fuel DODGE RAM 2002 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 2053 of 2255

EXTERIOR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EXTERIOR
DESCRIPTION.........................86
OPERATION...........................86
BODY SIDE MOLDINGS
REMOVAL.............................86
INSTALLATION.........................87
BODY STRIPES AND DECALS
REMOVAL.............................87
INSTALLATION.........................87
TAPE STRIPE
REMOVAL.............................88
INSTALLATION.........................89
EXTERIOR NAME PLATES
REMOVAL.............................89
INSTALLATION.........................89
COWL GRILLE
REMOVAL.............................90
INSTALLATION.........................90
ROOF JOINT MOLDING
REMOVAL.............................91
INSTALLATION.........................91
GRILLE
REMOVAL.............................91
INSTALLATION.........................91
GRILLE FRAME
REMOVAL.............................91
INSTALLATION.........................92
FRONT END SPLASH SHIELDS
REMOVAL.............................92
INSTALLATION.........................92LEFT FRONT FENDER
REMOVAL.............................93
INSTALLATION.........................93
RIGHT FRONT FENDER
REMOVAL.............................94
INSTALLATION.........................94
FUEL FILL DOOR
REMOVAL.............................95
INSTALLATION.........................95
REAR FENDER
REMOVAL.............................95
INSTALLATION.........................95
REAR SPLASH SHIELD
REMOVAL.............................96
INSTALLATION.........................96
REAR WHEELHOUSE LINER
REMOVAL.............................96
INSTALLATION.........................96
CARGO BOX
REMOVAL.............................97
INSTALLATION.........................97
SIDE VIEW MIRROR
REMOVAL.............................97
INSTALLATION.........................98
SIDE VIEW MIRROR - LOW MOUNTED
REMOVAL.............................98
INSTALLATION.........................98
SIDE VIEW MIRROR GLASS
REMOVAL.............................98
INSTALLATION.........................98
EXTERIOR
DESCRIPTION
Exterior sheet metal components make up the
exterior of the vehicle. Some exterior metal systems
are welded assemblies, such as doors and hoods.
Some exterior trim items are made of composite.
OPERATION
The exterior is finished in various metal stampings
and composite moldings. These assemblies give the
vehicle a finished appearance and protect the occu-
pants from the elements. Some components are part
of the energy absorbing system used to protect the
occupants in collisions. The exterior sheet metal is
repairable and adjustable for fit and finish. Welded
and bonded component systems are adjustable as asystem. Trim components made of composite are
stamped with the type of material used.
DaimlerChrysler uses various fasteners to retain
trim items. At times, it is not possible to remove trim
items without damaging the fastener. If it is not pos-
sible to remove an item without damaging a compo-
nent, cut or break the fasteners and use new ones
when installing the component.BODY SIDE MOLDINGS
REMOVAL
(1) Warm the effected stick-on molding and body
metal to approximately 38ÉC (100ÉF) using a suitable
heat lamp or heat gun.
(2) Pull stick-on molding from painted surface
(Fig. 1) and (Fig. 2).
23 - 86 EXTERIORBR/BE
Page 2062 of 2255
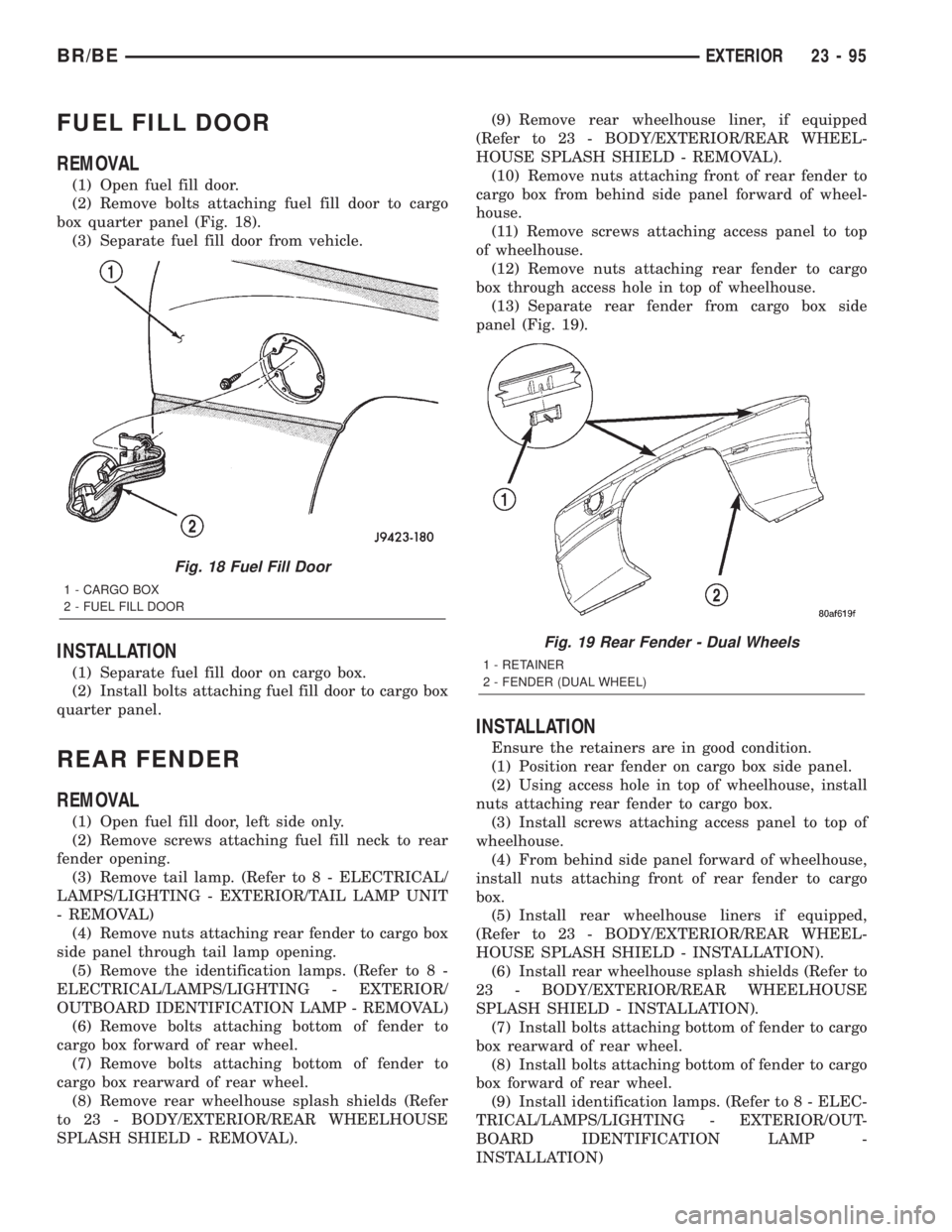
FUEL FILL DOOR
REMOVAL
(1) Open fuel fill door.
(2) Remove bolts attaching fuel fill door to cargo
box quarter panel (Fig. 18).
(3) Separate fuel fill door from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Separate fuel fill door on cargo box.
(2) Install bolts attaching fuel fill door to cargo box
quarter panel.
REAR FENDER
REMOVAL
(1) Open fuel fill door, left side only.
(2) Remove screws attaching fuel fill neck to rear
fender opening.
(3) Remove tail lamp. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/TAIL LAMP UNIT
- REMOVAL)
(4) Remove nuts attaching rear fender to cargo box
side panel through tail lamp opening.
(5) Remove the identification lamps. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/
OUTBOARD IDENTIFICATION LAMP - REMOVAL)
(6) Remove bolts attaching bottom of fender to
cargo box forward of rear wheel.
(7) Remove bolts attaching bottom of fender to
cargo box rearward of rear wheel.
(8) Remove rear wheelhouse splash shields (Refer
to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/REAR WHEELHOUSE
SPLASH SHIELD - REMOVAL).(9) Remove rear wheelhouse liner, if equipped
(Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/REAR WHEEL-
HOUSE SPLASH SHIELD - REMOVAL).
(10) Remove nuts attaching front of rear fender to
cargo box from behind side panel forward of wheel-
house.
(11) Remove screws attaching access panel to top
of wheelhouse.
(12) Remove nuts attaching rear fender to cargo
box through access hole in top of wheelhouse.
(13) Separate rear fender from cargo box side
panel (Fig. 19).
INSTALLATION
Ensure the retainers are in good condition.
(1) Position rear fender on cargo box side panel.
(2) Using access hole in top of wheelhouse, install
nuts attaching rear fender to cargo box.
(3) Install screws attaching access panel to top of
wheelhouse.
(4) From behind side panel forward of wheelhouse,
install nuts attaching front of rear fender to cargo
box.
(5) Install rear wheelhouse liners if equipped,
(Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/REAR WHEEL-
HOUSE SPLASH SHIELD - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install rear wheelhouse splash shields (Refer to
23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/REAR WHEELHOUSE
SPLASH SHIELD - INSTALLATION).
(7) Install bolts attaching bottom of fender to cargo
box rearward of rear wheel.
(8) Install bolts attaching bottom of fender to cargo
box forward of rear wheel.
(9) Install identification lamps. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/OUT-
BOARD IDENTIFICATION LAMP -
INSTALLATION)
Fig. 18 Fuel Fill Door
1 - CARGO BOX
2 - FUEL FILL DOOR
Fig. 19 Rear Fender - Dual Wheels
1 - RETAINER
2 - FENDER (DUAL WHEEL)
BR/BEEXTERIOR 23 - 95
Page 2063 of 2255
(10) Using tail lamp opening, install nuts attach-
ing rear fender to cargo box side panel.
(11) Install tail lamp. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/TAIL LAMP UNIT
- INSTALLATION)
(12) Install screws attaching fuel fill neck to rear
fender opening.
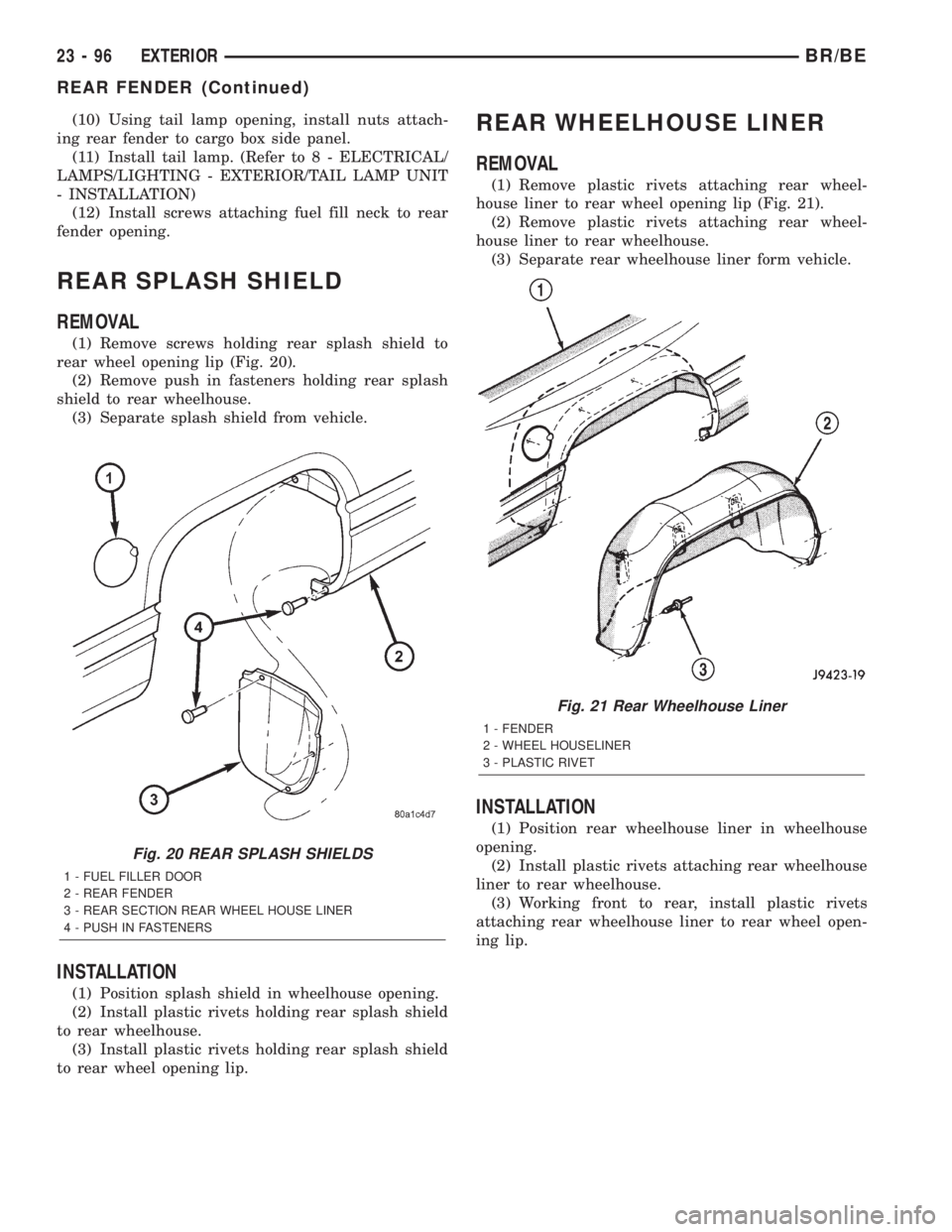
REAR SPLASH SHIELD
REMOVAL
(1) Remove screws holding rear splash shield to
rear wheel opening lip (Fig. 20).
(2) Remove push in fasteners holding rear splash
shield to rear wheelhouse.
(3) Separate splash shield from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position splash shield in wheelhouse opening.
(2) Install plastic rivets holding rear splash shield
to rear wheelhouse.
(3) Install plastic rivets holding rear splash shield
to rear wheel opening lip.
REAR WHEELHOUSE LINER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove plastic rivets attaching rear wheel-
house liner to rear wheel opening lip (Fig. 21).
(2) Remove plastic rivets attaching rear wheel-
house liner to rear wheelhouse.
(3) Separate rear wheelhouse liner form vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position rear wheelhouse liner in wheelhouse
opening.
(2) Install plastic rivets attaching rear wheelhouse
liner to rear wheelhouse.
(3) Working front to rear, install plastic rivets
attaching rear wheelhouse liner to rear wheel open-
ing lip.
Fig. 20 REAR SPLASH SHIELDS
1 - FUEL FILLER DOOR
2 - REAR FENDER
3 - REAR SECTION REAR WHEEL HOUSE LINER
4 - PUSH IN FASTENERS
Fig. 21 Rear Wheelhouse Liner
1 - FENDER
2 - WHEEL HOUSELINER
3 - PLASTIC RIVET
23 - 96 EXTERIORBR/BE
REAR FENDER (Continued)
Page 2064 of 2255

CARGO BOX
REMOVAL
CAUTION: The bolts attaching the cargo box to the
frame are specially coated to provide a locking action.
These bolts are not reusable and must be replaced
each time the cargo box is removed or replaced.
(1) Open fuel fill door.
(2) Remove screws attaching fuel fill neck adaptor
to cargo box side wall.
(3) Separate fuel fill neck from cargo box.
(4) Disengage tail lamp wire connector from main
body harness at left rear frame rail.
(5) Remove bolts attaching cargo box to frame rails
(Fig. 22).
(6) Using a suitable lifting device, separate cargo
box from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Using a suitable lifting device, position cargo
box on vehicle.
(2) Installnewbolts attaching cargo box to frame
rails. Tighten bolts to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Engage tail lamp wire connector to main body
harness at left rear frame rail.
(4) Install fuel fill neck.
SIDE VIEW MIRROR
REMOVAL
(1) Remove door trim panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/
DOOR - FRONT/TRIM PANEL - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove mirror flag door seal (Fig. 23).
(3) Disengage power mirror wire connector from
door harness, if equipped (Fig. 24).
(4) Remove nuts attaching sideview mirror to door
frame (Fig. 25).
(5) Separate harness grommet form door frame, if
equipped.
(6) Separate sideview mirror from vehicle.
Fig. 22 Cargo Box
1 - CARGO BOX
2 - FRAME
3 - BOLT
4 - AXLE
5 - BOLT
Fig. 23 Mirror Flag Door Seal
1 - MIRROR
2 - MIRROR FLAG SEAL
Fig. 24 Sideview MirrorÐPower
1 - POWER MIRROR
2 - NUT
3 - CONNECTOR
BR/BEEXTERIOR 23 - 97
Page 2180 of 2255

EMISSIONS CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL.................1
DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST
MODE...............................1
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE...............................2
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODES..............................2
DESCRIPTION - TASK MANAGER.........17
DESCRIPTION - MONITORED SYSTEMS . . . 17
DESCRIPTION - TRIP DEFINITION........19
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS -
GAS ENGINES.......................19DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS -
DIESEL ENGINES.....................20
OPERATION
OPERATION - GAS ENGINES............20
OPERATION - DIESEL..................20
OPERATION - TASK MANAGER..........21
OPERATION - NON-MONITORED
CIRCUITS - GAS ENGINES..............24
OPERATION - NON-MONITORED
CIRCUITS - DIESEL....................24
AIR INJECTION.........................26
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS................32
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL
Two different modules are used for powertrain con-
trol with the diesel engine. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) is used primarily for charging system,
transmission, A/C compressor clutch operation and
speed control functions. The Engine Control Module
(ECM) is used to control thefuel and emissions
systems.The PCM is located in the right/rear of
engine compartment (Fig. 1). The ECM is bolted to
the left side of the engine cylinder block (Fig. 2).
DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. Connectthe DRB scan tool to the data link connector and
access the state display screen. Then access either
State Display Inputs and Outputs or State Display
Sensors.
Fig. 1 Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Location
1 - PCM MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
2 - POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
3 - (3) 32±WAY CONNECTORS
BR/BEEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 1
Page 2181 of 2255

DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE
The Circuit Actuation Test Mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) may not internally recognize.
The PCM attempts to activate these outputs and
allow an observer to verify proper operation. Most of
the tests provide an audible or visual indication of
device operation (click of relay contacts, fuel spray,
etc.). Except for intermittent conditions, if a device
functions properly during testing, assume the device,its associated wiring, and driver circuit work cor-
rectly. Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
connector and access the Actuators screen.
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates the
PCM has recognized an abnormal condition in the
system.
Remember that DTC's are the results of a sys-
tem or circuit failure, but do not directly iden-
tify the failed component or components.
NOTE: For a list of DTC's, refer to the charts in this
section.
BULB CHECK
Each time the ignition key is turned to the ON
position, the malfunction indicator (check engine)
lamp on the instrument panel should illuminate for
approximately 2 seconds then go out. This is done for
a bulb check.
OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
(4) To erase DTC's, use the ªErase Trouble Codeº
data screen on the DRB scan tool.Do not erase any
DTC's until problems have been investigated
and repairs have been performed.
Fig. 2 Engine Control Module (ECM) Location
1 - ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
2 - HEX HEADED BOLT
3 - FUEL TRANSFER PUMP
4 - MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
5 - 50±WAY CONNECTOR
25 - 2 EMISSIONS CONTROLBR/BE
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2183 of 2255
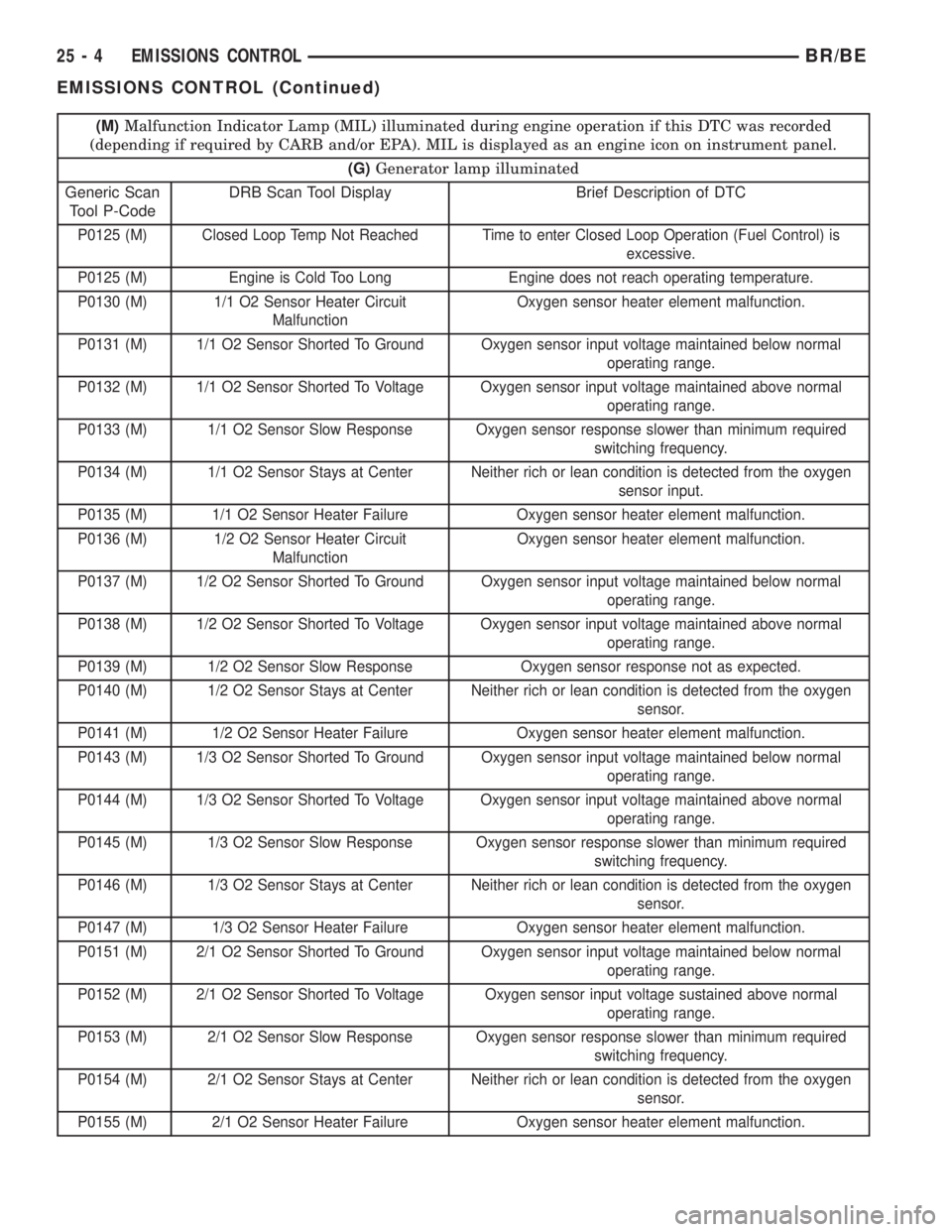
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0125 (M) Closed Loop Temp Not Reached Time to enter Closed Loop Operation (Fuel Control) is
excessive.
P0125 (M) Engine is Cold Too Long Engine does not reach operating temperature.
P0130 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionOxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0131 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0132 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0133 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0134 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor input.
P0135 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0136 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionOxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0137 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0138 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0139 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response not as expected.
P0140 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
P0141 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0143 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0144 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0145 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0146 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
P0147 (M) 1/3 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0151 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0152 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage sustained above normal
operating range.
P0153 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0154 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
P0155 (M) 2/1 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
25 - 4 EMISSIONS CONTROLBR/BE
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2184 of 2255
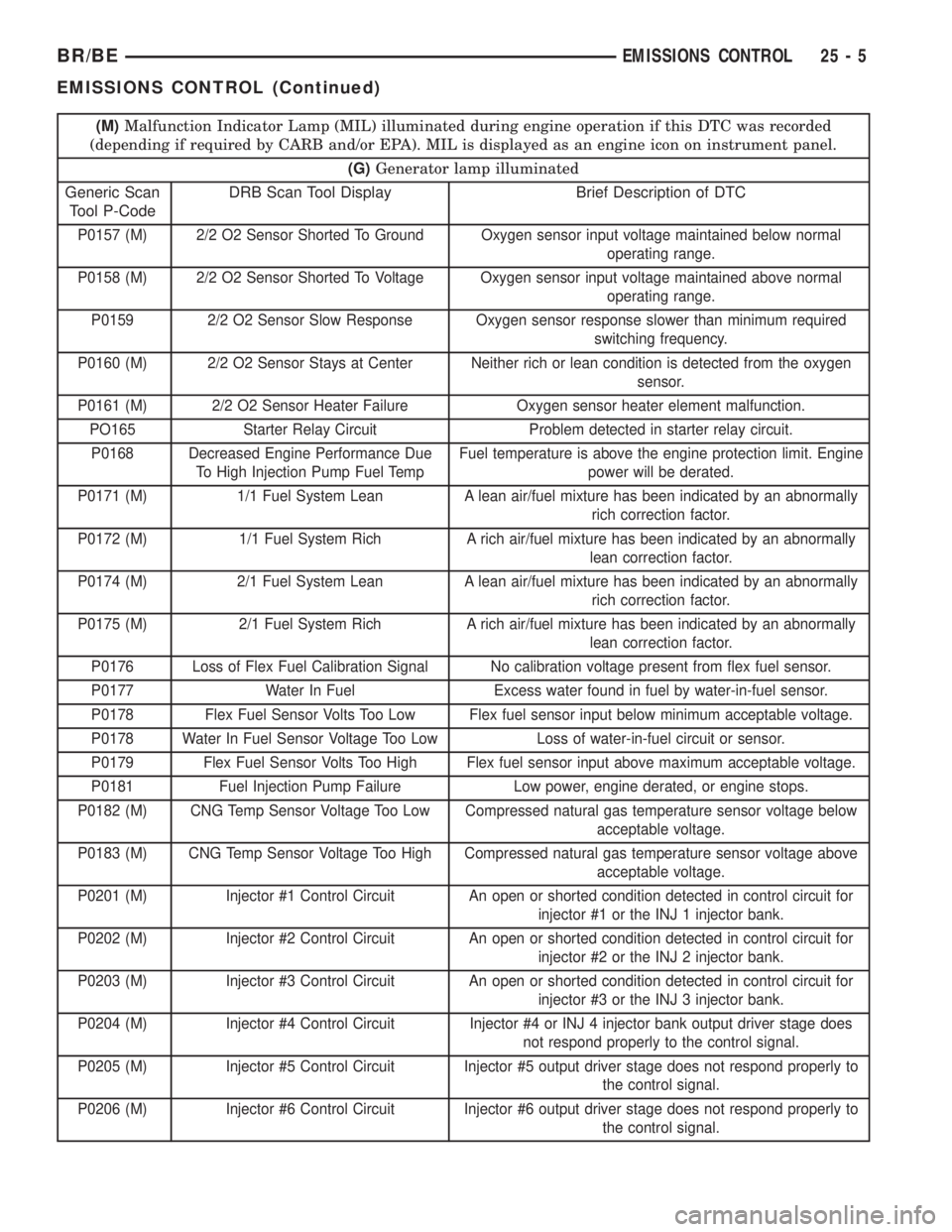
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0157 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0158 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0159 2/2 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0160 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor.
P0161 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
PO165 Starter Relay Circuit Problem detected in starter relay circuit.
P0168 Decreased Engine Performance Due
To High Injection Pump Fuel TempFuel temperature is above the engine protection limit. Engine
power will be derated.
P0171 (M) 1/1 Fuel System Lean A lean air/fuel mixture has been indicated by an abnormally
rich correction factor.
P0172 (M) 1/1 Fuel System Rich A rich air/fuel mixture has been indicated by an abnormally
lean correction factor.
P0174 (M) 2/1 Fuel System Lean A lean air/fuel mixture has been indicated by an abnormally
rich correction factor.
P0175 (M) 2/1 Fuel System Rich A rich air/fuel mixture has been indicated by an abnormally
lean correction factor.
P0176 Loss of Flex Fuel Calibration Signal No calibration voltage present from flex fuel sensor.
P0177 Water In Fuel Excess water found in fuel by water-in-fuel sensor.
P0178 Flex Fuel Sensor Volts Too Low Flex fuel sensor input below minimum acceptable voltage.
P0178 Water In Fuel Sensor Voltage Too Low Loss of water-in-fuel circuit or sensor.
P0179 Flex Fuel Sensor Volts Too High Flex fuel sensor input above maximum acceptable voltage.
P0181 Fuel Injection Pump Failure Low power, engine derated, or engine stops.
P0182 (M) CNG Temp Sensor Voltage Too Low Compressed natural gas temperature sensor voltage below
acceptable voltage.
P0183 (M) CNG Temp Sensor Voltage Too High Compressed natural gas temperature sensor voltage above
acceptable voltage.
P0201 (M) Injector #1 Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in control circuit for
injector #1 or the INJ 1 injector bank.
P0202 (M) Injector #2 Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in control circuit for
injector #2 or the INJ 2 injector bank.
P0203 (M) Injector #3 Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in control circuit for
injector #3 or the INJ 3 injector bank.
P0204 (M) Injector #4 Control Circuit Injector #4 or INJ 4 injector bank output driver stage does
not respond properly to the control signal.
P0205 (M) Injector #5 Control Circuit Injector #5 output driver stage does not respond properly to
the control signal.
P0206 (M) Injector #6 Control Circuit Injector #6 output driver stage does not respond properly to
the control signal.
BR/BEEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 5
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2185 of 2255
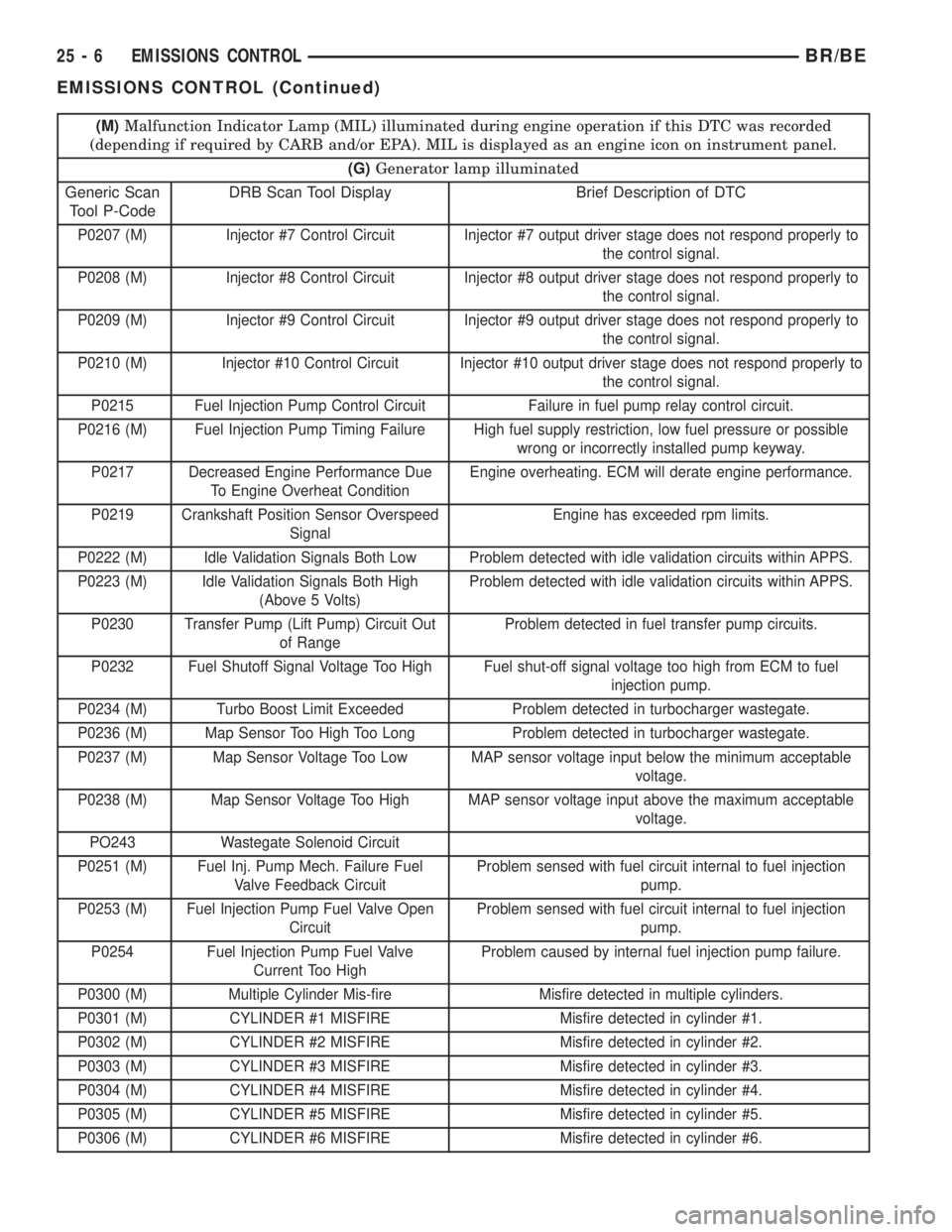
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0207 (M) Injector #7 Control Circuit Injector #7 output driver stage does not respond properly to
the control signal.
P0208 (M) Injector #8 Control Circuit Injector #8 output driver stage does not respond properly to
the control signal.
P0209 (M) Injector #9 Control Circuit Injector #9 output driver stage does not respond properly to
the control signal.
P0210 (M) Injector #10 Control Circuit Injector #10 output driver stage does not respond properly to
the control signal.
P0215 Fuel Injection Pump Control Circuit Failure in fuel pump relay control circuit.
P0216 (M) Fuel Injection Pump Timing Failure High fuel supply restriction, low fuel pressure or possible
wrong or incorrectly installed pump keyway.
P0217 Decreased Engine Performance Due
To Engine Overheat ConditionEngine overheating. ECM will derate engine performance.
P0219 Crankshaft Position Sensor Overspeed
SignalEngine has exceeded rpm limits.
P0222 (M) Idle Validation Signals Both Low Problem detected with idle validation circuits within APPS.
P0223 (M) Idle Validation Signals Both High
(Above 5 Volts)Problem detected with idle validation circuits within APPS.
P0230 Transfer Pump (Lift Pump) Circuit Out
of RangeProblem detected in fuel transfer pump circuits.
P0232 Fuel Shutoff Signal Voltage Too High Fuel shut-off signal voltage too high from ECM to fuel
injection pump.
P0234 (M) Turbo Boost Limit Exceeded Problem detected in turbocharger wastegate.
P0236 (M) Map Sensor Too High Too Long Problem detected in turbocharger wastegate.
P0237 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too Low MAP sensor voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0238 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too High MAP sensor voltage input above the maximum acceptable
voltage.
PO243 Wastegate Solenoid Circuit
P0251 (M) Fuel Inj. Pump Mech. Failure Fuel
Valve Feedback CircuitProblem sensed with fuel circuit internal to fuel injection
pump.
P0253 (M) Fuel Injection Pump Fuel Valve Open
CircuitProblem sensed with fuel circuit internal to fuel injection
pump.
P0254 Fuel Injection Pump Fuel Valve
Current Too HighProblem caused by internal fuel injection pump failure.
P0300 (M) Multiple Cylinder Mis-fire Misfire detected in multiple cylinders.
P0301 (M) CYLINDER #1 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #1.
P0302 (M) CYLINDER #2 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #2.
P0303 (M) CYLINDER #3 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #3.
P0304 (M) CYLINDER #4 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #4.
P0305 (M) CYLINDER #5 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #5.
P0306 (M) CYLINDER #6 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #6.
25 - 6 EMISSIONS CONTROLBR/BE
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2186 of 2255

(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0307 (M) CYLINDER #7 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #7
P0308 (M) CYLINDER #8 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #8.
P0309 (M) CYLINDER #9 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #9.
P0310 (M) CYLINDER #10 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #10.
P0320 (M) No Crank Referance Signal at PCM No reference signal (crankshaft position sensor) detected
during engine cranking.
P0320 (M) No RPM Signal to PCM (Crankshaft
Position Sensor Signal to JTEC)A CKP signal has not been detected at the PCM.
P0325 Knock Sensor #1 Circuit Knock sensor (#1) signal above or below minimum
acceptable threshold voltage at particular engine speeds.
P0330 Knock Sensor #2 Circuit Knock sensor (#2) signal above or below minimum
acceptable threshold voltage at particular engine speeds.
P0336 (M) Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
SignalProblem with voltage signal from CKP.
P0340 (M) No Cam Signal At PCM No fuel sync
P0341 (M) Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
SignalProblem with voltage signal from CMP.
P0350 Ignition Coil Draws Too Much Current A coil (1-5) is drawing too much current.
P0351 (M) Ignition Coil # 1 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0352 (M) Ignition Coil # 2 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0353 (M) Ignition Coil # 3 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0354 (M) Ignition Coil # 4 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (High Impedance).
P0355 (M) Ignition Coil # 5 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (High Impedance).
P0356 (M) Ignition Coil # 6 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0357 (M) Ignition Coil # 7 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0358 (M) Ignition Coil # 8 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0370 Fuel Injection Pump Speed/Position
Sensor Sig LostProblem caused by internal fuel injection pump failure.
P0380 (M) Intake Air Heater Relay #1 Control
CircuitProblem detected in #1 air heater solenoid/relay circuit (not
heater element)
P0381 (M) Wait To Start Lamp Inoperative Problem detected in wait-to-start bulb circuit.
P0382 (M) Intake Air Heater Relay #2 Control
CircuitProblem detected in #2 air heater solenoid/relay circuit (not
heater element)
P0387 Crankshaft Position Sensor Supply
Voltage Too LowCKP sensor voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
BR/BEEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 7
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)