Electronic DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 1220 of 2627

(3) Connect the electrical connectors by pushing
straight on and rotating the connector arm inboard,
until the connector is firmly locked in place on the
module assembly.
(4) Grasp the integrated power module with two
hands and install the assembly on the battery tray
(Fig. 5).
(5) Install the integrated power module retaining
bolt and screw.
(6) Connect the gray connector on the integrated
power module housing.
(7) Install the B+ terminal cable and nut on the
integrated power module B+ terminal. Snap the
cover in place.
(8) Connect the negative and positive battery
cables.
FRONT CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Front Control Module (FCM) is a micro con-
troller based module located in the left front corner
of the engine compartment. On this model the inte-
grated power module must be positioned aside in
order to access the front control module. The front
control module mates to the power distribution cen-
ter to form the Integrated Power Module (IPM). Theintegrated power module connects directly to the bat-
tery and provides the primary means of circuit pro-
tection and power distribution for all vehicle
electrical systems. The front control module controls
power to some of these vehicle systems electrical and
electromechanical loads based on inputs received
from hard wired switch inputs and data received on
the PCI bus circuit (J1850).
For information on theIntegrated Power Mod-
ule Refer to the Power Distribution Sectionof
the service manual.
OPERATION
As messages are sent over the PCI bus circuit, the
front control module reads these messages and con-
trols power to some of the vehicles electrical systems
by completing the circuit to ground (low side driver)
or completing the circuit to 12 volt power (high side
driver). The following functions areControlledby
the Front Control Module:
²Headlamp Power with Voltage Regulation
²Windshield Wiper ªON/OFFº Relay Actuation
²Windshield Wiper ªHI/LOº Relay Actuation
²Windshield Washer Pump Motor
²Fog Lamp Relay Actuation
²Park Lamp Relay Actuation
²Horn Relay Actuation
The following inputs areReceived/Monitoredby
the Front Control Module:
²B+ Connection Detection
²Power Ground
²Ambient Temperature Sensing
²Ignition Switch Run
²Washer Fluid Level Switch
²Windshield Wiper Park Switch
²PCI Bus Circuit
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FRONT CONTROL
MODULE
The front control module is a printed circuit board
based module with a on-board micro-processor. The
front control module interfaces with other electronic
modules in the vehicle via the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus (J1850). In
order to obtain conclusive testing the Programmable
Communications Interface (PCI) data bus network
and all of the electronic modules that provide inputs
to, or receive outputs from the front control module
must be checked. All PCI (J1850) communication
faults must be resolved prior to further diagnosing
any front control module related issues.
The front control module was designed to be diag-
nosed with an appropriate diagnostic scan tool, such
as the DRB IIIt. The most reliable, efficient, and
accurate means to diagnose the front control module
Fig. 5 INTEGRATED POWER MODULE MOUNTING
TABS
1 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE MOUNTING HOLES
2 - BATTERY TRAY ASSEMBLY
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
DR8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 5
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (Continued)
Page 1221 of 2627

requires the use of a DRB IIItscan tool and the
proper Body Diagnostic Procedures manual.
Before any testing of the front control module is
attempted, the battery should be fully charged and
all wire harness and ground connections inspected
around the affected areas on the vehicle.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the positive and negative battery
cables from the battery.
(2) Partially remove the integrated power module
from the engine compartment (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/POWER DISTRIBUTION/INTEGRATED
POWER MODULE - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the front control module retaining
screws.
(4) Using both hands, pull the front control module
straightfrom the integrated power module assembly
to disconnect the 49-way electrical connector and
remove the front control module from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the front control module on the inte-
grated power module assembly by pushing the
49-way electrical connector straight in.
(2) Install the front control module retaining
screws. Torque the screws to 7 in. lbs.
(3) Install the integrated power module (Refer to 8
- ELECTRICAL/POWER DISTRIBUTION/INTE-
GRATED POWER MODULE - INSTALLATION).
(4) Connect the positive and negative battery
cables.
IOD FUSE
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles are equipped with an Ignition-Off
Draw (IOD) fuse that is disconnected within the Inte-
grated Power Module when the vehicle is shipped
from the factory. Dealer personnel are to reconnect
the IOD fuse in the Integrated Power Module as part
of the preparation procedures performed just prior to
new vehicle delivery.
A laser printed fuse layout map is integral to the
Integrated Power Module cover to ensure proper fuse
identification. The IOD fuse is a 20 ampere mini
blade-type fuse, located in fuse cavity # 51 (Fig. 6).
The fuse is secured within a black molded plastic
fuse holder and puller unit that serves both as a tool
for disconnecting and reconnecting the fuse in its
Integrated Power Module cavity, and as a fuse holder
that conveniently stores the fuse in the same Inte-
grated Power Module cavity after it has been discon-
nected.
CIRCUITS INCLUDED WITH IOD FUSE
²Cluster (CCN)
²Diagnostic Connector
²Map Lamps
²Glove Box Lamp
²Courtesy Lamps
²Radio
²Underhood Lamp
OPERATION
The term ignition-off draw identifies a normal con-
dition where power is being drained from the battery
with the ignition switch in the Off position. The IOD
fuse feeds the memory and sleep mode functions for
some of the electronic modules in the vehicle as well
as various other accessories that require battery cur-
rent when the ignition switch is in the Off position.
The only reason the IOD fuse is disconnected is to
reduce the normal IOD of the vehicle electrical sys-
tem during new vehicle transportation and pre-deliv-
ery storage to reduce battery depletion, while still
allowing vehicle operation so that the vehicle can be
loaded, unloaded and moved as needed by both vehi-
cle transportation company and dealer personnel.
The IOD fuse is disconnected from Integrated
Power Module fuse cavity # 51 when the vehicle is
shipped from the assembly plant. Dealer personnel
must reconnect the IOD fuse when the vehicle is
being prepared for delivery in order to restore full
electrical system operation. Once the vehicle is pre-
pared for delivery, the IOD function of this fuse
Fig. 6 IOD FUSE LOCATION
1 - IOD FUSE
8W - 97 - 6 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTIONDR
FRONT CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1457 of 2627
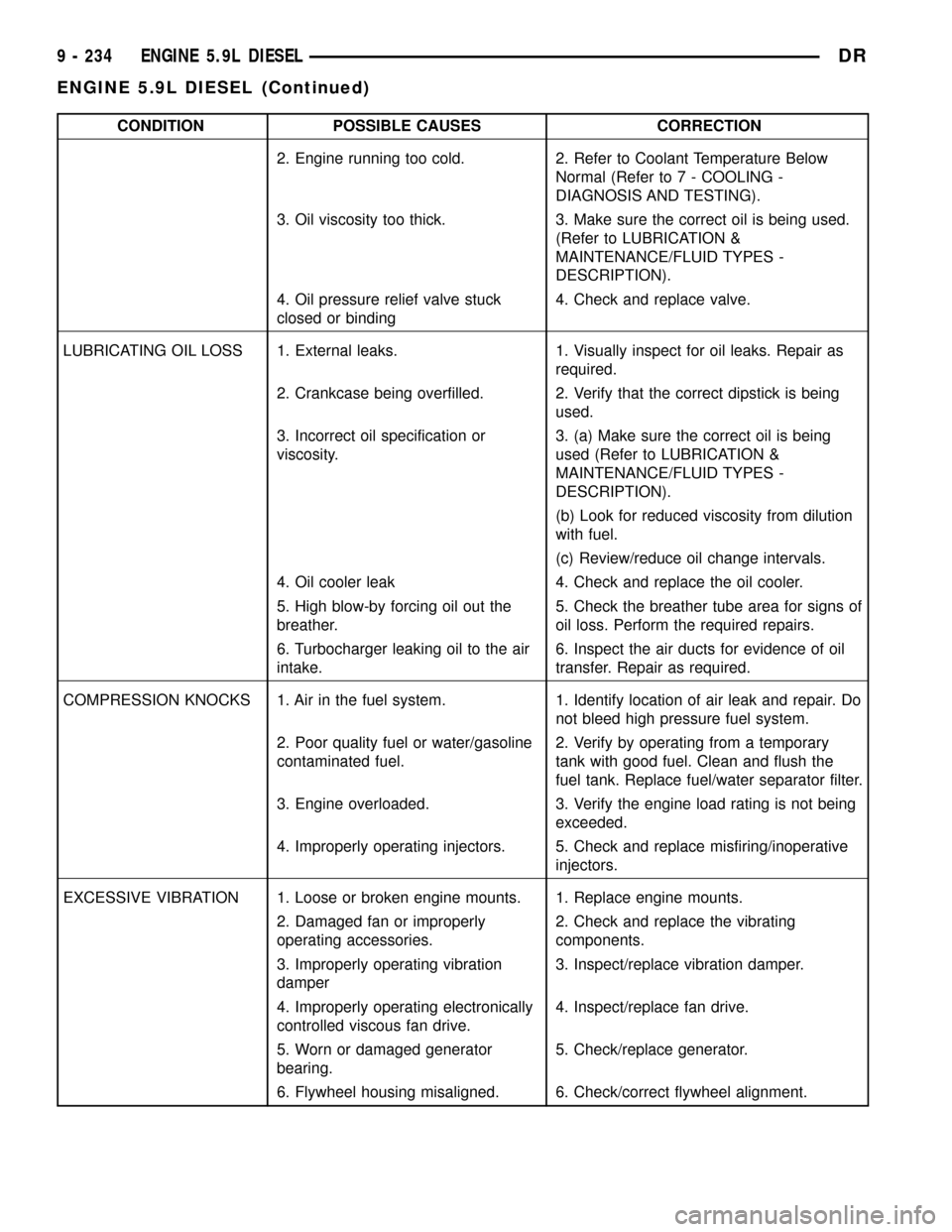
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
2. Engine running too cold. 2. Refer to Coolant Temperature Below
Normal (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
3. Oil viscosity too thick. 3. Make sure the correct oil is being used.
(Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
4. Oil pressure relief valve stuck
closed or binding4. Check and replace valve.
LUBRICATING OIL LOSS 1. External leaks. 1. Visually inspect for oil leaks. Repair as
required.
2. Crankcase being overfilled. 2. Verify that the correct dipstick is being
used.
3. Incorrect oil specification or
viscosity.3. (a) Make sure the correct oil is being
used (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
(b) Look for reduced viscosity from dilution
with fuel.
(c) Review/reduce oil change intervals.
4. Oil cooler leak 4. Check and replace the oil cooler.
5. High blow-by forcing oil out the
breather.5. Check the breather tube area for signs of
oil loss. Perform the required repairs.
6. Turbocharger leaking oil to the air
intake.6. Inspect the air ducts for evidence of oil
transfer. Repair as required.
COMPRESSION KNOCKS 1. Air in the fuel system. 1. Identify location of air leak and repair. Do
not bleed high pressure fuel system.
2. Poor quality fuel or water/gasoline
contaminated fuel.2. Verify by operating from a temporary
tank with good fuel. Clean and flush the
fuel tank. Replace fuel/water separator filter.
3. Engine overloaded. 3. Verify the engine load rating is not being
exceeded.
4. Improperly operating injectors. 5. Check and replace misfiring/inoperative
injectors.
EXCESSIVE VIBRATION 1. Loose or broken engine mounts. 1. Replace engine mounts.
2. Damaged fan or improperly
operating accessories.2. Check and replace the vibrating
components.
3. Improperly operating vibration
damper3. Inspect/replace vibration damper.
4. Improperly operating electronically
controlled viscous fan drive.4. Inspect/replace fan drive.
5. Worn or damaged generator
bearing.5. Check/replace generator.
6. Flywheel housing misaligned. 6. Check/correct flywheel alignment.
9 - 234 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1466 of 2627

(8) Replace injector o-ring and sealing washer on
injectors #5 and #6. Install injectors and torque using
the following steps:
²Step 1ÐInstall injector hold-down capscrews
and torque to 5 N´m (44 in. lbs.) torque.
²Step 2ÐLoosen injector hold-down capscrews.
²Step 3ÐInstall HPC connector tube and nut.
Torque nut to 15 N´m (11 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Step 4ÐTorque injector hold-down capscrews to
10 N´m (89 in. lbs.) torque.
²Step 5ÐTorque HPC connector tube nut to 50
N´m (37 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install #5 and #6 high pressure fuel lines. Fol-
low correct torque sequence per section 14. Torque
fuel line fittings to 30 N-m (22 ft-lb). Torque brace
capscrew to 24 N-m (18 ft-lb).
(10) Install rear engine lift bracket. Torque to 77
N-m (57 ft-lb).
(11) Install push tubes, rocker arms, and pedestals
for cylinders #4, #5, and #6. Torque the mounting
bolts to 36 N-m (27 ft-lbs).
(12) Reset valve lash on cylinders #4, #5, and #6.
Torque adjusting nuts to 24 N-m (18 ft-lbs).
(13) Install cylinder head cover. Torque to 24 N-m
(18 ft-lbs).(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD -
INSTALLATION).
(14) Connect breather tube and lube oil drain tube
to breather housing cover. Install breather housing.
Torque capscrews to 24 N-m (18 ft-lbs)
(15) Connect fuel supply and return hoses.
(16) Connect ECM ground to hydroform screw.
Connect ECM power connector.
(17) Install the APPS cable(s) to the APPS. Install
the throttle linkage cover.
(18) Install the power steering pump.
(19) Install the damper and speed indicator ring.
Torque to 40 N-m (30 ft-lb) plus 60 degrees.
(20) Connect the engine block heater connection.
(21) Connect the A/C compressor and pressure sen-
sor connectors
(22) Install the charge air cooler and a/c condenser
(if equipped). Install and tighten the charge air
cooler mounting bolts to 2 N-m (17 in-lbs).
(23) Connect the charge air cooler piping. Torque
all clamps to 8 N-m (72 in-lbs).
(24) Connect the a/c refrigerant lines to the a/c
condenser (if equipped).
(25) Install the radiator upper support panel.
(26) Install radiator.
(27) Connect the transmission quick-connect oil
cooler lines.(28) Raise vehicle.
(29) Connect a/c compressor suction/discharge hose
(if equipped).
(30) Install the radiator lower hose and clamps.
(31) Install the battery negative cables to the
engine block on the driver and passenger side.
(32) Install the transmission adapter with a new
camshaft rectangular ring seal. Torque to 77 N-m (57
ft-lb).
(33) Install the flywheel/flexplate. Torque to 137
N-m (101 ft-lb).
(34) Install the starter motor. Torque to 43 N-m
(32 ft-lb). (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/STARTING/
STARTER MOTOR - INSTALLATION).
(35) Connect engine to vehicle harness connectors.
(36) Install transmission and transfer case (if
equipped).
(37) Connect the exhaust pipe to the turbocharger
elbow.
(38) Connect the transmission auxiliary oil cooler
lines (if equipped).
(39) Lower the vehicle.
(40) Connect the heater core supply and return
hoses.
(41) Install the cooling fan and upper fan shroud
at the same time. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLATION).
(42) Install the coolant recovery bottle.
(43) Install the windshield washer bottle.
(44) Install the upper radiator hose and clamps.
(45) Raise vehicle.
(46) Connect electronically controlled fan drive
wire harness. Install lower radiator fan shroud.
(47) Change oil filter and install new engine oil.
(48) Fill the cooling system with coolant. (Refer to
7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(49) Connect grid heater harness at grid heater
relays.
(50) Connect electrical connections to rear of alter-
nator.
(51) Start the engine and inspect for engine oil,
coolant, and fuel leaks.
INSTALLATIONÐCRANKCASE BREATHER
(1) Install a new o-ring onto the breather element.
(2) Lubricate o-ring and install into cylinder head
cover. Torque capscrews to 10 N´m (89 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect breather tube and lube oil drain tube.
(4) Install breather cover (Fig. 4). Torque to 24
N´m (18 ft. lbs.)
(5) Install oil fill cap.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 243
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1495 of 2627
(6) Remove the wooden dowel rods and rubber
bands from the tappets.
(7) Lubricate the push rods with engine oil and
install in their original location.Verify that they
are seated in the tappets.
(8) Lubricate the valve tips with engine oil and
install the crossheads in their original locations.
(9) Lubricate the crossheads and push rod sockets
with engine oil and install the rocker arms and ped-
estals in their original locations. Tighten bolts to 36
N´m (27 ft. lbs.) torque.
(10)Verify valve lash adjustment (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST
VALVES & SEATS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(11) Install the cylinder head cover and reusable
gasket (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(12) Install gear housing cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/GEAR HOUSING COVER
- INSTALLATION). Install front crankshaft dust
seal.
(13) Install the crankshaft damper with the speed
indicator ring (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE
BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER - INSTALLATION).
(14) Install the fan support/hub assembly Refer to
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
INSTALLATION).
(15) Install the power steering pump.
(16) Install accessory drive belt tensioner. Torque
bolt to 43 Nm (32 ft. lbs.).
(17) Install the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(18) Install the charge air cooler (with a/c con-
denser and auxiliary transmission oil cooler, if
equipped) and tighten the mounting bolts to 2 N´m
(17 in. lbs.) torque.
(19) Connect charge air cooler inlet and outlet
pipes. Tighten clamps to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.) torque.
(20) Install the radiator upper support panel.
(21) Close radiator petcock and lower the radiator
into the engine compartment. Tighten the mounting
bolts to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.) torque.
(22) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(23) Connect radiator lower hose and install
clamp.
(24) Connect transmission auxiliary oil cooler lines
(if equipped).
(25) Lower vehicle.
(26) Install the fan shroud and tighten the mount-
ing screws to 6 N´m (50 in. lbs.) torque.
(27) Install the electronically controlled viscous
fan/drive assembly. Connect harness connector.(Refer
to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
INSTALLATION).(28) Install the coolant recovery and windshield
washer fluid reservoirs to the fan shroud.
(29) Connect the coolant recovery hose to the radi-
ator filler neck.
(30) Add engine coolant (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(31) Charge A/C system with refrigerant (if A/C
equipped) (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(32) Connect the battery negative cables.
(33) Start engine and check for engine oil and cool-
ant leaks.
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CONNECTING ROD
BEARING AND CRANKSHAFT JOURNAL
CLEARANCE
(1) Measure the connecting rod bore with bearings
removedand the bolts tightened to 100 N´m (73 ft.
lbs.) torque..
(2) Measure the connecting rod bore with the bear-
ingsinstalledand the bolts tightened to 100 N´m
(73 ft. lbs.) torque.
Measure within 20É arc from each side of the part-
ing line. Also measure 90É from parting line.
Record the smallest and largest diameter.
Measure the diameter of the rod journal at the
location shown (Fig. 63). Calculate the average diam-
eter for each side of the journal.
Determine minimum bearing clearance by calculat-
ing the differance between the smallest connecting
rod bore diameter with the bearing installed and the
average diameter for each side of the crankshaft jour-
nal.
Determine the maximum bearing clearance by cal-
culating the difference between the largest connect-
ing rod bore diameter and the average diameter with
the bearing installed for each side of the crankshaft
journal.
DESCRIPTION MEASUREMENT
CONNECTING ROD
BORE, BEARINGS
REMOVEDMIN. 72.99 mm (2.874
in.)
MAX. 73.01 mm (2.875
in.)
CONNECTING ROD
BORE, BEARINGS
INSTALLEDMIN. 69.05 mm (2.719
in.)
MAX. 69.10 mm (2.720
in.)
9 - 272 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) (Continued)
Page 1592 of 2627

(5) Position APPS assembly to bottom of battery
tray and install 3 bolts. Refer to Torque Specifica-
tions.
(6) Install wheelhouse liner. Refer to Body.
(7)The 5.7L V-8 engine is equipped with a
fully electronic accelerator pedal position sen-
sor. If equipped with a 5.7L, also perform the
following 3 steps:
(a) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(b) Turn ignition switch ON, but do not crank
engine.
(c) Leave ignition switch ON for a minimum of
10 seconds. This will allow PCM to learn electrical
parameters.
(d) The DRB IIItScan Tool may also be used to
learn electrical parameters. Go to the Miscella-
neous menu, and then select ETC Learn.
(8) If the previous step is not performed, a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) will be set.
(9) If necessary, use DRB IIItScan Tool to erase
any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) from PCM.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
3.7L V-6
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is mounted
into the right rear side of the cylinder block. It is
positioned and bolted into a machined hole.
4.7L V-8
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is mounted
into the right rear side of the cylinder block. It is
positioned and bolted into a machined hole.
5.7L V-8
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is mounted
into the right rear side of the cylinder block. It is
positioned and bolted into a machined hole.
OPERATION
3.7L V-6
Engine speed and crankshaft position are provided
through the CKP (Crankshaft Position) sensor. The
sensor generates pulses that are the input sent to the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The PCM inter-
prets the sensor input to determine the crankshaft
position. The PCM then uses this position, along with
other inputs, to determine injector sequence and igni-
tion timing.
Fig. 3 APPS REMOVE / INSTALL
1 - BOTTOM OF BATTERY TRAY
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - APPS
4 - SWING-DOWN DOOR
5 - CABLE (TO PEDAL)
6 - CABLE RELEASE TAB
Fig. 4 APPS CABLE
1 - APPS LEVER
2 - BALL SOCKET
3 - SWING-DOWN DOOR
4 - CABLE CLIP
5 - CABLE
DRFUEL INJECTION - GAS 14 - 23
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1602 of 2627

²Engine load
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance programs
²Shift-point strategies (certain automatic trans-
missions only)
²Idle speed
²Decel fuel shutoff
The MAP sensor signal is provided from a single
piezoresistive element located in the center of a dia-
phragm. The element and diaphragm are both made
of silicone. As manifold pressure changes, the dia-
phragm moves causing the element to deflect, which
stresses the silicone. When silicone is exposed to
stress, its resistance changes. As manifold vacuum
increases, the MAP sensor input voltage decreases
proportionally. The sensor also contains electronics
that condition the signal and provide temperature
compensation.
The PCM recognizes a decrease in manifold pres-
sure by monitoring a decrease in voltage from the
reading stored in the barometric pressure memory
cell. The MAP sensor is a linear sensor; meaning as
pressure changes, voltage changes proportionately.
The range of voltage output from the sensor is usu-
ally between 4.6 volts at sea level to as low as 0.3
volts at 26 in. of Hg. Barometric pressure is the pres-
sure exerted by the atmosphere upon an object. At
sea level on a standard day, no storm, barometric
pressure is approximately 29.92 in Hg. For every 100
feet of altitude, barometric pressure drops 0.10 in.
Hg. If a storm goes through, it can change baromet-
ric pressure from what should be present for that
altitude. You should know what the average pressure
and corresponding barometric pressure is for your
area.
REMOVAL
3.7L V-6
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor is
mounted into the front of the intake manifold (Fig.
21). An o-ring is used to seal the sensor to the intake
manifold (Fig. 22).
(1) Disconnect electrical connector at sensor.
(2) Clean area around MAP sensor.
(3) Remove 2 sensor mounting screws.
(4) Remove MAP sensor from intake manifold.
(5) Check condition of sensor o-ring (Fig. 22).
4.7L V-8
The MAP sensor is located on the front of the
intake manifold (Fig. 23). An o-ring seals the sensor
to the intake manifold.
(1) Disconnect electrical connector at sensor.
(2) Clean area around MAP sensor.
(3) Remove 2 sensor mounting bolts (Fig. 23).(4) Remove MAP sensor from intake manifold.
(5) Check condition of sensor o-ring (Fig. 22).
Fig. 21 MAP SENSOR - 3.7L V-6
1 - MOUNTING SCREWS
2 - MAP SENSOR
3 - ECT SENSOR
4 - FRONT OF INTAKE MANIFOLD
Fig. 22 MAP SENSOR O-RING 3.7L / 4.7L
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - O-RING
DRFUEL INJECTION - GAS 14 - 33
MAP SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1614 of 2627

FUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL FUEL SYSTEM
The fuel system used on the Cummins engine is an
electronically controlled, Bosch HPCR (High-Pressure
Common Rail) system. The HPCR system consists of
five main components:
²Electric Fuel Transfer (lift) Pump
²Fuel Pump/Gear Pump (attached to fuel injec-
tion pump)
²High-Pressure Fuel Injection Pump
²Fuel Injection Rail
²Fuel Injectors
Also to be considered as part of the overall fuel
system are:
²Accelerator Pedal
²Air Cleaner Housing/Element
²Fuel Drain Manifold (passage)
²Fuel Drain Valve (at filter)
²Fuel Filter/Water Separator
²Fuel Heater
²Fuel Heater Relay
²Fuel Level (gauge) Sending Unit
²Fuel Pressure Limiting Valve
²Fuel Tank
²Fuel Tank Module (containing fuel gauge send-
ing unit and separate fuel filter located at bottom of
tank module)
²Fuel Tank Filler/Vent Tube Assembly
²Fuel Tank Filler Tube Cap
²Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses
²High-Pressure Fuel Injector Lines
²In-Tank Fuel Filter (at bottom of fuel tank mod-
ule)
²Low-Pressure Fuel Supply Lines
²Low-Pressure Fuel Return Line
²Overflow Valve
²Quick-Connect Fuel Line Fittings
²Throttle Cable
²Water Draining (maintenance)
²Water-In-Fuel (WIF) Sensor
The fuel injection pump supplies high pressure to
the fuel rail independent of engine speed. This high
pressure fuel is then accumulated in the fuel rail.
High pressure fuel is constantly supplied to the injec-
tors by the fuel rail. The Engine Control Module
(ECM) controls the fueling and timing of the engine
by actuating the injectors.Fuel enters the system from the electric fuel trans-
fer (lift) pump, which is attached to the fuel filter
assembly. Fuel is forced through the fuel filter ele-
ment and then enters the Fuel Pump/Gear Pump,
which is attached to the rear of the fuel injection
pump. The Fuel Pump/Gear Pump is a low-pressure
pump and produce pressures ranging from 551.5 kpa
(80 psi) to 1241 kpa (180) psi. Fuel then enters the
fuel injection pump. Low pressure fuel is then sup-
plied to the FCA (Fuel Control Actuator).
The FCA is an electronically controlled solenoid
valve. The ECM controls the amount of fuel that
enters the high-pressure pumping chambers by open-
ing and closing the FCA based on a demanded fuel
pressure. The FPS (Fuel Pressure Sensor) on the fuel
rail monitors the actual fuel pressure and provides it
as an input to the ECM. When the actuator is
opened, the maximum amount of fuel is being sup-
plied to the fuel injection pump. Any fuel that does
not enter the injection pump is directed to the over-
flow valve. The overflow valve regulates how much
excess fuel is used for lubrication of the pump and
how much is returned to the tank through the drain
manifold.
Fuel entering the injection pump is pressurized to
between 300-1600 bar (4351-23,206 psi) by three
radial pumping chambers. The pressurized fuel is
then supplied to the fuel rail.
WARNING: HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES DELIVER
DIESEL FUEL UNDER EXTREME PRESSURE FROM
THE INJECTION PUMP TO THE FUEL INJECTORS.
THIS MAY BE AS HIGH AS 160,000 KPA (23,206
PSI). USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN INSPECTING
FOR HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS. INSPECT FOR
HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS WITH A SHEET OF
CARDBOARD. HIGH FUEL INJECTION PRESSURE
CAN CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY IF CONTACT IS
MADE WITH THE SKIN.
Certain fuel system components can be found in
(Fig. 1), or (Fig. 2).
DRFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 45
Page 1622 of 2627

(3) Check condition of relay terminals and PDC
connector terminals for damage or corrosion. Repair
if necessary before installing relay.
(4) Check for pin height (pin height should be the
same for all terminals within the PDC connector).
Repair if necessary before installing relay.
INSTALLATION
The fuel heater relay is located in the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC) (Fig. 6). Refer to label under
PDC cover for relay location.
(1) Install relay to PDC.
(2) Install cover to PDC.
FUEL INJECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION
A Robert Bosch high-pressure fuel injection pump
is used. The pump is attached to the back of the tim-
ing gear cover at the left / rear side of the engine.
OPERATION
The fuel injection pump supplies high pressure to
the fuel rail independent of engine speed. This high
pressure is then accumulated in the fuel rail. High
pressure fuel is constantly supplied to the injectors
by the fuel rail. The Engine Control Module (ECM)
controls the fueling and timing of the engine by actu-
ating the injectors.
Fuel enters the system from the electric fuel trans-
fer (lift) pump, which is attached to the fuel filter
assembly. Fuel is forced through the fuel filter ele-
ment and then enters the Fuel Pump/Gear Pump,
which is attached to the rear of the fuel injection
pump. The Fuel Pump/Gear Pump is a low-pressure
pump and produce pressures ranging from 551.5 kpa
(80 psi) to 1241 kpa (180) psi. Fuel then enters the
fuel injection pump. Low pressure fuel is then sup-
plied to the FCA (Fuel Control Actuator).
The FCA is an electronically controlled solenoid
valve. The ECM controls the amount of fuel that
enters the high-pressure pumping chambers by open-
ing and closing the FCA based on a demanded fuel
pressure. The FPS (Fuel Pressure Sensor) on the fuel
rail provides the actual fuel pressure. When the
actuator is opened, the maximum amount of fuel is
being supplied to the fuel injection pump. Any fuel
that does not enter the injection pump is directed to
the cascade overflow valve. The cascade overflow
valve regulates how much excess fuel is used for
lubrication of the pump and how much is returned to
the tank through the drain manifold.
Fuel entering the injection pump is pressurized to
between 300-1600 bar (4351-23206 psi) by three
radial pumping chambers. The pressurized fuel is
then supplied to the fuel rail.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL INJECTION
PUMP TIMING
With the Bosch injection pump, there are no
mechanical adjustments needed or necessary to
accomplish fuel injection timing. All timing and fuel
adjustments are electrically made by the engine
mounted Engine Control Module (ECM).
Fig. 6 POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER LOCATION
1 - CLIP
2 - BATTERY
3 - TRAY
4 - NEGATIVE CABLE
5 - POSITIVE CABLE
6 - CLIP
7 - FENDER INNER SHIELD
8 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
DRFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 53
FUEL HEATER RELAY (Continued)
Page 1638 of 2627

CAUTION: Do not attempt to remove sensor from
its mounting bracket as electronic calibration will
be destroyed (sensor-to-bracket mounting screws
are permanently attached). Two accelerator lever
set screws (Fig. 3) are used to position lever. Do
not attempt to alter positions of these set screws as
electronic calibration will be destroyed.
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
(2) Remove cable cover (Fig. 1). Cable cover is
attached with 2 Phillips screws, 2 plastic retention
clips and 2 push tabs (Fig. 1). Remove 2 Phillips
screws and carefully pry out 2 retention clips. After
clip removal, push rearward on front tab, and
upward on lower tab for cover removal.
(3) Using finger pressure only, disconnect end of
speed control servo cable from throttle lever pin by
pulling forward on connector while holding lever
rearward (Fig. 2).DO NOT try to pull connector
off perpendicular to lever pin. Connector will
be broken.
(4) Using two small screwdrivers, pry throttle
cable connector socket from throttle lever ball (Fig.
2).Be very careful not to bend throttle lever
arm.
(5) Disconnect transmission control cable at lever
arm (if equipped). Refer to 21, Transmission.
(6) Squeeze pinch tabs on speed control cable (Fig.
2) and pull cable rearward to remove from cable
mounting bracket.
(7) Squeeze pinch tabs on throttle cable (Fig. 2)
and pull cable rearward to remove from cable mount-
ing bracket.
(8) Refer to 21, Transmission for transmission con-
trol cable removal procedures.
(9) Disconnect wiring harness clip (Fig. 3) at bot-
tom of bracket.
(10) Remove 6 mounting bolts (Fig. 3) and par-
tially remove APPS assembly from engine. After
assembly is partially removed, disconnect electrical
connector from bottom of sensor by pushing on con-
nector tab (Fig. 4).
(11) Remove APPS assembly from engine.
Battery Tray Mounted Sensor :
The APPS is serviced (replaced) as one assembly
including the sensor, plastic housing and cable. The
APPS assembly is located under the left (drivers
side) vehicle battery tray (Fig. 5). Access to APPS is
gained from over top of left / front tire.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Disconnect APPS cable at accelerator pedal.
Refer to Accelerator Pedal Removal / Installation.
(3) Remove wheel house liner at left / front wheel.
Refer to Body.(4) Gain access to APPS electrical connector by
opening swing-down door (Fig. 6). Disconnect electri-
cal connector.
(5) Remove 3 mounting bolts (Fig. 6).
(6) Remove APPS assembly from battery tray.
Fig. 1 CABLE/LEVER/THROTTLE LINKAGE COVER
1 - CABLE/LEVER/LINKAGE COVER
2 - PUSH UP LOWER TAB
3 - SCREWS/CLIPS (2)
4 - TAB PUSH HERE
Fig. 2 SERVO CABLE AT THROTTLE LEVER
1 - PINCH (2) TABS
2 - CABLE MOUNTING BRACKET
3 - PINCH TABS (2)
4 - OFF
5 - THROTTLE CABLE
6 - THROTTLE LEVER
7 - THROTTLE LEVER PIN
8 - OFF
9 - CONNECTOR
10 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
DRFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 69
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR (Continued)