Causes DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 1413 of 2627

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION OR
SPARK PLUGS OIL FOULED1. CCV System malfunction 1. (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS
CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE
EMISSIONS - DESCRIPTION) for
correct operation
2. Defective valve stem seal(s) 2. Repair or replace seal(s)
3. Worn or broken piston rings 3. Hone cylinder bores. Install new
rings
4. Scuffed pistons/cylinder walls 4. Hone cylinder bores and replace
pistons as required
5. Carbon in oil control ring groove 5. Remove rings and de-carbon piston
6. Worn valve guides 6. Inspect/replace valve guides as
necessary
7. Piston rings fitted too tightly in
grooves7. Remove rings and check ring end
gap and side clearance. Replace if
necessary
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR DAMAGED
OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐHYDROSTATIC
LOCK
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Disconnect the negative cable(s) from the bat-
tery.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system, and
intake manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure
in the cylinder head. Remove the spark plugs.(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (coolant, fuel,
oil, etc.).
(7) Be sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt a small amount of engine oil into the
cylinders to lubricate the walls. This will prevent
damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs. Tighten the spark
plugs to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(15) Connect the negative cable(s) to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
REMOVAL
(1) Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release pro-
cedure (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIV-
ERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(3) Remove the air cleaner resonator and duct
work as an assembly.
(4) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
9 - 190 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)
Page 1432 of 2627

CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL -
REAR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR SEAL AREA
LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, camshaft bore
cup plugs, oil galley pipe plugs, oil filter runoff,
and main bearing cap to cylinder block mating sur-
faces. See Engine, for proper repair procedures of
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurized the crank-
case as outlined in the section, Inspection (Engine oil
Leaks in general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks or
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is specially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING), under the Oil Leak row, for components
inspections on possible causes and corrections.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT OIL
SEAL - REAR - REMOVAL).
REMOVAL
NOTE: This procedure can be performed in vehicle.
(1) If being preformed in vehicle, remove the
transmission.
(2) Remove the flexplate (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/FLEX PLATE - REMOVAL).
NOTE: The crankshaft oil seal CAN NOT be reused
after removal.
NOTE: The crankshaft rear oil seal remover Special
Tool 8506 must be installed deeply into the seal.
Continue to tighten the removal tool into the seal
until the tool can not be turned farther. Failure to
install tool correctly the first time will cause tool to
pull free of seal without removing seal from engine.
(3) Using Special Tool 8506, remove the crankshaft
rear oil seal.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The rear seal must be installed dry for
proper operation. Do not lubricate the seal lip or
outer edge.
(1) Position the plastic seal guide onto the crank-
shaft rear face. Then position the crankshaft rear oil
seal onto the guide.
(2) Using Special Tools 8349 Crankshaft Rear Oil
Seal Installer and C-4171 Driver Handle, with a
hammer, tap the seal into place. Continue to tap on
the driver handle until the seal installer seats
against the cylinder block crankshaft bore.
(3) Install the flexplate.
(4) Install the transmission.
CRANKSHAFT REAR OIL SEAL
RETAINER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the transmission.
(3) Remove the drive plate / flywheel.
(4) Remove the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the rear oil seal retainer mounting
bolts.
(6) Carefully remove the retainer from the engine
block.
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 209
Page 1445 of 2627

If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, distributor seal,
camshaft bore cup plugs oil galley pipe plugs, oil
filter runoff, and main bearing cap to cylinder
block mating surfaces.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as outlined in the, Inspection (Engine oil Leaks
in general)
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
SERVICE
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY.
ENGINE OIL SPECIFICATION
CAUTION: Do not use non-detergent or straight
mineral oil when adding or changing crankcase
lubricant. Engine failure can result.
API SERVICE GRADE CERTIFIED
Use an engine oil that is API Service Grade Certi-
fied. MOPARtprovides engine oils that conform to
this service grade.
SAE VISCOSITY
An SAE viscosity grade is used to specify the vis-
cosity of engine oil. Use only engine oils with multi-
ple viscosities such as 5W-30 in the 5.7L engines.
These are specified with a dual SAE viscosity grade
which indicates the cold-to-hot temperature viscosity
range. Select an engine oil that is best suited to your
particular temperature range and variation.
ENERGY CONSERVING OIL
An Energy Conserving type oil is recommended for
gasoline engines. The designation of ENERGY CON-
SERVING is located on the label of an engine oil con-
tainer.
CONTAINER IDENTIFICATION
Standard engine oil identification notations have
been adopted to aid in the proper selection of engine
oil. The identifying notations are located on the label
of engine oil plastic bottles and the top of engine oil
cans (Fig. 28).
OIL LEVEL INDICATOR (DIPSTICK)
The engine oil level indicator is located at the left
hand of the engine on the 5.7L engines.
CRANKCASE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION
CAUTION: Do not overfill crankcase with engine oil,
pressure loss or oil foaming can result.
Inspect engine oil level approximately every 800
kilometers (500 miles). Unless the engine has exhib-
ited loss of oil pressure, run the engine for about ten
Fig. 28 API SYMBOL
9 - 222 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1456 of 2627
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
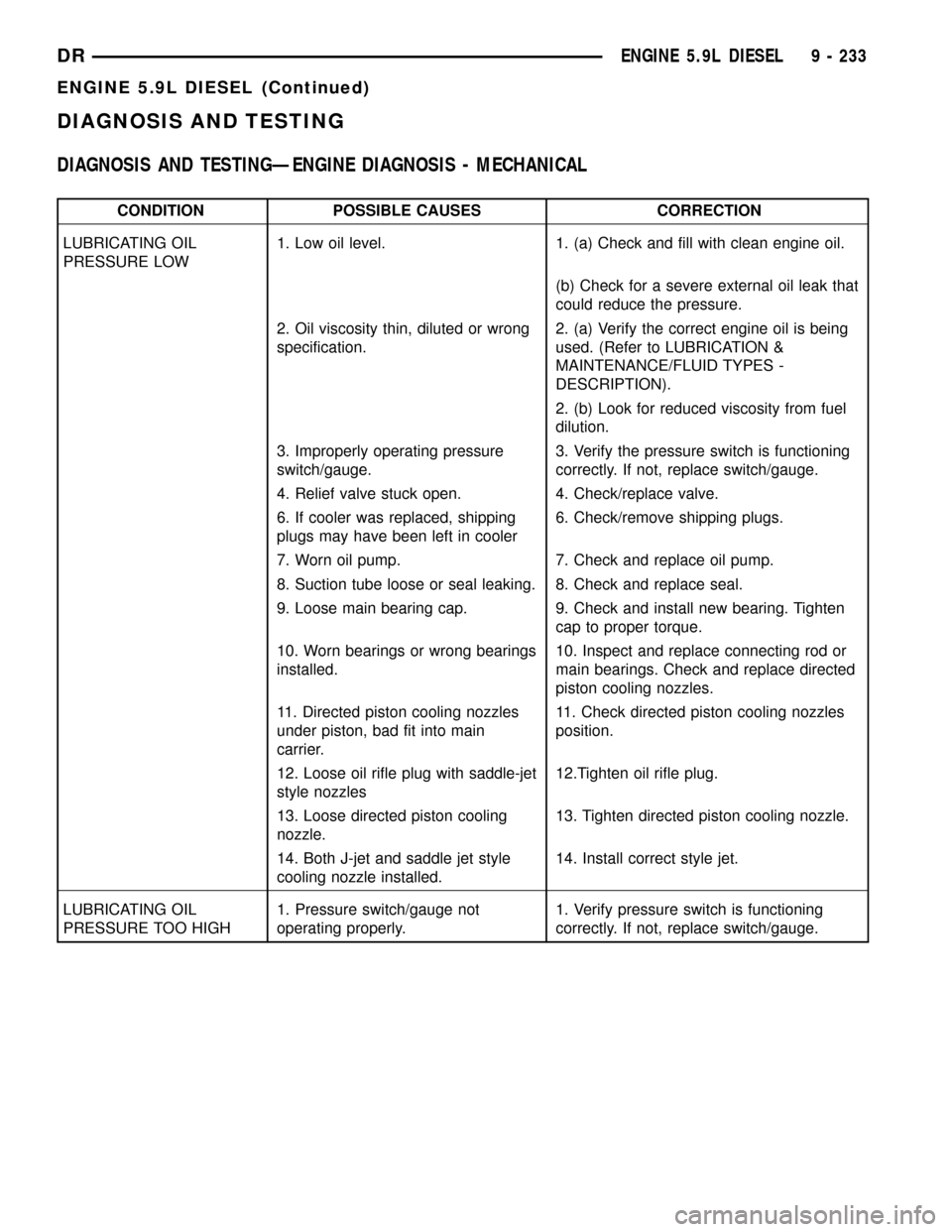
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
LUBRICATING OIL
PRESSURE LOW1. Low oil level. 1. (a) Check and fill with clean engine oil.
(b) Check for a severe external oil leak that
could reduce the pressure.
2. Oil viscosity thin, diluted or wrong
specification.2. (a) Verify the correct engine oil is being
used. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
2. (b) Look for reduced viscosity from fuel
dilution.
3. Improperly operating pressure
switch/gauge.3. Verify the pressure switch is functioning
correctly. If not, replace switch/gauge.
4. Relief valve stuck open. 4. Check/replace valve.
6. If cooler was replaced, shipping
plugs may have been left in cooler6. Check/remove shipping plugs.
7. Worn oil pump. 7. Check and replace oil pump.
8. Suction tube loose or seal leaking. 8. Check and replace seal.
9. Loose main bearing cap. 9. Check and install new bearing. Tighten
cap to proper torque.
10. Worn bearings or wrong bearings
installed.10. Inspect and replace connecting rod or
main bearings. Check and replace directed
piston cooling nozzles.
11. Directed piston cooling nozzles
under piston, bad fit into main
carrier.11. Check directed piston cooling nozzles
position.
12. Loose oil rifle plug with saddle-jet
style nozzles12.Tighten oil rifle plug.
13. Loose directed piston cooling
nozzle.13. Tighten directed piston cooling nozzle.
14. Both J-jet and saddle jet style
cooling nozzle installed.14. Install correct style jet.
LUBRICATING OIL
PRESSURE TOO HIGH1. Pressure switch/gauge not
operating properly.1. Verify pressure switch is functioning
correctly. If not, replace switch/gauge.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 233
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1457 of 2627
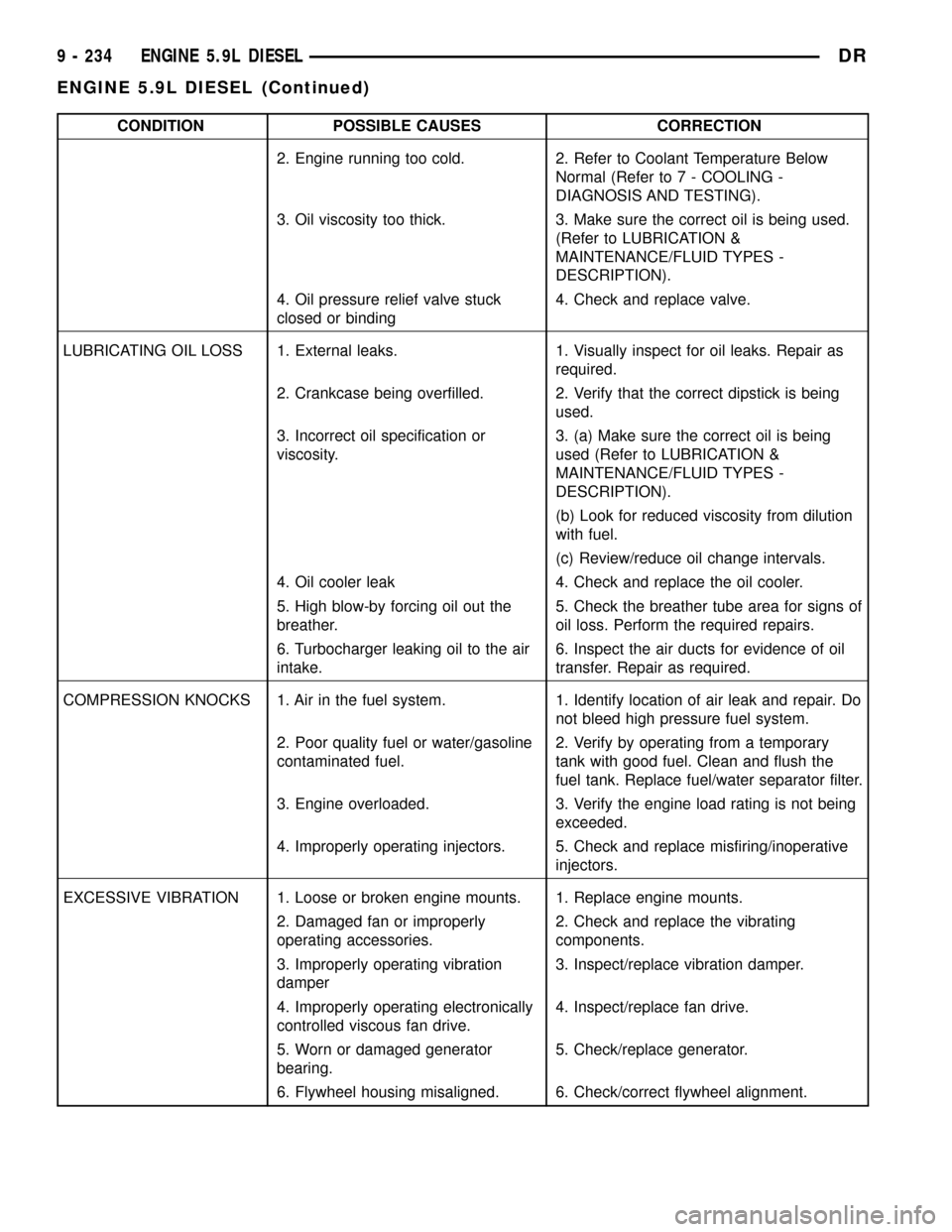
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
2. Engine running too cold. 2. Refer to Coolant Temperature Below
Normal (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
3. Oil viscosity too thick. 3. Make sure the correct oil is being used.
(Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
4. Oil pressure relief valve stuck
closed or binding4. Check and replace valve.
LUBRICATING OIL LOSS 1. External leaks. 1. Visually inspect for oil leaks. Repair as
required.
2. Crankcase being overfilled. 2. Verify that the correct dipstick is being
used.
3. Incorrect oil specification or
viscosity.3. (a) Make sure the correct oil is being
used (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
(b) Look for reduced viscosity from dilution
with fuel.
(c) Review/reduce oil change intervals.
4. Oil cooler leak 4. Check and replace the oil cooler.
5. High blow-by forcing oil out the
breather.5. Check the breather tube area for signs of
oil loss. Perform the required repairs.
6. Turbocharger leaking oil to the air
intake.6. Inspect the air ducts for evidence of oil
transfer. Repair as required.
COMPRESSION KNOCKS 1. Air in the fuel system. 1. Identify location of air leak and repair. Do
not bleed high pressure fuel system.
2. Poor quality fuel or water/gasoline
contaminated fuel.2. Verify by operating from a temporary
tank with good fuel. Clean and flush the
fuel tank. Replace fuel/water separator filter.
3. Engine overloaded. 3. Verify the engine load rating is not being
exceeded.
4. Improperly operating injectors. 5. Check and replace misfiring/inoperative
injectors.
EXCESSIVE VIBRATION 1. Loose or broken engine mounts. 1. Replace engine mounts.
2. Damaged fan or improperly
operating accessories.2. Check and replace the vibrating
components.
3. Improperly operating vibration
damper3. Inspect/replace vibration damper.
4. Improperly operating electronically
controlled viscous fan drive.4. Inspect/replace fan drive.
5. Worn or damaged generator
bearing.5. Check/replace generator.
6. Flywheel housing misaligned. 6. Check/correct flywheel alignment.
9 - 234 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1458 of 2627
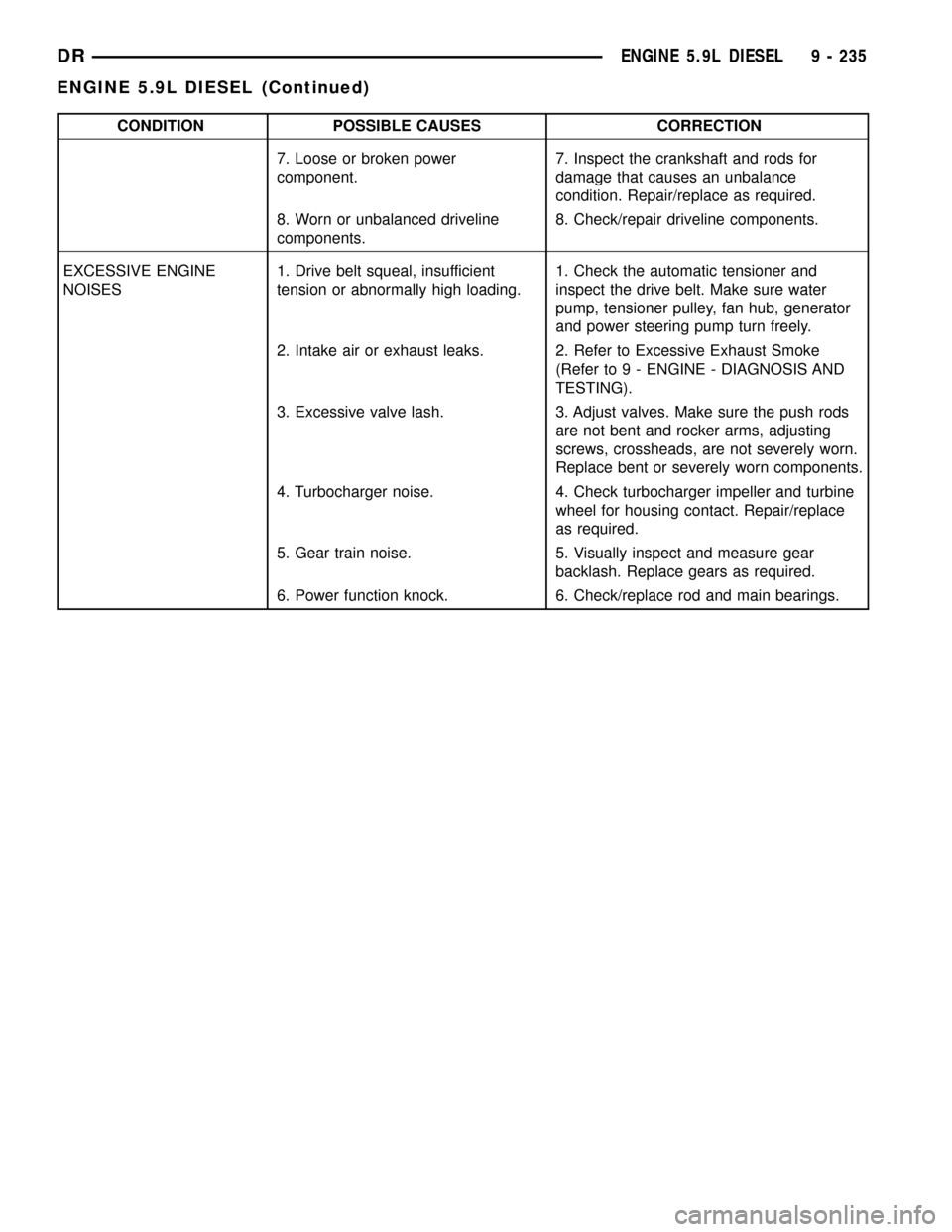
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
7. Loose or broken power
component.7. Inspect the crankshaft and rods for
damage that causes an unbalance
condition. Repair/replace as required.
8. Worn or unbalanced driveline
components.8. Check/repair driveline components.
EXCESSIVE ENGINE
NOISES1. Drive belt squeal, insufficient
tension or abnormally high loading.1. Check the automatic tensioner and
inspect the drive belt. Make sure water
pump, tensioner pulley, fan hub, generator
and power steering pump turn freely.
2. Intake air or exhaust leaks. 2. Refer to Excessive Exhaust Smoke
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
3. Excessive valve lash. 3. Adjust valves. Make sure the push rods
are not bent and rocker arms, adjusting
screws, crossheads, are not severely worn.
Replace bent or severely worn components.
4. Turbocharger noise. 4. Check turbocharger impeller and turbine
wheel for housing contact. Repair/replace
as required.
5. Gear train noise. 5. Visually inspect and measure gear
backlash. Replace gears as required.
6. Power function knock. 6. Check/replace rod and main bearings.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 235
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1459 of 2627
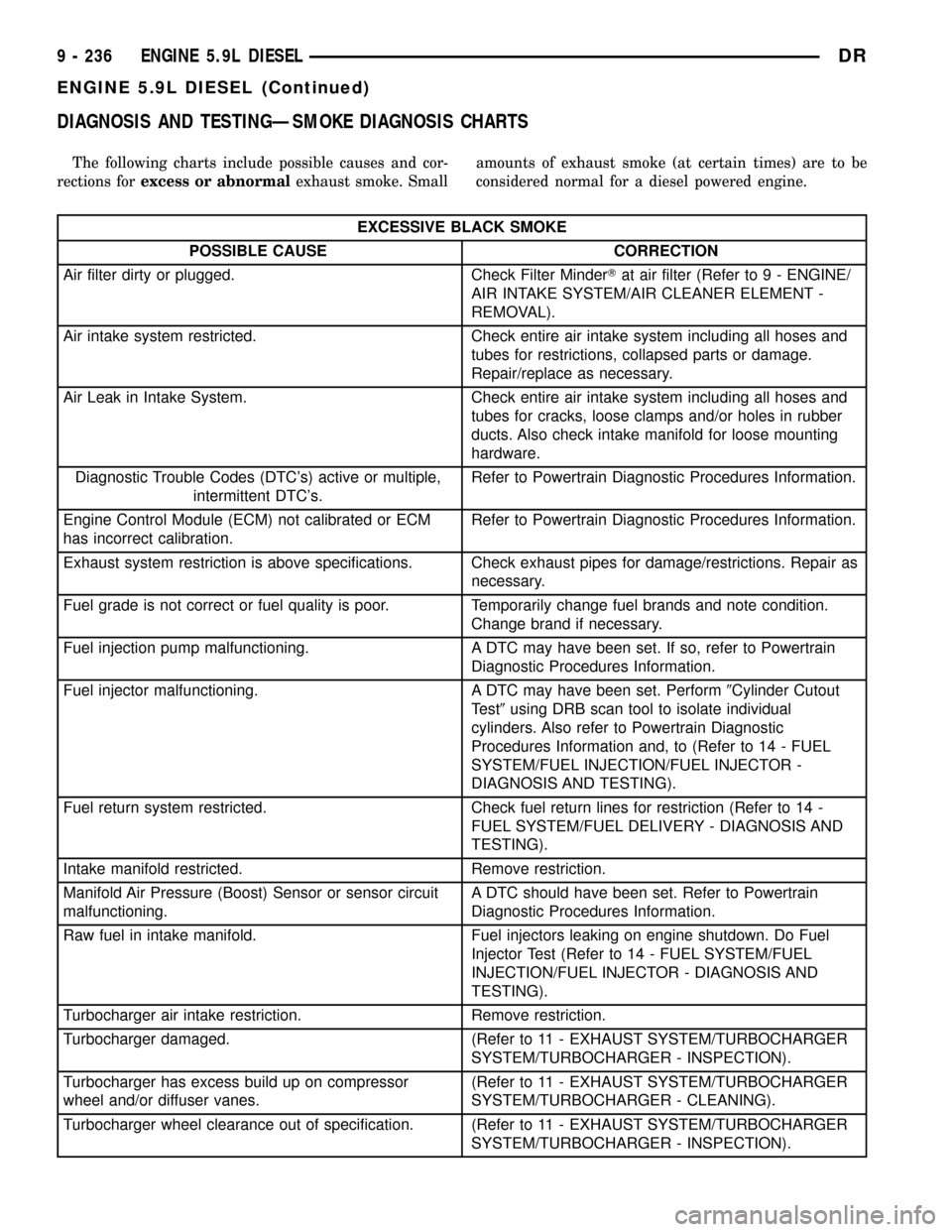
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐSMOKE DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
The following charts include possible causes and cor-
rections forexcess or abnormalexhaust smoke. Smallamounts of exhaust smoke (at certain times) are to be
considered normal for a diesel powered engine.
EXCESSIVE BLACK SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Air filter dirty or plugged. Check Filter MinderTat air filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER ELEMENT -
REMOVAL).
Air intake system restricted. Check entire air intake system including all hoses and
tubes for restrictions, collapsed parts or damage.
Repair/replace as necessary.
Air Leak in Intake System. Check entire air intake system including all hoses and
tubes for cracks, loose clamps and/or holes in rubber
ducts. Also check intake manifold for loose mounting
hardware.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) active or multiple,
intermittent DTC's.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Engine Control Module (ECM) not calibrated or ECM
has incorrect calibration.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Exhaust system restriction is above specifications. Check exhaust pipes for damage/restrictions. Repair as
necessary.
Fuel grade is not correct or fuel quality is poor. Temporarily change fuel brands and note condition.
Change brand if necessary.
Fuel injection pump malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. If so, refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Fuel injector malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. Perform9Cylinder Cutout
Test9using DRB scan tool to isolate individual
cylinders. Also refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information and, to (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fuel return system restricted. Check fuel return lines for restriction (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Intake manifold restricted. Remove restriction.
Manifold Air Pressure (Boost) Sensor or sensor circuit
malfunctioning.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Raw fuel in intake manifold. Fuel injectors leaking on engine shutdown. Do Fuel
Injector Test (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Turbocharger air intake restriction. Remove restriction.
Turbocharger damaged. (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - INSPECTION).
Turbocharger has excess build up on compressor
wheel and/or diffuser vanes.(Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - CLEANING).
Turbocharger wheel clearance out of specification. (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - INSPECTION).
9 - 236 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1462 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION/LEAKAGE TESTS
CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure batteries are completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise, the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnostic purposes.
(1) Disconnect the fuel inlet line to the fuel trans-
fer pump. Plug the fuel line from the fuel tank.
(2) Start the engine and idle until the engine stalls
(runs out of fuel).
(3) Disconnect all three injector wire harness con-
nectors at the rocker housing.
(4) Remove the breather cover and cylinder head
cover.
(5) Remove the high pressure fuel line between the
cylinder head and fuel rail for the cylinder to be
tested. Use tool# 9011 to cap this fuel rail on the cyl-
inder being tested.
(6) Remove the exhaust rocker lever.
(7) Use Tool 9010 to remove the injector and cop-
per sealing washer.
(8) Install the exhaust rocker lever and torque to
36 N´m (27 ft. lbs.).
(9) Cover the remaining rocker levers with clean
shop towels to prevent any oil splatter under the
hood.
(10) Place a rag over the compression test tool fit-
ting. Crank the engine for 2±3 seconds to purge any
fuel that may have drained into the cylinder when
the injector was removed.
(11) Connect the compression test gauge.
(12) Crank the engine for 5 seconds and record the
pressure reading. Repeat this step three times and
calculate the average of the three readings.
NOTE: The minimum cylinder pressure is 350 psi.
Cylinder pressure should be within 20% from cylin-
der to cylinder.
(13) Combustion pressure leakage can be checked
if cylinder pressure is below the specification. Per-
form the leakage test procedure on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer instructions.
(14) Upon completion of the test check an erase
any engine related fault codes.
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss
(1) Start and operate the engine until it attains
normal operating temperature.
(2) Remove the breather cover and cylinder head
cover.
(3) Disconnect all three injector wire harness con-
nectors at the rocker housing.
(4) Bring the cylinder to be tested to TDC.
(5) Remove the high pressure fuel line between the
cylinder head and the fuel rail for the cylinder to be
tested.
(6) Install capping Tool 9011 onto the rail.
(7) Remove the high pressure connector nut and
high pressure connector with Tool 9015.
(8) Remove the exhaust and intake rocker lever.
(9) Use Tool 9010 to remove the injector and cop-
per sealing washer.
(10) Install compression test Tool 9007 into the
injector bore.
(11) Connect the leakage tester and perform the
leakage test procedure on each cylinder according to
the tester manufacturer's instructions.
(12) Upon completion of the test check and erase
any engine related fault codes.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-PLACE
GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN II
MopartEngine RTV GEN II is used to seal com-
ponents exposed to engine oil. This material is a spe-
cially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 239
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1538 of 2627

OPERATION
Exhaust gas pressure and energy drive the tur-
bine, which in turn drives a centrifugal compressor
that compresses the inlet air, and forces the air into
the engine through the charge air cooler and plumb-
ing. Since heat is a by-product of this compression,
the air must pass through a charge air cooler to cool
the incoming air and maintain power and efficiency.
Increasing air flow to the engine provides:
²Improved engine performance
²Lower exhaust smoke density
²Improved operating economy
²Altitude compensation
²Noise reduction.
The turbocharger also uses a wastegate (Fig. 16),
which regulates intake manifold air pressure and
prevents over boosting at high engine speeds. When
the wastegate valve is closed, all of the exhaust gases
flow through the turbine wheel. As the intake mani-
fold pressure increases, the wastegate actuator opens
the valve, diverting some of the exhaust gases away
from the turbine wheel. This limits turbine shaft
speed and air output from the impeller.
The turbocharger is lubricated by engine oil that is
pressurized, cooled, and filtered. The oil is delivered
to the turbocharger by a supply line that is tapped
into the oil filter head. The oil travels into the bear-
ing housing, where it lubricates the shaft and bear-
ings (Fig. 17). A return pipe at the bottom of the
bearing housing, routes the engine oil back to the
crankcase.
The most common turbocharger failure is bearing
failure related to repeated hot shutdowns with inad-
equate ªcool-downº periods. A sudden engine shut
down after prolonged operation will result in the
transfer of heat from the turbine section of the tur-
bocharger to the bearing housing. This causes the oil
to overheat and break down, which causes bearing
and shaft damage the next time the vehicle is
started.
Letting the engine idle after extended operation
allows the turbine housing to cool to normal operat-
ing temperature. The following chart should be used
as a guide in determining the amount of engine idle
time required to sufficiently cool down the turbo-
charger before shut down, depending upon the type
of driving and the amount of cargo.
Fig. 16 Wastegate Operation
1 - SIGNAL LINE
2 - EXHAUST BYPASS VALVE
3 - WASTEGATE
4 - EXHAUST
5 - TURBINE
DREXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 13
TURBOCHARGER (Continued)
Page 1640 of 2627

INSTALLATION
Engine Mounted Sensor :
The APPS is serviced (replaced) as one assembly
including the lever, brackets and sensor. The APPS is
calibrated to its mounting bracket.
(1) Snap electrical connector into bottom of sensor.
(2) Position APPS assembly to engine and install 6
bolts. Tighten bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect wiring harness clip at bottom of
bracket.
(4) Refer to Group 21, Transmission for transmis-
sion control cable installation procedures.
(5) Install speed control cable into mounting
bracket. Be sure pinch tabs have secured cable.
(6) Install throttle cable into mounting bracket. Be
sure pinch tabs have secured cable.
(7) Connect throttle cable at lever (snaps on).
(8) Connect speed control cable to lever by pushing
cable connector rearward onto lever pin while hold-
ing lever forward.
(9) Install cable cover.
(10) Connect both negative battery cables to both
batteries.
(11) If necessary, use DRB IIItScan Tool to erase
any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) from ECM.Battery Tray Mounted Sensor :
(1) Install Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
(APPS) cable to accelerator pedal. Refer to Accelera-
tor Pedal Removal / Installation.
(2) Connect electrical connector to APPS.
(3) If necessary, connect cable to APPS lever ball
socket (snaps on).
(4) Snap APPS cable cover closed.
(5) Position APPS assembly to bottom of battery
tray and install 3 bolts. Refer to Torque Specifica-
tions.
(6) Install wheelhouse liner. Refer to Body.
(7) Perform the following procedure:
(a) Connect negative battery cables to both bat-
teries.
(b) Turn key switch ON, but do not crank
engine.
(c) Leave key switch ON for a minimum of 10
seconds. This will allow ECM to learn electrical
parameters.
(8) If necessary, use DRB IIItScan Tool to erase
any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) from ECM.
CAMSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP) on the 5.9L
diesel engine is located below the fuel injection
pump. It is bolted to the back of the timing gear
housing.
OPERATION
The diesel Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP) con-
tains a hall effect device. A rotating target wheel
(tonewheel) for the CMP is located on the camshaft
gear. This hall effect device detects notches located
on the back side of the camshaft gear. As the cam-
shaft gear rotates, the notches pass the tip of the
CMP.
When the leading edge of the notch passes the tip
of the CMP, the following occurs: The interruption of
magnetic field causes the voltage to switch high
resulting in a signal of approximately 5 volts.
When the trailing edge of the notch passes the tip
of the CMP, the following occurs: The change of the
magnetic field causes the signal voltage to switch low
to 0 volts.
The CMP (Fig. 8) provides a signal to the Engine
Control Module (ECM) at all times when the engine
is running. The ECM uses the CMP information pri-
marily on engine start-up. Once the engine is run-
ning, the ECM uses the CMP as a backup sensor for
engine speed. The Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP)
Fig. 7 APPS CABLE (OFF ENGINE MOUNTING)
1 - APPS LEVER
2 - BALL SOCKET
3 - SWING-DOWN DOOR
4 - CABLE CLIP
5 - CABLE
DRFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 71
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR (Continued)