injector DODGE RAM 2002 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 1378 of 2255

CAUTION: The high-pressure fuel lines must be
clamped securely in place in the holders. The lines
cannot contact each other or other components. Do
not attempt to weld high-pressure fuel lines or to
repair lines that are damaged. Only use the recom-
mended lines when replacement of high-pressure
fuel line is necessary.
REMOVAL
High-pressure lines are used between the fuel
injection pump and the fuel injectors only. All high-
pressure fuel lines are of the same length and inside
diameter. Correct high-pressure fuel line usage and
installation is critical to smooth engine operation.
CAUTION: Refer to Cleaning Fuel System Parts.
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables from
both batteries. Cover and isolate ends of cables.
(2) Thoroughly clean fuel lines at cylinder head
and injection pump ends.
(3) Remove cable cover (Fig. 47). Cable cover is
attached with 2 Phillips screws, 2 plastic retention
clips and 2 push tabs (Fig. 47). Remove 2 Phillips
screws and carefully pry out 2 retention clips. After
clip removal, push rearward on front tab, and
upward on lower tab for cover removal.Do not
remove any cables at lever.(4) Disconnect wiring harness (clip) at bottom of
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor (APPS) mounting
bracket (Fig. 48).
(5) Using 2 small screwdrivers, pry front wiring
clip (Fig. 49) from cable bracket housing. Position
wiring harness towards front of engine.
(6) Remove electrical connector from APPS by
pushing connector tab rearward while pulling down
on connector (Fig. 50).
(7) Disconnect 2 electrical cables from cable
mounting studs (Fig. 51) at intake air heater on top
of intake manifold.
(8) Remove engine oil dipstick from engine.
(9) Remove engine oil dipstick tube support
mounting bolt (Fig. 51) and position tube to side.
(10) Disconnect clamps and remove air tube
(intake manifold-to-intercooler) (Fig. 49).
(11) Remove 4 air intake housing mounting bolts
and remove housing (Fig. 52) and (Fig. 51). Position
ground cable at top of air intake housing to front of
engine.
(12) Remove intake manifold air heater element
block from engine (Fig. 53). Discard old upper and
lower gaskets
(13) Remove 3 cable bracket housing mounting
bolts (Fig. 52). Carefully position cable bracket and
cable assembly to side of engine.Leave cables con-
nected to lever.
Fig. 47 Cable/Lever/Throttle Linkage Cover
1 - CABLE/LEVER/LINKAGE COVER
2 - PUSH UP LOWER TAB
3 - SCREWS/CLIPS (2)
4 - TAB PUSH HERE
Fig. 48 Wiring Clip at APPS
1 - LEVER
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS (6)
3 - WIRE HARNESS CLIP
4 - CALIBRATION SCREWS (NO ADJUSTMENT)
5 - APPS ASSEMBLY
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 79
FUEL LINES (Continued)
Page 1380 of 2255

(14) Remove engine lifting bracket at rear of
intake manifold (2 bolts) (Fig. 54).
(15) Remove bolts from all fuel injection line sup-
port brackets at intake manifold.
(16) Place shop towels around fuel lines at fuel
injectors. Do not allow fuel to drip down side of
engine.CAUTION: WHEN LOOSENING OR TIGHTENING
HIGH-PRESSURE FITTINGS AT INJECTION PUMP,
USE A BACK-UP WRENCH ON DELIVERY VALVE AT
PUMP. DO NOT ALLOW DELIVERY VALVE TO
ROTATE.
(17) Loosen high-pressure line fittings at injection
pump (Fig. 55) beginning with cylinders 1, 2 and 4.
(18) Loosen high-pressure lines at cylinder head
for cylinders 1, 2 and 4 (Fig. 54).
(19) Carefully remove front line bundle from
engine.Do not bend lines while removing.While
removing front line bundle, note line position.
(20) Loosen high-pressure lines at injection pump
beginning with cylinders 3, 5 and 6.
(21) Loosen high-pressure lines at cylinder head
for cylinders 3, 5 and 6 (Fig. 54).
(22) Carefully remove rear line bundle from
engine.Do not bend lines while removing.While
removing rear line bundle, note line position.
INSTALLATION
High-pressure lines are used between the fuel
injection pump and the fuel injectors only. All high-
pressure fuel lines are of the same length and inside
diameter. Correct high-pressure fuel line usage and
installation is critical to smooth engine operation.
Fig. 53 Intake Manifold Air Heater (Elements)
1 - AIR HEATER ELEMENTS
2 - LOWER GASKET
3 - BLOCK
4 - UPPER GASKET
Fig. 54 High-Pressure Fuel Lines
Fig. 55 High Pressure Lines at Fuel Injection Pump
1 - FPCM ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES
3 - FITTINGS
4 - FUEL INJECTION PUMP
5 - FPCM
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 81
FUEL LINES (Continued)
Page 1381 of 2255

CAUTION: Be sure that the high-pressure fuel lines
are installed in the same order that they were
removed.
(1) Lubricate threads of injector line fittings with
clean engine oil.
(2) Loosen, but do not remove, all fuel line support
bracket bolts.
(3) Installrearinjection line bundle beginning
with cylinder head (fuel injector) connections, fol-
lowed by injection pump connections. Tighten all fit-
tings finger tight.
(4) Tighten fittings at fuel injector ends for cylin-
ders number 6 and 5 to 38 N´m (28 ft. lbs.) torque.
Do not tighten number 3 line at this time. It
will be tightened during bleeding procedure.
(5) Tighten 3 fittings at fuel injection pump ends
to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Installfrontinjection line bundle beginning
with cylinder head (fuel injector) connections, fol-
lowed by injection pump connections. Tighten all fit-
tings finger tight.
(7) Tighten fitting at fuel injector end for cylinder
number 2 to 38 N´m (28 ft. lbs.) torque.Do not
tighten lines number 1 or 4 at this time. They
will be tightened during bleeding procedure.
(8) Tighten remaining 3 fittings at fuel injection
pump ends to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install fuel line support bracket bolts to intake
manifold and tighten to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
CAUTION: Be sure fuel lines are not contacting
each other or any other component. Noise will
result.
(10) Install engine lifting bracket at rear of intake
manifold. Tighten 2 bolts to 77 N´m (57 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(11) Install cable bracket housing/cable assembly
and tighten 3 mounting bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(12) Clean any old gasket material below and
above intake manifold air heater element block. Also
clean mating areas at intake manifold and air intake
housing.
(13) Using new gaskets, position intake manifold
air heater element block to engine.
(14) Install air intake housing and position ground
cable. Install 4 mounting bolts and tighten to 24 N´m
(18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(15) Install air tube (intake manifold-to-charge air
cooler) (Fig. 49). Tighten clamps to 8 N´m (72 in. lbs.)
torque.
(16) Install engine oil dipstick tube support mount-
ing bolt and tighten to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(17) Install engine oil dipstick to engine.(18) Connect 2 electrical cables to cable mounting
studs.
(19) Connect electrical connector to bottom of
APPS by pushing connector upward until it snaps
into position.
(20) Connect wiring harness (clip) at bottom of
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor (APPS) mounting
bracket (Fig. 48).
(21) Connect front wiring clip (Fig. 49) to cable
bracket housing.
(22) Install cable cover (Fig. 47).
(23) Connect both negative battery cables to both
batteries.
(24) Bleed air from fuel system. Do this at fuel
injector ends of lines. Use cylinders numbers 1, 3 and
4 for bleeding. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
DELIVERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE). After
bleeding, tighten fittings to 38 N´m (28 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(25) Check lines/fittings for leaks.
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL FUEL TANK
The fuel tank is similar to the tank used with gas-
oline powered models. The tank is equipped with a
separate fuel return line and a different fuel tank
module for diesel powered models. A fuel tank
mounted, electric fuel pump is not used with diesel
powered models. Refer to Fuel Tank Module for addi-
tional information.
For removal and installation procedures, refer to
Fuel Tank - Gasoline Engines.
FUEL TANK MODULE
DESCRIPTION
An electric fuel pump isnot usedin the fuel tank
module for diesel powered engines. Fuel is supplied
by the engine mounted fuel transfer pump and the
fuel injection pump.
The fuel tank module is installed in the top of the
fuel tank (Fig. 56). The fuel tank module (Fig. 56)
contains the following components:
²Fuel reservoir
²A separate in-tank fuel filter
²Rollover valve
²Fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor)
²Fuel supply line connection
²Fuel return line connection
²Auxiliary non-pressurized fuel supply fitting
OPERATION
Refer to Fuel Gauge Sending Unit.
14 - 82 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL LINES (Continued)
Page 1382 of 2255
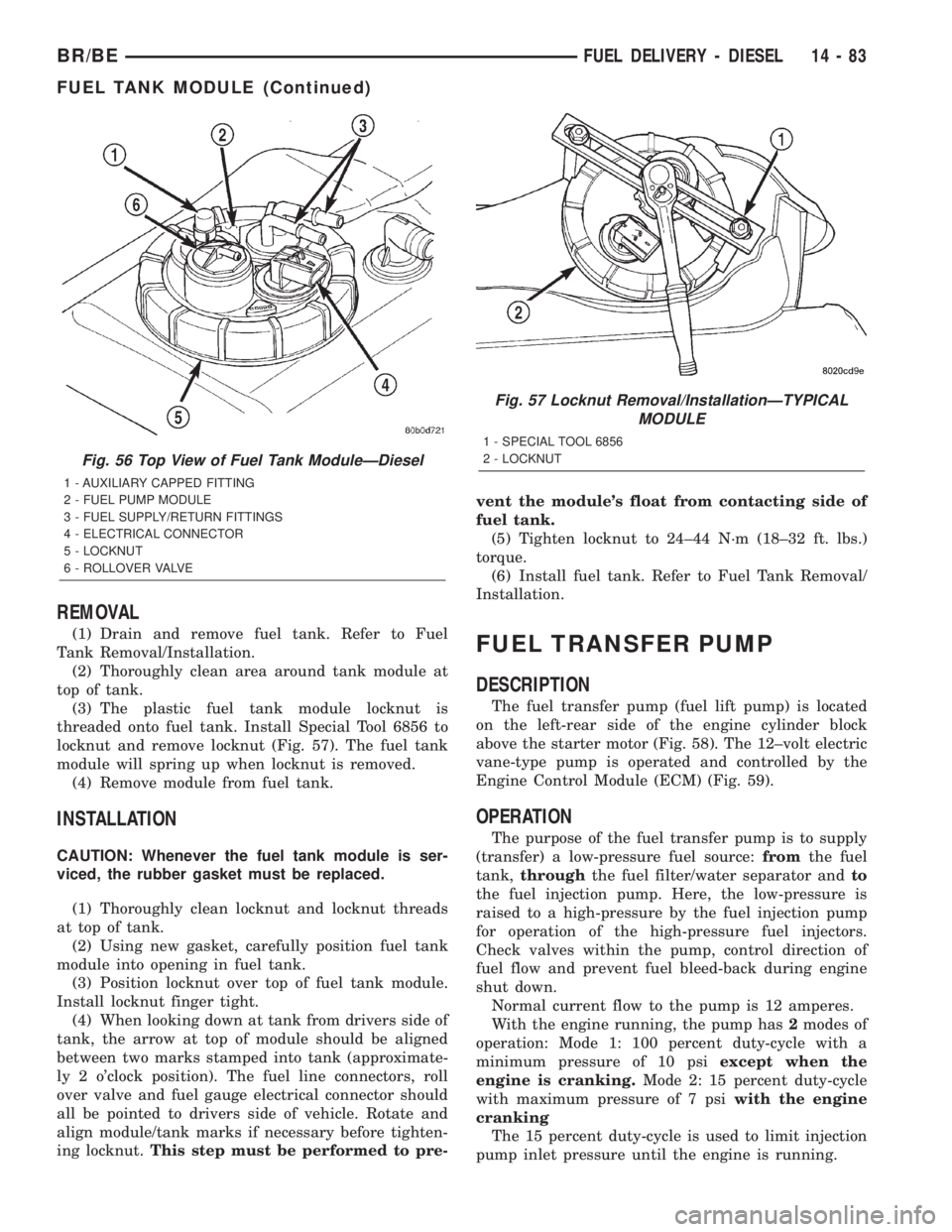
REMOVAL
(1) Drain and remove fuel tank. Refer to Fuel
Tank Removal/Installation.
(2) Thoroughly clean area around tank module at
top of tank.
(3) The plastic fuel tank module locknut is
threaded onto fuel tank. Install Special Tool 6856 to
locknut and remove locknut (Fig. 57). The fuel tank
module will spring up when locknut is removed.
(4) Remove module from fuel tank.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Whenever the fuel tank module is ser-
viced, the rubber gasket must be replaced.
(1) Thoroughly clean locknut and locknut threads
at top of tank.
(2) Using new gasket, carefully position fuel tank
module into opening in fuel tank.
(3) Position locknut over top of fuel tank module.
Install locknut finger tight.
(4) When looking down at tank from drivers side of
tank, the arrow at top of module should be aligned
between two marks stamped into tank (approximate-
ly 2 o'clock position). The fuel line connectors, roll
over valve and fuel gauge electrical connector should
all be pointed to drivers side of vehicle. Rotate and
align module/tank marks if necessary before tighten-
ing locknut.This step must be performed to pre-vent the module's float from contacting side of
fuel tank.
(5) Tighten locknut to 24±44 N´m (18±32 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(6) Install fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Removal/
Installation.
FUEL TRANSFER PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The fuel transfer pump (fuel lift pump) is located
on the left-rear side of the engine cylinder block
above the starter motor (Fig. 58). The 12±volt electric
vane-type pump is operated and controlled by the
Engine Control Module (ECM) (Fig. 59).
OPERATION
The purpose of the fuel transfer pump is to supply
(transfer) a low-pressure fuel source:fromthe fuel
tank,throughthe fuel filter/water separator andto
the fuel injection pump. Here, the low-pressure is
raised to a high-pressure by the fuel injection pump
for operation of the high-pressure fuel injectors.
Check valves within the pump, control direction of
fuel flow and prevent fuel bleed-back during engine
shut down.
Normal current flow to the pump is 12 amperes.
With the engine running, the pump has2modes of
operation: Mode 1: 100 percent duty-cycle with a
minimum pressure of 10 psiexcept when the
engine is cranking.Mode 2: 15 percent duty-cycle
with maximum pressure of 7 psiwith the engine
cranking
The 15 percent duty-cycle is used to limit injection
pump inlet pressure until the engine is running.
Fig. 56 Top View of Fuel Tank ModuleÐDiesel
1 - AUXILIARY CAPPED FITTING
2 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
3 - FUEL SUPPLY/RETURN FITTINGS
4 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
5 - LOCKNUT
6 - ROLLOVER VALVE
Fig. 57 Locknut Removal/InstallationÐTYPICAL
MODULE
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6856
2 - LOCKNUT
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 83
FUEL TANK MODULE (Continued)
Page 1388 of 2255
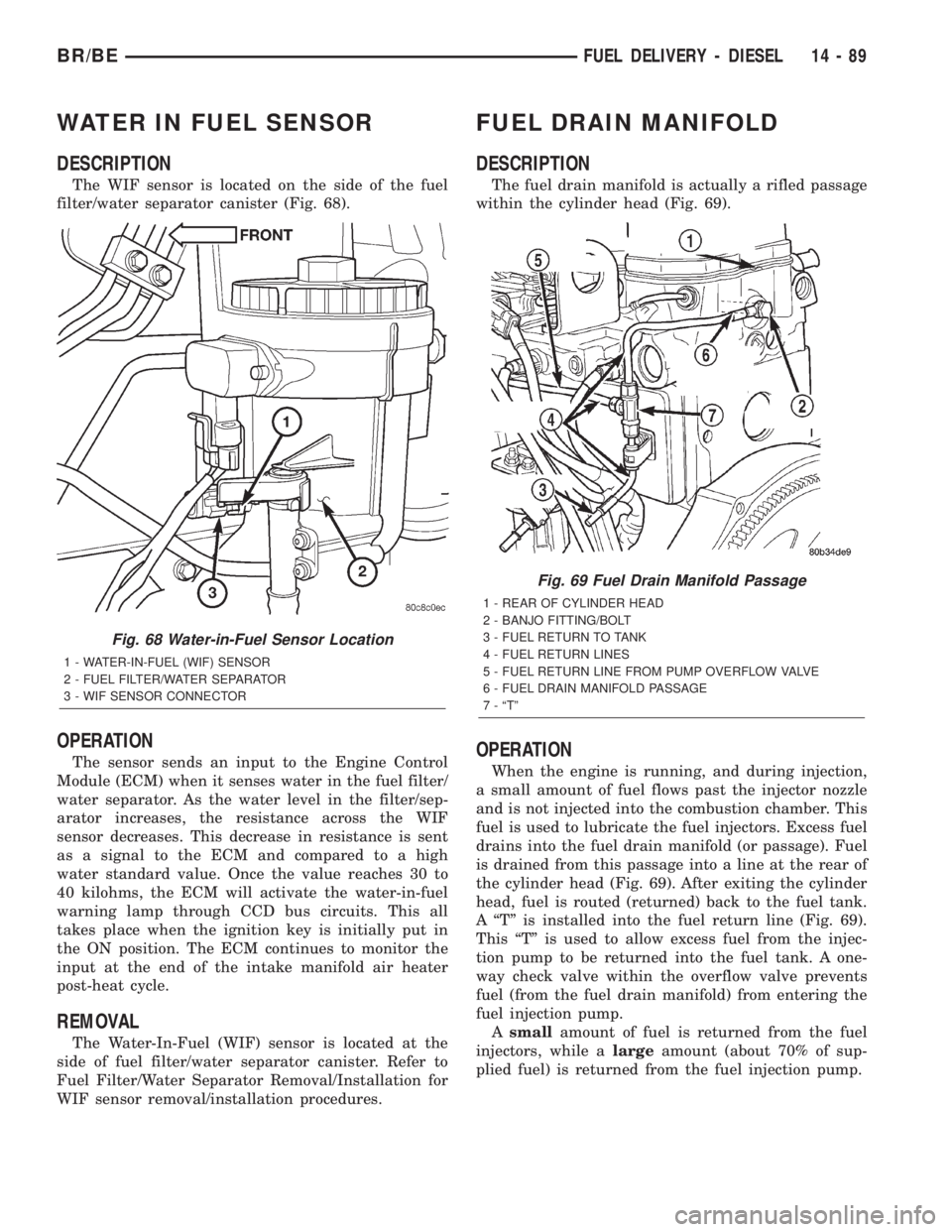
WATER IN FUEL SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The WIF sensor is located on the side of the fuel
filter/water separator canister (Fig. 68).
OPERATION
The sensor sends an input to the Engine Control
Module (ECM) when it senses water in the fuel filter/
water separator. As the water level in the filter/sep-
arator increases, the resistance across the WIF
sensor decreases. This decrease in resistance is sent
as a signal to the ECM and compared to a high
water standard value. Once the value reaches 30 to
40 kilohms, the ECM will activate the water-in-fuel
warning lamp through CCD bus circuits. This all
takes place when the ignition key is initially put in
the ON position. The ECM continues to monitor the
input at the end of the intake manifold air heater
post-heat cycle.
REMOVAL
The Water-In-Fuel (WIF) sensor is located at the
side of fuel filter/water separator canister. Refer to
Fuel Filter/Water Separator Removal/Installation for
WIF sensor removal/installation procedures.
FUEL DRAIN MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The fuel drain manifold is actually a rifled passage
within the cylinder head (Fig. 69).
OPERATION
When the engine is running, and during injection,
a small amount of fuel flows past the injector nozzle
and is not injected into the combustion chamber. This
fuel is used to lubricate the fuel injectors. Excess fuel
drains into the fuel drain manifold (or passage). Fuel
is drained from this passage into a line at the rear of
the cylinder head (Fig. 69). After exiting the cylinder
head, fuel is routed (returned) back to the fuel tank.
A ªTº is installed into the fuel return line (Fig. 69).
This ªTº is used to allow excess fuel from the injec-
tion pump to be returned into the fuel tank. A one-
way check valve within the overflow valve prevents
fuel (from the fuel drain manifold) from entering the
fuel injection pump.
Asmallamount of fuel is returned from the fuel
injectors, while alargeamount (about 70% of sup-
plied fuel) is returned from the fuel injection pump.
Fig. 68 Water-in-Fuel Sensor Location
1 - WATER-IN-FUEL (WIF) SENSOR
2 - FUEL FILTER/WATER SEPARATOR
3 - WIF SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 69 Fuel Drain Manifold Passage
1 - REAR OF CYLINDER HEAD
2 - BANJO FITTING/BOLT
3 - FUEL RETURN TO TANK
4 - FUEL RETURN LINES
5 - FUEL RETURN LINE FROM PUMP OVERFLOW VALVE
6 - FUEL DRAIN MANIFOLD PASSAGE
7 - ªTº
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 89
Page 1390 of 2255

FUEL INJECTION - DIESEL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL INJECTION - DIESEL
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL FUEL INJECTION
SYSTEM............................91
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BOOST
PRESSURE..........................93
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - DIESEL ENGINE.............94
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................95
OPERATION...........................95
REMOVAL.............................95
INSTALLATION.........................97
FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................97
OPERATION...........................98
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐFUEL INJECTOR
TEST...............................99
REMOVAL............................101
INSTALLATION........................102
FUEL INJECTION PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION........................103
OPERATION..........................103
FUEL TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................104
OPERATION..........................104
INTAKE AIR HEATER
DESCRIPTION........................104OPERATION..........................104
REMOVAL............................104
INSTALLATION........................105
INTAKE AIR HEATER RELAY
DESCRIPTION........................105
OPERATION..........................105
REMOVAL............................106
INSTALLATION........................106
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL.................106
OPERATION - DIESEL..................106
REMOVAL - DIESEL....................107
INSTALLATION - DIESEL................107
MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL.................108
OPERATION - DIESEL..................108
REMOVAL - DIESEL....................108
INSTALLATION........................108
PTO SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
OPERATION........................108
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE
REMOVAL............................109
INSTALLATION........................110
FUEL INJECTION - DIESEL
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL FUEL INJECTION
SYSTEM
The Engine Control Module (ECM) and Fuel Injec-
tion Pump Control Module (FPCM) are used prima-
rily for fuel system control. The ECM is a separate
replaceable component, while the FPCM is internal
to the fuel injection pump and is a non-serviceable
part. The ECM and FPCM are interconnected (wired
together) for fuel injection control.The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is used to
regulate or control the A/C, charging and speed con-
trol systems. It is also used to partially control cer-
tain electronic automatic transmission components.
The PCM also has control over certain instrument
panel components.
Refer to either Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
or Engine Control Module (ECM) for additional infor-
mation. Refer to (Fig. 1) for a partial list of fuel sys-
tem components.
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 91
Page 1391 of 2255
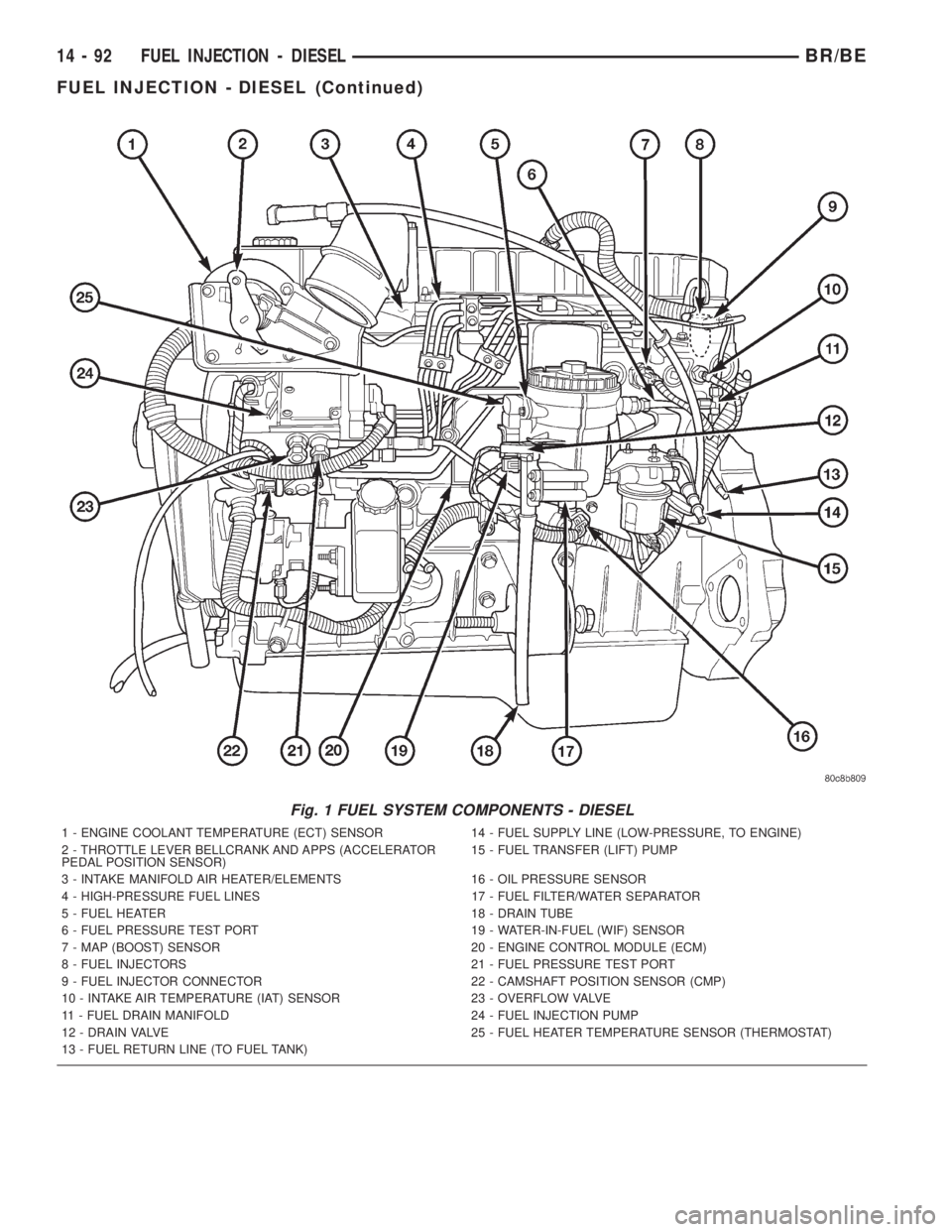
Fig. 1 FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS - DIESEL
1 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT) SENSOR 14 - FUEL SUPPLY LINE (LOW-PRESSURE, TO ENGINE)
2 - THROTTLE LEVER BELLCRANK AND APPS (ACCELERATOR
PEDAL POSITION SENSOR)15 - FUEL TRANSFER (LIFT) PUMP
3 - INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR HEATER/ELEMENTS 16 - OIL PRESSURE SENSOR
4 - HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES 17 - FUEL FILTER/WATER SEPARATOR
5 - FUEL HEATER 18 - DRAIN TUBE
6 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST PORT 19 - WATER-IN-FUEL (WIF) SENSOR
7 - MAP (BOOST) SENSOR 20 - ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
8 - FUEL INJECTORS 21 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST PORT
9 - FUEL INJECTOR CONNECTOR 22 - CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (CMP)
10 - INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT) SENSOR 23 - OVERFLOW VALVE
11 - FUEL DRAIN MANIFOLD 24 - FUEL INJECTION PUMP
12 - DRAIN VALVE 25 - FUEL HEATER TEMPERATURE SENSOR (THERMOSTAT)
13 - FUEL RETURN LINE (TO FUEL TANK)
14 - 92 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL INJECTION - DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1393 of 2255

SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - DIESEL ENGINE
DESCRIPTION N m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Bracket Bolts 12 9 105
Air Intake Housing Bolts 24 18 212
Banjo Fittings at top of Filter/Separator 24 18 212
Banjo Fittings at Fuel Return Lines 24 18 212
Banjo Fitting At Fuel Supply Line (Injector Pump) 24 18 212
Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP) Bolt 20 15 177
ECM Mounting Bolts 24 18 212
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 14 10 124
Engine Lifting Bracket Bolts 77 57 681
Fuel Drain Manifold ªTº Fitting 12 9 106
Fuel Filter Canister Bracket Bolts 24 18 212
Fuel Filter Canister Mounting Nut 14 10 124
Fuel Filter Drain Valve Mounting Screws 3-5 2-4 30-40
Fuel Heater Screws 2-3 1-2 15-20
Fuel Injector Clamp Bolts 10 7 89
Fuel Pump Module Locknut 24-44 18-32 212-389
Fuel Tank Mounting Nuts 41 30 363
Fuel Transfer Pump Mounting Nuts 12 9 106
High-Pressure Fuel Line Fittings (at Injectors) 38 28 336
High-Pressure Fuel Line Fittings (at Pump) 24 18 212
High-Pressure Fuel Line Clamps-to-Intake Manifold 24 18 212
Hose Clamps at Intercooler Tube 8 6 72
Injection Pump-to-Injection Pump Gear Nut 170 125
Injection Pump Mounting Nuts 43 32 380
Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor 14 10
Intake Manifold Air Heater Relay Bolts 4.5 40
Manifold Air Pressure (MAP) Sensor 14 10
PCM Mounting Bolts 4 35
Overflow Valve-to-Fuel Injection Pump 24 18
Water-In-Fuel (WIF) Sensor 2-3 15-20
14 - 94 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL INJECTION - DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1396 of 2255

(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
(2) Remove cable cover (Fig. 6). Cable cover is
attached with 2 Phillips screws, 2 plastic retention
clips and 2 push tabs (Fig. 6). Remove 2 Phillips
screws and carefully pry out 2 retention clips. After
clip removal, push rearward on front tab, and
upward on lower tab for cover removal.
(3) Using finger pressure only, disconnect end of
speed control servo cable from throttle lever pin by
pulling forward on connector while holding lever
rearward (Fig. 7).DO NOT try to pull connector
off perpendicular to lever pin. Connector will
be broken.
(4) Using two small screwdrivers, pry throttle
cable connector socket from throttle lever ball (Fig.
7).Be very careful not to bend throttle lever
arm.
(5) Disconnect transmission control cable at lever
arm (if equipped). Refer to 21, Transmission.
(6) Squeeze pinch tabs on speed control cable (Fig.
7) and pull cable rearward to remove from cable
mounting bracket.
(7) Squeeze pinch tabs on throttle cable (Fig. 7)
and pull cable rearward to remove from cable mount-
ing bracket.
(8) If equipped with an automatic transmission,
refer to 21, Transmission for transmission control
cable removal procedures.
(9) Disconnect wiring harness clip (Fig. 8) at bot-
tom of bracket.
(10) Remove 6 mounting bolts (Fig. 8) and par-
tially remove APPS assembly from engine. After
assembly is partially removed, disconnect electrical
connector from bottom of sensor by pushing on con-
nector tab (Fig. 9).
(11) Remove APPS assembly from engine.
INSTALLATION
The APPS is serviced (replaced) as one assembly
including the lever, brackets and sensor. The APPS is
calibrated to its mounting bracket. The APPS assem-
bly is located at left-front of engine below plastic
cable/lever/linkage cover (Fig. 6) .
(1) Snap electrical connector into bottom of sensor.
(2) Position APPS assembly to engine and install 6
bolts. Tighten bolts to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect wiring harness clip (Fig. 8) at bottom
of bracket.
(4) If equipped with an automatic transmission,
refer to Group 21, Transmission for transmission con-
trol cable installation procedures.
(5) Install speed control cable into mounting
bracket. Be sure pinch tabs (Fig. 7) have secured
cable.(6) Install throttle cable into mounting bracket. Be
sure pinch tabs (Fig. 7) have secured cable.
(7) Connect throttle cable at lever (snaps on).
(8) Connect speed control cable to lever by pushing
cable connector rearward onto lever pin while hold-
ing lever forward.
(9) Install cable cover.
(10) Connect both negative battery cables to both
batteries.
(11)ECM Calibration:Turn key to ON position.
Without starting engine, slowly press throttle pedal
to floor and then slowly release. This step must be
done (one time) to ensure accelerator pedal position
sensor calibration has been learned by ECM. If not
done, possible DTC's may be set.
(12) Use DRB scan tool to erase any DTC's from
ECM/PCM.
FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION
Six individual, high-pressure fuel injectors are
used. The injectors are vertically mounted (Fig. 10)
into a bored hole in the top of the cylinder head. This
bored hole is located between the intake/exhaust
valves.
Fig. 10 Fuel Injector Location
1 - CLAMP
2 - FUEL INJECTOR
3 - BORED HOLE
4 - SHIM
5 - BOLTS
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 97
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1397 of 2255
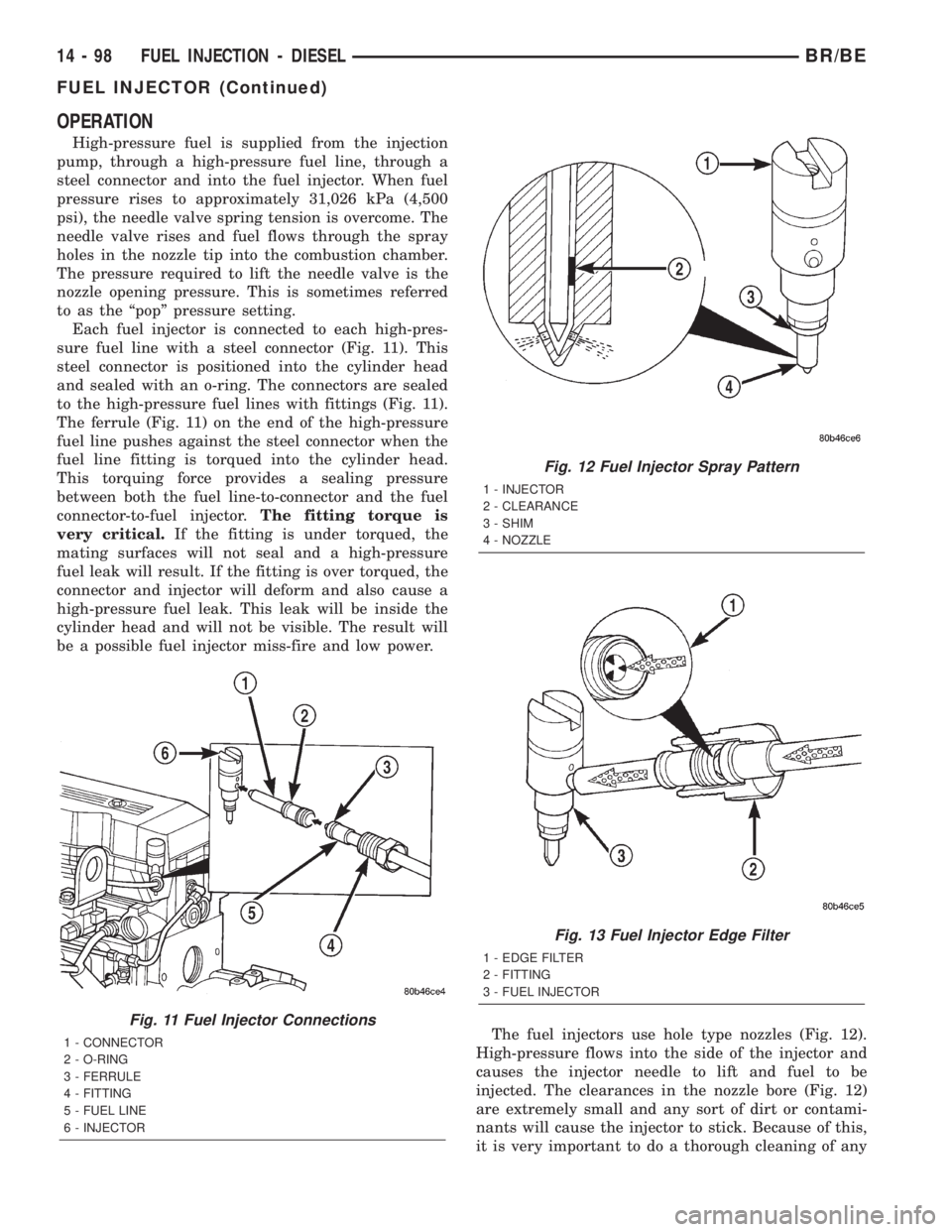
OPERATION
High-pressure fuel is supplied from the injection
pump, through a high-pressure fuel line, through a
steel connector and into the fuel injector. When fuel
pressure rises to approximately 31,026 kPa (4,500
psi), the needle valve spring tension is overcome. The
needle valve rises and fuel flows through the spray
holes in the nozzle tip into the combustion chamber.
The pressure required to lift the needle valve is the
nozzle opening pressure. This is sometimes referred
to as the ªpopº pressure setting.
Each fuel injector is connected to each high-pres-
sure fuel line with a steel connector (Fig. 11). This
steel connector is positioned into the cylinder head
and sealed with an o-ring. The connectors are sealed
to the high-pressure fuel lines with fittings (Fig. 11).
The ferrule (Fig. 11) on the end of the high-pressure
fuel line pushes against the steel connector when the
fuel line fitting is torqued into the cylinder head.
This torquing force provides a sealing pressure
between both the fuel line-to-connector and the fuel
connector-to-fuel injector.The fitting torque is
very critical.If the fitting is under torqued, the
mating surfaces will not seal and a high-pressure
fuel leak will result. If the fitting is over torqued, the
connector and injector will deform and also cause a
high-pressure fuel leak. This leak will be inside the
cylinder head and will not be visible. The result will
be a possible fuel injector miss-fire and low power.
The fuel injectors use hole type nozzles (Fig. 12).
High-pressure flows into the side of the injector and
causes the injector needle to lift and fuel to be
injected. The clearances in the nozzle bore (Fig. 12)
are extremely small and any sort of dirt or contami-
nants will cause the injector to stick. Because of this,
it is very important to do a thorough cleaning of any
Fig. 11 Fuel Injector Connections
1 - CONNECTOR
2 - O-RING
3 - FERRULE
4 - FITTING
5 - FUEL LINE
6 - INJECTOR
Fig. 12 Fuel Injector Spray Pattern
1 - INJECTOR
2 - CLEARANCE
3 - SHIM
4 - NOZZLE
Fig. 13 Fuel Injector Edge Filter
1 - EDGE FILTER
2 - FITTING
3 - FUEL INJECTOR
14 - 98 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)