wheel alignment DODGE RAM 2002 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 73 of 2255
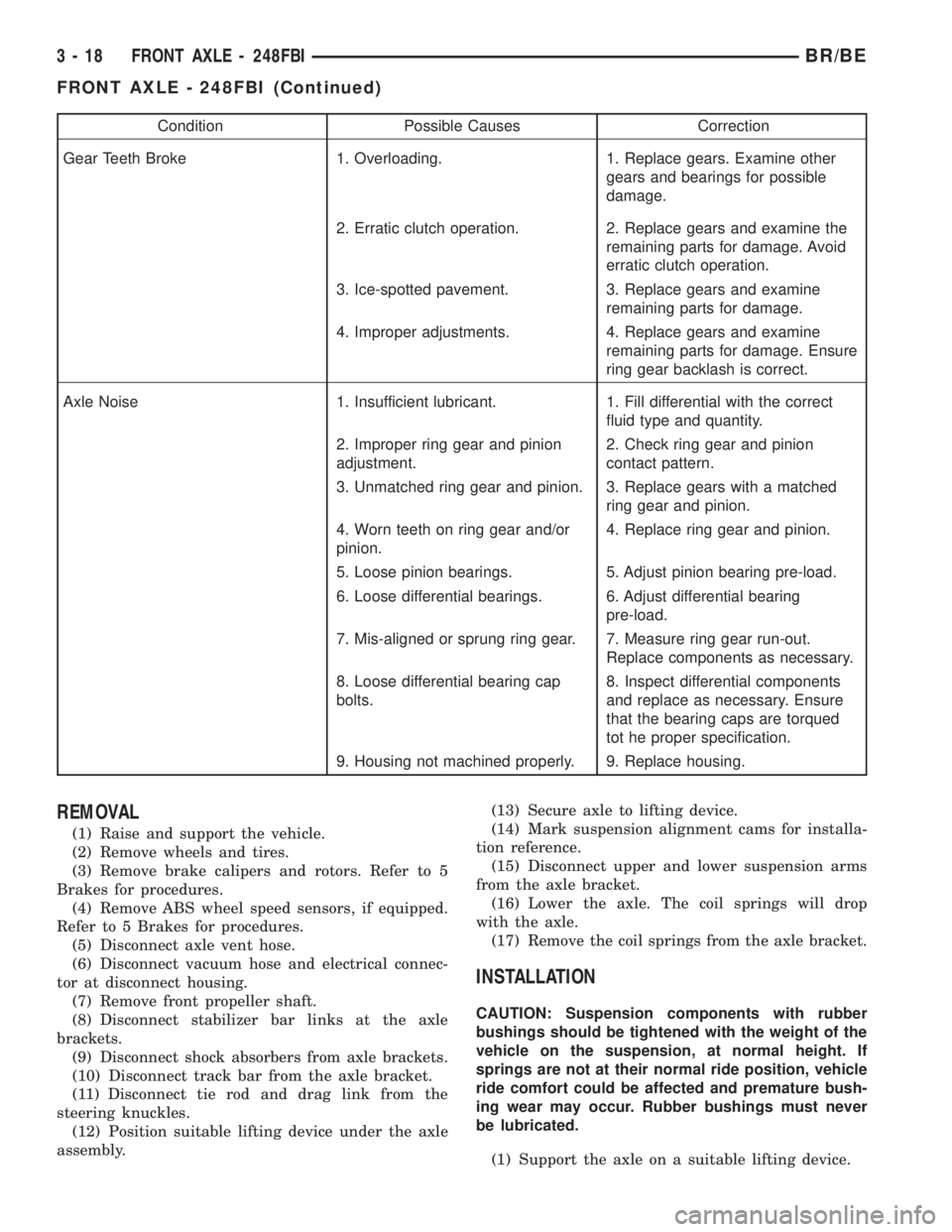
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove wheels and tires.
(3) Remove brake calipers and rotors. Refer to 5
Brakes for procedures.
(4) Remove ABS wheel speed sensors, if equipped.
Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.
(5) Disconnect axle vent hose.
(6) Disconnect vacuum hose and electrical connec-
tor at disconnect housing.
(7) Remove front propeller shaft.
(8) Disconnect stabilizer bar links at the axle
brackets.
(9) Disconnect shock absorbers from axle brackets.
(10) Disconnect track bar from the axle bracket.
(11) Disconnect tie rod and drag link from the
steering knuckles.
(12) Position suitable lifting device under the axle
assembly.(13) Secure axle to lifting device.
(14) Mark suspension alignment cams for installa-
tion reference.
(15) Disconnect upper and lower suspension arms
from the axle bracket.
(16) Lower the axle. The coil springs will drop
with the axle.
(17) Remove the coil springs from the axle bracket.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Suspension components with rubber
bushings should be tightened with the weight of the
vehicle on the suspension, at normal height. If
springs are not at their normal ride position, vehicle
ride comfort could be affected and premature bush-
ing wear may occur. Rubber bushings must never
be lubricated.
(1) Support the axle on a suitable lifting device.
3 - 18 FRONT AXLE - 248FBIBR/BE
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI (Continued)
Page 74 of 2255

(2) Secure axle to lifting device.
(3) Position the axle under the vehicle.
(4) Install springs, retainer clip and bolts.
(5) Raise axle and align it with the spring pads.
(6) Position upper and lower suspension arms in
the axle brackets. Install bolts, nuts and align the
suspension alignment cams to the reference marks.
Do not tighten at this time.
(7) Connect track bar to the axle bracket and
install the bolt. Do not tighten at this time.
(8) Install shock absorber and tighten bolts to 121
N´m (89 ft. lbs.).
(9) Install stabilizer bar link to the axle bracket.
Tighten the nut to 37 N´m (27 ft. lbs.).
(10) Install drag link and tie rod to the steering
knuckles and tighten the nuts to 88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.).
(11) Install ABS wheel speed sensors, if equipped.
Refer to 5 Brakes for procedures.
(12) Install rotors and brake calipers, refer to 5
Brakes for procedures.
(13) Connect the vent hose to the tube fitting.
(14) Connect vacuum hose and electrical connector
to disconnect housing.
(15) Install front propeller shaft.
(16) Check and add differential lubricant, if neces-
sary. Refer to Lubricant Specifications for lubricant
requirements.
(17) Install wheel and tire assemblies.
(18) Remove supports and lower the vehicle.
(19) Tighten upper suspension arm nuts at axle to
121 N´m (89 ft. lbs.). Tighten upper suspension arm
nuts at frame to 84 N´m (62 ft. lbs.).
(20) Tighten lower suspension arm nuts at axle to
84 N´m (62 ft. lbs.). Tighten the lower suspension
arm nuts at frame to 119 N´m (88 ft. lbs.).
(21) Tighten track bar bolt at the axle bracket to
176 N´m (130 ft. lbs.).
(22) Check front wheel alignment.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched sets
only. The identifying numbers for the ring and pinion
gear are etched into the face of each gear (Fig. 3). A
plus (+) number, minus (±) number or zero (0) is etched
into the face of the pinion gear. This number is the
amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth varies
from the standard depth setting of a pinion etched with
a (0). The standard setting from the center line of the
ring gear to the back face of the pinion is 127 mm (5.00
in.). The standard depth provides the best gear tooth
contact pattern. Refer to Backlash and Contact Pattern
in this section for additional information.
Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with a select shim/slinger. The shims are
placed between the rear pinion bearing and the pin-
ion gear head (Fig. 4).
Fig. 3 PINION GEAR ID NUMBERS
1 - PRODUCTION NUMBERS
2 - PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
3 - GEAR MATCHING NUMBER
Fig. 4 SHIM LOCATIONS
1 - PINION GEAR DEPTH SHIM/SLINGER
2 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING SHIM
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 248FBI 3 - 19
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI (Continued)
Page 104 of 2255
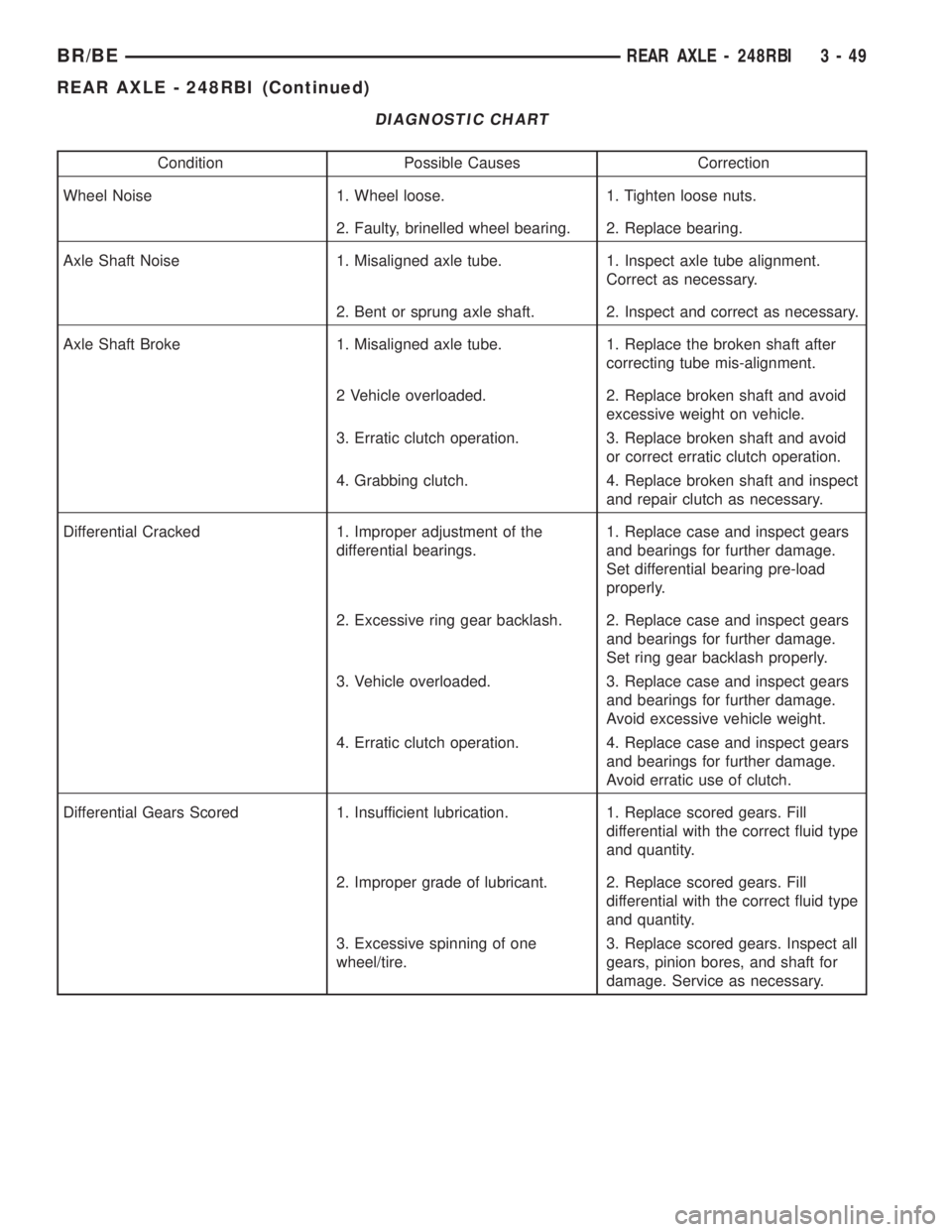
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid
or correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set differential bearing pre-load
properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 248RBI 3 - 49
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 106 of 2255
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position an axle lift under the axle and secure
it to the axle.
(3) Remove the wheels and tires.
(4) Remove RWAL sensor from the differential
housing, if necessary.
(5) Remove brake hose from the axle junction
block.
(6) Disconnect parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(7) Remove vent hose from the axle shaft tube.
(8) Mark propeller shaft and yoke for installation
alignment reference.
(9) Remove propeller shaft.
(10) Remove shock absorbers from the axle brack-
ets.
(11) Remove spring clamps and spring brackets.
(12) Remove axle from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Raise axle with lift and align to the leaf spring
centering bolts.
(2) Install spring clamps and spring brackets.
(3) Install shock absorbers and tighten to specifica-
tions.
(4) Install RWAL sensor to the differential hous-
ing, if necessary.
(5) Install parking brake cables and cable brackets
(6) Install brake hose to the axle junction block.
(7) Install axle vent hose.
(8) Install propeller shaft with reference marks
aligned.
(9) Install wheels and tires assemblies.
(10) Add gear lubricant, if necessary.
(11) Remove lift from the axle and lower the vehi-
cle.
ADJUSTMENTS
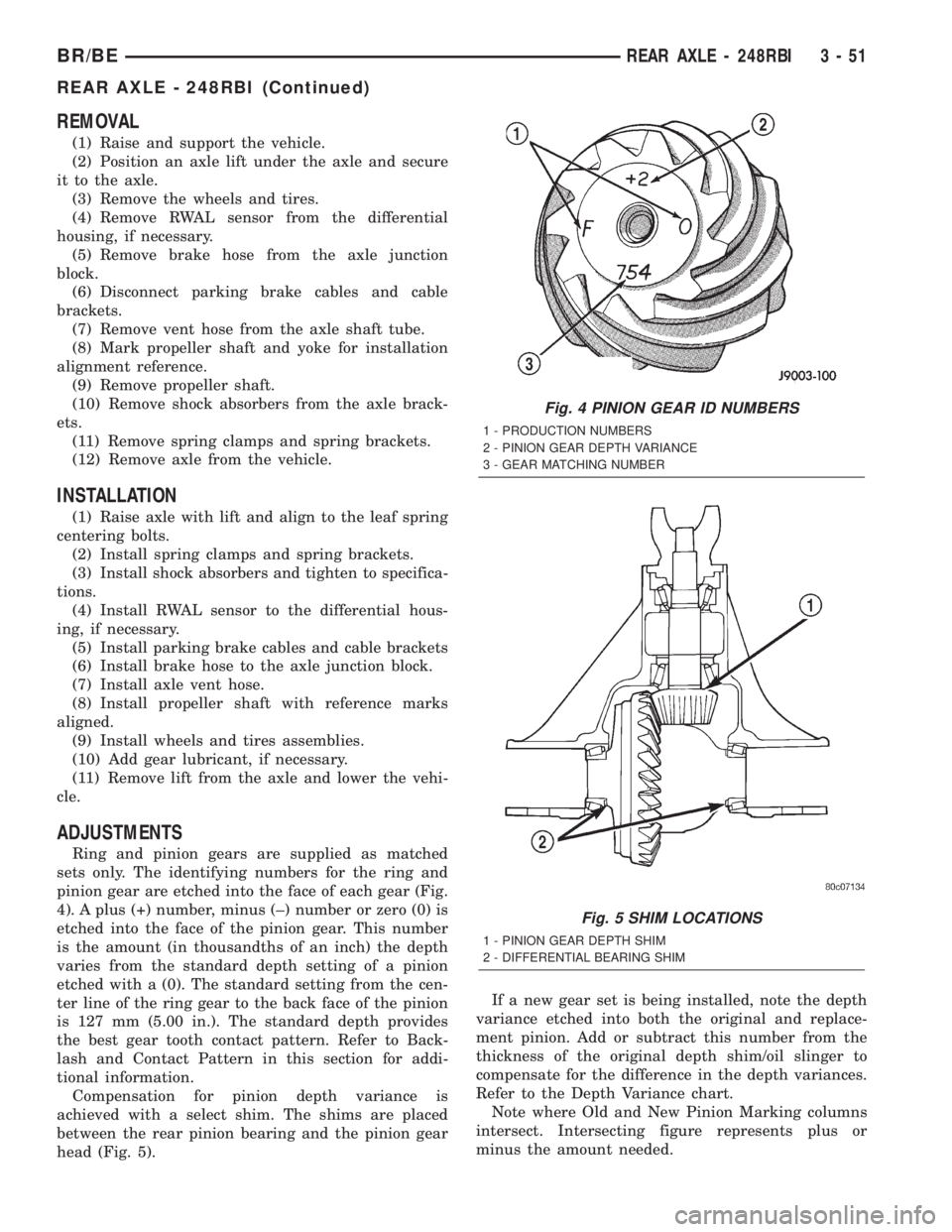
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched
sets only. The identifying numbers for the ring and
pinion gear are etched into the face of each gear (Fig.
4). A plus (+) number, minus (±) number or zero (0) is
etched into the face of the pinion gear. This number
is the amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth
varies from the standard depth setting of a pinion
etched with a (0). The standard setting from the cen-
ter line of the ring gear to the back face of the pinion
is 127 mm (5.00 in.). The standard depth provides
the best gear tooth contact pattern. Refer to Back-
lash and Contact Pattern in this section for addi-
tional information.
Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with a select shim. The shims are placed
between the rear pinion bearing and the pinion gear
head (Fig. 5).If a new gear set is being installed, note the depth
variance etched into both the original and replace-
ment pinion. Add or subtract this number from the
thickness of the original depth shim/oil slinger to
compensate for the difference in the depth variances.
Refer to the Depth Variance chart.
Note where Old and New Pinion Marking columns
intersect. Intersecting figure represents plus or
minus the amount needed.
Fig. 4 PINION GEAR ID NUMBERS
1 - PRODUCTION NUMBERS
2 - PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
3 - GEAR MATCHING NUMBER
Fig. 5 SHIM LOCATIONS
1 - PINION GEAR DEPTH SHIM
2 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING SHIM
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 248RBI 3 - 51
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 136 of 2255
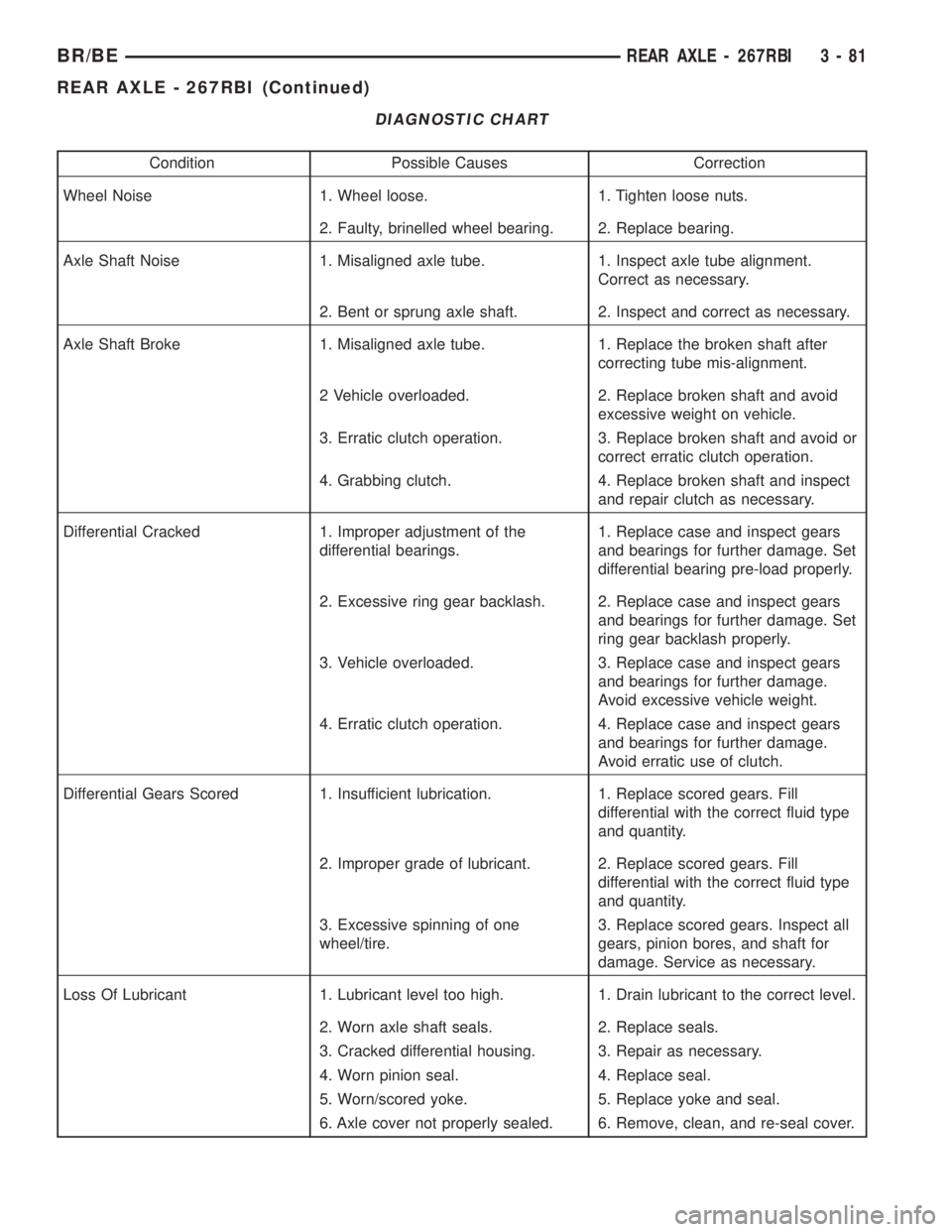
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid or
correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage. Set
differential bearing pre-load properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage. Set
ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
Loss Of Lubricant 1. Lubricant level too high. 1. Drain lubricant to the correct level.
2. Worn axle shaft seals. 2. Replace seals.
3. Cracked differential housing. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Worn pinion seal. 4. Replace seal.
5. Worn/scored yoke. 5. Replace yoke and seal.
6. Axle cover not properly sealed. 6. Remove, clean, and re-seal cover.
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 267RBI 3 - 81
REAR AXLE - 267RBI (Continued)
Page 137 of 2255
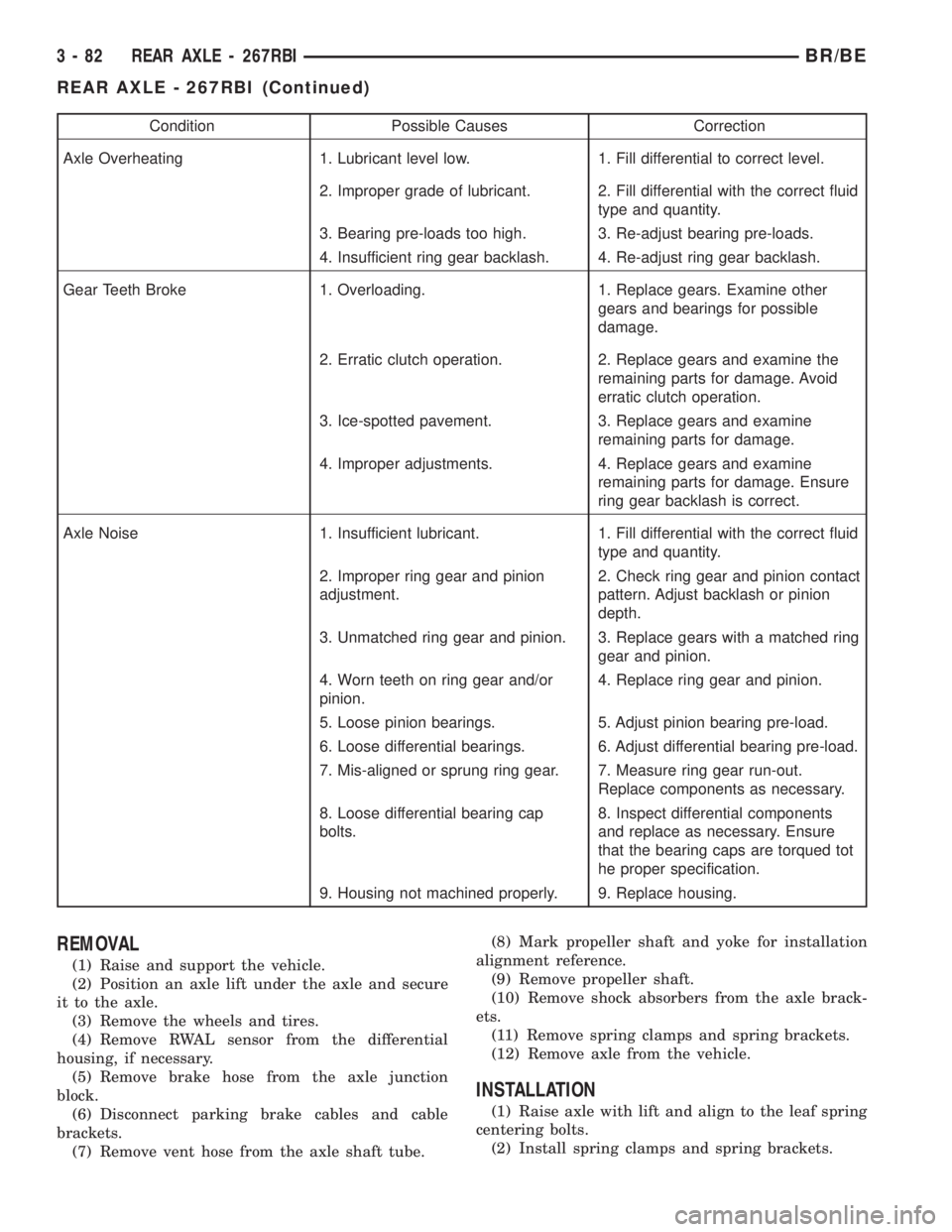
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct fluid
type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct fluid
type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion contact
pattern. Adjust backlash or pinion
depth.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched ring
gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued tot
he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position an axle lift under the axle and secure
it to the axle.
(3) Remove the wheels and tires.
(4) Remove RWAL sensor from the differential
housing, if necessary.
(5) Remove brake hose from the axle junction
block.
(6) Disconnect parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(7) Remove vent hose from the axle shaft tube.(8) Mark propeller shaft and yoke for installation
alignment reference.
(9) Remove propeller shaft.
(10) Remove shock absorbers from the axle brack-
ets.
(11) Remove spring clamps and spring brackets.
(12) Remove axle from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Raise axle with lift and align to the leaf spring
centering bolts.
(2) Install spring clamps and spring brackets.
3 - 82 REAR AXLE - 267RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 267RBI (Continued)
Page 165 of 2255
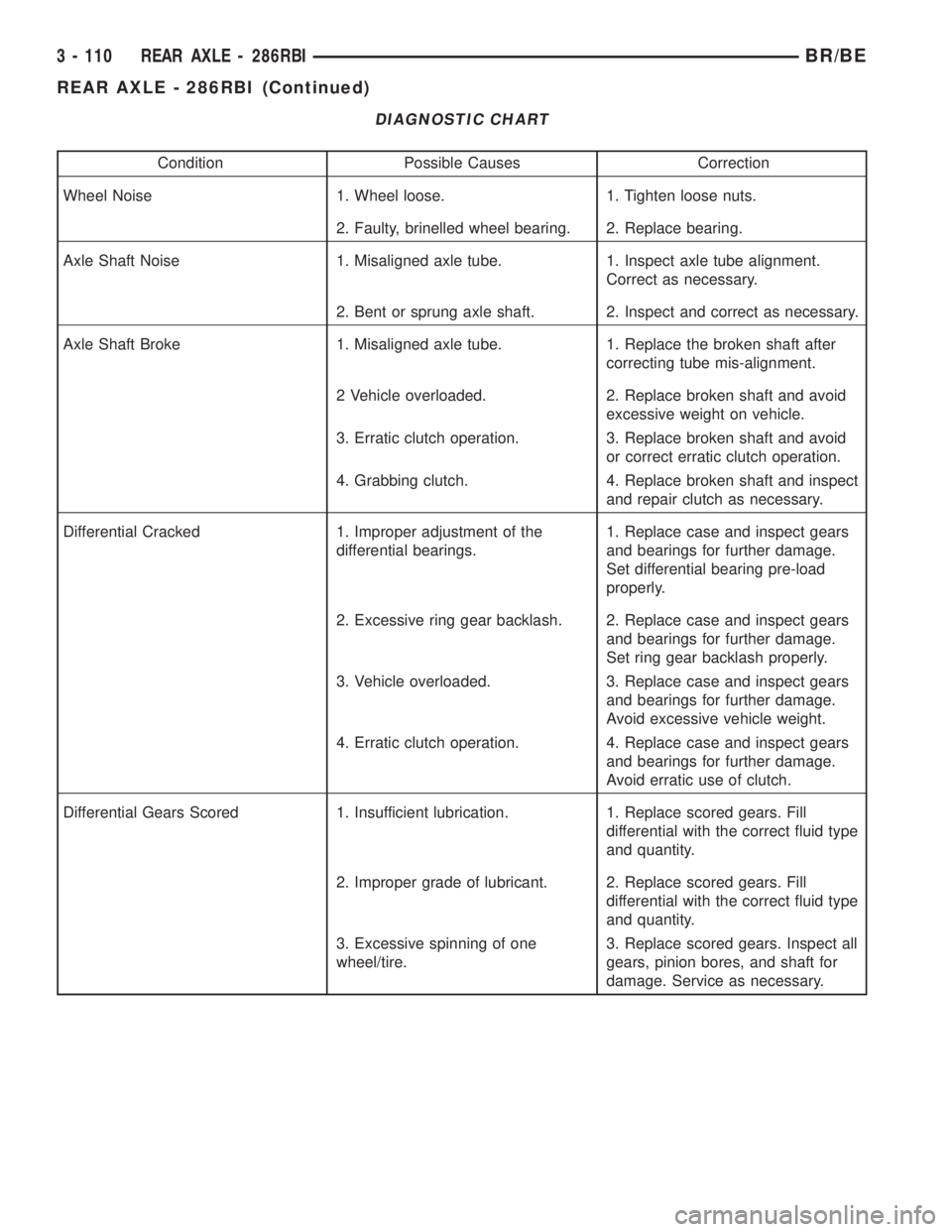
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
Axle Shaft Broke 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Replace the broken shaft after
correcting tube mis-alignment.
2 Vehicle overloaded. 2. Replace broken shaft and avoid
excessive weight on vehicle.
3. Erratic clutch operation. 3. Replace broken shaft and avoid
or correct erratic clutch operation.
4. Grabbing clutch. 4. Replace broken shaft and inspect
and repair clutch as necessary.
Differential Cracked 1. Improper adjustment of the
differential bearings.1. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set differential bearing pre-load
properly.
2. Excessive ring gear backlash. 2. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Set ring gear backlash properly.
3. Vehicle overloaded. 3. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid excessive vehicle weight.
4. Erratic clutch operation. 4. Replace case and inspect gears
and bearings for further damage.
Avoid erratic use of clutch.
Differential Gears Scored 1. Insufficient lubrication. 1. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Replace scored gears. Fill
differential with the correct fluid type
and quantity.
3. Excessive spinning of one
wheel/tire.3. Replace scored gears. Inspect all
gears, pinion bores, and shaft for
damage. Service as necessary.
3 - 110 REAR AXLE - 286RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 286RBI (Continued)
Page 167 of 2255

REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Position a suitable lifting device under the
axle.
(3) Secure axle to device.
(4) Remove the wheels and tires.
(5) Remove the RWAL sensor from the differential
housing, if necessary.
(6) Disconnect the brake hose at the axle junction
block.
(7) Disconnect the parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(8)
Disconnect the vent hose from the axle shaft tube.
(9) Mark the propeller shaft and companion flange
for installation alignment reference.
(10) Remove propeller shaft.
(11) Disconnect shock absorbers from axle.
(12)
Remove the spring clamps and spring brackets.
(13) Separate the axle from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Raise the axle with lifting device and align to
the leaf spring centering bolts.
(2) Install the spring clamps and spring brackets.
(3) Install the shock absorbers.
(4) Install the RWAL sensor to the differential
housing, if necessary
(5) Install the parking brake cables and cable
brackets.
(6)
Install the brake hose to the axle junction block.
(7) Install axle vent hose.
(8) Install the propeller shaft with reference marks
aligned.
(9) Install the wheels and tires.
(10) Add gear lubricant, if necessary. Refer to
Specifications for lubricant requirements.
(11) Remove lifting device from axle and lower the
vehicle.
ADJUSTMENTS
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched
sets only. The identifying numbers for the ring and
pinion gear are etched into the face of each gear (Fig.
4). A plus (+) number, minus (±) number or zero (0) is
etched into the face of the pinion gear. This number
is the amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth
varies from the standard depth setting of a pinion
etched with a (0). The standard setting from the cen-
ter line of the ring gear to the back face of the pinion
is 147.625 mm (5.812 in.). The standard depth pro-
vides the best teeth contact pattern. Refer to Back-
lash and Contact Pattern Analysis Paragraph in this
section for additional information.
Compensation for pinion depth variance is
achieved with select shims. The shims are placed
under the inner pinion bearing cone (Fig. 5).If a new gear set is being installed, note the depth
variance etched into both the original and replace-
ment pinion gear. Add or subtract the thickness of
the original depth shims to compensate for the differ-
ence in the depth variances. Refer to the Depth Vari-
ance charts.
Note where Old and New Pinion Marking columns
intersect. Intersecting figure represents plus or
minus amount needed.
Note the etched number on the face of the drive pin-
ion gear (±1, ±2, 0, +1, +2, etc.). The numbers represent
Fig. 4 PINION GEAR ID NUMBERS
1 - PRODUCTION NUMBERS
2 - PINION GEAR DEPTH VARIANCE
3 - GEAR MATCHING NUMBER
Fig. 5 SHIM LOCATIONS
1 - PINION BEARING PRELOAD SHIM
2 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING SHIM
3 - PINION GEAR DEPTH SHIM
3 - 112 REAR AXLE - 286RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 286RBI (Continued)
Page 235 of 2255

IMPROPER RELEASE OR CLUTCH ENGAGEMENT
Clutch release or engagement problems are caused
by wear or damage to one or more clutch compo-
nents. A visual inspection of the release components
will usually reveal the problem part.
Release problems can result in hard shifting and
noise. Items to look for are: leaks at the clutch cylin-
ders and interconnecting line; loose slave cylinder
bolts; worn/loose release fork and pivot stud; dam-
aged release bearing; and a worn clutch disc, or pres-
sure plate.
Normal condensation in vehicles that are stored or
out of service for long periods of time can generate
enough corrosion to make the disc stick to the fly-
wheel, or pressure plate. If this condition is experi-
enced, correction only requires that the disc be
loosened manually through the inspection plate open-
ing.
Engagement problems usually result in slip, chat-
ter/shudder, and noisy operation. The primary causes
are clutch disc contamination; clutch disc wear; mis-
alignment, or distortion; flywheel damage; or a com-
bination of the foregoing. A visual inspection is
required to determine the part actually causing the
problem.
CLUTCH MISALIGNMENT
Clutch components must be in proper alignment
with the crankshaft and transmission input shaft.
Misalignment caused by excessive runout or warpage
of any clutch component will cause grab, chatter and
improper clutch release.
CLUTCH COVER AND DISC RUNOUT
Check the clutch disc before installation. Axial
(face) runout of anewdisc should not exceed 0.50
mm (0.020 in.). Measure runout about 6 mm (1/4 in.)
from the outer edge of the disc facing. Obtain
another disc if runout is excessive.
Check condition of the clutch before installation. A
warped cover or diaphragm spring will cause grab
and incomplete release or engagement. Be careful
when handling the cover and disc. Impact can distort
the cover, diaphragm spring, release fingers and the
hub of the clutch disc.
Use an alignment tool when positioning the disc on
the flywheel. The tool prevents accidental misalign-
ment which could result in cover distortion and disc
damage.
A frequent cause of clutch cover distortion (and
consequent misalignment) is improper bolt tighten-
ing.
DIAGNOSIS CHART
The clutch inspection chart (Fig. 3) outlines items
to be checked before and during clutch installation.
Use the chart as a check list to help avoid overlook-
ing potential problem sources during service opera-
tions.
The diagnosis charts Diagnosis Chart describe
common clutch problems, causes and correction.
Fault conditions are listed at the top of each chart.
Conditions, causes and corrective action are outlined
in the indicated columns.
The charts are provided as a convenient reference
when diagnosing faulty clutch operation.
DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Disc facing worn out 1. Normal wear. 1. Replace cover and disc.
2. Driver frequently rides (slips) the
clutch. Results in rapid overheating
and wear.2. Replace cover and disc.
3. Insufficient clutch cover
diaphragm spring tension.3. Replace cover and disc.
Clutch disc facing contaminated with
oil, grease, or clutch fluid.1. Leak at rear main engine seal or
transmission input shaft seal.1. Replace appropriate seal.
2. Excessive amount of grease
applied to the input shaft splines.2. Remove grease and apply the
correct amount of grease.
3. Road splash, water entering
housing.3. Replace clutch disc. Clean clutch
cover and reuse if in good condition.
4. Slave cylinder leaking. 4. Replace hydraulic clutch linkage.
6 - 4 CLUTCHBR/BE
CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 236 of 2255
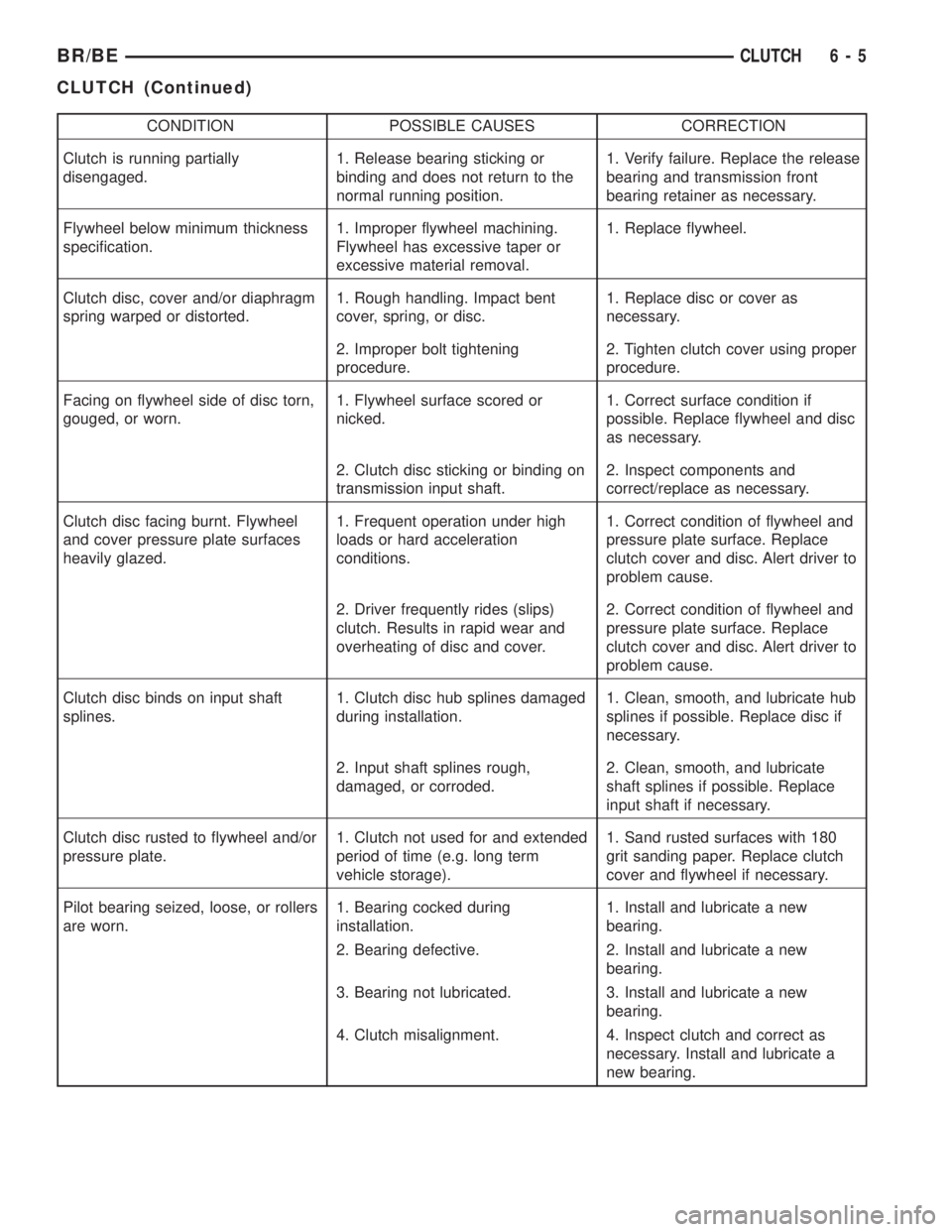
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Clutch is running partially
disengaged.1. Release bearing sticking or
binding and does not return to the
normal running position.1. Verify failure. Replace the release
bearing and transmission front
bearing retainer as necessary.
Flywheel below minimum thickness
specification.1. Improper flywheel machining.
Flywheel has excessive taper or
excessive material removal.1. Replace flywheel.
Clutch disc, cover and/or diaphragm
spring warped or distorted.1. Rough handling. Impact bent
cover, spring, or disc.1. Replace disc or cover as
necessary.
2. Improper bolt tightening
procedure.2. Tighten clutch cover using proper
procedure.
Facing on flywheel side of disc torn,
gouged, or worn.1. Flywheel surface scored or
nicked.1. Correct surface condition if
possible. Replace flywheel and disc
as necessary.
2. Clutch disc sticking or binding on
transmission input shaft.2. Inspect components and
correct/replace as necessary.
Clutch disc facing burnt. Flywheel
and cover pressure plate surfaces
heavily glazed.1. Frequent operation under high
loads or hard acceleration
conditions.1. Correct condition of flywheel and
pressure plate surface. Replace
clutch cover and disc. Alert driver to
problem cause.
2. Driver frequently rides (slips)
clutch. Results in rapid wear and
overheating of disc and cover.2. Correct condition of flywheel and
pressure plate surface. Replace
clutch cover and disc. Alert driver to
problem cause.
Clutch disc binds on input shaft
splines.1. Clutch disc hub splines damaged
during installation.1. Clean, smooth, and lubricate hub
splines if possible. Replace disc if
necessary.
2. Input shaft splines rough,
damaged, or corroded.2. Clean, smooth, and lubricate
shaft splines if possible. Replace
input shaft if necessary.
Clutch disc rusted to flywheel and/or
pressure plate.1. Clutch not used for and extended
period of time (e.g. long term
vehicle storage).1. Sand rusted surfaces with 180
grit sanding paper. Replace clutch
cover and flywheel if necessary.
Pilot bearing seized, loose, or rollers
are worn.1. Bearing cocked during
installation.1. Install and lubricate a new
bearing.
2. Bearing defective. 2. Install and lubricate a new
bearing.
3. Bearing not lubricated. 3. Install and lubricate a new
bearing.
4. Clutch misalignment. 4. Inspect clutch and correct as
necessary. Install and lubricate a
new bearing.
BR/BECLUTCH 6 - 5
CLUTCH (Continued)