ac compressor DODGE RAM 2002 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 1314 of 2255

The fuel rail is not repairable.
CAUTION: The left and right sections of the fuel rail
are connected with a flexible connecting hose. Do
not attempt to separate the rail halves at this con-
necting hose. Due to the design of this connecting
hose, it does not use any clamps. Never attempt to
install a clamping device of any kind to the hose.
When removing the fuel rail assembly for any rea-
son, be careful not to bend or kink the connecting
hose.
OPERATION - 8.0L
High pressure from the fuel pump is routed to the
fuel rail. The fuel rail then supplies the necessary
fuel to each individual fuel injector.
A fuel pressure test port is located on the fuel rail.
A quick-connect fitting with a safety latch clip is
used to attach the fuel line to the fuel rail.
The fuel rail is not repairable.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 5.9L
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH ENGINE TURNED
OFF). BEFORE SERVICING FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY,
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
To release fuel pressure, refer to Fuel System Pres-
sure Release Procedure found in this group.
CAUTION: The left and right fuel rails are replaced
as an assembly. Do not attempt to separate the rail
halves at the connecting hose (Fig. 24). Due to the
design of this connecting hose, it does use any
clamps. Never attempt to install a clamping device
of any kind to the hose. When removing the fuel rail
assembly for any reason, be careful not to bend or
kink the connecting hose.
(1) Remove negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Remove air cleaner.
(3) Perform fuel pressure release procedure.
(4) Remove throttle body from intake manifold.
Refer to Throttle Body removal in this group.
(5) If equipped with air conditioning, remove the
A-shaped A/C compressor-to-intake manifold support
bracket (three bolts) (Fig. 25).
(6) Disconnect electrical connectors at all fuel
injectors. To remove connector refer to (Fig. 26). Push
red colored slider away from injector (1). While push-
ing slider, depress tab (2) and remove connector (3)
from injector. The factory fuel injection wiring har-ness is numerically tagged (INJ 1, INJ 2, etc.) for
injector position identification. If harness is not
tagged, note wiring location before removal.
(7) Disconnect fuel tube (line) at side of fuel rail.
Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings for procedures,
(8) Remove the remaining fuel rail mounting bolts.
(9) Gently rock and pull theleftfuel rail until the
fuel injectors just start to clear the intake manifold.
Gently rock and pull therightfuel rail until the fuel
injectors just start to clear the intake manifold.
Repeat this procedure (left/right) until all fuel injec-
tors have cleared the intake manifold.
Fig. 24 Fuel Rail AssemblyÐTypical
1 - FUEL RAIL CONNECTING HOSE
2 - FUEL RAIL
3 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
Fig. 25 A/C Compressor Support BracketÐTypical
1 - AIR CONDITIONING COMPRESSOR SUPPORT BRACKET
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 15
FUEL RAIL (Continued)
Page 1328 of 2255

FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
VISUAL INSPECTIONÐ5.9L ENGINES
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected or incor-
rectly routed wires and hoses should be made. This
should be done before attempting to diagnose or ser-
vice the fuel injection system. A visual check will
help spot these faults and save unnecessary test and
diagnostic time. A thorough visual inspection will
include the following checks:
(1) Verify that the three 32±way electrical connec-
tors are fully inserted into the connector of the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) (Fig. 1).
(2) Inspect the battery cable connections. Be sure
that they are clean and tight.
(3) Inspect fuel pump relay and air conditioning
compressor clutch relay (if equipped). Inspect the
ASD relay connections. Inspect starter motor relay
connections. Inspect relays for signs of physical dam-
age and corrosion. The relays are located in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC) (Fig. 2). Refer to
label on PDC cover for relay location.
(4) Inspect ignition coil connections. Verify that
coil secondary cable is firmly connected to coil (Fig.
3).
(5) Verify that distributor cap is correctly attached
to distributor. Be sure that spark plug cables are
firmly connected to the distributor cap and the spark
plugs are in their correct firing order. Be sure that
coil cable is firmly connected to distributor cap and
coil. Be sure that camshaft position sensor wire con-nector (at the distributor) is firmly connected to har-
ness connector. Inspect spark plug condition. Refer to
8, Ignition. Connect vehicle to an oscilloscope and
inspect spark events for fouled or damaged spark
plugs or cables.
(6) Verify that generator output wire, generator
connector and ground wire are firmly connected to
the generator.
(7) Inspect the system body grounds for loose or
dirty connections. Refer to 8, Wiring for ground loca-
tions.
(8) Verify positive crankcase ventilation (PCV)
valve operation. Refer to 25, Emission Control Sys-
tem for additional information. Verify PCV valve
hose is firmly connected to PCV valve and manifold
(Fig. 4).
Fig. 1 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
1 - PCM MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
2 - POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
3 - (3) 32±WAY CONNECTORS
Fig. 2 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
1 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
Fig. 3 Ignition CoilÐ5.9L EnginesÐTypical
1 - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT TENSIONER
2 - COIL CONNECTOR
3 - IGNITION COIL
4 - COIL MOUNTING BOLTS
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 29
Page 1330 of 2255
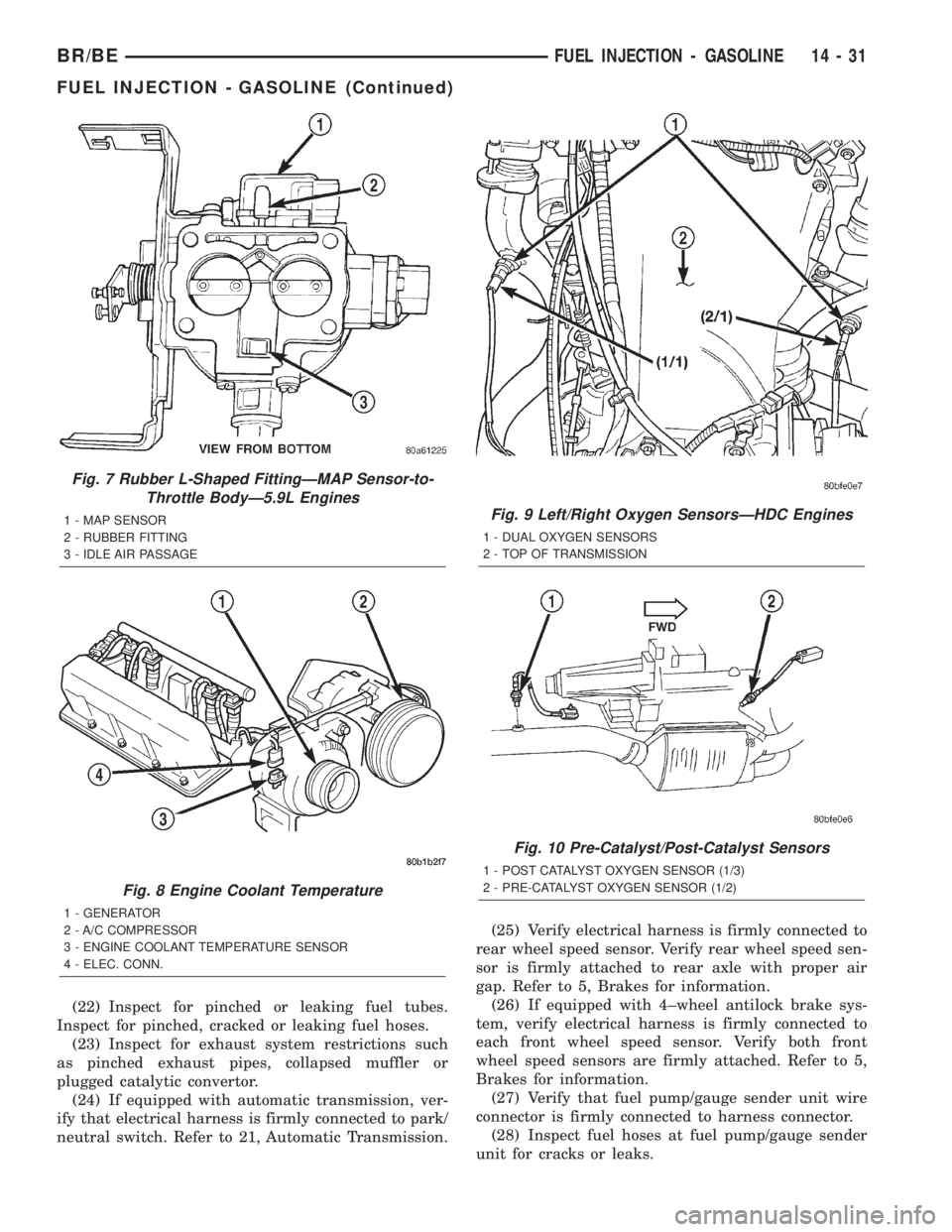
(22) Inspect for pinched or leaking fuel tubes.
Inspect for pinched, cracked or leaking fuel hoses.
(23) Inspect for exhaust system restrictions such
as pinched exhaust pipes, collapsed muffler or
plugged catalytic convertor.
(24) If equipped with automatic transmission, ver-
ify that electrical harness is firmly connected to park/
neutral switch. Refer to 21, Automatic Transmission.(25) Verify electrical harness is firmly connected to
rear wheel speed sensor. Verify rear wheel speed sen-
sor is firmly attached to rear axle with proper air
gap. Refer to 5, Brakes for information.
(26) If equipped with 4±wheel antilock brake sys-
tem, verify electrical harness is firmly connected to
each front wheel speed sensor. Verify both front
wheel speed sensors are firmly attached. Refer to 5,
Brakes for information.
(27) Verify that fuel pump/gauge sender unit wire
connector is firmly connected to harness connector.
(28) Inspect fuel hoses at fuel pump/gauge sender
unit for cracks or leaks.
Fig. 7 Rubber L-Shaped FittingÐMAP Sensor-to-
Throttle BodyÐ5.9L Engines
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - RUBBER FITTING
3 - IDLE AIR PASSAGE
Fig. 8 Engine Coolant Temperature
1 - GENERATOR
2 - A/C COMPRESSOR
3 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
4 - ELEC. CONN.
Fig. 9 Left/Right Oxygen SensorsÐHDC Engines
1 - DUAL OXYGEN SENSORS
2 - TOP OF TRANSMISSION
Fig. 10 Pre-Catalyst/Post-Catalyst Sensors
1 - POST CATALYST OXYGEN SENSOR (1/3)
2 - PRE-CATALYST OXYGEN SENSOR (1/2)
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 31
FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE (Continued)
Page 1331 of 2255

(29) Inspect transmission torque convertor housing
(automatic transmission) or clutch housing (manual
transmission) for damage to timing ring on drive
plate/flywheel.
(30) Verify that battery cable and solenoid feed
wire connections to the starter solenoid are tight and
clean. Inspect for chaffed wires or wires rubbing up
against other components.
VISUAL INSPECTIONÐ8.0L ENGINE
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected or incor-
rectly routed wires and hoses should be made. This
should be done before attempting to diagnose or ser-
vice the fuel injection system. A visual check will
help spot these faults and save unnecessary test and
diagnostic time. A thorough visual inspection will
include the following checks:
(1) Verify that the three 32±way electrical connec-
tors are fully inserted into the connector of the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) (Fig. 12).
(2) Inspect the battery cable connections. Be sure
that they are clean and tight.
(3) Inspect fuel pump relay and air conditioning
compressor clutch relay (if equipped). Inspect the
ASD relay connections. Inspect starter motor relay
connections. Inspect relays for signs of physical dam-
age and corrosion. The relays are located in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC) (Fig. 13). Refer to
label on PDC cover for relay location.
(4) Inspect ignition coil pack primary connections.
Verify that secondary cables are firmly connected to
coils (Fig. 14).
(5) Be sure that spark plug cables are firmly con-
nected and the spark plugs are in their correct firing
order. Be sure that camshaft position sensor wire
connector is firmly connected to harness connector.
Inspect spark plug condition. Refer to 8, Ignition.Connect vehicle to an oscilloscope and inspect spark
events for fouled or damaged spark plugs or cables.
(6) Verify that generator output wire, generator
connector and ground wire are firmly connected to
the generator.
(7) Inspect the system body grounds for loose or
dirty connections. Refer to 8, Wiring for ground loca-
tions.
(8) Verify crankcase ventilation (CCV) operation.
Refer to 25, Emission Control System for additional
information.
(9) Inspect fuel tube quick-connect fitting-to-fuel
rail connections.
(10) Verify that hose connections to all ports of
vacuum fittings on intake manifold are tight and not
leaking.
Fig. 11 Oxygen SensorsFig. 12 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
1 - PCM MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
2 - POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
3 - (3) 32±WAY CONNECTORS
Fig. 13 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
1 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
14 - 32 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE (Continued)
Page 1340 of 2255

To make the IAC go in the opposite direction, the
PCM just reverses polarity on both windings. If only
1 wire is open, the IAC can only be moved 1 step
(increment) in either direction. To keep the IAC
motor in position when no movement is needed, the
PCM will energize both windings at the same time.
This locks the IAC motor in place.
In the IAC motor system, the PCM will count
every step that the motor is moved. This allows the
PCM to determine the motor pintle position. If the
memory is cleared, the PCM no longer knows the
position of the pintle. So at the first key ON, the
PCM drives the IAC motor closed, regardless of
where it was before. This zeros the counter. From
this point the PCM will back out the IAC motor and
keep track of its position again.
When engine rpm is above idle speed, the IAC is
used for the following:
²Off-idle dashpot (throttle blade will close quickly
but idle speed will not stop quickly)
²Deceleration air flow control
²A/C compressor load control (also opens the pas-
sage slightly before the compressor is engaged so
that the engine rpm does not dip down when the
compressor engages)
²Power steering load control
The PCM can control polarity of the circuit to con-
trol direction of the stepper motor.
IAC Stepper Motor Program:The PCM is also
equipped with a memory program that records the
number of steps the IAC stepper motor most recently
advanced to during a certain set of parameters. For
example: The PCM was attempting to maintain a
1000 rpm target during a cold start-up cycle. The last
recorded number of steps for that may have been
125. That value would be recorded in the memory
cell so that the next time the PCM recognizes the
identical conditions, the PCM recalls that 125 steps
were required to maintain the target. This program
allows for greater customer satisfaction due to
greater control of engine idle.
Another function of the memory program, which
occurs when the power steering switch (if equipped),
or the A/C request circuit, requires that the IAC step-
per motor control engine rpm, is the recording of the
last targeted steps into the memory cell. The PCM
can anticipate A/C compressor loads. This is accom-
plished by delaying compressor operation for approx-
imately 0.5 seconds until the PCM moves the IAC
stepper motor to the recorded steps that were loaded
into the memory cell. Using this program helps elim-
inate idle-quality changes as loads change. Finally,
the PCM incorporates a9No-Load9engine speed lim-
iter of approximately 1800 - 2000 rpm, when it rec-
ognizes that the TPS is indicating an idle signal and
IAC motor cannot maintain engine idle.A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the IAC motor through the PCM.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 5.9L
The IAC motor is located on the back of the throt-
tle body (Fig. 31).
(1) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from IAC motor.
(3) Remove two mounting bolts (screws) (Fig. 31).
(4) Remove IAC motor from throttle body.
REMOVAL - 8.0L
The IAC motor is located on the back of the throt-
tle body (Fig. 32).
(1) Remove the air cleaner cover.
(2) Remove the 4 air cleaner housing mounting
nuts and remove housing from throttle body.
(3) Disconnect electrical connector from IAC motor.
(4) Remove two mounting bolts (screw).
(5) Remove IAC motor from throttle body.
Fig. 31 Mounting Bolts (Screws)ÐIAC MotorÐ5.9L
Engines
1 - MOUNTING SCREWS
2 - IDLE SPEED MOTOR
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 41
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (Continued)
Page 1573 of 2255
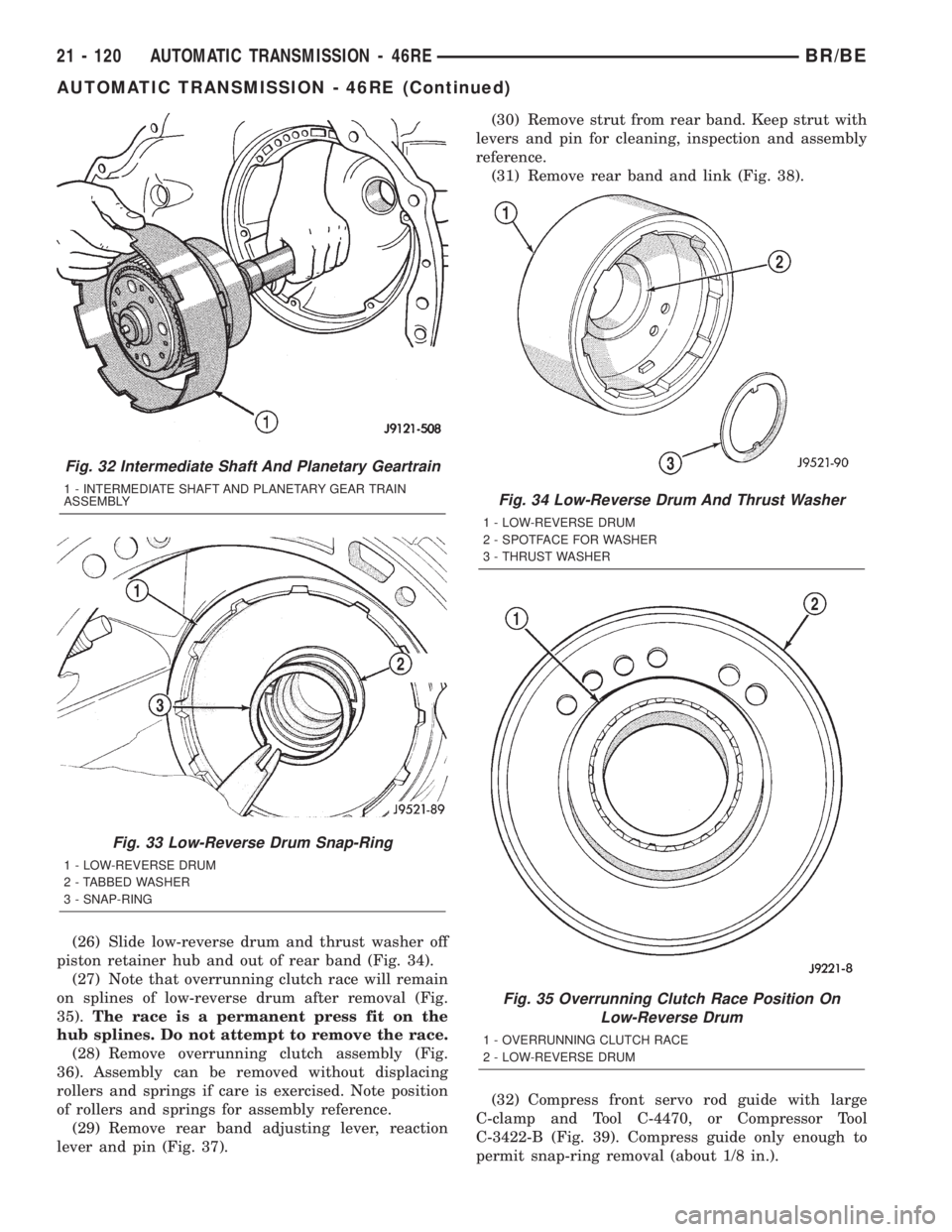
(26) Slide low-reverse drum and thrust washer off
piston retainer hub and out of rear band (Fig. 34).
(27) Note that overrunning clutch race will remain
on splines of low-reverse drum after removal (Fig.
35).The race is a permanent press fit on the
hub splines. Do not attempt to remove the race.
(28) Remove overrunning clutch assembly (Fig.
36). Assembly can be removed without displacing
rollers and springs if care is exercised. Note position
of rollers and springs for assembly reference.
(29) Remove rear band adjusting lever, reaction
lever and pin (Fig. 37).(30) Remove strut from rear band. Keep strut with
levers and pin for cleaning, inspection and assembly
reference.
(31) Remove rear band and link (Fig. 38).
(32) Compress front servo rod guide with large
C-clamp and Tool C-4470, or Compressor Tool
C-3422-B (Fig. 39). Compress guide only enough to
permit snap-ring removal (about 1/8 in.).
Fig. 32 Intermediate Shaft And Planetary Geartrain
1 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT AND PLANETARY GEAR TRAIN
ASSEMBLY
Fig. 33 Low-Reverse Drum Snap-Ring
1 - LOW-REVERSE DRUM
2 - TABBED WASHER
3 - SNAP-RING
Fig. 34 Low-Reverse Drum And Thrust Washer
1 - LOW-REVERSE DRUM
2 - SPOTFACE FOR WASHER
3 - THRUST WASHER
Fig. 35 Overrunning Clutch Race Position On
Low-Reverse Drum
1 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH RACE
2 - LOW-REVERSE DRUM
21 - 120 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE (Continued)
Page 1574 of 2255

(33) Remove servo piston snap-ring (Fig. 39).
Unseat one end of ring. Then carefully work removal
tool around back of ring until free of ring groove.
Exercise caution when removing snap-ring.
Servo bore can be scratched or nicked if care is
not exercised.
(34) Remove tools and remove servo piston and
spring.(35) Compress rear servo piston with C-clamp and
Tool C-4470, or Valve Spring Compressor C-3422-B
(Fig. 40). Compress servo spring retainer only
enough to permit snap-ring removal.
(36) Remove servo piston snap-ring (Fig. 40). Start
one end of ring out of bore. Then carefully work
removal tool around back of snap-ring until free of
ring groove.Exercise caution when removing
snap-ring. Servo bore can be scratched or
nicked if care is not exercised.
(37) Remove tools and remove rear servo retainer,
spring and piston assembly.
Fig. 36 Overrunning Clutch Removal
1 - CLUTCH CAM
2 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
Fig. 37 Rear Band Levers And Pins
1 - REAR BAND ADJUSTING LEVER
2 - REACTION LEVER
3 - BAND LINK
4 - REAR BAND REACTION PIN
Fig. 38 Rear Band And Link
1 - BAND LINK
2 - REAR BAND
Fig. 39 Front Servo Retaining Snap-Ring
1 - C-CLAMP
2 - FRONT SERVO ROD GUIDE
3 - SNAP-RING
4 - TOOL C-4470
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 121
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE (Continued)
Page 1576 of 2255

The planetary geartrain, front/rear clutch assem-
blies and oil pump are all much easier to install
when the transmission case is upright. Either tilt the
case upward with wood blocks, or cut a hole in the
bench large enough for the intermediate shaft and
rear support. Then lower the shaft and support into
the hole and support the rear of the case directly on
the bench.
FRONT/REAR SERVO
(1) Lubricate rear servo piston seal with Mopart
Door Ease or ATF +4. Lubricate servo bore in case
with ATF +4.
(2) Install rear servo piston in case. Position piston
at slight angle to bore and insert piston with twisting
motion (Fig. 41).
(3) Install rear servo spring and retainer in case
bore (Fig. 42). Be sure spring is seated on piston.
(4) Compress rear servo piston with C-clamp or
Valve Spring Compressor C-3422-B and install servo
piston snap-ring (Fig. 43).
(5) Lubricate front servo piston components and
servo bore in case with transmission fluid.
(6) Install front servo piston in bore. Carefully
ªrunº small, suitable tool around piston ring to press
it back into groove and ease installation (Fig. 44).
Rotate piston into bore at same time. Rock piston
slightly to ease piston ring past snap-ring groove and
into bore.
(7) Bottom front servo piston in bore and install
servo spring.
(8) Install front servo piston rod guide as follows:
(a) Place Tool SP-5560 (or similar size tool) on
guide and position C-clamp on tool and case (Fig.
45).(b) Slowly compress rod guide while simulta-
neously easing seal ring into bore with suitable
tool.
(9) Install rod guide snap-ring (Fig. 45).
Fig. 41 Rear Servo Piston
1 - REAR SERVO PISTON
Fig. 42 Rear Servo Piston Spring And Retainer
1 - PISTON SPRING
2 - REAR SERVO PISTON
3 - SPRING RETAINER
Fig. 43 Rear Servo Snap-Ring
1 - TOOL C-4470
2 - C-CLAMP
3 - REAR SERVO SPRING RETAINER
4 - RETAINER SNAP-RING
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 123
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE (Continued)
Page 1599 of 2255
SPECIAL TOOLS
RE TRANSMISSION
Flusher, Oil Cooler - 6906
Remover, Bushing - 6957
Installer, Bushing - 6951
Retainer, Detent Ball and Spring - 6583
Gauge, Block - 6312
Fixture, Engine Support - C-3487-A
Stand, Transmission Repair - C-3750-B
Compressor, Spring - C-3863-A
Spring Compressor and Alignment Shaft - 6227
Bar, Gauge - 6311
21 - 146 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46REBR/BE
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE (Continued)
Page 1600 of 2255
Studs, Oil Pump Pilot - C-3288-B
Gauge, Pressure - C-3292
Gauge, Pressure - C-3293SP
Set, Dial Indicator - C-3339
Compressor, Spring - C-3422-B
Puller, Slide Hammer - C-3752
Gauge, Throttle Setting - C-3763
Installer, Seal - C-3860-A
Remover, Seal - C-3985-B
Installer, Overdrive Piston Seal - 8114
BR/BEAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 147
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE (Continued)