Trans temp DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 1317 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either per-
formance (e.g., engine idles rough and stalls) or
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING) - PERFORMANCE and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)ÐMECHANICAL for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) and (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) for the fuel system diagnosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following diagnosis:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING).
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR DAMAGED
OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-PLACE
GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN II
MopartEngine RTV GEN II is used to seal com-
ponents exposed to engine oil. This material is a spe-
cially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
material to cure. This material is available in three
ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one
year this material will not properly cure. Always
inspect the package for the expiration date before
use.
MOPARtATF RTV
MopartATF RTV is a specifically designed black
silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and seal-
ing properties to seal components exposed to auto-
matic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and
moisture. This material is available in three ounce
tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one year
this material will not properly cure. Always inspect
the package for the expiration date before use.
MOPARtGASKET MAKER
MopartGasket Maker is an anaerobic type gasket
material. The material cures in the absence of air
when squeezed between two metallic surfaces. It will
not cure if left in the uncovered tube. The anaerobic
material is for use between two machined surfaces.
Do not use on flexible metal flanges.
MOPARtGASKET SEALANT
MopartGasket Sealant is a slow drying, perma-
nently soft sealer. This material is recommended for
sealing threaded fittings and gaskets against leakage
of oil and coolant. Can be used on threaded and
machined parts under all temperatures. This mate-
rial is used on engines with multi-layer steel (MLS)
cylinder head gaskets. This material also will pre-
vent corrosion. MopartGasket Sealant is available in
a 13 oz. aerosol can or 4oz./16 oz. can w/applicator.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET AND SEALER
APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier than using precut gas-
kets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
9 - 94 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1319 of 2627

(19) Disconnect throttle and speed control cables.
(20) Disconnect tube from both the left and right
side crankcase breathers (Fig. 2). Remove breathers
(21) Discharge A/C system (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/REFRIG-
ERANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(22) Remove A/C compressor (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COM-
PRESSOR - REMOVAL).
(23) Remove shroud, fan assembly (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/FAN DRIVE VISCOUS
CLUTCH - REMOVAL) and accessory drive belt
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE
BELTS - REMOVAL).
(24) Disconnect transmission oil cooler lines at the
radiator.
(25) Disconnect radiator upper and lower hoses.
(26) Remove radiator (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE/RADIATOR - REMOVAL), A/C condenser
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/A/C CONDENSER - REMOVAL) and
transmission oil cooler.
(27) Remove generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING/GENERATOR - REMOVAL).
(28) Disconnect the two heater hoses from the tim-
ing chain cover and heater core.
(29) Unclip and remove heater hoses and tubes
from the intake manifold.
(30) Disconnect engine harness at the following
points :
²Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor (Fig. 3)
²Fuel Injectors
²Throttle Position (TPS) Switch
²Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
²Engine Oil Pressure Switch
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Coil Over Plugs(31) Disconnect the vacuum lines at the throttle
body and intake manifold.
(32) Release fuel rail pressure (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE) then disconnect the fuel supply quick connect
fitting at the fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FITTING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(33) Remove power steering pump and position out
of the way.
(34) Install Special Tools 8400 Lifting Studs, into
the cylinder heads.
(35) Install Engine Lifting Fixture Special Tool
8347 (Fig. 4) following these steps.
²Holding the lifting fixture at a slight angle, slide
the large bore in the front plate over the hex portion
of the lifting stud.
²Position the two remaining fixture arms onto
the two Special Tools 8400 Lifting Studs, in the cyl-
inder heads.
²Pull foward and upward on the lifting fixture so
that the lifting stud rest in the slotted area below the
large bore.
Fig. 2 Crankcase Breather Connection Points
1 - CRANKCASE BREATHERS
Fig. 3 Throttle Body Connection Points
1 - THROTTLE BODY
2 - TPS
3 - IAC MOTOR
4 - IAT SENSOR
5 - MOUNTING SCREWS
9 - 96 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1321 of 2627

Position both the left and right side engine mount
brackets and install the through bolts and nuts.
Tighten nuts to4X2 vehicles95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
4X4 vehicles102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.).
(2)4X4 vehiclesInstall locknuts onto the engine
mount brackets. Tighten locknuts to 41 N´m (30 ft.
lbs.).
(3) Remove jack from under the transmission.
(4) Remove Engine Lifting Fixture Special Tool
8347 (Fig. 4).
(5) Remove Special Tools 8400 Lifting Studs.
(6) Position generator wiring behind the oil dip-
stick tube, then install the oil dipstick tube upper
mounting bolt.
(7) Connect both left and right side body ground
straps.
(8) Install power steering pump.
(9) Connect fuel supply line quick connect fitting
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/
QUICK CONNECT FITTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(10) Connect the vacuum lines at the throttle body
and intake manifold.
(11) Connect engine harness at the following
points (Fig. 3):
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
²Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
²Fuel Injectors
²Throttle Position (TPS) Switch
²Engine Oil Pressure Switch
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Coil Over Plugs
(12) Position and install heater hoses and tubes
onto intake manifold.
(13) Install the heater hoses onto the heater core
and the engine front cover.
(14) Install generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING/GENERATOR - INSTALLATION).
(15) Install A/C condenser (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C CON-
DENSER - INSTALLATION), radiator (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR - INSTALLATION)
and transmission oil cooler.
(16) Connect radiator upper and lower hoses.
(17) Connect the transmission oil cooler lines to
the radiator.
(18) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -INSTALLATION), fan assembly and shroud (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/FAN DRIVE VISCOUS
CLUTCH - INSTALLATION).
(19) Install A/C compressor (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COM-
PRESSOR - INSTALLATION).
(20) Install both breathers. Connect tube to both
crankcase breathers (Fig. 2).
(21) Connect throttle and speed control cables.
(22) Install throttle body resonator assembly and
air inlet hose. Tighten clamps 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.).
(23) Raise vehicle.
(24) Install transmission to engine mounting bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.).
(25) Install torque converter bolts (Automatic
Transmission Only).
(26) Connect crankshaft position sensor (Fig. 1).
(27)4X4 vehiclesPosition and install the axle
isolator bracket onto the axle, transmission and
engine block. Tighten bolts to specification (Refer to 9
- ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(28) Install starter (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - INSTALLATION).
CAUTION: The structural cover requires a specific
torque sequence. Failure to follow this sequence
may cause severe damage to the cover.
(29) Install structural cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/STRUCTURAL COVER - INSTAL-
LATION).
(30) Install exhaust crossover pipe.
(31) Install engine block heater power cable, If
equipped.
(32)4X4 vehiclesConnect axle vent tube to left
side engine mount.
(33) Lower vehicle.
(34) Check and fill engine oil.
(35) Recharge the A/C system (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/REFRIG-
ERANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(36) Refill the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(37) Install the battery tray and battery.
(38) Connect the battery positive and negative
cables.
(39) Start the engine and check for leaks.
9 - 98 ENGINE - 4.7LDR
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1433 of 2627

INSTALLATION
(1) Throughly clean all gasket resdue from the
engine block.
(2) Use extream care and clean all gasket resdue
from the retainer.
(3) Position the gasket onto the retainer.
(4) Position the retainer onto the engine block.
(5) Install the retainer mounting bolts. Tighten the
bolts to 15 N´m (132 in. lbs.) using a crisscross pat-
tern, starting with the bolt on the lower right.
(6) Install a new rear seal(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR
- INSTALLATION).
(7) Install the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install the drive plate / flywheel.
(9) Install the transmission.
(10) Check and verify engine oil level.
(11) Start engine and check for leaks.
FLEX PLATE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the transmission.
(2) Remove the bolts and flexplate.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the flexplate or flywheel onto the
crankshaft and install the bolts hand tight.
(2)For automatic transmissions:Tighten the
flexplate retaining bolts to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(3)For manual transmissions:Tighten the fly-
wheel retaining bolts to 75 N´m (55 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install the transmission.
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect tappet noise, check the oil pressure. If vehicle
has no oil pressure gauge, install a reliable gauge at
the pressure sending-unit. The pressure should be
between 207-552 kPa (30-70 psi) at 3,000 RPM.
Check the oil level after the engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Allow 5 minutes to stabilize
oil level, check dipstick. The oil level in the pan
should never be above the FULL mark or below the
ADD OIL mark on dipstick. Either of these two con-
ditions could be responsible for noisy tappets.
OIL LEVEL
HIGH
If oil level is above the FULL mark, it is possible
for the connecting rods to dip into the oil. With the
engine running, this condition could create foam in
the oil pan. Foam in oil pan would be fed to the
hydraulic tappets by the oil pump causing them to
lose length and allow valves to seat noisily.
LOW
Low oil level may allow oil pump to take in air. When
air is fed to the tappets, they lose length, which allows
valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on intake side of oil
pump through which air can be drawn will create the
same tappet action. Check the lubrication system from
the intake strainer to the pump cover, including the
relief valve retainer cap. When tappet noise is due to
aeration, it may be intermittent or constant, and usu-
ally more than one tappet will be noisy. When oil level
and leaks have been corrected, operate the engine at
fast idle. Run engine for a sufficient time to allow all of
the air inside the tappets to be bled out.
TAPPET NOISE DIAGNOSIS
(1) To determine source of tappet noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed.
(2) Feel each valve spring or rocker arm to detect
noisy tappet. The noisy tappet will cause the affected
spring and/or rocker arm to vibrate or feel rough in
operation.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy tappets. If such is
the case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
(3)
Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by excessive
leak-down around the unit plunger, or by the plunger
partially sticking in the tappet body cylinder. The tap-
pet should be replaced. A heavy click is caused by a tap-
pet check valve not seating, or by foreign particles
wedged between the plunger and the tappet body. This
will cause the plunger to stick in the down position.
This heavy click will be accompanied by excessive clear-
ance between the valve stem and rocker arm as valve
closes. In either case, tappet assembly should be
removed for inspection and cleaning.
(4) The valve train generates a noise very much
like a light tappet noise during normal operation.
Care must be taken to ensure that tappets are mak-
ing the noise. If more than one tappet seems to be
noisy, it's probably not the tappets.
9 - 210 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
CRANKSHAFT REAR OIL SEAL RETAINER (Continued)
Page 1443 of 2627

(8) Torque the (3) bolts that attach the front axle
to the left engine bracket to 101 N´m (75 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install the engine oil filter, if removed.
(10) Install the front crossmember(Refer to 13 -
FRAME & BUMPERS/FRAME/FRONT CROSS-
MEMBER - INSTALLATION).
(11) Install the skid plate.
(12) Lower the vehicle.
(13) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
REAR MOUNT
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
(2) Using a suitable jack, support transmission.
(3) Remove the nuts from the transmission mount
(Fig. 26).
(4) Remove the two bolts that attach the transmis-
sion mount to the engine bracket.
(5) Raise the transmission enough to remove the
mount from the crossmember.
(6) Remove the mount.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Threadlocking compound must be applied to
the bolts before installation.(1) Install the two bolts that attach the transmis-
sion mount to the transmission bracket.
(2) Torque the bolts to 61N´m (45 ft.lbs.) torque.
(3) Lower the transmission so the transmission
mount rests on the crossmember, and the studs of
the transmission mount are aligned in the slots in
the crossmember.
(4) Install the nuts onto the transmission mount
studs through the crossmember access slot.
(5) Torque the nuts to 54N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION
The lubrication system (Fig. 27) is a full flow fil-
tration pressure feed type.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHECKING
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure sending unit and install
gauge assembly C-3292.
(2) Run engine until thermostat opens.
(3) Oil Pressure:
²Curb Idle±25 kPa (4 psi) minimum
²3000 rpm±170 - 758 kPa (25 - 110 psi)
(4) If oil pressure is 0 at idle, shut off engine.
Check for a clogged oil pick-up screen or a pressure
relief valve stuck open.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL LEAK
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24 km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.If the oil leak source is not pos-
itively identified at this time, proceed with the air
leak detection test method.
Fig. 26 TRANSMISSION MOUNT
1 - MOUNT
2 - CROSSMEMBER
3 - NUT
4 - BOLT
9 - 220 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
FRONT MOUNT (Continued)
Page 1457 of 2627
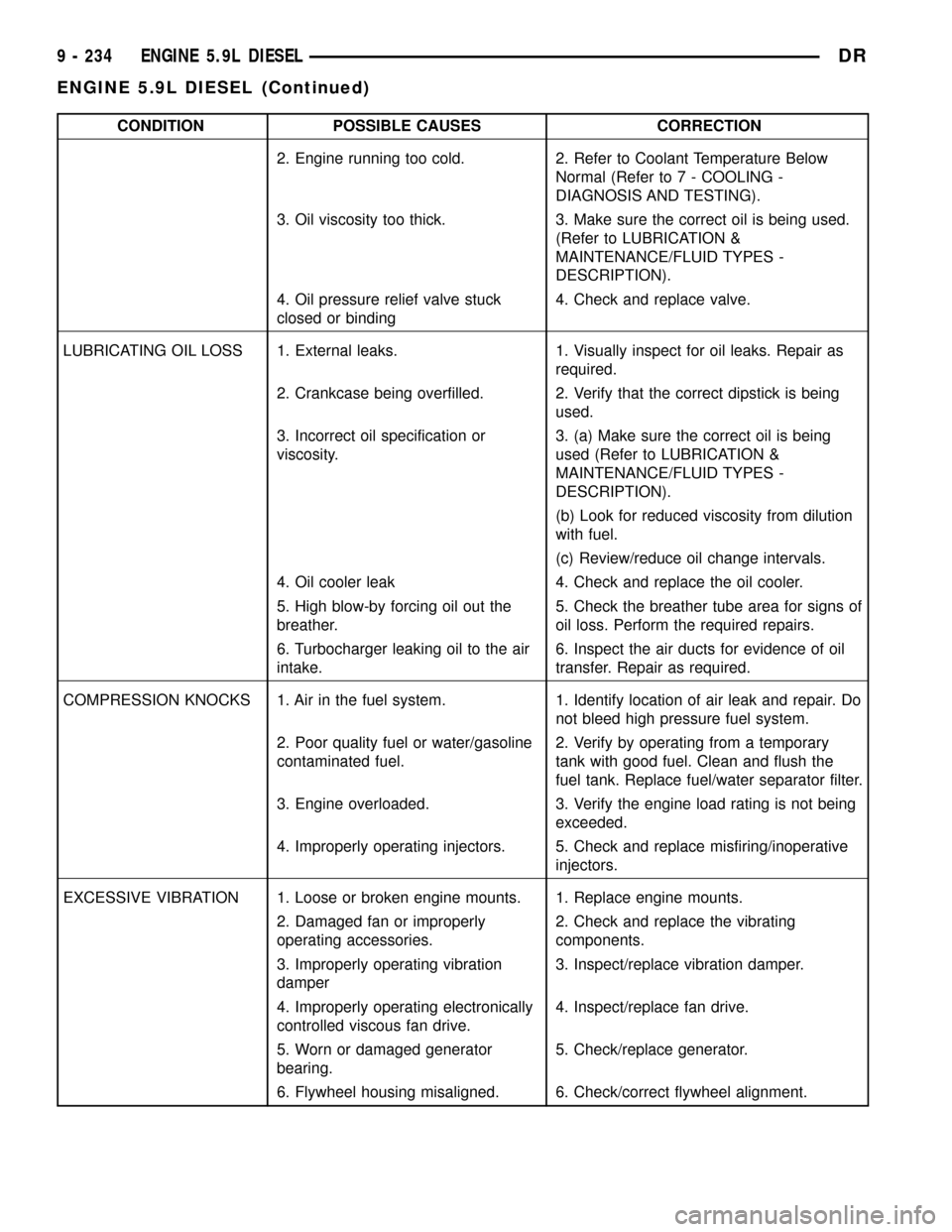
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
2. Engine running too cold. 2. Refer to Coolant Temperature Below
Normal (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
3. Oil viscosity too thick. 3. Make sure the correct oil is being used.
(Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
4. Oil pressure relief valve stuck
closed or binding4. Check and replace valve.
LUBRICATING OIL LOSS 1. External leaks. 1. Visually inspect for oil leaks. Repair as
required.
2. Crankcase being overfilled. 2. Verify that the correct dipstick is being
used.
3. Incorrect oil specification or
viscosity.3. (a) Make sure the correct oil is being
used (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
(b) Look for reduced viscosity from dilution
with fuel.
(c) Review/reduce oil change intervals.
4. Oil cooler leak 4. Check and replace the oil cooler.
5. High blow-by forcing oil out the
breather.5. Check the breather tube area for signs of
oil loss. Perform the required repairs.
6. Turbocharger leaking oil to the air
intake.6. Inspect the air ducts for evidence of oil
transfer. Repair as required.
COMPRESSION KNOCKS 1. Air in the fuel system. 1. Identify location of air leak and repair. Do
not bleed high pressure fuel system.
2. Poor quality fuel or water/gasoline
contaminated fuel.2. Verify by operating from a temporary
tank with good fuel. Clean and flush the
fuel tank. Replace fuel/water separator filter.
3. Engine overloaded. 3. Verify the engine load rating is not being
exceeded.
4. Improperly operating injectors. 5. Check and replace misfiring/inoperative
injectors.
EXCESSIVE VIBRATION 1. Loose or broken engine mounts. 1. Replace engine mounts.
2. Damaged fan or improperly
operating accessories.2. Check and replace the vibrating
components.
3. Improperly operating vibration
damper3. Inspect/replace vibration damper.
4. Improperly operating electronically
controlled viscous fan drive.4. Inspect/replace fan drive.
5. Worn or damaged generator
bearing.5. Check/replace generator.
6. Flywheel housing misaligned. 6. Check/correct flywheel alignment.
9 - 234 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1460 of 2627
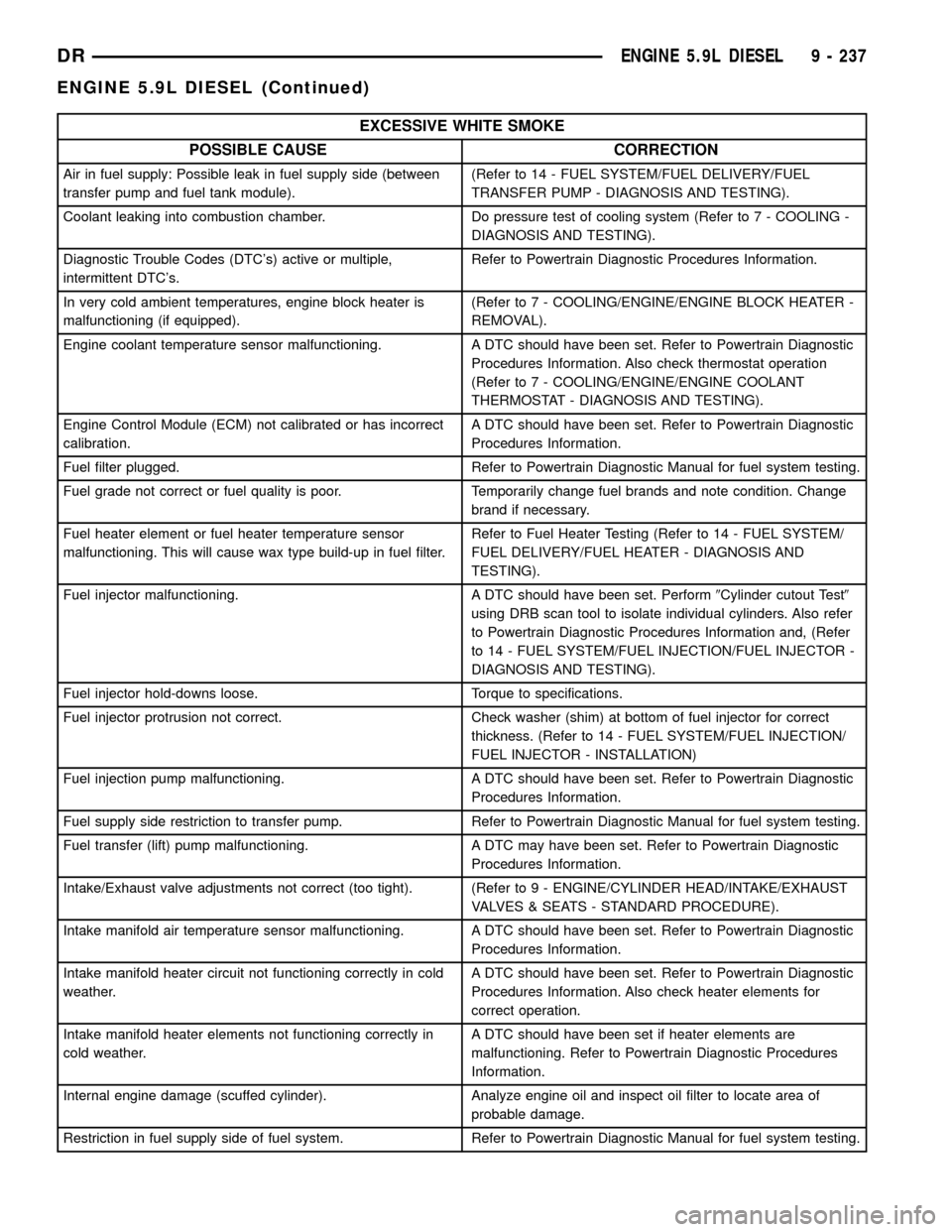
EXCESSIVE WHITE SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Air in fuel supply: Possible leak in fuel supply side (between
transfer pump and fuel tank module).(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL
TRANSFER PUMP - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Coolant leaking into combustion chamber. Do pressure test of cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) active or multiple,
intermittent DTC's.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
In very cold ambient temperatures, engine block heater is
malfunctioning (if equipped).(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK HEATER -
REMOVAL).
Engine coolant temperature sensor malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information. Also check thermostat operation
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE COOLANT
THERMOSTAT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Engine Control Module (ECM) not calibrated or has incorrect
calibration.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information.
Fuel filter plugged. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system testing.
Fuel grade not correct or fuel quality is poor. Temporarily change fuel brands and note condition. Change
brand if necessary.
Fuel heater element or fuel heater temperature sensor
malfunctioning. This will cause wax type build-up in fuel filter.Refer to Fuel Heater Testing (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL HEATER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Fuel injector malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Perform9Cylinder cutout Test9
using DRB scan tool to isolate individual cylinders. Also refer
to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information and, (Refer
to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fuel injector hold-downs loose. Torque to specifications.
Fuel injector protrusion not correct. Check washer (shim) at bottom of fuel injector for correct
thickness. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
FUEL INJECTOR - INSTALLATION)
Fuel injection pump malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information.
Fuel supply side restriction to transfer pump. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system testing.
Fuel transfer (lift) pump malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information.
Intake/Exhaust valve adjustments not correct (too tight). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST
VALVES & SEATS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Intake manifold air temperature sensor malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information.
Intake manifold heater circuit not functioning correctly in cold
weather.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information. Also check heater elements for
correct operation.
Intake manifold heater elements not functioning correctly in
cold weather.A DTC should have been set if heater elements are
malfunctioning. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
Information.
Internal engine damage (scuffed cylinder). Analyze engine oil and inspect oil filter to locate area of
probable damage.
Restriction in fuel supply side of fuel system. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system testing.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 237
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1462 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION/LEAKAGE TESTS
CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure batteries are completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise, the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnostic purposes.
(1) Disconnect the fuel inlet line to the fuel trans-
fer pump. Plug the fuel line from the fuel tank.
(2) Start the engine and idle until the engine stalls
(runs out of fuel).
(3) Disconnect all three injector wire harness con-
nectors at the rocker housing.
(4) Remove the breather cover and cylinder head
cover.
(5) Remove the high pressure fuel line between the
cylinder head and fuel rail for the cylinder to be
tested. Use tool# 9011 to cap this fuel rail on the cyl-
inder being tested.
(6) Remove the exhaust rocker lever.
(7) Use Tool 9010 to remove the injector and cop-
per sealing washer.
(8) Install the exhaust rocker lever and torque to
36 N´m (27 ft. lbs.).
(9) Cover the remaining rocker levers with clean
shop towels to prevent any oil splatter under the
hood.
(10) Place a rag over the compression test tool fit-
ting. Crank the engine for 2±3 seconds to purge any
fuel that may have drained into the cylinder when
the injector was removed.
(11) Connect the compression test gauge.
(12) Crank the engine for 5 seconds and record the
pressure reading. Repeat this step three times and
calculate the average of the three readings.
NOTE: The minimum cylinder pressure is 350 psi.
Cylinder pressure should be within 20% from cylin-
der to cylinder.
(13) Combustion pressure leakage can be checked
if cylinder pressure is below the specification. Per-
form the leakage test procedure on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer instructions.
(14) Upon completion of the test check an erase
any engine related fault codes.
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss
(1) Start and operate the engine until it attains
normal operating temperature.
(2) Remove the breather cover and cylinder head
cover.
(3) Disconnect all three injector wire harness con-
nectors at the rocker housing.
(4) Bring the cylinder to be tested to TDC.
(5) Remove the high pressure fuel line between the
cylinder head and the fuel rail for the cylinder to be
tested.
(6) Install capping Tool 9011 onto the rail.
(7) Remove the high pressure connector nut and
high pressure connector with Tool 9015.
(8) Remove the exhaust and intake rocker lever.
(9) Use Tool 9010 to remove the injector and cop-
per sealing washer.
(10) Install compression test Tool 9007 into the
injector bore.
(11) Connect the leakage tester and perform the
leakage test procedure on each cylinder according to
the tester manufacturer's instructions.
(12) Upon completion of the test check and erase
any engine related fault codes.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-PLACE
GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN II
MopartEngine RTV GEN II is used to seal com-
ponents exposed to engine oil. This material is a spe-
cially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 239
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1463 of 2627

material to cure. This material is available in three
ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one
year this material will not properly cure. Always
inspect the package for the expiration date before
use.
MOPARtATF RTV
MopartATF RTV is a specifically designed black
silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and seal-
ing properties to seal components exposed to auto-
matic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and
moisture. This material is available in three ounce
tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one year
this material will not properly cure. Always inspect
the package for the expiration date before use.
MOPARtGASKET MAKER
MopartGasket Maker is an anaerobic type gasket
material. The material cures in the absence of air
when squeezed between two metallic surfaces. It will
not cure if left in the uncovered tube. The anaerobic
material is for use between two machined surfaces.
Do not use on flexible metal flanges.
MOPARtGASKET SEALANT
MopartGasket Sealant is a slow drying, perma-
nently soft sealer. This material is recommended for
sealing threaded fittings and gaskets against leakage
of oil and coolant. Can be used on threaded and
machined parts under all temperatures. This mate-
rial is used on engines with multi-layer steel (MLS)
cylinder head gaskets. This material also will pre-
vent corrosion. MopartGasket Sealant is available in
a 13 oz. aerosol can or 4oz./16 oz. can w/applicator.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET AND SEALER
APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier than using precut gas-
kets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
to one gasket surface. Be certain the material sur-
rounds each mounting hole. Excess material can eas-
ily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
MopartEngine RTV GEN II or ATF RTV gasket
material should be applied in a continuous bead
approximately 3 mm (0.120 in.) in diameter. All
mounting holes must be circled. For corner sealing, a
3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 in.) drop is placed in the
center of the gasket contact area. Uncured sealant
may be removed with a shop towel. Components
should be torqued in place while the sealant is still
wet to the touch (within 10 minutes). The usage of a
locating dowel is recommended during assembly to
prevent smearing material off the location.MopartGasket Sealant in an aerosol can should be
applied using a thin, even coat sprayed completely
over both surfaces to be joined, and both sides of a
gasket. Then proceed with assembly. Material in a
can w/applicator can be brushed on evenly over the
sealing surfaces. Material in an aerosol can should be
used on engines with multi-layer steel gaskets.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR DAMAGED
OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐHYDROSTATIC
LOCK
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
(1) Disconnect the negative cable(s) from the bat-
tery.
(2) Inspect air cleaner, induction system, and
intake manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(3) Place a shop towel around the fuel injectors to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure
in the cylinder head. Remove the fuel injectors (Refer
to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL
INJECTOR - REMOVAL).
(4) With all injectors removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using the crankshaft barring tool (PN 7471±B).
(5) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (coolant, fuel,
oil, etc.).
(6) Be sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(7) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(8) Squirt a small amount of engine oil into the
cylinders to lubricate the walls. This will prevent
damage on restart.
(9) Install fuel injectors (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR -
INSTALLATION).
9 - 240 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1512 of 2627

LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION
NOTE: Refer to (Fig. 105) and (Fig. 106) for circuit
illustrations.
A gear driven gerotor type oil pump is mounted
behind the front gear cover in the lower right portion
on the engine.
OPERATION
A gerotor style oil pump draws oil from the crank-
case through the suction tube and delivers it through
the block where it enters the oil cooler cover and
pressure regulator valve. When oil pressure exceeds
517 kPa (75 PSI), the valve opens exposing the dump
port, which routes excess oil back to the oil pump.
At the same time, oil is directed to a cast in pas-
sage in the oil cooler cover, leading to the oil cooler
element. As the oil travels through the element
plates, it is cooled by engine coolant traveling past
the outside of the plates. It is then routed to the oil
filter head and through a full flow oil filter. If a
plugged filter is encountered, the filter by-pass valve
opens, allowing unfiltered oil to lubricate the engine.
This condition can be avoided by frequent oil and fil-
ter changes, per the maintenance schedules found in
the owners manual. The by-pass valve is calibrated
to open when it sees a pressure drop of more than
345 kPa (50 psi) across the oil filter.
The oil filter head then divides the oil between the
engine and the turbocharger. The turbocharger
receives filtered, cooled and pressurized oil through a
supply line from the filter head. The oil lubricates
the turbocharger and returns to the pan by way of a
drain tube connecting the bottom of the turbocharger
to a pressed in tube in the cylinder block.
Oil is then carried across the block to an angle
drilling which intersects the main oil rifle. The main
oil rifle runs the length of the block and delivers oil
to the crankshaft main journals and valve train. Oil
travels to the crankshaft through a series of transfer
drillings (one for each main bearing) and lubricates a
groove in the main bearing upper shell. From there
another drilling feeds the camshaft main journals.The saddle jet piston cooling nozzles are also sup-
plied by the main bearing upper shell. J-jet piston
cooling nozzles are supplied by a separate oil rifle.
Plugs are used in place of saddle jets when J-jets are
used. J-jet hole locations are plugged when saddle jet
cooling nozzles are used. Crankshaft internal cross-
drillings supply oil to the connecting rod journals.
Another series of transfer drillings intersecting the
main oil rifle supply the valve train components. Oil
travels up the drilling, through a hole in the head
gasket, and through a drilling in the cylinder head
(one per cylinder), where it enters the rocker arm
pedestal and is divided between the intake and
exhaust rocker arm. Oil travels up and around the
rocker arm mounting bolt, and lubricates the rocker
shaft by cross drillings that intersect the mounting
bolt hole. Grooves at both ends of the rocker shaft
supply oil through the rocker arm where the oil trav-
els to the push rod and socket balls (Fig. 105) and
(Fig. 106).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE OIL
PRESSURE
(1) Remove the 1/8 npt plug from the top of the oil
filter housing.
(2) Install Oil Pressure Line and Gauge Tool
C-3292 with a suitable adapter.
(3) Start engine and warm to operating tempera-
ture.
(4) Record engine oil pressure and compare with
engine oil pressure chart.
CAUTION: If engine oil pressure is zero at idle, DO
NOT RUN THE ENGINE.
Engine Oil Pressure (MIN)
At Idle 68.9 kPa (10 psi)
At 2500 rpm 206.9 kPa (30 psi)
If minimum engine oil pressure is below these
ranges, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
(5) Remove oil pressure gauge and install the 1/8
npt plug.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 289