diagram DODGE NEON 2000 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 392 of 1285

WIRING DIAGRAMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
AIR CONDITIONING-HEATER........... 8W-42-1
AIRBAG SYSTEM.................... 8W-43-1
ANTI-LOCK BRAKES.................. 8W-35-1
AUDIO SYSTEM..................... 8W-47-1
CHARGING SYSTEM.................. 8W-20-1
COMPONENT INDEX.................. 8W-02-1
CONNECTOR PIN-OUTS............... 8W-80-1
CONNECTOR/GROUND LOCATIONS...... 8W-90-1
FRONT LIGHTING.................... 8W-50-1
FUEL/IGNITION SYSTEM.............. 8W-30-1
FUSE BLOCK........................ 8W-11-1
GENERAL INFORMATION.............. 8W-01-1
GROUND DISTRIBUTION.............. 8W-15-1
HORN/CIGAR LIGHTER/POWER OUTLET . . 8W-41-1
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER............... 8W-40-1INTERIOR LIGHTING.................. 8W-44-1
POWER DISTRIBUTION............... 8W-10-1
POWER DOOR LOCKS................ 8W-61-1
POWER MIRRORS................... 8W-62-1
POWER SUNROOF................... 8W-64-1
POWER WINDOWS................... 8W-60-1
REAR LIGHTING..................... 8W-51-1
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER............ 8W-48-1
SPLICE INFORMATION................ 8W-70-1
SPLICE LOCATIONS.................. 8W-95-1
STARTING SYSTEM.................. 8W-21-1
TURN SIGNALS...................... 8W-52-1
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY SYSTEM..... 8W-39-1
WIPERS............................ 8W-53-1
PLWIRING DIAGRAMS 8W - 1
Page 394 of 1285

8W-01 GENERAL INFORMATION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
CIRCUIT FUNCTIONS......................4
CIRCUIT INFORMATION....................4
CONNECTOR INFORMATION................7
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE (ESD)
SENSITIVE DEVICES.....................8
INTRODUCTION..........................1
NOTES, CAUTIONS, and WARNINGS..........7
SECTION IDENTIFICATION..................5
SPLICE LOCATIONS.......................7
SYMBOLS...............................5
TAKE OUTS..............................8
TERMINOLOGY...........................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
INTERMITTENT AND POOR CONNECTIONS.....8
TROUBLESHOOTING TESTS................9
TROUBLESHOOTING TOOLS................8TROUBLESHOOTING WIRING PROBLEMS.....10
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CONNECTOR AND TERMINAL
REPLACEMENT........................13
CONNECTOR REPLACEMENT..............12
DIODE REPLACEMENT....................15
TERMINAL REPLACEMENT.................14
TERMINAL/CONNECTOR REPAIR- AUGAT
CONNECTORS.........................12
TERMINAL/CONNECTOR REPAIR-MOLEX
CONNECTORS.........................11
TERMINAL/CONNECTOR REPAIRÐTHOMAS
AND BETTS CONNECTORS...............11
WIRING REPAIR.........................10
SPECIAL TOOLS
WIRING/TERMINAL.......................16
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
INTRODUCTION
DiamlerChrysler wiring diagrams are designed to
provide information regarding the vehicles wiring
content. In order to effectively use DiamlerChrysler
wiring diagrams to diagnose and repair a
DiamlerChrysler vehicle, it is important to under-
stand all of their features and characteristics.
Diagrams are arranged such that the power (B+)
side of the circuit is placed near the top of the page,
and the ground (B-) side of the circuit is placed near
the bottom of the page.
All switches, components, and modules are shown
in the at rest position with the doors closed and the
key removed from the ignition.Components are shown two ways. A solid line
around a component indicates that the component is
complete. A dashed line around a component indi-
cates that the component being shown is not com-
plete. Incomplete components have a reference
number to indicate the page where the component is
shown complete.
It is important to realize that no attempt is made
on the diagrams to represent components and wiring
as they appear on the vehicle. For example, a short
piece of wire is treated the same as a long one. In
addition, switches and other components are shown
as simply as possible, with regard to function only.
PL8W - 01 GENERAL INFORMATION 8W - 01 - 1
Page 395 of 1285
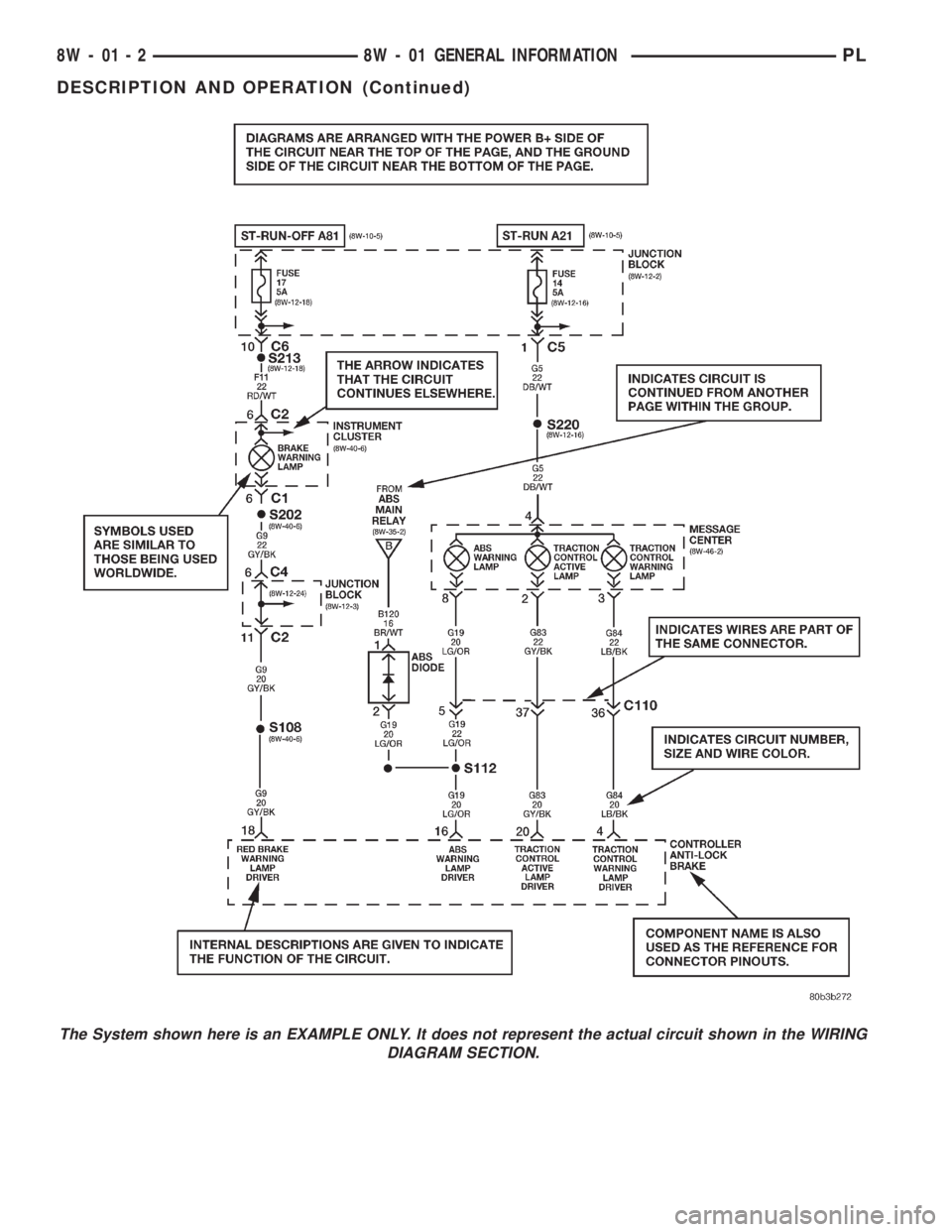
The System shown here is an EXAMPLE ONLY. It does not represent the actual circuit shown in the WIRING
DIAGRAM SECTION.
8W - 01 - 2 8W - 01 GENERAL INFORMATIONPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 396 of 1285
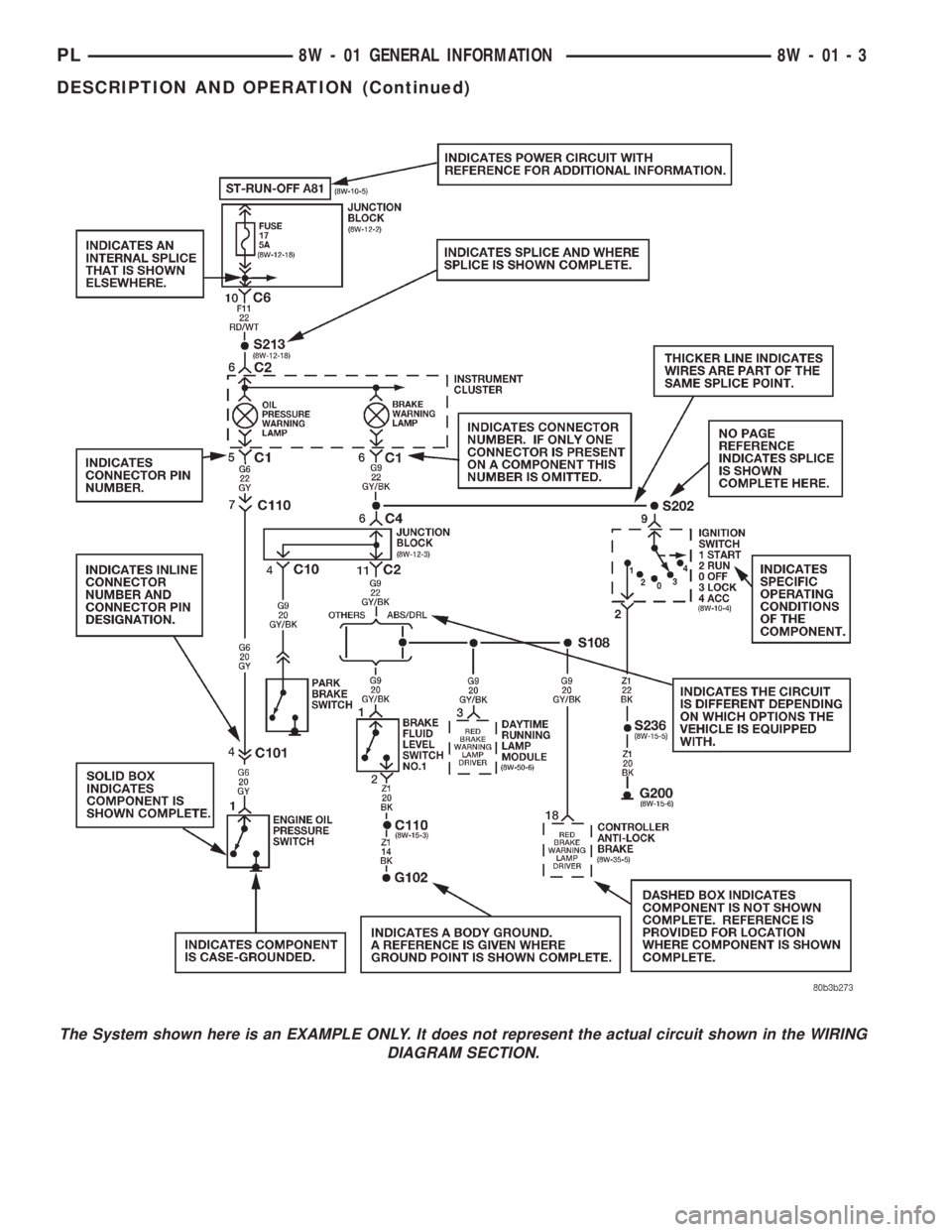
The System shown here is an EXAMPLE ONLY. It does not represent the actual circuit shown in the WIRING
DIAGRAM SECTION.
PL8W - 01 GENERAL INFORMATION 8W - 01 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 397 of 1285
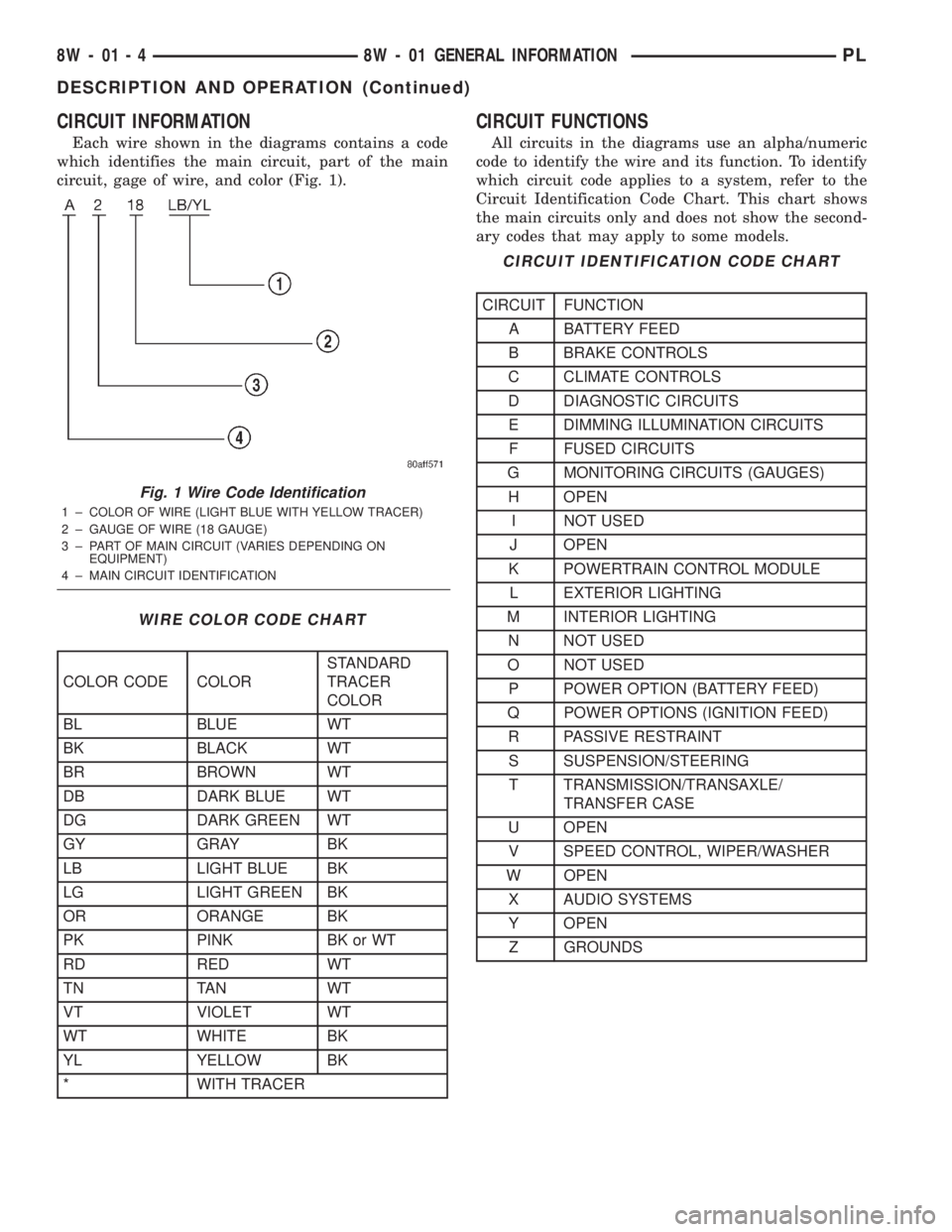
CIRCUIT INFORMATION
Each wire shown in the diagrams contains a code
which identifies the main circuit, part of the main
circuit, gage of wire, and color (Fig. 1).
CIRCUIT FUNCTIONS
All circuits in the diagrams use an alpha/numeric
code to identify the wire and its function. To identify
which circuit code applies to a system, refer to the
Circuit Identification Code Chart. This chart shows
the main circuits only and does not show the second-
ary codes that may apply to some models.
Fig. 1 Wire Code Identification
1 ± COLOR OF WIRE (LIGHT BLUE WITH YELLOW TRACER)
2 ± GAUGE OF WIRE (18 GAUGE)
3 ± PART OF MAIN CIRCUIT (VARIES DEPENDING ON
EQUIPMENT)
4 ± MAIN CIRCUIT IDENTIFICATION
WIRE COLOR CODE CHART
COLOR CODE COLORSTANDARD
TRACER
COLOR
BL BLUE WT
BK BLACK WT
BR BROWN WT
DB DARK BLUE WT
DG DARK GREEN WT
GY GRAY BK
LB LIGHT BLUE BK
LG LIGHT GREEN BK
OR ORANGE BK
PK PINK BK or WT
RD RED WT
TN TAN WT
VT VIOLET WT
WT WHITE BK
YL YELLOW BK
* WITH TRACER
CIRCUIT IDENTIFICATION CODE CHART
CIRCUIT FUNCTION
A BATTERY FEED
B BRAKE CONTROLS
C CLIMATE CONTROLS
D DIAGNOSTIC CIRCUITS
E DIMMING ILLUMINATION CIRCUITS
F FUSED CIRCUITS
G MONITORING CIRCUITS (GAUGES)
H OPEN
I NOT USED
J OPEN
K POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
L EXTERIOR LIGHTING
M INTERIOR LIGHTING
N NOT USED
O NOT USED
P POWER OPTION (BATTERY FEED)
Q POWER OPTIONS (IGNITION FEED)
R PASSIVE RESTRAINT
S SUSPENSION/STEERING
T TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
TRANSFER CASE
U OPEN
V SPEED CONTROL, WIPER/WASHER
W OPEN
X AUDIO SYSTEMS
Y OPEN
Z GROUNDS
8W - 01 - 4 8W - 01 GENERAL INFORMATIONPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 398 of 1285

SECTION IDENTIFICATION
The wiring diagrams are grouped into individual
sections. If a component is most likely found in a par-
ticular group, it will be shown complete (all wires,
connectors, and pins) within that group. For exam-
ple, the Auto Shutdown Relay is most likely to be
found in Group 30, so it is shown there complete. It
can, however, be shown partially in another group if
it contains some associated wiring.
SYMBOLS
International symbols are used throughout the wir-
ing diagrams. These symbols are consistent with
those being used around the world.
GROUP TOPIC
8W-01 thru
8W-09General Information and Diagram
Overview
8W-10 thru
8W-19Main Sources of Power and Vehicle
Grounding
8W-20 thru
8W-29Starting and Charging
8W-30 thru
8W-39Powertrain/Drivetrain Systems
8W-40 thru
8W-49Body Electrical items and A/C
8W-50 thru
8W-59Exterior Lighting, Wipers, and Trailer
To w
8W-60 thru
8W-69Power Accessories
8W-70 Splice Information
8W-80 Connector Pin Outs
8W-90 Connector Locations (including
grounds)
8W-95 Splice Locations
PL8W - 01 GENERAL INFORMATION 8W - 01 - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 399 of 1285
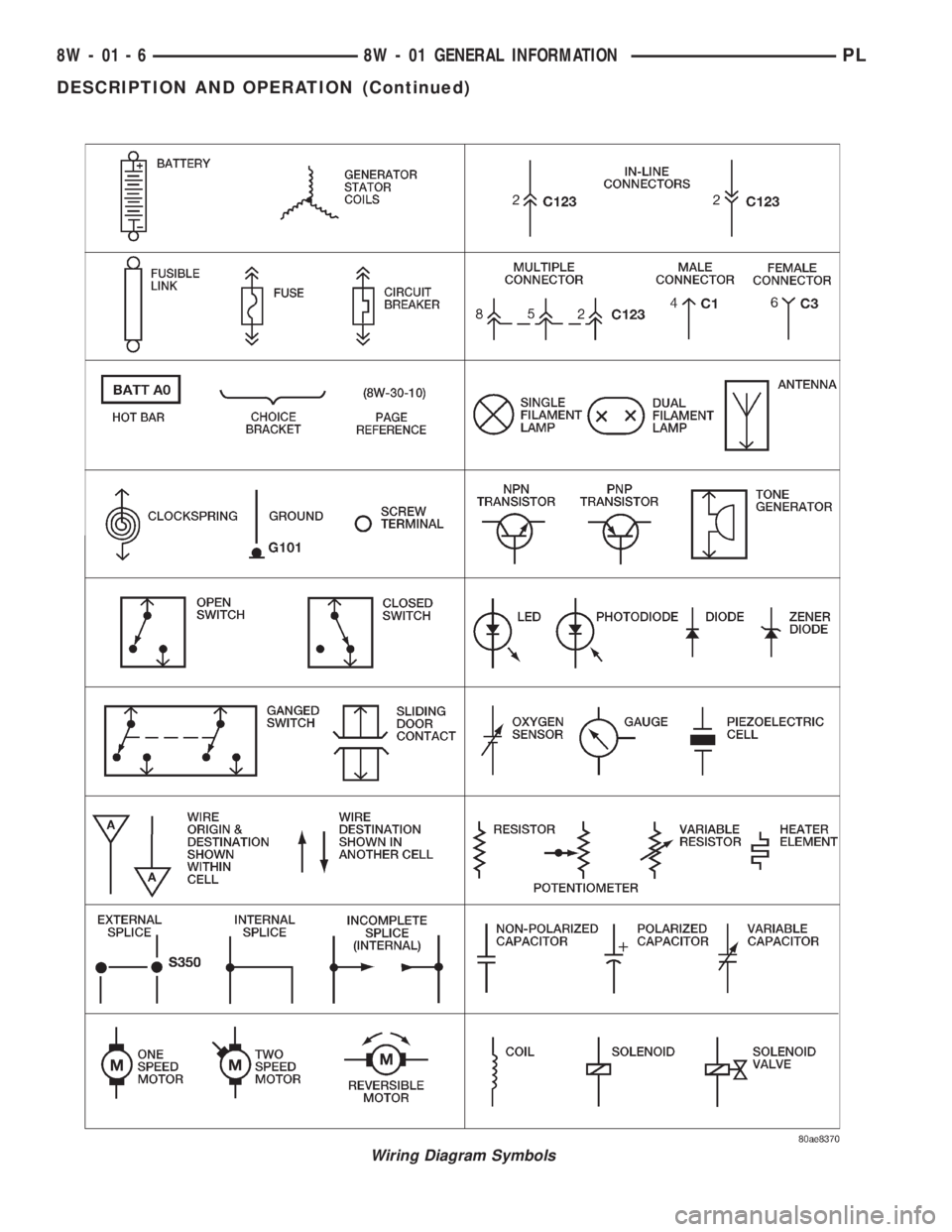
Wiring Diagram Symbols
8W - 01 - 6 8W - 01 GENERAL INFORMATIONPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 400 of 1285

TERMINOLOGY
This a list of terms with there definitions used in
the wiring diagrams.
Built-Up-Export....... Vehicles Built For Sale In
Markets Other Than North America
Except-Built-Up-Export . Vehicles Built For Sale In
North America
LHD ................Left Hand Drive Vehicles
RHD ...............Right Hand Drive Vehicles
ATX . . Automatic Transmission-Front Wheel Drive
MTX ....Manual Transmission-Front Wheel Drive
AT ....Automatic Transmission-Rear Wheel Drive
MT......Manual Transmission-Rear Wheel Drive
SOHC...........Single Over Head Cam Engine
DOHC............Dual Over Head Cam Engine
CONNECTOR INFORMATION
CAUTION: Not all connectors are serviced. Some
connectors are serviced only with a harness. A typ-
ical example might be the Supplemental Restraint
System connectors. Always check parts availability
before attempting a repair.
IDENTIFICATION
In-line connectors are identified by a number, as
follows:
²In-line connectors located on theengine com-
partment harnessareC100series numbers.
²Connectors located on theinstrument panel
harnessareC200series numbers.
²Connectors located on thebody harnessare
C300series numbers.
²Jumper harness connectorsareC400series
numbers.
²Grounds and ground connectorsare identi-
fied with aªGºand follow the same series number-
ing as the in-line connector.
Component connectors are identified by the compo-
nent name instead of a number. Multiple connectors
on a component use a C1, C2, etc. identifier.
LOCATIONS
Section 8W-90 contains connector/ground location
illustrations. The illustrations contain the connector
name (or number)/ground number and component
identification. Connector/ground location charts in
Section 8W-90 reference the illustration number for
components and connectors.
Section 8W-80 shows each connector and the cir-
cuits involved with that connector. The connectors
are identified using the name/number on the Dia-
gram pages.
SPLICE LOCATIONS
Splice Location charts in Section 8W-70 show the
entire splice, and provide references to other sections
the splice serves.
Section 8W-95 contains illustrations that show the
general location of the splices in each harness. The
illustrations show the splice by number, and provide
a written location.
NOTES, CAUTIONS, and WARNINGS
Throughout this group additional important infor-
mation is presented in three ways; Notes, Cautions,
and Warnings.
NOTESare used to help describe how switches or
components operate to complete a particular circuit.
They are also used to indicate different conditions
that may appear on the vehicle. For example, an
up-to and after condition.
CAUTIONSare used to indicate information that
could prevent making an error that may damage the
vehicle.
WARNINGSprovide information to prevent per-
sonal injury and vehicle damage. Below is a list of
general warnings that should be followed any time a
vehicle is being serviced.
WARNING: ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES FOR
EYE PROTECTION.
WARNING: USE SAFETY STANDS ANYTIME A PRO-
CEDURE REQUIRES BEING UNDER A VEHICLE.
WARNING: BE SURE THAT THE IGNITION SWITCH
ALWAYS IS IN THE OFF POSITION, UNLESS THE
PROCEDURE REQUIRES IT TO BE ON.
WARNING: SET THE PARKING BRAKE WHEN
WORKING ON ANY VEHICLE. AN AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION SHOULD BE IN PARK. A MANUAL
TRANSMISSION SHOULD BE IN NEUTRAL.
WARNING: OPERATE THE ENGINE ONLY IN A
WELL-VENTILATED AREA.
WARNING: KEEP AWAY FROM MOVING PARTS
WHEN THE ENGINE IS RUNNING, ESPECIALLY THE
FAN AND BELTS.
WARNING: TO PREVENT SERIOUS BURNS, AVOID
CONTACT WITH HOT PARTS SUCH AS THE RADIA-
TOR, EXHAUST MANIFOLD(S), TAIL PIPE, CATA-
LYTIC CONVERTER, AND MUFFLER.
PL8W - 01 GENERAL INFORMATION 8W - 01 - 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 402 of 1285
²Connectors are fully seated
²Spread terminals, or terminal push out
²Terminals in the wiring assembly are fully
seated into the connector/component and locked in
position
²Dirt or corrosion on the terminals. Any amount
of corrosion or dirt could cause an intermittent prob-
lem
²Damaged connector/component casing exposing
the item to dirt and moisture
²Wire insulation that has rubbed through causing
a short to ground
²Some or all of the wiring strands broken inside
of the insulation covering
²Wiring broken inside of the insulation.
TROUBLESHOOTING TESTS
Before beginning any tests on a vehicles electrical
system use the Wiring Diagrams and study the cir-
cuit. Also refer to the Troubleshooting Wiring Prob-
lems in this section.
TESTING FOR VOLTAGE POTENTIAL
(1) Connect the ground lead of a voltmeter to a
known good ground (Fig. 4).
(2) Connect the other lead of the voltmeter to the
selected test point. The vehicle ignition may need to
be turned ON to check voltage. Refer to the appropri-
ate test procedure.
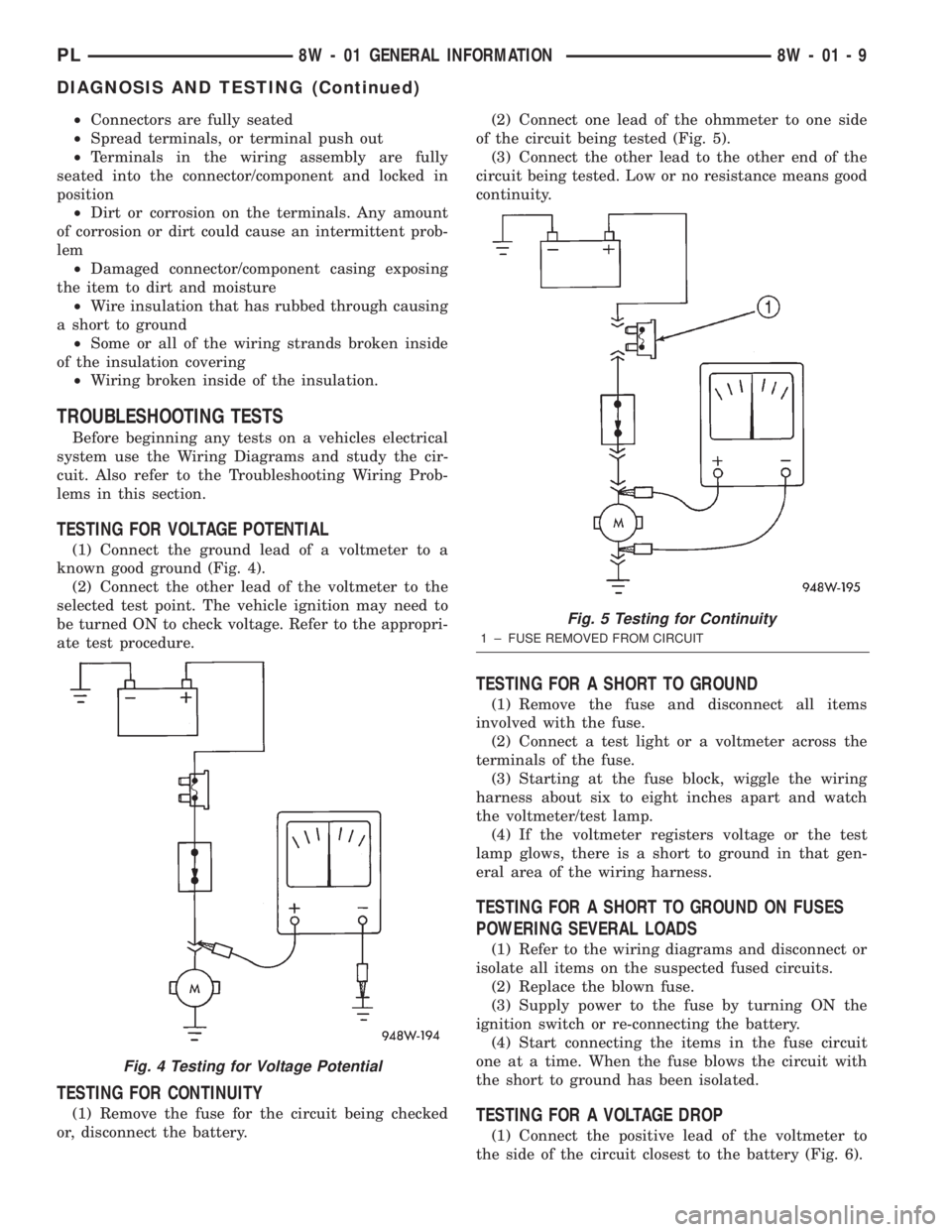
TESTING FOR CONTINUITY
(1) Remove the fuse for the circuit being checked
or, disconnect the battery.(2) Connect one lead of the ohmmeter to one side
of the circuit being tested (Fig. 5).
(3) Connect the other lead to the other end of the
circuit being tested. Low or no resistance means good
continuity.
TESTING FOR A SHORT TO GROUND
(1) Remove the fuse and disconnect all items
involved with the fuse.
(2) Connect a test light or a voltmeter across the
terminals of the fuse.
(3) Starting at the fuse block, wiggle the wiring
harness about six to eight inches apart and watch
the voltmeter/test lamp.
(4) If the voltmeter registers voltage or the test
lamp glows, there is a short to ground in that gen-
eral area of the wiring harness.
TESTING FOR A SHORT TO GROUND ON FUSES
POWERING SEVERAL LOADS
(1) Refer to the wiring diagrams and disconnect or
isolate all items on the suspected fused circuits.
(2) Replace the blown fuse.
(3) Supply power to the fuse by turning ON the
ignition switch or re-connecting the battery.
(4) Start connecting the items in the fuse circuit
one at a time. When the fuse blows the circuit with
the short to ground has been isolated.
TESTING FOR A VOLTAGE DROP
(1) Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to
the side of the circuit closest to the battery (Fig. 6).
Fig. 4 Testing for Voltage Potential
Fig. 5 Testing for Continuity
1 ± FUSE REMOVED FROM CIRCUIT
PL8W - 01 GENERAL INFORMATION 8W - 01 - 9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 403 of 1285

(2) Connect the other lead of the voltmeter to the
other side of the switch or component.
(3) Operate the item.
(4) The voltmeter will show the difference in volt-
age between the two points.
TROUBLESHOOTING WIRING PROBLEMS
When troubleshooting wiring problems there are
six steps which can aid in the procedure. The steps
are listed and explained below. Always check for non-
factory items added to the vehicle before doing any
diagnosis. If the vehicle is equipped with these items,
disconnect them to verify these add-on items are not
the cause of the problem.
(1) Verify the problem.
(2) Verify any related symptoms. Do this by per-
forming operational checks on components that are
in the same circuit. Refer to the wiring diagrams.
(3) Analyze the symptoms. Use the wiring dia-
grams to determine what the circuit is doing, where
the problem most likely is occurring and where the
diagnosis will continue.
(4) Isolate the problem area.
(5) Repair the problem.
(6) Verify proper operation. For this step check for
proper operation of all items on the repaired circuit.
Refer to the wiring diagrams.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
WIRING REPAIR
When replacing or repairing a wire, it is important
that the correct gage be used as shown in the wiring
diagrams. The wires must also be held securely in
place to prevent damage to the insulation.
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove 1 inch of insulation from each end of
the wire.
(3) Place a piece of heat shrink tubing over one
side of the wire. Make sure the tubing will be long
enough to cover and seal the entire repair area.
(4) Spread the strands of the wire apart on each
part of the exposed wire (example 1) (Fig. 7).
(5) Push the two ends of wire together until the
strands of wire are close to the insulation (example
2) (Fig. 7).
(6) Twist the wires together (example 3) (Fig. 7).
(7) Solder the connection together using rosin core
type solder only.Do not use acid core solder.
(8) Center the heat shrink tubing over the joint,
and heat using a heat gun. Heat the joint until the
tubing is tightly sealed and sealant comes out of both
ends of the tubing.
(9) Secure the wire to the existing ones to prevent
chafing or damage to the insulation.
(10) Connect battery and test all affected systems.
Fig. 6 Testing for Voltage Drop
Fig. 7 Wire Repair
1 ± EXAMPLE 1
2 ± EXAMPLE 2
3 ± EXAMPLE 3
8W - 01 - 10 8W - 01 GENERAL INFORMATIONPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)