ECO mode DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 4 of 2627

BODY CODE PLATE
DESCRIPTION
The Body Code Plate (Fig. 4) is located on the right
front hydroform fender rail just behind the headlight
assembly (Fig. 3). There are seven lines of informa-
tion on the body code plate. Lines 5, 6, and 7 are not
used to define service information. Information reads
from left to right, starting with line 4 in the center of
the plate to line 1 at the bottom of the plate.
The last code imprinted on a vehicle code plate will
be followed by the imprinted word END. When two
vehicle code plates are required, the last available
spaces on the first plate will be imprinted with the
letters CTD (for continued).
When a second vehicle code plate is necessary, the
first four spaces on each row will not be used because
of the plate overlap.
BODY CODE PLATEÐLINE 4
DIGITS 1 THROUGH 12
Vehicle Order Number
DIGITS 13, 14, AND 15
Transmission Codes
²DG4 = 4±speed Automatic (45RFE)
²DG8 = 4±speed Automatic (48RE)²DDC = 5±speed Manual (NV3500)
²DDP = 5±speed Manual (NV4500)
²DEC = 6±speed Manual (NV5600)
²DEE = 6±speed Manual Tremec (T-56)
DIGITS 16, 17, AND 18
Car Line Shell
²DR1=15004X2
²DR6=15004X4
²DR2=25004X2
²DR7=25004X4
²DR3=35004X2
²DR8=35004X4
DIGIT 19
Price Class
²L = Low
²H = Highline
DIGITS 20 AND 21
Body Type
²41 = Ram Truck Quad Cab, Short Box
²42 = Ram Truck Quad Cab, Long Box
²61 = Ram Truck Standard Cab, Short Box
²62 = Ram Truck Standard Cab, Long Box
Fig. 3 BODY CODE PLATE LOCATION
1 - FENDER
2 - RADIATOR CROSSMEMBER
3 - HYDROFORM FENDER RAIL
4 - RIVOT (2)
5 - BODY CODE PLATE
Fig. 4 BODY CODE PLATE
1 - PRIMARY PAINT
2 - SECONDARY PAINT
3 - TRANSMISSION CODE
4 - VEHICLE MODEL NUMBER
5 - ENGINE CODE
6 - INTERIOR TRIM CODE
7 - VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER
8 - TAILGATE CODE
9 - CARGO BOX CODE
10 - TAILGATE TRIM CODE
11 - BODY-IN-WHITE SEQUENCE
12 - MARKET CODE
13 - SPECIES CODE
14 - PAINT PROCEDURE
15 - VEHICLE ORDER NUMBER
DRINTRODUCTION 3
Page 23 of 2627
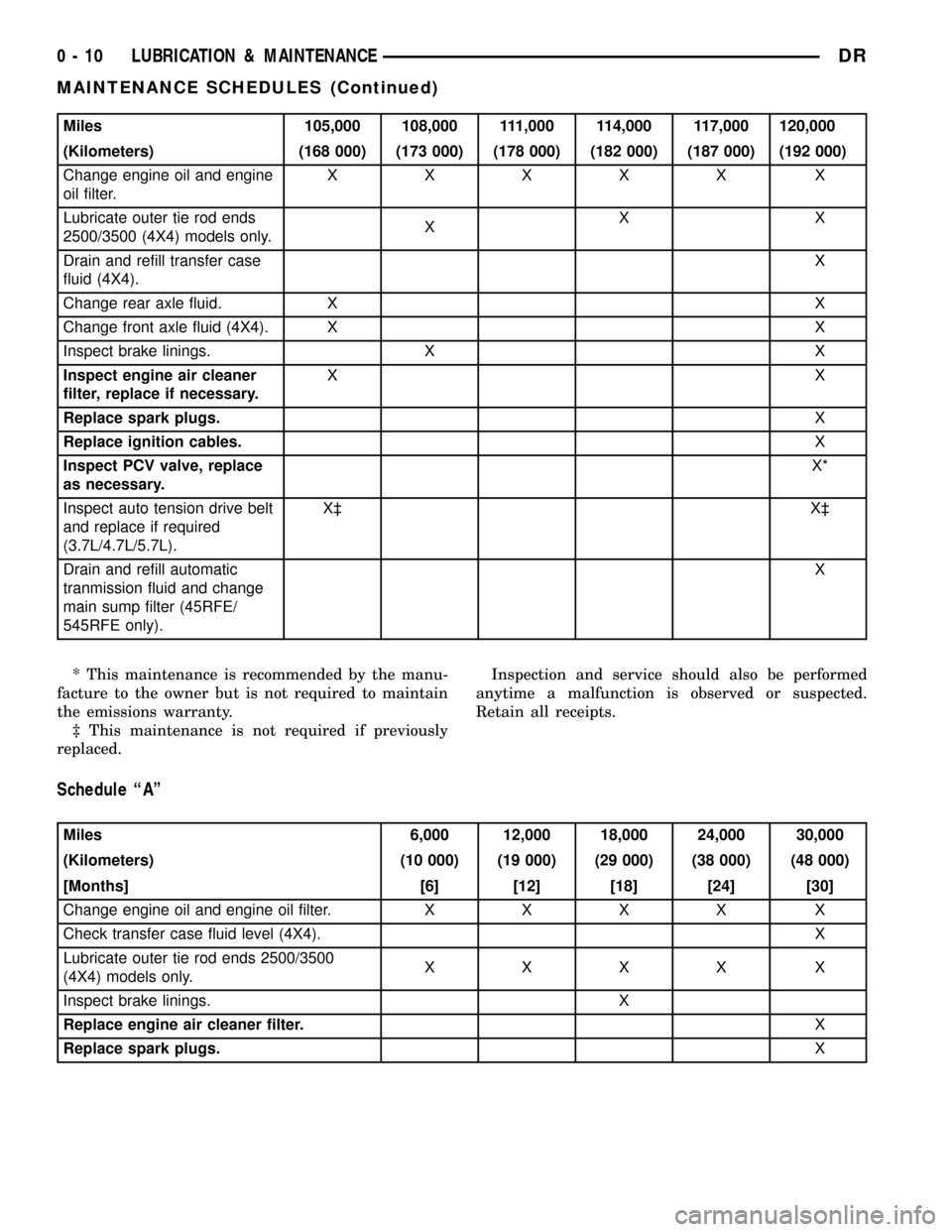
Miles 105,000 108,000 111,000 114,000 117,000 120,000
(Kilometers) (168 000) (173 000) (178 000) (182 000) (187 000) (192 000)
Change engine oil and engine
oil filter.XXXXX X
Lubricate outer tie rod ends
2500/3500 (4X4) models only.XXX
Drain and refill transfer case
fluid (4X4).X
Change rear axle fluid. X X
Change front axle fluid (4X4). X X
Inspect brake linings. X X
Inspect engine air cleaner
filter, replace if necessary.XX
Replace spark plugs.X
Replace ignition cables.X
Inspect PCV valve, replace
as necessary.X*
Inspect auto tension drive belt
and replace if required
(3.7L/4.7L/5.7L).X³ X³
Drain and refill automatic
tranmission fluid and change
main sump filter (45RFE/
545RFE only).X
* This maintenance is recommended by the manu-
facture to the owner but is not required to maintain
the emissions warranty.
³ This maintenance is not required if previously
replaced.Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
Retain all receipts.
Schedule ªAº
Miles 6,000 12,000 18,000 24,000 30,000
(Kilometers) (10 000) (19 000) (29 000) (38 000) (48 000)
[Months] [6] [12] [18] [24] [30]
Change engine oil and engine oil filter.XXXX X
Check transfer case fluid level (4X4). X
Lubricate outer tie rod ends 2500/3500
(4X4) models only.XXXX X
Inspect brake linings. X
Replace engine air cleaner filter.X
Replace spark plugs.X
0 - 10 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEDR
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 25 of 2627
![DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual Miles 102,000 108,000 114,000 120,000
(Kilometers) (163 000) (173 000) (182 000) (192 000)
[Months] [102] [108] [114] [120]
Change engine oil and engine oil filter. X X X X
Drain and refill transfer c DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual Miles 102,000 108,000 114,000 120,000
(Kilometers) (163 000) (173 000) (182 000) (192 000)
[Months] [102] [108] [114] [120]
Change engine oil and engine oil filter. X X X X
Drain and refill transfer c](/img/12/5702/w960_5702-24.png)
Miles 102,000 108,000 114,000 120,000
(Kilometers) (163 000) (173 000) (182 000) (192 000)
[Months] [102] [108] [114] [120]
Change engine oil and engine oil filter. X X X X
Drain and refill transfer case fluid (4X4). X
Flush and replace engine coolant, if not done at 60 mos. X
Lubricate outer tie rod ends 2500/3500 (4X4) models
only.XXX X
Inspect brake linings. X
Inspect auto tension drive belt and replace if required
(3.7L/4.7L/5.7L).X³X³
Replace ignition cables.X
Replace engine air cleaner filter.X
Replace spark plugs.X
Inspect PCV Valve, replace as necessary X*
* This maintenance is recommended by the manu-
facture to the owner but is not required to maintain
the emissions warranty.
³ This maintenance is not required if previously
replaced.
Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
WARNING: You can be badly injured working on or
around a motor vehicle. Do only that service work
for which you have the knowledge and the right
equipment. If you have any doubt about your ability
to perform a service job, take your vehicle to a
competent mechanic.
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES Ð 24±VALVE
CUMMINS TURBO DIESEL
There are two maintenance schedules that show
therequiredservice for your vehicle.
First is ScheduleªBº. It is for vehicles that are
operated under the conditions that are listed below
and at the beginning of the schedule.
²Day or night temperatures are below 0É C (32É
F).
²Stop and go driving.
²Extensive engine idling.
²Driving in dusty conditions.
²Short trips of less than 16 km (10 miles).
²More than 50% of your driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 32É C (90É F).²Trailer towing.
²Taxi, police, or delivery service (commercial ser-
vice).
²Off-road or desert operation.
NOTE: Most vehicles are operated under the condi-
tions listed for Schedule(B(.
Second is ScheduleªAº. It is for vehicles that are
not operated under any of the conditions listed under
Schedule9B9.
Use the schedule that best describes your driving
conditions. Where time and mileage are listed, follow
the interval that occurs first.
CAUTION: Failure to perform the required mainte-
nance items may result in damage to the vehicle.At Each Stop for Fuel
²Check the engine oil level about 15 minutes
after a fully warmed engine is shut off. Checking the
oil level while the vehicle is on level ground will
improve the accuracy of the oil level reading. Add oil
only when the level is at or below the ADD or MIN
mark.
²Check the windshield washer solvent and add if
required.
²Drain water from the fuel filter.
0 - 12 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEDR
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 273 of 2627

(5) Remove the reservoir from the master cylinder
by pulling upwards.
(6) Remove old grommets from cylinder body (Fig.
42).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Do not use any type of tool to install the
grommets. Tools may cut, or tear the grommets cre-
ating a leak problem after installation. Install the
grommets using finger pressure only.
(1) Lubricate the new grommets with clean brake
fluid and Install new grommets in cylinder body. Use
finger pressure to install and seat grommets.
(2) Start the reservoir in grommets. Then rock the
reservoir back and forth while pressing downward to
seat it into the grommets.
(3) Install the mounting bolt for the reservoir to
the master cylinder.
(4) Reconnect the electrical connector to the fluid
reservoir level switch.
(5) Remove the prop rod from the vehicle.
(6) Fill and bleed base brake system,(Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
BRAKE JUNCTION BLOCK
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the brake lines from the junction block
(Fig. 43).
(2) Remove the junction block mounting bolt and
remove the junction block from the bracket (Fig. 43).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the junction block on the bracket and
install the mounting bolt. Tighten the mounting bolt
to 23 N´m (210 in. lbs.) (Fig. 43).
(2) Install the brake lines into the junction block
and tighten to 19-23 N´m (170-200 in. lbs.) (Fig. 43).
(3) Bleed the base brake system, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
MASTER CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION
A two-piece master cylinder is used on all models.
The cylinder body containing the primary and sec-
ondary pistons is made of aluminum. The removable
fluid reservoir is made of nylon reinforced with glass
fiber. The reservoir stores reserve brake fluid for the
hydraulic brake circuits and has a switch for indicat-
ing low fluid levels. The reservoir is the only service-
able component.
The fluid compartments of the nylon reservoir are
interconnected to permit fluid level equalization.
However, the equalization feature does not affect cir-
cuit separation in the event of a front or rear brake
malfunction. The reservoir compartments will retain
enough fluid to operate the functioning hydraulic cir-
cuit.
Care must be exercised when removing/installing
the master cylinder connecting lines. The threads in
the cylinder fluid ports can be damaged if care is not
exercised. Start all brake line fittings by hand to
avoid cross threading.
Fig. 42 FLUID RESERVOIR
1 - MASTER CYLINDER CAP
2 - FLUID RESERVOIR
3 - FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
4 - MASTER CYLINDER
5 - MOUNTING BOLT
6 - GROMMETS
Fig. 43 JUNCTION BLOCK
1 - BRAKE LINES
2 - JUNCTION BLOCK
5 - 24 BRAKES - BASEDR
FLUID RESERVOIR (Continued)
Page 278 of 2627

(9)On vehicles equipped with adjustable
brake pedal.Reconnect the electrical connector to
the motor and the adjuster cable at the pedal.
(10) Install the steering column opening cover
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEER-
ING COLUMN OPENING COVER - INSTALLA-
TION).
(11) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
DESCRIPTION
All models use a tandem diaphragm, power brake
booster.
NOTE: The power brake booster is not a repairable
component. The booster must be replaced as an
assembly if diagnosis indicates a malfunction has
occurred.
OPERATION
The booster unit consists of a single housing
divided into two by a tandem diaphragm. The outer
edge of the diaphragm is secured to the housing. The
booster push rod, which connects the booster to the
brake pedal and master cylinder, is attached to the
center of the diaphragm. A check valve is used in the
booster outlet connected to the engine intake mani-
fold. Power assist is generated by utilizing a combi-
nation of vacuum and atmospheric pressure to boost
brake assist.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove master cylinder. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/MASTER CYLINDER -
REMOVAL).
(2) Disconnect vacuum line at booster.
(3) Remove clip securing booster push rod to brake
pedal (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHAN-
ICAL/PEDAL - REMOVAL). (Fig. 53).
(4) Remove the nuts from the booster mounting
studs (Fig. 53).
(5) Remove the booster and gasket from front cowl
panel.
INSTALLATION
(1) Guide the booster studs into the cowl panel
holes and seat the booster on the panel (Fig. 53).
(2) Install and tighten new booster attaching nuts
to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(3) Install the booster push rod on brake pedal and
install clip (Fig. 53).
(4) Install the booster check valve if removed and
connect the vacuum hose to the check valve.
(5) Install the master cylinder. (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/MASTER
CYLINDER - INSTALLATION).
(6) Fill and bleed the brake system. (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 52 PEDAL ASSEMBLY (ADJUSTABLE PEDALS
SHOWN)
1 - ADJUSTABLE PEDAL MOTOR
2 - PEDAL ASSEMBLY BRACKET
3 - MOUNTING NUT
4 - BRAKE & ACCELERATOR PEDAL
5 - BRAKE BOOSTER MOUNTING STUDS
Fig. 53 POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
1 - MOUNTING NUT
2 - POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
DRBRAKES - BASE 5 - 29
PEDAL (Continued)
Page 289 of 2627

Inspect the adjuster screw assembly. Replace the
assembly if the star wheel or threads are damaged,
or the components are severely rusted or corroded
(Fig. 77).
Discard the brake springs and retainer components
if worn, distorted or collapsed. Also replace the
springs if a brake drag condition had occurred. Over-
heating will distort and weaken the springs.
Inspect the brake shoe contact pads on the support
plate, replace the support plate if any of the pads are
worn or rusted through. Also replace the plate if it is
bent or distorted (Fig. 77).
INSTALLATION
NOTE: On a new vehicle or after parking brake lin-
ing replacement, it is recommended that the park-
ing brake system be conditioned prior to use. This
is done by making one stop from 25 mph on dry
pavement or concrete using light to moderate force
on the parking brake foot pedal.
(1) Reassemble the rear park brake shoes (Fig. 67)
or (Fig. 78).
(2) Install the axleshaft (Fig. 76) (Refer to 3 - DIF-
FERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/REAR AXLE - 9 1/4/
AXLE SHAFTS - INSTALLATION) or (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/REAR AXLE - 11
1/2 AA/10 1/2 AA/AXLE SHAFTS - INSTALLATION).
(3) Install the park brake cable to the lever behind
the support plate.
(4) Unlock the park brake cable.
(5) Install the disc brake rotor (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS -
INSTALLATION).(6) Install the disc brake caliper (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPERS - INSTALLATION).
(7) Adjust the rear brake shoes (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/PARKING BRAKE/SHOES - ADJUST-
MENTS).
Fig. 76 AXLE SHAFT
1 - AXLE SHAFT
2 - SUPPORT PLATE
3 - CALIPER
4 - PARK BRAKE SHOE ASSEMBLY
Fig. 77 PARK BRAKE SHOES
1 - SUPPORT PLATE
2 - SHOES
3 - RETURN SPRINGS
4 - RETAINER CLIPS
5 - ADJUSTER
Fig. 78 SHOE ASSEMBLY
1 - Park Brake Shoes
2 - Hold Downs
3 - Return Springs
5 - 40 BRAKES - BASEDR
SHOES (Continued)
Page 291 of 2627
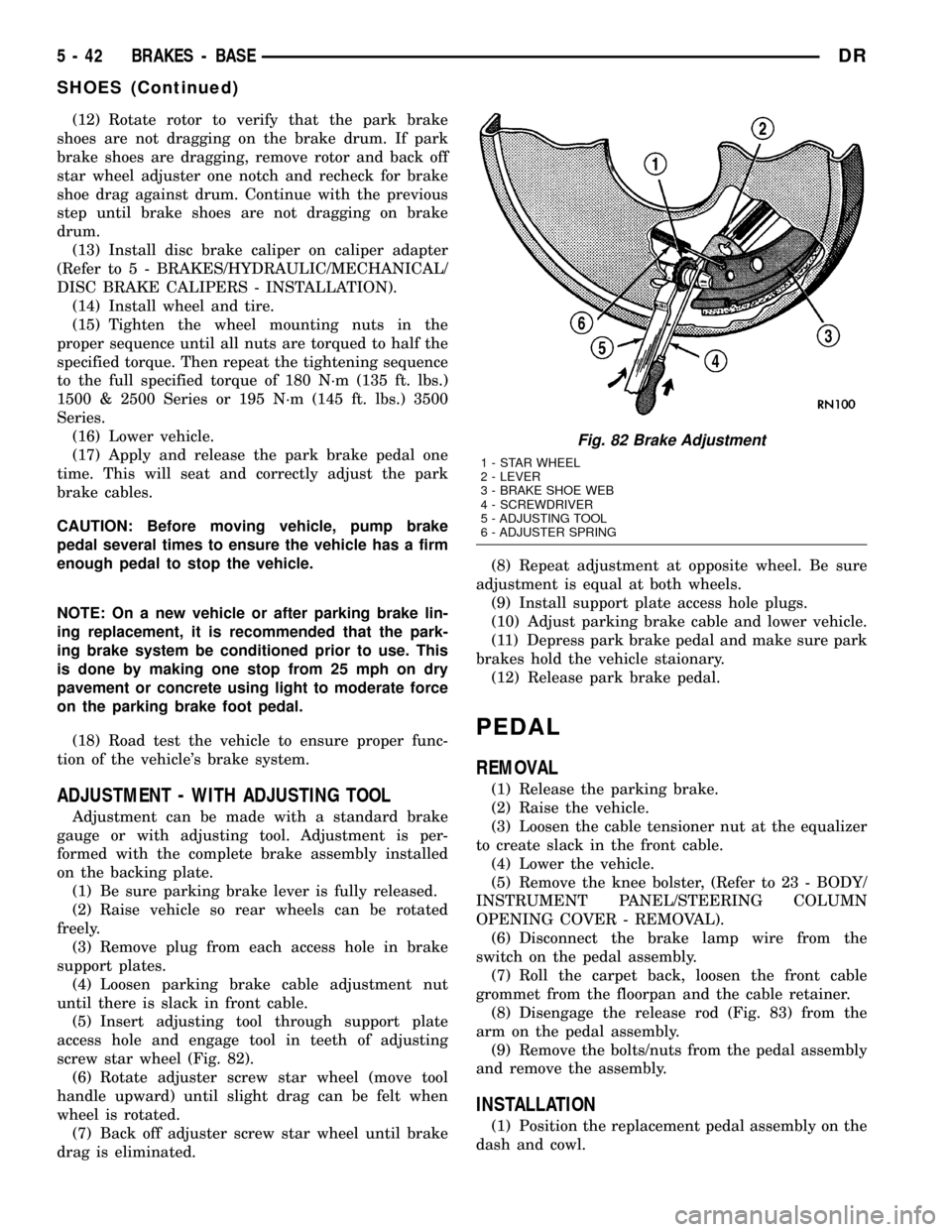

(12) Rotate rotor to verify that the park brake
shoes are not dragging on the brake drum. If park
brake shoes are dragging, remove rotor and back off
star wheel adjuster one notch and recheck for brake
shoe drag against drum. Continue with the previous
step until brake shoes are not dragging on brake
drum.
(13) Install disc brake caliper on caliper adapter
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - INSTALLATION).
(14) Install wheel and tire.
(15) Tighten the wheel mounting nuts in the
proper sequence until all nuts are torqued to half the
specified torque. Then repeat the tightening sequence
to the full specified torque of 180 N´m (135 ft. lbs.)
1500 & 2500 Series or 195 N´m (145 ft. lbs.) 3500
Series.
(16) Lower vehicle.
(17) Apply and release the park brake pedal one
time. This will seat and correctly adjust the park
brake cables.
CAUTION: Before moving vehicle, pump brake
pedal several times to ensure the vehicle has a firm
enough pedal to stop the vehicle.
NOTE: On a new vehicle or after parking brake lin-
ing replacement, it is recommended that the park-
ing brake system be conditioned prior to use. This
is done by making one stop from 25 mph on dry
pavement or concrete using light to moderate force
on the parking brake foot pedal.
(18) Road test the vehicle to ensure proper func-
tion of the vehicle's brake system.
ADJUSTMENT - WITH ADJUSTING TOOL
Adjustment can be made with a standard brake
gauge or with adjusting tool. Adjustment is per-
formed with the complete brake assembly installed
on the backing plate.
(1) Be sure parking brake lever is fully released.
(2) Raise vehicle so rear wheels can be rotated
freely.
(3) Remove plug from each access hole in brake
support plates.
(4) Loosen parking brake cable adjustment nut
until there is slack in front cable.
(5) Insert adjusting tool through support plate
access hole and engage tool in teeth of adjusting
screw star wheel (Fig. 82).
(6) Rotate adjuster screw star wheel (move tool
handle upward) until slight drag can be felt when
wheel is rotated.
(7) Back off adjuster screw star wheel until brake
drag is eliminated.(8) Repeat adjustment at opposite wheel. Be sure
adjustment is equal at both wheels.
(9) Install support plate access hole plugs.
(10) Adjust parking brake cable and lower vehicle.
(11) Depress park brake pedal and make sure park
brakes hold the vehicle staionary.
(12) Release park brake pedal.
PEDAL
REMOVAL
(1) Release the parking brake.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Loosen the cable tensioner nut at the equalizer
to create slack in the front cable.
(4) Lower the vehicle.
(5) Remove the knee bolster, (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEERING COLUMN
OPENING COVER - REMOVAL).
(6) Disconnect the brake lamp wire from the
switch on the pedal assembly.
(7) Roll the carpet back, loosen the front cable
grommet from the floorpan and the cable retainer.
(8) Disengage the release rod (Fig. 83) from the
arm on the pedal assembly.
(9) Remove the bolts/nuts from the pedal assembly
and remove the assembly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the replacement pedal assembly on the
dash and cowl.
Fig. 82 Brake Adjustment
1 - STAR WHEEL
2 - LEVER
3 - BRAKE SHOE WEB
4 - SCREWDRIVER
5 - ADJUSTING TOOL
6 - ADJUSTER SPRING
5 - 42 BRAKES - BASEDR
SHOES (Continued)
Page 316 of 2627

COOLING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COOLING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM FLOW
3.7L/4.7L/5.7L ENGINE..................1
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM FLOW -
5.9L DIESEL..........................3
DESCRIPTION - HOSE CLAMPS...........3
OPERATION
OPERATION - COOLING SYSTEM.........5
OPERATION - HOSE CLAMPS............5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)...................5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM - TESTING FOR LEAKS..........5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM DIESEL ENGINE................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
CHECKS............................10
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLANT
LEVEL CHECK........................17STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM CLEANING/REVERSE FLUSHING . . 17
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING
COOLING SYSTEM - ALL GAS ENGINES . . . 17
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFILLING
COOLING SYSTEM - ALL GAS ENGINES . . . 18
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING
COOLING SYSTEM 5.9L DIESEL ENGINE . . . 18
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFILLING
COOLING SYSTEM 5.9L DIESEL ENGINE . . . 19
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ADDING
ADDITIONAL COOLANT.................19
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE............................19
SPECIFICATIONS -....................20
SPECIAL TOOLS
COOLING...........................20
ACCESSORY DRIVE......................21
ENGINE...............................30
TRANSMISSION.........................67
COOLING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM FLOW
3.7L/4.7L/5.7L ENGINE
The cooling system regulates engine operating tem-
perature. It allows the engine to reach normal oper-
ating temperature as quickly as possible. It also
maintains normal operating temperature and pre-
vents overheating.The cooling system provides a means of heating
the passenger compartment and cooling the auto-
matic transmission fluid (if equipped). The cooling
system is pressurized and uses a centrifugal water
pump to circulate coolant through the system. The
coolant recovery/reserve system utilizes an ambient
overflow bottle (Fig. 2).
An optional factory installed maximum duty cool-
ing package is available on most models. This pack-
age will provide additional cooling capacity for
vehicles used under extreme conditions such as
trailer towing in high ambient temperatures (Fig. 1).
DRCOOLING 7 - 1
Page 320 of 2627

OPERATION
OPERATION - COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system regulates engine operating tem-
perature. It allows the engine to reach normal oper-
ating temperature as quickly as possible. It also
maintains normal operating temperature and pre-
vents overheating.
The cooling system also provides a means of heat-
ing the passenger compartment and cooling the auto-
matic transmission fluid (if equipped). The cooling
system is pressurized and uses a centrifugal water
pump to circulate coolant throughout the system.
All engines utilize an ambient overflow bottle for
coolant recovery/reserve.
An optional factory installed maximum duty cool-
ing package is available on most models. This pack-
age will provide additional cooling capacity for
vehicles used under extreme conditions such as
trailer towing in high ambient temperatures.
OPERATION - HOSE CLAMPS
The spring type hose clamp applies constant ten-
sion on a hose connection. To remove a spring type
hose clamp, only use constant tension clamp pliers
designed to compress the hose clamp.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)
COOLING SYSTEM RELATED DIAGNOSTICS
The Engine Control Module (ECM) has been pro-
grammed to monitor certain cooling system compo-
nents:
²If the engine has remained cool for too long a
period, such as with a stuck open thermostat, a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be set.
²If an open or shorted condition has developed in
the electronically controlled viscous fan clutch circuit,
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be set.
²If fan speed is not detected a DTC will be set.
²Coolant temperature sensor circuit problems can
set a DTC.
If the problem is sensed in a monitored circuit
often enough to indicated an actual problem, a DTC
is stored. The DTC will be stored in the ECM mem-
ory for eventual display to the service technician.
(Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL - DESCRIP-
TION).
ACCESSING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
To read DTC's and to obtain cooling system data,
(Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL - DESCRIP-
TION).
ERASING TROUBLE CODES
After the problem has been repaired, use the
DRBIIItscan tool to erase a DTC. Refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures ser-
vice information for operation of the DRBIIItscan
tool.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
- TESTING FOR LEAKS
ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT METHOD
A leak detection additive is available through the
parts department that can be added to cooling sys-
tem. The additive is highly visible under ultraviolet
light (black light). Pour one ounce of additive into
cooling system. Place heater control unit in HEAT
position. Start and operate the engine until the radi-
ator upper hose is warm to the touch. Aim the com-
mercially available black light tool at the components
to be checked. If leaks are present, the black light
will cause the additive to glow a bright green color.
The black light can be used in conjunction with a
pressure tester to determine if any external leaks
exist (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4 Spring Clamp Size Location
1 - SPRING CLAMP SIZE LOCATION
DRCOOLING 7 - 5
COOLING (Continued)
Page 351 of 2627

INSTALLATION
(1) Install fan blade assembly to electrically con-
trolled viscous fan drive. Tighten mounting bolts to
24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Position the fan blade/viscous fan drive to the
vehicle as an assembly.
(3) Install the viscous fan drive assembly onto fan
pulley hub shaft (Fig. 4). Tighten mounting nut to
115 N´m (85 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install upper fan shroud. Make sure the upper
shroud locks into the tabs on the lower radiator.
(5) Install two upper shroud mounting bolts.
Tighten to 11.8 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Position the electronically controlled viscous
fan drive wiring into the channel in the upper fan
shroud (Fig. 5). Make sure the wiring is not pinched.
(7) Install the lower fan shroud into position and
verify the two locking tabs have seated.
(8) Install two push pin fasteners to lock lower fan
shroud to the main assembly.
NOTE: Verify that the fan drive electrical wire does
not interfere with fan blade travel when the fan
blade is spun by hand.
(9) Connect the wiring harness connector and
install the harness bracket to the upper radiator
shroud.(10) Install the coolant recovery container (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/COOLANT RECOVERY
CONTAINER - INSTALLATION).
(11) Connect the battery negative cables.
NOTE:
Viscous Fan Drive Fluid Pump Out Requirement:
After installing a new viscous fan drive, bring the
engine speed up to approximately 2000 rpm and
hold for approximately two minutes. This will
ensure proper fluid distribution within the drive.
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
DESCRIPTION
WARNING: DO NOT OPERATE ENGINE UNLESS
BLOCK HEATER CORD HAS BEEN DISCONNECTED
FROM POWER SOURCE AND SECURED IN PLACE.
THE POWER CORD MUST BE SECURED IN ITS
RETAINING CLIPS AND ROUTED AWAY FROM
EXHAUST MANIFOLDS AND MOVING PARTS.
An optional engine block heater is available with
all models. The heater is equipped with a power cord.
The cord is attached to an engine compartment com-
ponent with tie-straps. The heater warms the engine
providing easier engine starting and faster warm-up
in low temperatures. The heater is mounted in a core
hole of the engine cylinder block in place of a freeze
plug with the heating element immersed in engine
coolant. The 3.7L/4.7L gas powered engines have the
block heater located to the rear on the right side of
the engine (Fig. 6).
OPERATION
The heater warms the engine coolant providing
easier engine starting and faster warm-up in low
temperatures. Connecting the power cord to a
grounded 110-120 volt AC electrical outlet with a
grounded three wire extension cord provides the elec-
tricity needed to heat the element.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE BLOCK
HEATER
If the unit does not operate, possible causes can be
either the power cord or the heater element. Test the
power cord for continuity with a 110-volt voltmeter or
110-volt test light. Test heater element continuity
with an ohmmeter or a 12-volt test light.
CAUTION: To prevent damage, the power cord must
be secured in it's retainer clips and away from any
components that may cause abrasion or damage,
such as linkages, exhaust components, etc.
Fig. 5 Electronically Controlled Viscous Fan Drive
Wiring
1 - UPPER SHROUD
2 - WIRING
3 - GROMMET
7 - 36 ENGINEDR
RADIATOR FAN - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)