harness DODGE RAM 2001 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2001, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2001Pages: 2889, PDF Size: 68.07 MB
Page 457 of 2889

INSTALLATION
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
NOTE: Before replacing a high-line/premium version
Central Timer Module (CTM), use a DRBIIITscan
tool to retrieve the current settings for the CTM pro-
grammable features. Refer to the appropriate diag-
nostic information. These settings should be
duplicated in the replacement high-line/premium
CTM using the DRBIIITscan tool before returning
the vehicle to service.(1) Position the CTM to the inboard side of the
instrument panel steering column opening.
(2) Reconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector(s) for the CTM (one connector for the base
version CTM, two connectors for the high-line/pre-
mium version) to the CTM connector receptacle(s)
(Fig. 3) or (Fig. 4).
(3) Position the CTM to the bracket on the inboard
side of the instrument panel steering column open-
ing.
(4) Install and tighten the two screws that secure
the CTM to the bracket on the inboard side of instru-
ment panel steering column opening. Tighten the
screws to 1.6 N´m (15 in. lbs.).
(5) Reinstall the steering column opening cover
onto the instrument panel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
STRUMENT PANEL/STEERING COLUMN OPEN-
ING COVER - INSTALLATION).
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
COMMUNICATION
DESCRIPTION - CCD DATA BUS
The Chrysler Collision Detection (also referred to
as CCD or C2D ) data bus system is a multiplex sys-
tem used for vehicle communications on many
Chrysler Corporation vehicles. Within the context of
the CCD system, the term ªcollisionª refers to the
system's ability to avoid collisions of the electronic
data that enters the data bus from various electronic
control modules at approximately the same time.
Multiplexing is a system that enables the trans-
mission of several messages over a single channel or
circuit. Many Chrysler vehicles use this principle for
communication between the various microprocessor-
based electronic control modules.
Many of the electronic control modules in a vehicle
require information from the same sensing device. In
the past, if information from one sensing device was
required by several controllers, a wire from each con-
troller needed to be connected in parallel to that sen-
sor. In addition, each controller utilizing analog
sensors required an Analog/Digital (A/D) converter in
order to ªreadª these sensor inputs. Multiplexing
reduces wire harness complexity, sensor current
loads and controller hardware because each sensing
device is connected to only one controller, which
reads and distributes the sensor information to the
other controllers over the data bus. Also, because
each controller on the data bus can access the con-
troller sensor inputs to every other controller on the
data bus, more function and feature capabilities are
possible.
Fig. 4 Central Timer Module (High-Line/Premium)
Remove/Install
1 - SCREWS
2 - BRACKET
3 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTORS
4 - CENTRAL TIMER MODULE (HIGH-LINE/PREMIUM)
8E - 6 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESBR/BE
BODY CONTROL/CENTRAL TIMER MODULE (Continued)
Page 458 of 2889

In addition to reducing wire harness complexity,
component sensor current loads and controller hard-
ware, multiplexing offers a diagnostic advantage. A
multiplex system allows the information flowing
between controllers to be monitored using a diagnos-
tic scan tool. The Chrysler system allows an elec-
tronic control module to broadcast message data out
onto the bus where all other electronic control mod-
ules can ªhearº the messages that are being sent.
When a module hears a message on the data bus
that it requires, it relays that message to its micro-
processor. Each module ignores the messages on the
data bus that are being sent to other electronic con-
trol modules.
With a diagnostic scan tool connected into the CCD
circuit, a technician is able to observe many of the
electronic control module function and message out-
puts while; at the same time, controlling many of the
sensor message inputs. The CCD data bus, along
with the use of a diagnostic scan tool and a logic-
based approach to test procedures, as found in the
Diagnostic Procedures manuals, allows the trained
automotive technician to more easily, accurately and
efficiently diagnose the many complex and integrated
electronic functions and features found on today's
vehicles.
OPERATION - CCD DATA BUS
The CCD data bus system was designed to run at a
7812.5 baud rate (or 7812.5 bits per second). In order
to successfully transmit and receive binary messages
over the CCD data bus, the system requires the fol-
lowing:
²Bus (+) and Bus (±) Circuits
²CCD Chips in Each Electronic Control Module
²Bus Bias and Termination
²Bus Messaging
²Bus Message Coding
Following are additional details of each of the
above system requirements.
BUS (+) AND BUS (±) CIRCUITS
The two wires (sometimes referred to as the ªtwist-
ed pairº) that comprise the CCD data bus are the D1
circuit [Bus (+)], and the D2 circuit [Bus (±)]. The9D9
in D1 and D2 identify these as diagnostic circuits.
Transmission and receipt of binary messages on the
CCD data bus is accomplished by cycling the voltage
differential between the Bus (+) and Bus (±) circuits.The two data bus wires are twisted together in
order to shield the wires from the effects of any Elec-
tro-Magnetic Interference (EMI) from switched volt-
age sources. An induced EMI voltage can be
generated in any wire by a nearby switched voltage
or switched ground circuit. By twisting the data bus
wires together, the induced voltage spike (either up
or down) affects both wires equally. Since both wires
are affected equally, a voltage differential still exists
between the Bus (+) and Bus (±) circuits, and the
data bus messages can still be broadcast or received.
The correct specification for data bus wire twisting is
one turn for every 44.45 millimeters (1
3¤4inches) of
wire.
CCD CHIPS
In order for an electronic control module to commu-
nicate on the CCD data bus, it must have a CCD
chip (Fig. 5). The CCD chip contains a differential
transmitter/receiver (or transceiver), which is used to
send and receive messages. Each module is wired in
parallel to the data bus through its CCD chip.
The differential transceiver sends messages by
using two current drivers: one current source driver,
and one current sink driver. The current drivers are
matched and allow 0.006 ampere to flow through the
data bus circuits. When the transceiver drivers are
turned On, the Bus (+) voltage increases slightly, and
the Bus (±) voltage decreases slightly. By cycling the
drivers On and Off, the CCD chip causes the voltage
on the data bus circuit to fluctuate to reflect the mes-
sage.
Fig. 5 CCD Chip
BR/BEELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 7
COMMUNICATION (Continued)
Page 463 of 2889
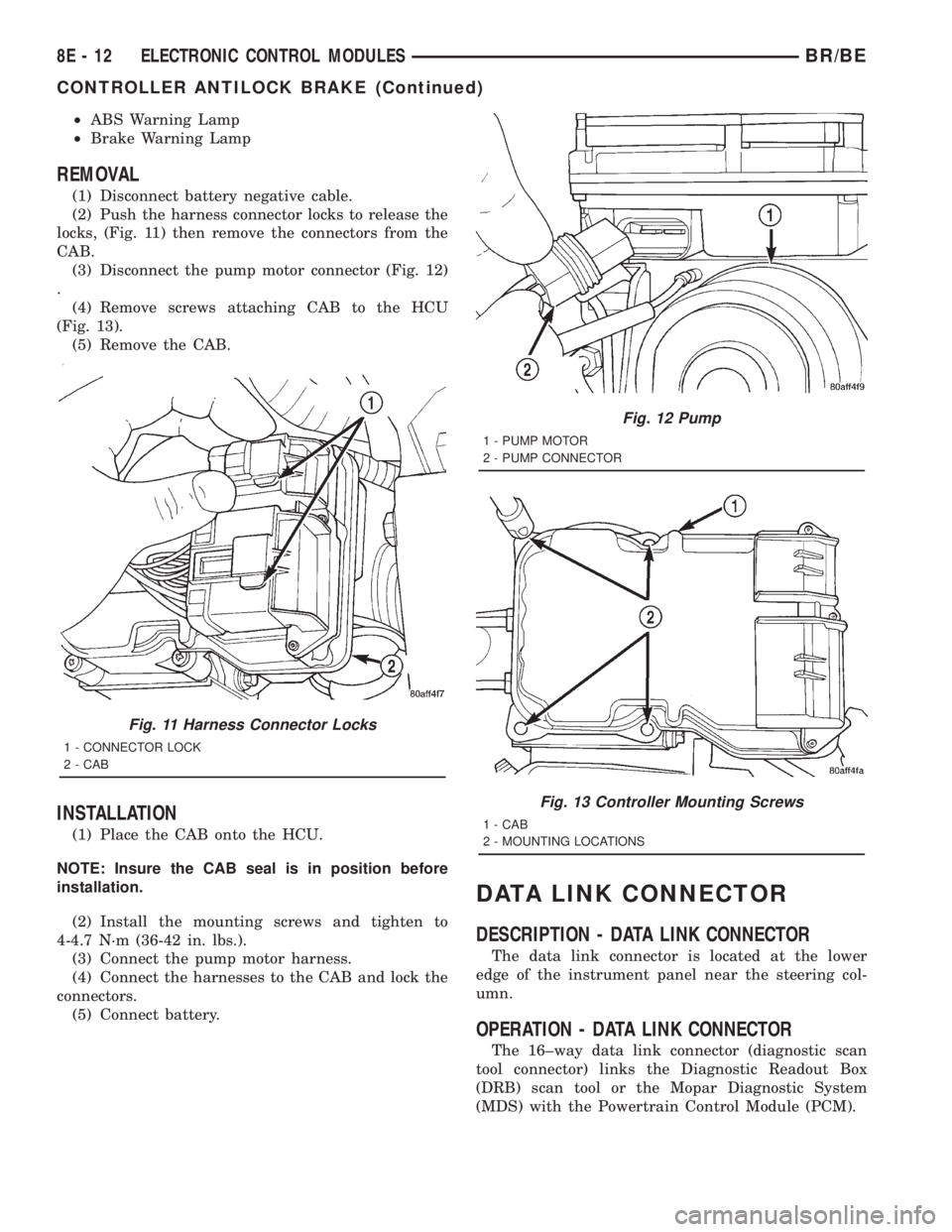
²ABS Warning Lamp
²Brake Warning Lamp
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Push the harness connector locks to release the
locks, (Fig. 11) then remove the connectors from the
CAB.
(3) Disconnect the pump motor connector (Fig. 12)
.
(4) Remove screws attaching CAB to the HCU
(Fig. 13).
(5) Remove the CAB.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place the CAB onto the HCU.
NOTE: Insure the CAB seal is in position before
installation.
(2) Install the mounting screws and tighten to
4-4.7 N´m (36-42 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the pump motor harness.
(4) Connect the harnesses to the CAB and lock the
connectors.
(5) Connect battery.
DATA LINK CONNECTOR
DESCRIPTION - DATA LINK CONNECTOR
The data link connector is located at the lower
edge of the instrument panel near the steering col-
umn.
OPERATION - DATA LINK CONNECTOR
The 16±way data link connector (diagnostic scan
tool connector) links the Diagnostic Readout Box
(DRB) scan tool or the Mopar Diagnostic System
(MDS) with the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
Fig. 11 Harness Connector Locks
1 - CONNECTOR LOCK
2 - CAB
Fig. 12 Pump
1 - PUMP MOTOR
2 - PUMP CONNECTOR
Fig. 13 Controller Mounting Screws
1 - CAB
2 - MOUNTING LOCATIONS
8E - 12 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESBR/BE
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE (Continued)
Page 487 of 2889

A vehicle that has not been operated for approxi-
mately twenty days, may discharge the battery to an
inadequate level. When a vehicle will not be used for
twenty days or more (stored), remove the IOD fuse
from the Power Distribution Center (PDC). This will
reduce battery discharging.
Excessive IOD can be caused by:
²Electrical items left on.
²Faulty or improperly adjusted switches.
²Faulty or shorted electronic modules and compo-
nents.
²An internally shorted generator.
²Intermittent shorts in the wiring.If the IOD is over thirty-five milliamperes, the
problem must be found and corrected before replac-
ing a battery. In most cases, the battery can be
charged and returned to service after the excessive
IOD condition has been corrected.
(1) Verify that all electrical accessories are off.
Turn off all lamps, remove the ignition key, and close
all doors. If the vehicle is equipped with an illumi-
nated entry system or an electronically tuned radio,
allow the electronic timer function of these systems
to automatically shut off (time out). This may take
up to three minutes. See the Electronic Module Igni-
tion-Off Draw Table for more information.
ELECTRONIC MODULE IGNITION-OFF DRAW (IOD) TABLE
ModuleTime Out?
(If Yes, Interval And Wake-Up Input)IODIOD After Time
Out
Radio No1to3
milliamperesN/A
Audio Power
AmplifierNoup to 1
milliampereN/A
Central Timer Module
(CTM)No4.75
milliamperes
(max.)N/A
Powertrain Control
Module (PCM)No 0.95 milliampere N/A
ElectroMechanical
Instrument Cluster
(EMIC)No 0.44 milliampere N/A
Combination Flasher No 0.08 milliampere N/A
(2) Determine that the underhood lamp is operat-
ing properly, then disconnect the lamp wire harness
connector or remove the lamp bulb.
(3) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(4) Set an electronic digital multi-meter to its
highest amperage scale. Connect the multi-meter
between the disconnected battery negative cable ter-
minal clamp and the battery negative terminal post.
Make sure that the doors remain closed so that the
illuminated entry system is not activated. The multi-
meter amperage reading may remain high for up to
three minutes, or may not give any reading at all
while set in the highest amperage scale, depending
upon the electrical equipment in the vehicle. The
multi-meter leads must be securely clamped to the
battery negative cable terminal clamp and the bat-
tery negative terminal post. If continuity between the
battery negative terminal post and the negative cable
terminal clamp is lost during any part of the IOD
test, the electronic timer function will be activated
and all of the tests will have to be repeated.(5) After about three minutes, the high-amperage
IOD reading on the multi-meter should become very
low or nonexistent, depending upon the electrical
equipment in the vehicle. If the amperage reading
remains high, remove and replace each fuse or circuit
breaker in the Power Distribution Center (PDC) and
then in the Junction Block (JB), one at a time until
the amperage reading becomes very low, or nonexist-
ent. Refer to the appropriate wiring information in
this service manual for complete PDC and JB fuse,
circuit breaker, and circuit identification. This will
isolate each circuit and identify the circuit that is the
source of the high-amperage IOD. If the amperage
reading remains high after removing and replacing
each fuse and circuit breaker, disconnect the wire
harness from the generator. If the amperage reading
now becomes very low or nonexistent, refer to Charg-
ing System for the proper charging system diagnosis
and testing procedures. After the high-amperage IOD
has been corrected, switch the multi-meter to pro-
gressively lower amperage scales and, if necessary,
repeat the fuse and circuit breaker remove-and-re-
8F - 16 BATTERY SYSTEMBR/BE
BATTERY (Continued)
Page 490 of 2889

(1) Clean and inspect the battery hold down hard-
ware. Refer toBatteryin the index of this service
manual for the location of the proper battery hold
down hardware cleaning and inspection procedures.
(2) Position the battery hold down strap across the
top of the battery case.
(3) Install and tighten the two battery hold down
bolts through the holes on each end of the hold down
strap and into the U-nuts on each side of the battery
tray. Tighten the bolts to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.).
(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable terminal
clamp to the battery negative terminal post. Tighten
the terminal clamp pinch-bolt hex nut to 4 N´m (35
in. lbs.).
BATTERY CABLE
DESCRIPTION
The battery cables (Fig. 20) are large gauge,
stranded copper wires sheathed within a heavy plas-
tic or synthetic rubber insulating jacket. The wire
used in the battery cables combines excellent flexibil-
ity and reliability with high electrical current carry-
ing capacity. Refer toWiring Diagramsin the index
of this service manual for the location of the proper
battery cable wire gauge information.The battery cables cannot be repaired and, if dam-
aged or faulty they must be replaced. Both the bat-
tery positive and negative cables are available for
service replacement only as a unit with the battery
positive cable wire harness or the battery negative
cable wire harness, which may include portions of
the wiring circuits for the generator and other com-
ponents on some models. Refer toWiring Diagrams
in the index of this service manual for the location of
more information on the various wiring circuits
included in the battery cable wire harnesses for the
vehicle being serviced.
GASOLINE ENGINE
Gasoline engine models feature a stamped brass
clamping type female battery terminal crimped onto
one end of the battery cable wire and then solder-
dipped. A square headed pinch-bolt and hex nut are
installed at the open end of the female battery termi-
nal clamp. The battery positive cable also includes a
red molded rubber protective cover for the female
battery terminal clamp. Large eyelet type terminals
are crimped onto the opposite end of the battery
cable wire and then solder-dipped. The battery posi-
tive cable wires have a red insulating jacket to pro-
vide visual identification and feature a larger female
battery terminal clamp to allow connection to the
larger battery positive terminal post. The battery
negative cable wires have a black insulating jacket
and a smaller female battery terminal clamp.
Fig. 19 Left Battery Hold Downs Remove/Install -
Typical for Right Battery
1 - BATTERY TRAY
2 - U-NUT (2)
3 - BATTERY
4 - BOLT (2)
5 - STRAP
Fig. 20 Battery Cables - Typical
1 - EYELET
2 - NUT
3 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
4 - POSITIVE CABLE
5 - SCREW
6 - NEGATIVE CABLE
7 - EYELET
8 - CLIP
BR/BEBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 19
BATTERY HOLDDOWN (Continued)
Page 491 of 2889

DIESEL ENGINE
Diesel engine models feature a clamping type
female battery terminal made of soft lead die cast
onto one end of the battery cable wire. A square
headed pinch-bolt and hex nut are installed at the
open end of the female battery terminal clamp. The
pinch-bolt on the left side battery positive cable
female terminal clamp also has a stud extending
from the head of the bolt. Large eyelet type terminals
are crimped onto the opposite end of the battery
cable wire and then solder-dipped. The battery posi-
tive cable wires have a red insulating jacket to pro-
vide visual identification and feature a larger female
battery terminal clamp to allow connection to the
larger battery positive terminal post. The battery
negative cable wires have a black insulating jacket
and a smaller female battery terminal clamp.
OPERATION
The battery cables connect the battery terminal
posts to the vehicle electrical system. These cables
also provide a return path for electrical current gen-
erated by the charging system for restoring the volt-
age potential of the battery. The female battery
terminal clamps on the ends of the battery cable
wires provide a strong and reliable connection of the
battery cable to the battery terminal posts. The ter-
minal pinch bolts allow the female terminal clamps
to be tightened around the male terminal posts on
the top of the battery. The eyelet terminals secured
to the ends of the battery cable wires opposite the
female battery terminal clamps provide secure and
reliable connection of the battery to the vehicle elec-
trical system.
GASOLINE ENGINE
The battery positive cable terminal clamp is
crimped onto the ends of two wires. One wire has an
eyelet terminal that connects the battery positive
cable to the B(+) terminal stud of the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC), and the other wire has an eye-
let terminal that connects the battery positive cable
to the B(+) terminal stud of the engine starter motor
solenoid. The battery negative cable terminal clamp
is also crimped onto the ends of two wires. One wire
has an eyelet terminal that connects the battery neg-
ative cable to the vehicle powertrain through a stud
on the front of the left engine cylinder head. The
other wire has an eyelet terminal that connects the
battery negative cable to the vehicle body through a
ground screw on the left front fender inner shield,
just ahead of the battery. An additional ground wire
with two eyelet terminals is used to provide ground
to the vehicle frame. One eyelet terminal of this
ground wire is installed under the head of the bat-
tery negative cable terminal clamp pinch-bolt, andthe other eyelet terminal is secured with a ground
screw to the outer surface of the left frame rail,
below the battery.
DIESEL ENGINE
The left battery positive cable terminal clamp is
die cast onto the ends of two wires. One wire has an
eyelet terminal that connects the left battery positive
cable to the B(+) terminal stud of the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC), and the other wire has an eye-
let terminal that connects the left battery positive
cable to the B(+) terminal stud of the engine starter
motor solenoid. The right battery positive cable ter-
minal clamp is die cast onto the end of a single wire.
The eyelet terminal on the other end of the right bat-
tery positive cable is connected to the stud on the
pinch-bolt of the left battery positive cable terminal
clamp. This stud also provides a connection point for
the eyelet terminals from the fuel heater relay and
intake air heater relay jumper harness take outs. All
of these eyelet terminals are secured to the left bat-
tery positive cable terminal clamp pinch-bolt stud
with a single hex nut.
The left battery negative cable terminal clamp is
die cast onto the ends of two wires. One wire has an
eyelet terminal that connects the left battery nega-
tive cable to the vehicle powertrain through a ground
screw on the left side of the engine block, below the
power steering and vacuum pumps. The other wire
has an eyelet terminal that connects the left battery
negative cable to the vehicle body through a ground
screw on the left front fender inner shield, just ahead
of the left battery. An additional ground wire with
two eyelet terminals is used to provide ground to the
vehicle frame. One eyelet terminal of this ground
wire is installed under the nut of the left battery
negative cable terminal clamp pinch-bolt, and the
other eyelet terminal is secured with a ground screw
to the outer surface of the left frame rail, below the
left battery. The right battery negative cable terminal
is also die cast onto the ends of two wires. One wire
has an eyelet terminal that connects the right bat-
tery negative cable to the vehicle powertrain through
a ground screw on the right side of the engine block,
just forward of the right engine mount. The other
wire has an eyelet terminal that connects the right
battery negative cable to the vehicle body through a
ground screw on the right front fender inner shield,
just behind the right battery.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - BATTERY CABLES
A voltage drop test will determine if there is exces-
sive resistance in the battery cable terminal connec-
tions or the battery cables. If excessive resistance is
found in the battery cable connections, the connec-
tion point should be disassembled, cleaned of all cor-
8F - 20 BATTERY SYSTEMBR/BE
BATTERY CABLE (Continued)
Page 492 of 2889

rosion or foreign material, then reassembled.
Following reassembly, check the voltage drop for the
battery cable connection and the battery cable again
to confirm repair.
When performing the voltage drop test, it is impor-
tant to remember that the voltage drop is giving an
indication of the resistance between the two points at
which the voltmeter probes are attached.EXAM-
PLE:When testing the resistance of the battery pos-
itive cable, touch the voltmeter leads to the battery
positive cable terminal clamp and to the battery pos-
itive cable eyelet terminal at the starter solenoid
B(+) terminal stud. If you probe the battery positive
terminal post and the battery positive cable eyelet
terminal at the starter solenoid B(+) terminal stud,
you are reading the combined voltage drop in the
battery positive cable terminal clamp-to-terminal
post connection and the battery positive cable.
VOLTAGE DROP TEST
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY SHOWS SIGNS OF
FREEZING, LEAKING, LOOSE POSTS, OR LOW
ELECTROLYTE LEVEL, DO NOT TEST, ASSIST-
BOOST, OR CHARGE. THE BATTERY MAY ARC
INTERNALLY AND EXPLODE. PERSONAL INJURY
AND/OR VEHICLE DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: EXPLOSIVE HYDROGEN GAS FORMS IN
AND AROUND THE BATTERY. DO NOT SMOKE,
USE FLAME, OR CREATE SPARKS NEAR THE BAT-
TERY. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: THE BATTERY CONTAINS SULFURIC
ACID, WHICH IS POISONOUS AND CAUSTIC. AVOID
CONTACT WITH THE SKIN, EYES, OR CLOTHING.
IN THE EVENT OF CONTACT, FLUSH WITH WATER
AND CALL A PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY. KEEP OUT
OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY IS EQUIPPED WITH
REMOVABLE CELL CAPS, BE CERTAIN THAT EACH
OF THE CELL CAPS IS IN PLACE AND TIGHT
BEFORE THE BATTERY IS RETURNED TO SER-
VICE. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT FROM LOOSE OR MISSING
CELL CAPS.
WARNING: MODELS EQUIPPED WITH THE DIESEL
ENGINE OPTION ALSO HAVE AN AUTOMATIC
SHUTDOWN (ASD) RELAY LOCATED IN THE
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC), IN THE
ENGINE COMPARTMENT. HOWEVER, REMOVAL OFTHE ASD RELAY MAY NOT PREVENT THE DIESEL
ENGINE FROM STARTING. BE CERTAIN TO ALSO
DISCONNECT THE FUEL SHUTDOWN SOLENOID
WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR ON MODELS WITH A
DIESEL ENGINE. FAILURE TO DO SO MAY RESULT
IN PERSONAL INJURY.
The following operation will require a voltmeter
accurate to 1/10 (0.10) volt. Before performing this
test, be certain that the following procedures are
accomplished:
²The battery is fully-charged and load tested.
Refer toBattery Chargingin the index of this ser-
vice manual for the location of the proper battery
charging procedures. Refer toBatteryin the index of
this service manual for the location of the battery
diagnosis and testing procedures, including the
proper battery load test procedures.
²Fully engage the parking brake.
²If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in the
Park position. If the vehicle is equipped with a man-
ual transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in
the Neutral position and block the clutch pedal in the
fully depressed position.
²Verify that all lamps and accessories are turned
off.
²To prevent a gasoline engine from starting,
remove the Automatic ShutDown (ASD) relay. The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC), in the engine compartment. See the fuse
and relay layout label affixed to the underside of the
PDC cover for ASD relay identification and location.
To prevent a diesel engine from starting, disconnect
the fuel shutdown solenoid wire harness connector
(Fig. 21).
(1) Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to
the battery negative terminal post. Connect the neg-
ative lead of the voltmeter to the battery negative
cable terminal clamp (Fig. 22). Rotate and hold the
ignition switch in the Start position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct the poor con-
nection between the battery negative cable terminal
clamp and the battery negative terminal post.
NOTE: If the vehicle is equipped with a dual battery
system, Step 1 must be performed twice, once for
each battery.
(2) Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to
the battery positive terminal post. Connect the nega-
tive lead of the voltmeter to the battery positive cable
terminal clamp (Fig. 23). Rotate and hold the ignition
switch in the Start position. Observe the voltmeter. If
voltage is detected, correct the poor connection
between the battery positive cable terminal clamp
and the battery positive terminal post.
BR/BEBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 21
BATTERY CABLE (Continued)
Page 494 of 2889

(4) Connect the voltmeter to measure between the
battery negative cable terminal clamp and a good
clean ground on the engine block (Fig. 25). Rotate
and hold the ignition switch in the Start position.
Observe the voltmeter. If the reading is above 0.2
volt, clean and tighten the battery negative cable
eyelet terminal connection to the engine block.
Repeat the test. If the reading is still above 0.2 volt,
replace the faulty battery negative cable.
NOTE: If the vehicle is equipped with a dual battery
system, Step 4 must be performed twice, once for
each battery.
POSITIVE CABLE REMOVAL - GASOLINE
Both the battery negative cable and the battery
positive cable are serviced in the battery wire har-
ness. If either battery cable is damaged or faulty, the
battery wire harness assembly must be replaced.
(1) Remove the positive battery cable from the bat-
tery.
(2) Remove the cover from the PDC.
(3) Remove the positive battery cable from the
PDC.
(4) Disconnect the starter motor signal wire har-
ness connector, located on the PDC housing.
(5) Disengage wire harness assembly pushpin
retainers.
(6) From under the vehicle, disengage wire har-
ness assembly pushpin retainers.
(7) Remove the positive battery cable from the
starter motor B+ terminal stud.
(8) Remove the starter motor trigger wire from the
starter motor.
(9) Remove the positive cable wire harness assem-
bly from the vehicle.
NEGATIVE CABLE REMOVAL - GASOLINE
Both the battery negative cable and the battery
positive cable are serviced in the battery wire har-
ness. If either battery cable is damaged or faulty, the
battery wire harness unit must be replaced.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position. Be
certain that all electrical accessories are turned off.
(2) Loosen the battery negative cable terminal
clamp pinch-bolt hex nut.
(3) Disconnect the battery negative cable terminal
clamp from the battery negative terminal post. If
necessary, use a battery terminal puller to remove
the terminal clamp from the battery post.
(4) Remove the negative cable jumper from the left
side of the radiator closure panel.
(5) Remove the negative cable jumper from the left
side of the frame assembly.
(6) Remove the PDC cover and remove the gener-
ator output wire from the PDC.
(7) Following the wire, remove the pushpin retain-
ers holding the wire assembly in place.
(8) Remove the negative cable eyelet from the
power steering pump pivot bolt.
(9) Remove the generator output wire from the
generator.
(10) Remove the negative battery cable assembly,
by fishing out from under the compressor mounting
bracket, if equipped.
POSITIVE CABLE INSTALLATION - GASOLINE
(1) Position the battery wire harness into the
engine compartment.
(2) Install the positive battery cable on the battery.
(3) Install the positive battery cable on the PDC.
(4) Install the cover on the PDC.
(5) Connect the starter motor signal wire harness
connector, located on the PDC housing.
(6) Install wire harness assembly pushpin retain-
ers in their original position.
(7) From under the vehicle, install wire harness
assembly pushpin retainers.
(8) Install and tighten the nut that secures the
battery positive cable eyelet terminal to the B(+) ter-
minal stud on the starter solenoid. Tighten the nut to
10 N´m (90 in. lbs.).
(9) Connect the starter motor trigger wire on the
starter motor.
(10) Reconnect the battery positive cable terminal
clamp to the battery positive terminal post. Tighten
the terminal clamp pinch-bolt hex nut to 4 N´m (35
in. lbs.).
(11) Apply a thin coating of petroleum jelly or
chassis grease to the exposed surfaces of the battery
cable terminal clamps and the battery terminal
posts.
Fig. 25 Test Ground Circuit
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
3 - ENGINE GROUND
BR/BEBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 23
BATTERY CABLE (Continued)
Page 495 of 2889

NEGATIVE CABLE INSTALLATION - GASOLINE
(1) Position the battery wire harness into the
engine compartment and under the compressor
mounting bracket, if equipped.
(2) Install and tighten the nut that secures the
battery negative cable ground eyelet terminal to the
stud on the power steering pump pivot bolt.
(3) Install the generator output cable eyelet termi-
nal onto the generator output terminal stud.
(4) Install and tighten the nut that secures the
generator output cable eyelet terminal to the genera-
tor output terminal stud. Tighten the nut to 8.4 N´m
(75 in. lbs.).
(5) Position the cover for the generator output ter-
minal stud housing onto the back of the generator
and snap it into place.
(6) Secure wire assembly in place with pushpin
retainers in there original positions.
(7) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
battery negative cable eyelet terminal to the radiator
closure panel, near the battery. Tighten the screw to
40 in. lbs.
(8) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
battery negative cable eyelet terminal to the left
front side of the frame assembly. Tighten the screw
to 80 in. lbs.
(9) Install and tighten the nut that secures the
battery positive cable eyelet terminal and the gener-
ator output cable eyelet terminal to the PDC B(+)
terminal stud. Tighten the nut to 80 in. lbs.
(10) Reconnect the battery negative cable terminal
clamp to the battery negative terminal post. Tighten
the terminal clamp pinch-bolt hex nut to 35 in. lbs.
(11)
Apply a thin coating of petroleum jelly or chassis
grease to the exposed surfaces of the battery cable ter-
minal clamps and the battery terminal posts.
BATTERY TRAY
DESCRIPTION
The battery is mounted in a molded plastic tray (Fig.
26) with an integral support located in the left front cor-
ner of the engine compartment. A U-nut held in a
molded formation on each side of the battery tray pro-
vides anchor points for the battery hold down bolts. The
battery tray is secured on the outboard side to the inner
fender shield by two hex screws with washers, and from
underneath the integral battery tray support is secured
to the left front wheelhouse inner panel by two stud
plates. Each stud plate has two studs and is secured by
two nuts with washers. The stud plate that secures the
front of the battery tray support to the wheelhouse innerpanel is installed through the wheelhouse panel from
the top. The stud plate that secures the rear of the bat-
tery tray support to the wheelhouse inner panel is
installed through the wheelhouse panel from the bottom.
A hole in the bottom of the battery tray is fitted
with a battery temperature sensor. Refer toBattery
Temperature Sensorin the index of this service
manual for the location of more information on the
battery temperature sensor. Models that are
equipped with an optional vehicle speed control sys-
tem have the speed control servo secured to the inte-
gral battery tray support. Refer toSpeed Control
Servoin the index of this service manual for the
location of more information on the speed control
servo and its mounting.
Models that are equipped with the diesel engine
option have a second battery tray located in the right
front corner of the engine compartment. This second
battery tray and its mounting are mirror image of
the standard equipment left battery tray. However,
the right battery tray and support have no provisions
for a battery temperature sensor or a speed control
servo mounting bracket.
Fig. 26 Battery Tray - Typical
1 - STUD PLATE (2)
2 - NUT AND WASHER (4)
3 - FRONT WHEELHOUSE INNER PANEL
4 - SPEED CONTROL SERVO
5 - TRAY
6 - SCREW AND WASHER (2)
7 - BATTERY TREMPERATURE SENSOR
8 - U-NUT (2)
9 - FENDER INNER SHIELD
8F - 24 BATTERY SYSTEMBR/BE
BATTERY CABLE (Continued)
Page 498 of 2889

CHARGING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION...........................27
OPERATION.............................27
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................27
CHARGING SYSTEM....................27
SPECIFICATIONS........................28
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION...........................29
OPERATION.............................29
REMOVAL..............................29INSTALLATION...........................29
GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION...........................29
OPERATION.............................29
REMOVAL..............................30
INSTALLATION...........................30
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION...........................31
OPERATION.............................31
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION
The charging system consists of:
²Generator
²Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) circuitry
within the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Ignition switch (refer to Ignition System for
information)
²Battery (refer to 8, Battery for information)
²Battery temperature sensor
²Check Gauges Lamp (if equipped)
²Voltmeter (refer to 8, Instrument Panel and
Gauges for information)
²Wiring harness and connections (refer to 8, Wir-
ing Diagrams for information)
OPERATION
The charging system is turned on and off with the
ignition switch. The system is on when the engine is
running and the ASD relay is energized. When the
ASD relay is on, voltage is supplied to the ASD relay
sense circuit at the PCM. This voltage is connected
through the PCM and supplied to one of the genera-
tor field terminals (Gen. Source +) at the back of the
generator.
The amount of direct current produced by the gen-
erator is controlled by the EVR (field control) cir-
cuitry contained within the PCM. This circuitry is
connected in series with the second rotor field termi-
nal and ground.
A battery temperature sensor, located in the bat-
tery tray housing, is used to sense battery tempera-
ture. This temperature data, along with data from
monitored line voltage, is used by the PCM to vary
the battery charging rate. This is done by cycling the
ground path to control the strength of the rotor mag-netic field. The PCM then compensates and regulates
generator current output accordingly.
All vehicles are equipped with On-Board Diagnos-
tics (OBD). All OBD-sensed systems, including EVR
(field control) circuitry, are monitored by the PCM.
Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in elec-
tronic memory for certain failures it detects. Refer to
On-Board Diagnostics in 25, Emission Control Sys-
tem for more DTC information and a list of codes.
The Check Gauges Lamp (if equipped) monitors:
charging system voltage,engine coolant tempera-
ture and engine oil pressure. If an extreme condition
is indicated, the lamp will be illuminated. This is
done as reminder to check the three gauges. The sig-
nal to activate the lamp is sent via the CCD bus cir-
cuits. The lamp is located on the instrument panel.
Refer to 8, Instrument Panel and Gauges for addi-
tional information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHARGING
SYSTEM
The following procedures may be used to diagnose
the charging system if:
²the check gauges lamp (if equipped) is illumi-
nated with the engine running
²the voltmeter (if equipped) does not register
properly
²an undercharged or overcharged battery condi-
tion occurs.
Remember that an undercharged battery is often
caused by:
²accessories being left on with the engine not
running
²a faulty or improperly adjusted switch that
allows a lamp to stay on. Refer to Ignition-Off Draw
Test in 8, Battery for more information.
BR/BECHARGING 8F - 27