stop start DODGE RAM 2001 Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2001Pages: 2889, PDF Size: 68.07 MB
Page 2803 of 2889

tional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. The
information obtained by the sensor is used to calcu-
late the fuel injector pulse width. This maintains a
14.7 to 1 Air Fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture ratio,
the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons (HC),
carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) from
the exhaust.
The O2S is also the main sensing element for the
Catalyst and Fuel Monitors.
The O2S can fail in any or all of the following
manners:
²slow response rate
²reduced output voltage
²dynamic shift
²shorted or open circuits
Response rate is the time required for the sensor to
switch from lean to rich once it is exposed to a richer
than optimum A/F mixture or vice versa. As the sen-
sor starts malfunctioning, it could take longer to
detect the changes in the oxygen content of the
exhaust gas.
The output voltage of the O2S ranges from 0 to 1
volt. A good sensor can easily generate any output
voltage in this range as it is exposed to different con-
centrations of oxygen. To detect a shift in the A/F
mixture (lean or rich), the output voltage has to
change beyond a threshold value. A malfunctioning
sensor could have difficulty changing beyond the
threshold value.
OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER MONITOR
If there is an oxygen sensor (O2S) shorted to volt-
age DTC, as well as a O2S heater DTC, the O2S
fault MUST be repaired first. Before checking the
O2S fault, verify that the heater circuit is operating
correctly.
Effective control of exhaust emissions is achieved
by an oxygen feedback system. The most important
element of the feedback system is the O2S. The O2S
is located in the exhaust path. Once it reaches oper-
ating temperature 300É to 350ÉC (572 É to 662ÉF), the
sensor generates a voltage that is inversely propor-
tional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. The
information obtained by the sensor is used to calcu-
late the fuel injector pulse width. This maintains a
14.7 to 1 Air Fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture ratio,
the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons (HC),
carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) from
the exhaust.
The voltage readings taken from the O2S sensor
are very temperature sensitive. The readings are not
accurate below 300ÉC. Heating of the O2S sensor is
done to allow the engine controller to shift to closed
loop control as soon as possible. The heating element
used to heat the O2S sensor must be tested to ensure
that it is heating the sensor properly.The O2S sensor circuit is monitored for a drop in
voltage. The sensor output is used to test the heater
by isolating the effect of the heater element on the
O2S sensor output voltage from the other effects.
LEAK DETECTION PUMP MONITOR (IF EQUIPPED)
The leak detection assembly incorporates two pri-
mary functions: it must detect a leak in the evapora-
tive system and seal the evaporative system so the
leak detection test can be run.
The primary components within the assembly are:
A three port solenoid that activates both of the func-
tions listed above; a pump which contains a switch,
two check valves and a spring/diaphragm, a canister
vent valve (CVV) seal which contains a spring loaded
vent seal valve.
Immediately after a cold start, between predeter-
mined temperature thresholds limits, the three port
solenoid is briefly energized. This initializes the
pump by drawing air into the pump cavity and also
closes the vent seal. During non test conditions the
vent seal is held open by the pump diaphragm
assembly which pushes it open at the full travel posi-
tion. The vent seal will remain closed while the
pump is cycling due to the reed switch triggering of
the three port solenoid that prevents the diaphragm
assembly from reaching full travel. After the brief
initialization period, the solenoid is de-energized
allowing atmospheric pressure to enter the pump
cavity, thus permitting the spring to drive the dia-
phragm which forces air out of the pump cavity and
into the vent system. When the solenoid is energized
and de energized, the cycle is repeated creating flow
in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump is con-
trolled in 2 modes:
Pump Mode: The pump is cycled at a fixed rate to
achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten the
overall test length.
Test Mode: The solenoid is energized with a fixed
duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur when
the diaphragm reaches the Switch closure point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5º H20.
The cycle rate of pump strokes is quite rapid as the
system begins to pump up to this pressure. As the
pressure increases, the cycle rate starts to drop off. If
there is no leak in the system, the pump would even-
tually stop pumping at the equalized pressure. If
there is a leak, it will continue to pump at a rate rep-
resentative of the flow characteristic of the size of the
leak. From this information we can determine if the
leak is larger than the required detection limit (cur-
rently set at .040º orifice by CARB). If a leak is
revealed during the leak test portion of the test, the
test is terminated at the end of the test mode and no
further system checks will be performed.
25 - 16 EMISSIONS CONTROLBR/BE
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2805 of 2889

DESCRIPTION - TRIP DEFINITION
The term ªTripº has different meanings depending
on what the circumstances are. If the MIL (Malfunc-
tion Indicator Lamp) is OFF, a Trip is defined as
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst
Monitor have been completed in the same drive cycle.
When any Emission DTC is set, the MIL on the
dash is turned ON. When the MIL is ON, it takes 3
good trips to turn the MIL OFF. In this case, it
depends on what type of DTC is set to know what a
ªTripº is.
For the Fuel Monitor or Mis-Fire Monitor (contin-
uous monitor), the vehicle must be operated in the
ªSimilar Condition Windowº for a specified amount of
time to be considered a Good Trip.
If a Non-Contiuous OBDII Monitor fails twice in a
row and turns ON the MIL, re-running that monitor
which previously failed, on the next start-up and
passing the monitor, is considered to be a Good Trip.
These will include the following:
²Oxygen Sensor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Purge Flow Monitor
²Leak Detection Pump Monitor (if equipped)
²EGR Monitor (if equipped)
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
If any other Emission DTC is set (not an OBDII
Monitor), a Good Trip is considered to be when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Monitor have
been completed; or 2 Minutes of engine run time if
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor or Catalyst Monitor have
been stopped from running.
It can take up to 2 Failures in a row to turn on the
MIL. After the MIL is ON, it takes 3 Good Trips to
turn the MIL OFF. After the MIL is OFF, the PCM
will self-erase the DTC after 40 Warm-up cycles. A
Warm-up cycle is counted when the ECT (Engine
Coolant Temperature Sensor) has crossed 160ÉF and
has risen by at least 40ÉF since the engine has been
started.
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS -
GAS ENGINES
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of agreater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater,
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum if
the TPS indicates a small throttle opening.
All open/short circuit checks, or any component
that has an associated limp-in, will set a fault after 1
trip with the malfunction present. Components with-
out an associated limp-in will take two trips to illu-
minate the MIL.
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS -
DIESEL ENGINES
There are several electrical components that will
affect vehicle emissions if they malfunction. If one of
these components is malfunctioning, a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) will be set by either the Power-
train Control Module (PCM) or the Engine Control
Module (ECM). The Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) will then be illuminated when the engine is
running.
These electrically operated components have input
(rationality) and output (functionality) checks. A
check is done by one or more components to check
the operation of another component.
Example:The Intake Manifold Air Temperature
(IAT) sensor is used to monitor intake manifold air
temperature over a period of time after a cold start.
If the temperature has not risen to a certain specifi-
cation during a specified time, a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) will be set for a problem in the manifold
air heater system.
All open/short circuit checks, or any component
that has an associated limp-in will set a DTC and
trigger the MIL after 1 trip with the malfunction
present. Components without an associated limp-in
will take two trips to illuminate the MIL.
OPERATION - GAS ENGINES
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
many different circuits in the fuel injection, ignition,
emission and engine systems. If the PCM senses a
problem with a monitored circuit often enough to
indicate an actual problem, it stores a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) in the PCM's memory. If the
problem is repaired or ceases to exist, the PCM can-
cels the code after 40 warm-up cycles. Diagnostic
trouble codes that affect vehicle emissions illuminate
the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL). The MIL is
displayed as an engine icon (graphic) on the instru-
ment panel. Refer to Malfunction Indicator Lamp in
this section.
Certain criteria must be met before the PCM
stores a DTC in memory. The criteria may be a spe-
25 - 18 EMISSIONS CONTROLBR/BE
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2808 of 2889

DTC Self Erasure
With one trip components or systems, the MIL is
illuminated upon test failure and DTCs are stored.
Two trip monitors are components requiring failure
in two consecutive trips for MIL illumination. Upon
failure of the first test, the Task Manager enters a
maturing code. If the component fails the test for a
second time the code matures and a DTC is set.
After three good trips the MIL is extinguished and
the Task Manager automatically switches the trip
counter to a warm-up cycle counter. DTCs are auto-
matically erased following 40 warm-up cycles if the
component does not fail again.
For misfire and fuel system monitors, the compo-
nent must pass the test under a Similar Conditions
Window in order to record a good trip. A Similar Con-
ditions Window is when engine RPM is within6375
RPM and load is within610% of when the fault
occurred.
NOTE: It is important to understand that a compo-
nent does not have to fail under a similar window of
operation to mature. It must pass the test under a
Similar Conditions Window when it failed to record
a Good Trip for DTC erasure for misfire and fuel
system monitors.
DTCs can be erased anytime with a DRB III. Eras-
ing the DTC with the DRB III erases all OBD II
information. The DRB III automatically displays a
warning that erasing the DTC will also erase all
OBD II monitor data. This includes all counter infor-
mation for warm-up cycles, trips and Freeze Frame.
Trip Indicator
TheTripis essential for running monitors and
extinguishing the MIL. In OBD II terms, a trip is a
set of vehicle operating conditions that must be met
for a specific monitor to run. All trips begin with a
key cycle.
Good Trip
The Good Trip counters are as follows:
²Specific Good Trip
²Fuel System Good Trip
²Misfire Good Trip
²Alternate Good Trip (appears as a Global Good
Trip on DRB III)
²Comprehensive Components
²Major Monitor
²Warm-Up Cycles
Specific Good Trip
The term Good Trip has different meanings
depending on the circumstances:
²If the MIL is OFF, a trip is defined as when the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor and the Catalyst Monitor
have been completed in the same drive cycle.²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by the Fuel
Monitor or Misfire Monitor (both continuous moni-
tors), the vehicle must be operated in the Similar
Condition Window for a specified amount of time.
²If the MIL is ON and a DTC was set by a Task
Manager commanded once-per-trip monitor (such as
the Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Catalyst Monitor, Purge
Flow Monitor, Leak Detection Pump Monitor, EGR
Monitor or Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor), a good
trip is when the monitor is passed on the next start-
up.
²If the MIL is ON and any other emissions DTC
was set (not an OBD II monitor), a good trip occurs
when the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst Mon-
itor have been completed, or two minutes of engine
run time if the Oxygen Sensor Monitor and Catalyst
Monitor have been stopped from running.
Fuel System Good Trip
To count a good trip (three required) and turn off
the MIL, the following conditions must occur:
²Engine in closed loop
²Operating in Similar Conditions Window
²Short Term multiplied by Long Term less than
threshold
²Less than threshold for a predetermined time
If all of the previous criteria are met, the PCM will
count a good trip (three required) and turn off the
MIL.
Misfire Good Trip
If the following conditions are met the PCM will
count one good trip (three required) in order to turn
off the MIL:
²Operating in Similar Condition Window
²1000 engine revolutions with no misfire
Warm-Up Cycles
Once the MIL has been extinguished by the Good
Trip Counter, the PCM automatically switches to a
Warm-Up Cycle Counter that can be viewed on the
DRB III. Warm-Up Cycles are used to erase DTCs
and Freeze Frames. Forty Warm-Up cycles must
occur in order for the PCM to self-erase a DTC and
Freeze Frame. A Warm-Up Cycle is defined as fol-
lows:
²Engine coolant temperature must start below
and rise above 160É F
²Engine coolant temperature must rise by 40É F
²No further faults occur
Freeze Frame Data Storage
Once a failure occurs, the Task Manager records
several engine operating conditions and stores it in a
Freeze Frame. The Freeze Frame is considered one
frame of information taken by an on-board data
recorder. When a fault occurs, the PCM stores the
input data from various sensors so that technicians
BR/BEEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 21
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2837 of 2889

BODY INTERIOR
INSPECTION - COMPASS
NOTE: Set variance after calibration.
(1) Calibrate and set compass variance (Fig. 26), if
so equipped (use appropriate procedures in service
information).
(2) Remove protective film from overhead console,
if equipped.
INSPECTION - FIT AND FINISH
(1) Remove any interior covers.
(2) Inspect the instrument panel, glove box door
(Fig. 27) and interior moldings for even gaps and
alignments.
(3) Check that the door panel material is clean,
free from wrinkles and installed correctly.
(4) Check that the seat material is clean, secure
and free of wrinkles.
(5) Check that the carpet is clean, secure and free
of wrinkles.
(6) Check that the headliner is clean, free of lint
and dirt smudges.
INSPECTION - LIGHTS AND SWITCHES
(1) Remove protective film from all switch bezels.
(2) Operate and visually inspect all interior lights
and switches, including:
²Dome/map lamps
²Vanity mirror lamps
²Glove box light²Ashtray light
²Cigar lighter light
²All gauge lights
²Radio display
²Door-mounted lights, if equipped
²Illuminated entry system, if equipped
(3) Visually inspect and operate all exterior lights
and their switches, including:
NOTE: Headlamp aim is preset during vehicle
assembly.
²Headlights, including high beam, optical horn
(ªflash to passº) and daylight running lamps (DRL's)
(Fig. 28)
²Tail/stop lamps (including center high-mounted
stop lamp)
²Parking lights Turn signals Brake lights (includ-
ing center high mounted stop lamp)
²Emergency flashers (Fig. 29)
²Fog/driving lights, if equipped
²Off-road or other lights, if equipped
²Cargo bed lights, if equipped
(4) Check ignition switch for proper operation in
all positions (accessory, lock, on, start and off).
INSPECTION - SEAT BELTS, SHOULDER
BELTS, RETRACTORS AND HEAD RESTRAINTS
(1) Inspect all seat belts and harnesses to ensure
that they connect and hold properly.
(2) Inspect the condition of the belts and anchors.
(3) Inspect for proper seat belt retraction.
Fig. 26 COMPASS OPERATION
Fig. 27 GLOVE BOX DOOR
30 - 12 NEW VEHICLE PREPARATIONBR/BE
Page 2841 of 2889
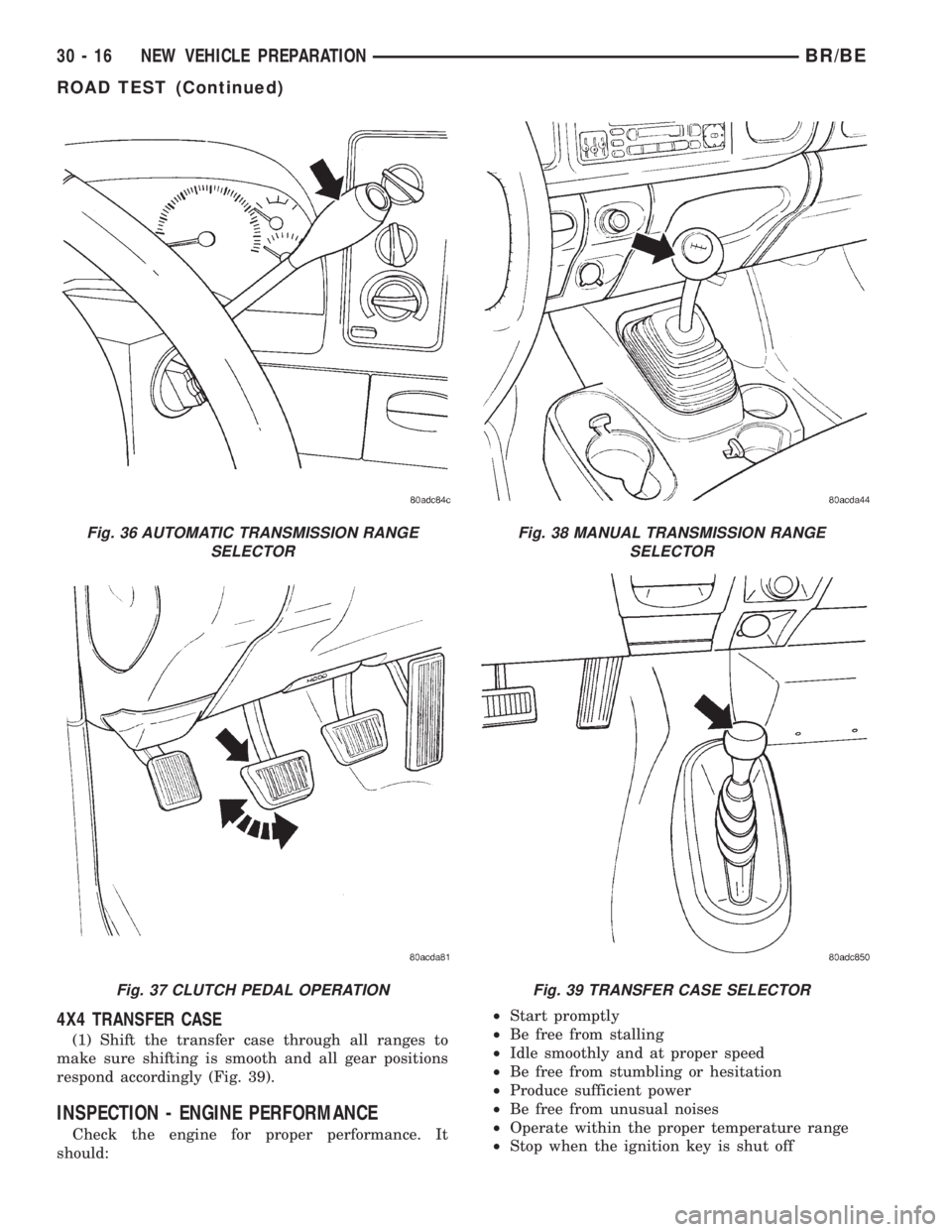
4X4 TRANSFER CASE
(1) Shift the transfer case through all ranges to
make sure shifting is smooth and all gear positions
respond accordingly (Fig. 39).
INSPECTION - ENGINE PERFORMANCE
Check the engine for proper performance. It
should:²Start promptly
²Be free from stalling
²Idle smoothly and at proper speed
²Be free from stumbling or hesitation
²Produce sufficient power
²Be free from unusual noises
²Operate within the proper temperature range
²Stop when the ignition key is shut off
Fig. 36 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION RANGE
SELECTOR
Fig. 37 CLUTCH PEDAL OPERATION
Fig. 38 MANUAL TRANSMISSION RANGE
SELECTOR
Fig. 39 TRANSFER CASE SELECTOR
30 - 16 NEW VEHICLE PREPARATIONBR/BE
ROAD TEST (Continued)
Page 2842 of 2889

INSPECTION - PARKING BRAKE
(1) Ensure that the parking brake is easy to oper-
ate (Fig. 40).
(2) Make sure the parking brake does not drag.
(3) With the vehicle stopped on a grade, firmly
apply the service brakes, place the transmission in
NEUTRAL and set the parking brake. Slowly release
the service brakes to see if the parking brake will
hold.
(4) Check that the parking brake warning light
comes on when the parking brake is applied, and is
off when the brake is released.
INSPECTION - SERVICE BRAKES
(1) Check brake warning light operation at vehicle
startup.
(2) Check ABS warning light operation at vehicle
startup.
(3) Inspect service brake pedal travel and feel (Fig.
41).
(4) Put the vehicle in gear and apply the brakes
while the car is in motion. Be sure brake operation is
smooth and positive.
(5) Make sure that the vehicle stops in a straight
line, without pulling to one side.
(6) Check that the brakes operate quietly, without
noise.
(7) Ensure there is no shudder or vibration when
braking.
INSPECTION - SPEED CONTROL
Check the following speed control functions (Fig.
42):²Check on/off switch
²Check ªsetº operation
²Check ªresumeº function
²Check ªaccelerateº and ªdecelerateº functions
²Check brake release function
²Check ªcancelº function
INSPECTION - TRIP COMPUTER/
MAINTENANCE REMINDER
NOTE: Reset the average fuel economy when the
road test is complete.
Check that all modes operate correctly (Fig. 43).
INSPECTION - RADIO
(1) Check for good AM/FM reception, ensure that
the cassette and/or compact disc (CD) player works
properly (Fig. 44).
(2) Check for good sound quality from all speakers.
(3) Ensure that the radio displays the correct time.
(4) Check the steering wheel controls (if equipped).
INSPECTION - HEATER/AIR CONDITIONER
(1) Check that heater/defroster works properly
(Fig. 45).
(2) Turn on the heater when the engine reaches
operating temperature.
(3) Operate the blower motor in all speeds.
(4) Operate system in all modes (heat, defrost,
etc.).
(5) Operate the rear heater (if equipped).
(6) Check for hot air output at all outlets.
Fig. 40 PARKING BRAKE OPERATION
Fig. 41 SERVICE BRAKE PEDAL
BR/BENEW VEHICLE PREPARATION 30 - 17
ROAD TEST (Continued)
Page 2867 of 2889

INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS -
VALVE SERVICE......................9-195
IN-TANK TRANSMISSION OIL COOLER -
STANDARD PROCEDURE, FLUSHING
COOLER AND TUBES - WITHOUT
RADIATOR...................7-80,7-83,7-86
IN-TANK TRANSMISSION OIL COOLER -
STANDARD PROCEDURE, FLUSHING
COOLERS AND TUBES - WITH
RADIATOR...................7-79,7-83,7-85
INTERIOR - CAUTION................23-118
INTERLOCK SYSTEM - INSPECTION,
SHIFT/CLUTCH.......................30-19
INTERMEDIATE - INSTALLATION, AXLE
SHAFTS.............................3-28
INTERMEDIATE - REMOVAL, AXLE
SHAFTS.............................3-28
INTERMEDIATE AXLE - INSTALLATION.....3-61
INTERMEDIATE AXLE - REMOVAL.........3-60
INTERNATIONAL SYMBOLS -
DESCRIPTION......................Intro.-6
INTERNATIONAL SYMBOLS -
DESCRIPTION.........................0-3
INTRODUCTION - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, ENGINE DIAGNOSIS . . 9-118,9-173,9-3
INTRODUCTION - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING-ENGINE DIAGNOSIS............9-61
INVERTED FLARING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, DOUBLE..................5-8
IOD FUSE - DESCRIPTION...........8W-97-4
IOD FUSE - INSTALLATION...........8W-97-5
IOD FUSE - OPERATION.............8W-97-5
IOD FUSE - REMOVAL................8W-97-5
ISO FLARING - STANDARD PROCEDURE....5-8
ITEMS - INSTALLATION, SHIPPED LOOSE . 30-14
JOINT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
LOWER BALL........................2-10
JOINT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
UPPER BALL.........................2-12
JOINT - INSTALLATION, LOWER BALL.....2-25
JOINT - INSTALLATION, UPPER BALL.....2-25
JOINT MOLDING - INSTALLATION, ROOF . . 23-91
JOINT MOLDING - REMOVAL, ROOF......23-91
JOINTS - DISASSEMBLY, SINGLE
CARDAN UNIVERSAL..................3-11
JOINTS - INSTALLATION, SINGLE
CARDAN UNIVERSAL..............3-34,3-66
JOINTS - REMOVAL, SINGLE CARDAN
UNIVERSAL......................3-33,3-65
JOUNCE BUMPER - DESCRIPTION.....2-28,2-9
JOUNCE BUMPER - OPERATION.......2-28,2-9
JOURNAL CLEARANCE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, CONNECTING ROD
BEARING AND CRANKSHAFT...........9-274
JUMP STARTING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE.........................0-27
JUNCTION BLOCK - DESCRIPTION.....8W-97-6
JUNCTION BLOCK - INSTALLATION....8W-97-7
JUNCTION BLOCK - OPERATION......8W-97-6
JUNCTION BLOCK - REMOVAL........8W-97-6
KEEPER - INSTALLATION, BACKLITE
LATCH ............................23-146
KEEPER - REMOVAL, BACKLITE LATCH . . 23-146
KEY LOCK CYLINDER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, IGNITION SWITCH............19-10
KEY-IN IGNITION SWITCH -
DESCRIPTION........................19-9
KEYLESS ENTRY - INSPECTION.........30-11
KEYLESS ENTRY SYSTEM -
DESCRIPTION, REMOTE................8N-2
KEYLESS ENTRY SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING, POWER LOCK &
REMOTE............................8N-4
KEYLESS ENTRY SYSTEM - OPERATION,
REMOTE............................8N-3
KEYLESS ENTRY TRANSMITTER -
DESCRIPTION, REMOTE................8N-7
KEYLESS ENTRY TRANSMITTER -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, REMOTE......8N-7
KEYLESS ENTRY TRANSMITTER -
OPERATION, REMOTE..................8N-7
KNOB - INSTALLATION, TURNING LOOP
HEIGHT ADJUSTER
...................8O-30
KNOB - REMOVAL, TURNING LOOP
HEIGHT ADJUSTER
...................8O-30
KNUCKLE - DESCRIPTION
............2-20,2-9
KNUCKLE - INSTALLATION
..........2-10,2-20
KNUCKLE - OPERATION
............2-10,2-20KNUCKLE - REMOVAL..............2-10,2-20
LABEL - DESCRIPTION, VECI.........Intro.-10
LABEL - DESCRIPTION, VEHICLE SAFETY
CERTIFICATION....................Intro.-12
LABEL - OPERATION, VECI...........Intro.-10
LABELS - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
INSPECTION - INFORMATION...........30-22
LAMP - DESCRIPTION, READING........8L-36
LAMP - DESCRIPTION, TAIL............8L-29
LAMP - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, FOG . . . 8L-9
LAMP - INSTALLATION, CENTER HIGH
MOUNTED STOP......................8L-6
LAMP - INSTALLATION, CLEARANCE......8L-6
LAMP - INSTALLATION, DOME..........8L-33
LAMP - INSTALLATION, FOG............8L-11
LAMP - INSTALLATION, LICENSE PLATE . . 8L-22
LAMP - INSTALLATION, MARKER........8L-23
LAMP - INSTALLATION, OUTBOARD
IDENTIFICATION.....................8L-29
LAMP - INSTALLATION, PARK/TURN
SIGNAL............................8L-29
LAMP - INSTALLATION, READING........8L-36
LAMP - INSTALLATION, TAIL...........8L-30
LAMP - INSTALLATION, UNDERHOOD....8L-32
LAMP - INSTALLATION, VANITY.........8L-37
LAMP - OPERATION, READING..........8L-36
LAMP - OPERATION, TAIL..............8L-29
LAMP - REMOVAL, CENTER HIGH
MOUNTED STOP......................8L-6
LAMP - REMOVAL, CLEARANCE..........8L-6
LAMP - REMOVAL, DOME..............8L-33
LAMP - REMOVAL, FOG...............8L-11
LAMP - REMOVAL, LICENSE PLATE......8L-22
LAMP - REMOVAL, MARKER...........8L-22
LAMP - REMOVAL, OUTBOARD
IDENTIFICATION.....................8L-28
LAMP - REMOVAL, PARK/TURN SIGNAL . . 8L-29
LAMP - REMOVAL, READING...........8L-36
LAMP - REMOVAL, TAIL...............8L-29
LAMP - REMOVAL, UNDERHOOD........8L-31
LAMP - REMOVAL, VANITY.............8L-37
LAMP AND SWITCH - INSTALLATION,
GLOVE BOX.........................8L-35
LAMP AND SWITCH - REMOVAL, GLOVE
BOX ...............................8L-35
LAMP (MIL) - DESCRIPTION,
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR.............8J-24
LAMP (MIL) - OPERATION,
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR.............8J-24
LAMP MODULE - DESCRIPTION,
DAYTIME RUNNING....................8L-9
LAMP MODULE - INSTALLATION,
DAYTIME RUNNING....................8L-9
LAMP MODULE - OPERATION, DAYTIME
RUNNING............................8L-9
LAMP MODULE - REMOVAL, DAYTIME
RUNNING............................8L-9
LAMP SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, BRAKE....8L-4
LAMP SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, BRAKE......................8L-5
LAMP SWITCH - INSTALLATION, BRAKE . . . 8L-5
LAMP SWITCH - OPERATION, BRAKE......8L-4
LAMP SWITCH - REMOVAL, BRAKE.......8L-5
LAMP UNIT - ADJUSTMENTS, FOG.......8L-12
LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION, CENTER
HIGH MOUNTED STOP.................8L-6
LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION, FOG.......8L-12
LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION, LICENSE
PLATE .............................8L-22
LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION, PARK/
TURN SIGNAL.......................8L-29
LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION, TAIL.......8L-30
LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION,
UNDERHOOD........................8L-32
LAMP UNIT - REMOVAL, CENTER HIGH
MOUNTED STOP......................8L-6
LAMP UNIT - REMOVAL, FOG...........8L-11
LAMP UNIT - REMOVAL, LICENSE PLATE . . 8L-22
LAMP UNIT - REMOVAL, PARK/TURN
SIGNAL............................8L-29
LAMP UNIT - REMOVAL, TAIL...........8L-30
LAMP UNIT - REMOVAL, UNDERHOOD . . . 8L-32
LASH ADJUSTMENT AND VERIFICATION
- STANDARD PROCEDURE, VALVE
.......9-256
LATCH - ADJUSTMENT
...............23-100
LATCH - ADJUSTMENT, FRONT DOOR
....23-72
LATCH - INSTALLATION
....23-100,23-64,23-72
LATCH - INSTALLATION, SAFETY
.......23-102LATCH - LOWER - INSTALLATION........23-80
LATCH - LOWER - REMOVAL...........23-80
LATCH - REMOVAL........23-100,23-64,23-72
LATCH - REMOVAL, SAFETY...........23-102
LATCH - UPPER - INSTALLATION........23-81
LATCH - UPPER - REMOVAL............23-81
LATCH AND KEEPER - INSTALLATION,
BACKLITE.........................23-146
LATCH AND KEEPER - REMOVAL,
BACKLITE.........................23-146
LATCH HANDLE - INSTALLATION........23-65
LATCH HANDLE - REMOVAL............23-65
LATCH RELEASE CABLE - INSTALLATION . 23-101
LATCH RELEASE CABLE - REMOVAL....23-101
LATCH STRIKER - ADJUSTMENT.......23-102
LATCH STRIKER - INSTALLATION . 23-102,23-65,
23-73
LATCH STRIKER - INSTALLATION, GLOVE
BOX ..............................23-113
LATCH STRIKER - LOWER -
INSTALLATION.......................23-82
LATCH STRIKER - LOWER - REMOVAL....23-82
LATCH STRIKER - REMOVAL.....23-102,23-65,
23-73
LATCH STRIKER - REMOVAL, GLOVE
BOX ..............................23-113
LATCH STRIKER - UPPER -
INSTALLATION.......................23-82
LATCH STRIKER - UPPER - REMOVAL....23-82
LATCH/SAFETY CATCH - INSPECTION,
HOOD..............................30-4
LEAK - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID . . . 21-148,21-319,
21-491,21-662
LEAK DETECTION PUMP - DESCRIPTION . . 25-33
LEAK DETECTION PUMP - INSTALLATION . 25-34
LEAK DETECTION PUMP - REMOVAL.....25-34
LEAK DOWN TEST - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, FUEL PRESSURE..............14-2
LEAKAGE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE....9-124,
9-179,9-67,9-9
LEAKAGE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
INTAKE MANIFOLD.....9-110,9-165,9-222,9-53
LEAKAGE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
POWER STEERING GEAR..............19-14
LEAKAGE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
PUMP.............................19-31
LEAKS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
COOLING SYSTEM.....................7-5
LEAKS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
ENGINE OIL...........9-104,9-160,9-215,9-47
LEAKS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINE............14-74
LEAKS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
REAR SEAL AREA.....................9-10
LEAKS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM...............24-43
LEAKS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
WATER .............................23-2
LEAKS - STANDARD PROCEDURES,
REPAIRING..........................22-8
LEFT FRONT FENDER - INSTALLATION....23-93
LEFT FRONT FENDER - REMOVAL.......23-92
LEVEL - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
EFFECTS OF INCORRECT FLUID . . 21-199,21-370,
21-545,21-715
LEVEL - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
BRAKE FLUID........................5-14
LEVEL - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
CHECKING BATTERY ELECTROLYTE.......8F-8
LEVEL - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
REFRIGERANT OIL...................24-57
LEVEL CHECK - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, COOLANT................7-16
LEVEL CHECK - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, FLUID.....21-199,21-370,21-545,
21-715
LEVEL, OIL - STANDARD PROCEDURE-
ENGINE OIL
.........................9-295
LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR -
DESCRIPTION, FUEL
..............14-7,14-73
LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR -
INSTALLATION, FUEL
..................14-9
LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR -
OPERATION, FUEL
................14-7,14-73
LEVEL SENDING UNIT / SENSOR -
REMOVAL, FUEL
......................14-8
20 INDEXBR/BE
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page
Page 2880 of 2889

SPECIFICATIONS, SPECIFICATIONS -
TORQUE............................23-61
SPECIFICATIONS, SPECIFICATIONS -
TORQUE............................13-9
SPECIFICATIONS, SPECIFICATIONS -
TORQUE............................24-8
SPECIFICATIONS, TORQUE - FUEL
DELIVERY...........................14-4
SPECIFICATIONS, TORQUE - GAS FUEL
INJECTION..........................14-35
SPECIFICATIONS, TORQUE -
GENERATOR/CHARGING SYSTEM........8F-28
SPECIFICATIONS, TORQUE - IGNITION.....8I-2
SPECIFICATIONS, TORQUE - STARTING
SYSTEM............................8F-38
SPEED CONTROL - INSPECTION.........30-17
SPEED CONTROL SERVO - DESCRIPTION . . 8P-5
SPEED CONTROL SERVO -
INSTALLATION.......................8P-10
SPEED CONTROL SERVO - OPERATION....8P-5
SPEED CONTROL SERVO - REMOVAL.....8P-6
SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM -
DESCRIPTION........................8P-1
SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM - OPERATION . . . 8P-2
SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM - TORQUE.....8P-4
SPEED INPUT - DESCRIPTION, VEHICLE . . . 8P-1
SPEED SENSOR - DESCRIPTION . 21-253,21-424,
21-597,21-770
SPEED SENSOR - OPERATION . . . 21-253,21-424,
21-597,21-770
SPEEDOMETER - DESCRIPTION...........8J-30
SPEEDOMETER - OPERATION...........8J-30
SPLASH SHIELD - INSTALLATION, REAR . . 23-96
SPLASH SHIELD - REMOVAL, REAR......23-96
SPLASH SHIELDS - INSTALLATION,
FRONT END.........................23-92
SPLASH SHIELDS - REMOVAL, FRONT
END ...............................23-92
SPLICE LOCATIONS - DESCRIPTION . . . 8W-95-1
SPLICING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
WIRE...........................8W-01-12
SPLIT BENCH - INSTALLATION, SEAT....23-134
SPLIT BENCH - INSTALLATION, SEAT
BACK.............................23-136
SPLIT BENCH - INSTALLATION, SEAT
BACK COVER.......................23-138
SPLIT BENCH - INSTALLATION, SEAT
CUSHION COVER....................23-140
SPLIT BENCH - INSTALLATION, SEAT
TRACK............................23-142
SPLIT BENCH - REMOVAL, SEAT.......23-134
SPLIT BENCH - REMOVAL, SEAT BACK . . 23-135
SPLIT BENCH - REMOVAL, SEAT BACK
COVER............................23-137
SPLIT BENCH - REMOVAL, SEAT
CUSHION COVER....................23-139
SPLIT BENCH - REMOVAL, SEAT TRACK . 23-142
SPOOL VALVE - INSTALLATION..........19-26
SPOOL VALVE - REMOVAL.............19-24
SPRING - DESCRIPTION........2-11,2-22,2-28
SPRING - INSTALLATION.......2-12,2-22,2-29
SPRING - OPERATION..........2-11,2-22,2-28
SPRING - REMOVAL...........2-11,2-22,2-28
SPRING AND SHOCK - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING............................2-26
SPRINGS - INSTALLATION, VALVES AND
VALVE .............................9-199
SPRINGS - REMOVAL, VALVES AND
VALVE .............................9-197
SPRINGS - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
VALVES, GUIDES.............9-138,9-25,9-82
SPRINGS, INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS - STANDARD PROCEDURE-
VALVES,GUIDES.....................9-253
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION, TIMING
BELT/CHAIN...........9-115,9-170,9-227,9-58
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL, TIMING
BELT/CHAIN...........9-114,9-170,9-226,9-57
SQUEAKS, RATTLES AND WIND NOISE -
INSPECTION........................30-15
STABILIZER BAR - DESCRIPTION . 2-12,2-22,2-30
STABILIZER BAR - INSTALLATION....2-12,2-23,
2-30
STABILIZER BAR - OPERATION
. . 2-12,2-22,2-30
STABILIZER BAR - REMOVAL
....2-12,2-22,2-30
STANCHION COVER - INSTALLATION
....23-143
STANCHION COVER - REMOVAL
........23-143
STANDARD CAB - INSTALLATION
........8O-19STANDARD CAB - REMOVAL...........8O-18
STARTER MOTOR - DESCRIPTION,
ENGINE............................8F-39
STARTER MOTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING...........................8F-39
STARTER MOTOR - INSTALLATION,
ENGINE............................8F-41
STARTER MOTOR - OPERATION, ENGINE . . 8F-39
STARTER MOTOR - REMOVAL, ENGINE . . . 8F-40
STARTER MOTOR RELAY -
DESCRIPTION, ENGINE................8F-42
STARTER MOTOR RELAY -
INSTALLATION, ENGINE................8F-43
STARTER MOTOR RELAY - OPERATION,
ENGINE............................8F-42
STARTER MOTOR RELAY - REMOVAL,
ENGINE............................8F-43
STARTER RELAY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING...........................8F-42
STARTING - DESCRIPTION.............8F-32
STARTING - OPERATION...............8F-32
STARTING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
JUMP...............................0-27
STARTING SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING...........................8F-33
STARTING SYSTEM - SPECIFICATIONS,
TORQUE............................8F-38
STARTING SYSTEM, SPECIFICATIONS.....8F-38
STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE -
DESCRIPTION........................25-1
STATIONARY GLASS - DESCRIPTION....23-145
STATIONARY GLASS - OPERATION......23-145
STEERING - DESCRIPTION..............19-1
STEERING - OPERATION................19-1
STEERING AND HANDLING -
INSPECTION........................30-15
STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER -
INSTALLATION......................23-116
STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER -
REMOVAL.........................23-115
STEERING FLOW AND PRESSURE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, POWER.......19-4
STEERING GEAR HOUSING PLUG -
INSTALLATION.......................19-27
STEERING GEAR HOUSING PLUG -
REMOVAL..........................19-27
STEERING GEAR LEAKAGE - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING, POWER................19-14
STEERING GEAR, SPECIAL TOOLS -
POWER............................19-20
STEERING GEAR, SPECIFICATIONS -
POWER............................19-19
STEERING LINKAGE, SPECIAL TOOLS....19-39,
19-42
STEERING PUMP - INITIAL OPERATION -
STANDARD PROCEDURE, POWER.......19-31
STEERING PUMP, SPECIAL TOOLS -
POWER............................19-36
STEERING SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, POWER.....................19-2
STEERING SYSTEM - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, FLUSHING POWER........19-32
STEERING WHEEL - INSTALLATION......19-13
STEERING WHEEL - REMOVAL..........19-13
STEM SEAL - INSTALLATION, VALVE.....9-198
STEM SEALS - REMOVAL, VALVE........9-197
STEPS - NEW VEHICLE PREPARATION
FORM, FINAL........................30-22
STOP LAMP - INSTALLATION, CENTER
HIGH MOUNTED......................8L-6
STOP LAMP - REMOVAL, CENTER HIGH
MOUNTED...........................8L-6
STOP LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION,
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED...............8L-6
STOP LAMP UNIT - REMOVAL, CENTER
HIGH MOUNTED......................8L-6
STORAGE - DESCRIPTION, PRE
DELIVERY..........................30-19
STORAGE - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
PRE DELIVERY......................30-20
STORAGE BIN - INSTALLATION
.........23-116
STORAGE BIN - REMOVAL
............23-116
STOWAGE TRAY - INSTALLATION, REAR
FLOOR
............................23-121
STOWAGE TRAY - REMOVAL, REAR
FLOOR
............................23-121
STRAP - INSTALLATION, CAB-TO- BED
GROUND
...........................8A-14STRAP - INSTALLATION, ENGINE-TO-
BODY GROUND......................8A-13
STRAP - INSTALLATION, HEATER CORE
GROUND...........................8A-15
STRAP - REMOVAL, CAB-TO- BED
GROUND...........................8A-14
STRAP - REMOVAL, ENGINE-TO-BODY
GROUND...........................8A-13
STRAP - REMOVAL, HEATER CORE
GROUND...........................8A-14
STRETCH - INSPECTION, MEASURING
TIMING CHAIN........9-114,9-170,9-227,9-58
STRIKER - ADJUSTMENT, LATCH.......23-102
STRIKER - INSTALLATION, GLOVE BOX
LATCH ............................23-113
STRIKER - INSTALLATION, LATCH . 23-102,23-65,
23-73
STRIKER - LOWER - INSTALLATION,
LATCH .............................23-82
STRIKER - LOWER - REMOVAL, LATCH . . . 23-82
STRIKER - REMOVAL, GLOVE BOX
LATCH ............................23-113
STRIKER - REMOVAL, LATCH....23-102,23-65,
23-73
STRIKER - UPPER - INSTALLATION,
LATCH .............................23-82
STRIKER - UPPER - REMOVAL, LATCH . . . 23-82
STRIPE - INSTALLATION, TAPE..........23-88
STRIPE - REMOVAL, TAPE.............23-88
STRIPES AND DECALS - INSTALLATION,
BODY..............................23-87
STRIPES AND DECALS - REMOVAL,
BODY..............................23-87
STRUCTURAL ADHESIVE LOCATIONS,
SPECIFICATIONS.....................23-44
STUDS - INSTALLATION...............22-12
STUDS - REMOVAL...................22-12
SUCTION AND DISCHARGE LINE -
INSTALLATION.......................24-51
SUCTION AND DISCHARGE LINE -
REMOVAL..........................24-50
SUN VISOR - INSTALLATION..........23-127
SUN VISOR - REMOVAL..............23-127
SUPPLIES - DESCRIPTION, 5 VOLT......8E-17
SUPPLIES - OPERATION, 5 VOLT........8E-19
SUPPLY - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
VACUUM............................8P-2
SUPPLY RESTRICTIONS - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING, FUEL..................14-56
SUPPORT - INSTALLATION, LUMBAR....23-133
SUPPORT - REMOVAL, LUMBAR.......23-133
SUPPORT BRACKET - INSTALLATION,
REARVIEW MIRROR.................23-126
SUPPORT PLATE - INSTALLATION........5-32
SUPPORT PLATE - REMOVAL............5-32
SUPPRESSION COMPONENTS -
DESCRIPTION, RADIO NOISE...........8A-12
SUPPRESSION COMPONENTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, RADIO
NOISE.............................8A-12
SUSPENSION - STANDARD
PROCEDURES, ALIGNMENT LINK/COIL.....2-5
SUSPENSION, SPECIAL TOOLS -
INDEPENDENT FRONT...................2-9
SUSPENSION, SPECIAL TOOLS -
LINK/COIL...........................2-16
SUSPENSION-REAR, SPECIAL TOOLS.....2-28
SWITCH - DESCRIPTION
...............8P-12
SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, A/C HIGH
PRESSURE
.........................24-20
SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, A/C LOW
PRESSURE
.........................24-21
SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, BLOWER
MOTOR
............................24-24
SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, BRAKE LAMP
....8L-4
SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, CLUTCH
PEDAL POSITION
.....................6-22
SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, DOOR AJAR
....8L-34
SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, DOOR
CYLINDER LOCK
......................8N-5
SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, DRIVER
POWER SEAT
.......................8N-16
SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, DRIVER SEAT
HEATER
.............................8G-7
SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, HEADLAMP
....8L-18
SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, HORN
..........8H-4
SWITCH - DESCRIPTION, IGNITION
......19-11
BR/BEINDEX 33
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page