service DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 1225 of 2627

REMOVAL.............................38
INSTALLATION.........................38
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION.........................38
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE
HONING............................38
CLEANING............................39
INSPECTION..........................39
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION.........................40
REMOVAL.............................40
INSPECTION..........................41
INSTALLATION.........................42
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE
MAIN BEARING FITTING................44
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - FRONT
REMOVAL.............................46
INSTALLATION.........................46
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR
REMOVAL.............................47
INSTALLATION.........................47
FLEX PLATE
REMOVAL.............................48
INSTALLATION.........................48
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION.........................48
STANDARD PROCEDURE
CONNECTING ROD BEARING FITTING....49
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON FITTING..51
REMOVAL.............................51
CLEANING............................52
INSPECTION..........................52
INSTALLATION.........................52
PISTON RINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING.............................53
VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL.............................55
INSTALLATION.........................56
STRUCTURAL COVER
DESCRIPTION.........................57
OPERATION...........................57
REMOVAL.............................57
INSTALLATION.........................57
FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL.............................58
INSTALLATION.........................59
REAR MOUNT
REMOVAL.............................61
INSTALLATION.........................61
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION.........................61
OPERATION...........................61
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
LEAK...............................64DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHECKING
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE................65
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR SEAL
AREA LEAKS.........................65
OIL PAN
DESCRIPTION.........................66
REMOVAL.............................66
CLEANING............................66
INSPECTION..........................66
INSTALLATION.........................66
OIL PRESSURE SENSOR/SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................67
OPERATION...........................67
REMOVAL.............................67
INSTALLATION.........................67
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL.............................67
DISASSEMBLY.........................68
INSPECTION..........................68
ASSEMBLY............................69
INSTALLATION.........................69
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL.............................70
INSTALLATION.........................70
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
SERVICE............................71
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION.........................72
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKS.....................72
REMOVAL.............................73
INSTALLATION.........................73
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION.........................74
REMOVAL.............................74
INSTALLATION.........................74
VALVE TIMING
DESCRIPTION.........................76
OPERATION...........................76
STANDARD PROCEDURE
MEASURING TIMING CHAIN WEAR.......77
SERVICE PROCEDURE - TIMING
VERIFICATION........................77
BALANCE SHAFT
REMOVAL.............................80
INSTALLATION.........................80
IDLER SHAFT
REMOVAL.............................81
INSTALLATION.........................81
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
REMOVAL.............................81
INSTALLATION.........................81
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS
REMOVAL.............................83
INSPECTION..........................84
INSTALLATION.........................85
9 - 2 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
Page 1227 of 2627
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either per-
formance (e.g., engine idles rough and stalls) or
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING) - PERFORMANCE and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)ÐMECHANICAL for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) and (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) for the fuel system diagnosis.Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following diagnosis:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING).
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
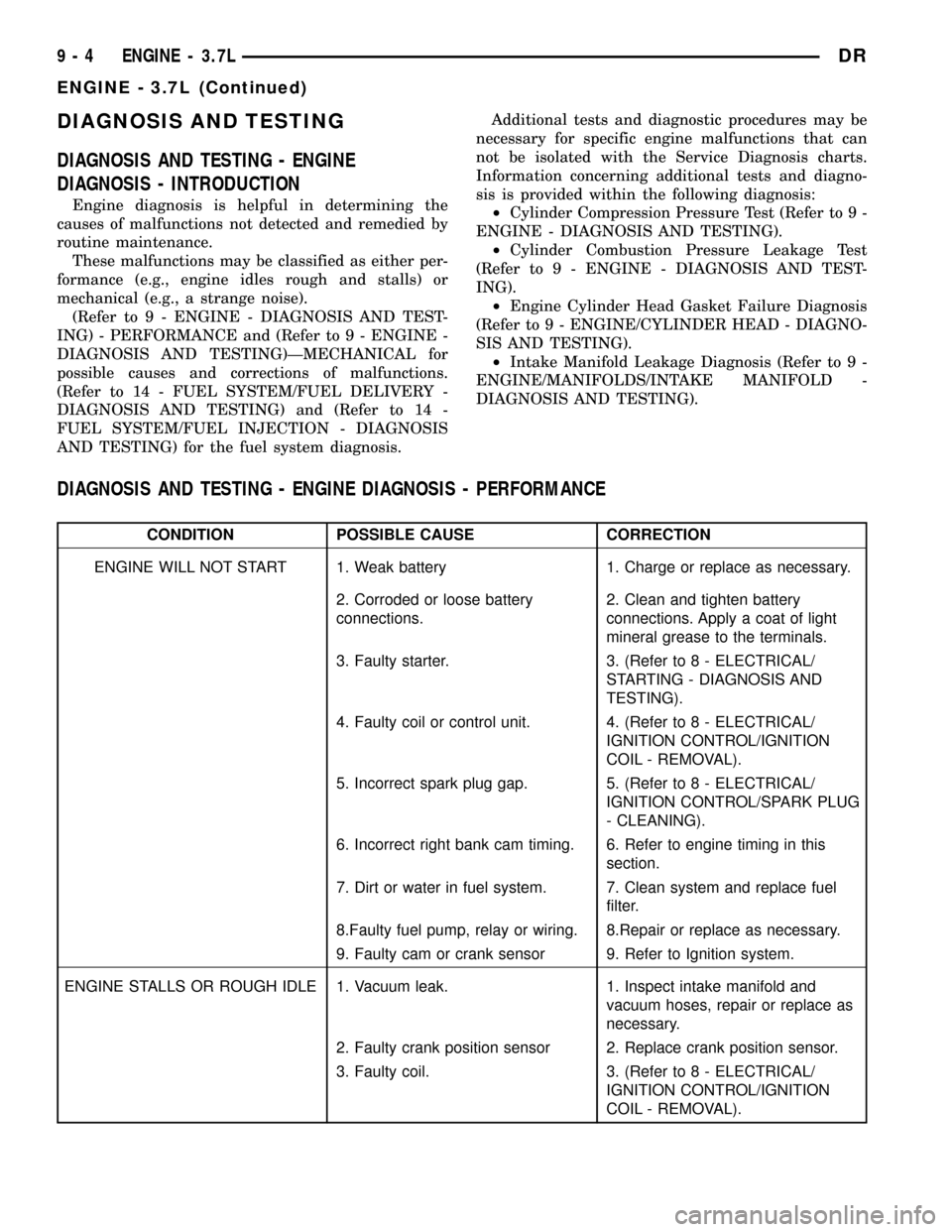
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery 1. Charge or replace as necessary.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to the terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
4. Faulty coil or control unit. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
6. Incorrect right bank cam timing. 6. Refer to engine timing in this
section.
7. Dirt or water in fuel system. 7. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
8.Faulty fuel pump, relay or wiring. 8.Repair or replace as necessary.
9. Faulty cam or crank sensor 9. Refer to Ignition system.
ENGINE STALLS OR ROUGH IDLE 1. Vacuum leak. 1. Inspect intake manifold and
vacuum hoses, repair or replace as
necessary.
2. Faulty crank position sensor 2. Replace crank position sensor.
3. Faulty coil. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
9 - 4 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)
Page 1229 of 2627
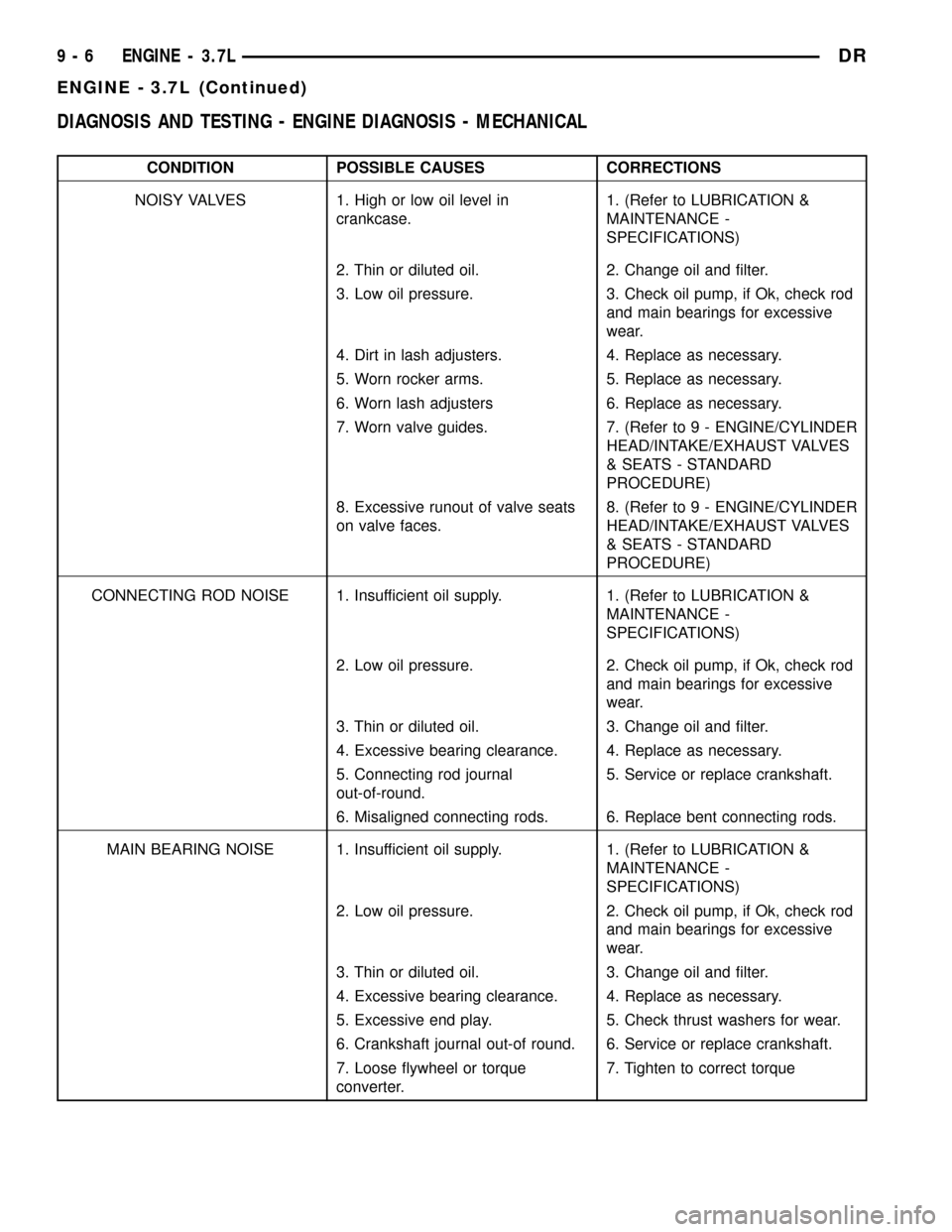
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTIONS
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil and filter.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
4. Dirt in lash adjusters. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Worn rocker arms. 5. Replace as necessary.
6. Worn lash adjusters 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Worn valve guides. 7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
8. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.8. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.5. Service or replace crankshaft.
6. Misaligned connecting rods. 6. Replace bent connecting rods.
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Excessive end play. 5. Check thrust washers for wear.
6. Crankshaft journal out-of round. 6. Service or replace crankshaft.
7. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.7. Tighten to correct torque
9 - 6 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)
Page 1256 of 2627

(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Oil leak or excessive cam bore wear in cylin-
der head.
(11) Faulty lash adjuster.
a. Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head and cam on camshaft at
base circle. Depress part of rocker arm over adjuster.
Normal adjusters should feel very firm. Spongy
adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace.
c. Before installation, make sure adjusters are at
least partially full of oil. This can be verified by little
or no plunger travel when lash adjuster is depressed.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
(3) Disconnect the exhaust pipe at the right side
exhaust manifold.
(4) Drain the engine coolant(Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Remove the intake manifold(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL).
(7) Remove the cylinder head cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove the fan shroud(Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
(9) Remove oil fill housing from cylinder head.
(10) Remove accessory drive belt(Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(11) Rotate the crankshaft until the damper timing
mark is aligned with TDC indicator mark.
(12) Verify the V6 mark on the camshaft sprocket
is at the 12 o'clock position. Rotate the crankshaft
one turn if necessary.
(13) Remove the crankshaft damper(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
REMOVAL).
(14) Remove the timing chain cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(15) Lock the secondary timing chains to the idler
sprocket using Special Tool 8429 Timing Chain Hold-
ing Fixture.NOTE: Mark the secondary timing chain prior to
removal to aid in installation.
(16) Mark the secondary timing chain, one link on
each side of the V6 mark on the camshaft drive gear.
(17) Remove the right side secondary chain ten-
sioner(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIM-
ING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(18) Remove the cylinder head access plug.
(19) Remove the right side secondary chain
guide(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
CAUTION: The nut on the right side camshaft
sprocket should not be removed for any reason, as
the sprocket and camshaft sensor target wheel is
serviced as an assembly. If the nut was removed,
torque nut to 5 N´m (44 in. lbs.).
(20) Remove the retaining bolt and the camshaft
drive gear.
CAUTION: Do not allow the engine to rotate. severe
damage to the valve train can occur.
CAUTION: Do not overlook the four smaller bolts at
the front of the cylinder head. Do not attempt to
remove the cylinder head without removing these
four bolts.
CAUTION: Do not hold or pry on the camshaft tar-
get wheel for any reason. A damaged target wheel
can result in a vehicle no start condition.
NOTE: The cylinder head is attached to the cylinder
block with twelve bolts.
(21) Remove the cylinder head retaining bolts.
(22) Remove the cylinder head and gasket. Discard
the gasket.
CAUTION: Do not lay the cylinder head on its gas-
ket sealing surface, do to the design of the cylinder
head gasket any distortion to the cylinder head
sealing surface may prevent the gasket from prop-
erly sealing resulting in leaks.
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 33
CYLINDER HEAD - RIGHT (Continued)
Page 1258 of 2627

CAUTION: The nut on the right side camshaft
sprocket should not be removed for any reason, as
the sprocket and camshaft sensor target wheel is
serviced as an assembly. If the nut was removed,
torque nut to 5 NM ( 60 in. lbs.).
(7) Position the secondary chain onto the camshaft
drive gear, making sure one marked chain link is on
either side of the V6 mark on the gear then using
Special Tool 8428 Camshaft Wrench, position the
gear onto the camshaft.
CAUTION: Remove excess oil from camshaft
sprocket retaining bolt before reinstalling bolt. Fail-
ure to do so may cause over-torquing of bolt result-
ing in bolt failure.
(8) Install the camshaft drive gear retaining bolt.
(9) Install the right side secondary chain guide(Re-
fer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/
CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION).
(10) Install the cylinder head access plug.
(11) Re-set and install the right side secondary
chain tensioner(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIM-
ING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS -
INSTALLATION).
(12) Remove Special Tool 8429.
(13) Install the timing chain cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(14) Install the crankshaft damper(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
INSTALLATION). Tighten damper bolt 175 N´m (130
Ft. Lbs.).
(15) Install accessory drive belt(Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTAL-
LATION).
(16) Install the fan shroud(Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLATION).
(17) Install the cylinder head cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(18) Install the intake manifold(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION).
(19) Install oil fill housing onto cylinder head.
(20) Refill the cooling system(Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(21) Raise the vehicle.
(22) Install the exhaust pipe onto the right
exhaust manifold.
(23) Lower the vehicle.
(24) Reconnect battery negative cable.
(25) Start the engine and check for leaks.CAMSHAFT(S)
DESCRIPTION
The camshafts consist of powdered metal steel
lobes which are sinter-bonded to a steel tube. Four
bearing journals are machined into the camshaft.
Camshaft end play is controlled by two thrust walls
that border the nose piece journal. Engine oil enters
the hollow camshafts at the third journal and lubri-
cates every intake lobe rocker through a drilled pas-
sage in the intake lobe.
REMOVAL
CAUTION: When the timing chain is removed and
the cylinder heads are still installed, DO NOT force-
fully rotate the camshafts or crankshaft indepen-
dently of each other. Severe valve and/or piston
damage can occur.
CAUTION: When removing the cam sprocket, timing
chains or camshaft, Failure to use special tool 8379
will result in hydraulic tensioner ratchet over exten-
sion, Requiring timing chain cover removal to re-set
the tensioner ratchet.
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Set engine to TDC cylinder No. 1, camshaft
sprocket V6 marks at the 12 o'clock position.
(3) Mark one link on the secondary timing chain
on both sides of the V6 mark on the camshaft
sprocket to aid in installation.
CAUTION: Do not hold or pry on the camshaft tar-
get wheel for any reason, Severe damage will occur
to the target wheel. A damaged target wheel could
cause a vehicle no start condition.
(4) Loosen butDO NOTremove the camshaft
sprocket retaining bolt. Leave bolt snug against
sprocket.
NOTE: The timing chain tensioners must be
secured prior to removing the camshaft sprockets.
Failure to secure tensioners will allow the tension-
ers to extend, requiring timing chain cover removal
in order to reset tensioners.
CAUTION: Do not force wedge past the narrowest
point between the chain strands. Damage to the
tensioners may occur.
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 35
CYLINDER HEAD - RIGHT (Continued)
Page 1264 of 2627
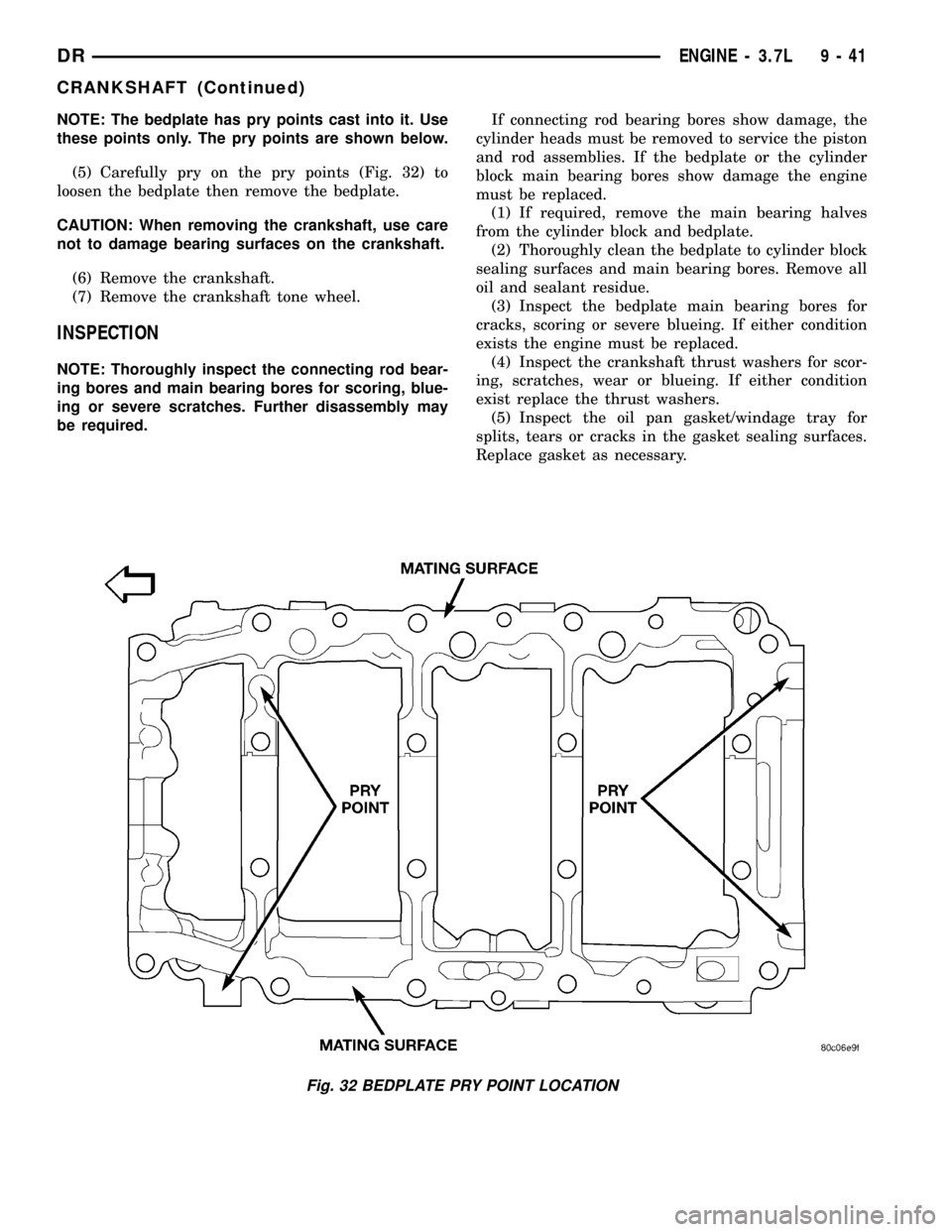
NOTE: The bedplate has pry points cast into it. Use
these points only. The pry points are shown below.
(5) Carefully pry on the pry points (Fig. 32) to
loosen the bedplate then remove the bedplate.
CAUTION: When removing the crankshaft, use care
not to damage bearing surfaces on the crankshaft.
(6) Remove the crankshaft.
(7) Remove the crankshaft tone wheel.
INSPECTION
NOTE: Thoroughly inspect the connecting rod bear-
ing bores and main bearing bores for scoring, blue-
ing or severe scratches. Further disassembly may
be required.If connecting rod bearing bores show damage, the
cylinder heads must be removed to service the piston
and rod assemblies. If the bedplate or the cylinder
block main bearing bores show damage the engine
must be replaced.
(1) If required, remove the main bearing halves
from the cylinder block and bedplate.
(2) Thoroughly clean the bedplate to cylinder block
sealing surfaces and main bearing bores. Remove all
oil and sealant residue.
(3) Inspect the bedplate main bearing bores for
cracks, scoring or severe blueing. If either condition
exists the engine must be replaced.
(4) Inspect the crankshaft thrust washers for scor-
ing, scratches, wear or blueing. If either condition
exist replace the thrust washers.
(5) Inspect the oil pan gasket/windage tray for
splits, tears or cracks in the gasket sealing surfaces.
Replace gasket as necessary.
Fig. 32 BEDPLATE PRY POINT LOCATION
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 41
CRANKSHAFT (Continued)
Page 1268 of 2627
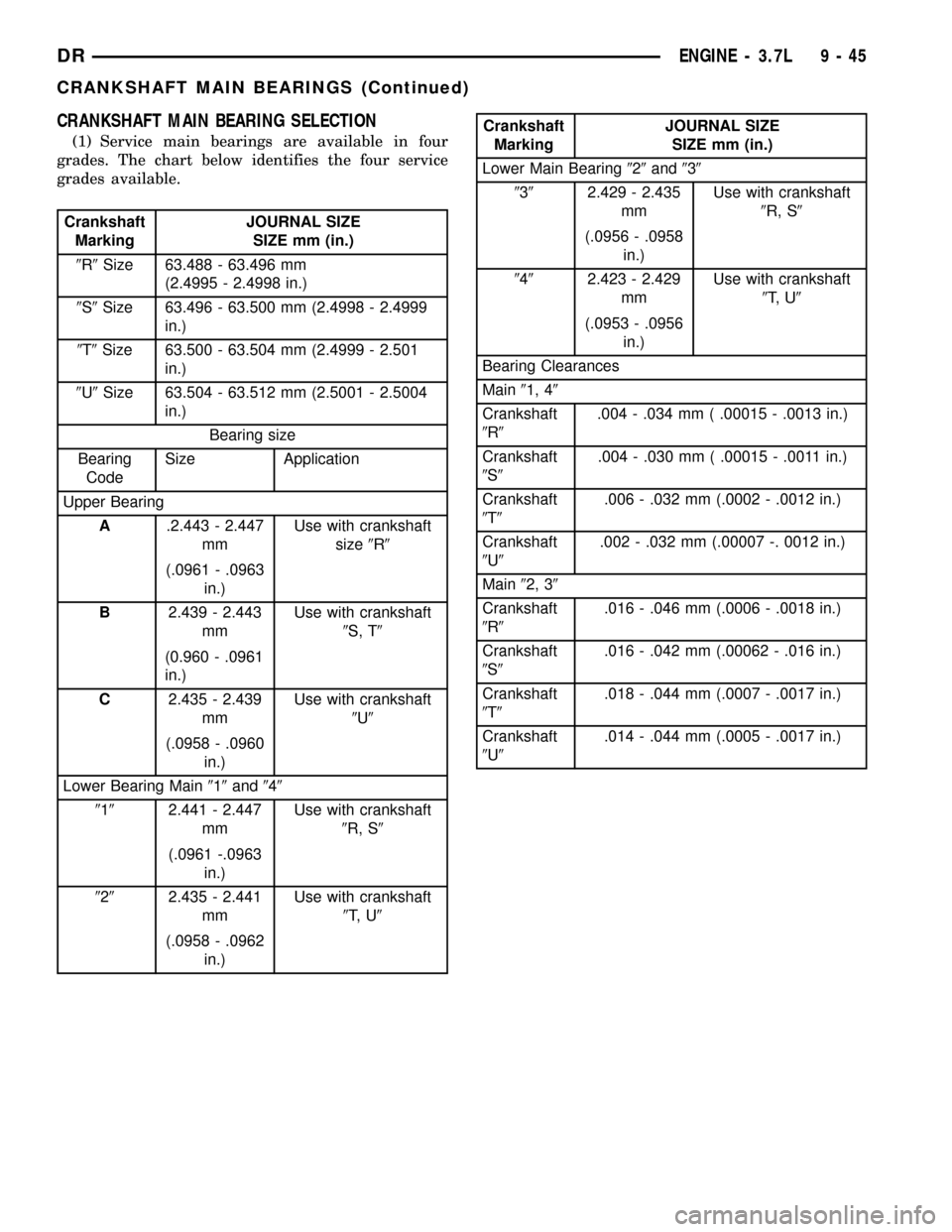
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING SELECTION
(1) Service main bearings are available in four
grades. The chart below identifies the four service
grades available.
Crankshaft
MarkingJOURNAL SIZE
SIZE mm (in.)
9R9Size 63.488 - 63.496 mm
(2.4995 - 2.4998 in.)
9S9Size 63.496 - 63.500 mm (2.4998 - 2.4999
in.)
9T9Size 63.500 - 63.504 mm (2.4999 - 2.501
in.)
9U9Size 63.504 - 63.512 mm (2.5001 - 2.5004
in.)
Bearing size
Bearing
CodeSize Application
Upper Bearing
A.2.443 - 2.447
mmUse with crankshaft
size9R9
(.0961 - .0963
in.)
B2.439 - 2.443
mmUse with crankshaft
9S, T9
(0.960 - .0961
in.)
C2.435 - 2.439
mmUse with crankshaft
9U9
(.0958 - .0960
in.)
Lower Bearing Main919and949
9192.441 - 2.447
mmUse with crankshaft
9R, S9
(.0961 -.0963
in.)
9292.435 - 2.441
mmUse with crankshaft
9T, U9
(.0958 - .0962
in.)
Crankshaft
MarkingJOURNAL SIZE
SIZE mm (in.)
Lower Main Bearing929and939
9392.429 - 2.435
mmUse with crankshaft
9R, S9
(.0956 - .0958
in.)
9492.423 - 2.429
mmUse with crankshaft
9T, U9
(.0953 - .0956
in.)
Bearing Clearances
Main91, 49
Crankshaft
9R9.004 - .034 mm ( .00015 - .0013 in.)
Crankshaft
9S9.004 - .030 mm ( .00015 - .0011 in.)
Crankshaft
9T9.006 - .032 mm (.0002 - .0012 in.)
Crankshaft
9U9.002 - .032 mm (.00007 -. 0012 in.)
Main92, 39
Crankshaft
9R9.016 - .046 mm (.0006 - .0018 in.)
Crankshaft
9S9.016 - .042 mm (.00062 - .016 in.)
Crankshaft
9T9.018 - .044 mm (.0007 - .0017 in.)
Crankshaft
9U9.014 - .044 mm (.0005 - .0017 in.)
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 45
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1273 of 2627
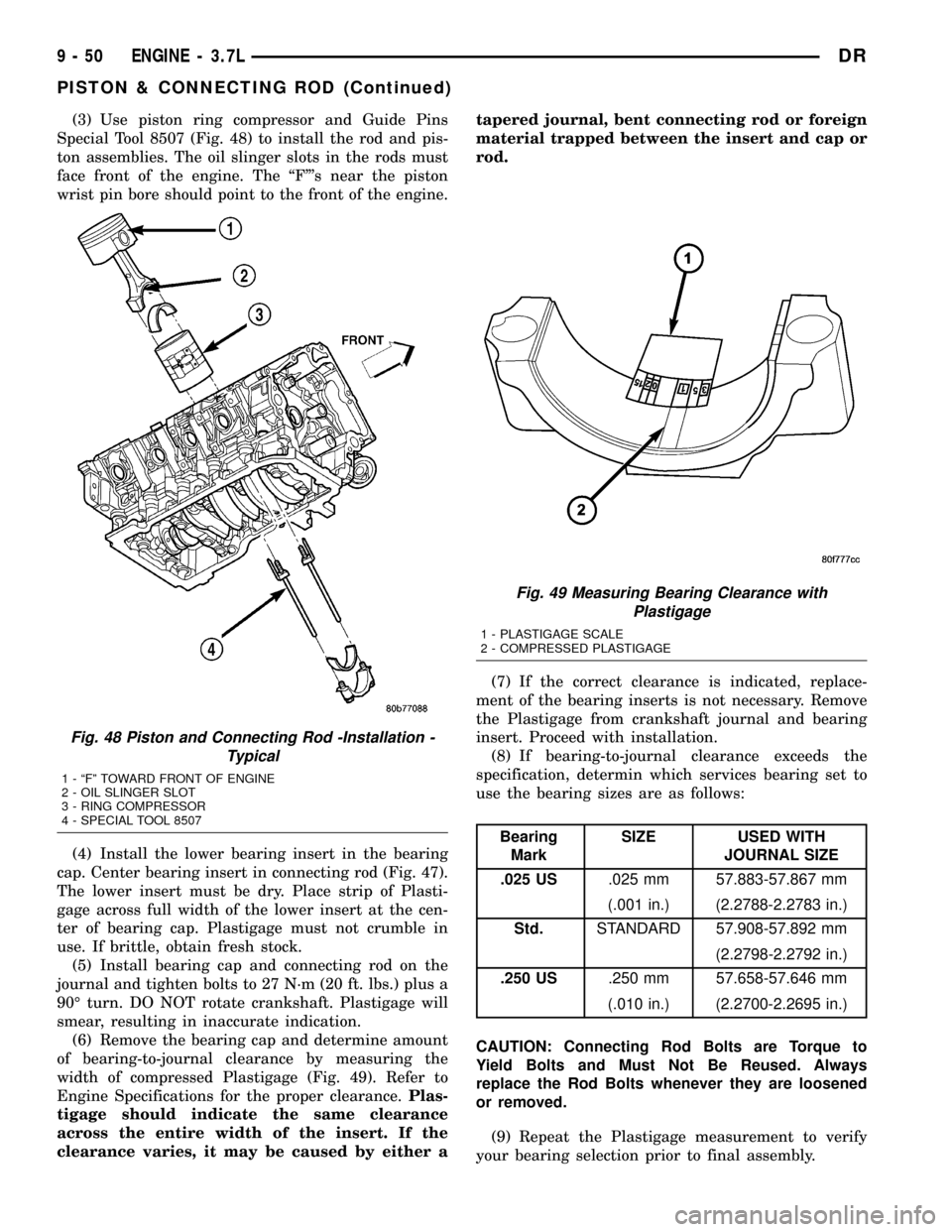
(3) Use piston ring compressor and Guide Pins
Special Tool 8507 (Fig. 48) to install the rod and pis-
ton assemblies. The oil slinger slots in the rods must
face front of the engine. The ªFº's near the piston
wrist pin bore should point to the front of the engine.
(4) Install the lower bearing insert in the bearing
cap. Center bearing insert in connecting rod (Fig. 47).
The lower insert must be dry. Place strip of Plasti-
gage across full width of the lower insert at the cen-
ter of bearing cap. Plastigage must not crumble in
use. If brittle, obtain fresh stock.
(5) Install bearing cap and connecting rod on the
journal and tighten bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus a
90É turn. DO NOT rotate crankshaft. Plastigage will
smear, resulting in inaccurate indication.
(6) Remove the bearing cap and determine amount
of bearing-to-journal clearance by measuring the
width of compressed Plastigage (Fig. 49). Refer to
Engine Specifications for the proper clearance.Plas-
tigage should indicate the same clearance
across the entire width of the insert. If the
clearance varies, it may be caused by either atapered journal, bent connecting rod or foreign
material trapped between the insert and cap or
rod.
(7) If the correct clearance is indicated, replace-
ment of the bearing inserts is not necessary. Remove
the Plastigage from crankshaft journal and bearing
insert. Proceed with installation.
(8) If bearing-to-journal clearance exceeds the
specification, determin which services bearing set to
use the bearing sizes are as follows:
Bearing
MarkSIZE USED WITH
JOURNAL SIZE
.025 US.025 mm 57.883-57.867 mm
(.001 in.) (2.2788-2.2783 in.)
Std.STANDARD 57.908-57.892 mm
(2.2798-2.2792 in.)
.250 US.250 mm 57.658-57.646 mm
(.010 in.) (2.2700-2.2695 in.)
CAUTION: Connecting Rod Bolts are Torque to
Yield Bolts and Must Not Be Reused. Always
replace the Rod Bolts whenever they are loosened
or removed.
(9) Repeat the Plastigage measurement to verify
your bearing selection prior to final assembly.
Fig. 48 Piston and Connecting Rod -Installation -
Typical
1 - ªFº TOWARD FRONT OF ENGINE
2 - OIL SLINGER SLOT
3 - RING COMPRESSOR
4 - SPECIAL TOOL 8507
Fig. 49 Measuring Bearing Clearance with
Plastigage
1 - PLASTIGAGE SCALE
2 - COMPRESSED PLASTIGAGE
9 - 50 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1274 of 2627

(10) Once you have selected the proper insert,
install the insert and cap. Tighten the connecting rod
bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus a 90É turn.
Slide snug-fitting feeler gauge between the con-
necting rod and crankshaft journal flange (Fig. 50).
Refer to Engine Specifications for the proper clear-
ance. Replace the connecting rod if the side clearance
is not within specification.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON FITTING
(1) To correctly select the proper size piston, a cyl-
inder bore gauge, capable of reading in 0.003 mm (
.0001 in.) INCREMENTS is required. If a bore gauge
is not available, do not use an inside micrometer.
(2) Measure the inside diameter of the cylinder
bore at a point 38.0 mm (1.5 inches) below top of
bore. Start perpendicular (across or at 90 degrees) to
the axis of the crankshaft at point A and then take
an additional bore reading 90 degrees to that at point
B (Fig. 52).
(3) The coated pistons will be serviced with the
piston pin and connecting rod pre-assembled.
(4) The coating material is applied to the piston
after the final piston machining process. Measuring
the outside diameter of a coated piston will not pro-
vide accurate results (Fig. 51). Therefore measuring
the inside diameter of the cylinder bore with a dial
Bore Gauge isMANDATORY. To correctly select the
proper size piston, a cylinder bore gauge capable of
reading in 0.003 mm (.0001 in.) increments is
required.
(5) Piston installation into the cylinder bore
requires slightly more pressure than that required
for non-coated pistons. The bonded coating on the
piston will give the appearance of a line-to-line fit
with the cylinder bore.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the following components:
²Oil pan and gasket/windage tray (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
²Cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) -
REMOVAL) and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
Fig. 50 Checking Connecting Rod Side Clearance -
Typical
Fig. 51 DO NOT MEASURE MOLY COATED PISTON
1 - MOLY COATED
2 - MOLY COATED
Fig. 52 BORE GAUGE - TYPICAL
1 - FRONT
2 - BORE GAUGE
3 - CYLINDER BORE
4 - 38 MM (1.5 in)
DRENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 51
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1287 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL LEAK
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24 km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.If the oil leak source is not posi-
tively identified at this time, proceed with the air
leak detection test method.
Air Leak Detection Test Method
(1) Disconnect the breather cap to air cleaner hose
at the breather cap end. Cap or plug breather cap
nipple.
(2) Remove the PCV valve from the cylinder head
cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve grommet.
(3) Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and
regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kPa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
(4) Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provide the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
(5) If the leakage occurs at the rear oil seal area,
refer to the section, Inspection for Rear Seal Area
Leak.
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply
and remove the air hose and all plugs and caps.
Install the PCV valve and breather cap hose.(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, distributor seal,
camshaft bore cup plugs oil galley pipe plugs, oil
filter runoff, and main bearing cap to cylinder
block mating surfaces.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as outlined in the, Inspection (Engine oil Leaks
in general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
9 - 64 ENGINE - 3.7LDR
LUBRICATION (Continued)