radiator DODGE NEON 2000 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 985 of 1285

FLUSHING COOLERS AND TUBES
When a transaxle failure has contaminated the
fluid, the transaxle oil cooler(s) must be flushed (both
radiator and remote). The cooler bypass valve in the
transaxle must be replaced also. The torque con-
verter must also be replaced with an exchange unit.
This will ensure that metal particles or sludged oil
are not later transferred back into the reconditioned
(or replaced) transaxle.
The recommended procedure for flushing the cool-
ers and tubes is to use Tool 6906A Cooler Flusher.
WARNING: WEAR PROTECTIVE EYEWEAR THAT
MEETS THE REQUIREMENTS OF OSHA AND ANSI
Z87.1±1968. WEAR STANDARD INDUSTRIAL RUB-
BER GLOVES.
KEEP LIT CIGARETTES, SPARKS, FLAMES, AND
OTHER IGNITION SOURCES AWAY FROM THE
AREA TO PREVENT THE IGNITION OF COMBUSTI-
BLE LIQUIDS AND GASES. KEEP A CLASS (B) FIRE
EXTINGUISHER IN THE AREA WHERE THE
FLUSHER WILL BE USED.
KEEP THE AREA WELL VENTILATED.
DO NOT LET FLUSHING SOLVENT COME IN CON-
TACT WITH YOUR EYES OR SKIN: IF EYE CONTAM-
INATION OCCURS, FLUSH EYES WITH WATER FOR
15 TO 20 SECONDS. REMOVE CONTAMINATED
CLOTHING AND WASH AFFECTED SKIN WITH
SOAP AND WATER. SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION.
COOLER FLUSH USING TOOL 6906A
(1) Remove cover plate filler plug on Tool 6906A.
Fill reservoir 1/2 to 3/4 full of fresh flushing solution.
Flushing solvents are petroleum based solutions gen-
erally used to clean automatic transmission compo-
nents.DO NOTuse solvents containing acids, water,
gasoline, or any other corrosive liquids.
(2) Reinstall filler plug on Tool 6906A.
(3) Verify pump power switch is turned OFF. Con-
nect red alligator clip to positive (+) battery post.
Connect black (-) alligator clip to a good ground.
(4) Disconnect the cooler lines at the transmission.
NOTE: When flushing transmission cooler and
lines, ALWAYS reverse flush.
(5) Connect the BLUE pressure line to the OUT-
LET (From) cooler line.
(6) Connect the CLEAR return line to the INLET
(To) cooler line
(7) Turn pump ON for two to three minutes to
flush cooler(s) and lines. Monitor pressure readingsand clear return lines. Pressure readings should sta-
bilize below 20 psi. for vehicles equipped with a sin-
gle cooler and 30 psi. for vehicles equipped with dual
coolers. If flow is intermittent or exceeds these pres-
sures, replace cooler.
(8) Turn pump OFF.
(9) Disconnect CLEAR suction line from reservoir
at cover plate. Disconnect CLEAR return line at
cover plate, and place it in a drain pan.
(10) Turn pump ON for 30 seconds to purge flush-
ing solution from cooler and lines. Turn pump OFF.
(11) Place CLEAR suction line into a one quart
container of MopartATF+4 (Automatic Transmission
Fluid) Type 9602.
(12) Turn pump ON until all transmission fluid is
removed from the one quart container and lines. This
purges any residual cleaning solvent from the trans-
mission cooler and lines. Turn pump OFF.
(13) Disconnect alligator clips from battery. Recon-
nect flusher lines to cover plate, and remove flushing
adapters from cooler lines.
OIL PUMP VOLUME CHECK
After the new or repaired transmission has been
installed, fill to the proper level with MopartATF+4
(Automatic Transmission Fluid) Type 9602. The vol-
ume should be checked using the following proce-
dure:
(1) Disconnect theFrom coolerline at the trans-
mission and place a collecting container under the
disconnected line.
CAUTION: With the fluid set at the proper level,
fluid collection should not exceed (1) quart or inter-
nal damage to the transmission may occur.
(2) Run the engineat curb idle speed, with the
shift selector in neutral.
(3) If fluid flow is intermittent or it takes more
than 20 seconds to collect one quart of ATF, discon-
nect theTo Coolerline at the transaxle.
(4) Refill the transaxle to proper level and recheck
pump volume.
(5) If flow is found to be within acceptable limits,
replace the cooler. Then fill transmission to the
proper level, using MopartATF+4 (Automatic Trans-
mission Fluid) Type 9602.
(6) If fluid flow is still found to be inadequate,
check the line pressure using the Transaxle Hydrau-
lic Pressure Test procedure.
21 - 72 TRANSAXLEPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1098 of 1285
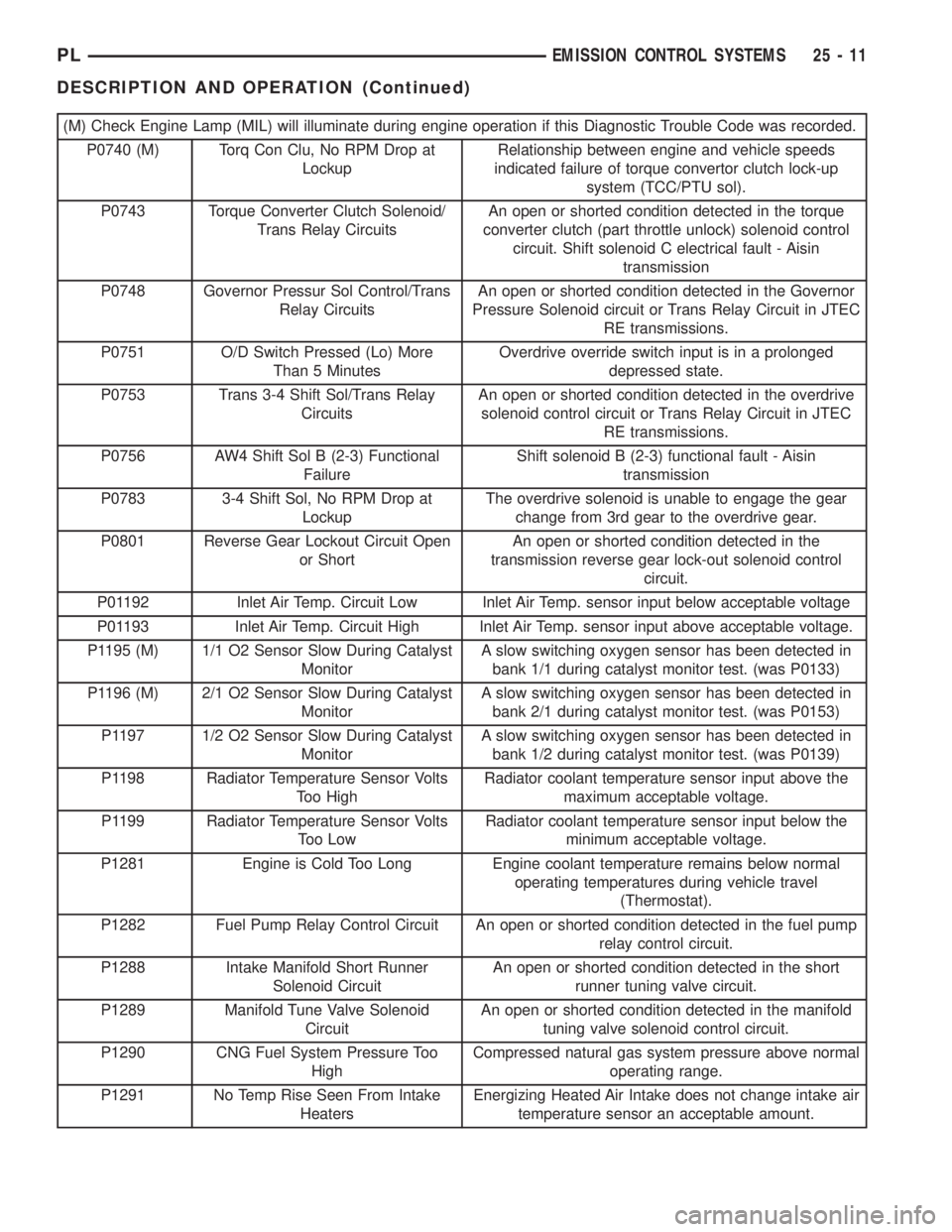
(M) Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
P0740 (M) Torq Con Clu, No RPM Drop at
LockupRelationship between engine and vehicle speeds
indicated failure of torque convertor clutch lock-up
system (TCC/PTU sol).
P0743 Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid/
Trans Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the torque
converter clutch (part throttle unlock) solenoid control
circuit. Shift solenoid C electrical fault - Aisin
transmission
P0748 Governor Pressur Sol Control/Trans
Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the Governor
Pressure Solenoid circuit or Trans Relay Circuit in JTEC
RE transmissions.
P0751 O/D Switch Pressed (Lo) More
Than 5 MinutesOverdrive override switch input is in a prolonged
depressed state.
P0753 Trans 3-4 Shift Sol/Trans Relay
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the overdrive
solenoid control circuit or Trans Relay Circuit in JTEC
RE transmissions.
P0756 AW4 Shift Sol B (2-3) Functional
FailureShift solenoid B (2-3) functional fault - Aisin
transmission
P0783 3-4 Shift Sol, No RPM Drop at
LockupThe overdrive solenoid is unable to engage the gear
change from 3rd gear to the overdrive gear.
P0801 Reverse Gear Lockout Circuit Open
or ShortAn open or shorted condition detected in the
transmission reverse gear lock-out solenoid control
circuit.
P01192 Inlet Air Temp. Circuit Low Inlet Air Temp. sensor input below acceptable voltage
P01193 Inlet Air Temp. Circuit High Inlet Air Temp. sensor input above acceptable voltage.
P1195 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in
bank 1/1 during catalyst monitor test. (was P0133)
P1196 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in
bank 2/1 during catalyst monitor test. (was P0153)
P1197 1/2 O2 Sensor Slow During Catalyst
MonitorA slow switching oxygen sensor has been detected in
bank 1/2 during catalyst monitor test. (was P0139)
P1198 Radiator Temperature Sensor Volts
Too HighRadiator coolant temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P1199 Radiator Temperature Sensor Volts
Too LowRadiator coolant temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P1281 Engine is Cold Too Long Engine coolant temperature remains below normal
operating temperatures during vehicle travel
(Thermostat).
P1282 Fuel Pump Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the fuel pump
relay control circuit.
P1288 Intake Manifold Short Runner
Solenoid CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the short
runner tuning valve circuit.
P1289 Manifold Tune Valve Solenoid
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the manifold
tuning valve solenoid control circuit.
P1290 CNG Fuel System Pressure Too
HighCompressed natural gas system pressure above normal
operating range.
P1291 No Temp Rise Seen From Intake
HeatersEnergizing Heated Air Intake does not change intake air
temperature sensor an acceptable amount.
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1100 of 1285
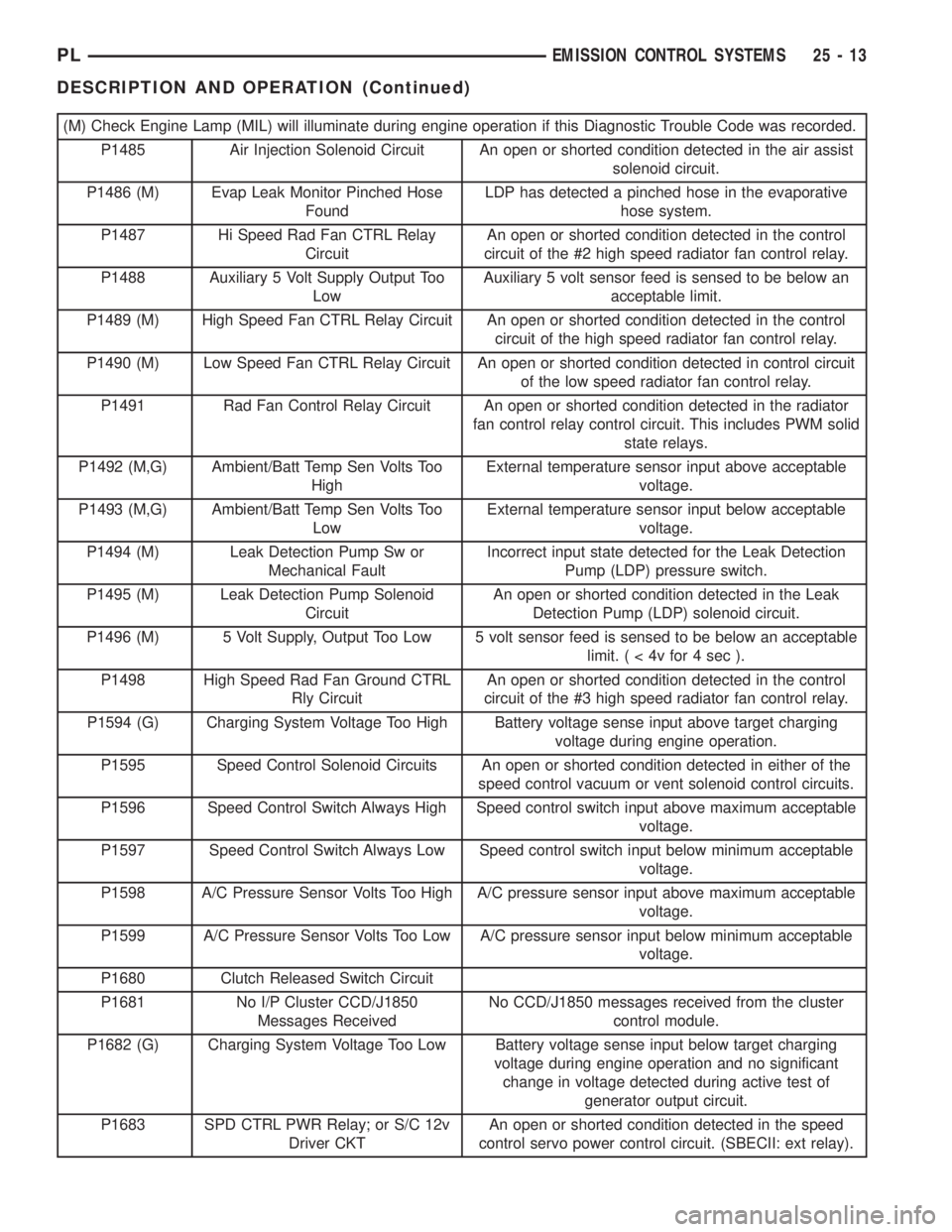
(M) Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
P1485 Air Injection Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the air assist
solenoid circuit.
P1486 (M) Evap Leak Monitor Pinched Hose
FoundLDP has detected a pinched hose in the evaporative
hose system.
P1487 Hi Speed Rad Fan CTRL Relay
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the control
circuit of the #2 high speed radiator fan control relay.
P1488 Auxiliary 5 Volt Supply Output Too
LowAuxiliary 5 volt sensor feed is sensed to be below an
acceptable limit.
P1489 (M) High Speed Fan CTRL Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the control
circuit of the high speed radiator fan control relay.
P1490 (M) Low Speed Fan CTRL Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in control circuit
of the low speed radiator fan control relay.
P1491 Rad Fan Control Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the radiator
fan control relay control circuit. This includes PWM solid
state relays.
P1492 (M,G) Ambient/Batt Temp Sen Volts Too
HighExternal temperature sensor input above acceptable
voltage.
P1493 (M,G) Ambient/Batt Temp Sen Volts Too
LowExternal temperature sensor input below acceptable
voltage.
P1494 (M) Leak Detection Pump Sw or
Mechanical FaultIncorrect input state detected for the Leak Detection
Pump (LDP) pressure switch.
P1495 (M) Leak Detection Pump Solenoid
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the Leak
Detection Pump (LDP) solenoid circuit.
P1496 (M) 5 Volt Supply, Output Too Low 5 volt sensor feed is sensed to be below an acceptable
limit.(<4vfor4sec).
P1498 High Speed Rad Fan Ground CTRL
Rly CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the control
circuit of the #3 high speed radiator fan control relay.
P1594 (G) Charging System Voltage Too High Battery voltage sense input above target charging
voltage during engine operation.
P1595 Speed Control Solenoid Circuits An open or shorted condition detected in either of the
speed control vacuum or vent solenoid control circuits.
P1596 Speed Control Switch Always High Speed control switch input above maximum acceptable
voltage.
P1597 Speed Control Switch Always Low Speed control switch input below minimum acceptable
voltage.
P1598 A/C Pressure Sensor Volts Too High A/C pressure sensor input above maximum acceptable
voltage.
P1599 A/C Pressure Sensor Volts Too Low A/C pressure sensor input below minimum acceptable
voltage.
P1680 Clutch Released Switch Circuit
P1681 No I/P Cluster CCD/J1850
Messages ReceivedNo CCD/J1850 messages received from the cluster
control module.
P1682 (G) Charging System Voltage Too Low Battery voltage sense input below target charging
voltage during engine operation and no significant
change in voltage detected during active test of
generator output circuit.
P1683 SPD CTRL PWR Relay; or S/C 12v
Driver CKTAn open or shorted condition detected in the speed
control servo power control circuit. (SBECII: ext relay).
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 13
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1105 of 1285

Immediately after a cold start, between predeter-
mined temperature thresholds limits, the three port
solenoid is briefly energized. This initializes the
pump by drawing air into the pump cavity and also
closes the vent seal. During non test conditions the
vent seal is held open by the pump diaphragm
assembly which pushes it open at the full travel posi-
tion. The vent seal will remain closed while the
pump is cycling due to the reed switch triggering of
the three port solenoid that prevents the diaphragm
assembly from reaching full travel. After the brief
initialization period, the solenoid is de-energized
allowing atmospheric pressure to enter the pump
cavity, thus permitting the spring to drive the dia-
phragm which forces air out of the pump cavity and
into the vent system. When the solenoid is energized
and de energized, the cycle is repeated creating flow
in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump is con-
trolled in 2 modes:
Pump Mode:The pump is cycled at a fixed rate to
achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten the
overall test length.
Test Mode:The solenoid is energized with a fixed
duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur when
the diaphragm reaches the Switch closure point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5º H20.
The cycle rate of pump strokes is quite rapid as the
system begins to pump up to this pressure. As the
pressure increases, the cycle rate starts to drop off. If
there is no leak in the system, the pump would even-
tually stop pumping at the equalized pressure. If
there is a leak, it will continue to pump at a rate rep-
resentative of the flow characteristic of the size of the
leak. From this information we can determine if the
leak is larger than the required detection limit (cur-
rently set at.040º orifice by CARB). If a leak is
revealed during the leak test portion of the test, the
test is terminated at the end of the test mode and no
further system checks will be performed.
After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained by turning on the
LDP's solenoid until the purge system is activated.
Purge activation in effect creates a leak. The cycle
rate is again interrogated and when it increases due
to the flow through the purge system, the leak check
portion of the diagnostic is complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
Evaporative system functionality will be verified by
using the stricter evap purge flow monitor. At an
appropriate warm idle the LDP will be energized to
seal the canister vent. The purge flow will be clocked
up from some small value in an attempt to see a
shift in the 02 control system. If fuel vapor, indicatedby a shift in the 02 control, is present the test is
passed. If not, it is assumed that the purge system is
not functioning in some respect. The LDP is again
turned off and the test is ended.
Enabling Conditions for Systems with LDP
²Ambient Air Temperature
²Barometric Pressure
²Fuel level
²Engine Temperature
²No stalling
²Battery voltage
NON-LDP VEHICLESÐOn a vehicle without an
EVAP leak detection pump system, changes in short
term memory and movement in target IAC at idle or
idle speed change, are used to monitor the system.
There are two stages for this test.
Stage OneÐStage one is a non-intrusive test.
The PCM compares adaptive memory values between
purge and purge-free cells. The PCM uses these val-
ues to determine the amount of fuel vapors entering
the system. If the difference between the cells
exceeds a predetermined value, the test passes. If
not, then the monitor advances to state two.
Stage TwoÐOnce the enabling conditions are
met, the PCM de-energizes the Duty Cycle Purge
(DCP) solenoid. The PCM then waits until engine
RPM, Short Term Compensation and Idle Air Control
have all stabilized. Once stable, the PCM increments
the DCP solenoid cycle rate approximately 6% every
8 engine revolutions. If during the test any one of
three conditions occur before the DCP cycle reaches
100%, the EVAP system is considered to be opera-
tional and the test passes. These conditions are as
follows:
²RPM rises by a predetermined amount
²Short Term drops by a predetermined amount
²Idle Air Control closes by a predetermined
amount
When none of the previous conditions occur, the
test fails and the PCM increments a counter by one.
When the PCM runs the test three times during a
trip, and the counter has been incremented to three,
the monitor fails and a Freeze Frame is stored.
Enabling Conditions (Stage Two)ÐThe follow-
ing conditions must be met to enable the EVAP Mon-
itor (without LDP)
²Ambient Air Temperature
²Barometric Pressure
²Fuel level
²Engine Temperature
²Engine run time
²RPM stable
²MAP
²Generator, radiator fans, A/C clutch
Pending Conditions-With or Without LDPÐ
The EVAP Monitor is suspended and does not run,
25 - 18 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1107 of 1285

NOTE: Comprehensive component monitors are
continuous. Therefore, enabling conditions do not
apply.
Input RationalityÐWhile input signals to the
PCM are constantly being monitored for electrical
opens and shorts, they are also tested for rationality.
This means that the input signal is compared against
other inputs and information to see if it makes sense
under the current conditions.
PCM sensor inputs that are checked for rationality
include:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Oxygen Sensor (O2S)
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Ambient/Battery Temperature Sensors
²Power Steering Switch
²Oxygen Sensor Heater
²Engine Controller
²Brake Switch
²Leak Detection Pump Switch
²P/N Switch
²Trans Controls
Output FunctionalityÐPCM outputs are tested
for functionality in addition to testing for opens and
shorts. When the PCM provides a voltage to an out-
put component, it can verify that the command was
carried out by monitoring specific input signals for
expected changes. For example, when the PCM com-
mands the Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor to a specific
position under certain operating conditions, it expects
to see a specific (target) idle speed (RPM). If it does
not, it stores a DTC.
PCM outputs monitored for functionality include:
²Fuel Injectors
²Ignition Coils
²Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
²Idle Air Control
²Purge Solenoid
²EGR Solenoid
²LDP Solenoid
²Radiator Fan Control
²Trans Controls
OXYGEN SENSOR (O2S) MONITOR
DESCRIPTIONÐEffective control of exhaust
emissions is achieved by an oxygen feedback system.
The most important element of the feedback system
is the O2S. The O2S is located in the exhaust path.
Once it reaches operating temperature 300É to 350ÉC
(572É to 662ÉF), the sensor generates a voltage that
is inversely proportional to the amount of oxygen inthe exhaust. When there is a large amount of oxygen
in the exhaust caused by a lean condition, the sensor
produces a low voltage, below 450 mV. When the oxy-
gen content is lower, caused by a rich condition, the
sensor produces a higher voltage, above 450mV.
The information obtained by the sensor is used to
calculate the fuel injector pulse width. This main-
tains a 14.7 to 1 air fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture
ratio, the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons
(HC), carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrous oxide (NOx)
from the exhaust.
The O2S is also the main sensing element for the
EGR, Catalyst and Fuel Monitors.
The O2S may fail in any or all of the following
manners:
²Slow response rate (Big Slope)
²Reduced output voltage (Half Cycle)
²Heater Performance
Slow Response Rate (Big Slope)ÐResponse
rate is the time required for the sensor to switch
from lean to rich signal output once it is exposed to a
richer than optimum A/F mixture or vice versa. As
the PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio, the sensor must
be able to rapidly detect the change. As the sensor
ages, it could take longer to detect the changes in the
oxygen content of the exhaust gas. The rate of
change that an oxygen sensor experiences is called
'Big Slope'. The PCM checks the oxygen sensor volt-
age in increments of a few milliseconds.
Reduced Output Voltage (Half Cycle)ÐThe
output voltage of the O2S ranges from 0 to 1 volt. A
good sensor can easily generate any output voltage in
this range as it is exposed to different concentrations
of oxygen. To detect a shift in the A/F mixture (lean
or rich), the output voltage has to change beyond a
threshold value. A malfunctioning sensor could have
difficulty changing beyond the threshold value. Each
time the voltage signal surpasses the threshold, a
counter is incremented by one. This is called the Half
Cycle Counter.
Heater PerformanceÐThe heater is tested by a
separate monitor. Refer to the Oxygen Sensor Heater
Monitor.
OPERATIONÐAs the Oxygen Sensor signal
switches, the PCM monitors the half cycle and big
slope signals from the oxygen sensor. If during the
test neither counter reaches a predetermined value, a
malfunction is entered and a Freeze Frame is stored.
Only one counter reaching its predetermined value is
needed for the monitor to pass.
The Oxygen Sensor Monitor is a two trip monitor
that is tested only once per trip. When the Oxygen
Sensor fails the test in two consecutive trips, the
MIL is illuminated and a DTC is set. The MIL is
extinguished when the Oxygen Sensor monitor
passes in three consecutive trips. The DTC is erased
25 - 20 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1140 of 1285

(12) Position patch in cutout against support
squares and adjust patch until the gap is equal along
all sides (Fig. 11).
(13) Drill 3 mm (0.125 in.) holes in the support
squares through the pre-drilled holes in the patch.
(14) Apply a coat of epoxy to the exposed ends of
the support squares (Fig. 12).
(15) Install screws to hold the patch to support
squares (Fig. 13). Tighten screws until patch surface
is flush with panel surface.
(16) Allow epoxy to cure, and remove all screws.
(17) Using a 125 mm (5 in.) 24 grit disc grinder,
grind a 50 mm (2 in.) to 75 mm (3 in.) wide and 2
mm (0.080 in.) deep path across the gaps around the
patch (Fig. 14). With compressed air, blow dust from
around patch.
(18) Apply adhesive backed nylon mesh (dry wall
tape) over gaps around patch (Fig. 15).
(19) Mix enough epoxy to cover the entire patch
area.
(20) Apply epoxy over the mesh around patch, and
smooth epoxy with a wide spreader to reduce finish
grinding. Use two to three layers of mesh and epoxy
to create a stronger repair (Fig. 16).
PATCHED PANEL SURFACING
After patch panel is installed, the patch area can
be finished using the same methods as finishing
other types of body panels. If mesh material is
exposed in the patched area, grind surface down, and
apply a coat of high quality rigid plastic body filler.
Prime, block sand, and paint as required.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
GRILLE
REMOVAL
(1) Release hood latch, open and support hood on
prop rod.
(2) Remove screws attaching grille to parking
lamps (Fig. 17).
(3) Remove screw attaching grille to radiator clo-
sure panel.
(4) Remove grille from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place grille into position on vehicle.
Fig. 10 Secure Support Squares To Body Panel
1 ± SUPPORT SQUARES
2 ± SCREWS
3 ± DAMAGED BODY PANEL
Fig. 11 Position Patch In Cutout And Align
1 ± CUTOUT
2 ± SUPPORT SQUARES
Fig. 12 Apply Epoxy To Support Squares
1 ± APPLICATOR
2 ± SUPPORT SQUARES
3 ± EPOXY
PLBODY 23 - 23
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1141 of 1285
(2) Install screw attaching grille to radiator clo-
sure panel.
(3) Install screws attaching grille to parking
lamps.
HOOD LATCH
REMOVAL
(1) Release hood latch and open hood.
(2) Support hood on prop rod.
(3) Remove grille.
(4) Remove screws attaching hood latch to radiator
closure panel (Fig. 18).
(5) Remove hood latch from closure panel.
(6) Disengage remote release cable from latch.
INSTALLATION
(1) Engage remote release cable into latch.
(2) Place hood latch onto radiator closure panel.
(3) Install bolts attaching latch to closure panel.
(4) Install grille.
(5) Close hood and verify alignment of hood and
that latch is securely engaged.
HOOD LATCH STRIKER
REMOVAL
(1) Release hood latch and open hood.
(2) Remove bolts attaching striker to inside of
hood.
Fig. 13 Install Screws
1 ± PATCH
2 ± GAP
Fig. 14 Grind Surface
1 ± PATCH
2 ± GAP
3 ± DISC GRINDER
Fig. 15 Cover Gaps With Mesh
1 ± GROUND DOWN AREA
2 ± PATCH
3 ± MESH
Fig. 16 Cover Mesh With Epoxy
1 ± EPOXY
2 ± MESH
3 ± PATCH
4 ± SPREADER
23 - 24 BODYPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1144 of 1285
COWL COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Release hood latch and open hood.
(2) Remove windshield wiper arms, refer to Group
8K, Windshield Wiper and Washer Systems for
proper procedures.
(3) Remove the five screws holding cowl cover to
cowl at base of windshield opening (Fig. 23).(4) Remove hood to cowl seal, at the leading edge
of cowl cover. Pull the seal towards the front of the
vehicle.
(5) Separate the cowl cover from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place cowl panel in place on vehicle.
Fig. 20 Hood
1 ± FENDER TO HOOD HINGE SEAL
2 ± HOOD TO RADIATOR WEATHERSTRIP
3 ± FENDER TO HOOD SEAL4 ± COWL SIDE TO COWL TOP
5 ± COWL PLENUM TO HOOD WEATHERSTRIP
Fig. 21
1 ± HOOD
2 ± HOOD SILENCERFig. 22 Hood Hinge
1 ± HOOD HINGE
2 ± HOOD
3 ± HOOD HINGE
PLBODY 23 - 27
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1199 of 1285
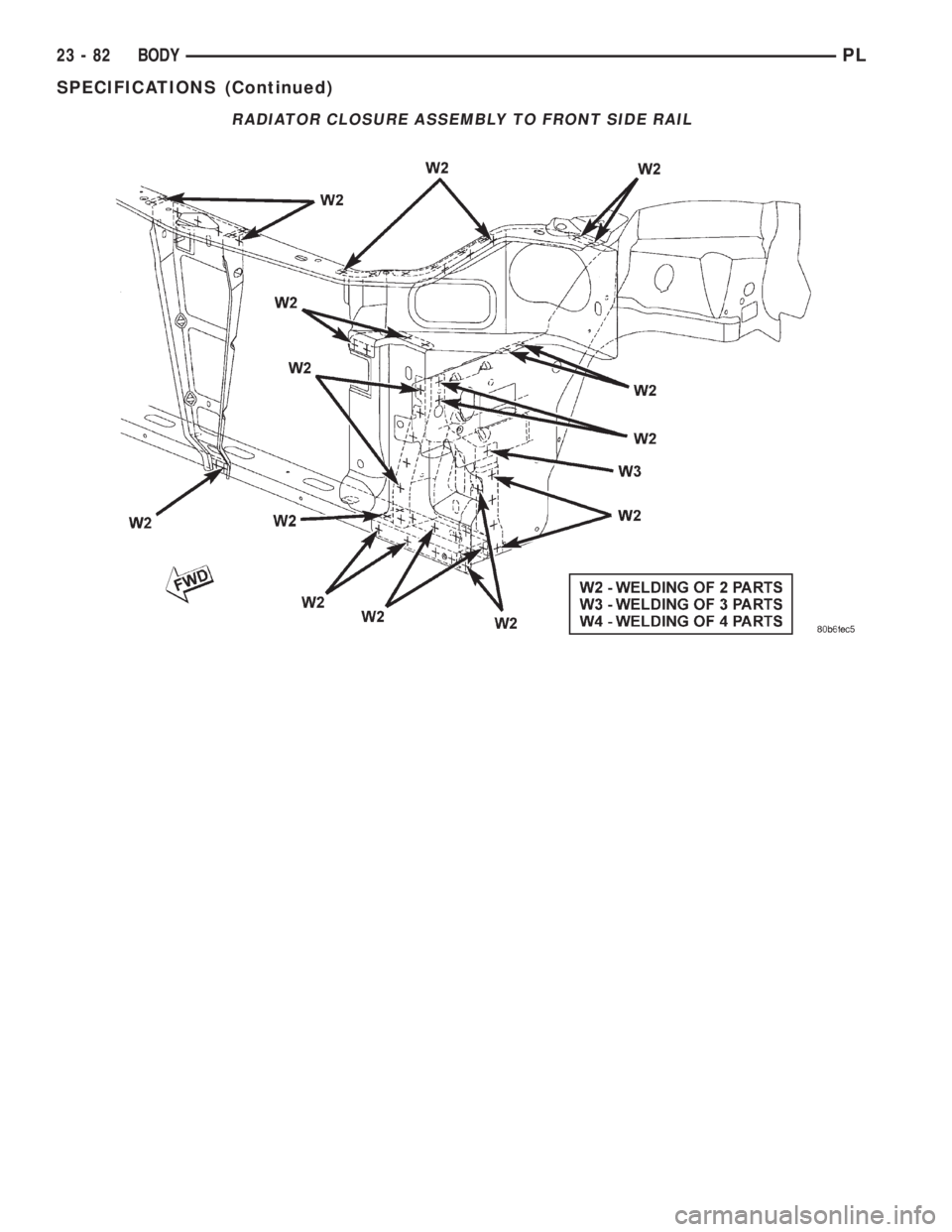
RADIATOR CLOSURE ASSEMBLY TO FRONT SIDE RAIL
23 - 82 BODYPL
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 1244 of 1285

WARNING: PROTECT SKIN AND EYES FROM CON-
TACTING CO2 PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
(7) If suction side low pressure is within specified
range, freeze the expansion valve control head (Fig.
13) for 30 seconds. Use a super cold substance (liquid
CO2).Do not spray refrigerant on the expansion
valve for this test.Suction side low pressure should
drop to 34.5 kPa (5 psi) If not, replace expansion
valve.(8) Allow expansion valve to thaw. The low pres-
sure gauge reading should stabilize at 103 to 241
kPa (15 to 35 psi). If not, replace expansion valve.
(9) When expansion valve test is complete, test
A/C overall performance. Refer to the Heater and A/C
Performance Test in this section. Remove all test
equipment before returning vehicle to use.
HEATER PERFORMANCE TEST
PRE-DIAGNOSTIC PREPARATIONS
Review Safety Precautions and Warnings in this
group before performing the following procedures.
Check the coolant level, drive belt tension, vacuum
line connections, radiator air flow and fan operation.
Start engine and allow to warm up to normal tem-
perature.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE RADIATOR CAP
WHEN ENGINE IS HOT, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
If vehicle has been run recently, wait 15 minutes
before removing cap. Place a rag over the cap and
turn it to the first safety stop. Allow pressure to
escape through the overflow tube. When the system
stabilizes, remove the cap completely.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT: TEST AND ACTION
Engine coolant is provided to the heater system by
two 16 mm (5/8 inch inside diameter) heater hoses.
With engine idling at normal running temperature,
set the control to maximum heat, floor, and high
blower setting. Using a test thermometer, check the
air temperature coming from the floor outlets, refer
to Temperature Reference chart.
If the floor outlet air temperature is insufficient,
refer to Group 7, Cooling Systems for specifications.
Both heater hoses should be HOT to the touch (cool-
ant return hose should be slightly cooler than the
supply hose). If coolant return hose is much cooler
than the supply hose, locate and repair engine cool-
ant flow obstruction in heater system.
Fig. 12 Evaporator Probe Harness Connector
1 ± PIN #3
2 ± PIN #2
3 ± PIN #1
Fig. 13 Expansion Valve & Low Pressure Cut-Off
Switch - Typical
1 ± EXPANSION VALVE
2 ± LOW PRESSURE CUT OFF SWITCH
3 ± SUCTION LINE
4 ± CONTROL HEAD
TEMPERATURE REFERENCE CHART
Ambient Temp. Minimum
FloorOutlet
Temp.
Celsius Fahrenheit Celsius Fahrenheit
15.5É 60É 62.2É 144É
21.1É 70É 63.8É 147É
26.6É 80É 65.5É 150É
32.2É 90É 67.2É 153É
PLHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 13
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)