injector DODGE RAM 2002 Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 1213 of 2255

INSPECTION
The cylinder head cover gasket and isolators
are reusable.However, should cracks be present in
the rubber/silicone construction, the defective compo-
nents should be replaced.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the gasket as shown in (Fig. 34). Make
sure the gasket is properly located around the cylin-
der head bolts, with the words ªtop frontº facing up
and towards front of engine.
(2) Place two bolts and isolators into the rear two
mounting holes and install the cover.
(3) Install the remaining bolts and isolators. Start-
ing with the center bolt, torque in a circular pattern
to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
(4) Connect both battery negative cables.
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS
DESCRIPTION
The valves are made of heat resistant steel, and
have chrome plated stems to prevent scuffing. Theintake and exhaust valves are both similar in head
diameter and overall length, but they have unique
face angles which makes them non-interchangeable.
The valves are distinguished by unique dimples on
the exhaust valve head (Fig. 35) .
The exhaust valve springs are made from high
strength, chrome silicon steel. The exhaust valve
springs are also exhaust brake compatible.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - VALVES,GUIDES
AND SPRINGS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove cylinder head (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(2) Support cylinder head on stands, or install
head bolts upside down (through combustion surface
side) to protect injector tips from damage from work
bench.
(3) Remove the injector clamp (Fig. 36) from the
cylinder(s) to be serviced.Do not remove the bolt
shown in (Fig. 36).
(4) Install the valve spring compressor mounting
base (special tool 8319±A) as shown in (Fig. 37).
Reinstall the injector clamp bolt finger tight.
(5) Install the compressor top plate, washer, and
nut. Using a suitable wrench, tighten the nut (clock-
wise) to compress the valve springs (Fig. 38) and
remove the locks.
(6) Rotate the compressor nut counter-clockwise to
relieve tension on the springs. Remove the spring
compressor.
(7) Remove the retainers, springs, valve seals (if
necessary), and valves (Fig. 39). Arrange or number
Fig. 34 Cylinder Head Cover and Gasket
1 - BOLT (5)
2 - GASKET
3 - ªTOP FRONTº
4 - ISOLATOR (5)
Fig. 35 Valve Identification
1 - INTAKE VALVES
2 - EXHAUST VALVES
9 - 138 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELBR/BE
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) (Continued)
Page 1214 of 2255

all components so they can be installed in their orig-
inal locations.
(8) Repeat the procedure on all cylinders to be ser-
viced.
CLEANING
Clean the valve stems with crocus cloth or a
Scotch-BriteŸ pad. Remove carbon with a soft wire
brush. Clean valves, springs, retainers, and valve
retaining locks in a suitable solvent. Rinse in hot
water and blow dry with compressed air.
INSPECTION
Visually inspect the valves for abnormal wear on
the heads, stems, and tips. Replace any valve that is
worn out or bent (Fig. 40).
Measure the valve stem diameter in three places
as shown in (Fig. 41). Measure the cylinder head
valve guide bore (Fig. 42). Subtract the corresponding
Fig. 36 Injector Clamp Removal/Installation
1 - DO NOT REMOVE
2 - INJECTOR CLAMP
Fig. 37 Spring Compressor Mounting BaseÐPart of
Tool 8319±A
1 - COMPRESSOR MOUNTING BASE
Fig. 38 Compressing Valve Springs with Tool
8319±A
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8319
Fig. 39 Valve Spring, Seal, and Retainers
1 - VALVE RETAINING LOCKS
2 - VALVE
3 - SEAL
4 - SPRING
5 - RETAINER
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 139
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1215 of 2255
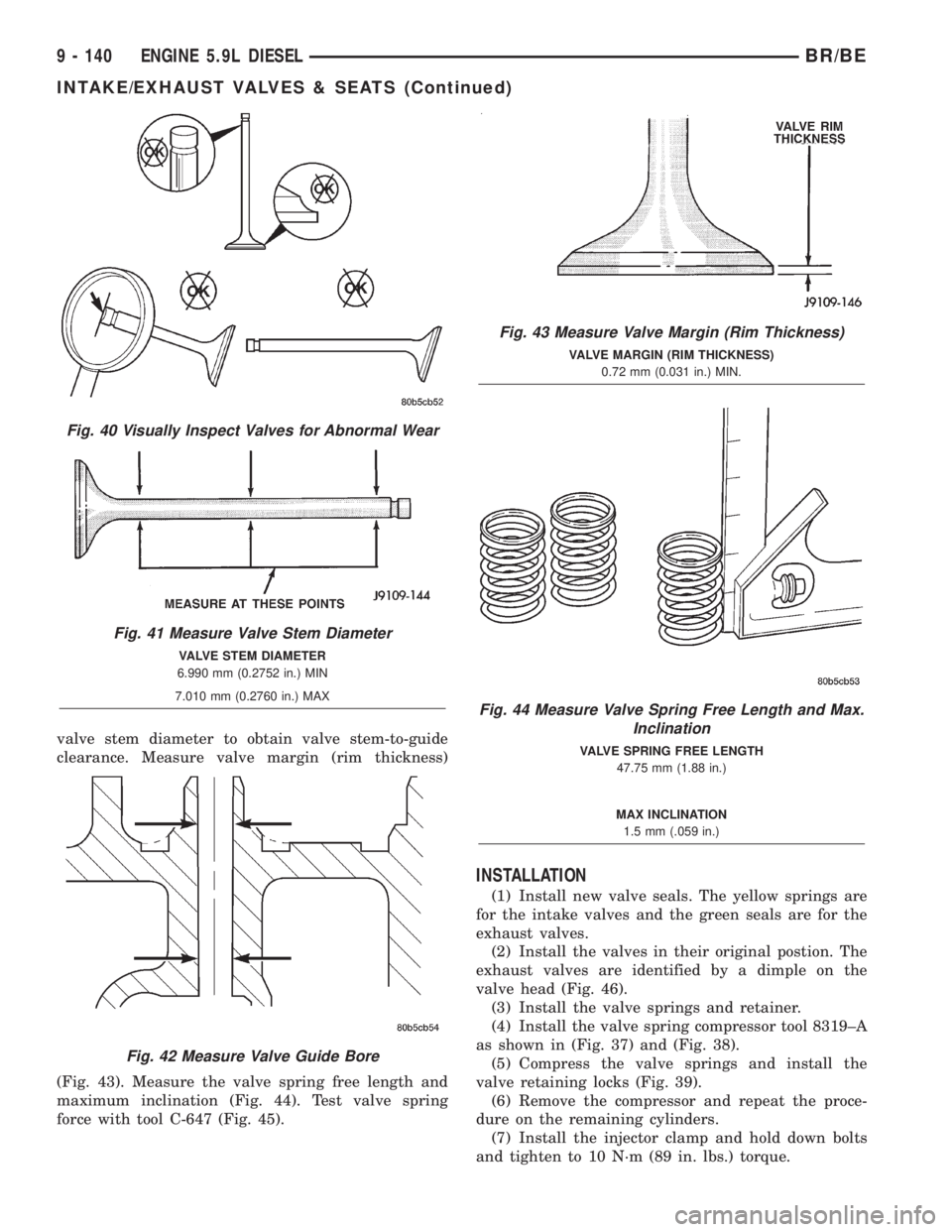
valve stem diameter to obtain valve stem-to-guide
clearance. Measure valve margin (rim thickness)
(Fig. 43). Measure the valve spring free length and
maximum inclination (Fig. 44). Test valve spring
force with tool C-647 (Fig. 45).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install new valve seals. The yellow springs are
for the intake valves and the green seals are for the
exhaust valves.
(2) Install the valves in their original postion. The
exhaust valves are identified by a dimple on the
valve head (Fig. 46).
(3) Install the valve springs and retainer.
(4) Install the valve spring compressor tool 8319±A
as shown in (Fig. 37) and (Fig. 38).
(5) Compress the valve springs and install the
valve retaining locks (Fig. 39).
(6) Remove the compressor and repeat the proce-
dure on the remaining cylinders.
(7) Install the injector clamp and hold down bolts
and tighten to 10 N´m (89 in. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 40 Visually Inspect Valves for Abnormal Wear
Fig. 41 Measure Valve Stem Diameter
VALVE STEM DIAMETER
6.990 mm (0.2752 in.) MIN
7.010 mm (0.2760 in.) MAX
Fig. 42 Measure Valve Guide Bore
Fig. 43 Measure Valve Margin (Rim Thickness)
VALVE MARGIN (RIM THICKNESS)
0.72 mm (0.031 in.) MIN.
Fig. 44 Measure Valve Spring Free Length and Max.
Inclination
VALVE SPRING FREE LENGTH
47.75 mm (1.88 in.)
MAX INCLINATION
1.5 mm (.059 in.)
9 - 140 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELBR/BE
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1218 of 2255

(9) Install the cylinder head cover (Fig. 47) (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER
HEAD COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(10) Install the fuel pump gear access cover.
(11) Connect the battery negative cables.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cables.
(2) Remove the cylinder head cover (Fig. 52) (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER
HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the rocker arms and crossheads (Fig.
53) from the cylinder(s) to be serviced. Mark each
component so they can be installed in their original
position.
(4) Remove the crankcase breather vapor canister
and breather housing (Fig. 55).
(5) Using the crankshaft barring tool #7471±B
(Fig. 51), rotate the engine to line up the mark on
the pump gear with the TDC mark on the cover.At
this engine position, cylinders #1 and #6 can be
serviced.
(6) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(7) With the fuel injection pump gear mark aligned
at TDC, add a paint mark anywhere on the gear
housing cover next to the crankshaft damper. Place
another mark on the vibration damper in alignment
with the mark you just made on the cover.
(8) Divide the crankshaft damper into three
equally sized segments as follows:
(a) Using a tape measure, measure the circum-
ference of the crankshaft damper and divide the
measurement by three (3).
(b) Measure that distance in a counter-clockwise
direction from the first balancer mark and place
another mark on the balancer.
(c) From the second damper mark, again mea-
sure in a counter-clockwise direction and place a
mark on the damper at the same distance you
measured when placing the second damper mark.
The damper should now be marked in three
equally spaced locations and the fuel pump gear
mark should still be aligned with the TDC mark on
the cover.
(9) Compress the valve springs at cyls. #1 and #6
as follows:
(a) Remove the injector clamp (Fig. 54) from the
cylinder(s) to be serviced.Do not remove the
bolt shown in (Fig. 54).
(b) Install the valve spring compressor mounting
base as shown in (Fig. 56). Reinstall the injector
clamp bolt finger tight.
(c) Install the top plate, washer, and nut. Using
a suitable wrench tighten the nut (clock-wise) (Fig.57) to compress the valve springs and remove the
collets.
(d) Rotate the compressor nut counter-clockwise
to relieve tension on springs. Remove spring com-
pressor.
(e) Remove and replace retainers, springs, and
seals as necessary.
(f)Do not rotate the engine until the
springs and retainers are re-installed.
(g) Install seals, springs and retainers. Install
spring compressor, compress valve springs and
install the collets.
(h) Release the spring tension and remove the
compressor. Verify that the collets are seated by
tapping on the valve stem with a plastic hammer.
(10) Using the crankshaft barring tool, rotate the
engine until the next crankshaft damper paint mark
aligns with the mark you placed on the cover.In this
position, cylinders #2 and #5 can be serviced.
(11) Repeat the valve spring compressing proce-
dure previously performed and service the retainers,
springs, and seals as necessary.
(12) Using the crankshaft barring tool, rotate the
engine until the next crankshaft damper paint mark
aligns with the mark you placed on the cover.In this
position, cylinders #3 and #4 can be serviced.
(13) Repeat the spring compressing procedure pre-
viously performed and service the retainers, springs,
and seals as necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install all injector clamps into their original
location (Fig. 54). Tighten the hold down bolt to 10
N´m (89 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Lubricate the valve tips and install the cross-
heads in their original locations.
Fig. 51 Rotating Engine with Barring Tool
1 - REAR FLANGE
2 - BARRING TOOL
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 143
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1219 of 2255
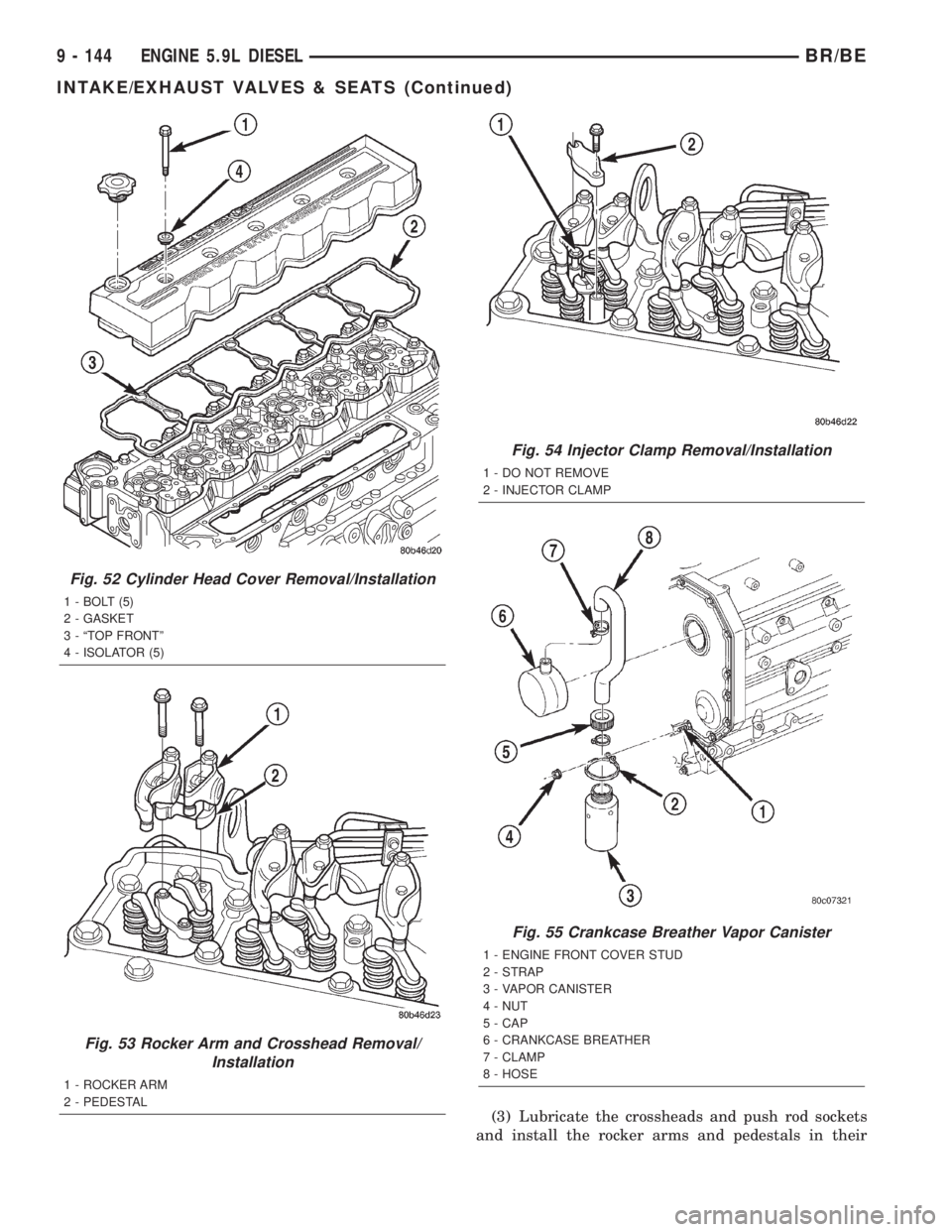
(3) Lubricate the crossheads and push rod sockets
and install the rocker arms and pedestals in their
Fig. 52 Cylinder Head Cover Removal/Installation
1 - BOLT (5)
2 - GASKET
3 - ªTOP FRONTº
4 - ISOLATOR (5)
Fig. 53 Rocker Arm and Crosshead Removal/
Installation
1 - ROCKER ARM
2 - PEDESTAL
Fig. 54 Injector Clamp Removal/Installation
1 - DO NOT REMOVE
2 - INJECTOR CLAMP
Fig. 55 Crankcase Breather Vapor Canister
1 - ENGINE FRONT COVER STUD
2 - STRAP
3 - VAPOR CANISTER
4 - NUT
5 - CAP
6 - CRANKCASE BREATHER
7 - CLAMP
8 - HOSE
9 - 144 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELBR/BE
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1220 of 2255

original locations (Fig. 53). Tighten bolts to 36 N´m
(27 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4)Verify valve lash adjustment (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST
VALVES & SEATS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Install cylinder head cover and reusable gasket
(Fig. 52) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(7) Connect battery negative cables.
ROCKER ARM / ADJUSTER
ASSY
DESCRIPTION
The 24±valve overhead system incorporates rocker
arms that are designed to allow fuel injector service
without removing the rocker arms and pedestals. The
unique intake and exhaust rocker arms have their
own rocker shafts and are lubricated by passages
intersecting the cylinder block main oil rifle. Cross-
heads are used (Fig. 58), which allow each rocker
arm to operate two valves.
The solid push rods are hardened at the rocker
arm and tappet contact areas for superior strength
and durability.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cables.
(2) Remove cylinder head cover (Fig. 59) (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the rocker arm/pedestal fasteners (Fig.
60) and remove rocker arm and pedestal from cylin-
der head. Mark the arms and pedestals so they can
be installed in their original position.
CAUTION: When removing the rocker arms, the
sockets (Fig. 61) may come loose and fall into the
engine. Make sure they stay with the arm upon
removal/installation.
Fig. 56 Spring Compressor Mounting BaseÐPart of
Tool 8319±A
1 - COMPRESSOR MOUNTING BASE
Fig. 57 Compressing Valve Springs with Tool
8319±A
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8319
Fig. 58 Overhead System Components
1 - EXHAUST ROCKER ARM
2 - INTAKE ROCKER ARM
3 - ROCKER SHAFT
4 - SOCKET
5 - ADJUSTING SCREW LOCK NUT
6 - PUSH ROD
7 - PEDESTAL
8 - CROSSHEAD
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 145
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1262 of 2255

(7) Position the charge air cooler inlet pipe to the
turbocharger. With the clamp in position, tighten the
clamp nut to 8 N´m (72 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Position the air inlet hose to the turbocharger
(Fig. 170). Tighten the clamp to 8 N´m (72 in. lbs.)
torque.
(9) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(10) Connect the exhaust pipe to the turbocharger
(Fig. 169) and tighten the bolts to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(11) Lower the vehicle.
(12) Connect the battery negative cables.
(13) Start the engine to check for leaks.
VALVE TIMING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIMING
VERIFICATION
(1) Remove the cylinder head cover.
(2) Remove fuel injector from cylinder number 1.
(3) Remove the crankcase breather from the gear
housing cover.
(4) Using Special Tool 7471B rotate the engine
until the timing mark on the fuel pump gear is
aligned with the TDC mark on the gear housing
cover.
(5) Using a 8 in.x 1/4 in. dowel rod inserted into
cylinder number 1, rock the crankshaft back and
forth to verify piston number 1 is at TDC.
(6) With piston number 1 at TDC the timing mark
on the fuel pump gear should be aligned with the
TDC mark on the gear housing cover. If marks do not
line up, remove the gear housing cover.
(7) With cylinder number still at TDC, inspect the
keyway on the crankshaft gear for proper alignment
(12 o'clock position).
(8) If the keyway is not at 12 o'clock position
replace the crankshaft gear assembly.
(9) If the keyway is at 12 o'clock position, verify
timing mark alignment between the camshaft gear,
crankshaft gear and the fuel pump gear, if not
aligned inspect keyway on camshaft gear.
(10) Inspect keyway on camshaft gear for proper
alignment with the key in the camshaft, if alignment
is off replace the camshaft/gear assembly.
(11) If timing marks alignment is off and no dam-
age is found at either the crankshaft or camshaft
gear keyways, realign timing marks as necessary.
GEAR HOUSING
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cables.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.(3) Partially drain engine coolant into container
suitable for re-use (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Remove radiator upper hose.
(6) Disconnect coolant recovery bottle hose from
radiator filler neck and lift bottle off of fan shroud.
(7) Disconnect windshield washer pump supply
hose and electrical connections and lift washer bottle
off of fan shroud.
(8) Remove the fan shroud-to-radiator mounting
bolts.
(9) Remove viscous fan/drive assembly (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
(10) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(11) Remove the cooling fan support/hub from the
front of the engine (Fig. 173).
(12) Raise the vehicle on hoist.
(13) Remove the crankshaft damper (Fig. 174)
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION
DAMPER - REMOVAL).
(14) Lower the vehicle.
(15) Remove the gear cover-to-housing bolts and
gently pry the cover away from the housing (Fig.
175), taking care not to mar the gasket surfaces.
(16) Remove the fuel injection pump (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL INJEC-
TION PUMP - REMOVAL).
(17) Disconnect the camshaft position sensor con-
nector.
Fig. 173 Fan Support/Hub Assembly - Removal/
Installation
1 - FAN SUPPORT/HUB
2 - FAN PULLEY
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 187
EXHAUST MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1301 of 2255

FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE
DESCRIPTION - FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
The fuel delivery system consists of:
²the fuel pump module containing the electric
fuel pump, fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator, rollover
valve (certain modules), fuel gauge sending unit (fuel
level sensor) and a separate fuel filter located at bot-
tom of pump module
²fuel tubes/lines/hoses
²quick-connect fittings
²fuel injector rail
²fuel injectors
²fuel tank
²fuel tank filler/vent tube assembly
²fuel tank filler tube cap
²accelerator pedal
²throttle cable
OPERATION - FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
Fuel is returned through the fuel pump module
and back into the fuel tank through the fuel filter/
fuel pressure regulator. A separate fuel return line
from the engine to the tank is not used with any gas-
oline powered engine.
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
fuel pump module assembly, fuel pump module lock-
nut/gasket and fuel tank check valve(s) (refer to 25,
Emission Control System for Fuel Tank Check Valve
information).
A fuel filler/vent tube assembly using a pressure/
vacuum, 1/4 turn fuel filler cap is used. The fuel
filler tube contains a flap door located below the fuel
fill cap.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system. This is designed to
reduce the emission of fuel vapors into the atmo-
sphere. The description and function of the Evapora-
tive Control System is found in 25, Emission Control
Systems.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PRESSURE
LEAK DOWN TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Pressure Test and Fuel Pump Capacity Test.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply linefull of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
Abnormally long periods of cranking to restart a
hotengine that has been shut down for a short
period of time may be caused by:
²Fuel pressure bleeding past a fuel injector(s).
²Fuel pressure bleeding past the check valve in
the fuel pump module.
(1) Disconnect the fuel inlet line at fuel rail. Refer
to Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps for proce-
dures. On some engines, air cleaner housing removal
may be necessary before fuel line disconnection.
(2) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(3) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose between disconnected fuel line
and fuel rail (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 CONNECTING ADAPTER TOOLÐTYPICAL
1 - VEHICLE FUEL LINE
2 - TEST PORT ªTº
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 6923, 6631, 6541 OR 6539
4 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST GAUGE
5 - FUEL LINE CONNECTION AT RAIL
6 - FUEL RAIL
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINEBR/BE
Page 1302 of 2255

(4) Connect the 0-414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure
test gauge (from Gauge Set 5069) to the test port on
the appropriate Adaptor Tool.The DRBtIII Scan
Tool along with the PEP module, the 500 psi
pressure transducer, and the transducer-to-test
port adapter may also be used in place of the
fuel pressure gauge.
The fittings on both tools must be in good
condition and free from any small leaks before
performing the proceeding test.
(5) Start engine and bring to normal operating
temperature.
(6) Observe test gauge. Normal operating pressure
should be 339 kPa +/±34 kPa (49.2 psi +/±5 psi).
(7) Shut engine off.
(8) Pressure should not fall below30 psi for five
minutes.
(9) If pressure falls below 30 psi, it must be deter-
mined if a fuel injector, the check valve within the
fuel pump module, or a fuel tube/line is leaking.
(10) Again, start engine and bring to normal oper-
ating temperature.
(11) Shut engine off.
(12)Testing for fuel injector or fuel rail leak-
age:Clamp off the rubber hose portion of Adaptor
Tool between the fuel rail and the test port ªTº on
Adapter Tool. If pressure now holds at or above 30
psi, a fuel injector or the fuel rail is leaking.
(13)Testing for fuel pump check valve, filter/
regulator check valve or fuel tube/line leakage:
Clamp off the rubber hose portion of Adaptor Tool
between the vehicle fuel line and test port ªTº on
Adapter Tool. If pressure now holds at or above 30
psi, a leak may be found at a fuel tube/line. If no
leaks are found at fuel tubes or lines, one of the
check valves in either the electric fuel pump or filter/
regulator may be leaking.
Note: A quick loss of pressure usually indicates a
defective check valve in the filter/regulator. A slow
loss of pressure usually indicates a defective check
valve in the electric fuel pump.
The electric fuel pump is not serviced separately.
Replace the fuel pump module assembly. The filter/
regulator may be replaced separately on certain
applications. Refer to Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Reg-
ulator Removal/Installation for additional informa-
tion.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE
Use following procedure if the fuel injector
rail is, or is not equipped with a fuel pressure
test port.
(1) Remove fuel fill cap.(2) Remove fuel pump relay from Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC). For location of relay, refer to label
on underside of PDC cover.
(3) Start and run engine until it stalls.
(4) Attempt restarting engine until it will no
longer run.
(5) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
CAUTION: Steps 1, 2, 3 and 4 must be performed to
relieve high pressure fuel from within fuel rail. Do
not attempt to use following steps to relieve this
pressure as excessive fuel will be forced into a cyl-
inder chamber.
(6) Unplug connector from any fuel injector.
(7) Attach one end of a jumper wire with alligator
clips (18 gauge or smaller) to either injector terminal.
(8) Connect other end of jumper wire to positive
side of battery.
(9) Connect one end of a second jumper wire to
remaining injector terminal.
CAUTION: Powering an injector for more than a few
seconds will permanently damage the injector.
(10) Momentarily touch other end of jumper wire
to negative terminal of battery for no more than a
few seconds.
(11) Place a rag or towel below fuel line quick-con-
nect fitting at fuel rail.
(12) Disconnect quick-connect fitting at fuel rail.
Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(13) Return fuel pump relay to PDC.
(14) One or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
may have been stored in PCM memory due to fuel
pump relay removal. The DRBtscan tool must be
used to erase a DTC.
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE -
GAS ENGINES
All Gasoline Powered Engines:339 kPa 34
kPa (49.2 psi 5 psi)
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 3
FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE (Continued)
Page 1304 of 2255

FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE
REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION
A combination fuel filter and fuel pressure regula-
tor (Fig. 2) is used on all engines. It is located on the
top of the fuel pump module. A separate frame
mounted fuel filter is not used with any engine.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
OPERATION
Fuel Pressure Regulator Operation:The pres-
sure regulator is a mechanical device that is not con-
trolled by engine vacuum or the powertrain control
module (PCM).
The regulator is calibrated to maintain fuel system
operating pressure of approximately 339 kPa 34
kPa (49.2 psi 5 psi) at the fuel injectors. It contains
a diaphragm, calibrated springs and a fuel return
valve. The internal fuel filter (Fig. 2) is also part of
the assembly.
Fuel is supplied to the filter/regulator by the elec-
tric fuel pump through an opening tube at the bot-
tom of filter/regulator (Fig. 2) .
The regulator acts as a check valve to maintain
some fuel pressure when the engine is not operating.
This will help to start the engine. A second checkvalve is located at the outlet end of the electric fuel
pump.Refer to Fuel PumpÐDescription and
Operation for more information. Also refer to
the Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test and the Fuel
Pump Pressure Tests.
If fuel pressure at the pressure regulator exceeds
approximately 49.2 psi, an internal diaphragm opens
and excess fuel pressure is routed back into the tank
through the bottom of pressure regulator.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE, EVEN WITH ENGINE OFF.
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRES-
SURE REGULATOR, FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
MUST BE RELEASED.
Refer to Fuel System Pressure Release in Fuel
Delivery System section of this group.
The fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator (Fig. 3) is
located at top of fuel pump module (Fig. 4) or (Fig.
5).
Fuel pump module removal is not necessary.
(1) Drain fuel tank and remove tank. Refer to Fuel
Tank Removal/Installation.
Fig. 2 Side ViewÐFilter/Regulator
1 - INTERNAL FUEL FILTER
2 - FUEL FLOW TO FUEL INJECTORS
3 - FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 - EXCESS FUEL BACK TO TANK
5 - FUEL INLET
6 - RUBBER GROMMET
7 - TOP OF PUMP MODULE
Fig. 3 Fuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator
1 - INTERNAL FUEL FILTER
2 - FUEL FLOW TO FUEL INJECTORS
3 - FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 - EXCESS FUEL BACK TO TANK
5 - FUEL INLET
6 - RUBBER GROMMET
7 - TOP OF PUMP MODULE
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 5