing improper spark
control.
IGNITION SWITCH
In the RUN position, the ignition switch connects
power from the Power Distribution Center (PDC) to a
fuse in the fuse block, back to a bus bar in the PDC.
The bus bar feeds circuits for the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM), Proportional purge solenoid, EGR
solenoid, and ABS system. The bus bar in the PDC
feeds the coil side of the radiator fan relay, A/C com-
pressor clutch relay, and the fuel pump relay. It also
feeds the Airbag Control Module (ACM)
LOCK KEY CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION
The lock cylinder is inserted in the end of the
housing opposite the ignition switch.
OPERATION
The ignition key rotates the cylinder to 5 different
detents (Fig. 9) :
²Accessory
²Off (lock)
²Unlock
²On/Run
²Start
Fig. 7 Target MagnetÐTypical
1 ± CAM MAGNET/TARGET
2 ± CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
Fig. 8 Target Magnet Polarity
1 ± TARGET MAGNET
Fig. 9 Ignition Lock Cylinder Detents
PLIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 243 of 1285
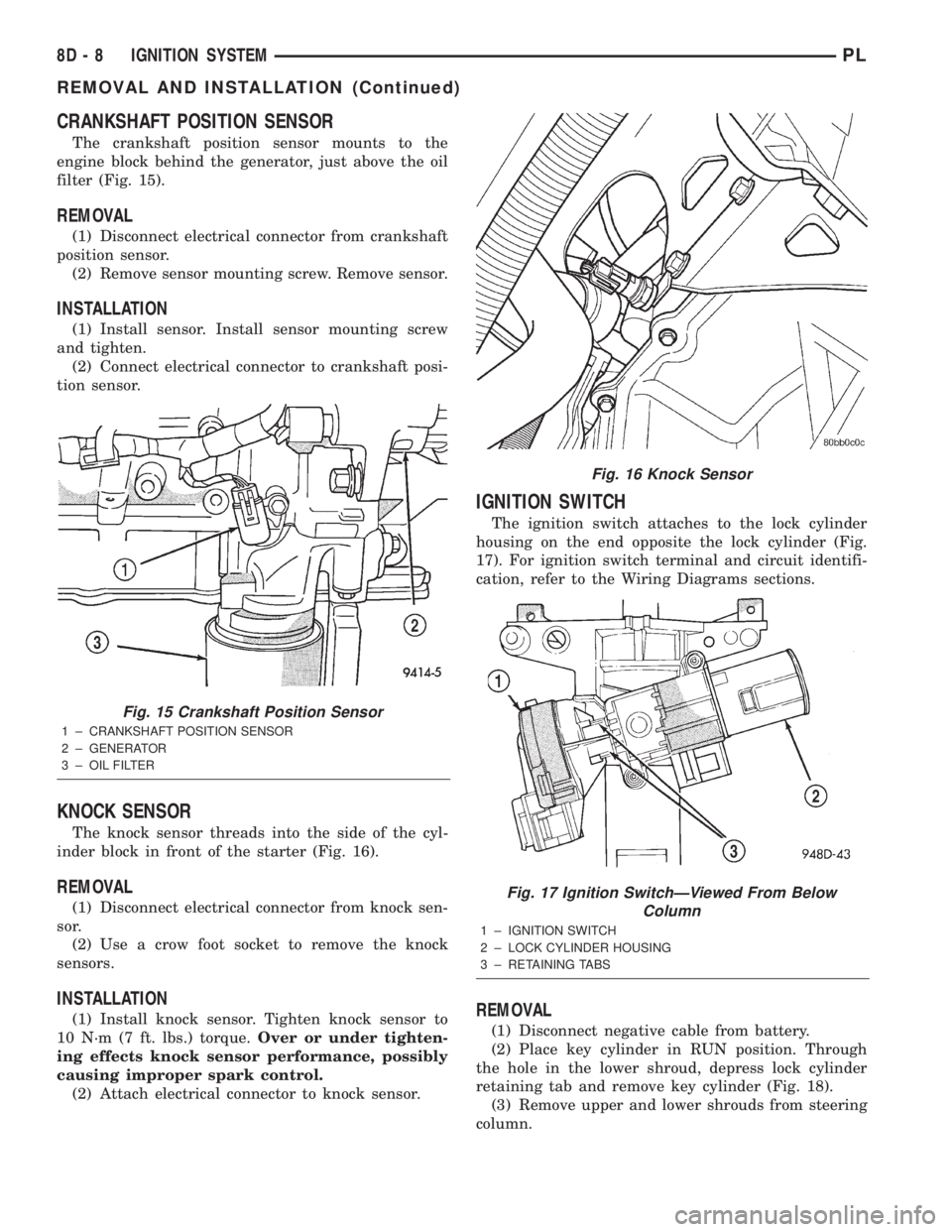
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The crankshaft position sensor mounts to the
engine block behind the generator, just above the oil
filter (Fig. 15).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from crankshaft
position sensor.
(2) Remove sensor mounting screw. Remove sensor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install sensor. Install sensor mounting screw
and tighten.
(2) Connect electrical connector to crankshaft posi-
tion sensor.
KNOCK SENSOR
The knock sensor threads into the side of the cyl-
inder block in front of the starter (Fig. 16).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from knock sen-
sor.
(2) Use a crow foot socket to remove the knock
sensors.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install knock sensor. Tighten knock sensor to
10 N´m (7 ft. lbs.) torque.Over or under tighten-
ing effects knock sensor performance, possibly
causing improper spark control.
(2) Attach electrical connector to knock sensor.
IGNITION SWITCH
The ignition switch attaches to the lock cylinder
housing on the end opposite the lock cylinder (Fig.
17). For ignition switch terminal and circuit identifi-
cation, refer to the Wiring Diagrams sections.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Place key cylinder in RUN position. Through
the hole in the lower shroud, depress lock cylinder
retaining tab and remove key cylinder (Fig. 18).
(3) Remove upper and lower shrouds from steering
column.
Fig. 15 Crankshaft Position Sensor
1 ± CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 ± GENERATOR
3 ± OIL FILTER
Fig. 16 Knock Sensor
Fig. 17 Ignition SwitchÐViewed From Below
Column
1 ± IGNITION SWITCH
2 ± LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING
3 ± RETAINING TABS
8D - 8 IGNITION SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 244 of 1285
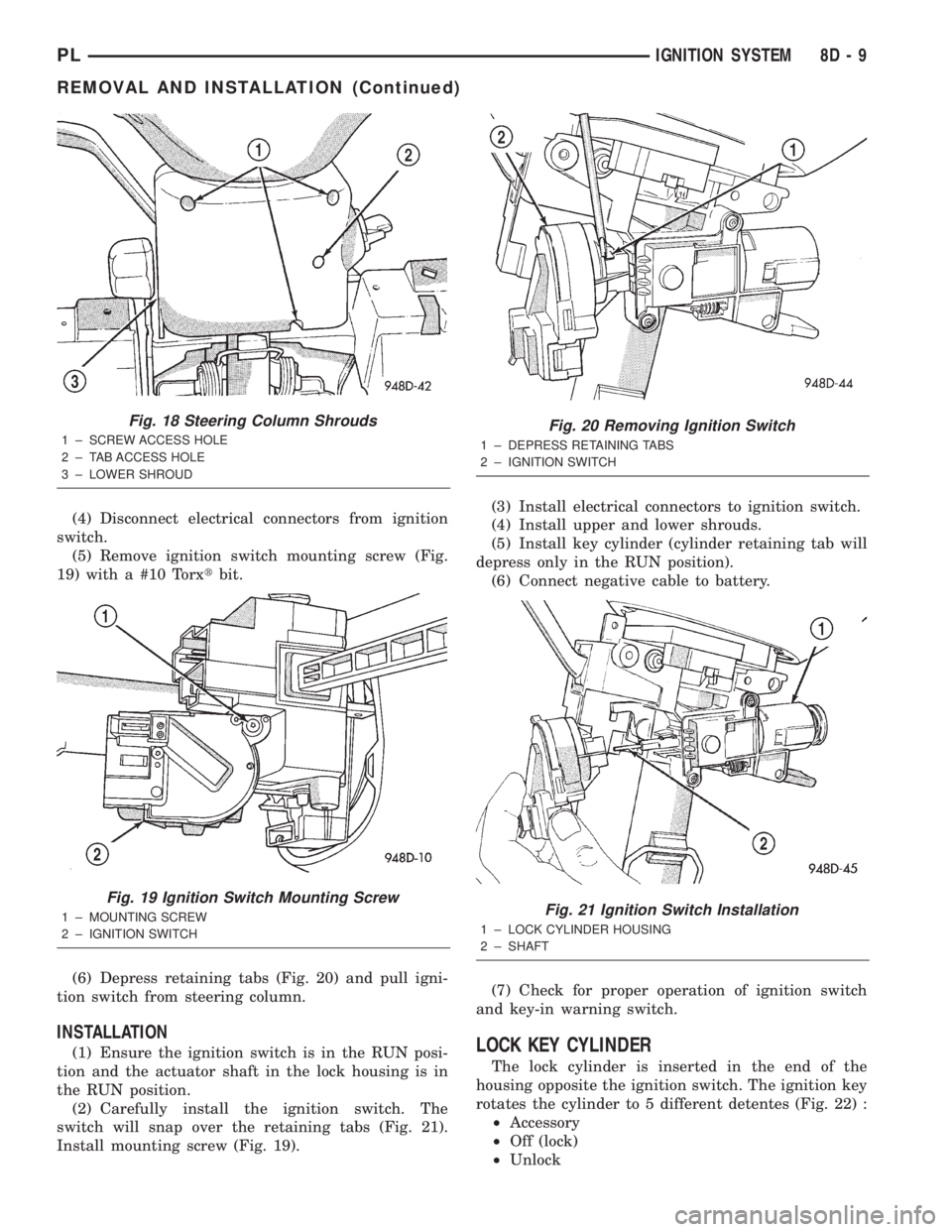
(4) Disconnect electrical connectors from ignition
switch.
(5) Remove ignition switch mounting screw (Fig.
19) with a #10 Torxtbit.
(6) Depress retaining tabs (Fig. 20) and pull igni-
tion switch from steering column.
INSTALLATION
(1) Ensure the ignition switch is in the RUN posi-
tion and the actuator shaft in the lock housing is in
the RUN position.
(2) Carefully install the ignition switch. The
switch will snap over the retaining tabs (Fig. 21).
Install mounting screw (Fig. 19).(3) Install electrical connectors to ignition switch.
(4) Install upper and lower shrouds.
(5) Install key cylinder (cylinder retaining tab will
depress only in the RUN position).
(6) Connect negative cable to battery.
(7) Check for proper operation of ignition switch
and key-in warning switch.LOCK KEY CYLINDER
The lock cylinder is inserted in the end of the
housing opposite the ignition switch. The ignition key
rotates the cylinder to 5 different detentes (Fig. 22) :
²Accessory
²Off (lock)
²Unlock
Fig. 18 Steering Column Shrouds
1 ± SCREW ACCESS HOLE
2 ± TAB ACCESS HOLE
3 ± LOWER SHROUD
Fig. 19 Ignition Switch Mounting Screw
1 ± MOUNTING SCREW
2 ± IGNITION SWITCH
Fig. 20 Removing Ignition Switch
1 ± DEPRESS RETAINING TABS
2 ± IGNITION SWITCH
Fig. 21 Ignition Switch Installation
1 ± LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING
2 ± SHAFT
PLIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)