Causes DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 560 of 2627
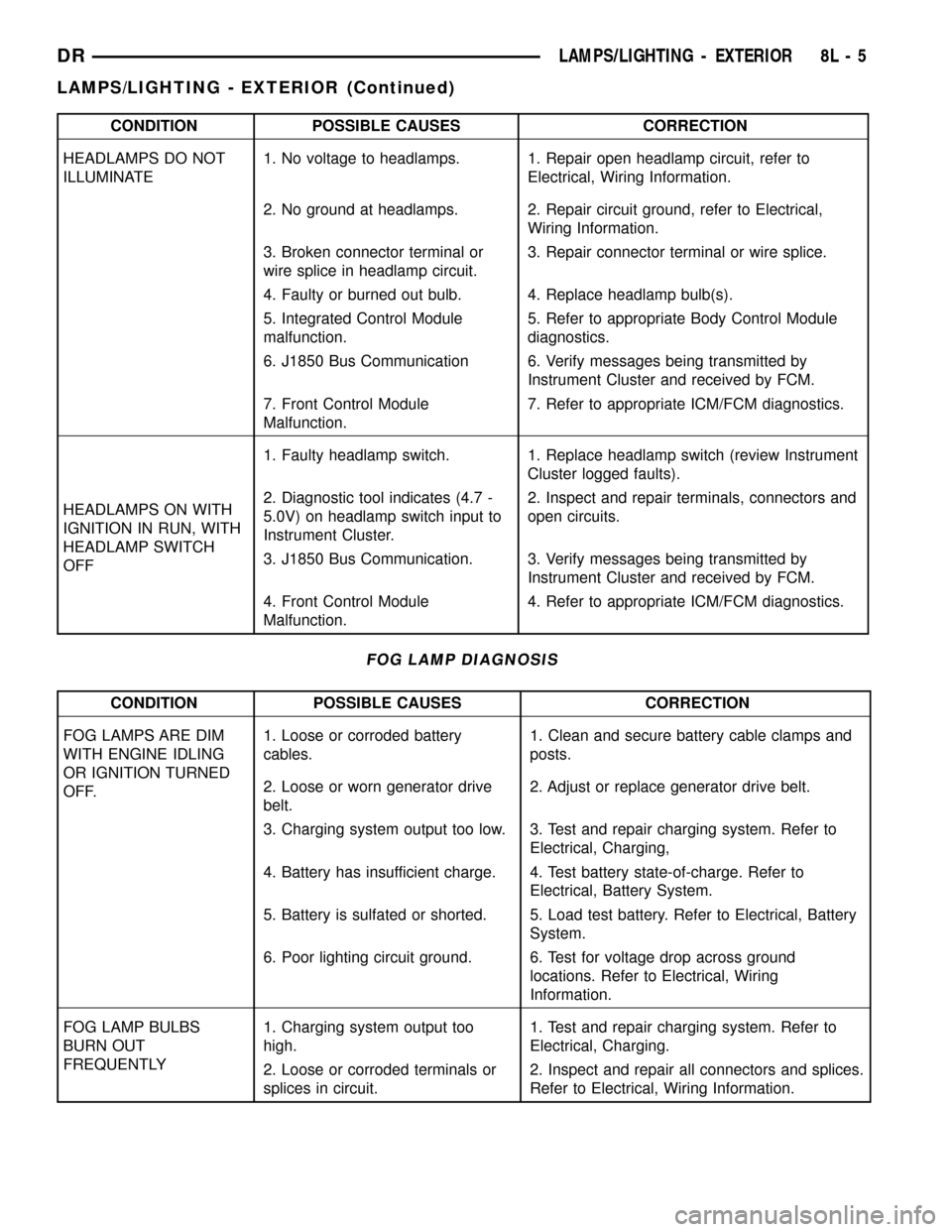
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
HEADLAMPS DO NOT
ILLUMINATE1. No voltage to headlamps. 1. Repair open headlamp circuit, refer to
Electrical, Wiring Information.
2. No ground at headlamps. 2. Repair circuit ground, refer to Electrical,
Wiring Information.
3. Broken connector terminal or
wire splice in headlamp circuit.3. Repair connector terminal or wire splice.
4. Faulty or burned out bulb. 4. Replace headlamp bulb(s).
5. Integrated Control Module
malfunction.5. Refer to appropriate Body Control Module
diagnostics.
6. J1850 Bus Communication 6. Verify messages being transmitted by
Instrument Cluster and received by FCM.
7. Front Control Module
Malfunction.7. Refer to appropriate ICM/FCM diagnostics.
HEADLAMPS ON WITH
IGNITION IN RUN, WITH
HEADLAMP SWITCH
OFF1. Faulty headlamp switch. 1. Replace headlamp switch (review Instrument
Cluster logged faults).
2. Diagnostic tool indicates (4.7 -
5.0V) on headlamp switch input to
Instrument Cluster.2. Inspect and repair terminals, connectors and
open circuits.
3. J1850 Bus Communication. 3. Verify messages being transmitted by
Instrument Cluster and received by FCM.
4. Front Control Module
Malfunction.4. Refer to appropriate ICM/FCM diagnostics.
FOG LAMP DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
FOG LAMPS ARE DIM
WITH ENGINE IDLING
OR IGNITION TURNED
OFF.1. Loose or corroded battery
cables.1. Clean and secure battery cable clamps and
posts.
2. Loose or worn generator drive
belt.2. Adjust or replace generator drive belt.
3. Charging system output too low. 3. Test and repair charging system. Refer to
Electrical, Charging,
4. Battery has insufficient charge. 4. Test battery state-of-charge. Refer to
Electrical, Battery System.
5. Battery is sulfated or shorted. 5. Load test battery. Refer to Electrical, Battery
System.
6. Poor lighting circuit ground. 6. Test for voltage drop across ground
locations. Refer to Electrical, Wiring
Information.
FOG LAMP BULBS
BURN OUT
FREQUENTLY1. Charging system output too
high.1. Test and repair charging system. Refer to
Electrical, Charging.
2. Loose or corroded terminals or
splices in circuit.2. Inspect and repair all connectors and splices.
Refer to Electrical, Wiring Information.
DRLAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR 8L - 5
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR (Continued)
Page 561 of 2627
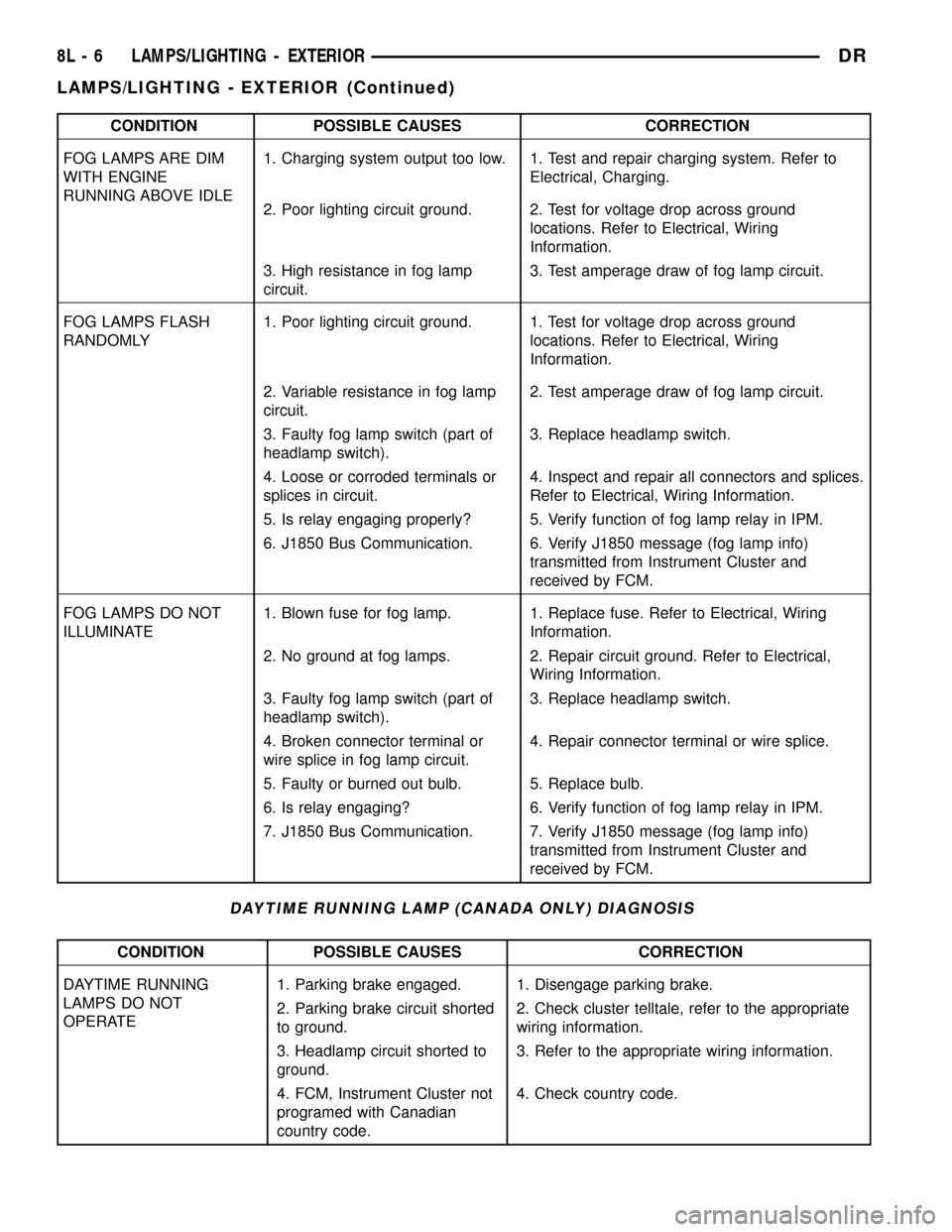
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
FOG LAMPS ARE DIM
WITH ENGINE
RUNNING ABOVE IDLE1. Charging system output too low. 1. Test and repair charging system. Refer to
Electrical, Charging.
2. Poor lighting circuit ground. 2. Test for voltage drop across ground
locations. Refer to Electrical, Wiring
Information.
3. High resistance in fog lamp
circuit.3. Test amperage draw of fog lamp circuit.
FOG LAMPS FLASH
RANDOMLY1. Poor lighting circuit ground. 1. Test for voltage drop across ground
locations. Refer to Electrical, Wiring
Information.
2. Variable resistance in fog lamp
circuit.2. Test amperage draw of fog lamp circuit.
3. Faulty fog lamp switch (part of
headlamp switch).3. Replace headlamp switch.
4. Loose or corroded terminals or
splices in circuit.4. Inspect and repair all connectors and splices.
Refer to Electrical, Wiring Information.
5. Is relay engaging properly? 5. Verify function of fog lamp relay in IPM.
6. J1850 Bus Communication. 6. Verify J1850 message (fog lamp info)
transmitted from Instrument Cluster and
received by FCM.
FOG LAMPS DO NOT
ILLUMINATE1. Blown fuse for fog lamp. 1. Replace fuse. Refer to Electrical, Wiring
Information.
2. No ground at fog lamps. 2. Repair circuit ground. Refer to Electrical,
Wiring Information.
3. Faulty fog lamp switch (part of
headlamp switch).3. Replace headlamp switch.
4. Broken connector terminal or
wire splice in fog lamp circuit.4. Repair connector terminal or wire splice.
5. Faulty or burned out bulb. 5. Replace bulb.
6. Is relay engaging? 6. Verify function of fog lamp relay in IPM.
7. J1850 Bus Communication. 7. Verify J1850 message (fog lamp info)
transmitted from Instrument Cluster and
received by FCM.
DAYTIME RUNNING LAMP (CANADA ONLY) DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
DAYTIME RUNNING
LAMPS DO NOT
OPERATE1. Parking brake engaged. 1. Disengage parking brake.
2. Parking brake circuit shorted
to ground.2. Check cluster telltale, refer to the appropriate
wiring information.
3. Headlamp circuit shorted to
ground.3. Refer to the appropriate wiring information.
4. FCM, Instrument Cluster not
programed with Canadian
country code.4. Check country code.
8L - 6 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORDR
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR (Continued)
Page 611 of 2627
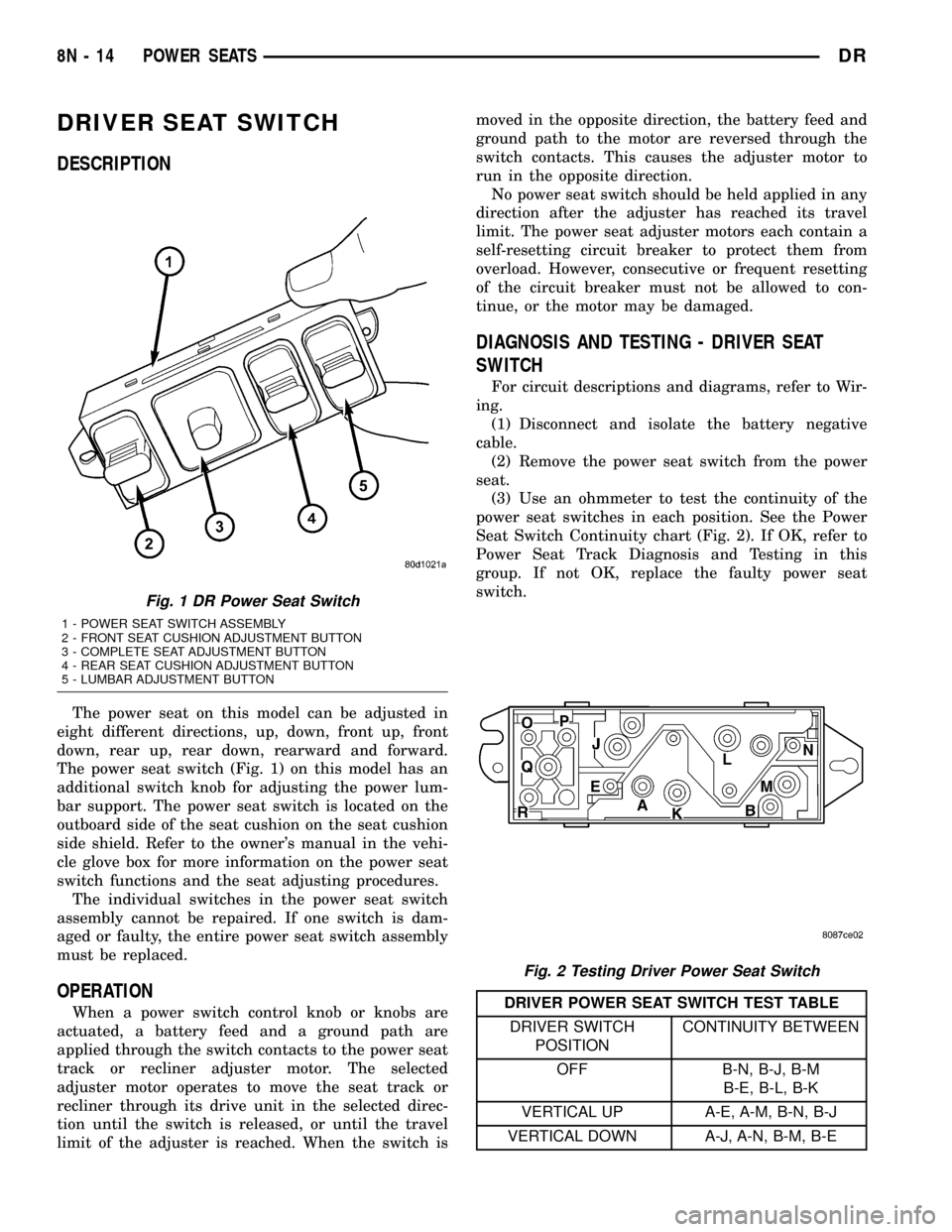
DRIVER SEAT SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The power seat on this model can be adjusted in
eight different directions, up, down, front up, front
down, rear up, rear down, rearward and forward.
The power seat switch (Fig. 1) on this model has an
additional switch knob for adjusting the power lum-
bar support. The power seat switch is located on the
outboard side of the seat cushion on the seat cushion
side shield. Refer to the owner's manual in the vehi-
cle glove box for more information on the power seat
switch functions and the seat adjusting procedures.
The individual switches in the power seat switch
assembly cannot be repaired. If one switch is dam-
aged or faulty, the entire power seat switch assembly
must be replaced.
OPERATION
When a power switch control knob or knobs are
actuated, a battery feed and a ground path are
applied through the switch contacts to the power seat
track or recliner adjuster motor. The selected
adjuster motor operates to move the seat track or
recliner through its drive unit in the selected direc-
tion until the switch is released, or until the travel
limit of the adjuster is reached. When the switch ismoved in the opposite direction, the battery feed and
ground path to the motor are reversed through the
switch contacts. This causes the adjuster motor to
run in the opposite direction.
No power seat switch should be held applied in any
direction after the adjuster has reached its travel
limit. The power seat adjuster motors each contain a
self-resetting circuit breaker to protect them from
overload. However, consecutive or frequent resetting
of the circuit breaker must not be allowed to con-
tinue, or the motor may be damaged.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DRIVER SEAT
SWITCH
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to Wir-
ing.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the power seat switch from the power
seat.
(3) Use an ohmmeter to test the continuity of the
power seat switches in each position. See the Power
Seat Switch Continuity chart (Fig. 2). If OK, refer to
Power Seat Track Diagnosis and Testing in this
group. If not OK, replace the faulty power seat
switch.
DRIVER POWER SEAT SWITCH TEST TABLE
DRIVER SWITCH
POSITIONCONTINUITY BETWEEN
OFF B-N, B-J, B-M
B-E, B-L, B-K
VERTICAL UP A-E, A-M, B-N, B-J
VERTICAL DOWN A-J, A-N, B-M, B-E
Fig. 1 DR Power Seat Switch
1 - POWER SEAT SWITCH ASSEMBLY
2 - FRONT SEAT CUSHION ADJUSTMENT BUTTON
3 - COMPLETE SEAT ADJUSTMENT BUTTON
4 - REAR SEAT CUSHION ADJUSTMENT BUTTON
5 - LUMBAR ADJUSTMENT BUTTON
Fig. 2 Testing Driver Power Seat Switch
8N - 14 POWER SEATSDR
Page 612 of 2627

DRIVER POWER SEAT SWITCH TEST TABLE
DRIVER SWITCH
POSITIONCONTINUITY BETWEEN
HORIZONTAL
FORWARDA-L, B-K
HORIZONTAL
REARWARDA-K, B-L
FRONT TILT UP A-M, B-N
FRONT TILT DOWN A-N, B-M
REAR TILT UP A-E, B-J
REAR TILT DOWN A-J, B-E
LUMBAR OFF O-P, O-R, P-R
LUMPAR UP (INFLATE) O-P, Q-R
LUMBAR DOWN
(DEFLATE)O-R, P-Q
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the seat cushion side shield from the
seat. Refer to the Body section of the service manual
for the procedure.
(3) Pull the switch bezel or side shield unit out
from the seat far enough to access the switch wire
harness connector. Gently pry the locking tabs of the
switch away from the wire harness connector and
carefully unplug the connector from the power seat
switch module.
(4) Remove the screws that secure the power seat
switch.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the power seat switch on the seat
cushion side shield and install the screws that secure
the power seat switch to seat cushion side shield.
(2) Connect the electrical connector.
(3) Install the seat cushion side shield on the seat.
Refer to the Body section of the service manual for
the procedure.
(4) If equipped, install the screw that secures the
recliner lever to the recliner mechanism release shaft
on the outboard side of the front seat.
(5) Connect the battery negative cable.
PASSENGER SEAT SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The power seat on this model can be adjusted in
eight different directions, up, down, front up, front
down, rear up, rear down, rearward and forward.
The power seat switch (Fig. 3) on this model has an
additional switch knob for adjusting the power lum-bar support. The power seat switch is located on the
outboard side of the seat cushion on the seat cushion
side shield. Refer to the owner's manual in the vehi-
cle glove box for more information on the power seat
switch functions and the seat adjusting procedures.
The individual switches in the power seat switch
assembly cannot be repaired. If one switch is dam-
aged or faulty, the entire power seat switch assembly
must be replaced.
OPERATION
When a power switch control knob or knobs are
actuated, a battery feed and a ground path are
applied through the switch contacts to the power seat
track or recliner adjuster motor. The selected
adjuster motor operates to move the seat track or
recliner through its drive unit in the selected direc-
tion until the switch is released, or until the travel
limit of the adjuster is reached. When the switch is
moved in the opposite direction, the battery feed and
ground path to the motor are reversed through the
switch contacts. This causes the adjuster motor to
run in the opposite direction.
No power seat switch should be held applied in any
direction after the adjuster has reached its travel
limit. The power seat adjuster motors each contain a
self-resetting circuit breaker to protect them from
overload. However, consecutive or frequent resetting
of the circuit breaker must not be allowed to con-
tinue, or the motor may be damaged.
Fig. 3 DR Power Seat Switch
1 - POWER SEAT SWITCH ASSEMBLY
2 - FRONT SEAT CUSHION ADJUSTMENT BUTTON
3 - COMPLETE SEAT ADJUSTMENT BUTTON
4 - REAR SEAT CUSHION ADJUSTMENT BUTTON
5 - LUMBAR ADJUSTMENT BUTTON
DRPOWER SEATS 8N - 15
DRIVER SEAT SWITCH (Continued)
Page 615 of 2627

shield that helps to shroud it from unintentional
actuation when entering or leaving the vehicle.
The power lumbar switches cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the seat switch
assembly must be replaced.
OPERATION
When the power lumbar switch paddle is actuated,
a battery feed and a ground path are applied through
the switch contacts to the power lumbar adjuster
motor. The motor operates to move the lumbar
adjuster through its drive unit in the selected direc-
tion until the switch is released, or until the travel
limit of the adjuster is reached. When the switch is
moved in the opposite direction, the battery feed and
ground path to the motor are reversed through the
switch contacts. This causes the motor to run in the
opposite direction.
The power lumbar switch should not be held
applied in either direction after the adjuster has
reached its travel limit. The power lumbar adjuster
motor contains a self-resetting circuit breaker to pro-
tect it from overload. However, consecutive or fre-
quent resetting of the circuit breaker must not be
allowed to continue, or the motor may be damaged.
REMOVAL
The power lumbar switch is integral with the other
power seat switches. Refer to the appropriate driver
or passenger power front seat switch removal and/or
installation procedure.
LUMBAR MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The power lumbar seat option includes an electri-
cally operated lumbar support mechanism. The only
visible evidence of this option is the separate power
lumbar switch control paddle that is located on the
outboard seat cushion switch bezel, next to the other
power seat switch control knobs. The power lumbar
adjuster and motor are concealed beneath the seat
back trim cover and padding, where they are secured
to a molded plastic back panel and to the seat back
frame.
The power lumbar adjuster cannot be repaired, and
is serviced only as a unit with the seat back frame. If
the power lumbar adjuster or the seat back frame
are damaged or faulty, the entire seat back frame
unit must be replaced (Refer to 23 - BODY/SEATS/
SEAT BACK - REMOVAL).
OPERATION
The power lumbar adjuster mechanism includes a
reversible electric motor that is secured to theinboard side of the seat back panel and is connected
to a worm-drive gearbox. The motor and gearbox
operate the lumbar adjuster mechanism in the center
of the seat back driving a nut up or down a fixed
drive screw. The action of this nut extends or con-
tracts the plastic lumbar support band. The more
this band is contracted, the more outward pressure is
applied against the center of the seat back padding,
providing additional lumbar support.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - LUMBAR MOTOR
Actuate the power lumbar switch to move the
power lumbar adjuster in each direction. The power
lumbar adjuster should move in both directions. It
should be noted that the power lumber adjuster nor-
mally operates very quietly and exhibits little visible
movement. If the power lumbar adjuster fails to oper-
ate in only one direction, move the adjuster a short
distance in the opposite direction and test again to be
certain that the adjuster is not at its travel limit. If
the power lumbar adjuster fails to operate in only
one direction, Test the appropriate power seat switch
as described in this group. If the power lumbar
adjuster fails to operate in either direction, perform
the following tests. For complete circuit diagrams,
refer toWiring.
(1) Check the power seat circuit breaker. If OK, go
to Step 2. If not OK, replace the faulty power seat
circuit breaker.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the power seat cir-
cuit breaker. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, repair
the open fused B(+) circuit to the fuse in the Inte-
grated Power Module as required.
(3) Remove the outboard seat cushion side shield
from the seat. Disconnect the seat wire harness con-
nector from the power lumbar switch connector
receptacle. Check for battery voltage at the fused
B(+) circuit cavity of the power seat wire harness
connector for the power lumbar switch. If OK, go to
Step 4. If not OK, repair the open fused B(+) circuit
to the power seat as required.
(4) Check for continuity between the ground cir-
cuit cavity of the power seat wire harness connector
for the power lumbar switch and a good ground.
There should be continuity. If OK, go to Step 5. If not
OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground as
required.
(5) Test the power lumbar switch. . If the switch
tests OK, test the circuits of the power seat wire har-
ness between the power lumbar adjuster motor and
the power lumbar switch for shorts or opens. If the
circuits check OK, replace the faulty seat back frame
assembly. If the circuits are not OK, repair the power
seat wire harness as required.
8N - 18 POWER SEATSDR
LUMBAR CONTROL SWITCH (Continued)
Page 630 of 2627

AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Airbag Control Module (ACM) is also some-
times referred to as the Occupant Restraint Control-
ler (ORC) (Fig. 7). The ACM is concealed below the
instrument panel center stack in the passenger com-
partment of the vehicle, where it is secured by three
screws to a stamped steel mounting bracket welded
onto the top of the floor panel transmission tunnel
just forward of the instrument panel center support
bracket. Concealed within a hollow in the center of
the die cast aluminum ACM housing is the electronic
circuitry of the ACM which includes a microproces-
sor, an electronic impact sensor, an electronic safing
sensor, and an energy storage capacitor. A stamped
metal cover plate is secured to the bottom of the
ACM housing with four screws to enclose and protect
the internal electronic circuitry and components.
An arrow printed on the label on the top of the
ACM housing provides a visual verification of the
proper orientation of the unit, and should always be
pointed toward the front of the vehicle. The ACM
housing has integral mounting flanges on three cor-
ners. The mounting flange to the left of the connector
receptacle has an integral locating pin on its lower
surface. Both left side flanges have round mounting
holes, while the flange on the right side has a slotted
mounting hole. A molded plastic electrical connector
with two receptacles, one containing twenty-four ter-
minal pins and the other containing thirty-two termi-
nal pins, exits the rearward facing side of the ACM
housing. These terminal pins connect the ACM to the
vehicle electrical system through two dedicated takeouts and connectors of the instrument panel wire
harness.
The impact sensor and safing sensor internal to
the ACM are calibrated for the specific vehicle, and
are only serviced as a unit with the ACM. In addi-
tion, there are unique versions of the ACM for light
and heavy-duty models, and for vehicles with or
without the optional side curtain airbags. The ACM
cannot be repaired or adjusted and, if damaged or
faulty, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The microprocessor in the Airbag Control Module
(ACM) contains the supplemental restraint system
logic circuits and controls all of the supplemental
restraint system components. The ACM uses
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) and can communicate
with other electronic modules in the vehicle as well
as with the DRBIIItscan tool using the Programma-
ble Communications Interface (PCI) data bus net-
work. This method of communication is used for
control of the airbag indicator in the ElectroMechani-
cal Instrument Cluster (EMIC) and for supplemental
restraint system diagnosis and testing through the
16-way data link connector located on the driver side
lower edge of the instrument panel. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT CLUSTER/AIRBAG
INDICATOR - OPERATION).
The ACM microprocessor continuously monitors all
of the supplemental restraint system electrical cir-
cuits to determine the system readiness. If the ACM
detects a monitored system fault, it sets an active
and stored Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and sends
electronic messages to the EMIC over the PCI data
bus to turn on the airbag indicator. An active fault
only remains for the duration of the fault, or in some
cases for the duration of the current ignition switch
cycle, while a stored fault causes a DTC to be stored
in memory by the ACM. For some DTCs, if a fault
does not recur for a number of ignition cycles, the
ACM will automatically erase the stored DTC. For
other internal faults, the stored DTC is latched for-
ever.
In standard cab models, the ACM also monitors a
resistor multiplexed input from the passenger airbag
on/off switch and provides a control output for the
Off indicator in the switch through a passenger air-
bag indicator driver circuit. If the passenger airbag
on/off switch is set to the Off position, the ACM turns
on the passenger airbag on/off switch Off indicator
and will internally disable the passenger airbag from
being deployed. The ACM also turns on the on/off
switch Off indicator for about seven seconds each
time the ignition switch is turned to the On position
as a bulb test. Following the bulb test, the ACM con-
trols the status of the Off indicator based upon the
Fig. 7 Airbag Control Module
1 - AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE
2 - ORIENTATION ARROW
3 - LABEL
4 - CONNECTOR RECEPTACLE (2)
DRRESTRAINTS 8O - 11
Page 672 of 2627

retracted or extracted is a sure indication that the
seat belt tensioner has been deployed and requires
replacement. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RE-
STRAINTS/FRONT OUTBOARD SEAT BELT &
RETRACTOR - REMOVAL).
OPERATION
The seat belt tensioners are deployed by a signal
generated by the Airbag Control Module (ACM)
through the driver and passenger seat belt tensioner
line 1 and line 2 (or squib) circuits. When the ACM
sends the proper electrical signal to the tensioners,
the electrical energy generates enough heat to ini-
tiate a small pyrotechnic gas generator. The gas gen-
erator is installed at the top of the tensioner housing
which contains a long metal tape that is routed
through two chambers within the housing. Each end
of the tape is wound around the outer sleeve of a
mechanical clutch mechanism secured to one end of
the torsion bar upon which the retractor spool is
secured. As the gas expands, it is directed against
the metal tape within the two chambers of the hous-
ing causing the tape to unwind from the clutch
sleeve. As the clutch rotates it engages the torsion
bar, which drives the seat belt retractor spool causing
the slack to be removed from the seat belt.
Once a seat belt tensioning sequence has been
completed, the forward momentum of the occupant
results in deformation of the torsion bar. As the tor-
sion bar deforms it allows the seat belt webbing to
unwind from the retractor spool, which causes the
metal tape to be wound back onto the clutch sleeve
until it is pulled tight against two cutter blades
within the housing, which immediately cut the metal
tape.
Removing excess slack from the seat belt not only
keeps the occupant properly positioned for an airbag
deployment following a frontal impact of the vehicle,
but also helps to reduce injuries that the occupant
might experience in these situations as a result of a
harmful contact with the steering wheel, steering col-
umn, instrument panel and/or windshield. The tor-
sion bar is designed to deform in order to control the
loading being applied to the occupant by the seat belt
during a frontal impact, further reducing the poten-
tial for occupant injuries.
The ACM monitors the condition of the seat belt
tensioners through circuit resistance. The ACM will
illuminate the airbag indicator in the ElectroMe-
chanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC) and store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) for any fault that is
detected. For proper diagnosis of the seat belt ten-
sioners, a DRBIIItscan tool is required. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information.
SEAT BELT TENSION
REDUCER
DESCRIPTION
A seat belt tension reducer is standard equipment
for the driver side front outboard seat belt on stan-
dard cab versions of this model (Fig. 49). The tension
reducer is integral to the driver side front outboard
seat belt and retractor unit, which is secured to the
inner B-pillar on the left side of the vehicle. The
retractor is concealed beneath the molded plastic
inner B-pillar trim. The seat belt tension reducer
consists primarily of a 12-volt Direct Current (DC)
solenoid and an integral connector receptacle that is
located on the forward facing end housing of the
retractor. The seat belt tension reducer is controlled
by a battery current output of the ignition switch and
a ground path provided by the seat belt switch, and
is connected to the vehicle electrical system through
a dedicated take out of the body wire harness by a
keyed and latching molded plastic connector insula-
tor to ensure a secure connection.
The seat belt tension reducer cannot be repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, the entire driver side front
outboard seat belt and retractor unit must be
replaced. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/
FRONT OUTBOARD SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR -
REMOVAL).
Fig. 49 Seat Belt Tension Reducer
1 - TENSIONER HOUSING OR CHAMBER
2 - GAS GENERATOR
3 - TENSIONER PIGTAIL WIRE
4 - SPOOL
5 - TENSION REDUCER (DRIVER SIDE ON STANDARD CAB
ONLY)
6 - REDUCER CONNECTOR RECEPTACLE
DRRESTRAINTS 8O - 53
SEAT BELT TENSIONER (Continued)
Page 685 of 2627

CABLE
DESCRIPTION
The speed control servo cable is connected between
the speed control vacuum servo diaphragm and the
throttle body control linkage. This cable is used with
3.7L/4.7L gas powered engines only. It is also used if
equipped with a 5.9L diesel engine equipped with an
automatic transmission.
A speed control servo cableis not usedif equipped
with either a 5.9L diesel engine equipped with a
manual transmission, or any 5.7L engine/transmis-
sion combinations.
OPERATION
This cable causes the throttle control linkage to
open or close the throttle valve in response to move-
ment of the vacuum servo diaphragm.
REMOVAL
3.7L / 4.7L GAS
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Remove air intake tube at top of throttle body.
The accelerator cable must be partially removed to
gain access to speed control cable.
(3) Hold throttle in wide open position. While held
in this position, slide throttle cable pin (Fig. 1) from
throttle body bellcrank.
(4) Using a pick or small screwdriver, press release
tab (Fig. 2) to release plastic cable mount from
bracket.Press on tab only enough to release
cable from bracket. If tab is pressed too much,
it will be broken.Slide plastic mount (Fig. 2)
towards right side of vehicle to remove throttle cable
from throttle body bracket.
(5) Using finger pressure only, disconnect servo
cable connector (Fig. 3) at throttle body bellcrank pin
by pushing connector off bellcrank pin towards front
of vehicle.DO NOT try to pull connector off per-
pendicular to the bellcrank pin. Connector will
be broken.
(6) Slide speed control cable plastic mount towards
right of vehicle to remove cable from throttle body
bracket (Fig. 4).
(7) Remove servo cable from servo. Refer to Servo
Removal/Installation.
5.9L Diesel Ð Auto. Trans.
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
(2) Remove cable/lever/linkage cover. Refer to
Speed Control Servo Removal/Installation.
(3) Remove (disconnect) servo cable from servo.
Refer to Speed Control Servo Removal/Installation.(4) Using finger pressure only, disconnect end of
servo cable from throttle lever pin by pulling forward
on connector while holding lever rearward (Fig. 5).
DO NOT try to pull connector off perpendicular
to lever pin. Connector will be broken.
(5) Squeeze 2 pinch tabs (Fig. 5) on sides of speed
control cable at mounting bracket and push cable
rearward out of bracket.
Fig. 1 THROTTLE CABLE PIN - 3.7L / 4.7L
1 - THROTTLE CABLE PIN
2 - THROTTLE BODY BELLCRANK
3 - PUSH UP HERE
Fig. 2 THROTTLE CABLE RELEASE TAB - 3.7L /
4.7L
1 - THROTTLE CABLE
2 - RELEASE TAB
3 - PICK OR SCREWDRIVER
4 - PLASTIC CABLE MOUNT
8P - 4 SPEED CONTROLDR
Page 702 of 2627

the wiper motor was operating at high speed, the
FCM immediately de-energizes the wiper high/low
relay causing the wiper motor to return to low speed
operation. Then one of two events will occur. The
event that occurs depends upon the position of the
wiper blades on the windshield at the moment that
the control knob Off position is selected.
If the wiper blades are in the down position on the
windshield when the Off position is selected, the
park switch that is integral to the wiper motor is
closed to ground and provides a hard wired park
switch sense input to the FCM. The FCM then de-en-
ergizes the wiper on/off relay and the wiper motor
ceases to operate. If the wiper blades are not in the
down position on the windshield at the moment the
Off position is selected, the park switch is an open
circuit and the FCM keeps the wiper on/off relay
energized, which causes the wiper motor to continue
running at low speed until the wiper blades are in
the down position on the windshield and the park
switch input to the FCM is again closed to ground.
INTERMITTENT WIPE MODE
When the control knob on the control stalk of the
multi-function switch is moved to one of the Delay
interval positions the instrument cluster sends an
electronic wiper switch delay message to the FCM,
then the FCM electronic intermittent wipe logic cir-
cuit responds by calculating the correct length of
time between wiper sweeps based upon the selected
delay interval input. The FCM monitors the changing
state of the wiper motor park switch through a hard
wired park switch sense input. This input allows the
FCM to determine the proper intervals at which to
energize and de-energize the wiper on/off relay to
operate the wiper motor intermittently for one low
speed cycle at a time.
The FCM logic is also programmed to provide vehi-
cle speed sensitivity to the selected intermittent wipe
delay intervals. In order to provide this feature the
FCM monitors electronic vehicle speed messages
from the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) and dou-
bles the selected delay interval whenever the vehicle
speed is about sixteen kilometers-per-hour (ten miles-
per-hour) or less.
PULSE WIPE MODE
When the control knob on the control stalk of the
multi-function switch is depressed to the momentary
Wash position for less than about one-half second,
the instrument cluster sends an electronic washer
switch message to the FCM, then the FCM the ener-
gizes the wiper on/off relay for one complete wipe
cycle. The FCM de-energizes the relay when the state
of the park switch sense changes to ground, parking
the wiper blades near the base of the windshield.WASH MODE
When the control knob on the control stalk of the
multi-function switch is depressed to the momentary
Wash position for more than about one-half second,
the instrument cluster sends an electronic washer
switch message to the FCM, then the FCM directs
battery current to the washer pump/motor unit. This
will cause the washer pump/motor unit to be ener-
gized for as long as the Wash switch is held closed up
to about thirty seconds, and to de-energize when the
front Wash switch is released.
When the control knob is depressed to the momen-
tary Wash position while the wiper system is operat-
ing in one of the Delay interval positions, the washer
pump/motor operation is the same. However, the
FCM also energizes the wiper on/off relay to override
the selected delay interval and operate the wiper
motor in a continuous low speed mode for as long as
the control knob is held depressed, then de-energizes
the relay and reverts to the selected delay mode
interval several wipe cycles after the control knob is
released. If the control knob is held depressed for
more than about thirty seconds, the FCM will sus-
pend washer pump/motor operation until the knob is
released for about two seconds, then cycled back to
the Wash position.
WIPE-AFTER-WASH MODE
When the control knob on the control stalk of the
multi-function switch is depressed to the momentary
Wash position for more than about one-half second
while the wiper system is not operating, the instru-
ment cluster sends an electronic washer switch mes-
sage to the FCM, then the FCM the directs battery
current to the washer pump/motor unit and energizes
the wiper on/off relay. This will cause the washer
pump/motor unit to be energized and operate the
wiper motor in a continuous low speed mode for as
long as the Wash switch is held closed up to about
thirty seconds. When the control knob is released,
the FCM de-energizes the washer pump/motor unit,
but allows the wiper motor to operate for several
additional wipe cycles before it de-energizes the
wiper on/off relay and parks the wiper blades near
the base of the windshield.
If the control knob is held depressed for more than
about thirty seconds, the FCM will suspend washer
pump/motor operation until the knob is released for
about two seconds, then cycled back to the Wash
position; however, the wipers will continue to operate
for as long as the Wash switch is held closed. The
FCM monitors the changing state of the wiper motor
park switch through a hard wired wiper park switch
sense circuit input. This input allows the FCM to
count the number of wipe cycles that occur after the
Wash switch is released, and to determine the proper
DRWIPERS/WASHERS 8R - 5
WIPERS/WASHERS (Continued)
Page 709 of 2627

domed upper surface of the washer nozzle is visible
on the top of the plenum cover/grille panel, and the
nozzle orifice is oriented towards the windshield
glass. The washer plumbing fittings for the washer
nozzles are concealed beneath the cowl plenum cover/
grille panel. These fluidic washer nozzles are con-
structed of molded plastic. The cowl plenum cover/
grille panel must be removed from the vehicle to
access the nozzles for service. The washer nozzles
cannot be adjusted or repaired. If faulty or damaged,
they must be replaced.
OPERATION
The two washer nozzles are designed to dispense
washer fluid into the wiper pattern area on the out-
side of the windshield glass. Pressurized washer fluid
is fed to each nozzle from the washer reservoir by the
washer pump/motor unit through a single hose,
which is attached to a barbed nipple on each washer
nozzle below the cowl plenum cover/grille panel. A
fluidic matrix within the washer nozzle causes the
pressurized washer fluid to be emitted from the noz-
zle orifice as an oscillating stream to more effectively
cover a larger area of the glass to be cleaned.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove both wiper arms from the wiper pivots.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/
WIPER ARM - REMOVAL).
(2) Unlatch and open the hood.
(3) Remove the cowl plenum cover/grille panel
from over the cowl plenum. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EX-
TERIOR/COWL GRILLE - REMOVAL).(4) From the underside of the cowl plenum cover/
grille panel, disconnect the washer nozzle hose from
the barbed nipple of the washer nozzle (Fig. 11).
(5) From the underside of the cowl plenum cover/
grille panel, release the integral snap features of the
washer nozzle and push the nozzle out through the
mounting hole toward the top side of the cowl ple-
num cover/grille panel.
(6) Remove the washer nozzle from the top of the
cowl plenum cover/grille panel.
INSTALLATION
(1) From the top of the cowl plenum cover/grille
panel, position the nipple end of the washer nozzle
through the mounting hole and engage the anti-rota-
tion tab of the nipple into the anti-rotation notch in
the mounting hole.
(2) Using hand pressure, push firmly and evenly
on the top of the washer nozzle until the integral
snap features lock into place on the underside of the
cowl plenum cover/grille panel.
(3) From the underside of the cowl plenum cover/
grille panel, reconnect the washer hose to the barbed
nipple of the washer nozzle (Fig. 11).
(4) Reinstall the washer hose for the washer noz-
zle into its routing clips on the underside of the cowl
plenum cover/grille panel.
(5) Reinstall the cowl plenum cover/grille panel
over the cowl plenum. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERI-
OR/COWL GRILLE - INSTALLATION).
(6) Close and latch the hood.
Fig. 10 Washer Nozzle
1 - HOOD
2 - LATCH (2)
3 - NIPPLE
4 - ANTI-ROTATION TAB
5 - ORIFICE
Fig. 11 Washer Nozzle Remove/Install
1 - COWL PLENUM COVER/GRILLE PANEL (UNDERSIDE)
2 - ANTI-ROTATION TAB (LARGE)
3 - NIPPLE
4 - ANTI-ROTATION TAB (SMALL)
5 - PLIERS
6 - LATCH (2)
8R - 12 WIPERS/WASHERSDR
WASHER NOZZLE (Continued)