Body DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 295 of 2627

Brake fluid apply pressure is modulated according
to wheel speed, degree of slip and rate of decelera-
tion. Sensors at each front wheel convert wheel speed
into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted
to the CAB for processing and determination of
wheel slip and deceleration rate.
The ABS system has three fluid pressure control
channels. The front brakes are controlled separately
and the rear brakes in tandem. A speed sensor input
signal indicating a wheel slip condition activates the
CAB antilock program.
There are Two solenoid valves (Isolation and Dump
valve) which are used in each antilock control chan-
nel. The valves are all located within the HCU valve
body and work in pairs to either increase, hold, or
decrease apply pressure as needed in the individual
control channels.
During an ABS stop the ISO valve is energized
which acts to prevent further pressure build-up to
the calipers. Then the Dump valve dumps off pres-
sure until the wheel unlocks. This will continue until
the wheels quit slipping altogether.STANDARD PROCEDURE - ABS BRAKE
BLEEDING
ABS system bleeding requires conventional bleed-
ing methods plus use of the DRB scan tool. The pro-
cedure involves performing a base brake bleeding,
followed by use of the scan tool to cycle and bleed the
HCU pump and solenoids. A second base brake bleed-
ing procedure is then required to remove any air
remaining in the system.
(1) Perform base brake bleeding,(Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE) OR (Refer to
5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Connect scan tool to the Data Link Connector.
(3) Select ANTILOCK BRAKES, followed by MIS-
CELLANEOUS, then ABS BRAKES. Follow the
instructions displayed. When scan tool displays TEST
COMPLETE, disconnect scan tool and proceed.
(4) Perform base brake bleeding a second time,(Re-
fer to 5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE) OR
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Top off master cylinder fluid level and verify
proper brake operation before moving vehicle.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
ABS Assembly
Mounting Bolts15 11 Ð
ABS Assembly
CAB Screws3.5 Ð 31
ABS Assembly
Brake Line Fittings19 Ð 170
Wheel Speed Sensors
Front Sensor Bolt21 Ð 190
Wheel Speed Sensors
Bracket To Knuckle6.7 Ð 60
Wheel Speed Sensors
Rear Sensor Stud22.5 Ð 200
Controller
Mounting Screws6Ð53
RWAL Module
Mounting Bolts15 11 Ð
RWAL Valve
Brake Line Fittings19 Ð 170
Rear Wheel Speed
Sensor
Mounting Bolt24 Ð 200
5 - 46 BRAKES - ABSDR
BRAKES - ABS (Continued)
Page 298 of 2627

TONE WHEEL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WHEEL
SPEED SENSOR
Diagnosis of base brake conditions which are
mechanical in nature should be performed first. This
includes brake noise, lack of power assist, parking
brake, or vehicle vibration during normal braking.
The Antilock brake system performs several self-
tests every time the ignition switch is turned on and
the vehicle is driven. The CAB monitors the system
inputs and outputs circuits to verify the system is
operating properly. If the CAB senses a malfunction
in the system it will set a DTC into memory and trig-
ger the warning lamp.
NOTE: The MDS or DRB III scan tool is used to
diagnose the Antilock Brake system. For test proce-
dures refer to the Chassis Diagnostic Manual.
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL
DESCRIPTION - ELECTRONIC VARIABLE
BRAKE PROPORTIONING
Vehicles equipped with ABS use electronic variable
brake proportioning (EVBP) to balance front-to-rear
braking. The EVBP is used in place of a rear propor-
tioning valve. The EVBP system uses the ABS sys-
tem to control the slip of the rear wheels in partial
braking range. The braking force of the rear wheels
is controlled electronically by using the inlet and out-
let valves located in the integrated control unit
(ICU).
OPERATION - ELECTRONIC VARIABLE BRAKE
PROPORTIONING
EVBP is able to decrease, hold and increase rear
brake pressure without activating full ABS control.
Upon entry into EVBP the inlet valve for the rear
brake circuit is switched on so that the fluid supply
from the master cylinder is shut off. In order to
decrease the rear brake pressure, the outlet valve for
the rear brake circuit is pulsed. This allows fluid to
enter the low pressure accumulator (LPA) in the
hydraulic control unit (HCU) resulting in a drop in
fluid pressure to the rear brakes. In order to increase
the rear brake pressure, the outlet valve is switched
off and the inlet valve is pulsed. This increases the
pressure to the rear brakes.
The EVBP will remain functional during many
ABS fault modes. If both the red BRAKE and amber
ABS warning indicators are illuminated, the EVBP
may not be functioning.
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL
UNIT)
DESCRIPTION
The HCU consists of a valve body, pump motor, low
pressure accumulators, inlet valves, outlet valves and
noise attenuators.
OPERATION
Accumulators in the valve body store extra fluid
released to the system for ABS mode operation. The
pump provides the fluid volume needed and is oper-
ated by a DC type motor. The motor is controlled by
the CAB.
The valves modulate brake pressure during
antilock braking and are controlled by the CAB.
The HCU provides three channel pressure control
to the front and rear brakes. One channel controls
the rear wheel brakes in tandem. The two remaining
channels control the front wheel brakes individually.
During antilock braking, the solenoid valves are
opened and closed as needed.
During normal braking, the HCU solenoid valves
and pump are not activated. The master cylinder and
power booster operate the same as a vehicle without
an ABS brake system.
NOTE: The three modes mentioned below do occur
but not necessarily in the order listed everytime.
During antilock braking, solenoid valve pressure
modulation occurs in three stages, pressure increase,
pressure hold, and pressure decrease. The valves are
all contained in the valve body portion of the HCU.
PRESSURE DECREASE
The outlet valve is opened and the inlet valve is
closed during the pressure decrease cycle.
A pressure decrease cycle is initiated when speed
sensor signals indicate high wheel slip at one or
more wheels. At this point, the CAB closes the inlet
then opens the outlet valve, which also opens the
return circuit to the accumulators. Fluid pressure is
allowed to bleed off (decrease) as needed to prevent
wheel lock.
Once the period of high wheel slip has ended, the
CAB closes the outlet valve and begins a pressure
increase or hold cycle as needed.
PRESSURE HOLD
Both solenoid valves are closed in the pressure
hold cycle but only the inlet valve is energized. Fluid
apply pressure in the control channel is maintained
at a constant rate. The CAB maintains the hold cycle
until sensor inputs indicate a pressure change is nec-
essary.
DRBRAKES - ABS 5 - 49
Page 339 of 2627
INSTALLATION
(1) Install tensioner assembly to water inlet
bracket. A dowel is located on back of tensioner. Align
this dowel to hole in tensioner mounting bracket.
Tighten bolt to 43 N´m (32 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOLING/AC-
CESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLA-
TION).
DRIVE BELT - 3.7L / 4.7L
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ACCESSORY
DRIVE BELT
VISUAL DIAGNOSIS
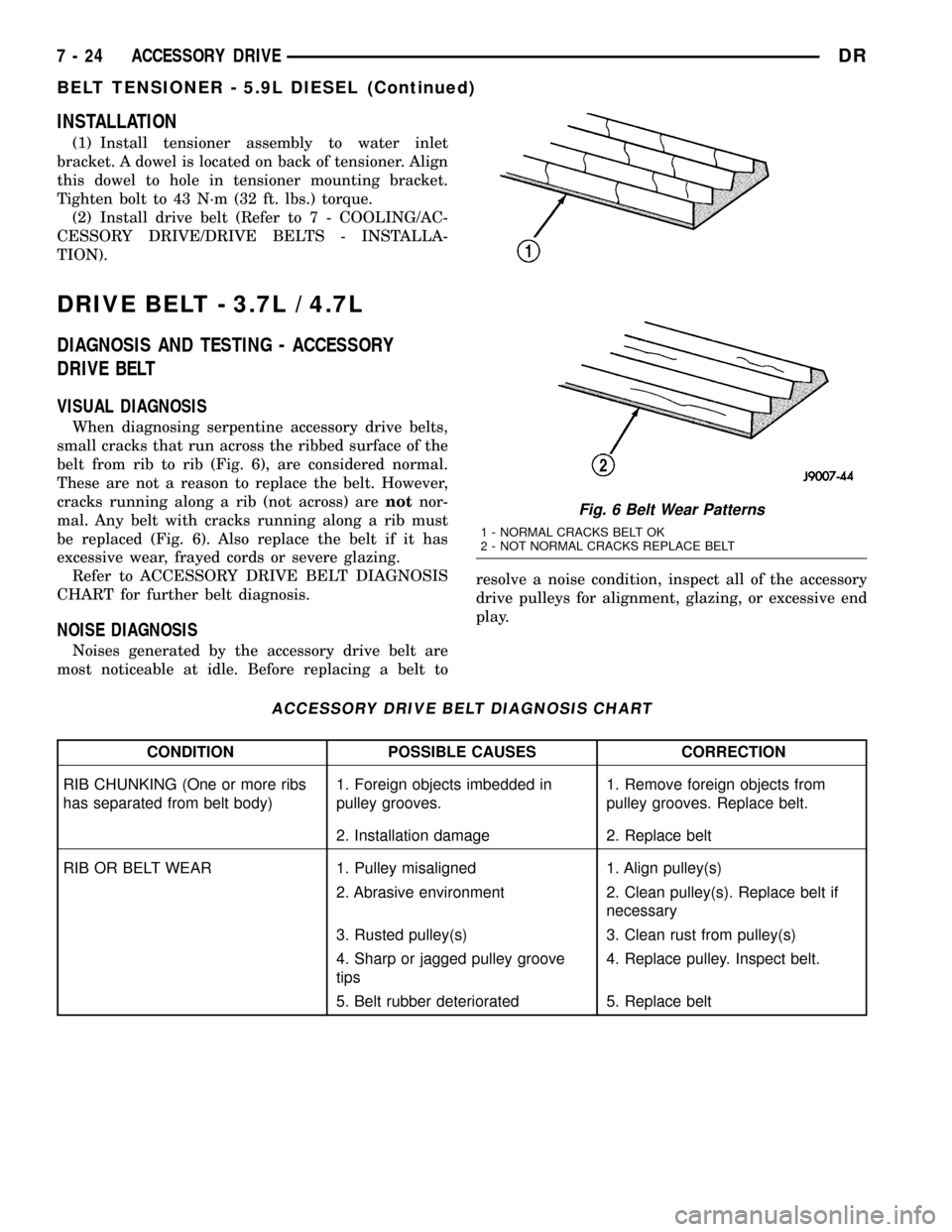
When diagnosing serpentine accessory drive belts,
small cracks that run across the ribbed surface of the
belt from rib to rib (Fig. 6), are considered normal.
These are not a reason to replace the belt. However,
cracks running along a rib (not across) arenotnor-
mal. Any belt with cracks running along a rib must
be replaced (Fig. 6). Also replace the belt if it has
excessive wear, frayed cords or severe glazing.
Refer to ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT DIAGNOSIS
CHART for further belt diagnosis.
NOISE DIAGNOSIS
Noises generated by the accessory drive belt are
most noticeable at idle. Before replacing a belt toresolve a noise condition, inspect all of the accessory
drive pulleys for alignment, glazing, or excessive end
play.
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
RIB CHUNKING (One or more ribs
has separated from belt body)1. Foreign objects imbedded in
pulley grooves.1. Remove foreign objects from
pulley grooves. Replace belt.
2. Installation damage 2. Replace belt
RIB OR BELT WEAR 1. Pulley misaligned 1. Align pulley(s)
2. Abrasive environment 2. Clean pulley(s). Replace belt if
necessary
3. Rusted pulley(s) 3. Clean rust from pulley(s)
4. Sharp or jagged pulley groove
tips4. Replace pulley. Inspect belt.
5. Belt rubber deteriorated 5. Replace belt
Fig. 6 Belt Wear Patterns
1 - NORMAL CRACKS BELT OK
2 - NOT NORMAL CRACKS REPLACE BELT
7 - 24 ACCESSORY DRIVEDR
BELT TENSIONER - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 340 of 2627

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
BELT SLIPS 1. Belt slipping because of
insufficient tension1. Inspect/Replace tensioner if
necessary
2. Belt or pulley exposed to
substance that has reduced friction
(belt dressing, oil, ethylene glycol)2. Replace belt and clean pulleys
3. Driven component bearing failure
(seizure)3. Replace faulty component or
bearing
4. Belt glazed or hardened from
heat and excessive slippage4. Replace belt.
LONGITUDAL BELT CRACKING 1. Belt has mistracked from pulley
groove1. Replace belt
2. Pulley groove tip has worn away
rubber to tensile member2. Replace belt
9GROOVE JUMPING9
(Belt does not maintain correct
position on pulley)1. Incorrect belt tension 1. Inspect/Replace tensioner if
necessary
2. Pulley(s) not within design
tolerance2. Replace pulley(s)
3. Foreign object(s) in grooves 3. Remove foreign objects from
grooves
4. Pulley misalignment 4. Align component
5. Belt cordline is broken 5. Replace belt
BELT BROKEN
(Note: Identify and correct problem
before new belt is installed)1. Incorrect belt tension 1. Replace Inspect/Replace
tensioner if necessary
2. Tensile member damaged during
belt installation2. Replace belt
3. Severe misalignment 3. Align pulley(s)
4. Bracket, pulley, or bearing failure 4. Replace defective component
and belt
NOISE
(Objectionable squeal, squeak, or
rumble is heard or felt while drive
belt is in operation)1. Incorrect belt tension 1. Inspect/Replace tensioner if
necessary
2. Bearing noise 2. Locate and repair
3. Belt misalignment 3. Align belt/pulley(s)
4. Belt to pulley mismatch 4. Install correct belt
5. Driven component induced
vibration5. Locate defective driven
component and repair
TENSION SHEETING FABRIC
FAILURE
(Woven fabric on outside,
circumference of belt has cracked or
separated from body of belt)1. Tension sheeting contacting
stationary object1. Correct rubbing condition
2. Excessive heat causing woven
fabric to age2. Replace belt
3. Tension sheeting splice has
fractured3. Replace belt
DRACCESSORY DRIVE 7 - 25
DRIVE BELT - 3.7L / 4.7L (Continued)
Page 341 of 2627
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
CORD EDGE FAILURE
(Tensile member exposed at edges
of belt or separated from belt body)1. Incorrect belt tension 1. Inspect/Replace tensioner if
necessary
2. Belt contacting stationary object 2. Replace belt
3. Pulley(s) out of tolerance 3. Replace pulley
4. Insufficient adhesion between
tensile member and rubber matrix4. Replace belt
REMOVAL
CAUTION: DO NOT LET TENSIONER ARM SNAP
BACK TO THE FREEARM POSITION, SEVER DAM-
AGE MAY OCCUR TO THE TENSIONER.
Belt tension is not adjustable. Belt adjustment is
maintained by an automatic (spring load) belt ten-
sioner.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
(2) Rotate belt tensioner until it contacts it's stop.
Remove belt, then slowly rotate the tensioner into
the freearm position. (Fig. 7).
INSTALLATION
Belt tension is not adjustable. Belt adjustment is
maintained by an automatic ( spring load ) belt ten-
sioner.
(1) Check condition of all pulleys.
CAUTION: When installing the serpentine accessory
drive belt, the belt MUST be routed correctly. If not,
the engine may overheat due to the water pump
rotating in the wrong direction (Fig. 7).
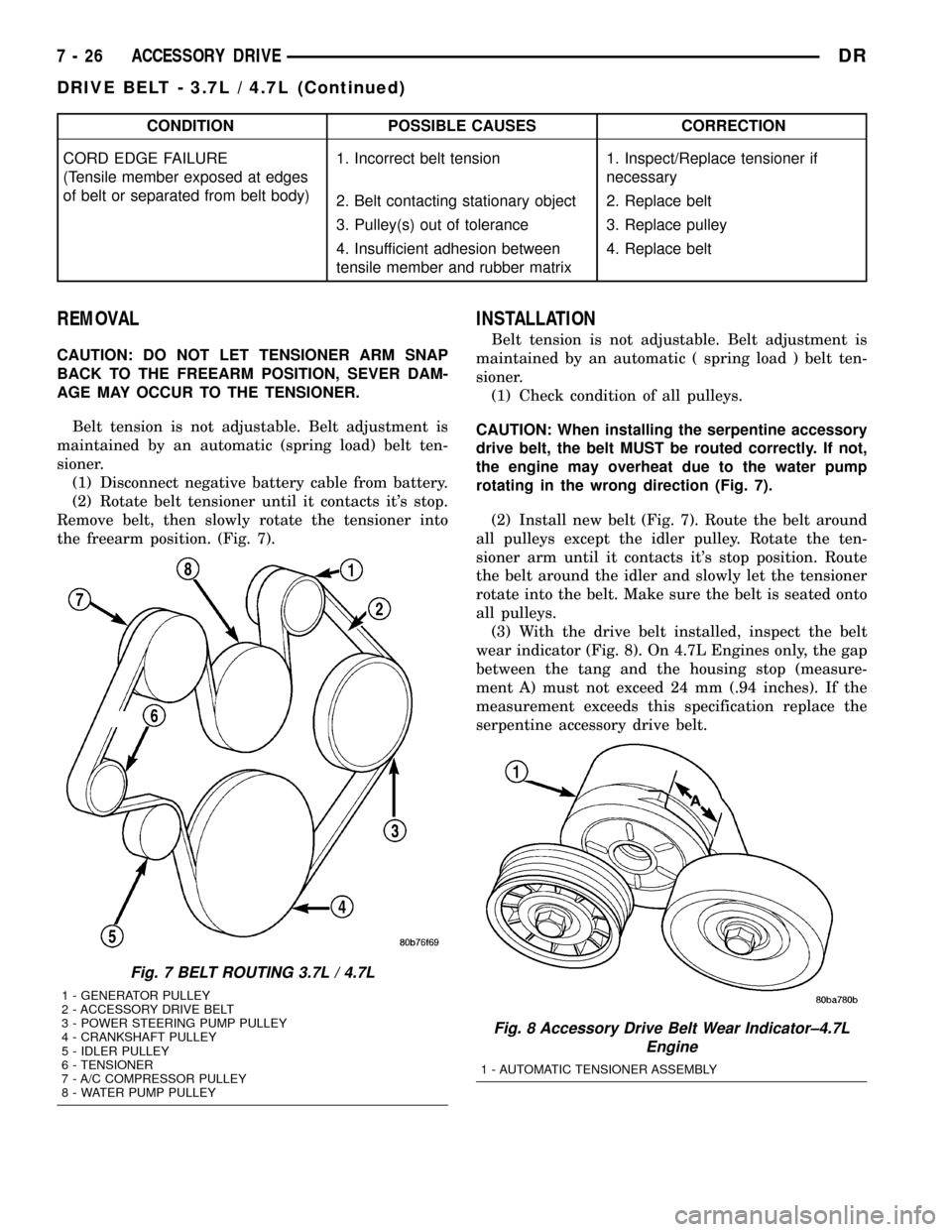
(2) Install new belt (Fig. 7). Route the belt around
all pulleys except the idler pulley. Rotate the ten-
sioner arm until it contacts it's stop position. Route
the belt around the idler and slowly let the tensioner
rotate into the belt. Make sure the belt is seated onto
all pulleys.
(3) With the drive belt installed, inspect the belt
wear indicator (Fig. 8). On 4.7L Engines only, the gap
between the tang and the housing stop (measure-
ment A) must not exceed 24 mm (.94 inches). If the
measurement exceeds this specification replace the
serpentine accessory drive belt.
Fig. 7 BELT ROUTING 3.7L / 4.7L
1 - GENERATOR PULLEY
2 - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
3 - POWER STEERING PUMP PULLEY
4 - CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
5 - IDLER PULLEY
6 - TENSIONER
7 - A/C COMPRESSOR PULLEY
8 - WATER PUMP PULLEY
Fig. 8 Accessory Drive Belt Wear Indicator±4.7L
Engine
1 - AUTOMATIC TENSIONER ASSEMBLY
7 - 26 ACCESSORY DRIVEDR
DRIVE BELT - 3.7L / 4.7L (Continued)
Page 342 of 2627
DRIVE BELT - 5.9L DIESEL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐACCESSORY
DRIVE BELT
VISUAL DIAGNOSIS
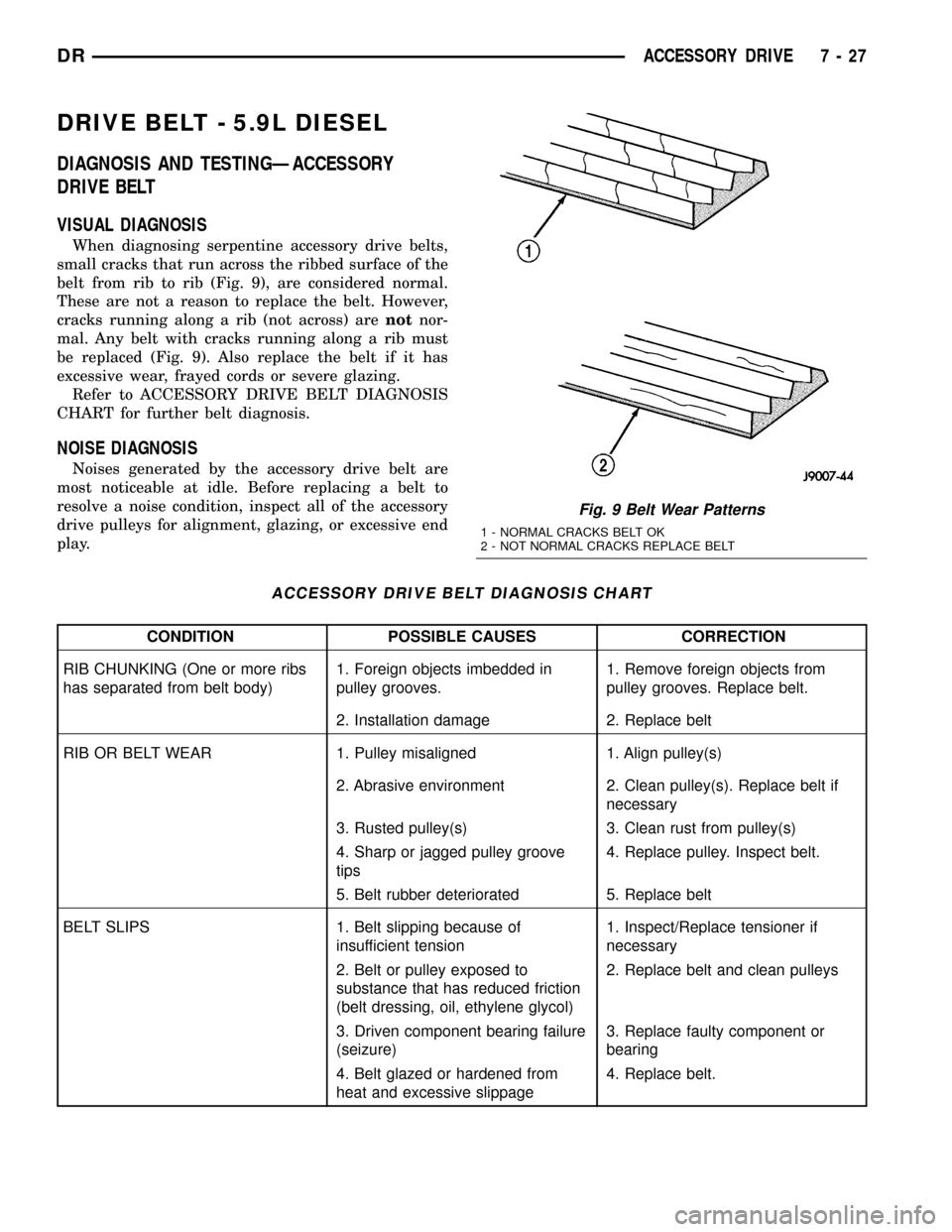
When diagnosing serpentine accessory drive belts,
small cracks that run across the ribbed surface of the
belt from rib to rib (Fig. 9), are considered normal.
These are not a reason to replace the belt. However,
cracks running along a rib (not across) arenotnor-
mal. Any belt with cracks running along a rib must
be replaced (Fig. 9). Also replace the belt if it has
excessive wear, frayed cords or severe glazing.
Refer to ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT DIAGNOSIS
CHART for further belt diagnosis.
NOISE DIAGNOSIS
Noises generated by the accessory drive belt are
most noticeable at idle. Before replacing a belt to
resolve a noise condition, inspect all of the accessory
drive pulleys for alignment, glazing, or excessive end
play.
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
RIB CHUNKING (One or more ribs
has separated from belt body)1. Foreign objects imbedded in
pulley grooves.1. Remove foreign objects from
pulley grooves. Replace belt.
2. Installation damage 2. Replace belt
RIB OR BELT WEAR 1. Pulley misaligned 1. Align pulley(s)
2. Abrasive environment 2. Clean pulley(s). Replace belt if
necessary
3. Rusted pulley(s) 3. Clean rust from pulley(s)
4. Sharp or jagged pulley groove
tips4. Replace pulley. Inspect belt.
5. Belt rubber deteriorated 5. Replace belt
BELT SLIPS 1. Belt slipping because of
insufficient tension1. Inspect/Replace tensioner if
necessary
2. Belt or pulley exposed to
substance that has reduced friction
(belt dressing, oil, ethylene glycol)2. Replace belt and clean pulleys
3. Driven component bearing failure
(seizure)3. Replace faulty component or
bearing
4. Belt glazed or hardened from
heat and excessive slippage4. Replace belt.
Fig. 9 Belt Wear Patterns
1 - NORMAL CRACKS BELT OK
2 - NOT NORMAL CRACKS REPLACE BELT
DRACCESSORY DRIVE 7 - 27
Page 343 of 2627
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
LONGITUDAL BELT CRACKING 1. Belt has mistracked from pulley
groove1. Replace belt
2. Pulley groove tip has worn away
rubber to tensile member2. Replace belt
9GROOVE JUMPING9
(Belt does not maintain correct
position on pulley)1. Incorrect belt tension 1. Inspect/Replace tensioner if
necessary
2. Pulley(s) not within design
tolerance2. Replace pulley(s)
3. Foreign object(s) in grooves 3. Remove foreign objects from
grooves
4. Pulley misalignment 4. Align component
5. Belt cordline is broken 5. Replace belt
BELT BROKEN
(Note: Identify and correct problem
before new belt is installed)1. Incorrect belt tension 1. Replace Inspect/Replace
tensioner if necessary
2. Tensile member damaged during
belt installation2. Replace belt
3. Severe misalignment 3. Align pulley(s)
4. Bracket, pulley, or bearing failure 4. Replace defective component
and belt
NOISE (Objectional squeal, squeak,
or rumble is heard or felt while drive
belt is in operation)1. Incorrect belt tension 1. Inspect/Replace tensioner if
necessary
2. Bearing noise 2. Locate and repair
3. Belt misalignment 3. Align belt/pulley(s)
4. Belt to pulley mismatch 4. Install correct belt
5. Driven component induced
vibration5. Locate defective driven
component and repair
TENSION SHEETING FABRIC
FAILURE
(Woven fabric on outside,
circumference of belt has cracked or
separated from body of belt)1. Tension sheeting contacting
stationary object1. Correct rubbing condition
2. Excessive heat causing woven
fabric to age2. Replace belt
3. Tension sheeting splice has
fractured3. Replace belt
CORD EDGE FAILURE
(Tensile member exposed at edges
of belt or separated from belt body)1. Incorrect belt tension 1. Inspect/Replace tensioner if
necessary
2. Belt contacting stationary object 2. Replace belt
3. Pulley(s) out of tolerance 3. Replace pulley
4. Insufficient adhesion between
tensile member and rubber matrix4. Replace belt
NOTE: The engine speed sensor face is very close
to the accessory drive belt. Inspect engine speed
sensor and wire harness for damage when acces-sory drive belt has been replaced due to failure or
abnormal conditions.
7 - 28 ACCESSORY DRIVEDR
DRIVE BELT - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 376 of 2627

(5) Remove the radiator fan (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
(6) Remove accessory drive belt (Fig. 46) (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(7) Remove the lower radiator hose clamp and
remove the lower hose at the water pump.
(8) Remove the water pump mounting bolts.
CAUTION: Do not pry water pump at timing chain
case/cover. The machined surfaces may be dam-
aged resulting in leaks.
(9) Remove the water pump and gasket. Discard
gasket.
CLEANING
Clean the gasket mating surface. Use caution not
to damage the gasket sealing surface.
INSPECTION
Inspect the water pump assembly for cracks in the
housing, water leaks from shaft seal, worn bearing or
impeller rubbing either the pump body or timing
chain case/cover.
INSTALLATION
The water pump on 3.7L/4.7L engine is bolted
directly to the engine timing chain case cover.
(1) Clean the gasket mating surfaces.(2) Using a new gasket, position water pump and
install the mounting bolts. (Fig. 47). Tighten the
water pump mounting bolts to 58 N´m (43 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 45 Viscous Fan and Fan Drive 4.7L Engine
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6958 SPANNER WRENCH WITH ADAPTER
PINS 8346
2-FAN
Fig. 46 Automatic Belt TensionerÐ4.7L
1 - AUTOMATIC TENSIONER
2 - WATER PUMP PULLEY
Fig. 47 Water Pump InstallationÐ3.7L/4.7L Typical
1 - WATER PUMP
2 - TIMING CHAIN COVER
DRENGINE 7 - 61
WATER PUMP - 3.7L/4.7L (Continued)
Page 377 of 2627

(3) Spin the water pump to be sure that the pump
impeller does not rub against the timing chain case/
cover.
(4) Connect the radiator lower hose to the water
pump.
(5) Relax the tension from the belt tensioner (Fig.
46). Install the drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOLING/AC-
CESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLA-
TION).
CAUTION: When installing the serpentine accessory
drive belt, the belt must be routed correctly. If not,
the engine may overheat due to the water pump
rotating in the wrong direction. Refer to (Fig. 48) for
the correct belt routing. Or, refer to the Belt Routing
Label located in the engine compartment. The cor-
rect belt with correct length must be used.
(6) Install the radiator fan (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLATION).
(7) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(8) Connect the negative battery cable.
(9) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.WATER PUMP - 5.9L DIESEL
DESCRIPTION
The water pump is mounted to the front of the
engine block between the automatic belt tensioner
and the fan drive pulley.
The water pump impeller is pressed onto the rear
of a shaft that rotates in a bearing pressed into the
water pump body. The body has a small hole for ven-
tilation. The water pump seals are lubricated by
antifreeze in the coolant mixture. Additional lubrica-
tion is not necessary.
OPERATION
The diesel engine water pump draws coolant from
the radiator outlet and circulates it through engine,
heater core and back to radiator inlet. The crank-
shaft pulley drives the water pump with a serpentine
drive belt.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐWATER PUMP
A quick test to determine if pump is working is to
check if heater warms properly. A defective water
pump will not be able to circulate heated coolant
through the long heater hose to the heater core.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cables.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove water pump mounting bolts (Fig. 49).
(5) Clean water pump sealing surface on cylinder
block.
CLEANING
Clean gasket mating surfaces as necessary.
INSPECTION
Visually inspect the water pump and replace if it
has any of the following conditions:
²The body is cracked or damaged
²Water leaks from the shaft seal. This is evident
by traces of coolant below the vent hole
²Loose or rough turning bearing.
²Impeller rubbing the pump body
INSTALLATION
(1) Install new O-ring seal in groove on water
pump (Fig. 50).
(2) Install water pump with the weep hole facing
downward. Tighten mounting bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft.
lbs.) torque.
Fig. 48 Belt Routing 3.7L
1 - GENERATOR PULLEY
2 - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
3 - POWER STEERING PUMP PULLEY
4 - CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
5 - IDLER PULLEY
6 - TENSIONER
7 - A/C COMPRESSOR PULLEY
8 - WATER PUMP PULLEY
7 - 62 ENGINEDR
WATER PUMP - 3.7L/4.7L (Continued)
Page 381 of 2627

(15) Remove the heater hose fitting from water
pump if pump replacement is necessary. Note posi-
tion (direction) of fitting before removal. Fitting must
be re-installed to same position.
CAUTION: Do not pry the water pump at timing
chain case/cover. The machined surfaces may be
damaged resulting in leaks.
CLEANING
Clean gasket mating surfaces as necessary.
INSPECTION
Visually inspect the water pump and replace if it
has any of the following conditions:
²The body is cracked or damaged
²Water leaks from the shaft seal. This is evident
by traces of coolant below the vent hole
²Loose or rough turning bearing. Also inspect
thermal fan drive
²Impeller rubbing the pump body
INSTALLATION
(1) If water pump is being replaced, install the
heater hose fitting to the pump. Tighten fitting to 16
N´m (144 in. lbs.) torque. After fitting has been
torqued, position fitting as shown in (Fig. 57). When
positioning fitting, do not back off (rotate counter-
clockwise). Use a sealant on the fitting such as
MopartThread Sealant With Teflon. Refer to the
directions on the package.
CAUTION: This heater hose fitting must be installed
to pump before pump is installed to engine.
(2) Clean the o-ring mating surfaces at rear of
water pump and front of timing chain/case cover.
(3) Apply a small amount of petroleum jelly to
o-ring (Fig. 56). This will help retain o-ring to water
pump.
(4) Install water pump to engine as follows: Guide
water pump fitting into bypass hose as pump is being
installed. Install water pump bolts (Fig. 55). Tighten
water pump mounting bolts to 40 N´m (30 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(5) Position bypass hose clamp to bypass hose.
(6) Spin water pump to be sure that pump impel-
ler does not rub against timing chain case/cover.
(7) Connect radiator lower hose to water pump.
(8) Connect heater hose and hose clamp to heater
hose fitting.
(9) Install drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOLING/AC-
CESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLA-
TION).
(10) Position fan shroud and fan blade/viscous fan
drive assembly to vehicle as a complete unit.(11) Install fan shroud to radiator. Tighten bolts to
6 N´m (50 in. lbs.) torque.
(12) Install fan blade/viscous fan drive assembly to
water pump shaft.
(13) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(14) Connect negative battery cable.
(15) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.
Fig. 57 Heater Hose Fitting Position - 8.0L V-10
1 - HEATER HOSE FITTING
2 - WATER PUMP
7 - 66 ENGINEDR
WATER PUMP - 8.0L (Continued)