torque DODGE RAM 2002 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 100 of 2255
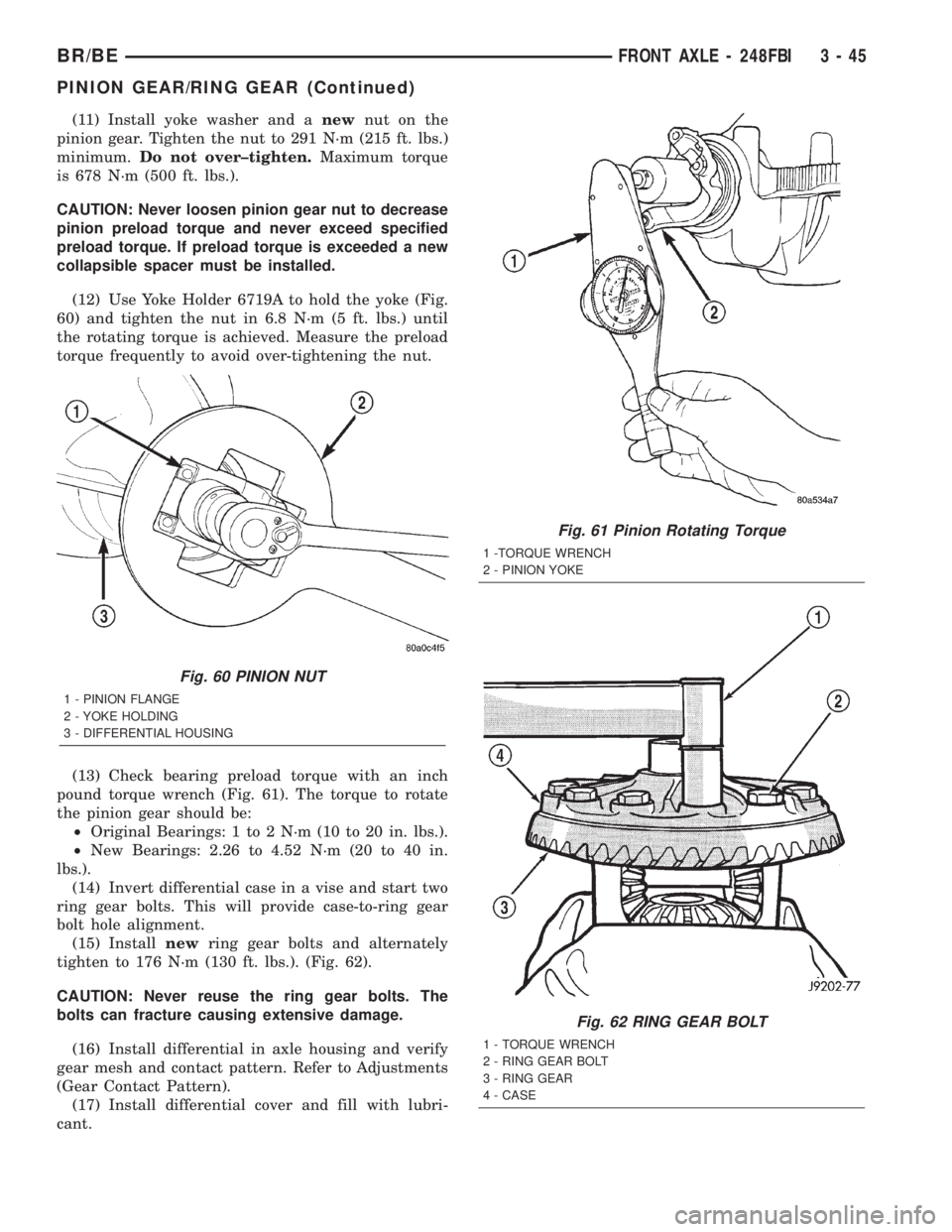
(11) Install yoke washer and anewnut on the
pinion gear. Tighten the nut to 291 N´m (215 ft. lbs.)
minimum.Do not over±tighten.Maximum torque
is 678 N´m (500 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Never loosen pinion gear nut to decrease
pinion preload torque and never exceed specified
preload torque. If preload torque is exceeded a new
collapsible spacer must be installed.
(12) Use Yoke Holder 6719A to hold the yoke (Fig.
60) and tighten the nut in 6.8 N´m (5 ft. lbs.) until
the rotating torque is achieved. Measure the preload
torque frequently to avoid over-tightening the nut.
(13) Check bearing preload torque with an inch
pound torque wrench (Fig. 61). The torque to rotate
the pinion gear should be:
²Original Bearings: 1 to 2 N´m (10 to 20 in. lbs.).
²New Bearings: 2.26 to 4.52 N´m (20 to 40 in.
lbs.).
(14) Invert differential case in a vise and start two
ring gear bolts. This will provide case-to-ring gear
bolt hole alignment.
(15) Installnewring gear bolts and alternately
tighten to 176 N´m (130 ft. lbs.). (Fig. 62).
CAUTION: Never reuse the ring gear bolts. The
bolts can fracture causing extensive damage.
(16) Install differential in axle housing and verify
gear mesh and contact pattern. Refer to Adjustments
(Gear Contact Pattern).
(17) Install differential cover and fill with lubri-
cant.
Fig. 60 PINION NUT
1 - PINION FLANGE
2 - YOKE HOLDING
3 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
Fig. 61 Pinion Rotating Torque
1 -TORQUE WRENCH
2 - PINION YOKE
Fig. 62 RING GEAR BOLT
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - RING GEAR BOLT
3 - RING GEAR
4 - CASE
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 248FBI 3 - 45
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR (Continued)
Page 101 of 2255

REAR AXLE - 248RBI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
REAR AXLE - 248RBI
DESCRIPTION.........................46
OPERATION...........................46
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AXLE..........47
REMOVAL.............................51
INSTALLATION.........................51
ADJUSTMENTS........................51
SPECIFICATIONS
REAR AXLE - 248RBI..................59
SPECIAL TOOLS
REAR AXLE - 248RBI..................59
AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL.............................62
INSTALLATION.........................62
AXLE BEARINGS
REMOVAL.............................62
INSTALLATION.........................62
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL.............................63INSTALLATION.........................63
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL.............................64
DISASSEMBLY.........................65
ASSEMBLY............................66
INSTALLATION.........................66
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRAC-LOKT.....67
DISASSEMBLY.........................68
ASSEMBLY............................70
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS
REMOVAL.............................72
INSTALLATION.........................72
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR/TONE RING
REMOVAL.............................73
INSTALLATION.........................75
REAR AXLE - 248RBI
DESCRIPTION
The Rear Beam-design Iron (RBI) axle housings consist
of an iron center casting (differential housing) with axle
shaft tubes extending from either side. The tubes are
pressed into the differential housing and welded. The
axles are equipped with full-floating axle shafts, meaning
that loads are supported by the axle housing tubes.
The differential case for the standard differentials
and the Trac-loktdifferential are a one-piece design.
Differential bearing preload and ring gear backlash
are adjusted by the use of shims located between the
differential bearing cones and case. Pinion bearing
preload is set and maintained by the use of a collaps-
ible spacer. The removable, stamped steel cover pro-
vides a means for inspection and service.
OPERATION
STANDARD DIFFERENTIAL
The axle receives power from the transmission/
transfer case through the rear propeller shaft. The
rear propeller shaft is connected to the pinion gear
which rotates the differential through the gear mesh
with the ring gear bolted to the differential case. The
engine power is transmitted to the axle shaftsthrough the pinion mate and side gears. The side
gears are splined to the axle shafts.
During straight-ahead driving, the differential pin-
ion gears do not rotate on the pinion mate shaft. This
occurs because input torque applied to the gears is
divided and distributed equally between the two side
gears. As a result, the pinion gears revolve with the
pinion mate shaft but do not rotate around it (Fig. 1).Fig. 1 STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING
1 - IN STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING EACH WHEEL ROTATES AT
100% OF CASE SPEED
2 - PINION GEAR
3 - SIDE GEAR
4 - PINION GEARS ROTATE WITH CASE
3 - 46 REAR AXLE - 248RBIBR/BE
Page 102 of 2255

When turning corners, the outside wheel must
travel a greater distance than the inside wheel to
complete a turn. The difference must be compensated
for to prevent the tires from scuffing and skidding
through turns. To accomplish this, the differential
allows the axle shafts to turn at unequal speeds (Fig.
2). In this instance, the input torque applied to the
pinion gears is not divided equally. The pinion gears
now rotate around the pinion mate shaft in opposite
directions. This allows the side gear and axle shaft
attached to the outside wheel to rotate at a faster
speed.
TRAC-LOKTDIFFERENTIAL
The differential clutches are engaged by two con-
current forces. The first being the preload force
exerted through Belleville spring washers within the
clutch packs. The second is the separating forces gen-
erated by the side gears as torque is applied through
the ring gear (Fig. 3).
This design provides the differential action needed
for turning corners and for driving straight ahead
during periods of unequal traction. When one wheel
looses traction, the clutch packs transfer additional
torque to the wheel having the most traction. The
differential resist wheel spin on bumpy roads and
provide more pulling power when one wheel looses
traction. Pulling power is provided continuously until
both wheels loose traction. If both wheels slip due to
unequal traction, Trac-loktoperation is normal. In
extreme cases of differences of traction, the wheel
with the least traction may spin.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AXLE
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant, incorrect backlash, incorrect pinion depth, toothcontact, worn/damaged gears, or the carrier housing
not having the proper offset and squareness.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The noise can also occur during a specific type
of driving condition. These conditions are accelera-
tion, deceleration, coast, or constant load.
When road testing, first warm-up the axle fluid by
driving the vehicle at least 5 miles and then acceler-
ate the vehicle to the speed range where the noise is
the greatest. Shift out-of-gear and coast through the
peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
Fig. 2 DIFFERENTIAL ON TURNS
1 - PINION GEARS ROTATE ON PINION SHAFTFig. 3 TRAC-LOK LIMITED SLIP DIFFERENTIAL
1 - CASE
2 - RING GEAR
3 - DRIVE PINION
4 - PINION GEAR
5 - MATE SHAFT
6 - CLUTCH PACK
7 - SIDE GEAR
8 - CLUTCH PACK
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 248RBI 3 - 47
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 105 of 2255
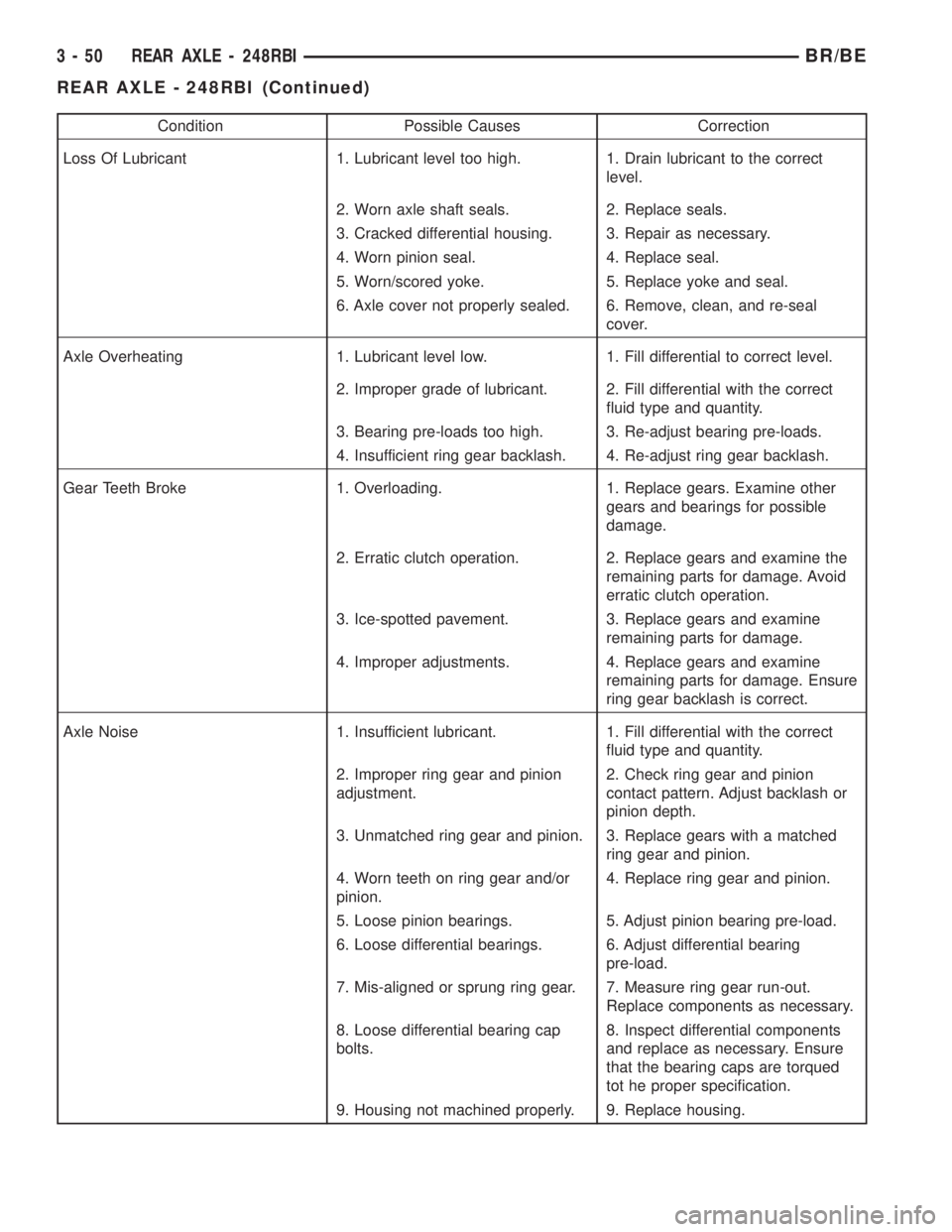
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Loss Of Lubricant 1. Lubricant level too high. 1. Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2. Worn axle shaft seals. 2. Replace seals.
3. Cracked differential housing. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Worn pinion seal. 4. Replace seal.
5. Worn/scored yoke. 5. Replace yoke and seal.
6. Axle cover not properly sealed. 6. Remove, clean, and re-seal
cover.
Axle Overheating 1. Lubricant level low. 1. Fill differential to correct level.
2. Improper grade of lubricant. 2. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
3. Bearing pre-loads too high. 3. Re-adjust bearing pre-loads.
4. Insufficient ring gear backlash. 4. Re-adjust ring gear backlash.
Gear Teeth Broke 1. Overloading. 1. Replace gears. Examine other
gears and bearings for possible
damage.
2. Erratic clutch operation. 2. Replace gears and examine the
remaining parts for damage. Avoid
erratic clutch operation.
3. Ice-spotted pavement. 3. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage.
4. Improper adjustments. 4. Replace gears and examine
remaining parts for damage. Ensure
ring gear backlash is correct.
Axle Noise 1. Insufficient lubricant. 1. Fill differential with the correct
fluid type and quantity.
2. Improper ring gear and pinion
adjustment.2. Check ring gear and pinion
contact pattern. Adjust backlash or
pinion depth.
3. Unmatched ring gear and pinion. 3. Replace gears with a matched
ring gear and pinion.
4. Worn teeth on ring gear and/or
pinion.4. Replace ring gear and pinion.
5. Loose pinion bearings. 5. Adjust pinion bearing pre-load.
6. Loose differential bearings. 6. Adjust differential bearing
pre-load.
7. Mis-aligned or sprung ring gear. 7. Measure ring gear run-out.
Replace components as necessary.
8. Loose differential bearing cap
bolts.8. Inspect differential components
and replace as necessary. Ensure
that the bearing caps are torqued
tot he proper specification.
9. Housing not machined properly. 9. Replace housing.
3 - 50 REAR AXLE - 248RBIBR/BE
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 110 of 2255

(13) Rotate dial indicator out of the way on the
pilot stud.
(14) Remove differential case and dummy bearings
from the housing.(15) Install the pinion gear in the housing. Install
the pinion yoke and establish the correct pinion
rotating torque.
(16) Install differential case and dummy bearings
D-343 in the housing (without shims), install bearing
caps and tighten bolts snug.
(17) Seat ring gear side dummy bearing (Fig. 13).
(18) Position the dial indicator plunger on a flat
surface between the ring gear bolt heads (Fig. 14).
(19) Push and hold differential case toward pinion
gear and zero the dial indicator (Fig. 17).
Fig. 14 DIFFERENTIAL SIDE PLAY MEASUREMENT
1 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
2 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
3 - PILOT STUD
4 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 15 DIAL INDICATOR LOCATION
1 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO PINION GEAR SIDE
2 - PILOT STUD
3 - DIAL INDICATOR ARM
4 - DIAL INDICATOR FACE
Fig. 16 DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO RING GEAR SIDE
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO RING GEAR SIDE
3 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
Fig. 17 DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO PINION GEAR
SIDE
1 - DIAL INDICATOR FACE
2 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE TO PINION GEAR SIDE
3 - PINION GEAR
4 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
5 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 248RBI 3 - 55
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 114 of 2255
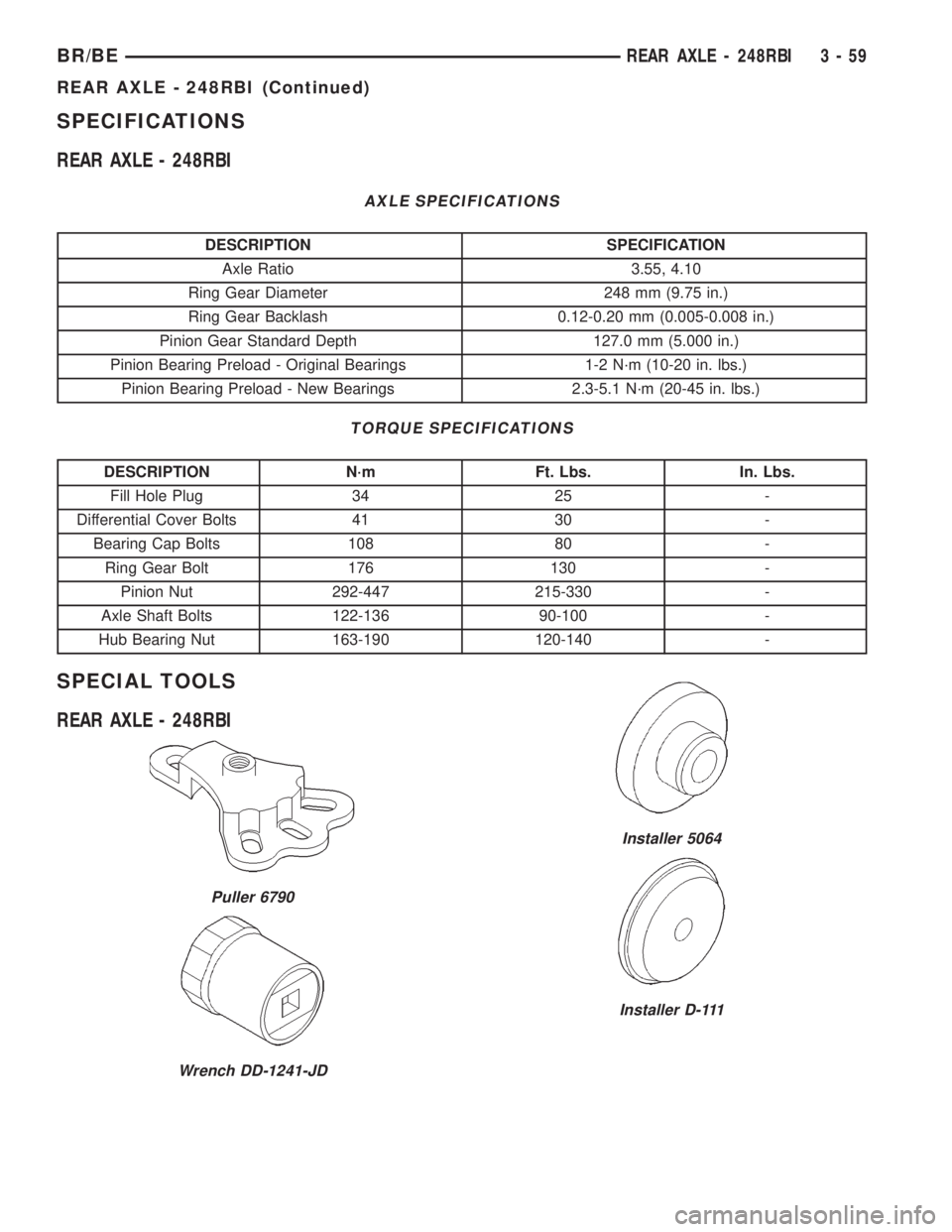
SPECIFICATIONS
REAR AXLE - 248RBI
AXLE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Axle Ratio 3.55, 4.10
Ring Gear Diameter 248 mm (9.75 in.)
Ring Gear Backlash 0.12-0.20 mm (0.005-0.008 in.)
Pinion Gear Standard Depth 127.0 mm (5.000 in.)
Pinion Bearing Preload - Original Bearings 1-2 N´m (10-20 in. lbs.)
Pinion Bearing Preload - New Bearings 2.3-5.1 N´m (20-45 in. lbs.)
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Fill Hole Plug 34 25 -
Differential Cover Bolts 41 30 -
Bearing Cap Bolts 108 80 -
Ring Gear Bolt 176 130 -
Pinion Nut 292-447 215-330 -
Axle Shaft Bolts 122-136 90-100 -
Hub Bearing Nut 163-190 120-140 -
SPECIAL TOOLS
REAR AXLE - 248RBI
Puller 6790
Wrench DD-1241-JD
Installer 5064
Installer D-111
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 248RBI 3 - 59
REAR AXLE - 248RBI (Continued)
Page 118 of 2255
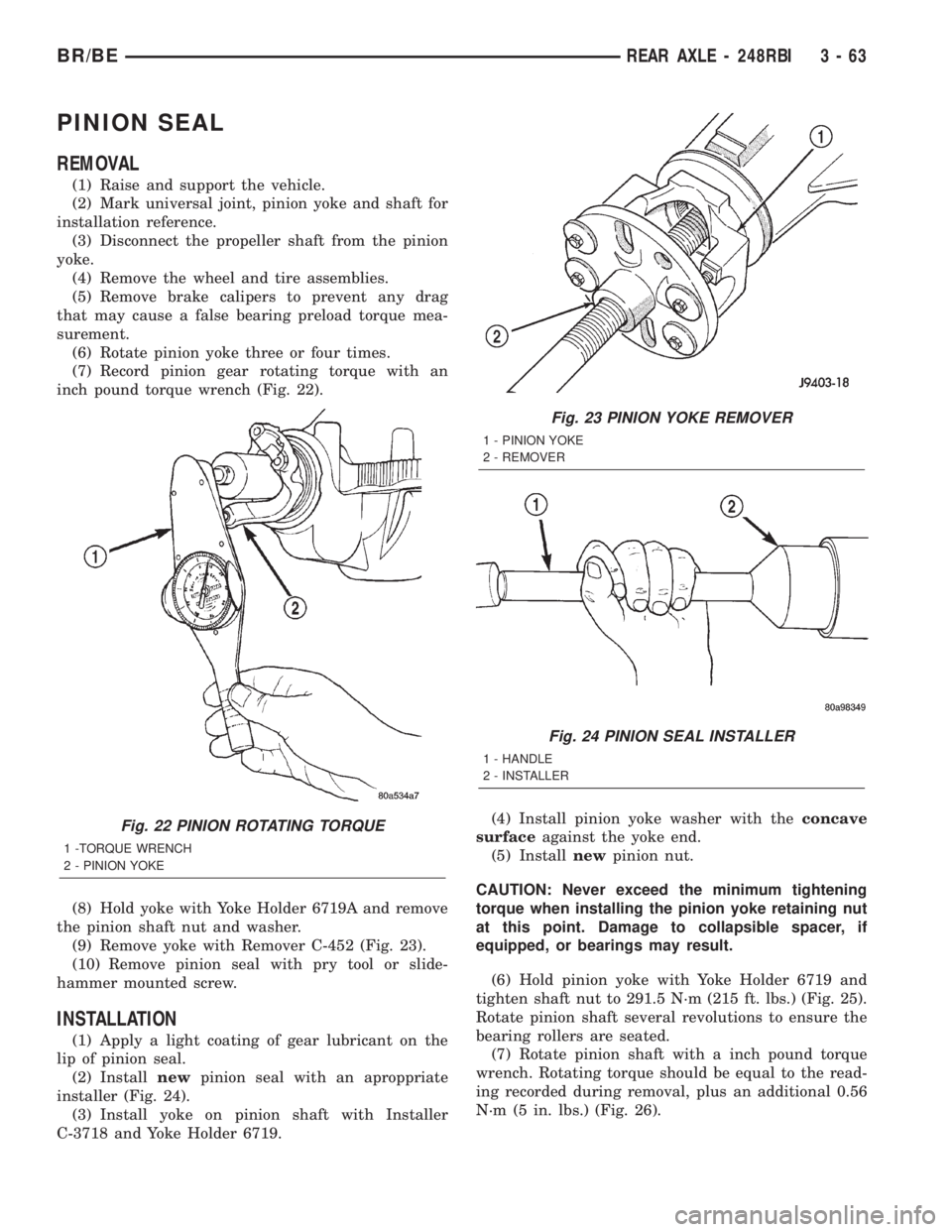
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Mark universal joint, pinion yoke and shaft for
installation reference.
(3) Disconnect the propeller shaft from the pinion
yoke.
(4) Remove the wheel and tire assemblies.
(5) Remove brake calipers to prevent any drag
that may cause a false bearing preload torque mea-
surement.
(6) Rotate pinion yoke three or four times.
(7) Record pinion gear rotating torque with an
inch pound torque wrench (Fig. 22).
(8) Hold yoke with Yoke Holder 6719A and remove
the pinion shaft nut and washer.
(9) Remove yoke with Remover C-452 (Fig. 23).
(10) Remove pinion seal with pry tool or slide-
hammer mounted screw.
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a light coating of gear lubricant on the
lip of pinion seal.
(2) Installnewpinion seal with an aproppriate
installer (Fig. 24).
(3) Install yoke on pinion shaft with Installer
C-3718 and Yoke Holder 6719.(4) Install pinion yoke washer with theconcave
surfaceagainst the yoke end.
(5) Installnewpinion nut.
CAUTION: Never exceed the minimum tightening
torque when installing the pinion yoke retaining nut
at this point. Damage to collapsible spacer, if
equipped, or bearings may result.
(6) Hold pinion yoke with Yoke Holder 6719 and
tighten shaft nut to 291.5 N´m (215 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 25).
Rotate pinion shaft several revolutions to ensure the
bearing rollers are seated.
(7) Rotate pinion shaft with a inch pound torque
wrench. Rotating torque should be equal to the read-
ing recorded during removal, plus an additional 0.56
N´m (5 in. lbs.) (Fig. 26).
Fig. 22 PINION ROTATING TORQUE
1 -TORQUE WRENCH
2 - PINION YOKE
Fig. 23 PINION YOKE REMOVER
1 - PINION YOKE
2 - REMOVER
Fig. 24 PINION SEAL INSTALLER
1 - HANDLE
2 - INSTALLER
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 248RBI 3 - 63
Page 119 of 2255
CAUTION: Never loosen pinion gear nut to decrease
pinion rotating torque and never exceed specified pre-
load torque. If preload torque is exceeded a new pin-ion nut and collapsible spacer, if equipped, must be
installed.
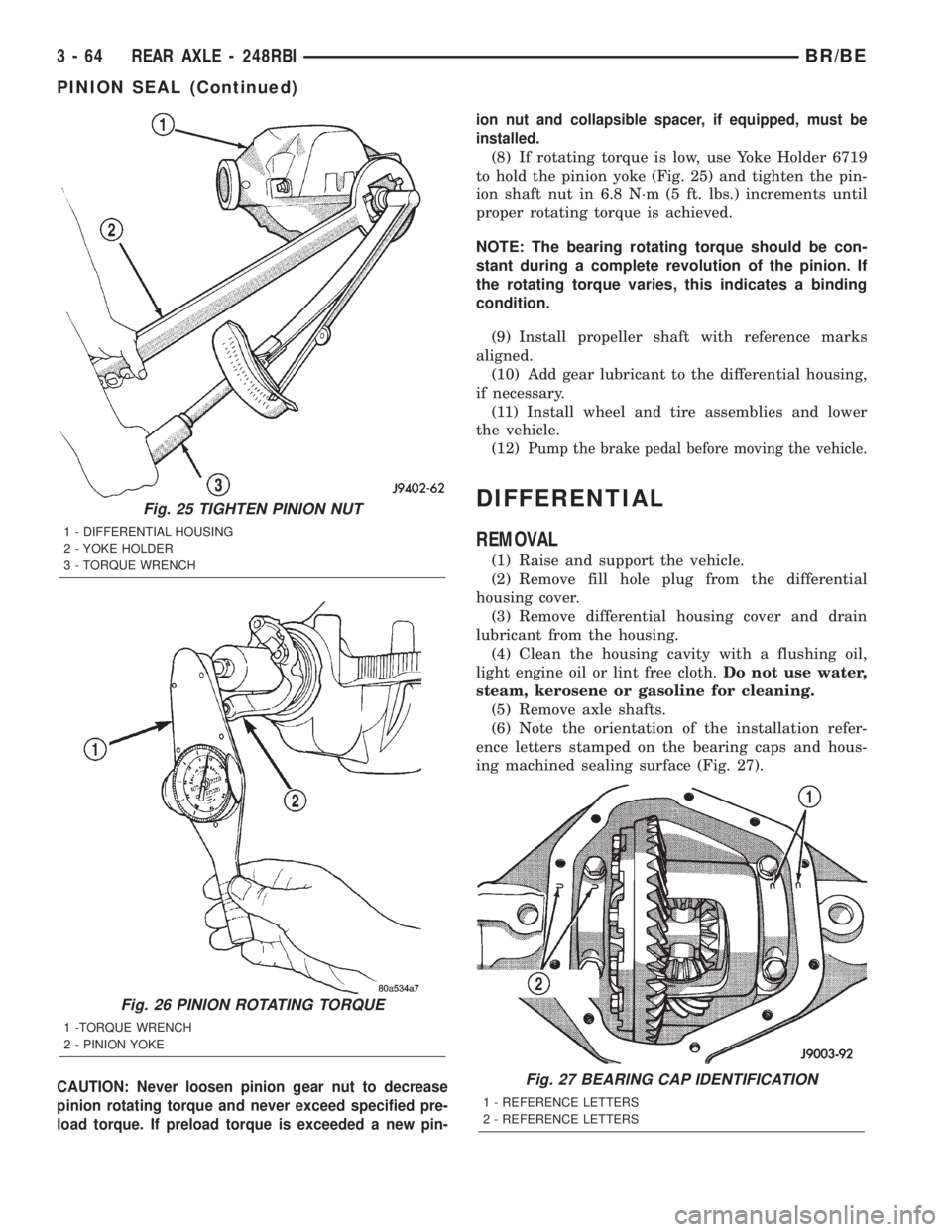
(8) If rotating torque is low, use Yoke Holder 6719
to hold the pinion yoke (Fig. 25) and tighten the pin-
ion shaft nut in 6.8 N´m (5 ft. lbs.) increments until
proper rotating torque is achieved.
NOTE: The bearing rotating torque should be con-
stant during a complete revolution of the pinion. If
the rotating torque varies, this indicates a binding
condition.
(9) Install propeller shaft with reference marks
aligned.
(10) Add gear lubricant to the differential housing,
if necessary.
(11) Install wheel and tire assemblies and lower
the vehicle.
(12)
Pump the brake pedal before moving the vehicle.
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove fill hole plug from the differential
housing cover.
(3) Remove differential housing cover and drain
lubricant from the housing.
(4) Clean the housing cavity with a flushing oil,
light engine oil or lint free cloth.Do not use water,
steam, kerosene or gasoline for cleaning.
(5) Remove axle shafts.
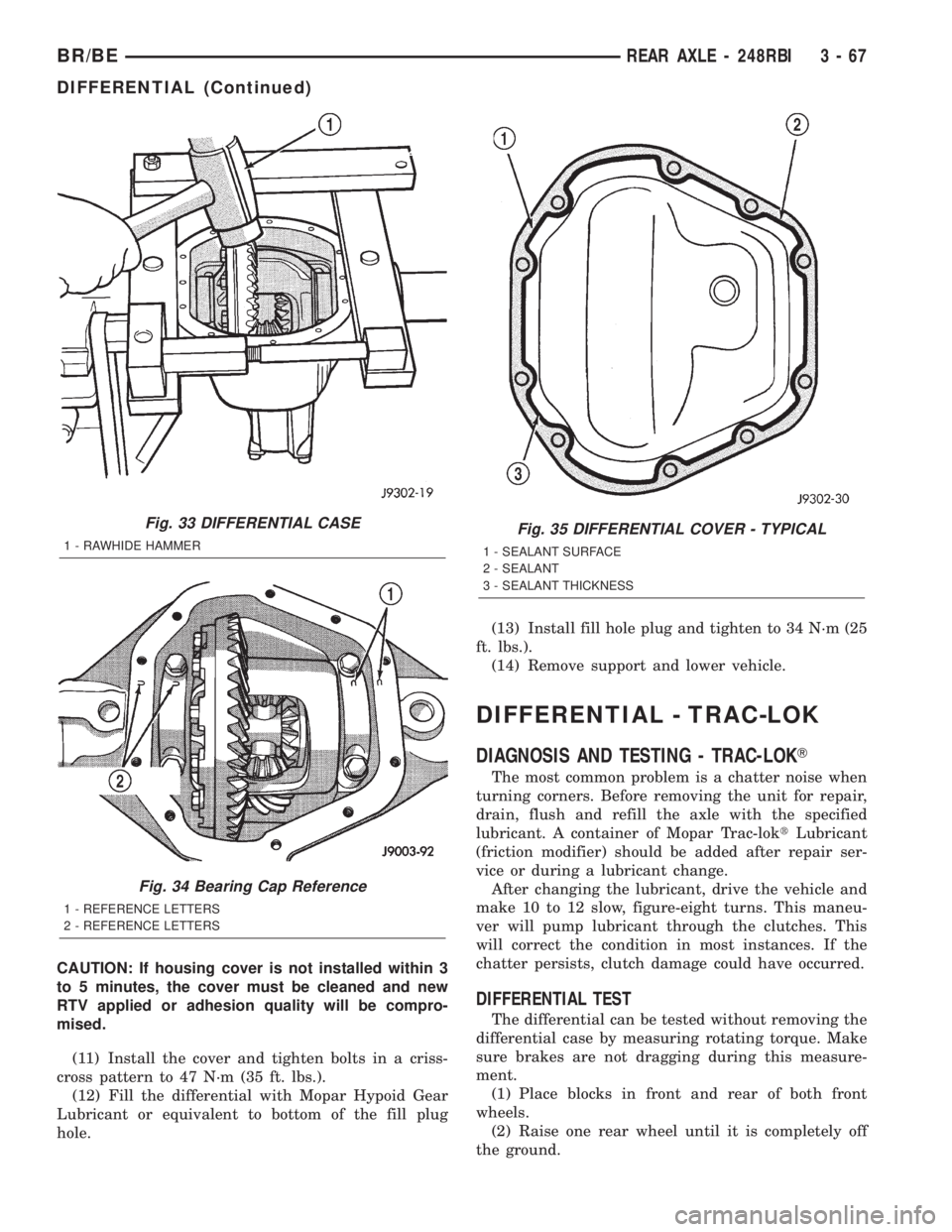
(6) Note the orientation of the installation refer-
ence letters stamped on the bearing caps and hous-
ing machined sealing surface (Fig. 27).
Fig. 25 TIGHTEN PINION NUT
1 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
2 - YOKE HOLDER
3 - TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 26 PINION ROTATING TORQUE
1 -TORQUE WRENCH
2 - PINION YOKE
Fig. 27 BEARING CAP IDENTIFICATION
1 - REFERENCE LETTERS
2 - REFERENCE LETTERS
3 - 64 REAR AXLE - 248RBIBR/BE
PINION SEAL (Continued)
Page 122 of 2255
CAUTION: If housing cover is not installed within 3
to 5 minutes, the cover must be cleaned and new
RTV applied or adhesion quality will be compro-
mised.
(11) Install the cover and tighten bolts in a criss-
cross pattern to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.).
(12) Fill the differential with Mopar Hypoid Gear
Lubricant or equivalent to bottom of the fill plug
hole.(13) Install fill hole plug and tighten to 34 N´m (25
ft. lbs.).
(14) Remove support and lower vehicle.
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRAC-LOKT
The most common problem is a chatter noise when
turning corners. Before removing the unit for repair,
drain, flush and refill the axle with the specified
lubricant. A container of Mopar Trac-loktLubricant
(friction modifier) should be added after repair ser-
vice or during a lubricant change.
After changing the lubricant, drive the vehicle and
make 10 to 12 slow, figure-eight turns. This maneu-
ver will pump lubricant through the clutches. This
will correct the condition in most instances. If the
chatter persists, clutch damage could have occurred.
DIFFERENTIAL TEST
The differential can be tested without removing the
differential case by measuring rotating torque. Make
sure brakes are not dragging during this measure-
ment.
(1) Place blocks in front and rear of both front
wheels.
(2) Raise one rear wheel until it is completely off
the ground.
Fig. 33 DIFFERENTIAL CASE
1 - RAWHIDE HAMMER
Fig. 34 Bearing Cap Reference
1 - REFERENCE LETTERS
2 - REFERENCE LETTERS
Fig. 35 DIFFERENTIAL COVER - TYPICAL
1 - SEALANT SURFACE
2 - SEALANT
3 - SEALANT THICKNESS
BR/BEREAR AXLE - 248RBI 3 - 67
DIFFERENTIAL (Continued)
Page 123 of 2255
(3) Engine off, transmission in neutral, and park-
ing brake off.
(4) Remove wheel and bolt Special Tool 6790 or
equivalent tool to studs.
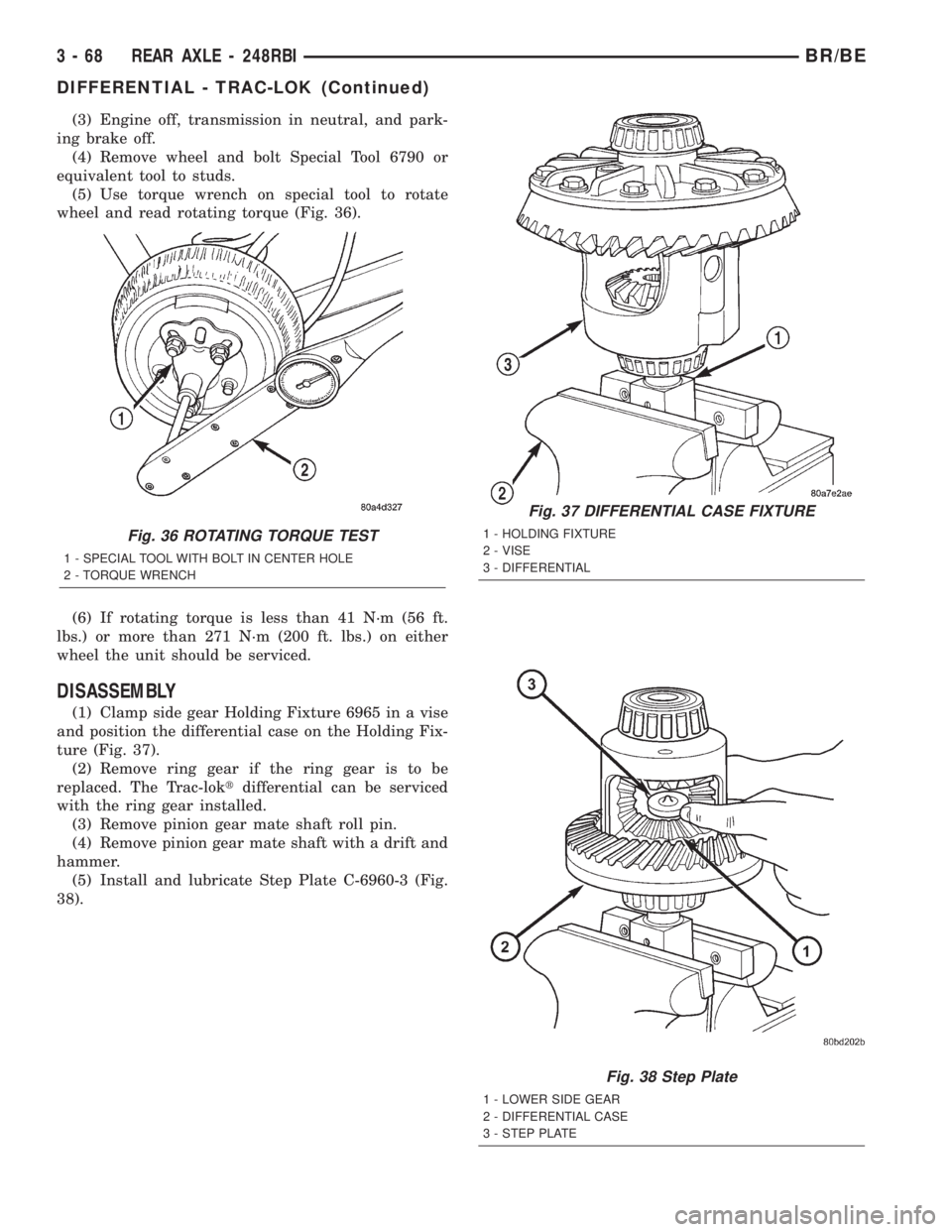
(5) Use torque wrench on special tool to rotate
wheel and read rotating torque (Fig. 36).
(6) If rotating torque is less than 41 N´m (56 ft.
lbs.) or more than 271 N´m (200 ft. lbs.) on either
wheel the unit should be serviced.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Clamp side gear Holding Fixture 6965 in a vise
and position the differential case on the Holding Fix-
ture (Fig. 37).
(2) Remove ring gear if the ring gear is to be
replaced. The Trac-loktdifferential can be serviced
with the ring gear installed.
(3) Remove pinion gear mate shaft roll pin.
(4) Remove pinion gear mate shaft with a drift and
hammer.
(5) Install and lubricate Step Plate C-6960-3 (Fig.
38).
Fig. 36 ROTATING TORQUE TEST
1 - SPECIAL TOOL WITH BOLT IN CENTER HOLE
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 37 DIFFERENTIAL CASE FIXTURE
1 - HOLDING FIXTURE
2 - VISE
3 - DIFFERENTIAL
Fig. 38 Step Plate
1 - LOWER SIDE GEAR
2 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
3 - STEP PLATE
3 - 68 REAR AXLE - 248RBIBR/BE
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK (Continued)