Gauge DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 1614 of 2627

FUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL FUEL SYSTEM
The fuel system used on the Cummins engine is an
electronically controlled, Bosch HPCR (High-Pressure
Common Rail) system. The HPCR system consists of
five main components:
²Electric Fuel Transfer (lift) Pump
²Fuel Pump/Gear Pump (attached to fuel injec-
tion pump)
²High-Pressure Fuel Injection Pump
²Fuel Injection Rail
²Fuel Injectors
Also to be considered as part of the overall fuel
system are:
²Accelerator Pedal
²Air Cleaner Housing/Element
²Fuel Drain Manifold (passage)
²Fuel Drain Valve (at filter)
²Fuel Filter/Water Separator
²Fuel Heater
²Fuel Heater Relay
²Fuel Level (gauge) Sending Unit
²Fuel Pressure Limiting Valve
²Fuel Tank
²Fuel Tank Module (containing fuel gauge send-
ing unit and separate fuel filter located at bottom of
tank module)
²Fuel Tank Filler/Vent Tube Assembly
²Fuel Tank Filler Tube Cap
²Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses
²High-Pressure Fuel Injector Lines
²In-Tank Fuel Filter (at bottom of fuel tank mod-
ule)
²Low-Pressure Fuel Supply Lines
²Low-Pressure Fuel Return Line
²Overflow Valve
²Quick-Connect Fuel Line Fittings
²Throttle Cable
²Water Draining (maintenance)
²Water-In-Fuel (WIF) Sensor
The fuel injection pump supplies high pressure to
the fuel rail independent of engine speed. This high
pressure fuel is then accumulated in the fuel rail.
High pressure fuel is constantly supplied to the injec-
tors by the fuel rail. The Engine Control Module
(ECM) controls the fueling and timing of the engine
by actuating the injectors.Fuel enters the system from the electric fuel trans-
fer (lift) pump, which is attached to the fuel filter
assembly. Fuel is forced through the fuel filter ele-
ment and then enters the Fuel Pump/Gear Pump,
which is attached to the rear of the fuel injection
pump. The Fuel Pump/Gear Pump is a low-pressure
pump and produce pressures ranging from 551.5 kpa
(80 psi) to 1241 kpa (180) psi. Fuel then enters the
fuel injection pump. Low pressure fuel is then sup-
plied to the FCA (Fuel Control Actuator).
The FCA is an electronically controlled solenoid
valve. The ECM controls the amount of fuel that
enters the high-pressure pumping chambers by open-
ing and closing the FCA based on a demanded fuel
pressure. The FPS (Fuel Pressure Sensor) on the fuel
rail monitors the actual fuel pressure and provides it
as an input to the ECM. When the actuator is
opened, the maximum amount of fuel is being sup-
plied to the fuel injection pump. Any fuel that does
not enter the injection pump is directed to the over-
flow valve. The overflow valve regulates how much
excess fuel is used for lubrication of the pump and
how much is returned to the tank through the drain
manifold.
Fuel entering the injection pump is pressurized to
between 300-1600 bar (4351-23,206 psi) by three
radial pumping chambers. The pressurized fuel is
then supplied to the fuel rail.
WARNING: HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES DELIVER
DIESEL FUEL UNDER EXTREME PRESSURE FROM
THE INJECTION PUMP TO THE FUEL INJECTORS.
THIS MAY BE AS HIGH AS 160,000 KPA (23,206
PSI). USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN INSPECTING
FOR HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS. INSPECT FOR
HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS WITH A SHEET OF
CARDBOARD. HIGH FUEL INJECTION PRESSURE
CAN CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY IF CONTACT IS
MADE WITH THE SKIN.
Certain fuel system components can be found in
(Fig. 1), or (Fig. 2).
DRFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 45
Page 1626 of 2627

FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT /
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) is
attached to the side of the fuel tank module. The
sending unit consists of a float, an arm, and a vari-
able resistor track (card).
OPERATION
The fuel tank module on diesel powered models
has 2 different circuits (wires). Two of these circuits
are used at the fuel gauge sending unit for fuel
gauge operation. The diesel engine does not have a
fuel tank module mounted electric fuel pump. The
electric fuel pump (fuel transfer pump) is mounted to
the engine.
For Fuel Gauge Operation:A constant input
voltage source of about 12 volts (battery voltage) is
supplied to the resistor track on the fuel gauge send-
ing unit. This is fed directly from the Engine Control
Module (ECM).NOTE: For diagnostic purposes,
this 12V power source can only be verified with
the circuit opened (fuel tank module electrical
connector unplugged). With the connectors
plugged, output voltages will vary from about .6
volts at FULL, to about 7.0 volts at EMPTY.The
resistor track is used to vary the voltage (resistance)
depending on fuel tank float level. As fuel level
increases, the float and arm move up, which
decreases voltage. As fuel level decreases, the float
and arm move down, which increases voltage. The
varied voltage signal is returned back to the ECM
through the sensor return circuit.
Both of the electrical circuits between the fuel
gauge sending unit and the ECM are hard-wired (not
multi-plexed). After the voltage signal is sent from
the resistor track, and back to the ECM, the ECM
will interpret the resistance (voltage) data and send
a message across the multi-plex bus circuits to the
instrument panel cluster. Here it is translated into
the appropriate fuel gauge level reading. Refer to
Instrument Panel for additional information.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
For diesel removal and installation procedures,
refer to the gas section of Fuel System/Fuel Delivery.
See Fuel Level Sending Unit/Sensor Removal/Instal-
lation.
FUEL LINES
DESCRIPTION
Low-Pressure Lines Are:
²the fuel supply line from fuel tank to fuel trans-
fer (lift) pump.
²the fuel return line back to fuel tank.
²the fuel drain (manifold) line at rear of cylinder
head.
²the fuel supply line from fuel filter to fuel injec-
tion pump.
²the fuel injection pump return line.
High-Pressure Lines Are:
²the fuel line from fuel injection pump to fuel
rail.
²the 6 fuel lines from fuel rail up to injector con-
nector tubes
WARNING: HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES DELIVER
DIESEL FUEL UNDER EXTREME PRESSURE FROM
THE INJECTION PUMP TO THE FUEL INJECTORS.
THIS MAY BE AS HIGH AS 160,000 KPA (23,206
PSI). USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN INSPECTING
FOR HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS. INSPECT FOR
HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS WITH A SHEET OF
CARDBOARD. HIGH FUEL INJECTION PRESSURE
CAN CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY IF CONTACT IS
MADE WITH THE SKIN.
OPERATION
High-Pressure Lines
CAUTION: The high-pressure fuel lines must be
held securely in place in their holders. The lines
cannot contact each other or other components. Do
not attempt to weld high-pressure fuel lines or to
repair lines that are damaged. If lines are ever
kinked or bent, they must be replaced. Use only the
recommended lines when replacement of high-pres-
sure fuel line is necessary.
High-pressure fuel lines deliver fuel (under pres-
sure) of up to approximately 160,000 kPa (23,206
PSI) from the injection pump to the fuel injectors.
The lines expand and contract from the high-pres-
sure fuel pulses generated during the injection pro-
cess. All high-pressure fuel lines are of the same
length and inside diameter. Correct high-pressure
fuel line usage and installation is critical to smooth
engine operation.
DRFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 57
Page 1632 of 2627

FUEL TANK MODULE
DESCRIPTION
An electric fuel pump isnot usedin the fuel tank
module for diesel powered engines. Fuel is supplied
by the engine mounted fuel transfer (lift) pump.
The fuel tank module is installed in the top of the
fuel tank (Fig. 21). The fuel tank module contains
the following components:
²Fuel reservoir
²A separate in-tank fuel filter
²Fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor)
²Fuel supply line connection
²Fuel return line connection
²Auxiliary non-pressurized fitting
OPERATION
Refer to Fuel Gauge Sending Unit.
REMOVAL
(1) Drain and remove fuel tank. Refer to Fuel
Tank Removal/Installation.
(2) Thoroughly clean area around tank module at
top of tank.
(3) The plastic fuel tank module locknut is
threaded onto fuel tank. Install Special Tool 6856 to
locknut and remove locknut (Fig. 22). The fuel tank
module will spring up when locknut is removed.
(4) Remove module from fuel tank.
Fig. 20 FUEL TANK MOUNTING
1 - FUEL TANK
2 - STRAP MOUNTING STUDS
3 - VEHICLE FRAME4 - MOUNTING STRAPS
5 - STRAP NUTS
DRFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 63
FUEL TANK (Continued)
Page 1633 of 2627

INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Whenever the fuel tank module is ser-
viced, the rubber gasket must be replaced.
(1) Thoroughly clean locknut and locknut threads
at top of tank.(2) Using new gasket, carefully position fuel tank
module into opening in fuel tank.
(3) Position locknut over top of fuel tank module.
Install locknut finger tight.
(4) When looking down at tank from drivers side of
tank, the fuel line connectors and fuel gauge electri-
cal connector should all be pointed to drivers side of
vehicle. Rotate and align if necessary before tighten-
ing locknut.This step must be performed to pre-
vent the module's float from contacting side of
fuel tank.
(5) Tighten locknut to 24 - 44 N´m (18 - 32 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(6) Install fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Removal/
Installation.
FUEL TRANSFER PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The fuel transfer pump (fuel lift pump) is attached
to the rear of the fuel filter/water separator housing.
The 12±volt electric pump is operated and controlled
by the Engine Control Module (ECM).
OPERATION
The purpose of the fuel transfer pump is to supply
(transfer) a low-pressure fuel source:fromthe fuel
tank,throughthe fuel filter/water separator andto
the fuel injection pump. Here, the low-pressure is
raised to a high-pressure by the fuel injection pump
for operation of the high-pressure fuel injectors.
Check valves within the pump, control direction of
fuel flow and prevent fuel bleed-back during engine
shut down.
Maximum current flow to the pump is 5 amperes.
With the engine running, the pump has a 100 per-
cent duty-cycle.
The transfer pump is self-priming: When the key is
first turned on (without cranking engine), the pump
will operate for approximately 2 seconds and then
shut off. The pump will also operate for up to 25 sec-
onds after the starter is engaged, and then disen-
gaged and the engine is not running. The pump
shuts off immediately if the key is on and the engine
stops running.
The fuel volume of the transfer pump will always
provide more fuel than the fuel injection pump
requires. Excess fuel is returned from the injection
pump through an overflow valve, and then back to
the fuel tank.
REMOVAL
The fuel transfer pump (fuel lift pump) is attached
to the rear of the fuel filter/water separator housing
(Fig. 23).
Fig. 21 FUEL TANK MODULE - DIESEL
1 - TOP OF FUEL TANK
2 - AUX. FITTING
3 - ELEC. CONNECTOR
4 - FUEL TANK MODULE (TOP)
5 - LOCKNUT
6 - FUEL SUPPLY LINE
7 - FUEL RETURN LINE
Fig. 22 LOCKNUT REMOVAL/INSTALLATION -
TYPICAL MODULE
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6856
2 - LOCKNUT
14 - 64 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELDR
FUEL TANK MODULE (Continued)
Page 1659 of 2627
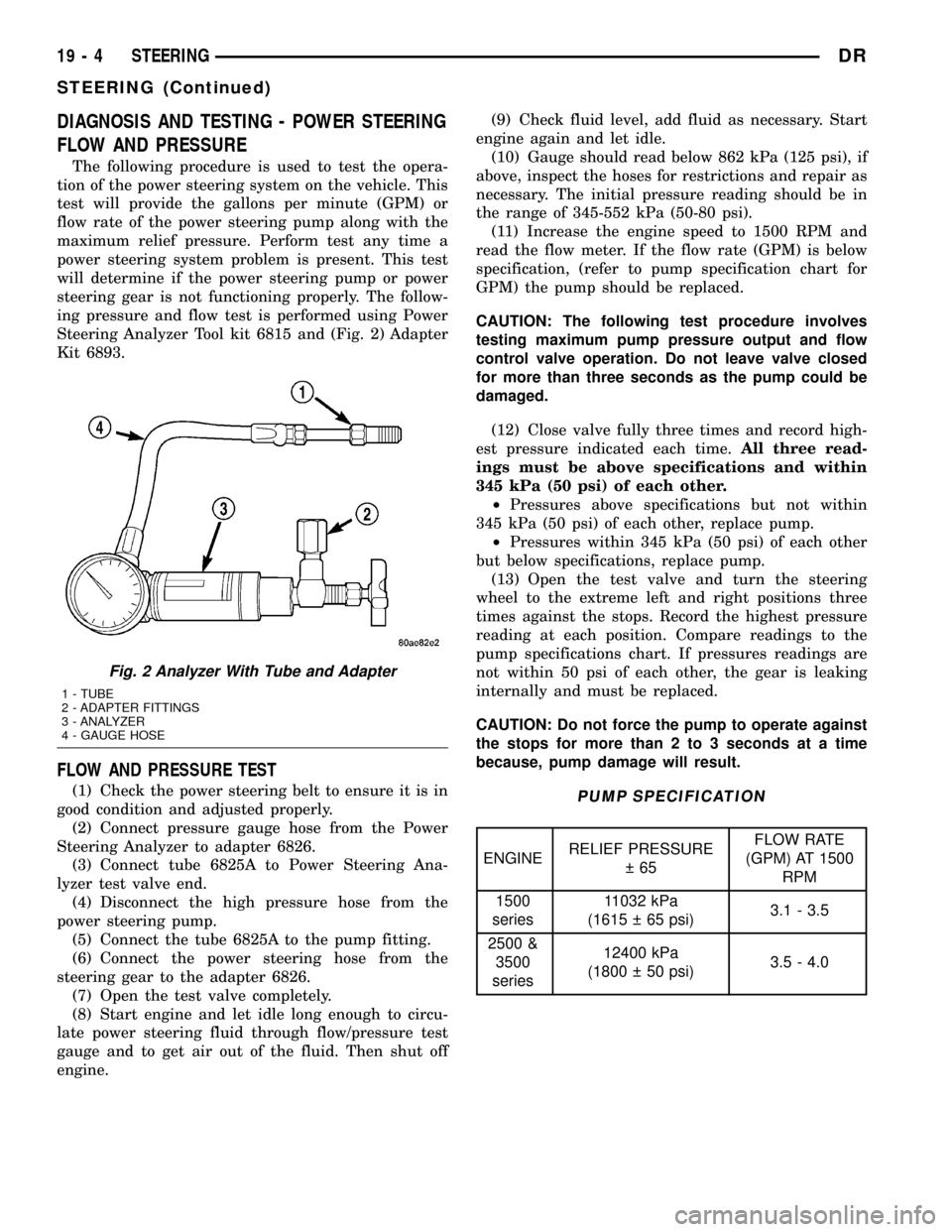
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER STEERING
FLOW AND PRESSURE
The following procedure is used to test the opera-
tion of the power steering system on the vehicle. This
test will provide the gallons per minute (GPM) or
flow rate of the power steering pump along with the
maximum relief pressure. Perform test any time a
power steering system problem is present. This test
will determine if the power steering pump or power
steering gear is not functioning properly. The follow-
ing pressure and flow test is performed using Power
Steering Analyzer Tool kit 6815 and (Fig. 2) Adapter
Kit 6893.
FLOW AND PRESSURE TEST
(1) Check the power steering belt to ensure it is in
good condition and adjusted properly.
(2) Connect pressure gauge hose from the Power
Steering Analyzer to adapter 6826.
(3) Connect tube 6825A to Power Steering Ana-
lyzer test valve end.
(4) Disconnect the high pressure hose from the
power steering pump.
(5) Connect the tube 6825A to the pump fitting.
(6) Connect the power steering hose from the
steering gear to the adapter 6826.
(7) Open the test valve completely.
(8) Start engine and let idle long enough to circu-
late power steering fluid through flow/pressure test
gauge and to get air out of the fluid. Then shut off
engine.(9) Check fluid level, add fluid as necessary. Start
engine again and let idle.
(10) Gauge should read below 862 kPa (125 psi), if
above, inspect the hoses for restrictions and repair as
necessary. The initial pressure reading should be in
the range of 345-552 kPa (50-80 psi).
(11) Increase the engine speed to 1500 RPM and
read the flow meter. If the flow rate (GPM) is below
specification, (refer to pump specification chart for
GPM) the pump should be replaced.
CAUTION: The following test procedure involves
testing maximum pump pressure output and flow
control valve operation. Do not leave valve closed
for more than three seconds as the pump could be
damaged.
(12) Close valve fully three times and record high-
est pressure indicated each time.All three read-
ings must be above specifications and within
345 kPa (50 psi) of each other.
²Pressures above specifications but not within
345 kPa (50 psi) of each other, replace pump.
²Pressures within 345 kPa (50 psi) of each other
but below specifications, replace pump.
(13) Open the test valve and turn the steering
wheel to the extreme left and right positions three
times against the stops. Record the highest pressure
reading at each position. Compare readings to the
pump specifications chart. If pressures readings are
not within 50 psi of each other, the gear is leaking
internally and must be replaced.
CAUTION: Do not force the pump to operate against
the stops for more than 2 to 3 seconds at a time
because, pump damage will result.PUMP SPECIFICATION
ENGINERELIEF PRESSURE
65FLOW RATE
(GPM) AT 1500
RPM
1500
series11032 kPa
(1615 65 psi)3.1 - 3.5
2500 &
3500
series12400 kPa
(1800 50 psi)3.5 - 4.0
Fig. 2 Analyzer With Tube and Adapter
1 - TUBE
2 - ADAPTER FITTINGS
3 - ANALYZER
4 - GAUGE HOSE
19 - 4 STEERINGDR
STEERING (Continued)
Page 1823 of 2627

(10) Install reverse countershaft rear bearing onto
the countershaft reverse gear assembly with Installer
C-4652 and Handle C-4171.
(11) Install reverse idler gear rear bearing, bearing
spacer, front bearing, and front thrust washer onto
the idler gear shaft.
(12) Install idler and reverse countershaft gears
together (Fig. 90).
(13) Install reverse idler thrust washer from the
reverse idler.
(14) Install crossover cam rollers and pin (Fig. 91).EXTENSION/ADAPTER HOUSING
(1) Install extension housing bushing with
Installer 8156 and Handle C-4171, if necessary. The
oil feed hole must be at the 12 o'clock position when
installed.
(2) On 4X2 vehicles, install extension housing seal
with Installer 8154 and Handle C-4171, with the
weep hole at the bottom.
NOTE: Drain hole located in the dust boot portion
of the seal must face downward ( toward the
ground) when installed.
(3) On 4X4 vehicles, install adapter housing seal
with Installer C-3860-A and Handle C-4171.
(4) Install the crossover cam bushing into the
extension/adapter housing with Installer 8239 and
Handle C-4171.
(5) Clean the rear of the transmission case of all
sealer.
(6) Install reverse countershaft gear bearing race
onto the reverse countershaft gear bearing.
(7) Measure the distance from the back of the
bearing race to Gauge Bar 6311 (Fig. 92).
(8) Measure thickness of the gauge bar and record
the total of the two measurements.
(9) Clean all the sealer from the extension/adapter
housing.
Fig. 90 REVERSE IDLER AND COUNTERSHAFT
GEARS
1 - REVERSE IDLER GEAR
2 - COUNTERSHAFT REVERSE GEAR
Fig. 91 CROSSOVER CAM ROLLERS AND PIN
1 - CROSSOVER CAM PIN
2 - CROSSOVER CAM ROLLERS
Fig. 92 Measure Height of Reverse Countershaft
1 - MEASURE DISTANCE FROM RACE TO GAUGE BAR
21 - 120 MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600DR
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1824 of 2627

(10) Place Gauge Bar 6311 across the housing face.
Measure the distance from the top of the bar to the
bottom of the reverse countershaft bearing race bore
(Fig. 93).
(11) Subtract thickness of the gauge bar from the
measurement and record the result.
(12) The difference between the two measurements
is the end-play for the reverse countershaft gear
assembly.
(13) Install shims to achieve 0.15-0.25 mm (0.006-
0.010 in.) end-play for the reverse countershaft gear
assembly into the reverse countershaft bearing race
bore.
(14) Use Installer to install the reverse counter-
shaft bearing race into the extension/adapter hous-
ing.
(15) Install back-up lamp switch into the exten-
sion/adapter housing and tighten to 28 N´m (20
ft.lbs.).
(16) Install crossover cam into the extension/
adapter housing.
(17) Install bolt to hold the crossover cam to the
extension/adapter housing (Fig. 94).
(18) Install crossover detent plunger, spring and
plug into the extension/adapter housing. Tighten the
plug to 47.5 N´m (35 ft.lbs.) (Fig. 95).
(19) Apply sealer to the surface of the transmis-
sion case.
(20) Install extension/adapter housing onto the
transmission case.(21) Install bolts to hold the extension/adapter
housing onto the transmission gear case. Tighten
bolts to 48 N´m (35 ft.lbs.).
(22) Install shift rail blocker bolt and tighten bolt
to 55 N´m (41 ft.lbs.).
(23) Install primary shift rail detent plunger,
spring and plug into the transmission case. Tighten
detent plug to 47.5 N´m (35 ft.lbs.).
(24) Install shift tower onto the transmission case
and tighten bolts to 9 N´m (7 ft.lbs.).
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If installing a new transmission, use all com-
ponents supplied with the transmission. If a new
shift tower is supplied with the new transmission,
do not re-use the original shift tower.
Fig. 93 MEASURE DEPTH OF REVERSE
COUNTERSHAFT GEAR BEARING RACE BORE
1 - GAUGE BAR TO BEARING RACE BORE MEASUREMENT
Fig. 94 CROSSOVER CAM BOLT
1 - CROSSOVER CAM
2 - BOLT
3 - EXTENSION HOUSING
Fig. 95 CROSSOVER CAM DETENT PLUG
1 - DETENT PLUG
2 - EXTENSION HOUSING
DRMANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 21 - 121
MANUAL TRANSMISSION - NV5600 (Continued)
Page 1844 of 2627
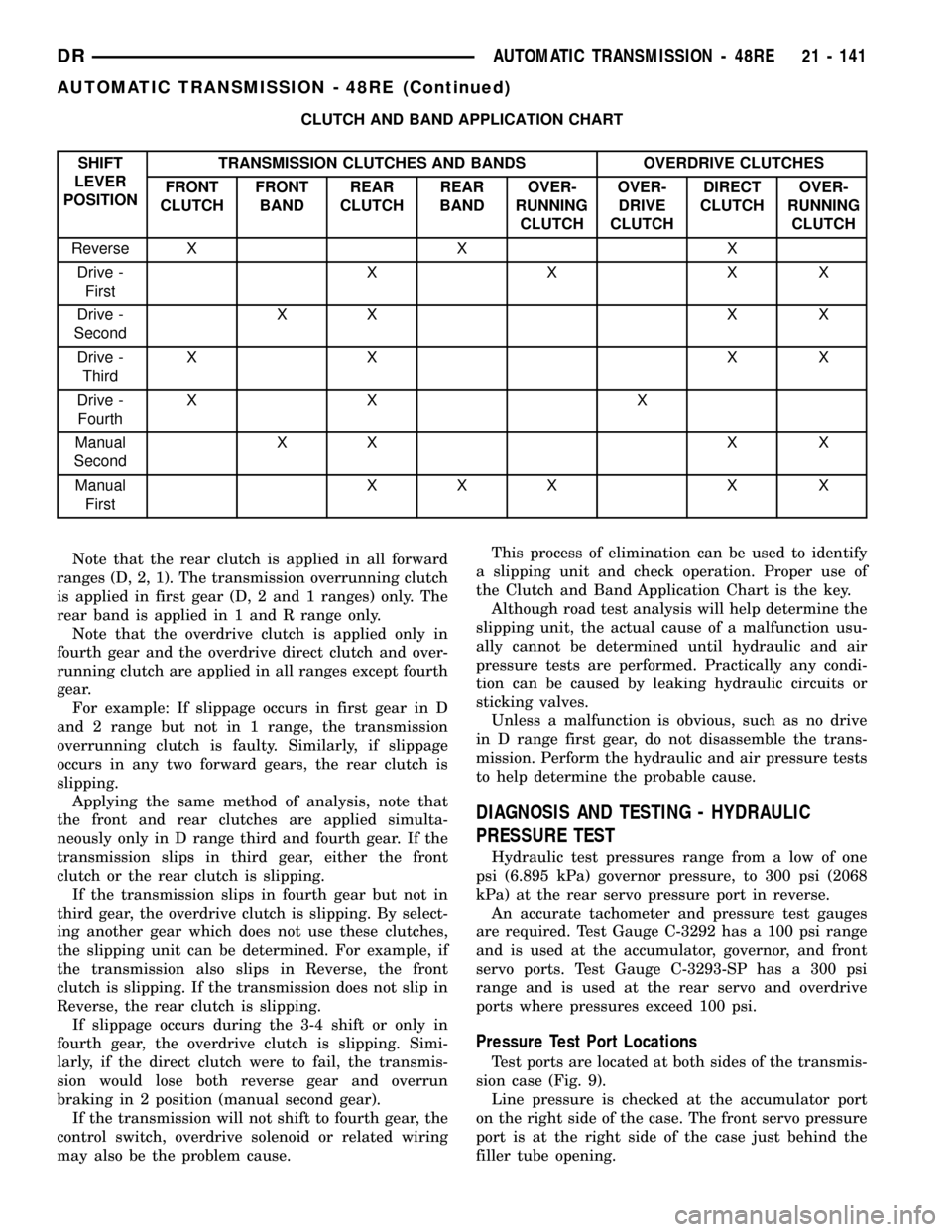
CLUTCH AND BAND APPLICATION CHART
SHIFT
LEVER
POSITIONTRANSMISSION CLUTCHES AND BANDS OVERDRIVE CLUTCHES
FRONT
CLUTCHFRONT
BANDREAR
CLUTCHREAR
BANDOVER-
RUNNING
CLUTCHOVER-
DRIVE
CLUTCHDIRECT
CLUTCHOVER-
RUNNING
CLUTCH
Reverse X X X
Drive -
FirstXXXX
Drive -
SecondXX X X
Drive -
ThirdXX XX
Drive -
FourthXX X
Manual
SecondXX X X
Manual
FirstXXX X X
Note that the rear clutch is applied in all forward
ranges (D, 2, 1). The transmission overrunning clutch
is applied in first gear (D, 2 and 1 ranges) only. The
rear band is applied in 1 and R range only.
Note that the overdrive clutch is applied only in
fourth gear and the overdrive direct clutch and over-
running clutch are applied in all ranges except fourth
gear.
For example: If slippage occurs in first gear in D
and 2 range but not in 1 range, the transmission
overrunning clutch is faulty. Similarly, if slippage
occurs in any two forward gears, the rear clutch is
slipping.
Applying the same method of analysis, note that
the front and rear clutches are applied simulta-
neously only in D range third and fourth gear. If the
transmission slips in third gear, either the front
clutch or the rear clutch is slipping.
If the transmission slips in fourth gear but not in
third gear, the overdrive clutch is slipping. By select-
ing another gear which does not use these clutches,
the slipping unit can be determined. For example, if
the transmission also slips in Reverse, the front
clutch is slipping. If the transmission does not slip in
Reverse, the rear clutch is slipping.
If slippage occurs during the 3-4 shift or only in
fourth gear, the overdrive clutch is slipping. Simi-
larly, if the direct clutch were to fail, the transmis-
sion would lose both reverse gear and overrun
braking in 2 position (manual second gear).
If the transmission will not shift to fourth gear, the
control switch, overdrive solenoid or related wiring
may also be the problem cause.This process of elimination can be used to identify
a slipping unit and check operation. Proper use of
the Clutch and Band Application Chart is the key.
Although road test analysis will help determine the
slipping unit, the actual cause of a malfunction usu-
ally cannot be determined until hydraulic and air
pressure tests are performed. Practically any condi-
tion can be caused by leaking hydraulic circuits or
sticking valves.
Unless a malfunction is obvious, such as no drive
in D range first gear, do not disassemble the trans-
mission. Perform the hydraulic and air pressure tests
to help determine the probable cause.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST
Hydraulic test pressures range from a low of one
psi (6.895 kPa) governor pressure, to 300 psi (2068
kPa) at the rear servo pressure port in reverse.
An accurate tachometer and pressure test gauges
are required. Test Gauge C-3292 has a 100 psi range
and is used at the accumulator, governor, and front
servo ports. Test Gauge C-3293-SP has a 300 psi
range and is used at the rear servo and overdrive
ports where pressures exceed 100 psi.
Pressure Test Port Locations
Test ports are located at both sides of the transmis-
sion case (Fig. 9).
Line pressure is checked at the accumulator port
on the right side of the case. The front servo pressure
port is at the right side of the case just behind the
filler tube opening.
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 141
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1845 of 2627

The rear servo and governor pressure ports are at
the right rear of the transmission case. The overdrive
clutch pressure port is at the left rear of the case.
Test One - Transmission In Manual Low
This test checks pump output, pressure regulation,
and condition of the rear clutch and servo circuit.
Both test gauges are required for this test.
(1) Connect tachometer to engine. Position tachom-
eter so it can be observed from driver seat if helper
will be operating engine. Raise vehicle on hoist that
will allow rear wheels to rotate freely.
(2) Connect 100 psi Gauge C-3292 to accumulator
port. Then connect 300 psi Gauge C-3293-SP to rear
servo port.
(3) Disconnect throttle and gearshift cables from
levers on transmission valve body manual shaft.
(4) Have helper start and run engine at 1000 rpm.
(5) Move transmission shift lever fully forward
into 1 range.
(6) Gradually move transmission throttle lever
from full forward to full rearward position and note
pressures on both gauges:²Line pressure at accumulator port should be
54-60 psi (372-414 kPa) with throttle lever forward
and gradually increase to 90-96 psi (621-662 kPa) as
throttle lever is moved rearward.
²Rear servo pressure should be same as line pres-
sure within 3 psi (20.68 kPa).
Test Two - Transmission In 2 Range
This test checks pump output, line pressure and
pressure regulation. Use 100 psi Test Gauge C-3292
for this test.
(1) Leave vehicle in place on hoist and leave Test
Gauge C-3292 connected to accumulator port.
(2) Have helper start and run engine at 1000 rpm.
(3) Move transmission shift lever one detent rear-
ward from full forward position. This is 2 range.
(4) Move transmission throttle lever from full for-
ward to full rearward position and read pressure on
gauge.
(5) Line pressure should be 54-60 psi (372-414
kPa) with throttle lever forward and gradually
increase to 90-96 psi (621-662 kPa) as lever is moved
rearward.
Test Three - Transmission In D Range Third Gear
This test checks pressure regulation and condition
of the clutch circuits. Both test gauges are required
for this test.
(1) Turn OD switch off.
(2) Leave vehicle on hoist and leave Gauge C-3292
in place at accumulator port.
(3) Move Gauge C-3293-SP over to front servo port
for this test.
(4) Have helper start and run engine at 1600 rpm
for this test.
(5) Move transmission shift lever two detents rear-
ward from full forward position. This is D range.
(6) Read pressures on both gauges as transmission
throttle lever is gradually moved from full forward to
full rearward position:
²Line pressure at accumulator in D range third
gear, should be 54-60 psi (372-414 kPa) with throttle
lever forward and increase as lever is moved rear-
ward.
²Front servo pressure in D range third gear,
should be within 3 psi (21 kPa) of line pressure up to
kickdown point.
Test Four - Transmission In Reverse
This test checks pump output, pressure regulation
and the front clutch and rear servo circuits. Use 300
psi Test Gauge C-3293-SP for this test.
(1) Leave vehicle on hoist and leave gauge C-3292
in place at accumulator port.
(2) Move 300 psi Gauge C-3293-SP back to rear
servo port.
Fig. 9 Pressure Test Port Locations
1 - REAR SERVO TEST PORT
2 - GOVERNOR TEST PORT
3 - ACCUMULATOR TEST PORT
4 - FRONT SERVO TEST PORT
5 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH TEST PORT
21 - 142 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1846 of 2627

(3) Have helper start and run engine at 1600 rpm
for test.
(4)
Move transmission shift lever four detents rear-
ward from full forward position. This is Reverse range.
(5) Move transmission throttle lever fully forward
then fully rearward and note reading at Gauge
C-3293-SP.
(6) Pressure should be 145 - 175 psi (1000-1207
kPa) with throttle lever forward and increase to 230 -
280 psi (1586-1931 kPa) as lever is gradually moved
rearward.
Test Five - Governor Pressure
This test checks governor operation by measuring
governor pressure response to changes in vehicle
speed. It is usually not necessary to check governor
operation unless shift speeds are incorrect or if the
transmission will not downshift. The test should be
performed on the road or on a hoist that will allow
the rear wheels to rotate freely.
(1) Move 100 psi Test Gauge C-3292 to governor
pressure port.
(2) Move transmission shift lever two detents rear-
ward from full forward position. This is D range.
(3) Have helper start and run engine at curb idle
speed. Then firmly apply service brakes so wheels
will not rotate.
(4) Note governor pressure:
²
Governor pressure should be no more than 20.6
kPa (3 psi) at curb idle speed and wheels not rotating.
²If pressure exceeds 20.6 kPa (3 psi), a fault
exists in governor pressure control system.
(5) Release brakes, slowly increase engine speed,
and observe speedometer and pressure test gauge (do
not exceed 30 mph on speedometer). Governor pres-
sure should increase in proportion to vehicle speed.
Or approximately 6.89 kPa (1 psi) for every 1 mph.
(6) Governor pressure rise should be smooth and
drop back to no more than 20.6 kPa (3 psi), after
engine returns to curb idle and brakes are applied to
prevent wheels from rotating.
(7)
Compare results of pressure test with analysis
chart.
Test Six - Transmission In Overdrive Fourth Gear
This test checks line pressure at the overdrive
clutch in fourth gear range. Use 300 psi Test Gauge
C-3293-SP for this test. The test should be performed
on the road or on a chassis dyno.
(1)
Remove tachometer; it is not needed for this test.
(2) Move 300 psi Gauge to overdrive clutch pres-
sure test port. Then remove other gauge and reinstall
test port plug.
(3) Lower vehicle.
(4) Turn OD switch on.(5) Secure test gauge so it can be viewed from
drivers seat.
(6) Start engine and shift into D range.
(7) Increase vehicle speed gradually until 3-4 shift
occurs and note gauge pressure.
(8) Pressure should be 524-565 kPa (76-82 psi)
with closed throttle and increase to 690-896 kPa
(100-130 psi) at 1/2 to 3/4 throttle. Note that pres-
sure can increase to around 965 kPa (140 psi) at full
throttle.
(9) Return to shop or move vehicle off chassis
dyno.
PRESSURE TEST ANALYSIS CHART
TEST CONDITION INDICATION
Line pressure OK during
any one testPump and regulator
valve OK
Line pressure OK in R
but low in D, 2, 1Leakage in rear clutch
area (seal rings, clutch
seals)
Pressure low in D Fourth
Gear RangeOverdrive clutch piston
seal, or check ball
problem
Pressure OK in 1, 2 but
low in D3 and RLeakage in front clutch
area
Pressure OK in 2 but low
in R and 1Leakage in rear servo
Front servo pressure in 2 Leakage in servo; broken
servo ring or cracked
servo piston
Pressure low in all
positionsClogged filter, stuck
regulator valve, worn or
faulty pump, low oil level
Governor pressure too
high at idle speedGovernor pressure
solenoid valve system
fault. Refer to diagnostic
book.
Governor pressure low at
all mph figuresFaulty governor pressure
solenoid, transmission
control module, or
governor pressure
sensor
Lubrication pressure low
at all throttle positionsClogged fluid cooler or
lines, seal rings leaking,
worn pump bushings,
pump, clutch retainer, or
clogged filter.
Line pressure high Output shaft plugged,
sticky regulator valve
Line pressure low Sticky regulator valve,
clogged filter, worn pump
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 143
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)