tow DODGE RAM 2002 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 438 of 2255

If the heated seat system failure is identified by
flashing heated seat switch indicator lamps, go to the
appropriate diagnosis and testing procedure in this
section and confirm the condition, using the step by
step procedure. If the monitored failure is confirmed,
replace the component. If the monitored failure is not
confirmed, replace the heated seat module with a
known good unit and retest the system.
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM TESTING
Refer toWiring Diagramsfor the location of com-
plete heated seat system wiring diagrams. Before
testing the individual components in the heated seat
system, perform the following preliminary checks:
WARNING: DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCON-
NECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE
CABLE, THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIR-
BAG SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE
BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DIS-
ABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE
THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN
ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSI-
BLE PERSONAL INJURY.
²If the heated seat switch back lighting and the
cluster illumination lamps do not illuminate with the
headlamps or park lamps turned On, refer to the
Instrument Clustersection of the service manual
for the location of cluster illumination lamps diagno-
sis and testing procedures. If the heated seat switch
back lighting does not illuminate, but the cluster illu-
mination lamps do illuminate with the headlamps or
park lamps turned On, refer toDiagnosis and Test-
ing the Heated Seat Switchin this section for the
location of the heated seat switch diagnosis and test-
ing procedures.
²If a single indicator lamp for one heated seat
switch does not operate and the heated seat elements
do heat, refer toDiagnosis and Testing the
Heated Seat Switchin this section for heated seat
switch diagnosis and testing procedures.
²If both indicator lamps for a heated seat switch
operate, but the heated seat elements do not heat,
refer toDiagnosis and Testing the Heated Seat
Modulein Electronic Control Modules for heated
seat module diagnosis and testing procedures.
²If none of the indicator lamps for both heated
seat switches will operate and the heated seat ele-
ments for both seats do not heat, refer toDiagnosis
and Testing the Heated Seat Relayin the Power
Distribution section of the service manual for heated
seat relay diagnosis and testing procedures.²If the an indicator lamp on either heated seat
switch remains illuminated after the heated seat has
been turned Off, refer toDiagnosis and Testing
the Heated Seat Modulein Electronic Control
Modules for heated seat module diagnosis and test-
ing procedures. Also refer to the Body Diagnostic
Manual for additional diagnosis and testing proce-
dures.DRIVER SEAT HEATER
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The heated seat switches are both mounted in a
heated seat switch bezel (Fig. 2), which replaces the
standard equipment cubby bin located in the lower
right corner of the instrument cluster bezel next to
the radio receiver. The two switches are snapped into
the mounting holes of the heated seat switch bezel,
and the heated seat switch bezel is secured with
three screws to the instrument panel. The mounts for
the heated seat switch bezel are concealed behind the
instrument cluster bezel. The two heated seat
switches are identical in appearance and construc-
tion, except for the location of a keyway in the single
connector receptacle on the back of each switch. The
instrument panel wire harness connectors for the
heated seat switches are keyed to match the connec-
Fig. 2 Heated Seat Switches
1 - Driver Switch
2 - Passenger Switch
3 - Indicator Lamps
4 - Heated Seat Switch Bezel
BR/BEHEATED SEAT SYSTEM 8G - 7
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 439 of 2255

tor receptacles on the switches so that the two
heated seat switches can only be connected to the
proper heated seat electrical.
The momentary, bidirectional rocker-type heated
seat switch provides a resistor-multiplexed signal to
the heated seat module on the mux circuit. Each
switch has a center neutral position and momentary
Low and High positions so that both the driver and
the front seat passenger can select a preferred level
of seat heating. Each heated seat switch has two
Light-Emitting Diode (LED) indicator lamps, which
indicate the selected mode (Low or High) of the seat
heater. These indicator lamps also provide diagnostic
feedback for the heated seat system. Each switch
also has an incandescent bulb, which provides dim-
mer controlled back lighting of the switch when the
headlamps or park lamps are on.
The two LED indicator lamps and the incandescent
bulb in each heated seat switch cannot be repaired. If
the indicator lamps or back lighting bulb are faulty
or damaged, the individual heated seat switch must
be replaced.
OPERATION
The heated seat switches receive battery current
through a fused ignition switch output (run) circuit
when the ignition switch is in the On position.
Depressing the heated seat switch rocker to its
momentary High or Low position provides a hard-
wired resistor multiplexed voltage request signal to
the heated seat module to power the heated seat ele-
ment of the selected seat and maintain the requested
temperature setting. If the heated seat switch is
depressed to a different position (Low or High) than
the currently selected state, the heated seat module
will change states to support the new selection. If a
heated seat switch is depressed a second time to the
same position as the currently selected state, the
heated seat module interprets the second input as a
request to turn the seat heater off. The heated seat
module will then turn the heated seat elements for
that seat off.
The indicator lamps in the heated seat switches
receive battery current through a fused ignition
switch output (run) circuit when the ignition switch
is in the On position. The ground side of each indi-
cator lamp is controlled by a separate (high or low/
driver or passenger) indicator lamp driver circuit by
the heated seat module. The heated seat module con-
trol of the switch indicator lamps also allows the
module to provide diagnostic feedback to the vehicle
operator to indicate monitored heated seat system
faults by flashing the indicator lamps on and off. One
side of the incandescent back lighting bulb in each
heated seat switch is connected to ground at all
times. The other side of the incandescent bulb is con-nected to the fused panel lamps dimmer switch sig-
nal circuit. These bulbs are energized when the park
lamps or headlamps are turned on, and their illumi-
nation intensity is controlled by the panel lamps dim-
mer switch.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
SWITCH
Refer toWiring Diagramsfor the location of com-
plete heated seat system wiring diagrams.
WARNING: DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCON-
NECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE
(GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR
THE AIRBAG SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE
BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DIS-
ABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE
THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN
ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSI-
BLE PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) If the problem being diagnosed involves inoper-
ative heated seat switch back lighting and the cluster
illumination lamps operate, go to Step 2. If the prob-
lem being diagnosed involves inoperative heated seat
switch back lighting and the cluster illumination
lamps are also inoperative, refer toInstrument
Clusterin the index of this service manual for the
proper cluster illumination lamps diagnosis and test-
ing procedures. If the problem being diagnosed
involves inoperative heated seat switch indicator
lamps and the heated seat elements do not heat,
refer to Step 4. If the problem being diagnosed
involves inoperative heated seat switch indicator
lamps and the heated seat elements do heat, go to
Step 8. If the problem being diagnosed involves a
heated seat switch indicator lamp that remains illu-
minated after the heated seat has been turned Off,
refer toHeated Seat Modulein Electronic Control
Modules for the location of the proper heated seat
module diagnosis and testing procedures. Also refer
to the Body Diagnostic Manual for additional diagno-
sis and testing procedures.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the heated seat switch and bezel unit
from the instrument panel. Disconnect the instru-
ment panel wire harness connector from the connec-
tor receptacle on the back of the heated seat switch
to be tested. Check for continuity between the ground
circuit cavity of the instrument panel wire harness
connector for the heated seat switch and a good
ground. There should be continuity. If OK, go to Step
8G - 8 HEATED SEAT SYSTEMBR/BE
DRIVER SEAT HEATER SWITCH (Continued)
Page 442 of 2255

One temperature sensor is used for each outboard
seating position of the front seat, and it is located in
the center insert area of the seat cushion cover. The
heated seat sensors and their pigtail wires are also
captured between a covering and the adhesive foam
rubber backing. The heated seat sensors are Nega-
tive Thermal Coefficient (NTC) thermistors. The sen-
sors for both front seats receive a voltage feed from a
single output of the heated seat module, but the mod-
ule receives individual sensor inputs from the driver
side and passenger side sensors.
The heated seat elements and sensors should not
be repaired. If damaged or faulty, the heated seat ele-
ment assembly must be replaced. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/HEATED SEATS/HEATED SEAT
ELEMENT - REMOVAL).
OPERATION
One end of the heated seat element resistor wire is
connected to a ground feed at all times through a
splice in the heated seat module ground circuit. Bat-
tery current is directed to the other end of the heated
seat element resistor wire by the energized N-chan-
nel Field Effect Transistor (N-FET) located within
the heated seat module. The heated seat module will
energize the N-FET only when the heated seat
switch is in the Low or High position and the heated
seat sensor indicates that the seat cushion surface
temperature is below the selected (Low or High) tem-
perature set point. As electrical current passes
through the heating element grid, the resistance of
the wire used in the element disperses some of that
electrical current in the form of heat. The heat pro-
duced by the heated seat element grid then radiates
through the underside of the seat cushion and seat
back trim covers, warming the seat cover and its
occupant.
The resistance of the heated seat sensor increases
and decreases as the surface temperature of the seat
cushion cover changes. The heated seat module sup-
plies each sensor with a voltage feed, then detects
the sensor resistance by monitoring the voltage of the
separate sensor return circuits. The heated seat mod-
ule compares the heated seat sensor resistance (seat
cushion surface temperature) with the heated seat
switch resistance (Low or High set point) to deter-
mine when the heated seat element grids need to be
cycled on or off in order to maintain the selected tem-
perature set point.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
ELEMENT AND SENSOR
The heated seat module will self-diagnose shorted
or open heated seat element circuits and sensor cir-
cuits. Refer to Heated Seat System Diagnosis and
Testing in this section for additional diagnosis and
testing procedures. To manually check the heated
seat element and sensor circuits, proceed as follows.
The wire harness connectors for the seat cushion and
seat back heating elements and sensor are located
under the seat, near the rear edge of the seat cush-
ion frame (Fig. 6) . Refer toWiring Diagramsfor
the location of complete heated seat system wiring
diagrams.
HEATED SEAT ELEMENTS
(1) Position the appropriate seat in the full for-
ward position.
(2) Make certain the ignition switch is in the OFF
position.
Fig. 6 PASSENGER SEAT WIRE HARNESS
ROUTING
1 - SEAT BACK HEATED SEAT WIRE HARNESS
2 - PASSENGER SEAT BACK
3 - SEAT BACK ELEMENT CONNECTOR
4 - SEAT CUSHION ELEMENT CONNECTOR
BR/BEHEATED SEAT SYSTEM 8G - 11
HEATED SEAT ELEMENT (Continued)
Page 446 of 2255

ical dimensions are smaller than those of the conven-
tional ISO relay.
The heated seat relay cannot be repaired or
adjusted and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor or diode, and three (two fixed and one mov-
able) electrical contacts. The movable (common feed)
relay contact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When the elec-
tromagnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable
contact away from the normally closed fixed contact,
and holds it against the other (normally open) fixed
contact. When the electromagnetic coil is de-ener-
gized, spring pressure returns the movable contact to
the normally closed position. The resistor or diode is
connected in parallel with the electromagnetic coil in
the relay, and helps to dissipate voltage spikes that
are produced when the coil is de-energized.
The heated seat relay is controlled by the premium
version of the Central Timer Module (CTM), which
controls the ground feed to the coil ground terminal
of the relay to energize and de-energize the electro-
magnetic coil of the relay. The CTM monitors engine
operation through messages it receives from the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM) over the Chrysler Col-
lision Detection (CCD) data bus network. The CTM is
programmed to energize the relay only when the
engine is running, and to de-energize the relay when
the engine is not running. Refer toCentral Timer
Modulein the index of this service manual for the
location of more information on the premium CTM.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
RELAY
The heated seat relay (Fig. 15) is located in the
Junction Block (JB) on the left end of the instrument
panel in the passenger compartment of the vehicle.
Refer toWiring Diagramsfor the location of com-
plete heated seat system wiring diagrams.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIRBAGS,
DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE ATTEMPT-
ING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY
NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT TWO MIN-
UTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DIS-
CHARGE BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE
WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM. FAILURE TO
TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT
IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSI-
BLE PERSONAL INJURY.
RELAY TEST
(1) Remove the heated seat relay from the JB.
Refer toHeated Seat Relayin this section for the
location of the proper heated seat relay removal pro-
cedures.
(2) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 5 ohms. If OK, go to Step
4. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(4) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, perform the Relay Circuit Test that
follows. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) is
connected to battery voltage and should be hot at all
times. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to the fused B(+) fuse in the Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC) as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is
connected to terminal 30 in the de-energized position,
but is not used for this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal (87) is con-
nected to the common feed terminal (30) in the ener-
gized position. This terminal supplies battery voltage
to the heated seat module. There should be continu-
ity between the cavity for relay terminal 87 and the
B(+) to heated seat module circuit cavity of the
heated seat module wire harness connector at all
times. If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open
Fig. 15 Heated Seat Relay
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
BR/BEHEATED SEAT SYSTEM 8G - 15
HEATED SEAT RELAY (Continued)
Page 447 of 2255

B(+) to heated seat module circuit to the heated seat
module as required.
(4) The coil battery terminal (86) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is connected to bat-
tery voltage and should be hot at all times. Check for
battery voltage at the cavity for relay terminal 86. If
OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, repair the open circuit to
the fused B(+) fuse in the PDC as required.
(5) The coil ground terminal (85) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is grounded by the
premium version of the Central Timer Module (CTM)
in response to an engine speed message received over
the Chrysler Collision Detection (CCD) data bus from
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) when the
engine is running. Check for continuity between the
cavity for relay terminal 85 and the heated seat relay
control circuit cavity of the CTM wire harness con-
nector. There should be continuity at all times. If OK,
use a DRBIIItscan tool and the proper diagnostic
procedures manual to test the operation of the CTM
and CCD data bus. If not OK, repair the open heated
seat relay control circuit as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the fuse access panel by inserting a
finger in the finger recess molded into the panel and
then pulling the panel sharply away from the left
outboard end of the instrument panel.
(3) The heated seat relay is located on the forward
side of the Junction Block (JB), just above the com-
bination flasher (Fig. 16) .
(4) Grasp the heated seat relay firmly and pull it
straight out from the JB.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the heated seat relay in the proper
receptacle in the JB.
(2) Align the heated seat relay terminals with the
terminal cavities in the JB receptacle.
(3) Push in firmly on the heated seat relay until
the terminals are fully seated in the terminal cavities
in the JB receptacle.
(4) Insert the tabs on the forward edge of the fuse
access panel in the notches on the forward edge of
the instrument panel fuse access panel opening.
(5) Press the rear edge of the fuse access panel in
toward the instrument panel until the panel snaps
back into place.
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
PASSENGER SEAT HEATER
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The heated seat switches are both mounted in a
heated seat switch bezel (Fig. 17), which replaces the
standard equipment cubby bin located in the lower
right corner of the instrument cluster bezel next to
the radio receiver. The two switches are snapped into
the mounting holes of the heated seat switch bezel,
and the heated seat switch bezel is secured with
three screws to the instrument panel. The mounts for
the heated seat switch bezel are concealed behind the
instrument cluster bezel. The two heated seat
switches are identical in appearance and construc-
tion, except for the location of a keyway in the single
connector receptacle on the back of each switch. The
instrument panel wire harness connectors for the
heated seat switches are keyed to match the connec-
tor receptacles on the switches so that the two
heated seat switches can only be connected to the
proper heated seat electrical.
The momentary, bidirectional rocker-type heated
seat switch provides a resistor-multiplexed signal to
the heated seat module on the mux circuit. Each
switch has a center neutral position and momentary
Low and High positions so that both the driver and
Fig. 16 Heated Seat
1 - JUNCTION BLOCK
2 - HEATED SEAT RELAY
3 - INSTRUMENT PANEL
4 - COMBINATION FLASHER
8G - 16 HEATED SEAT SYSTEMBR/BE
HEATED SEAT RELAY (Continued)
Page 448 of 2255

the front seat passenger can select a preferred level
of seat heating. Each heated seat switch has two
Light-Emitting Diode (LED) indicator lamps, which
indicate the selected mode (Low or High) of the seat
heater. These indicator lamps also provide diagnostic
feedback for the heated seat system. Each switch
also has an incandescent bulb, which provides dim-
mer controlled back lighting of the switch when the
headlamps or park lamps are on.
The two LED indicator lamps and the incandescent
bulb in each heated seat switch cannot be repaired. If
the indicator lamps or back lighting bulb are faulty
or damaged, the individual heated seat switch must
be replaced.
OPERATION
The heated seat switches receive battery current
through a fused ignition switch output (run) circuit
when the ignition switch is in the On position.
Depressing the heated seat switch rocker to its
momentary High or Low position provides a hard-
wired resistor multiplexed voltage request signal to
the heated seat module to power the heated seat ele-
ment of the selected seat and maintain the requested
temperature setting. If the heated seat switch is
depressed to a different position (Low or High) than
the currently selected state, the heated seat module
will change states to support the new selection. If a
heated seat switch is depressed a second time to thesame position as the currently selected state, the
heated seat module interprets the second input as a
request to turn the seat heater off. The heated seat
module will then turn the heated seat elements for
that seat off.
The indicator lamps in the heated seat switches
receive battery current through a fused ignition
switch output (run) circuit when the ignition switch
is in the On position. The ground side of each indi-
cator lamp is controlled by a separate (high or low/
driver or passenger) indicator lamp driver circuit by
the heated seat module. The heated seat module con-
trol of the switch indicator lamps also allows the
module to provide diagnostic feedback to the vehicle
operator to indicate monitored heated seat system
faults by flashing the indicator lamps on and off. One
side of the incandescent back lighting bulb in each
heated seat switch is connected to ground at all
times. The other side of the incandescent bulb is con-
nected to the fused panel lamps dimmer switch sig-
nal circuit. These bulbs are energized when the park
lamps or headlamps are turned on, and their illumi-
nation intensity is controlled by the panel lamps dim-
mer switch.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
SWITCH
Refer toWiring Diagramsfor the location of com-
plete heated seat system wiring diagrams.
WARNING: DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCON-
NECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE
(GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR
THE AIRBAG SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE
BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DIS-
ABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE
THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN
ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSI-
BLE PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) If the problem being diagnosed involves inoper-
ative heated seat switch back lighting and the cluster
illumination lamps operate, go to Step 2. If the prob-
lem being diagnosed involves inoperative heated seat
switch back lighting and the cluster illumination
lamps are also inoperative, refer toInstrument
Clusterin the index of this service manual for the
proper cluster illumination lamps diagnosis and test-
ing procedures. If the problem being diagnosed
involves inoperative heated seat switch indicator
lamps and the heated seat elements do not heat,
refer to Step 4. If the problem being diagnosed
Fig. 17 Heated Seat Switches
1 - Driver Switch
2 - Passenger Switch
3 - Indicator Lamps
4 - Heated Seat Switch Bezel
BR/BEHEATED SEAT SYSTEM 8G - 17
PASSENGER SEAT HEATER SWITCH (Continued)
Page 453 of 2255

ELECTRICAL/VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY - GEN-
ERAL INFORMATION) for more information on the
VTSS. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER LOCKS -
GENERAL INFORMATION) for more information on
the RKE system.
HORN
DESCRIPTION
The standard single, low-note, electromagnetic dia-
phragm-type horn is secured with a bracket to the
right front fender wheel house extension in the
engine compartment. The high-note horn for the
optional dual-note horn system is connected in paral-
lel with and secured with a bracket just forward of
the low-note horn. Each horn is grounded through its
wire harness connector and circuit to a ground splice
joint connector, and receives battery feed through the
closed contacts of the horn relay.
The horns cannot be repaired or adjusted and, if
faulty or damaged, they must be individually
replaced.
OPERATION
Within the two halves of the molded plastic horn
housing are a flexible diaphragm, a plunger, an elec-
tromagnetic coil and a set of contact points. The dia-
phragm is secured in suspension around its
perimeter by the mating surfaces of the horn hous-
ing. The plunger is secured to the center of the dia-
phragm and extends into the center of the
electromagnet. The contact points control the current
flow through the electromagnet.
When the horn is energized, electrical current
flows through the closed contact points to the electro-
magnet. The resulting electromagnetic field draws
the plunger and diaphragm toward it until that
movement mechanically opens the contact points.
When the contact points open, the electromagnetic
field collapses allowing the plunger and diaphragm to
return to their relaxed positions and closing the con-
tact points again. This cycle continues repeating at a
very rapid rate producing the vibration and move-
ment of air that creates the sound that is directed
through the horn outlet.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN
For complete circuit diagrams, refer to the appro-
priate wiring information. The wiring information
includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and connector
repair procedures, details of wire harness routing
and retention, connector pin-out information and
location views for the various wire harness connec-
tors, splices and grounds.(1) Disconnect the wire harness connector(s) from
the horn connector receptacle(s). Measure the resis-
tance between the ground circuit cavity of the horn(s)
wire harness connector(s) and a good ground. There
should be no measurable resistance. If OK, go to Step
2. If not OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground
as required.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the horn relay out-
put circuit cavity of the horn(s) wire harness connec-
tor(s). There should be zero volts. If OK, go to Step 3.
If not OK, repair the shorted horn relay output cir-
cuit or replace the faulty horn relay as required.
(3) Depress the horn switch. There should now be
battery voltage at the horn relay output circuit cavity
of the horn(s) wire harness connector(s). If OK,
replace the faulty horn(s). If not OK, repair the open
horn relay output circuit to the horn relay as
required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Disconnect the wire harness connector(s) from
the horn connector receptacle(s) (Fig. 1) .
(3) Remove the screw that secures the horn and
mounting bracket unit(s) to the right fender wheel
house front extension.
(4) Remove the horn and mounting bracket unit(s)
from the right fender wheel house front extension.
Fig. 1 Horns Remove/Install
1 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
2 - SCREWS
3 - INNER FENDER
4 - LOW NOTE HORN
5 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
6 - WHEELHOUSE EXTENSION
7 - HIGH NOTE HORN
8H - 2 HORNBR/BE
HORN (Continued)
Page 461 of 2255
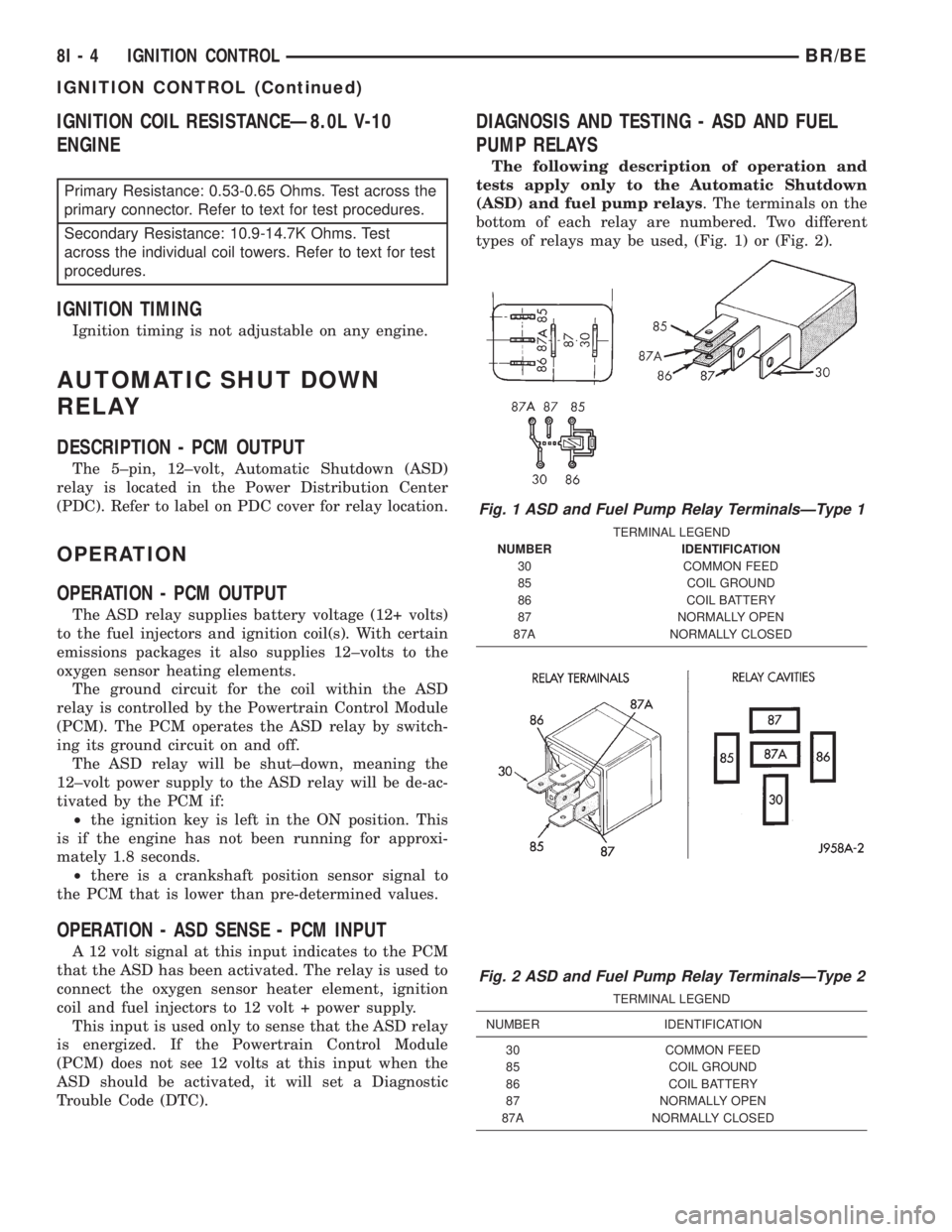
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCEÐ8.0L V-10
ENGINE
Primary Resistance: 0.53-0.65 Ohms. Test across the
primary connector. Refer to text for test procedures.
Secondary Resistance: 10.9-14.7K Ohms. Test
across the individual coil towers. Refer to text for test
procedures.
IGNITION TIMING
Ignition timing is not adjustable on any engine.
AUTOMATIC SHUT DOWN
RELAY
DESCRIPTION - PCM OUTPUT
The 5±pin, 12±volt, Automatic Shutdown (ASD)
relay is located in the Power Distribution Center
(PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT
The ASD relay supplies battery voltage (12+ volts)
to the fuel injectors and ignition coil(s). With certain
emissions packages it also supplies 12±volts to the
oxygen sensor heating elements.
The ground circuit for the coil within the ASD
relay is controlled by the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM operates the ASD relay by switch-
ing its ground circuit on and off.
The ASD relay will be shut±down, meaning the
12±volt power supply to the ASD relay will be de-ac-
tivated by the PCM if:
²the ignition key is left in the ON position. This
is if the engine has not been running for approxi-
mately 1.8 seconds.
²there is a crankshaft position sensor signal to
the PCM that is lower than pre-determined values.
OPERATION - ASD SENSE - PCM INPUT
A 12 volt signal at this input indicates to the PCM
that the ASD has been activated. The relay is used to
connect the oxygen sensor heater element, ignition
coil and fuel injectors to 12 volt + power supply.
This input is used only to sense that the ASD relay
is energized. If the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) does not see 12 volts at this input when the
ASD should be activated, it will set a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ASD AND FUEL
PUMP RELAYS
The following description of operation and
tests apply only to the Automatic Shutdown
(ASD) and fuel pump relays. The terminals on the
bottom of each relay are numbered. Two different
types of relays may be used, (Fig. 1) or (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1 ASD and Fuel Pump Relay TerminalsÐType 1
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
Fig. 2 ASD and Fuel Pump Relay TerminalsÐType 2
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
8I - 4 IGNITION CONTROLBR/BE
IGNITION CONTROL (Continued)
Page 471 of 2255
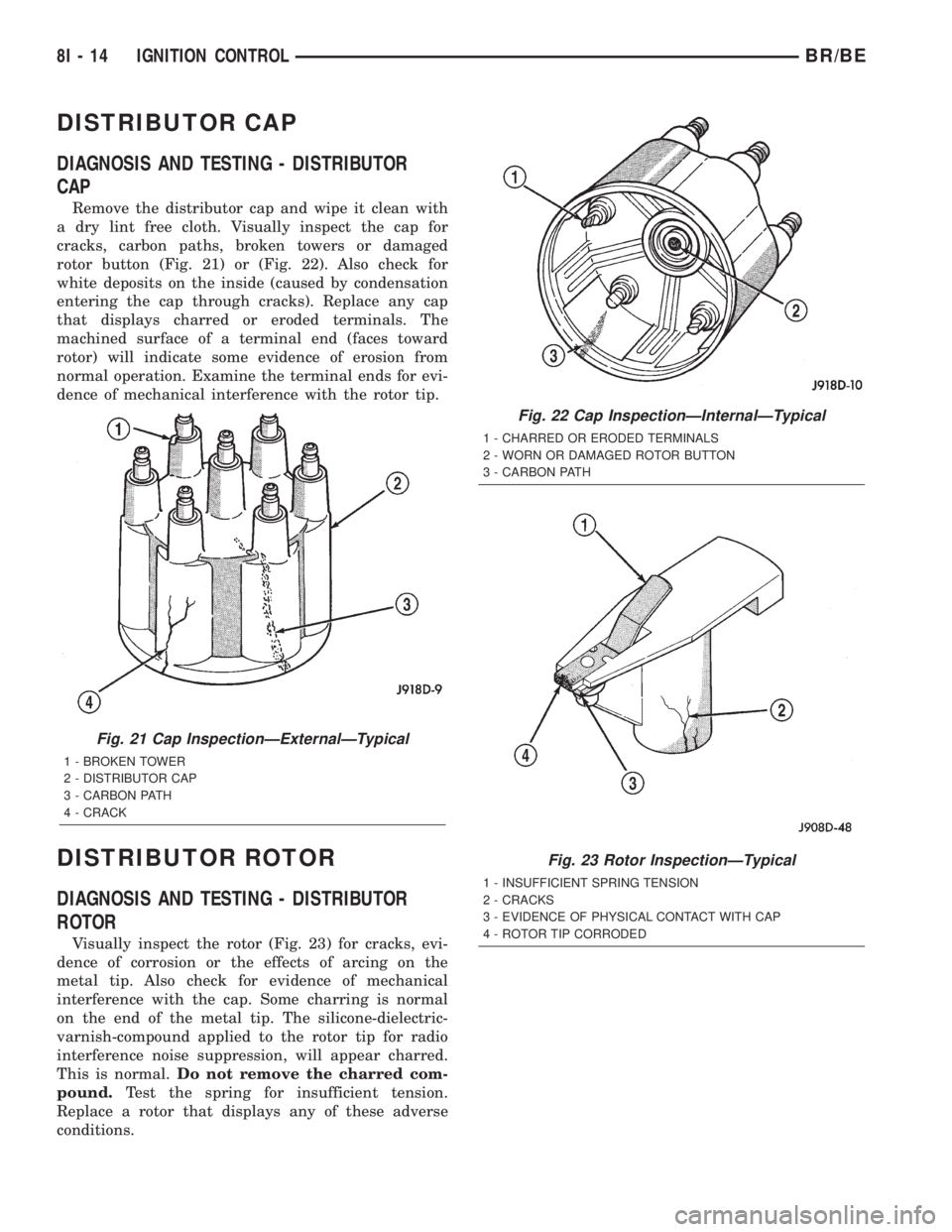
DISTRIBUTOR CAP
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DISTRIBUTOR
CAP
Remove the distributor cap and wipe it clean with
a dry lint free cloth. Visually inspect the cap for
cracks, carbon paths, broken towers or damaged
rotor button (Fig. 21) or (Fig. 22). Also check for
white deposits on the inside (caused by condensation
entering the cap through cracks). Replace any cap
that displays charred or eroded terminals. The
machined surface of a terminal end (faces toward
rotor) will indicate some evidence of erosion from
normal operation. Examine the terminal ends for evi-
dence of mechanical interference with the rotor tip.
DISTRIBUTOR ROTOR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DISTRIBUTOR
ROTOR
Visually inspect the rotor (Fig. 23) for cracks, evi-
dence of corrosion or the effects of arcing on the
metal tip. Also check for evidence of mechanical
interference with the cap. Some charring is normal
on the end of the metal tip. The silicone-dielectric-
varnish-compound applied to the rotor tip for radio
interference noise suppression, will appear charred.
This is normal.Do not remove the charred com-
pound.Test the spring for insufficient tension.
Replace a rotor that displays any of these adverse
conditions.
Fig. 21 Cap InspectionÐExternalÐTypical
1 - BROKEN TOWER
2 - DISTRIBUTOR CAP
3 - CARBON PATH
4 - CRACK
Fig. 22 Cap InspectionÐInternalÐTypical
1 - CHARRED OR ERODED TERMINALS
2 - WORN OR DAMAGED ROTOR BUTTON
3 - CARBON PATH
Fig. 23 Rotor InspectionÐTypical
1 - INSUFFICIENT SPRING TENSION
2 - CRACKS
3 - EVIDENCE OF PHYSICAL CONTACT WITH CAP
4 - ROTOR TIP CORRODED
8I - 14 IGNITION CONTROLBR/BE
Page 477 of 2255

(2) Prior to removing the spark plug, spray com-
pressed air around the spark plug hole and the area
around the spark plug. This will help prevent foreign
material from entering the combustion chamber.
(3) Remove the spark plug using a quality socket
with a rubber or foam insert.
(4) Inspect the spark plug condition. Refer to
Spark Plug Condition in the Diagnostics and Testing
section of this group.
CLEANING
The plugs may be cleaned using commercially
available spark plug cleaning equipment. After clean-
ing, file center electrode flat with a small point file or
jewelers file before adjusting gap.
CAUTION: Never use a motorized wire wheel brush
to clean spark plugs. Metallic deposits will remain
on spark plug insulator and will cause plug misfire.
INSTALLATION
Special care should be taken when installing spark
plugs into the cylinder head spark plug wells. Be
sure the plugs do not drop into the plug wells as elec-
trodes can be damaged.
Always tighten spark plugs to the specified torque.
Over tightening can cause distortion resulting in a
change in the spark plug gap or a cracked porcelain
insulator.
When replacing the spark plug and ignition coil
cables, route the cables correctly and secure them in
the appropriate retainers. Failure to route the cables
properly can cause the radio to reproduce ignition
noise. It could cause cross ignition of the spark plugs
or short circuit the cables to ground.
(1) Start the spark plug into the cylinder head by
hand to avoid cross threading.
(2) Tighten spark plugs to 35-41 N´m (26-30 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(3) Install spark plug cables over spark plugs.
SPARK PLUG CABLE
DESCRIPTION
Spark plug cables are sometimes referred to as sec-
ondary ignition wires.
OPERATION
The spark plug cables transfer electrical current
from the ignition coil(s) and/or distributor, to individ-
ual spark plugs at each cylinder. The resistive spark
plug cables are of nonmetallic construction. The
cables provide suppression of radio frequency emis-
sions from the ignition system.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPARK PLUG
CABLES
Cable routing is important on certain engines. To
prevent possible ignition crossfire, be sure the cables
are clipped into the plastic routing looms. Try to pre-
vent any one cable from contacting another. Before
removing cables, note their original location and
routing. Never allow one cable to be twisted around
another.
Check the spark plug cable connections for good
contact at the coil(s), distributor cap towers, and
spark plugs. Terminals should be fully seated. The
insulators should be in good condition and should fit
tightly on the coil, distributor and spark plugs. Spark
plug cables with insulators that are cracked or torn
must be replaced.
Clean high voltage ignition cables with a cloth
moistened with a non-flammable solvent. Wipe the
cables dry. Check for brittle or cracked insulation.
On 5.9L engines, spark plug cable heat shields are
pressed into the cylinder head to surround each
spark plug cable boot and spark plug (Fig. 36). These
shields protect the spark plug boots from damage
(due to intense engine heat generated by the exhaust
manifolds) and should not be removed. After the
spark plug cable has been installed, the lip of the
cable boot should have a small air gap to the top of
the heat shield (Fig. 36).
TESTING
When testing secondary cables for damage with an
oscilloscope, follow the instructions of the equipment
manufacturer.
If an oscilloscope is not available, spark plug cables
may be tested as follows:
Fig. 36 Heat ShieldsÐ5.9L Engines
1 - AIR GAP
2 - SPARK PLUG BOOT HEAT SHIELD
8I - 20 IGNITION CONTROLBR/BE
SPARK PLUG (Continued)