Evap DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 1111 of 2627
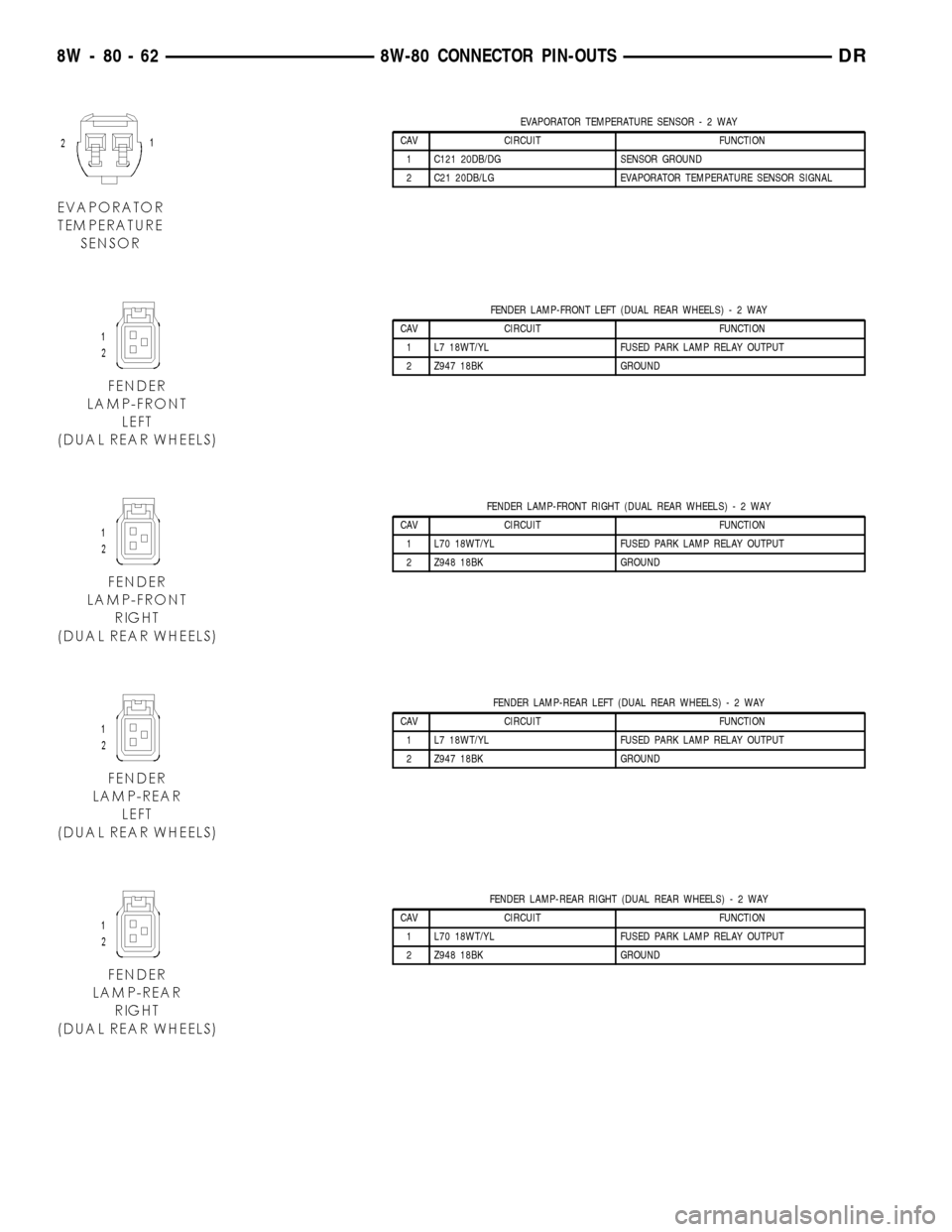
EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR-2WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 C121 20DB/DG SENSOR GROUND
2 C21 20DB/LG EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR SIGNAL
FENDER LAMP-FRONT LEFT (DUAL REAR WHEELS)-2WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 L7 18WT/YL FUSED PARK LAMP RELAY OUTPUT
2 Z947 18BK GROUND
FENDER LAMP-FRONT RIGHT (DUAL REAR WHEELS)-2WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 L70 18WT/YL FUSED PARK LAMP RELAY OUTPUT
2 Z948 18BK GROUND
FENDER LAMP-REAR LEFT (DUAL REAR WHEELS)-2WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 L7 18WT/YL FUSED PARK LAMP RELAY OUTPUT
2 Z947 18BK GROUND
FENDER LAMP-REAR RIGHT (DUAL REAR WHEELS)-2WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 L70 18WT/YL FUSED PARK LAMP RELAY OUTPUT
2 Z948 18BK GROUND
8W - 80 - 62 8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN-OUTSDR
Page 1139 of 2627

POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE C3 (NGC) - WHITE 38 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1- -
2- -
3 K51 20BR/WT ASD RELAY CONTROL
4- -
5 V35 20VT/OR (4.7L) S/C VENT CONTROL
6 K173 18BR/VT CONDENSER FAN RELAY CONTROL
7 V32 20VT/YL (4.7L) S/C POWER SUPPLY
8 K106 18VT/LB NVLD SOLENOID CONTROL
9 K299 18BR/WT O2 1/2 HEATER CONTROL
10 K399 18BR/GY O2 2/2 HEATER CONTROL
11 C13 20LB/OR A/C CLUTCH RELAY CONTROL
12 V36 20VT/YL (4.7L) S/C VACUUM CONTROL
13 - -
14 V32 20VT/YL (5.7L) BRAKE SWITCH NO. 2 SIGNAL
15 V937 20VT/BR (5.7L) S/C SWITCH RETURN
16 K167 20BR/YL (5.7L) APPS NO. 1 RETURN
17 K400 20BR/VT (5.7L) APPS NO. 2 RETURN
18 V38 20VT/OR (5.7L) S/C SWITCH NO. 2 SIGNAL
19 K342 16BR/WT ASD RELAY OUTPUT
20 K52 18DB/WT EVAP PURGE CONTROL
21 T41 20YL/DB TRS T41 SENSE
22 G113 18VT PTO SWITCH SENSE
23 B29 20DG/WT BRAKE SWITCH SIGNAL
24 - -
25 K23 20BR/WT (5.7L) APPS NO. 1 SIGNAL
26 - -
27 - -
28 K342 16BR/WT ASD RELAY OUTPUT
29 K70 18DB/BR EVAP PURGE RETURN
30 K66 18DB/WT P/S SWITCH SIGNAL
31 - -
32 K25 18DB/VT BATT TEMP SIGNAL
33 N4 18DB/WT (3.7L/4.7L) FUEL LEVEL SENSOR SIGNAL
33 N4 20DB/WT (5.7L) FUEL LEVEL SENSOR SIGNAL
34 V37 20VT S/C SWITCH NO. 1 SIGNAL
35 K107 18VT/WT NVLD SWITCH SIGNAL
36 K29 20WT/BR (5.7L) APPS NO. 2 SIGNAL
37 K31 20BR FUEL PUMP RELAY CONTROL
38 T752 20DG/OR STARTER RELAY CONTROL
8W - 80 - 90 8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN-OUTSDR
Page 1157 of 2627
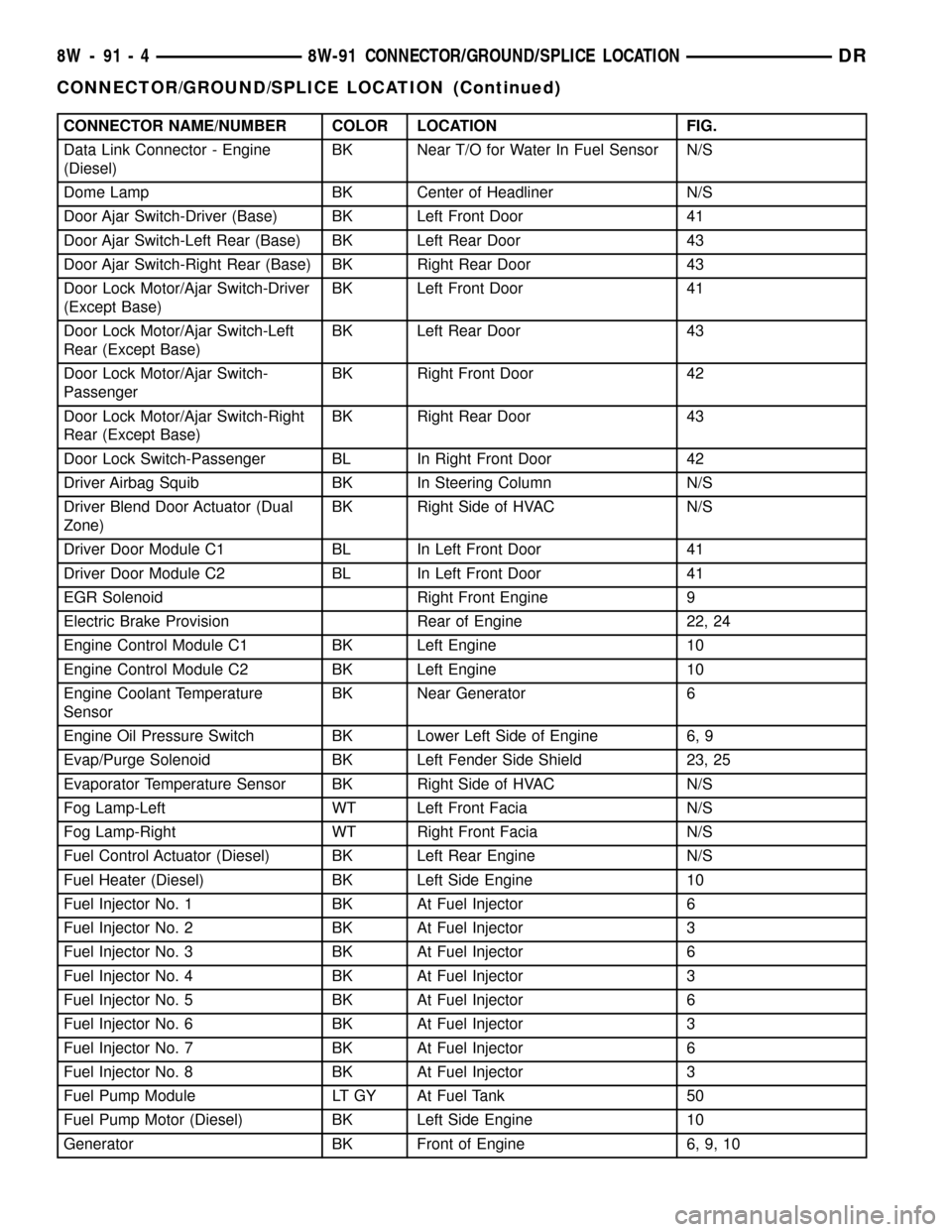
CONNECTOR NAME/NUMBER COLOR LOCATION FIG.
Data Link Connector - Engine
(Diesel)BK Near T/O for Water In Fuel Sensor N/S
Dome Lamp BK Center of Headliner N/S
Door Ajar Switch-Driver (Base) BK Left Front Door 41
Door Ajar Switch-Left Rear (Base) BK Left Rear Door 43
Door Ajar Switch-Right Rear (Base) BK Right Rear Door 43
Door Lock Motor/Ajar Switch-Driver
(Except Base)BK Left Front Door 41
Door Lock Motor/Ajar Switch-Left
Rear (Except Base)BK Left Rear Door 43
Door Lock Motor/Ajar Switch-
PassengerBK Right Front Door 42
Door Lock Motor/Ajar Switch-Right
Rear (Except Base)BK Right Rear Door 43
Door Lock Switch-Passenger BL In Right Front Door 42
Driver Airbag Squib BK In Steering Column N/S
Driver Blend Door Actuator (Dual
Zone)BK Right Side of HVAC N/S
Driver Door Module C1 BL In Left Front Door 41
Driver Door Module C2 BL In Left Front Door 41
EGR Solenoid Right Front Engine 9
Electric Brake Provision Rear of Engine 22, 24
Engine Control Module C1 BK Left Engine 10
Engine Control Module C2 BK Left Engine 10
Engine Coolant Temperature
SensorBK Near Generator 6
Engine Oil Pressure Switch BK Lower Left Side of Engine 6, 9
Evap/Purge Solenoid BK Left Fender Side Shield 23, 25
Evaporator Temperature Sensor BK Right Side of HVAC N/S
Fog Lamp-Left WT Left Front Facia N/S
Fog Lamp-Right WT Right Front Facia N/S
Fuel Control Actuator (Diesel) BK Left Rear Engine N/S
Fuel Heater (Diesel) BK Left Side Engine 10
Fuel Injector No. 1 BK At Fuel Injector 6
Fuel Injector No. 2 BK At Fuel Injector 3
Fuel Injector No. 3 BK At Fuel Injector 6
Fuel Injector No. 4 BK At Fuel Injector 3
Fuel Injector No. 5 BK At Fuel Injector 6
Fuel Injector No. 6 BK At Fuel Injector 3
Fuel Injector No. 7 BK At Fuel Injector 6
Fuel Injector No. 8 BK At Fuel Injector 3
Fuel Pump Module LT GY At Fuel Tank 50
Fuel Pump Motor (Diesel) BK Left Side Engine 10
Generator BK Front of Engine 6, 9, 10
8W - 91 - 4 8W-91 CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATIONDR
CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATION (Continued)
Page 1413 of 2627

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION OR
SPARK PLUGS OIL FOULED1. CCV System malfunction 1. (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS
CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE
EMISSIONS - DESCRIPTION) for
correct operation
2. Defective valve stem seal(s) 2. Repair or replace seal(s)
3. Worn or broken piston rings 3. Hone cylinder bores. Install new
rings
4. Scuffed pistons/cylinder walls 4. Hone cylinder bores and replace
pistons as required
5. Carbon in oil control ring groove 5. Remove rings and de-carbon piston
6. Worn valve guides 6. Inspect/replace valve guides as
necessary
7. Piston rings fitted too tightly in
grooves7. Remove rings and check ring end
gap and side clearance. Replace if
necessary
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR DAMAGED
OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐHYDROSTATIC
LOCK
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Disconnect the negative cable(s) from the bat-
tery.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system, and
intake manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure
in the cylinder head. Remove the spark plugs.(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (coolant, fuel,
oil, etc.).
(7) Be sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt a small amount of engine oil into the
cylinders to lubricate the walls. This will prevent
damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs. Tighten the spark
plugs to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(15) Connect the negative cable(s) to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
REMOVAL
(1) Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release pro-
cedure (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIV-
ERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(3) Remove the air cleaner resonator and duct
work as an assembly.
(4) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
9 - 190 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)
Page 1423 of 2627

þ Loss of engine power
þ Engine misfiring
þ Poor fuel economy
²Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
þ Engine overheating
þ Loss of coolant
þ Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
þ Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test in this
section. An engine cylinder head gasket leaking
between adjacent cylinders will result in approxi-
mately a 50±70% reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Drain cooling system.
(3) Remove the air cleaner resonator and duct
work.
(4) Remove the generator.
(5) Remove closed crankcase ventilation system.
(6) Disconnect the evaporation control system.
(7) Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release pro-
cedure (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIV-
ERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE). Disconnect the
fuel supply line (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FITTING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(8) Disconnect heater hoses.
(9) Remove cylinder head covers and gaskets.
(10) Remove intake manifold and throttle body as
an assembly.
(11) Remove rocker arm assemblies and push rods.
Identify to ensure installation in original locations.
(12) Remove the head bolts from each cylinder
head and remove cylinder heads. Discard the cylin-
der head gasket.
CLEANING
Clean all surfaces of cylinder block and cylinder
heads.
Clean cylinder block front and rear gasket surfaces
using a suitable solvent.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect the cylinder head for out-of-flatness,
using a straightedge and a feeler gauge. If tolerances
exceed 0.0508 mm (0.002 in.) replace the cylinder
head.
(2) Inspect the valve seats for damage. Service the
valve seats as necessary.
(3) Inspect the valve guides for wear, cracks or
looseness. If either condition exist, replace the cylin-
der head.
(4) Inspect pushrods. Replace worn or bent push-
rods.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean all surfaces of cylinder block and cylin-
der heads.
(2) Clean cylinder block front and rear gasket sur-
faces using a suitable solvent.
CAUTION: The head gaskets are not interchange-
able between left and right sides. They are marked
ªLº and ªRº to indicate left and right sides.
(3) Position new cylinder head gaskets onto the
cylinder block.
9 - 200 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1424 of 2627
CAUTION: The head gaskets are marked ªTOPº to
indicate which side goes up.
(4) Position cylinder heads onto head gaskets and
cylinder block.
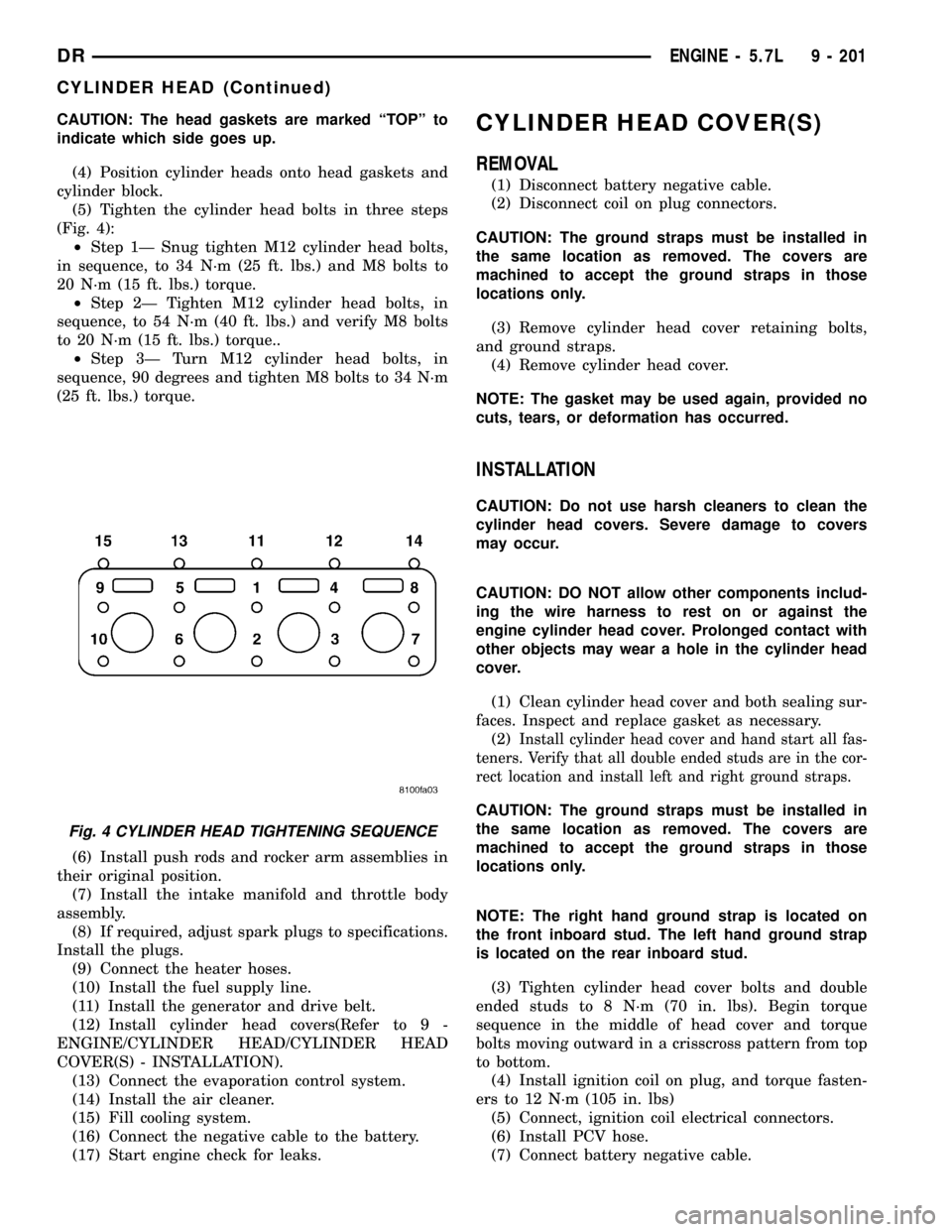
(5) Tighten the cylinder head bolts in three steps
(Fig. 4):
²Step 1Ð Snug tighten M12 cylinder head bolts,
in sequence, to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) and M8 bolts to
20 N´m (15 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Step 2Ð Tighten M12 cylinder head bolts, in
sequence, to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) and verify M8 bolts
to 20 N´m (15 ft. lbs.) torque..
²Step 3Ð Turn M12 cylinder head bolts, in
sequence, 90 degrees and tighten M8 bolts to 34 N´m
(25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Install push rods and rocker arm assemblies in
their original position.
(7) Install the intake manifold and throttle body
assembly.
(8) If required, adjust spark plugs to specifications.
Install the plugs.
(9) Connect the heater hoses.
(10) Install the fuel supply line.
(11) Install the generator and drive belt.
(12) Install cylinder head covers(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(13) Connect the evaporation control system.
(14) Install the air cleaner.
(15) Fill cooling system.
(16) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
(17) Start engine check for leaks.CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Disconnect coil on plug connectors.
CAUTION: The ground straps must be installed in
the same location as removed. The covers are
machined to accept the ground straps in those
locations only.
(3) Remove cylinder head cover retaining bolts,
and ground straps.
(4) Remove cylinder head cover.
NOTE: The gasket may be used again, provided no
cuts, tears, or deformation has occurred.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Do not use harsh cleaners to clean the
cylinder head covers. Severe damage to covers
may occur.
CAUTION: DO NOT allow other components includ-
ing the wire harness to rest on or against the
engine cylinder head cover. Prolonged contact with
other objects may wear a hole in the cylinder head
cover.
(1) Clean cylinder head cover and both sealing sur-
faces. Inspect and replace gasket as necessary.
(2)
Install cylinder head cover and hand start all fas-
teners. Verify that all double ended studs are in the cor-
rect location and install left and right ground straps.
CAUTION: The ground straps must be installed in
the same location as removed. The covers are
machined to accept the ground straps in those
locations only.
NOTE: The right hand ground strap is located on
the front inboard stud. The left hand ground strap
is located on the rear inboard stud.
(3) Tighten cylinder head cover bolts and double
ended studs to 8 N´m (70 in. lbs). Begin torque
sequence in the middle of head cover and torque
bolts moving outward in a crisscross pattern from top
to bottom.
(4) Install ignition coil on plug, and torque fasten-
ers to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs)
(5) Connect, ignition coil electrical connectors.
(6) Install PCV hose.
(7) Connect battery negative cable.
Fig. 4 CYLINDER HEAD TIGHTENING SEQUENCE
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 201
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1571 of 2627

OPERATION
Fuel is returned through the fuel pump module
and back into the fuel tank through the fuel filter/
fuel pressure regulator. A separate fuel return line
from the engine to the tank is not used.
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
fuel pump module assembly, fuel pump module lock-
nut/gasket, and fuel tank check valve (refer to Fuel
Tank Check Valve for information).
A fuel filler/vent tube assembly using a pressure/
vacuum, 1/4 turn fuel filler cap is used. The fuel
filler tube contains a flap door located below the fuel
fill cap.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system. This is designed to
reduce the emission of fuel vapors into the atmo-sphere. The description and function of the Evapora-
tive Control System is found in Emission Control
Systems.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE
Use following procedure if the fuel injector
rail is, or is not equipped with a fuel pressure
test port.
(1) Remove fuel fill cap.
Fig. 1 FUEL DELIVERY COMPONENTS
1 - FUEL TANK 8 - LDP FRESH AIR FILTER
2 - CHECK VALVE 9 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
3 - LIQUID EXPANSION CHAMBER 10 - EVAP CANISTERS (2)
4 - FUEL FILTER / FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR 11 - FUEL TANK STRAPS (2)
5 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING AND FUEL LINE (TO ENGINE) 12 - CHECK VALVE
6 - EVAP LINE CONNECTION 13 - FUEL PUMP MODULE LOCK RING
7 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP FRESH AIR LINE 14 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERY - GASDR
FUEL DELIVERY - GAS (Continued)
Page 1573 of 2627
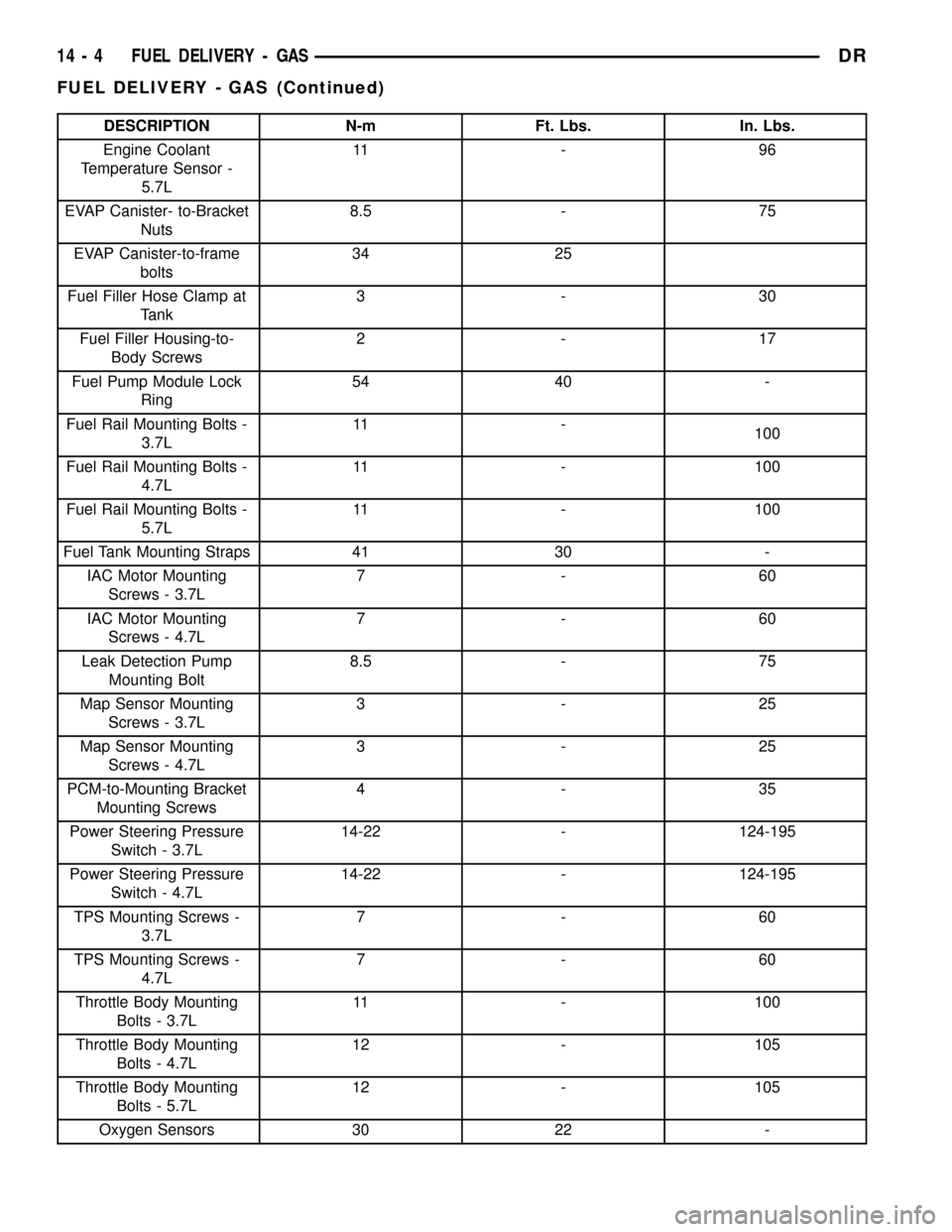
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Engine Coolant
Temperature Sensor -
5.7L11 - 9 6
EVAP Canister- to-Bracket
Nuts8.5 - 75
EVAP Canister-to-frame
bolts34 25
Fuel Filler Hose Clamp at
Tank3-30
Fuel Filler Housing-to-
Body Screws2-17
Fuel Pump Module Lock
Ring54 40 -
Fuel Rail Mounting Bolts -
3.7L11 -
100
Fuel Rail Mounting Bolts -
4.7L11 - 100
Fuel Rail Mounting Bolts -
5.7L11 - 100
Fuel Tank Mounting Straps 41 30 -
IAC Motor Mounting
Screws - 3.7L7-60
IAC Motor Mounting
Screws - 4.7L7-60
Leak Detection Pump
Mounting Bolt8.5 - 75
Map Sensor Mounting
Screws - 3.7L3-25
Map Sensor Mounting
Screws - 4.7L3-25
PCM-to-Mounting Bracket
Mounting Screws4-35
Power Steering Pressure
Switch - 3.7L14-22 - 124-195
Power Steering Pressure
Switch - 4.7L14-22 - 124-195
TPS Mounting Screws -
3.7L7-60
TPS Mounting Screws -
4.7L7-60
Throttle Body Mounting
Bolts - 3.7L11 - 100
Throttle Body Mounting
Bolts - 4.7L12 - 105
Throttle Body Mounting
Bolts - 5.7L12 - 105
Oxygen Sensors 30 22 -
14 - 4 FUEL DELIVERY - GASDR
FUEL DELIVERY - GAS (Continued)
Page 1575 of 2627

OPERATION
Fuel Pressure Regulator Operation:The pres-
sure regulator is a mechanical device that is not con-
trolled by engine vacuum or the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM).
The regulator is calibrated to maintain fuel system
operating pressure of approximately 58 2 psi at the
fuel injectors. It contains a diaphragm, calibrated
springs and a fuel return valve. The internal fuel fil-
ter (Fig. 2) is also part of the assembly.
Fuel is supplied to the filter/regulator by the elec-
tric fuel pump through an opening tube at the bot-
tom of filter/regulator (Fig. 2).
The regulator acts as a check valve to maintain
some fuel pressure when the engine is not operating.
This will help to start the engine. A second check
valve is located at the outlet end of the electric fuel
pump.Refer to Fuel Pump - Description and
Operation for more information.
If fuel pressure at the pressure regulator exceeds
approximately 60 psi, an internal diaphragm opens
and excess fuel pressure is routed back into the tank
through the bottom of pressure regulator.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT /
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) is
attached to the side of the fuel pump module. The
sending unit consists of a float, an arm, and a vari-
able resistor track (card).
OPERATION
The fuel pump module has 4 different circuits
(wires). Two of these circuits are used for the fuel
gauge sending unit for fuel gauge operation, and for
certain OBD II emission requirements. The other 2
wires are used for electric fuel pump operation.
For Fuel Gauge Operation:A constant current
source is supplied to the resistor track on the fuel
gauge sending unit. This is fed directly from the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM).NOTE: For
diagnostic purposes, this 12V power source can
only be verified with the circuit opened (fuel
pump module electrical connector unplugged).
With the connectors plugged, output voltages
will vary from about 0.6 volts at FULL, to about
8.6 volts at EMPTY (about 8.6 volts at EMPTY
for Jeep models, and about 7.0 volts at EMPTY
for Dodge Truck models).The resistor track is
used to vary the voltage (resistance) depending on
fuel tank float level. As fuel level increases, the float
and arm move up, which decreases voltage. As fuel
level decreases, the float and arm move down, which
increases voltage. The varied voltage signal is
returned back to the PCM through the sensor return
circuit.
Both of the electrical circuits between the fuel
gauge sending unit and the PCM are hard-wired (not
multi-plexed). After the voltage signal is sent from
the resistor track, and back to the PCM, the PCM
will interpret the resistance (voltage) data and send
a message across the multi-plex bus circuits to the
instrument panel cluster. Here it is translated into
the appropriate fuel gauge level reading. Refer to
Instrument Panel for additional information.
For OBD II Emission Monitor Requirements:
The PCM will monitor the voltage output sent from
the resistor track on the sending unit to indicate fuel
level. The purpose of this feature is to prevent the
OBD II system from recording/setting false misfire
and fuel system monitor diagnostic trouble codes.
The feature is activated if the fuel level in the tank
is less than approximately 15 percent of its rated
capacity. If equipped with a Leak Detection Pump
(EVAP system monitor), this feature will also be acti-
vated if the fuel level in the tank is more than
approximately 85 percent of its rated capacity.
Fig. 2 SIDE VIEW - FILTER/REGULATOR
1 - INTERNAL FUEL FILTER
2 - FUEL FLOW TO FUEL INJECTORS
3 - FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 - EXCESS FUEL BACK TO TANK
5 - FUEL INLET
6 - RUBBER GROMMET
7 - TOP OF PUMP MODULE
14 - 6 FUEL DELIVERY - GASDR
FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR (Continued)
Page 1586 of 2627

(15) Install air duct to air box.
(16) Connect battery cable to battery.
(17) Start engine and check for leaks.
5.7L V-8
(1) If fuel injectors are to be installed, refer to Fuel
Injector Removal/Installation.
(2) Clean out fuel injector machined bores in
intake manifold.
(3) Apply a small amount of engine oil to each fuel
injector o-ring. This will help in fuel rail installation.
(4) Position fuel rail/fuel injector assembly to
machined injector openings in intake manifold.
(5) Guide each injector into intake manifold. Be
careful not to tear injector o-rings.
(6) Pushrightside of fuel rail down until fuel
injectors have bottomed on shoulders. Pushleftfuel
rail down until injectors have bottomed on shoulders.
(7) Install 4 fuel rail holdown clamps and 4 mount-
ing bolts. Refer to Torque Specifications.
(8) Position spark plug cable tray and cable assem-
bly to intake manifold. Snap 4 cable tray retaining
clips into intake manifold.
(9) Install all cables to spark plugs and ignition
coils.
(10) Connect electrical connector to throttle body.
(11) Install electrical connectors to all 8 ignition
coils. Refer to Ignition Coil Removal/Installation.
(12) Connect electrical connector to throttle body.
(13) Connect electrical connectors at all fuel injec-
tors. To install connector, refer to (Fig. 17). Push con-
nector onto injector (1) and then push and lock red
colored slider (2). Verify connector is locked to injec-
tor by lightly tugging on connector.
(14) Connect fuel line latch clip and fuel line to
fuel rail. Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(15) Install air resonator to throttle body (2 bolts).
(16) Install flexible air duct to air box.
(17) Connect battery cable to battery.
(18) Start engine and check for leaks.
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION
The fuel tank is constructed of a plastic material.
Its main functions are for fuel storage and for place-
ment of the fuel pump module, and (if equipped) cer-
tain ORVR components.
OPERATION
All models pass a full 360 degree rollover test
without fuel leakage. To accomplish this, fuel and
vapor flow controls are required for all fuel tank con-
nections.Two check (control) valves are mounted into the
top of the fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Check Valve
for additional information.
An evaporation control system is connected to the
fuel tank to reduce emissions of fuel vapors into the
atmosphere. When fuel evaporates from the fuel
tank, vapors pass through vent hoses or tubes to a
charcoal canister where they are temporarily held.
When the engine is running, the vapors are drawn
into the intake manifold. Certain models are also
equipped with a self-diagnosing system using a Leak
Detection Pump (LDP) and/or an On-Board Refueling
Vapor Recovery (ORVR) system. Refer to Emission
Control System for additional information.
REMOVAL- EXCEPT DIESEL
Fuel Tank Draining
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM MAY BE UNDER
CONSTANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH THE
ENGINE OFF. THIS PRESSURE MUST BE
RELEASED BEFORE SERVICING FUEL TANK.
Two different procedures may be used to drain fuel
tank: through the fuel fill fitting on tank, or using
the DRBtscan tool. Due to a one-way check valve
installed into the fuel fill opening fitting at the tank,
the tank cannot be drained conventionally at the fill
cap.
The quickest draining procedure involves removing
the rubber fuel fill hose.
As an alternative procedure, the electric fuel pump
may be activated allowing tank to be drained at fuel
rail connection. Refer to DRB scan tool for fuel pump
activation procedures. Before disconnecting fuel line
at fuel rail, release fuel pressure. Refer to the Fuel
System Pressure Release Procedure for procedures.
Attach end of special test hose tool number 6541,
6539, 6631 or 6923 at fuel rail disconnection (tool
number will depend on model and/or engine applica-
tion). Position opposite end of this hose tool to an
approved gasoline draining station. Activate fuel
pump and drain tank until empty.
If electric fuel pump is not operating, fuel must be
drained through fuel fill fitting at tank. Refer to fol-
lowing procedures.
(1) Release fuel system pressure.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Thoroughly clean area around fuel fill fitting
and rubber fuel fill hose at tank.
(4) If vehicle is equipped with 4 doors and a 6 foot
(short) box, remove left-rear tire/wheel.
(5) Loosen clamp (Fig. 23) and disconnect rubber
fuel fill hose at tank fitting. Using an approved gas
holding tank, drain fuel tank through this fitting.
DRFUEL DELIVERY - GAS 14 - 17
FUEL RAIL (Continued)