power DODGE RAM 2002 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 216 of 2255

(4) Clamp hose shut between vacuum source and
check valve.
(5) Stop engine and observe vacuum gauge.
(6) If vacuum drops more than one inch HG (33
millibars) within 15 seconds, booster diaphragm or
check valve is faulty.
POWER BOOSTER CHECK VALVE TEST
(1) Disconnect vacuum hose from check valve.
(2) Remove check valve and valve seal from
booster.
(3) Use a hand operated vacuum pump for test.
(4) Apply 15-20 inches vacuum at large end of
check valve (Fig. 48).
(5) Vacuum should hold steady. If gauge on pump
indicates vacuum loss, check valve is faulty and
should be replaced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MASTER CYLINDER
BLEEDING
A new master cylinder should be bled before instal-
lation on the vehicle. Required bleeding tools include
bleed tubes and a wood dowel to stroke the pistons.
Bleed tubes can be fabricated from brake line.
(1) Mount master cylinder in vise.
(2) Attach bleed tubes to cylinder outlet ports.
Then position each tube end into reservoir (Fig. 49).(3) Fill reservoir with fresh brake fluid.
(4) Press cylinder pistons inward with wood dowel.
Then release pistons and allow them to return under
spring pressure. Continue bleeding operations until
air bubbles are no longer visible in fluid.
REMOVAL
(1) Pump the brake pedal several times to deplete
booster vacuum reserve.
(2) Remove brake lines from the master cylinder
(Fig. 50) .
(3) Remove mounting nuts from the master cylin-
der (Fig. 50) .
(4) Remove the master cylinder.
Fig. 47 Typical Booster Vacuum Test Connections
1 - TEE FITTING
2 - SHORT CONNECTING HOSE
3 - CHECK VALVE
4 - CHECK VALVE HOSE
5 - CLAMP TOOL
6 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
7 - VACUUM GAUGE
Fig. 48 Vacuum Check Valve And Seal
1 - BOOSTER CHECK VALVE
2 - APPLY TEST VACUUM HERE
3 - VALVE SEAL
Fig. 49 Master Cylinder Bleeding±Typical
1 - BLEEDING TUBES
2 - RESERVOIR
BR/BEBRAKES - BASE 5 - 27
MASTER CYLINDER (Continued)
Page 224 of 2255

BRAKES - ABS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................36
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ANTILOCK
BRAKES............................36
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - RWAL SERVICE
PRECAUTIONS.......................36
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BLEEDING ABS
BRAKE SYSTEM......................36
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................37
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................38
OPERATION...........................38
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4X2......................39REMOVAL - 4X4......................39
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4X2...................39
INSTALLATION - 4X4...................39
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WHEEL
SPEED SENSOR......................40
REMOVAL.............................40
INSTALLATION.........................40
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT)
DESCRIPTION.........................40
OPERATION...........................40
REMOVAL.............................41
INSTALLATION.........................41
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION
The antilock brake system (ABS) is an electroni-
cally operated, all wheel brake control system. 2500
and 3500 vehicles have Electronic Brake Distribution
(EBD) designed into the systen which eliminates the
combination/proportioning valve.
The system is designed to prevent wheel lockup
and maintain steering control during periods of high
wheel slip when braking. Preventing lockup is accom-
plished by modulating fluid pressure to the wheel
brake units.
The hydraulic system is a three channel design.
The front wheel brakes are controlled individually
and the rear wheel brakes in tandem (Fig. 1). The
ABS electrical system is separate from other electri-
cal circuits in the vehicle. A specially programmed
controller antilock brake unit operates the system
components.
ABS system major components include:
²Controller Antilock Brakes (CAB)
²Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU)
²Wheel Speed Sensors (WSS)²ABS Warning Light
Fig. 1 Antilock Brake System
1 - MASTER CYLINDER AND RESERVOIR
2 - POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
3 - WIRES TO WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
4 - RIGHT REAR WHEEL
5 - LEFT REAR WHEEL
6 - HYDRAULIC BRAKE LINES TO WHEELS
7 - COMBINATION VALVE
8 - HARNESS
9 - RIGHT FRONT WHEEL
10 - LEFT FRONT WHEEL
11 - CAB/HCU
BR/BEBRAKES - ABS 5 - 35
Page 225 of 2255

OPERATION
Battery voltage is supplied to the CAB when a
speed of 15 miles per hour is reached. The CAB per-
forms a system initialization procedure at this point.
Initialization consists of a static and dynamic self
check of system electrical components.
The static and dynamic checks occurs at ignition
start up. During the dynamic check, the CAB briefly
cycles the pump and solenoids to verify operation. An
audible noise may be heard during this self check.
This noise should be considered normal.
If an ABS component exhibits a fault during ini-
tialization, the CAB illuminates the amber warning
light and registers a fault code in the microprocessor
memory.
The CAB monitors wheel speed sensor inputs con-
tinuously while the vehicle is in motion. However,
the CAB will not activate any ABS components as
long as sensor inputs indicate normal braking.
During normal braking, the master cylinder, power
booster and wheel brake units all function as they
would in a vehicle without ABS. The HCU compo-
nents are not activated.
The purpose of the antilock system is to prevent
wheel lockup during periods of high wheel slip. Pre-
venting lockup helps maintain vehicle braking action
and steering control.
The antilock CAB activates the system whenever
sensor signals indicate periods of wheel slip. Periods
of wheel slip occur when brake stops involve high
pedal pressure and rate of vehicle deceleration.
The antilock system prevents lockup during a
wheel slip condition by modulating fluid apply pres-
sure to the wheel brake units.
Brake fluid apply pressure is modulated according
to wheel speed, degree of slip and rate of decelera-
tion. Sensors at each front wheel convert wheel speed
into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted
to the CAB for processing and determination of
wheel slip and deceleration rate.
The ABS system has three fluid pressure control
channels. The front brakes are controlled separately
and the rear brakes in tandem. A speed sensor input
signal indicating a wheel slip condition activates the
CAB antilock program.
There are Two solenoid valves (Isolation and Dump
valve) which are used in each antilock control chan-
nel. The valves are all located within the HCU valve
body and work in pairs to either increase, hold, or
decrease apply pressure as needed in the individual
control channels.
During an ABS stop the ISO valve actuates, Stop-
ping anymore pressure build Ðup to the calipers.
Then the Dump valve dumps off pressure until the
wheel unlocks. This will continue until the wheels
quit slipping altogether.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ANTILOCK
BRAKES
The ABS brake system performs several self-tests
every time the ignition switch is turned on and the
vehicle is driven. The CAB monitors the systems
input and output circuits to verify the system is oper-
ating correctly. If the on board diagnostic system
senses that a circuit is malfunctioning the system
will set a trouble code in its memory.
NOTE: An audible noise may be heard during the
self-test. This noise should be considered normal.
NOTE: The MDS or DRB III scan tool is used to
diagnose the ABS system. For additional informa-
tion refer to the Antilock Brake section in Group
8W. For test procedures refer to the Chassis Diag-
nostic Manual.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - RWAL SERVICE
PRECAUTIONS
The RWAL uses an electronic control module, the
CAB. This module is designed to withstand normal
current draws associated with vehicle operation.
Care must be taken to avoid overloading the CAB
circuits.In testing for open or short circuits, do
not ground or apply voltage to any of the cir-
cuits unless instructed to do so for a diagnostic
procedure.These circuits should only be tested
using a high impedance multi-meter or the DRB
tester as described in this section. Power should
never be removed or applied to any control module
with the ignition in the ON position. Before removing
or connecting battery cables, fuses, or connectors,
always turn the ignition to the OFF position.
CAUTION: Use only factory wiring harnesses. Do
not cut or splice wiring to the brake circuits. The
addition of after-market electrical equipment (car
phone, radar detector, citizen band radio, trailer
lighting, trailer brakes, ect.) on a vehicle equipped
with antilock brakes may affect the function of the
antilock brake system.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BLEEDING ABS
BRAKE SYSTEM
ABS system bleeding requires conventional bleed-
ing methods plus use of the DRB scan tool. The pro-
cedure involves performing a base brake bleeding,
followed by use of the scan tool to cycle and bleed the
5 - 36 BRAKES - ABSBR/BE
BRAKES - ABS (Continued)
Page 229 of 2255

NOTE: Check the sensor wire routing. Be sure the
wire is clear of all chassis components and is not
twisted or kinked at any spot.
(6) Install the tire and wheel assembly.
(7) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
(8) Reconnect the ABS wheel speed sensor wire
electrical connector inside the engine compartment.
(9) Apply the brakes several times to seat the
brake shoes and caliper piston. Do not move the vehi-
cle until a firm brake pedal is obtained.
(10) Verify the wheel speed sensor operation with
a scan tool.
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WHEEL
SPEED SENSOR
Diagnosis of base brake conditions which are
mechanical in nature should be performed first. This
includes brake noise, lack of power assist, parking
brake, or vehicle vibration during normal braking.
The Antilock brake system performs several self-
tests every time the ignition switch is turned on and
the vehicle is driven. The CAB monitors the system
inputs and outputs circuits to verify the system is
operating properly. If the CAB senses a malfunction
in the system it will set a DTC into memory and trig-
ger the warning lamp.
NOTE: The MDS or DRB III scan tool is used to
diagnose the Antilock Brake system. For test proce-
dures refer to the Chassis Diagnostic Manual.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove brake line mounting nut and remove
the brake line from the sensor stud.
(3) Remove mounting stud from the sensor and
shield (Fig. 6) .
(4) Remove sensor and shield from differential
housing.
(5) Disconnect sensor wire harness and remove
sensor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Connect harness to sensor.Be sure seal is
securely in place between sensor and wiring
connector.
(2) Install O-ring on sensor (if removed).
(3) Insert sensor in differential housing.
(4) Install sensor shield.
(5) Install the sensor mounting stud and tighten to
24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).(6) Install the brake line on the sensor stud and
install the nut.
(7) Lower vehicle.
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL
UNIT)
DESCRIPTION
The hydraulic control unit (HCU) consists of a
valve body, pump, two accumulators and a motor.
The assembly is mounted on the driverside inner
fender under the hood.
OPERATION
The pump, motor, and accumulators are combined
into an assembly attached to the valve body. The
accumulators store the extra fluid which had to be
dumped from the brakes. This is done to prevent the
wheels from locking up. The pump provides the fluid
volume needed and is operated by a DC type motor.
The motor is controlled by the CAB.
During normal braking, the HCU solenoid valves
and pump are not activated. The master cylinder and
power booster operate the same as a vehicle without
an ABS brake system.
The valve body contains the solenoid valves. The
valves modulate brake pressure during antilock brak-
ing and are controlled by the CAB.
The HCU provides three channel pressure control
to the front and rear brakes. One channel controls
the rear wheel brakes in tandem. The two remaining
channels control the front wheel brakes individually.
Fig. 6 Rear Speed Sensor Mounting
1 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
2 - AXLE
5 - 40 BRAKES - ABSBR/BE
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (Continued)
Page 232 of 2255

CLUTCH
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................2
WARNING.............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH........2
SPECIFICATIONS - CLUTCH...............7
CLUTCH DISC
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................8
CLUTCH HOUSING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH
HOUSING............................9
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................11
CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12FLYWHEEL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLYWHEEL.....13
DISASSEMBLY.........................13
ASSEMBLY............................14
PILOT BEARING
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................14
CLUTCH PEDAL
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................15
LINKAGE
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................16
CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................17
OPERATION...........................17
CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The clutch mechanism consists of a flywheel, dry-
type disc, diaphragm style pressure plate (Fig. 1) and
hydraulic linkage. The flywheel is bolted to the rear
flange of the crankshaft. The clutch pressure plate is
bolted to the flywheel with the clutch disc between
these two components. The clutch system provides
the mechanical, link between the engine and the
transmission. The system is designed to transfer the
torque output of the engine, to the transmission
while isolating the transmission from the engine fir-
ing pulses to minimize concerns such as gear rattle.
Fig. 1 ENGINE POWERFLOW
BR/BECLUTCH 6 - 1
Page 254 of 2255

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)
COOLING SYSTEM RELATED DIAGNOSTICS
The powertrain control module (PCM) has been
programmed to monitor certain cooling system com-
ponents:
²If the engine has remained cool for too long a
period, such as with a stuck open thermostat, a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be set.
²If an open or shorted condition has developed in
the relay circuit controlling the electric radiator fan,
a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be set.
If the problem is sensed in a monitored circuit
often enough to indicated an actual problem, a DTC
is stored. The DTC will be stored in the PCM mem-
ory for eventual display to the service technician.
(Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL - DESCRIP-
TION).
ACCESSING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
To read DTC's and to obtain cooling system data,
(Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL - DESCRIP-
TION).
ERASING TROUBLE CODES
After the problem has been repaired, use the DRB
scan tool to erase a DTC. Refer to the appropriate
Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service informa-
tion for operation of the DRB scan tool.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
LEAKS
ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT METHOD
A leak detection additive is available through the
parts department that can be added to cooling sys-
tem. The additive is highly visible under ultraviolet
light (black light). Pour one ounce of additive into
cooling system. Place heater control unit in HEAT
position. Start and operate engine until radiator
upper hose is warm to touch. Aim the commercially
available black light tool at components to be
checked. If leaks are present, black light will cause
additive to glow a bright green color.
The black light can be used in conjunction with a
pressure tester to determine if any external leaks
exist (Fig. 5).
PRESSURE TESTER METHOD
The engine should be at normal operating temper-
ature. Recheck the system cold if cause of coolant
loss is not located during the warm engine examina-
tion.WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING.
Carefully remove radiator pressure cap from filler
neck and check coolant level. Push down on cap to
disengage it from stop tabs. Wipe inside of filler neck
and examine lower inside sealing seat for nicks,
cracks, paint, dirt and solder residue. Inspect radia-
tor-to- reserve/overflow tank hose for internal
obstructions. Insert a wire through the hose to be
sure it is not obstructed.
Inspect cams on outside of filler neck. If cams are
damaged, seating of pressure cap valve and tester
seal will be affected.
Attach pressure tester (7700 or an equivalent) to
radiator filler neck (Fig. 6).
Operate tester pump to apply 103.4 kPa (15 psi)
pressure to system. If hoses enlarge excessively or
bulges while testing, replace as necessary. Observe
gauge pointer and determine condition of cooling sys-
tem according to following criteria:
Holds Steady:If pointer remains steady for two
minutes, serious coolant leaks are not present in sys-
tem. However, there could be an internal leak that
does not appear with normal system test pressure. If
it is certain that coolant is being lost and leaks can-
not be detected, inspect for interior leakage or per-
form Internal Leakage Test.
Drops Slowly:Indicates a small leak or seepage
is occurring. Examine all connections for seepage or
slight leakage with a flashlight. Inspect radiator,
Fig. 5 Leak Detection Using Black LightÐTypical
1 - TYPICAL BLACK LIGHT TOOL
BR/BECOOLING 7 - 5
COOLING (Continued)
Page 268 of 2255

ACCESSORY DRIVE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BELT TENSIONERS - 5.9L
DESCRIPTION.........................19
OPERATION...........................19
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................20
BELT TENSIONERS - 8.0L
DESCRIPTION.........................20
OPERATION...........................21
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................22
BELT TENSIONERS - 5.9L DIESEL
DESCRIPTION.........................23
OPERATION...........................23
REMOVAL.............................23
INSTALLATION.........................23
DRIVE BELTS - 5.9L
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ACCESSORY
DRIVE BELT.........................24
REMOVAL.............................26INSTALLATION.........................26
DRIVE BELTS - 8.0L
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐACCESSORY
DRIVE BELT.........................27
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29
DRIVE BELTS - 5.9L DIESEL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐACCESSORY
DRIVE BELT.........................30
REMOVAL.............................32
INSTALLATION.........................32
VACUUM PUMP - 5.9L DIESEL
DESCRIPTION.........................33
OPERATION...........................34
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐVACUUM PUMP
OUTPUT............................34
REMOVAL.............................34
INSTALLATION.........................36
BELT TENSIONERS - 5.9L
DESCRIPTION
Correct drive belt tension is required to ensure
optimum performance of the belt driven engine acces-
sories. If specified tension is not maintained, belt
slippage may cause; engine overheating, lack of
power steering assist, loss of air conditioning capac-
ity, reduced generator output rate, and greatly
reduced belt life.
It is not necessary to adjust belt tension on the
5.9L engines. These engines are equipped with an
automatic belt tensioner (Fig. 1). The tensioner main-
tains correct belt tension at all times. Due to use of
this belt tensioner, do not attempt to use a belt ten-
sion gauge on 5.9L engines.
OPERATION
The automatic belt tensioner maintains belt ten-
sion by using internal spring pressure, a pivoting
arm and pulley to press against the drive belt.
REMOVAL
WARNING: BECAUSE OF HIGH SPRING PRES-
SURE, DO NOT ATTEMPT TO DISASSEMBLE AUTO-
MATIC TENSIONER. UNIT IS SERVICED AS AN
ASSEMBLY (EXCEPT FOR PULLEY).(1) Remove accessory drive belt. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(2) Disconnect wiring and secondary cable from
ignition coil.
(3) Remove ignition coil from coil mounting
bracket (two bolts). Do not remove coil mounting
bracket from cylinder head.
Fig. 1 Automatic Belt Tensioner - 5.9L Engines
1 - AUTOMATIC TENSIONER
2 - COIL AND BRACKET
3 - SCREW AND WASHER
BR/BEACCESSORY DRIVE 7 - 19
Page 269 of 2255

(4) Remove tensioner assembly from mounting
bracket (one nut) (Fig. 2).
(5) Remove pulley bolt. Remove pulley from ten-
sioner.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install pulley and pulley bolt to tensioner.
Tighten bolt to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install tensioner assembly to mounting
bracket. An indexing tab is located on back of ten-
sioner. Align this tab to slot in mounting bracket.
Tighten nut to 67 N´m (50 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect all wiring to ignition coil.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to coil case, coil
mounting bolts must be torqued.(4) Install coil to coil bracket. If nuts and bolts are
used to secure coil to coil bracket, tighten to 11 N´m
(100 in. lbs.) torque. If coil mounting bracket has
been tapped for coil mounting bolts, tighten bolts to 5
N´m (50 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install drive belt. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/AC-
CESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLA-
TION).
(6) Check belt indexing marks (Fig. 2).
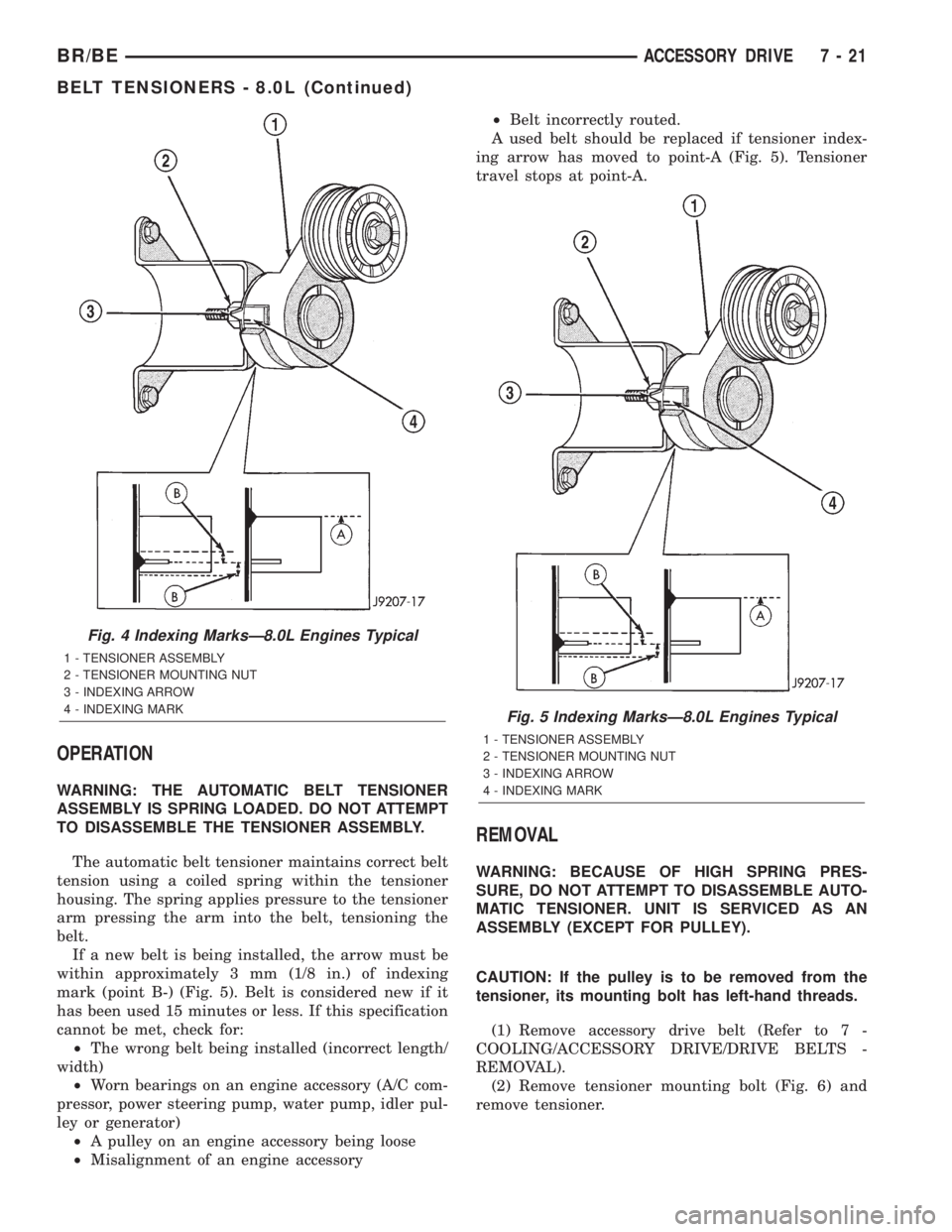
BELT TENSIONERS - 8.0L
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: Do not attempt to check belt tension with
a belt tension gauge on vehicles equipped with an
automatic belt tensioner.
Drive belts on 8.0L engines are equipped with a
spring loaded automatic belt tensioner (Fig. 3) This
belt tensioner will be used with all belt configura-
tions, such as with or without power steering or air
conditioning.
The tensioner is equipped with an indexing arrow
(Fig. 4) on back of tensioner and an indexing mark
on tensioner housing.
Fig. 2 Tensioner Indexing Marks and Mounting Nut
1 - TENSIONER ASSEMBLY
2 - TENSIONER MOUNTING NUT
3 - INDEXING ARROW
4 - INDEXING MARK
Fig. 3 Belt TensionerÐ8.0L V-10 Engines
1 - PULLEY BOLT
2 - IDLER PULLEY
3 - TENSIONER PULLEY
4 - TENSIONER
5 - TENSIONER MOUNTING BOLT
7 - 20 ACCESSORY DRIVEBR/BE
BELT TENSIONERS - 5.9L (Continued)
Page 270 of 2255
OPERATION
WARNING: THE AUTOMATIC BELT TENSIONER
ASSEMBLY IS SPRING LOADED. DO NOT ATTEMPT
TO DISASSEMBLE THE TENSIONER ASSEMBLY.
The automatic belt tensioner maintains correct belt
tension using a coiled spring within the tensioner
housing. The spring applies pressure to the tensioner
arm pressing the arm into the belt, tensioning the
belt.
If a new belt is being installed, the arrow must be
within approximately 3 mm (1/8 in.) of indexing
mark (point B-) (Fig. 5). Belt is considered new if it
has been used 15 minutes or less. If this specification
cannot be met, check for:
²The wrong belt being installed (incorrect length/
width)
²Worn bearings on an engine accessory (A/C com-
pressor, power steering pump, water pump, idler pul-
ley or generator)
²A pulley on an engine accessory being loose
²Misalignment of an engine accessory²Belt incorrectly routed.
A used belt should be replaced if tensioner index-
ing arrow has moved to point-A (Fig. 5). Tensioner
travel stops at point-A.
REMOVAL
WARNING: BECAUSE OF HIGH SPRING PRES-
SURE, DO NOT ATTEMPT TO DISASSEMBLE AUTO-
MATIC TENSIONER. UNIT IS SERVICED AS AN
ASSEMBLY (EXCEPT FOR PULLEY).
CAUTION: If the pulley is to be removed from the
tensioner, its mounting bolt has left-hand threads.
(1) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(2) Remove tensioner mounting bolt (Fig. 6) and
remove tensioner.
Fig. 4 Indexing MarksÐ8.0L Engines Typical
1 - TENSIONER ASSEMBLY
2 - TENSIONER MOUNTING NUT
3 - INDEXING ARROW
4 - INDEXING MARK
Fig. 5 Indexing MarksÐ8.0L Engines Typical
1 - TENSIONER ASSEMBLY
2 - TENSIONER MOUNTING NUT
3 - INDEXING ARROW
4 - INDEXING MARK
BR/BEACCESSORY DRIVE 7 - 21
BELT TENSIONERS - 8.0L (Continued)
Page 272 of 2255

BELT TENSIONERS - 5.9L
DIESEL
DESCRIPTION
Drive belts on all engines are equipped with a
spring loaded automatic belt tensioner (Fig. 9). This
tensioner maintains constant belt tension at all times
and requires no maintenance or adjustment.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to check belt tension with
a belt tension gauge on vehicles equipped with an
automatic belt tensioner.
OPERATION
WARNING: THE AUTOMATIC BELT TENSIONER
ASSEMBLY IS SPRING LOADED. DO NOT ATTEMPT
TO DISASSEMBLE THE TENSIONER ASSEMBLY.
The automatic belt tensioner maintains correct belt
tension using a coiled spring within the tensioner
housing. The spring applies pressure to the tensioner
arm pressing the arm into the belt, tensioning the
belt.
If a new belt is being installed, the arrow must be
within approximately 3 mm (1/8 in.) of indexing
mark. Belt is considered new if it has been used 15
minutes or less. If this specification cannot be met,
check for:
²The wrong belt being installed (incorrect length/
width)²Worn bearings on an engine accessory (A/C com-
pressor, power steering pump, water pump, idler pul-
ley or generator)
²A pulley on an engine accessory being loose
²Misalignment of an engine accessory
²Belt incorrectly routed.
REMOVAL
WARNING: BECAUSE OF HIGH SPRING PRES-
SURE, DO NOT ATTEMPT TO DISASSEMBLE AUTO-
MATIC TENSIONER. UNIT IS SERVICED AS AN
ASSEMBLY.
(1) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(2) Remove tensioner mounting bolt (Fig. 10) and
remove tensioner.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install tensioner assembly to mounting
bracket. A dowel is located on back of tensioner. Align
this dowel to hole in tensioner mounting bracket.
Tighten bolt to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOLING/AC-
CESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLA-
TION).
Fig. 9 Belt
1 - WATER PUMP
2 - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
3 - AUTOMATIC BELT TENSIONER
4 - 3/89SQUARE BOLT
5 - MOUNT. BOLT
Fig. 10 Automatic Belt Tensioner Diesel EngineÐ
Typical
1 - WATER PUMP
2 - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
3 - AUTOMATIC BELT TENSIONER
4 - 3/89SQUARE BOLT
5 - MOUNT. BOLT
BR/BEACCESSORY DRIVE 7 - 23