torque DODGE RAM 2001 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2001Pages: 2889, PDF Size: 68.07 MB
Page 553 of 2889
SPARK PLUG
DESCRIPTION
The 3.9L V-6 and 5.2L/5.9L V-8 engines use resis-
tor type spark plugs. The 8.0L V-10 engine uses
inductive type spark plugs.
Spark plug resistance values range from 6,000 to
20,000 ohms (when checked with at least a 1000 volt
spark plug tester).Do not use an ohmmeter to
check the resistance values of the spark plugs.
Inaccurate readings will result.
OPERATION
To prevent possible pre-ignition and/or mechanical
engine damage, the correct type/heat range/number
spark plug must be used.
Always use the recommended torque when tighten-
ing spark plugs. Incorrect torque can distort the
spark plug and change plug gap. It can also pull the
plug threads and do possible damage to both the
spark plug and the cylinder head.
Remove the spark plugs and examine them for
burned electrodes and fouled, cracked or broken por-
celain insulators. Keep plugs arranged in the order
in which they were removed from the engine. A sin-gle plug displaying an abnormal condition indicates
that a problem exists in the corresponding cylinder.
Replace spark plugs at the intervals recommended in
Group O, Lubrication and Maintenance
Spark plugs that have low mileage may be cleaned
and reused if not otherwise defective, carbon or oil
fouled. Also refer to Spark Plug Conditions.
CAUTION: Never use a motorized wire wheel brush
to clean the spark plugs. Metallic deposits will
remain on the spark plug insulator and will cause
plug misfire.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPARK PLUG
CONDITIONS
NORMAL OPERATING
The few deposits present on the spark plug will
probably be light tan or slightly gray in color. This is
evident with most grades of commercial gasoline
(Fig. 29). There will not be evidence of electrode
burning. Gap growth will not average more than
approximately 0.025 mm (.001 in) per 3200 km (2000
miles) of operation. Spark plugs that have normal
wear can usually be cleaned, have the electrodes
filed, have the gap set and then be installed.
Some fuel refiners in several areas of the United
States have introduced a manganese additive (MMT)
for unleaded fuel. During combustion, fuel with MMT
causes the entire tip of the spark plug to be coated
with a rust colored deposit. This rust color can be
misdiagnosed as being caused by coolant in the com-
bustion chamber. Spark plug performance may be
affected by MMT deposits.
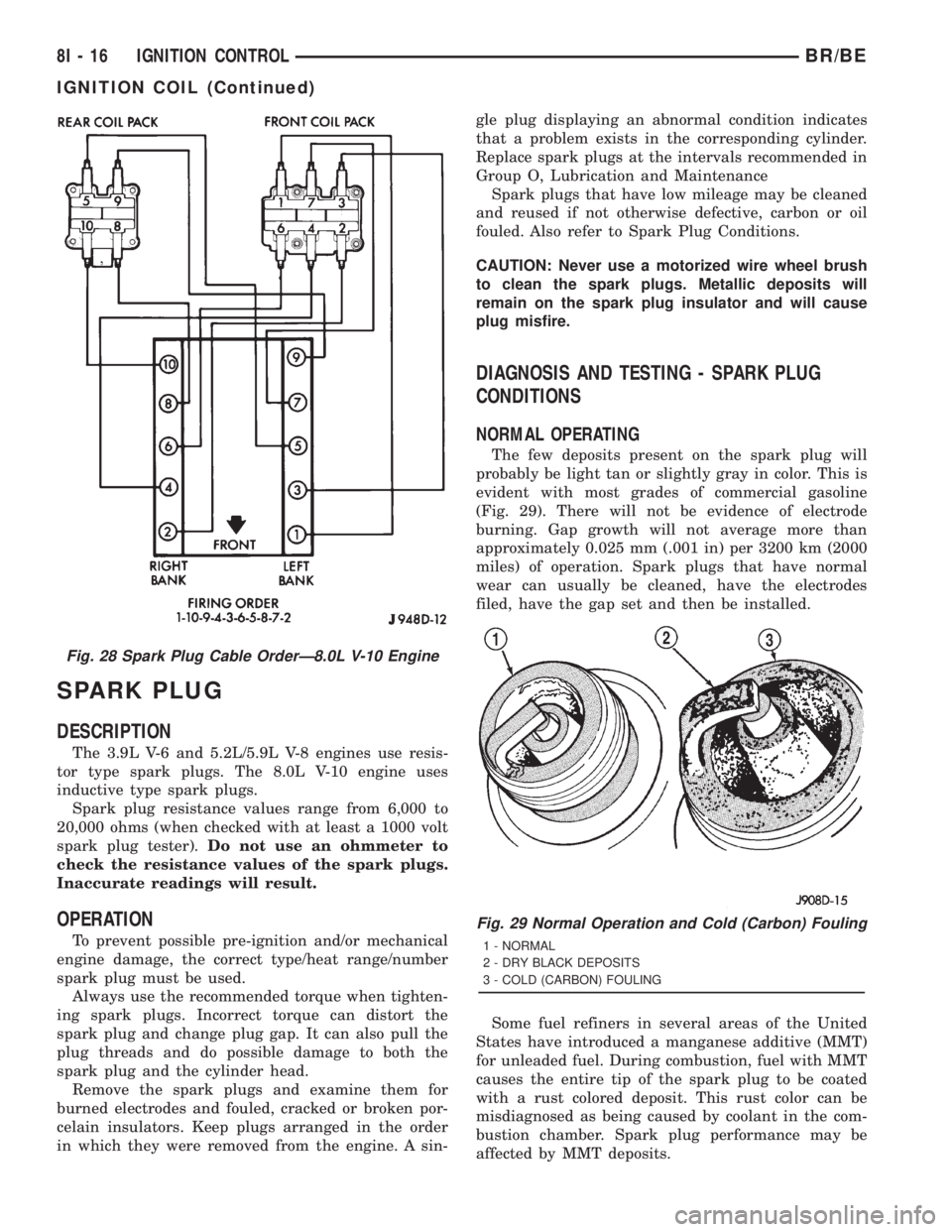
Fig. 28 Spark Plug Cable OrderÐ8.0L V-10 Engine
Fig. 29 Normal Operation and Cold (Carbon) Fouling
1 - NORMAL
2 - DRY BLACK DEPOSITS
3 - COLD (CARBON) FOULING
8I - 16 IGNITION CONTROLBR/BE
IGNITION COIL (Continued)
Page 554 of 2889

COLD FOULING/CARBON FOULING
Cold fouling is sometimes referred to as carbon
fouling. The deposits that cause cold fouling are basi-
cally carbon (Fig. 29). A dry, black deposit on one or
two plugs in a set may be caused by sticking valves
or defective spark plug cables. Cold (carbon) fouling
of the entire set of spark plugs may be caused by a
clogged air cleaner element or repeated short operat-
ing times (short trips).
WET FOULING OR GAS FOULING
A spark plug coated with excessive wet fuel or oil
is wet fouled. In older engines, worn piston rings,
leaking valve guide seals or excessive cylinder wear
can cause wet fouling. In new or recently overhauled
engines, wet fouling may occur before break-in (nor-
mal oil control) is achieved. This condition can usu-
ally be resolved by cleaning and reinstalling the
fouled plugs.
OIL OR ASH ENCRUSTED
If one or more spark plugs are oil or oil ash
encrusted (Fig. 30), evaluate engine condition for the
cause of oil entry into that particular combustion
chamber.
ELECTRODE GAP BRIDGING
Electrode gap bridging may be traced to loose
deposits in the combustion chamber. These deposits
accumulate on the spark plugs during continuous
stop-and-go driving. When the engine is suddenly
subjected to a high torque load, deposits partially liq-
uefy and bridge the gap between electrodes (Fig. 31).This short circuits the electrodes. Spark plugs with
electrode gap bridging can be cleaned using standard
procedures.
SCAVENGER DEPOSITS
Fuel scavenger deposits may be either white or yel-
low (Fig. 32). They may appear to be harmful, but
this is a normal condition caused by chemical addi-
tives in certain fuels. These additives are designed to
change the chemical nature of deposits and decrease
spark plug misfire tendencies. Notice that accumula-
tion on the ground electrode and shell area may be
heavy, but the deposits are easily removed. Spark
plugs with scavenger deposits can be considered nor-
mal in condition and can be cleaned using standard
procedures.
Fig. 30 Oil or Ash Encrusted
Fig. 31 Electrode Gap Bridging
1 - GROUND ELECTRODE
2 - DEPOSITS
3 - CENTER ELECTRODE
Fig. 32 Scavenger Deposits
1 - GROUND ELECTRODE COVERED WITH WHITE OR
YELLOW DEPOSITS
2 - CENTER ELECTRODE
BR/BEIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 17
SPARK PLUG (Continued)
Page 556 of 2889

CLEANING
The plugs may be cleaned using commercially
available spark plug cleaning equipment. After clean-
ing, file center electrode flat with a small point file or
jewelers file before adjusting gap.
CAUTION: Never use a motorized wire wheel brush
to clean spark plugs. Metallic deposits will remain
on spark plug insulator and will cause plug misfire.
INSTALLATION
Special care should be taken when installing spark
plugs into the cylinder head spark plug wells. Be
sure the plugs do not drop into the plug wells as elec-
trodes can be damaged.
Always tighten spark plugs to the specified torque.
Over tightening can cause distortion resulting in a
change in the spark plug gap or a cracked porcelain
insulator.
When replacing the spark plug and ignition coil
cables, route the cables correctly and secure them in
the appropriate retainers. Failure to route the cables
properly can cause the radio to reproduce ignition
noise. It could cause cross ignition of the spark plugs
or short circuit the cables to ground.
(1) Start the spark plug into the cylinder head by
hand to avoid cross threading.
(2) Tighten spark plugs to 35-41 N´m (26-30 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(3) Install spark plug cables over spark plugs.
SPARK PLUG CABLE
DESCRIPTION
Spark plug cables are sometimes referred to as sec-
ondary ignition wires.
OPERATION
The spark plug cables transfer electrical current
from the ignition coil(s) and/or distributor, to individ-
ual spark plugs at each cylinder. The resistive spark
plug cables are of nonmetallic construction. The
cables provide suppression of radio frequency emis-
sions from the ignition system.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPARK PLUG
CABLES
Cable routing is important on certain engines. To
prevent possible ignition crossfire, be sure the cables
are clipped into the plastic routing looms. Try to pre-
vent any one cable from contacting another. Before
removing cables, note their original location and
routing. Never allow one cable to be twisted around
another.
Check the spark plug cable connections for good
contact at the coil(s), distributor cap towers, and
spark plugs. Terminals should be fully seated. The
insulators should be in good condition and should fit
tightly on the coil, distributor and spark plugs. Spark
plug cables with insulators that are cracked or torn
must be replaced.
Clean high voltage ignition cables with a cloth
moistened with a non-flammable solvent. Wipe the
cables dry. Check for brittle or cracked insulation.
On 3.9L/5.2L/5.9L engines, spark plug cable heat
shields are pressed into the cylinder head to sur-
round each spark plug cable boot and spark plug
(Fig. 37). These shields protect the spark plug boots
from damage (due to intense engine heat generated
by the exhaust manifolds) and should not be
removed. After the spark plug cable has been
installed, the lip of the cable boot should have a
small air gap to the top of the heat shield (Fig. 37).
TESTING
When testing secondary cables for damage with an
oscilloscope, follow the instructions of the equipment
manufacturer.
If an oscilloscope is not available, spark plug cables
may be tested as follows:
CAUTION: Do not leave any one spark plug cable
disconnected for longer than necessary during test-
ing. This may cause possible heat damage to the
catalytic converter. Total test time must not exceed
ten minutes.
Fig. 36 Heat ShieldsÐ3.9L/5.2L/5.9L Engines
1 - AIR GAP
2 - SPARK PLUG BOOT HEAT SHIELD
BR/BEIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 19
SPARK PLUG (Continued)
Page 686 of 2889

STANDARD PROCEDURE - CLOCKSPRING
CENTERING
The clockspring is designed to wind and unwind
when the steering wheel is rotated, but is only
designed to rotate the same number of turns (about
five complete rotations) as the steering wheel can be
turned from stop to stop. Centering the clockspring
indexes the clockspring tape to other steering compo-
nents so that it can operate within its designed
travel limits. The rotor of a centered clockspring can
be rotated two and one-half turns in either direction
from the centered position, without damaging the
clockspring tape.
However, if the clockspring is removed for service
or if the steering column is disconnected from the
steering gear, the clockspring tape can change posi-
tion relative to the other steering components. The
clockspring must then be re-centered following com-
pletion of such service or the clockspring tape may be
damaged. Service replacement clocksprings are
shipped pre-centered and with the auto-locking tabs
engaged (raised). These auto-locking tabs should not
be disengaged until the clockspring has been
installed on the steering column. If the auto-locking
tabs are disengaged before the clockspring is
installed on a steering column, the clockspring cen-
tering procedure must be performed.
WARNING: DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCON-
NECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE
(GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR
THE AIRBAG SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE
BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DIS-
ABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE
THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN
ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSI-
BLE PERSONAL INJURY.
NOTE: Before starting this procedure, be certain to
turn the steering wheel until the front wheels are in
the straight-ahead position.
(1) Place the front wheels in the straight-ahead
position.
(2) Remove the clockspring from the steering col-
umn. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/
CLOCKSPRING - REMOVAL).(3) Depress the two plastic clockspring auto-lock-
ing tabs (Fig. 8).
(4) Keeping the auto-locking tabs depressed, rotate
the clockspring rotor clockwise to the end of its
travel.Do not apply excessive torque.
(5) From the end of the clockwise travel, rotate the
rotor about two and one-half turns counterclockwise,
then release the auto-locking tabs. The clockspring
pigtail wire for the horn switch should end up at the
top, and the pigtail wires for the airbag, optional
speed control switches, and optional remote radio
switches at the bottom. The clockspring is now cen-
tered.
(6) The front wheels should still be in the straight-
ahead position. Reinstall the clockspring onto the
steering column. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RE-
STRAINTS/CLOCKSPRING - INSTALLATION).
REMOVAL
The clockspring cannot be repaired. It must be
replaced if faulty or damaged, or if the driver airbag
has been deployed.
Fig. 8 Clockspring Auto-Locking Tabs
1 - AIRBAG MODULE WIRE
2 - SPEED CONTROL WIRING
3 - HORN WIRE
4 - CLOCKSPRING ASSEMBLY
5 - AUTO-LOCKING TABS
BR/BERESTRAINTS 8O - 11
CLOCKSPRING (Continued)
Page 709 of 2889

SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Servo Mounting Bracket
Nuts8.5 75
Switch Module Mounting
Screws326
Vacuum Reservoir
Mounting Screws2.2
20
CABLE
DESCRIPTION
The speed control servo cable is connected between
the speed control vacuum servo diaphragm and the
throttle body control linkage.
OPERATION
This cable causes the throttle control linkage to
open or close the throttle valve in response to move-
ment of the vacuum servo diaphragm.
REMOVAL - GAS ENGINES
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Remove air cleaner (all except 8.0L V-10
engine).
(3) Using finger pressure only, remove speed con-
trol cable connector at bellcrank by pushing connec-
tor off the bellcrank pin (Fig. 1) or (Fig. 2). DO NOT
try to pull connector off perpendicular to the
bellcrank pin. Connector will be broken.
(4) Squeeze 2 tabs on sides of speed control cable
at throttle body mounting bracket (locking plate) and
push out of bracket.
(5) Remove servo cable from servo. Refer to Speed
Control Servo Removal/Installation in this group.
REMOVAL - DIESEL WITH AUTO. TRANS.
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
(2) Remove cable/lever/linkage cover. Refer to
Speed Control Servo Removal/Installation.
(3) Remove (disconnect) servo cable from servo.
Refer to Speed Control Servo Removal/Installation.
(4) Using finger pressure only, disconnect end of
servo cable from throttle lever pin by pulling forward
on connector while holding lever rearward (Fig.
3).DO NOT try to pull connector off perpendic-
ular to lever pin. Connector will be broken.
(5) Squeeze 2 pinch tabs (Fig. 3) on sides of speed
control cable at mounting bracket and push cable
rearward out of bracket.
(6) Remove cable from vehicle.
INSTALLATION - GAS ENGINES
(1) Install end of cable to speed control servo.
Refer to Speed Control Servo Removal/Installation.
(2) Install cable into throttle body mounting
bracket (injection pump bracket on diesel engine).
Cable snaps into bracket.
(3) Install speed control cable connector at throttle
body bellcrank pin (injection pump bellcrank pin on
diesel engine). Connector snaps onto pin.
(4) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(5) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
INSTALLATION - DIESEL WITH AUTO. TRANS.
(1) Install (connect) end of speed control servo
cable to speed control servo. Refer to Speed Control
Servo Removal/Installation.
(2) Install cable through mounting hole on mount-
ing bracket. Cable snaps into bracket.
(3) Connect servo cable to throttle lever by push-
ing cable connector rearward onto lever pin while
holding lever forward.
(4) Connect negative battery cables to both batter-
ies.
Fig. 1 Servo Cable at Throttle BodyÐV-6/V-8 Engine
1 - VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL CABLE
8P - 4 SPEED CONTROLBR/BE
SPEED CONTROL (Continued)
Page 715 of 2889

(9) Using finger pressure only, disconnect end of
servo cable from throttle lever pin by pulling forward
on connector while holding lever rearward (Fig. 16).
DO NOT try to pull connector off perpendicular
to lever pin. Connector will be broken.
(10) Position battery tray up far enough for access
to speed control servo electrical connector and vac-
uum line.
(11) Disconnect electrical connector and vacuum
line at servo.
(12) Position battery tray with attached servo
assembly to gain access to 2 servo mounting nuts
(Fig. 18) or (Fig. 19).
(13) Remove 2 mounting nuts holding servo cable
sleeve to bracket (Fig. 19).
(14) Pull speed control cable sleeve and servo away
from servo mounting bracket to expose cable retain-
ing clip (Fig. 19) and remove clip. Note: The servo
mounting bracket displayed in (Fig. 19) is a typical
bracket and may/may not be applicable to this model
vehicle.
(15) Remove servo from mounting bracket. While
removing, note orientation of servo to bracket.
INSTALLATION
V-6/V-8 ENGINES
(1) Position servo to mounting bracket.
(2) Align hole in cable connector with hole in servo
pin. Install cable-to-servo retaining clip.
(3) Insert servo studs through holes in servo
mounting bracket.
(4) Insert servo studs through holes in servo cable
sleeve.
(5) Install servo mounting nuts and tighten to 8.5
N´m (75 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect vacuum line to servo.
(7) Connect electrical connector to servo terminals.
(8) Install three bolts retaining servo/servo mount-
ing bracket to battery tray.
(9) Connect servo cable to throttle body. Refer to
Servo Cable Removal/Installation in this group.
(10) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(11) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
Fig. 16 Servo Cable at Throttle Lever
1 - PINCH (2) TABS
2 - CABLE MOUNTING BRACKET
3 - PINCH TABS (2)
4 - OFF
5 - THROTTLE CABLE
6 - THROTTLE LEVER
7 - THROTTLE LEVER PIN
8 - OFF
9 - CONNECTOR
10 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
Fig. 17 Servo LocationÐRemoval/Installation
1 - BATTERY TRAY
2 - SERVO ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - SERVO BRACKET SCREWS (3)
8P - 10 SPEED CONTROLBR/BE
SPEED CONTROL SERVO (Continued)
Page 716 of 2889
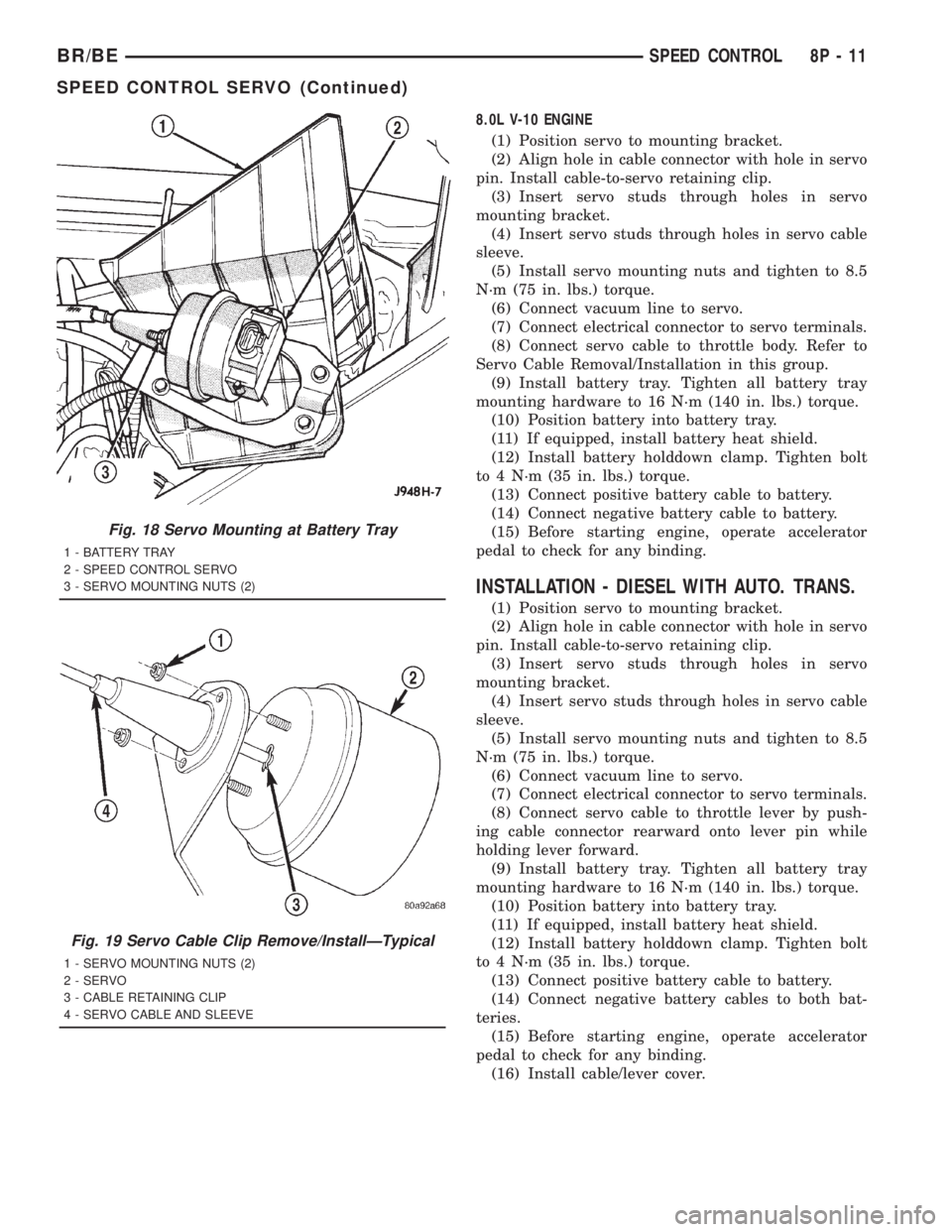
8.0L V-10 ENGINE
(1) Position servo to mounting bracket.
(2) Align hole in cable connector with hole in servo
pin. Install cable-to-servo retaining clip.
(3) Insert servo studs through holes in servo
mounting bracket.
(4) Insert servo studs through holes in servo cable
sleeve.
(5) Install servo mounting nuts and tighten to 8.5
N´m (75 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect vacuum line to servo.
(7) Connect electrical connector to servo terminals.
(8) Connect servo cable to throttle body. Refer to
Servo Cable Removal/Installation in this group.
(9) Install battery tray. Tighten all battery tray
mounting hardware to 16 N´m (140 in. lbs.) torque.
(10) Position battery into battery tray.
(11) If equipped, install battery heat shield.
(12) Install battery holddown clamp. Tighten bolt
to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(13) Connect positive battery cable to battery.
(14) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(15) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
INSTALLATION - DIESEL WITH AUTO. TRANS.
(1) Position servo to mounting bracket.
(2) Align hole in cable connector with hole in servo
pin. Install cable-to-servo retaining clip.
(3) Insert servo studs through holes in servo
mounting bracket.
(4) Insert servo studs through holes in servo cable
sleeve.
(5) Install servo mounting nuts and tighten to 8.5
N´m (75 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect vacuum line to servo.
(7) Connect electrical connector to servo terminals.
(8) Connect servo cable to throttle lever by push-
ing cable connector rearward onto lever pin while
holding lever forward.
(9) Install battery tray. Tighten all battery tray
mounting hardware to 16 N´m (140 in. lbs.) torque.
(10) Position battery into battery tray.
(11) If equipped, install battery heat shield.
(12) Install battery holddown clamp. Tighten bolt
to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(13) Connect positive battery cable to battery.
(14) Connect negative battery cables to both bat-
teries.
(15) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
(16) Install cable/lever cover.
Fig. 18 Servo Mounting at Battery Tray
1 - BATTERY TRAY
2 - SPEED CONTROL SERVO
3 - SERVO MOUNTING NUTS (2)
Fig. 19 Servo Cable Clip Remove/InstallÐTypical
1 - SERVO MOUNTING NUTS (2)
2 - SERVO
3 - CABLE RETAINING CLIP
4 - SERVO CABLE AND SLEEVE
BR/BESPEED CONTROL 8P - 11
SPEED CONTROL SERVO (Continued)
Page 718 of 2889

²If the actual speed is not within 20 mph of the
set speedThe previous disengagement conditions are
programmed for added safety.
Once the speed control has been disengaged,
depressing the ACCEL switch restores the vehicle to
the target speed that was stored in the ECM's RAM.
NOTE: Depressing the OFF switch will erase the set
speed stored in the ECM's RAM.
If, while the speed control is engaged, the driver
wishes to increase vehicle speed, the ECM is pro-
grammed for an acceleration feature. With the
ACCEL switch held closed, the vehicle accelerates
slowly to the desired speed. The new target speed is
stored in the ECM's RAM when the ACCEL switch is
released. The ECM also has a9tap-up9feature in
which vehicle speed increases at a rate of approxi-
mately 2 mph for each momentary switch activation
of the ACCEL switch.
The ECM also provides a means to decelerate with-
out disengaging speed control. To decelerate from an
existing recorded target speed, depress and hold the
COAST switch until the desired speed is reached.
Then release the switch. The ON, OFF switch oper-
ates two components: the ECM's ON, OFF input, and
the battery voltage to the brake switch, which powers
the speed control servo.
REMOVAL
WARNING: BEFORE BEGINNING ANY AIRBAG SYS-
TEM COMPONENT REMOVAL OR INSTALLATION,
REMOVE AND ISOLATE THE NEGATIVE (-)
CABLE(S) FROM THE BATTERY. THIS IS THE ONLY
SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM.
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR SYSTEM CAPACI-
TOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE FURTHER SYSTEM
SERVICE. FAILURE TO DO THIS COULD RESULT IN
ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSI-
BLE INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate negative battery
cable(s).
(2) Remove airbag module. Refer to 8, Restraint
Systems for procedures.
(3) Remove switch-to-steering wheel mounting
screws (Fig. 20).
(4) Remove switch.
(5) Remove electrical connector at switch.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install electrical connector to switch.
(2) Install switch and mounting screws.
(3) Tighten screws to 3 N´m (26 in. lbs. +/± 2 in.
lbs.) torque.(4) Install airbag module. Refer to 8, Restraint
Systems for procedures.
(5) Connect negative battery cable(s).
VACUUM RESERVOIR
DESCRIPTION
Gasoline Powered Engines :A vacuum reservoir
is used to supply the vacuum needed to maintain
proper speed control operation when engine vacuum
drops, such as in climbing a grade while driving. A
one-way check valve is used in the vacuum line
between the reservoir and the vacuum source. This
check valve is used to trap engine vacuum in the res-
ervoir. On certain vehicle applications, this reservoir
is shared with the heating/air-conditioning system.
The vacuum reservoir cannot be repaired and must
be replaced if faulty.
Diesel Powered Engines With Auto. Trans. :A
vacuum reservoir is not used if equipped with a die-
sel powered engine. Instead, an engine driven pump
(vacuum pump) is used to supply vacuum for speed
control operation. This vacuum pump is used with
the diesel engine only if it is equipped with an auto-
matic transmission. Refer to Vacuum Pump in 9,
Engines for information.
REMOVAL
The vacuum reservoir is located under the plastic
cowel plenum cover at lower base of windshield. The
vacuum reservoir is not used if equipped with a die-
sel engine.
Fig. 20 Speed Control Switches
1 - MOUNTING SCREWS (2)
2 - SPEED CONTROL SWITCHES (2)
BR/BESPEED CONTROL 8P - 13
SWITCH (Continued)
Page 719 of 2889

(1) Disconnect and isolate battery negative cable.
(2) Remove both windshield wiper arm/blade
assemblies. Refer to 8, Wiper and Washer Systems.
(3) Remove rubber weather-strip at front edge of
cowel grill (Fig. 21).
(4) Release cowel grill plastic anchor screws (Fig.
22).
(5) Lift cowel plenum cover/grille panel from vehi-
cle far enough to access vacuum reservoir.
(6) Disconnect vacuum supply line from vacuum
reservoir (Fig. 23).
(7) Remove 2 vacuum reservoir mounting screws.
(8) Remove vacuum reservoir from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
The vacuum reservoir is located under the plastic
cowel plenum cover at lower base of windshield. The
vacuum reservoir is not used if equipped with a die-
sel engine.
(1) Install vacuum reservoir and two mounting
screws. Tighten screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect vacuum supply hose to vacuum reser-
voir.
(3) Position cowel plenum cover/grille panel to
vehicle.
(4) Install and tighten cowel cover fasteners to
vehicle body.
(5) Install rubber weather-strip at front edge of
cowel grill.
(6) Install windshield wiper arms. Refer to 8,
Wiper and Washer Systems.
(7) Connect negative battery to cable.
Fig. 21 Cowel Grille Panel Weather-strip
1 - COWL GRILLE
2 - WEATHERSTRIP
Fig. 22 Plastic Anchor Screws Remove/Install
1 - PLASTIC SCREW ANCHOR
2 - COWL GRILLE
Fig. 23 Vacuum Reservoir Remove/Install
1 - COWL PLENUM
2 - VACUUM RESERVOIR
8P - 14 SPEED CONTROLBR/BE
VACUUM RESERVOIR (Continued)
Page 1081 of 2889

POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE C2 (DIESEL) - BLACK 32 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
9- -
10 K20 18DG GENERATOR FIELD
11 K54 18OR/BK (A/T) TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID CONTROL
12 - -
13 - -
14 - -
15 - -
16 - -
17 - -
18 - --
19 - -
20 - -
21 T60 18BR (A/T) 3-4 SHIFT SOLENOID CONTROL
22 - -
23 - -
24 - -
25 T13 18DB/BK OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR GROUND
26 - -
27 G7 18WT/OR (A/T) VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR SIGNAL
28 T14 18LG/BK OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR SIGNAL
29 T25 18LG/WT (A/T) GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR SIGNAL
30 K30 18PK (A/T) TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY CONTROL
31 K7 18OR (A/T) 5V SUPPLY
32 - -
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE C2 (GAS) - BLACK 32 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 T54 18VT (A/T) TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR SIGNAL
2 K26 18VT/TN (5.2L/5.9L/8.0L) FUEL INJECTOR NO. 7 DRIVER
3 K115 18TN/BK (8.0L) FUEL INJECTOR NO. 9 DRIVER
4 K11 18WT/DB FUEL INJECTOR NO. 1 DRIVER
5 K13 18YL/WT FUEL INJECTOR NO. 3 DRIVER
6 K38 18GY FUEL INJECTOR NO. 5 DRIVER
7- -
8 K88 18VT/WT (A/T) GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID CONTROL
9- -
10 K20 18DG GENERATOR FIELD
11 K54 18OR/BK TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID CONTROL
12 K58 18BR/DB FUEL INJECTOR NO. 6 DRIVER
13 K28 18GY/LB (5.2L/5.9L/8.0L) FUEL INJECTOR NO. 8 DRIVER
14 K116 18WT (8.0L) FUEL INJECTOR NO. 10 DRIVER
15 K12 18TN FUEL INJECTOR NO. 2 DRIVER
16 K14 18LB/BR FUEL INJECTOR NO. 4 DRIVER
17 - -
18 - -
19 - -
20 - -
21 T60 18BR (A/T) 3-4 SHIFT SOLENOID CONTROL
22 - -
23 G60 18GY/OR ENGINE OIL PRESSURE SENSOR SIGNAL
24 - -
8W - 80 - 68 8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN-OUTSBR/BE