heating DODGE RAM 2002 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2002, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2002Pages: 2255, PDF Size: 62.07 MB
Page 1184 of 2255

(15) Install the fuel lines (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FIT-
TING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(16) Using a new gasket, install the air cleaner
housing. Tighten the nuts to 11 N´m (96 in. lbs.)
torque. Install the air cleaner filter and cover.
(17) Install the A/C compressor (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C
COMPRESSOR - INSTALLATION). Position the com-
pressor brace and install the bolts. Tighten the brace
bolts to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(18) Install the generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/CHARGING/GENERATOR - INSTALLATION).
Position the generator brace and install the bolts.
Tighten the brace bolts to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(19) Install the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(20) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(21) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
(22) Start engine check for leaks.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
Engine exhaust manifolds (Fig. 75) are made of
high molybdenum ductile cast iron. A special ribbed
design helps control permanent dimensional changes
during heat cycles.
OPERATION
The exhaust manifolds collect the engine exhaust
exiting the combustion chambers, then channels the
exhaust gases to the exhaust pipes attached to the
manifolds.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Remove the bolts and nuts attaching the
exhaust pipe to the engine exhaust manifold..
(4) Lower the vehicle.
(5) Remove the exhaust heat shields (Fig. 76).
(6) Remove the dipstick bracket from the exhaust
manifold (right side only).
(7) Remove bolts attaching manifold to cylinder
head.
(8) Remove manifold from the cylinder head. Dis-
card the gasket.
CLEANING
Clean mating surfaces on cylinder head and mani-
fold. Wash with solvent and blow dry with com-
pressed air.
INSPECTION
Inspect manifold for cracks.
Inspect mating surfaces of manifold for flatness
with a straight edge. Gasket surfaces must be flat
within 0.2 mm per 300 mm (0.008 inch per foot).
INSTALLATION
(1) Using a new gasket position the engine
exhaust manifold onto the cylinder head. Install bolts
and stud bolts in the proper position (Fig. 76).
Tighten the bolts to 22 N´m (16 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 75 Exhaust ManifoldÐ8.0L Engine
1 - EXHAUST MANIFOLD
Fig. 76 8.0L Engine Exhaust ManifoldÐTypical
1 - EXHAUST MANIFOLD
2 - HEAT SHIELD
BR/BEENGINE 8.0L 9 - 109
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1186 of 2255

(6) Prime oil pump by squirting oil in the oil filter
mounting hole and filling the J-trap of the front tim-
ing cover. When oil is running out, install oil filter
that has been filled with oil.
(7) Install water pump and housing assembly
using new o-ring (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
WATER PUMP - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install generator, air pump, and bracket assem-
bly.
(9) Install A/C compressor (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COM-
PRESSOR - INSTALLATION).
(10) (10) Install the radiator fan (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLA-
TION).
(11) Position the fan shroud and install the bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.) torque.
(12) Install the serpentine belt (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTAL-
LATION).
(13) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(14) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
(15) Road test vehicle and check for leaks.
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove timing chain cover and gasket using
extreme caution to avoid damaging oil pan gasket
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Aline camshaft and crankshaft centerline.
Remove camshaft sprocket attaching bolt and remove
timing chain and camshaft sprockets.
(3) Use puller 6444 and jaws 6820 to remove
crankshaft sprocket (Fig. 79).
INSPECTIONÐMEASURING TIMING CHAIN
STRETCH
(1) Place a scale next to the timing chain so that
any movement of the chain may be measured.
(2) Place a torque wrench and socket over cam-
shaft sprocket attaching bolt. Apply torque in the
direction of crankshaft rotation to take up slack; 41
N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque with cylinder head installed
or 20 N´m (15 ft. lbs.) torque with cylinder head
removed. With a torque applied to the camshaft
sprocket bolt, crankshaft should not be permitted to
move. It may be necessary to block the crankshaft to
prevent rotation.
(3) Hold a scale with dimensional reading even
with the edge of a chain link. With cylinder heads
installed, apply 14 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque in thereverse direction. With the cylinder heads removed,
apply 20 N´m (15 ft. lbs.) torque in the reverse direc-
tion. Note the amount of chain movement (Fig. 80).
(4) Install a new timing chain, if its movement
exceeds 3.175 mm (1/8 inch).
INSTALLATION
(1) Line up key in crankshaft with keyway in
sprocket, press on crankshaft timing sprocket, use
tools C-3688, C-3718 and MB-990799, seat sprocket
against crankshaft shoulder (Fig. 81).
Fig. 79 Crankshaft Sprocket Removal.
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6444
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 6820
Fig. 80 Measuring Timing Chain Stretch
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - 3.175 MM
(0.125 IN.)
BR/BEENGINE 8.0L 9 - 111
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) (Continued)
Page 1198 of 2255

(1) Disconnect the negative cable(s) from the bat-
tery.
(2) Inspect air cleaner, induction system, and
intake manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(3) Place a shop towel around the fuel injectors to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure
in the cylinder head. Remove the fuel injectors (Refer
to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL
INJECTOR - REMOVAL).
(4) With all injectors removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(5) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (coolant, fuel,
oil, etc.).
(6) Be sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(7) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(8) Squirt a small amount of engine oil into the
cylinders to lubricate the walls. This will prevent
damage on restart.
(9) Install new fuel injectors (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR -
INSTALLATION).
(10) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL FIL-
TER - REMOVAL).
(11) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(12) Install a new oil filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION/OIL FILTER - INSTALLATION).
(13) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES - SPECIFICA-
TIONS).
(14) Connect the negative cable(s) to the battery.
(15) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
REMOVAL
REMOVALÐENGINE
(1) Disconnect both battery negative cables.
(2) Recover A/C refrigerant (if A/C equipped) (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMB-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(4) Drain engine coolant (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Remove engine oil drain plug and drain engine
oil.
(6) Lower vehicle.
(7) Remove radiator upper hose.
(8) Remove the cooling fan shroud-to-radiator
mounting bolts.(9) Remove viscous fan/drive assembly (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
Remove the cooling fan and shroud together.
(10) Disconnect the coolant recovery bottle hose
from the radiator filler neck and remove bottle from
fan shroud (Fig. 2).
(11) Disconnect heater core supply and return
hoses from the cylinder head fitting and coolant pipe.
(12) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(13) Remove transmission and transfer case (if
equipped.).
(14) Disconnect exhaust pipe from turbocharger
extension pipe (Fig. 3).
(15) Remove starter motor (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - REMOVAL).
(16) Disconnect A/C suction/discharge hose from
the rear of the A/C compressor.
(17) Lower vehicle.
(18) Disconnect lower radiator hose from radiator
outlet.
(19)Automatic Transmission models:Discon-
nect transmission oil cooler lines from radiator using
special tool #6931.
(20) Remove radiator (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE/RADIATOR - REMOVAL).
(21) Remove upper radiator support panel.
Fig. 2 Coolant Recovery Bottle
1 - T-SLOTS
2 - ALIGNMENT PIN
3 - FAN SHROUD
4 - COOLANT RESERVE/OVERFLOW TANK
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 123
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1227 of 2255
Overall variation end to end or side to side is 0.075
mm (0.003 inch).
If the surface exceeds the limit, .
Inspect the cylinder bores for damage or excessive
wear.
Measure the cylinder bores (Fig. 80). If the cylin-
der bores exceeds the limit, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Inspect the camshaft bores for scoring or excessive
wear.
Measure the camshaft bores (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
- SPECIFICATIONS). Limit for the No.1 bore applies
to the ID of the bushing.
If a bore exceeds the limit, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK) - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
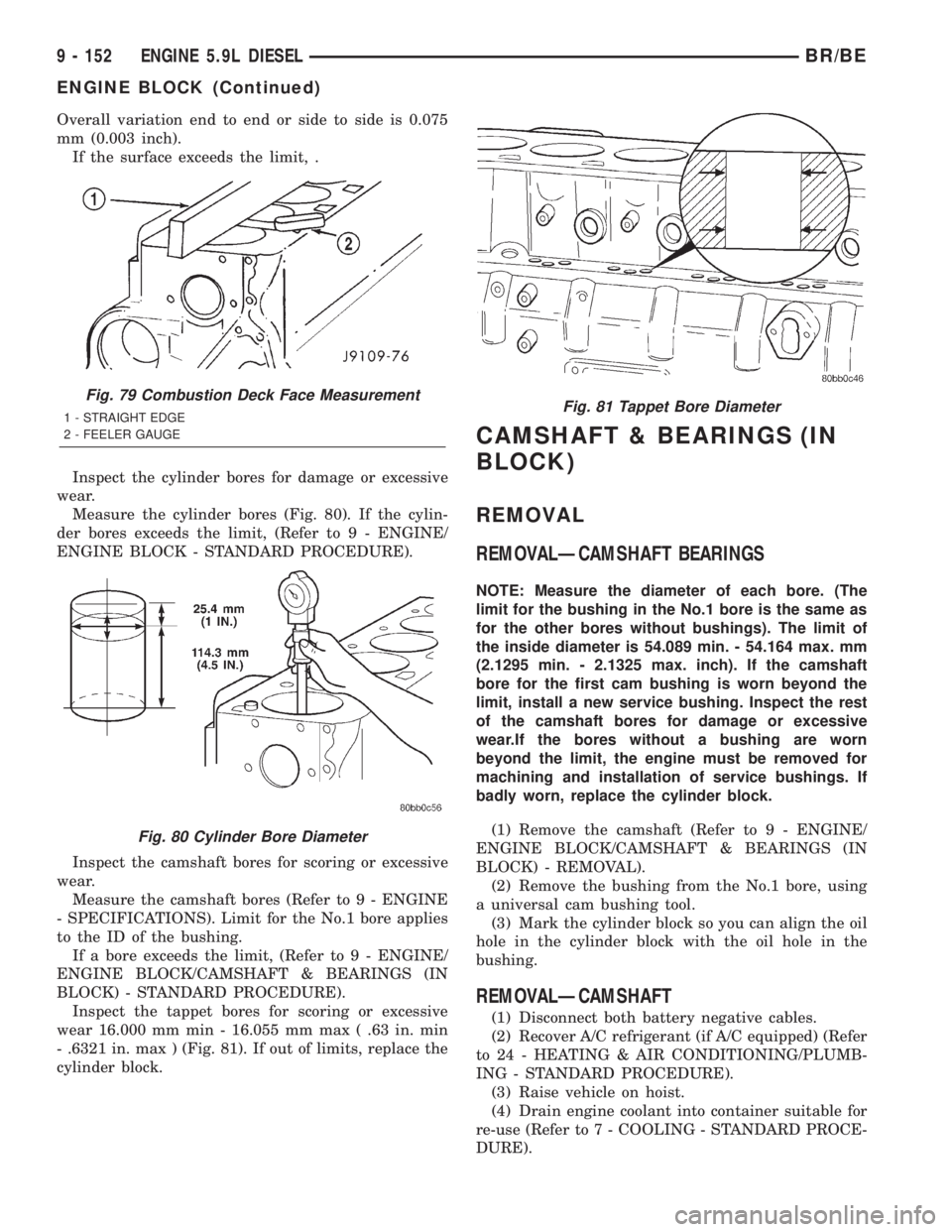
Inspect the tappet bores for scoring or excessive
wear 16.000 mm min - 16.055 mm max ( .63 in. min
- .6321 in. max ) (Fig. 81). If out of limits, replace the
cylinder block.
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK)
REMOVAL
REMOVALÐCAMSHAFT BEARINGS
NOTE: Measure the diameter of each bore. (The
limit for the bushing in the No.1 bore is the same as
for the other bores without bushings). The limit of
the inside diameter is 54.089 min. - 54.164 max. mm
(2.1295 min. - 2.1325 max. inch). If the camshaft
bore for the first cam bushing is worn beyond the
limit, install a new service bushing. Inspect the rest
of the camshaft bores for damage or excessive
wear.If the bores without a bushing are worn
beyond the limit, the engine must be removed for
machining and installation of service bushings. If
badly worn, replace the cylinder block.
(1) Remove the camshaft (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN
BLOCK) - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the bushing from the No.1 bore, using
a universal cam bushing tool.
(3) Mark the cylinder block so you can align the oil
hole in the cylinder block with the oil hole in the
bushing.
REMOVALÐCAMSHAFT
(1) Disconnect both battery negative cables.
(2) Recover A/C refrigerant (if A/C equipped) (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMB-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(4) Drain engine coolant into container suitable for
re-use (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
Fig. 79 Combustion Deck Face Measurement
1 - STRAIGHT EDGE
2 - FEELER GAUGE
Fig. 80 Cylinder Bore Diameter
Fig. 81 Tappet Bore Diameter
9 - 152 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELBR/BE
ENGINE BLOCK (Continued)
Page 1233 of 2255

(11) Install the cylinder head cover and reusable
gasket (Fig. 85) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - INSTALLA-
TION).
(12) Install gear housing cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/GEAR HOUSING COVER
- INSTALLATION).
(13) Install the crankshaft damper (Fig. 83) (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION
DAMPER - INSTALLATION).
(14) Install the fan support/hub assembly (Fig. 82)
and tighten bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(15) Install the crankcase breather housing (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - INSTALLATION).
(16) Install the charge air cooler (with a/c con-
denser and auxiliary transmission oil cooler, if
equipped) and tighten the mounting bolts to 2 N´m
(17 in. lbs.) torque.
(17) Connect charge air cooler inlet and outlet
pipes. Tighten clamps to 10 N´m (100 in. lbs.) torque.
(18) Install the radiator upper support panel.
(19) Close radiator petcock and lower the radiator
into the engine compartment. Tighten the mounting
bolts to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.) torque.
(20) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(21) Connect radiator lower hose and install
clamp.
(22) Connect transmission auxiliary oil cooler lines
(if equipped).
(23) Lower vehicle.
(24) Install the fan shroud and tighten the mount-
ing screws to 6 N´m (50 in. lbs.) torque.
(25) Install the viscous fan/drive assembly (Refer
to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
INSTALLATION).
(26) Install the coolant recovery and windshield
washer fluid reservoirs to the fan shroud.
(27) Connect the coolant recovery hose to the radi-
ator filler neck.
(28) Install the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(29) Install the front bumper assembly (Refer to 13
- FRAMES & BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT
BUMPER - INSTALLATION).
(30) Add engine coolant (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(31) Charge A/C system with refrigerant (if A/C
equipped) (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(32) Connect the battery negative cables.
(33) Start engine and check for engine oil and cool-
ant leaks.CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐCONNECTING ROD
BEARING AND CRANKSHAFT JOURNAL
CLEARANCE
Measure the connecting rod bore with the bearings
installed and the bolts tightened to 100 N´m (73 ft.
lbs.) torque.
Record the smaller diameter.
Measure the diameter of the rod journal at the
location shown (Fig. 99). Calculate the average diam-
eter for each side of the journal.
The clearance is the difference between the con-
necting rod bore (smallest diameter) and the average
diameter for each side of the crankshaft journal.
Fig. 99 Connecting Rod Journal Diameter Limits
CONNECTING ROD JOURNAL DIAMETER
LIMITS CHART
DESCRIPTION MEASUREMENT
CRANKSHAFT ROD JOURNAL
DIAMETERMINIMUM 68.962 mm
(2.715 in.)
MAXIMUM 69.013 mm
(2.717 in.)
OUT-OF-ROUND MAXIMUM 0.050 mm (0.002 in.)
TAPER MAXIMUM 0.013 mm
(0.0005 in.)
BEARING CLEARANCE MAXIMUM 0.089 mm
(0.0035 in.)
9 - 158 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELBR/BE
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) (Continued)
Page 1273 of 2255

INSPECTION
Look at the stainless steel body of the converter,
inspect for bulging or other distortion that could be a
result of overheating. If the converter has a heat
shield attached make sure it is not bent or loose.
If you suspect internal damage to the catalyst, tap-
ping the bottom of the catalyst with a rubber mallet
may indicate a damaged core.
INSTALLATION
(1) Assemble converter and clamps loosely in
place.
(2) Install the exhaust pipe onto exhaust mani-
folds, tighten 31 N´m (23 ft. lbs.).
(3) Tighten all clamp nuts to 48 N´m (35 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(4) Lower the vehicle.
(5) Start the engine and inspect for exhaust leaks
and exhaust system contact with the body panels. A
minimum of 25.4 mm (1.0 in.) is required between
exhaust system components and body/frame parts.
Adjust the alignment, if needed.
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - 5.9L
HD/8.0L
DESCRIPTION
The stainless steel catalytic converter is located
under the vehicle, attached to the exhaust pipe(s).
OPERATION
The catalytic converter captures and burns any
unburned fuel mixture exiting the combustion cham-
bers during the exhaust stroke of the engine. This
process aids in reducing emissions output.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Saturate the bolts and nuts with heat valve
lubricant. Allow 5 minutes for penetration.
(3) Remove clamps and nuts (Fig. 5) (Fig. 6).
(4) Remove the catalytic converter.
INSPECTION
Look at the stainless steel body of the converter,
inspect for bulging or other distortion that could be a
result of overheating. If the converter has a heat
shield attached make sure it is not bent or loose.
If you suspect internal damage to the catalyst, tap-
ping the bottom of the catalyst with a rubber mallet
may indicate a damaged core.
Fig. 4 Catalytic Converter and Exhaust Pipe 3.9L,
5.2L and 5.9L Light Duty ( California )
1 - BOLT
2 - RETAINER
3 - EXHAUST MANIFOLD
4 - NUT
5 - MINI CATALYTIC CONVERTER
6 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER WITH PIPES
Fig. 5 Catalytic Converter 5.9L Heavy Duty
1 - DOWN PIPE RIGHT
2 - CLAMP
3 - CLAMP
4 - HANGER ASSY. DUAL CLAMP
5 - MUFFLER
6 - EXTENSION PIPE
7 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
8 - DOWN PIPE LEFT
11 - 6 EXHAUST SYSTEMBR/BE
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - 3.9L/5.2L/5.9L (Continued)
Page 1286 of 2255

(4) Discharge the A/C system (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE) and remove the A/C condenser
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/A/C CONDENSER - REMOVAL) (Fig.
31) (if A/C equipped).
(5) Remove the transmission auxiliary cooler (Fig.
31) (Refer to 7 - COOLING/TRANSMISSION/TRANS
COOLER - REMOVAL).
(6) Remove the boost tubes from the charge air
cooler (Fig. 32).
(7) Remove the charge air cooler bolts. Pivot the
charge air cooler forward and up to remove.
CLEANING
CAUTION: Do not use caustic cleaners to clean the
charge air cooler. Damage to the charge air cooler
will result.
NOTE: If internal debris cannot be removed from
the cooler, the charge air cooler MUST be replaced.
(1) If the engine experiences a turbocharger failure
or any other situation where oil or debris get into the
charge air cooler, the charge air cooler must be
cleaned internally.
(2) Position the charge air cooler so the inlet and
outlet tubes are vertical.
(3) Flush the cooler internally with solvent in the
direction opposite of normal air flow.(4) Shake the cooler and lightly tap on the end
tanks with a rubber mallet to dislodge trapped
debris.
(5) Continue flushing until all debris or oil are
removed.
(6) Rinse the cooler with hot soapy water to
remove any remaining solvent.
(7) Rinse thoroughly with clean water and blow
dry with compressed air.
INSPECTION
Visually inspect the charge air cooler for cracks,
holes, or damage. Inspect the tubes, fins, and welds
for tears, breaks, or other damage. Replace the
charge air cooler if damage is found.
Pressure test the charge air cooler, using Charge
Air Cooler Tester Kit #3824556. This kit is available
through CumminstService Products. Instructions
are provided with the kit.
Fig. 31 Condenser and Transmission Auxiliary
Cooler
1 - A/C CONDENSOR
2 - TRANSMISSION COOLER
3 - INTERCOOLER
Fig. 32 Air Intake System Tubes
1 - CLAMP
2 - INTERCOOLER INLET DUCT
3 - CLAMP
4 - VALVE COVER
5 - AIR INLET HOUSING
6 - CLAMP
7 - INTERCOOLER OUTLET DUCT
8 - CLAMP
9 - INTERCOOLER
BR/BEEXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 19
CHARGE AIR COOLER AND PLUMBING (Continued)
Page 1287 of 2255

INSTALLATION
(1) Position the charge air cooler. Install the bolts
and tighten to 2 N´m (17 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install the air intake system tubes to the
charge air cooler. With the clamps in position, tighten
the clamps to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install the transmission auxiliary cooler (if
equipped) (Refer to 7 - COOLING/TRANSMISSION/
TRANS COOLER - INSTALLATION).
(4) Install the A/C condenser (if A/C equipped)
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/A/C CONDENSER - INSTALLATION).Recharge A/C system (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
(5) Install the front support bracket. Install and
tighten the bolts.
(6) Install the front bumper (Refer to 13 -
FRAMES & BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT
BUMPER - INSTALLATION).
(7) Connect the battery negative cables.
(8) Start engine and check for boost system leaks.
11 - 20 EXHAUST SYSTEMBR/BE
CHARGE AIR COOLER AND PLUMBING (Continued)
Page 1344 of 2255

(2) Clean the area around the sensor before
removal.
(3) Remove the two sensor mounting bolts.
(4) Remove the sensor from the intake manifold.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 5.9L
The MAP sensor is located on the front of the
throttle body (Fig. 35). An L-shaped rubber fitting is
used to connect the MAP sensor to throttle body (Fig.
36).
(1) Install rubber L-shaped fitting to MAP sensor.
(2) Position sensor to throttle body while guiding
rubber fitting over throttle body vacuum nipple.
(3) Install MAP sensor mounting bolts (screws).
Tighten screws to 3 N´m (25 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install air cleaner.
INSTALLATION - 8.0L
The MAP sensor is mounted into the right upper
side of the intake manifold (Fig. 37). A rubber gasket
is used to seal the sensor to the intake manifold. The
rubber gasket is part of the sensor and is not ser-
viced separately.
(1) Check the condition of the sensor seal. Clean
the sensor and lubricate the rubber gasket with clean
engine oil.
(2) Clean the sensor opening in the intake mani-
fold.
(3) Install the sensor into the intake manifold.
(4) Install sensor mounting bolts. Tighten bolts to
2 N´m (20 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install the electrical connector to sensor.
O2 SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Oxygen Sensors (O2S) are attached to, and
protrude into the vehicle exhaust system. Depending
on the emission package, the vehicle may use a total
of either 2 or 4 sensors.
Medium and Heavy Duty 8.0L V-10 Engine:
Four sensors are used (2 upstream, 1 pre-catalyst
and 1 post-catalyst). With this emission package, the
1/1 upstream sensor (left side) is located in the left
exhaust downpipe before both the pre-catalyst sensor
(1/2), and the main catalytic convertor. The 2/1
upstream sensor (right side) is located in the right
exhaust downpipe before both the pre-catalyst sensor
(1/2), and the main catalytic convertor. The pre-cata-
lyst sensor (1/2) is located after the 1/1 and 2/1 sen-
sors, and just before the main catalytic convertor.
The post-catalyst sensor (1/3) is located just after the
main catalytic convertor.
Heavy Duty 5.9L Engine:Two sensors are used.
They arebothreferred to as upstream sensors (left
side is referred to as 1/1 and right side is referred to
as 2/1). With this emission package, a sensor is
located in each of the exhaust downpipes before the
main catalytic convertor.
OPERATION
An O2 sensor is a galvanic battery that provides
the PCM with a voltage signal (0-1 volt) inversely
proportional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust.
In other words, if the oxygen content is low, the volt-
age output is high; if the oxygen content is high the
output voltage is low. The PCM uses this information
to adjust injector pulse-width to achieve the
14.7±to±1 air/fuel ratio necessary for proper engine
operation and to control emissions.
The O2 sensor must have a source of oxygen from
outside of the exhaust stream for comparison. Cur-
rent O2 sensors receive their fresh oxygen (outside
air) supply through the O2 sensor case housing.
Four wires (circuits) are used on each O2 sensor: a
12±volt feed circuit for the sensor heating element; a
ground circuit for the heater element; a low-noise
sensor return circuit to the PCM, and an input cir-
cuit from the sensor back to the PCM to detect sen-
sor operation.
Oxygen Sensor Heaters/Heater Relays:
Depending on the emissions package, the heating ele-
ments within the sensors will be supplied voltage
from either the ASD relay, or 2 separate oxygen sen-
sor relays. Refer to 8, Wiring Diagrams to determine
which relays are used.
The O2 sensor uses a Positive Thermal Co-efficient
(PTC) heater element. As temperature increases,
resistance increases. At ambient temperatures
Fig. 37 MAP Sensor LocationÐ8.0L V-10 EngineÐ
Typical
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS
3 - THROTTLE BODY
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 45
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1345 of 2255

around 70ÉF, the resistance of the heating element is
approximately 4.5 ohms. As the sensor's temperature
increases, resistance in the heater element increases.
This allows the heater to maintain the optimum
operating temperature of approximately 930É-1100ÉF
(500É-600É C). Although the sensors operate the
same, there are physical differences, due to the envi-
ronment that they operate in, that keep them from
being interchangeable.
Maintaining correct sensor temperature at all
times allows the system to enter into closed loop
operation sooner. Also, it allows the system to remain
in closed loop operation during periods of extended
idle.
In Closed Loop operation, the PCM monitors cer-
tain O2 sensor input(s) along with other inputs, and
adjusts the injector pulse width accordingly. During
Open Loop operation, the PCM ignores the O2 sensor
input. The PCM adjusts injector pulse width based
on preprogrammed (fixed) values and inputs from
other sensors.
Upstream Sensors:Two upstream sensors are
used (1/1 and 2/1). The 1/1 sensor is the first sensor
to receive exhaust gases from the #1 cylinder. They
provide an input voltage to the PCM. The input tells
the PCM the oxygen content of the exhaust gas. The
PCM uses this information to fine tune fuel delivery
to maintain the correct oxygen content at the down-
stream oxygen sensors. The PCM will change the air/
fuel ratio until the upstream sensors input a voltage
that the PCM has determined will make the down-
stream sensors output (oxygen content) correct.
The upstream oxygen sensors also provide an input
to determine mini-catalyst efficiency. Main catalytic
convertor efficiency is not calculated with this pack-
age.
Downstream Sensors:Two downstream sensors
are used (1/2 and 2/2). The downstream sensors are
used to determine the correct air-fuel ratio. As the
oxygen content changes at the downstream sensor,
the PCM calculates how much air-fuel ratio change is
required. The PCM then looks at the upstream oxy-
gen sensor voltage, and changes fuel delivery until
the upstream sensor voltage changes enough to cor-
rect the downstream sensor voltage (oxygen content).
The downstream oxygen sensors also provide an
input to determine mini-catalyst efficiency. Main cat-
alytic convertor efficiency is not calculated with this
package.
Medium and Heavy Duty 8.0L V-10 Engine:
Four oxygen sensors are used (2 upstream, 1 pre-cat-
alyst and 1 post-catalyst). The upstream sensors (1/1
and 2/1) will fine-tune the air-fuel ratio through the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The pre-catalyst
(1/2) and post-catalyst (1/3) sensors will determine
catalytic convertor efficiency (efficiency of the maincatalytic convertor). This is also done through the
PCM.
Heavy Duty 5.9L Engine:Downstream sensors
are not used with this emissions package, meaning
catalytic convertor efficiency is not calculated with
this package. Two upstream sensors are used. The
left upstream sensor (1/1) will monitor cylinders 1, 3,
5 and 7. The right upstream sensor (2/1) will monitor
cylinders 2, 4, 6 and 8. The PCM monitors the oxy-
gen content of the sensors, and will fine-tune the air-
fuel ratio.
Engines equipped with either a downstream sen-
sor(s), or a post-catalytic sensor, will monitor cata-
lytic convertor efficiency. If efficiency is below
emission standards, the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) will be illuminated and a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) will be set. Refer to Monitored Systems
in Emission Control Systems for additional informa-
tion.
REMOVAL
Never apply any type of grease to the oxygen
sensor electrical connector, or attempt any sol-
dering of the sensor wiring harness.
The O2S (oxygen sensors) are numbered 1/1, 1/2,
1/3, 2/1 and 2/2.
On HDC engines, the pre-catalyst/post catalyst
O2S sensors are located at the inlet and outlet ends
of the catalytic converter (Fig. 38).
The 1/1 and 2/1 sensors are located before the
mini-cats (Fig. 39). The 1/2 and 2/2 sensors are
located after the mini-cats (Fig. 39).
WARNING: THE EXHAUST MANIFOLD, EXHAUST
PIPES AND CATALYTIC CONVERTER BECOME
VERY HOT DURING ENGINE OPERATION. ALLOW
ENGINE TO COOL BEFORE REMOVING OXYGEN
SENSOR.
Fig. 38 Pre-catalyst/Post catalyst Oxygen SensorsÐ
HDC Engines
1 - POST CATALYST OXYGEN SENSOR (1/3)
2 - PRE-CATALYST OXYGEN SENSOR (1/2)
14 - 46 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
O2 SENSOR (Continued)