stop start DODGE RAM 2001 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2001Pages: 2889, PDF Size: 68.07 MB
Page 344 of 2889

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
16. Thermostat partially or completely
shut.16. Check thermostat operation and
replace as necessary. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE COOLANT
THERMOSTAT - REMOVAL) .
17. Viscous fan drive not operating
properly.17. Check fan drive operation and replace
as necessary. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH
- REMOVAL) .
18. Cylinder head gasket leaking. 18. Check for cylinder head gasket leaks.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING).
19. Heater core leaking. 19. Check heater core for leaks. (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). Repair as necessary.
TEMPERATURE
GAUGE READING IS
INCONSISTENT
(FLUCTUATES,
CYCLES OR IS
ERRATIC)1. During cold weather operation, with the
heater blower in the high position, the
gauge reading may drop slightly.1. A normal condition. No correction is
necessary.
2. Temperature gauge or engine mounted
gauge sensor defective or shorted. Also,
corroded or loose wiring in this circuit.2. Check operation of gauge and repair if
necessary. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING).
3. Gauge reading rises when vehicle is
brought to a stop after heavy use (engine
still running)3. A normal condition. No correction is
necessary. Gauge should return to normal
range after vehicle is driven.
4. Gauge reading high after re-starting a
warmed up (hot) engine.4. A normal condition. No correction is
necessary. The gauge should return to
normal range after a few minutes of
engine operation.
5. Coolant level low in radiator (air will
build up in the cooling system causing
the thermostat to open late).5. Check and correct coolant leaks. (Refer
to 7 - COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
6. Cylinder head gasket leaking allowing
exhaust gas to enter cooling system
causing a thermostat to open late.6. (a) Check for cylinder head gasket
leaks. (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
(b) Check for coolant in the engine oil.
Inspect for white steam emitting from the
exhaust system. Repair as necessary.
7. Water pump impeller loose on shaft. 7. Check water pump and replace as
necessary. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/WATER PUMP - REMOVAL).
8. Loose accessory drive belt. (water
pump slipping)8. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY
DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). Check and correct as
necessary.
9. Air leak on the suction side of the
water pump allows air to build up in
cooling system causing thermostat to
open late.9. Locate leak and repair as necessary.
BR/BECOOLING 7 - 9
COOLING (Continued)
Page 351 of 2889

(3) Fill coolant reserve/overflow tank to the FULL
mark.
(4) Start and operate engine until thermostat
opens. Upper radiator hose should be warm to touch.
(5) If necessary, add 50/50 water and antifreeze
mixture to the coolant reserve/overflow tank to main-
tain coolant level. This level should be between the
ADD and FULL marks. The level in the reserve/over-
flow tank may drop below the ADD mark after three
or four warm-up and cool-down cycles.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐADDING
ADDITIONAL COOLANT
Do not remove radiator cap to add coolant to
system.When adding coolant to maintain correct
level, do so at coolant reserve/overflow tank. Use a
50/50 mixture of ethylene glycol antifreeze containing
Alugard 340-2yand low mineral content water.
Remove radiator cap only for testing or when refill-
ing system after service. Removing cap unnecessarily
can cause loss of coolant and allow air to enter sys-
tem, which produces corrosion.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐCOOLANT LEVEL
CHECK
NOTE: Do not remove radiator cap for routine cool-
ant level inspections. The coolant level can be
checked at coolant recovery bottle .
The coolant reserve/overflow system provides a
quick method for determining coolant level without
removing radiator pressure cap. With engine not run-
ning, open the coolant recovery bottle cap and
remove coolant level indicator dipstick to observe
coolant level in coolant recovery bottle. The coolant
level should be between ADD and FULL marks. If
the coolant level is at or below the ADD mark, fill
the recovery bottle with a 50/50 mixture of antifreeze
and water ONE QUART AT A TIME. Repeat this pro-
cedure until the coolant level is at the FULL mark
(Fig. 8).
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐCOOLING SYSTEM
CLEANING/REVERSE FLUSHING
CLEANING
Drain cooling system and refill with water. Run
engine with radiator cap installed until upper radia-
tor hose is hot. Stop engine and drain water from
system. If water is dirty, fill system with water, run
engine and drain system. Repeat until water drains
clean.
REVERSE FLUSHING
Reverse flushing of cooling system is the forcing of
water through the cooling system. This is done using
air pressure in the opposite direction of normal cool-
ant flow. It is usually only necessary with very dirty
systems with evidence of partial plugging.
REVERSE FLUSHING RADIATOR
Disconnect radiator hoses from radiator inlet and
outlet. Attach a section of radiator hose to radiator
bottom outlet fitting and insert flushing gun. Con-
nect a water supply hose and air supply hose to
flushing gun.
CAUTION: Internal radiator pressure must not
exceed 138 kPa (20 psi) as damage to radiator may
result.
Allow radiator to fill with water. When radiator is
filled, apply air in short blasts. Allow radiator to
refill between blasts. Continue this reverse flushing
until clean water flows out through rear of radiator
cooling tube passages. Have radiator cleaned more
extensively by a radiator repair shop.
Fig. 8 COOLANT RESERVE/OVERFLOW TANKÐALL
EXCEPT 8.0L V-10 ENGINE
1 - T-SLOTS
2 - ALIGNMENT PIN
3 - FAN SHROUD
4 - COOLANT RESERVE/OVERFLOW TANK
7 - 16 COOLINGBR/BE
COOLING (Continued)
Page 390 of 2889

to be used with cool or cold temperatures only.
If used with high outside temperatures, serious
engine damage could result.Refer to the litera-
ture supplied with the cover for additional informa-
tion.
(1) To determine if the thermostat is defective, it
must be removed from the vehicle (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE COOLANT THERMO-
STAT - REMOVAL).
(2) After the thermostat has been removed, exam-
ine the thermostat and inside of thermostat housing
for contaminants. If contaminants are found, the
thermostat may already be in a ªstuck openº position.
Flush the cooling system before replacing thermostat
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(3) Place the thermostat into a container filled
with water.
(4) Place the container on a hot plate or other suit-
able heating device.
(5) Place a commercially available radiator ther-
mometer into the water.
(6) Apply heat to the water while observing the
thermostat and thermometer.
(7) When the water temperature reaches 83ÉC
(181ÉF) the thermostat should start to open (valve
will start to move). If the valve starts to move before
this temperature is reached, it is opening too early.
Replace thermostat. The thermostat should be fully
open (valve will stop moving) at 95ÉC (203ÉF). If the
valve is still moving when the water temperature
reaches 203É, it is opening too late. Replace thermo-
stat. If the valve refuses to move at any time, replace
thermostat.
REMOVAL
WARNING: DO NOT LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND PRES-
SURIZED. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
Do not waste reusable coolant. If the solution is
clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for
reuse.
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cables.
(2) Drain cooling system until coolant level is
below thermostat (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
6094). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER HPC-20)
MAY BE USED FOR LARGER CLAMPS. ALWAYSWEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVICING CON-
STANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only an original equipment clamp
with a matching number or letter.
(3) Remove radiator hose clamp and hose from
thermostat housing.
(4) Remove the three (3) water outlet-to-cylinder
head bolts and remove the water outlet connector
(Fig. 27).
(5) Clean the mating surfaces of the water outlet
connector and clean the thermostat seat groove at
the top of the thermostat housing (Fig. 27).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the thermostat into the groove in the
top of the thermostat housing (Fig. 27).
(2) Install the water outlet connector and bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install the radiator upper hose and clamp.
(4) Fill the cooling system with coolant (Refer to 7
- COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Connect the battery negative cables.
(6) Start the engine and check for coolant leaks.
Run engine to check for proper thermostat operation.
Fig. 27 Thermostat Removal/Installation
1 - WATER OUTLET CONNECTOR
2 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
3 - THERMOSTAT
BR/BEENGINE 7 - 55
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 460 of 2889
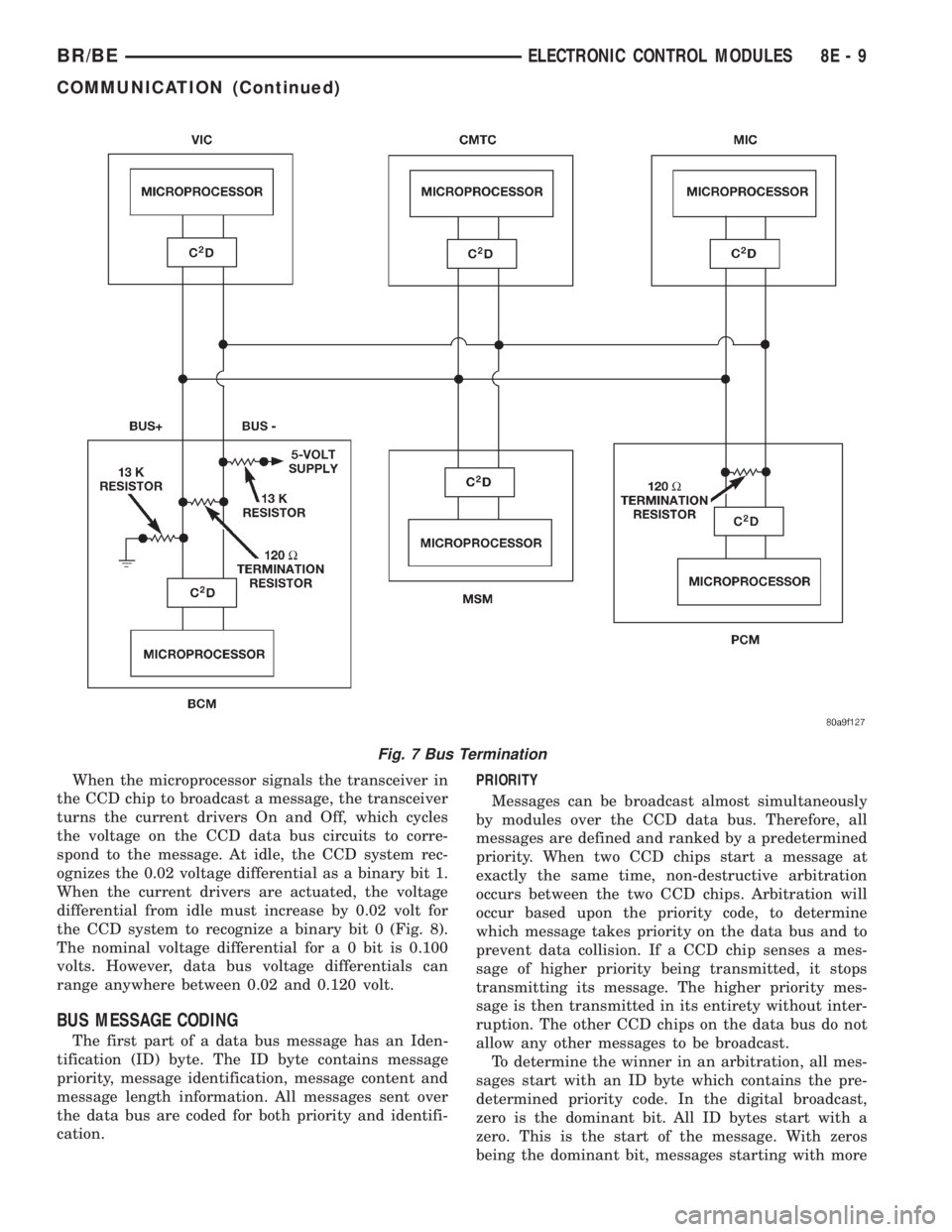
When the microprocessor signals the transceiver in
the CCD chip to broadcast a message, the transceiver
turns the current drivers On and Off, which cycles
the voltage on the CCD data bus circuits to corre-
spond to the message. At idle, the CCD system rec-
ognizes the 0.02 voltage differential as a binary bit 1.
When the current drivers are actuated, the voltage
differential from idle must increase by 0.02 volt for
the CCD system to recognize a binary bit 0 (Fig. 8).
The nominal voltage differential for a 0 bit is 0.100
volts. However, data bus voltage differentials can
range anywhere between 0.02 and 0.120 volt.
BUS MESSAGE CODING
The first part of a data bus message has an Iden-
tification (ID) byte. The ID byte contains message
priority, message identification, message content and
message length information. All messages sent over
the data bus are coded for both priority and identifi-
cation.PRIORITY
Messages can be broadcast almost simultaneously
by modules over the CCD data bus. Therefore, all
messages are defined and ranked by a predetermined
priority. When two CCD chips start a message at
exactly the same time, non-destructive arbitration
occurs between the two CCD chips. Arbitration will
occur based upon the priority code, to determine
which message takes priority on the data bus and to
prevent data collision. If a CCD chip senses a mes-
sage of higher priority being transmitted, it stops
transmitting its message. The higher priority mes-
sage is then transmitted in its entirety without inter-
ruption. The other CCD chips on the data bus do not
allow any other messages to be broadcast.
To determine the winner in an arbitration, all mes-
sages start with an ID byte which contains the pre-
determined priority code. In the digital broadcast,
zero is the dominant bit. All ID bytes start with a
zero. This is the start of the message. With zeros
being the dominant bit, messages starting with more
Fig. 7 Bus Termination
BR/BEELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 9
COMMUNICATION (Continued)
Page 592 of 2889

problems are found, the following procedure will help
locate a short or open in the left or right turn signal
indicator circuit. Refer to the appropriate wiring
information. The wiring information includes wiring
diagrams, proper wire and connector repair proce-
dures, details of wire harness routing and retention,
connector pin-out information and location views for
the various wire harness connectors, splices and
grounds.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the instrument cluster.
(2) Connect the battery negative cable. Activate
the hazard warning system by moving the hazard
warning switch button to the On position. Check for
battery voltage at the inoperative (right or left) turn
signal circuit cavity of the instrument panel wire
harness connector (Connector C2) for the instrument
cluster. There should be a switching (on and off) bat-
tery voltage signal. If OK, replace the faulty turn sig-
nal indicator bulb. If not OK, repair the open (right
or left) turn signal circuit to the left multi-function
switch as required.
UPSHIFT INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION
An upshift indicator is standard equipment on all
instrument clusters. However, on vehicles not
equipped with a manual transmission, this indicator
is disabled. The upshift indicator is located near the
fuel gauge in the instrument cluster overlay, to the
left of center. The upshift indicator consists of an
upward pointed arrow icon that is a stenciled cutout
in the opaque layer of the instrument cluster overlay.
The dark outer layer of the overlay prevents the indi-
cator from being clearly visible when it is not illumi-
nated. An amber lens behind the cutout in the
opaque layer of the overlay causes the icon to appear
in amber through the translucent outer layer of the
overlay when the indicator is illuminated from
behind by a replaceable incandescent bulb and bulb
holder unit located on the instrument cluster elec-
tronic circuit board. The upshift indicator is serviced
as a unit with the instrument cluster.
OPERATION
The upshift indicator gives an indication to the
vehicle operator when the transmission should be
shifted to the next highest gear in order to achieve
the best fuel economy. This indicator is controlled by
a transistor on the instrument cluster circuit board
based upon the cluster programming and electronic
messages received by the cluster from the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) over the Chrysler Collision
Detection (CCD) data bus. The upshift indicator bulbreceives battery current on the instrument cluster
electronic circuit board through the fused ignition
switch output (st-run) circuit whenever the ignition
switch is in the On or Start positions; therefore, the
lamp will always be off when the ignition switch is in
any position except On or Start. The bulb only illu-
minates when it is provided a path to ground by the
instrument cluster transistor. On models not
equipped with a manual transmission, the incandes-
cent bulb and bulb holder unit are not installed at
the factory when the vehicle is built. The instrument
cluster will turn on the upshift indicator for the fol-
lowing reasons:
²Upshift Lamp-On Message- Each time the
cluster receives an upshift lamp-on message from the
PCM indicating the engine speed and load conditions
are right for a transmission upshift to occur, the
upshift indicator is illuminated. The indicator
remains illuminated until the cluster receives an
upshift lamp-off message from the PCM or until the
ignition switch is turned to the Off position, which-
ever occurs first. The PCM will normally send an
upshift lamp-off message three to five seconds after a
lamp-on message, if an upshift is not performed. The
indicator will then remain off until the vehicle stops
accelerating and is brought back into the range of
indicator operation, or until the transmission is
shifted into another gear.
²Actuator Test- Each time the cluster is put
through the actuator test, the indicator will be
turned on during the bulb check portion of the test to
confirm the functionality of the indicator and the
cluster control circuitry.
The PCM continually monitors the engine speed
and load conditions to determine the proper fuel and
ignition requirements. The PCM then sends the
proper messages to the instrument cluster. If the
upshift indicator fails to light during normal vehicle
operation, replace the bulb with a known good unit.
For further diagnosis of the upshift indicator or the
instrument cluster circuitry that controls the indica-
tor, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). For
proper diagnosis of the PCM, the CCD data bus, or
the message inputs to the instrument cluster that
control the upshift indicator, a DRBIIItscan tool is
required. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic infor-
mation.
VOLTAGE GAUGE
DESCRIPTION
A voltage gauge is standard equipment on all
instrument clusters. The voltage gauge is located in
the upper left quadrant of the instrument cluster,
BR/BEINSTRUMENT CLUSTER 8J - 33
TURN SIGNAL INDICATORS (Continued)
Page 686 of 2889

STANDARD PROCEDURE - CLOCKSPRING
CENTERING
The clockspring is designed to wind and unwind
when the steering wheel is rotated, but is only
designed to rotate the same number of turns (about
five complete rotations) as the steering wheel can be
turned from stop to stop. Centering the clockspring
indexes the clockspring tape to other steering compo-
nents so that it can operate within its designed
travel limits. The rotor of a centered clockspring can
be rotated two and one-half turns in either direction
from the centered position, without damaging the
clockspring tape.
However, if the clockspring is removed for service
or if the steering column is disconnected from the
steering gear, the clockspring tape can change posi-
tion relative to the other steering components. The
clockspring must then be re-centered following com-
pletion of such service or the clockspring tape may be
damaged. Service replacement clocksprings are
shipped pre-centered and with the auto-locking tabs
engaged (raised). These auto-locking tabs should not
be disengaged until the clockspring has been
installed on the steering column. If the auto-locking
tabs are disengaged before the clockspring is
installed on a steering column, the clockspring cen-
tering procedure must be performed.
WARNING: DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCON-
NECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE
(GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR
THE AIRBAG SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE
BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DIS-
ABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE
THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN
ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSI-
BLE PERSONAL INJURY.
NOTE: Before starting this procedure, be certain to
turn the steering wheel until the front wheels are in
the straight-ahead position.
(1) Place the front wheels in the straight-ahead
position.
(2) Remove the clockspring from the steering col-
umn. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/
CLOCKSPRING - REMOVAL).(3) Depress the two plastic clockspring auto-lock-
ing tabs (Fig. 8).
(4) Keeping the auto-locking tabs depressed, rotate
the clockspring rotor clockwise to the end of its
travel.Do not apply excessive torque.
(5) From the end of the clockwise travel, rotate the
rotor about two and one-half turns counterclockwise,
then release the auto-locking tabs. The clockspring
pigtail wire for the horn switch should end up at the
top, and the pigtail wires for the airbag, optional
speed control switches, and optional remote radio
switches at the bottom. The clockspring is now cen-
tered.
(6) The front wheels should still be in the straight-
ahead position. Reinstall the clockspring onto the
steering column. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RE-
STRAINTS/CLOCKSPRING - INSTALLATION).
REMOVAL
The clockspring cannot be repaired. It must be
replaced if faulty or damaged, or if the driver airbag
has been deployed.
Fig. 8 Clockspring Auto-Locking Tabs
1 - AIRBAG MODULE WIRE
2 - SPEED CONTROL WIRING
3 - HORN WIRE
4 - CLOCKSPRING ASSEMBLY
5 - AUTO-LOCKING TABS
BR/BERESTRAINTS 8O - 11
CLOCKSPRING (Continued)
Page 708 of 2889

(3) If vacuum is less than ten inches of mercury,
determine source of leak. Check vacuum line to
engine for leaks. Also check actual engine intake
manifold vacuum. If manifold vacuum does not meet
this requirement, check for poor engine performance
and repair as necessary.
(4) If vacuum line to engine is not leaking, check
for leak at vacuum reservoir. To locate and gain
access to reservoir, refer to Vacuum Reservoir Remov-
al/Installation in this group. Disconnect vacuum line
at reservoir and connect a hand-operated vacuum
pump to reservoir fitting. Apply vacuum. Reservoir
vacuum should not bleed off. If vacuum is being lost,
replace reservoir.
(5) Verify operation of one-way check valve and
check it for leaks.
(a) Locate one-way check valve. The valve is
located in vacuum line between vacuum reservoir
and engine vacuum source. Disconnect vacuum
hoses (lines) at each end of valve.
(b) Connect a hand-operated vacuum pump to
reservoir end of check valve. Apply vacuum. Vac-
uum should not bleed off. If vacuum is being lost,
replace one-way check valve.
(c) Connect a hand-operated vacuum pump to
vacuum source end of check valve. Apply vacuum.
Vacuum should flow through valve. If vacuum is
not flowing, replace one-way check valve. Seal the
fitting at opposite end of valve with a finger and
apply vacuum. If vacuum will not hold, diaphragm
within check valve has ruptured. Replace valve.
Diesel Engines With Automatic Trans.
On diesel powered engines equipped with an auto-
matic transmission: an engine driven vacuum pump,
a one-way check valve and vacuum lines are used to
supply vacuum to the speed control servo. A vacuum
reservoir is not used.
(1) Disconnect vacuum hose at speed control servo
and install a vacuum gauge into the disconnected
hose.
(2) Start engine and observe gauge at idle. For
vacuum testing and vacuum specifications, refer to
Vacuum Pump OutputÐDiesel Engine in 9, Engines.
(3) If vacuum pump output is OK, determine other
source of leak. Check all vacuum lines to: speed con-
trol servo, engine vacuum pump and heating/air con-
ditioning system for leaks.
(4) Verify operation of one-way check valve and
check it for leaks.(a) Locate one-way check valve. The valve is
located in vacuum line between speed control servo
and engine vacuum pump. Disconnect vacuum
hoses (lines) at each end of valve.
(b) Connect a hand-operated vacuum pump to
reservoir end of check valve. Apply vacuum. Vac-
uum should not bleed off. If vacuum is being lost,
replace one-way check valve.
(c) Connect a hand-operated vacuum pump to
vacuum source end of check valve. Apply vacuum.
Vacuum should flow through valve. If vacuum is
not flowing, replace one-way check valve. Seal the
fitting at opposite end of valve with a finger and
apply vacuum. If vacuum will not hold, diaphragm
within check valve has ruptured. Replace valve.
Diesel Engine With Manual Trans.
Vacuum is not used for any part of the speed con-
trol system if equipped with a diesel engine and a
manual transmission.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST
Perform a vehicle road test to verify reports of
speed control system malfunction. The road test
should include attention to the speedometer.
If a road test verifies a system problem and the
speedometer operates properly, check for:
²A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). If a DTC
exists, conduct tests per the Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures service manual.
²A misadjusted brake (stop) lamp switch. This
could also cause an intermittent problem.
²Loose, damaged or corroded electrical connec-
tions at the servo. Corrosion should be removed from
electrical terminals and a light coating of Mopar
MultiPurpose Grease, or equivalent, applied.
²Leaking vacuum reservoir.
²Loose or leaking vacuum hoses or connections.
²Defective one-way vacuum check valve.
²Secure attachment of both ends of the speed con-
trol servo cable.
²Smooth operation of throttle linkage and throttle
body air valve.
²Failed speed control servo. Do the servo vacuum
test.
CAUTION: When test probing for voltage or conti-
nuity at electrical connectors, care must be taken
not to damage connector, terminals or seals. If
these components are damaged, intermittent or
complete system failure may occur.
BR/BESPEED CONTROL 8P - 3
SPEED CONTROL (Continued)
Page 721 of 2889

tem of the vehicle. These hard wired circuits are
integral to several wire harnesses, which are routed
throughout the vehicle and retained by many differ-
ent methods. These circuits may be connected to each
other, to the vehicle electrical system and to the
VTSS components through the use of a combination
of soldered splices, splice block connectors, and many
different types of wire harness terminal connectors
and insulators. Refer to the appropriate wiring infor-
mation. The wiring information includes wiring dia-
grams, proper wire and connector repair procedures,
further details on wire harness routing and reten-
tion, as well as pin-out and location views for the
various wire harness connectors, splices and grounds.
OPERATION
A Central Timer Module (CTM) is used on this
model to control and integrate many of the electronic
functions and features included in the Vehicle Theft
Security System (VTSS). In the VTSS, the CTM
receives inputs indicating the status of the door ajar
switches, the door cylinder lock switch, and the igni-
tion switch. The programming in the CTM allows it
to process the information from all of these inputs
and send control outputs to energize or de-energize
the horn relay, the headlamp relay, and the VTSS
indicator. The control of these inputs and outputs are
what constitute all of the features of the VTSS. Fol-
lowing is information on the operation of each of the
VTSS features. Refer to the owner's manual in the
vehicle glove box for more information on the fea-
tures, use and operation of the VTSS.
ENABLING
The high-line or premium version of the CTM must
have the VTSS function electronically enabled in
order for the VTSS to perform as designed. The logic
in the CTM keeps its VTSS function dormant until it
is enabled using a DRBIIIž scan tool. The VTSS
function of the high-line or premium CTM is enabled
on vehicles equipped with the VTSS option at the
factory, but a service replacement CTM must be
VTSS-enabled by the dealer using a DRBIIIž scan
tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
The VTSS engine no-run feature is disabled when
it is shipped from the factory. This is done by pro-
gramming within the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The logic in the PCM prevents the VTSS
engine no-run feature from arming until the engine
start counter within the PCM sees twenty engine
starts. The VTSS no-run feature must be enabled by
the dealer when the vehicle is received from the
assembly plant. Once the VTSS engine no-run fea-
ture has been enabled, it cannot be disabled unless
the PCM is replaced with a new unit. The sameVTSS engine no-run feature enable logic will apply
anytime the PCM is replaced with a new unit.
ARMING
Passive arming of the VTSS occurs when the vehi-
cle is exited with the key removed from the ignition
switch, the headlamps are turned off, and the doors
are locked while they are open using the power lock
switch, or locked after they are closed by turning
either front door lock cylinder to the lock position
using the key. The power lock switch will not func-
tion if the key is in the ignition switch or the head-
lamps are turned on with the driver side front door
open. The VTSS will not arm if the doors are locked
using the mechanical lock button. Active arming of
the VTSS occurs when the ªLockº button on the
Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) transmitter is
depressed to lock the vehicle. For active arming to
occur, the doors must be closed and the ignition
switch must be in the Off position when the RKE
transmitter ªLockº button is depressed. However,
once the VTSS arming process has been completed,
the ignition switch can be turned to the Accessory
position without triggering the alarm.
Once the VTSS begins passive or active arming,
the security indicator lamp in the overhead console
will flash rapidly for about fifteen seconds. This indi-
cates that the VTSS arming is in progress. Turning a
key in the ignition switch, opening a door, or unlock-
ing a door by any means during the fifteen second
arming process will cause the VTSS indicator to stop
flashing and the arming process to abort. Once the
fifteen second arming function is successfully com-
pleted, the indicator will flash at a slower rate, indi-
cating that the VTSS is armed.
DISARMING
Passive disarming of the VTSS occurs when the
vehicle is unlocked using the key to unlock either
front door. Active disarming of the VTSS occurs when
the vehicle is unlocked by depressing the ªUnlockº
button of the RKE transmitter. Once the alarm has
been activated (horn pulsing, headlamps flashing,
and the engine no-run feature), either disarming
method will also deactivate the alarm. Depressing
the ªPanicº button on the RKE transmitter willnot
disarm the VTSS.
POWER-UP MODE
When the armed VTSS senses that the battery has
been disconnected and reconnected, it enters its pow-
er-up mode. In the power-up mode the alarm system
remains armed following a battery failure or discon-
nect. If the VTSS was armed prior to a battery dis-
connect or failure, the technician or vehicle operator
will have to actively or passively disarm the alarm
system after the battery is reconnected. The pow-
8Q - 2 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITYBR/BE
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY (Continued)
Page 756 of 2889

8W-02 COMPONENT INDEX
Component Page
4WD Switch.......................... 8W-31
A/C Compressor Clutch Relay............ 8W-42
A/C Compressor Clutch................. 8W-42
A/C-Heater Control.................... 8W-42
A/C Heater Temperature Select........... 8W-42
A/C High Pressure Switch............... 8W-42
A/C Low Pressure Switch................ 8W-42
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor......... 8W-30
Aftermarket Center High Mounted
Stop Lamp......................... 8W-51
Aftermarket Trailer Tow Connector........ 8W-54
Airbag Control Module.................. 8W-43
Ambient Temperature Sensor............ 8W-49
Ash Receiver Lamp.................... 8W-44
Automatic Day/Night Mirror............. 8W-49
Automatic Shut Down Relay............. 8W-30
Auxiliary Battery...................... 8W-20
Back-Up Lamp Switch.................. 8W-51
Back-Up Lamps....................... 8W-51
Battery Temperature Sensor............. 8W-30
Battery............................. 8W-20
Blend Door Actuator................... 8W-42
Blower Motor Relay.................... 8W-42
Blower Motor Resistor Block............. 8W-42
Blower Motor......................... 8W-42
Brake Lamp Switch.................... 8W-51
Brake Pressure Switch............... 8W-34, 35
Bypass Jumper....................... 8W-21
Camshaft Position Sensor............... 8W-30
Capacitor......................... 8W-10, 30
Cargo Lamps......................... 8W-44
Center High Mounted Stop Lamps........ 8W-51
Center Identification Lamp.............. 8W-50
Central Timer Module.................. 8W-45
Cigar Lighter......................... 8W-41
Circuit Breakers...................... 8W-12
Clockspring.................. 8W-33, 41, 43, 47
Clutch Pedal Position Switch............. 8W-21
Combination Flasher................... 8W-52
Controller Antilock Brake............ 8W-34, 35
Crankshaft Position Sensor.............. 8W-30
Cummins Bus........................ 8W-18
Cup Holder Lamp..................... 8W-44
Cylinder Lock Switches................ 8W-39
Data Link Connector................... 8W-18
Daytime Running Lamp Module.......... 8W-50
Dome Lamp.......................... 8W-44
Door Ajar Switches.................... 8W-45
Door Lock Motors..................... 8W-61
Door Window/Lock Switches.......... 8W-60, 61
Driver Airbag......................... 8W-43
Duty Cycle EVAP/Purge Solenoid......... 8W-30Component Page
Electric Brake Provision................ 8W-54
Engine Control Module.............. 8W-30, 70
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor....... 8W-30
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor.............. 8W-30
Engine Starter Motor Relay.............. 8W-21
Engine Starter Motor................... 8W-21
Fender Lamp......................... 8W-51
Fog Lamp Indicator.................... 8W-50
Fog Lamp Relay....................... 8W-50
Fog Lamp............................ 8W-50
Fuel Heater Relay..................... 8W-30
Fuel Heater.......................... 8W-30
Fuel Injection Pump................... 8W-30
Fuel Injectors......................... 8W-30
Fuel Transfer Pump.................... 8W-30
Fuses (JB)........................... 8W-12
Fuses (PDC).......................... 8W-10
Fusible Link....................... 8W-20, 30
Generator............................ 8W-20
Glove Box Lamp And Switch............. 8W-44
Grounds............................. 8W-15
Headlamp Beam Select Switch........... 8W-50
Headlamp Switch...................... 8W-50
Headlamp........................... 8W-50
Heated Mirror Relay................... 8W-62
Heated Mirror Switch.................. 8W-62
Heated Seat Cushions.................. 8W-63
Heated Seat Relay..................... 8W-12
Heated Seat Switches.................. 8W-63
High Beam Indicator................... 8W-40
High Note Horn....................... 8W-41
Horn Relay.......................... 8W-41
Horn Switch.......................... 8W-41
Idle Air Control Motor.................. 8W-30
Ignition Coil 4-Pack.................... 8W-30
Ignition Coil 6-Pack.................... 8W-30
Ignition Coil.......................... 8W-30
Ignition Switch....................... 8W-10
Instrument Cluster.................... 8W-40
Intake Air Heater Relays................ 8W-30
Intake Air Heater..................... 8W-30
Intake Air Temperature Sensor........... 8W-30
Intermittent Wiper Switch............... 8W-53
Joint Connectors . . 8W-10, 12, 15, 30, 31, 34, 35, 40,
44, 45, 51, 53, 70
Junction Block........................ 8W-12
Leak Detection Pump.................. 8W-30
License Lamp......................... 8W-51
Low Note Horn....................... 8W-41
Lumbar Motors....................... 8W-63
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor........ 8W-30
Manifold Air Pressure Sensor............ 8W-30
BR/BE8W-02 COMPONENT INDEX 8W - 02 - 1
Page 758 of 2889

8W-10 POWER DISTRIBUTION
Component Page
A/C Compressor Clutch Relay.......... 8W-10-27
A/C Compressor Clutch............... 8W-10-27
Aftermarket Center High Mounted
Stop Lamp....................... 8W-10-13
Aftermarket Trailer Tow Connector...... 8W-10-21
Automatic Shut Down Relay......... 8W-10-14, 20
Auxiliary Battery..................... 8W-10-8
Battery............................ 8W-10-8
Blower Motor Relay.................. 8W-10-23
Blower Motor....................... 8W-10-23
Brake Lamp Switch.................. 8W-10-13
Capacitor.......................... 8W-10-16
Center High Mounted Stop Lamp No. 1 . . . 8W-10-13
Center High Mounted Stop Lamp No. 2 . . . 8W-10-13
Central Timer Module C1............. 8W-10-22
Central Timer Module C2............. 8W-10-26
Circuit Breaker 2.................... 8W-10-10
Clockspring........................ 8W-10-26
Combination Flasher................. 8W-10-13
Controller Antilock Brake............. 8W-10-23
Daytime Running Lamp Module........ 8W-10-25
Electric Brake Provision............ 8W-10-13, 21
Engine Control Module............... 8W-10-12
Engine Starter Motor Relay............ 8W-10-23
Engine Starter Motor................. 8W-10-23
Fog Lamp Relay..................... 8W-10-25
Fuel Heater Relay................... 8W-10-20
Fuel Heater........................ 8W-10-20
Fuel Injection Pump.................. 8W-10-12
Fuel Injector No. 1................ 8W-10-15, 16
Fuel Injector No. 2................ 8W-10-15, 16
Fuel Injector No. 3................ 8W-10-15, 16
Fuel Injector No. 4................ 8W-10-15, 16
Fuel Injector No. 5................ 8W-10-15, 16
Fuel Injector No. 6................ 8W-10-15, 16
Fuel Injector No. 7................ 8W-10-15, 16
Fuel Injector No. 8................ 8W-10-15, 16
Fuel Injector No. 9................... 8W-10-16
Fuel Injector No. 10.................. 8W-10-16
Fuel Pump Module................... 8W-10-11
Fuel Pump Relay................. 8W-10-11, 12
Fuse 1 (JB)........................ 8W-10-10
Fuse 1 (PDC)..................... 8W-10-10, 8
Fuse 2 (PDC).................. 8W-10-8, 10, 22
Fuse 3 (PDC).................. 8W-10-8, 11, 12
Fuse 4 (JB)........................ 8W-10-10
Fuse 4 (PDC)..................... 8W-10-13, 8
Fuse 5 (PDC)..................... 8W-10-13, 8
Fuse 6 (PDC).................. 8W-10-14, 20, 8
Fuse 7 (PDC)..................... 8W-10-20, 8
Fuse 8 (PDC)..................... 8W-10-21, 8
Fuse 9 (PDC)..................... 8W-10-23, 8
Fuse 10 (PDC).................... 8W-10-22, 8
Fuse 11 (PDC).................... 8W-10-23, 8
Fuse 12 (JB)....................... 8W-10-10
Fuse 12 (PDC).................... 8W-10-23, 8
Fuse 13 (JB)....................... 8W-10-10Component Page
Fuse 14 (JB)....................... 8W-10-10
Fuse B (PDC)..................... 8W-10-24, 9
Fuse C (PDC)..................... 8W-10-24, 9
Fuse E (PDC)..................... 8W-10-24, 9
Fuse F (PDC)..................... 8W-10-24, 9
Fuse G (PDC)..................... 8W-10-25, 9
Fuse GEN (PDC).................. 8W-10-27, 8
Fuse H (PDC).................... 8W-10-26, 9
Fuse I (PDC)..................... 8W-10-26, 9
Fuse J (PDC)..................... 8W-10-27, 9
Fuse K (PDC)..................... 8W-10-14, 9
Fuse L (PDC)..................... 8W-10-27, 9
G201............................. 8W-10-22
Generator......................... 8W-10-27
Headlamp Beam Select Switch.......... 8W-10-25
Headlamp Switch.................... 8W-10-24
High Note Horn..................... 8W-10-26
Horn Relay...................... 8W-10-26, 9
Ignition Coil 4-Pack.................. 8W-10-16
Ignition Coil 6-Pack.................. 8W-10-16
Ignition Coil........................ 8W-10-15
Ignition Switch................... 8W-10-10, 22
Joint Connector No. 1.............. 8W-10-25, 26
Joint Connector No. 2..... 8W-10-11, 12, 14, 20, 21
Joint Connector No. 5................ 8W-10-22
Joint Connector No. 6........... 8W-10-13, 22, 26
Joint Connector No. 8................ 8W-10-22
Junction Block................... 8W-10-10, 13
Left Fog Lamp...................... 8W-10-25
Left Headlamp...................... 8W-10-24
Left Outboard Headlamp........... 8W-10-24, 25
Low Note Horn..................... 8W-10-26
Oxygen Sensor 1/1 Left Bank Up . . 8W-10-17, 18, 19
Oxygen Sensor 1/1 Upstream........... 8W-10-17
Oxygen Sensor 1/2 Downstream......... 8W-10-17
Oxygen Sensor 1/2 Left Bank Down...... 8W-10-19
Oxygen Sensor 1/2 Pre-Catalyst......... 8W-10-18
Oxygen Sensor 1/3 Post-Catalyst........ 8W-10-18
Oxygen Sensor 2/1 Right Bank Up . 8W-10-17, 18, 19
Oxygen Sensor 2/2 Right Bank Down..... 8W-10-19
Oxygen Sensor Downstream Relay.... 8W-10-18, 19
Power Distribution Center . 8W-10-2, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12,
13, 14, 20, 21, 22, 23,
24, 25, 26, 27
Power Outlet....................... 8W-10-27
Powertrain Control Module . 8W-10-11, 12, 15, 16, 20
Quad High Beam Relay............... 8W-10-24
Right Fog Lamp..................... 8W-10-25
Right Headlamp..................... 8W-10-24
Right Outboard Headlamp.......... 8W-10-24, 25
Security Relay...................... 8W-10-25
Trailer Tow Connector................ 8W-10-21
Trailer Tow Relay.................... 8W-10-21
Transmission Control Relay............ 8W-10-26
Transmission Solenoid Assembly........ 8W-10-26
Turn Signal/Hazard Switch............ 8W-10-13
BR/BE8W-10 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 10 - 1