change wheel DODGE RAM 2003 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2003, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2003Pages: 2895, PDF Size: 83.15 MB
Page 1430 of 2895
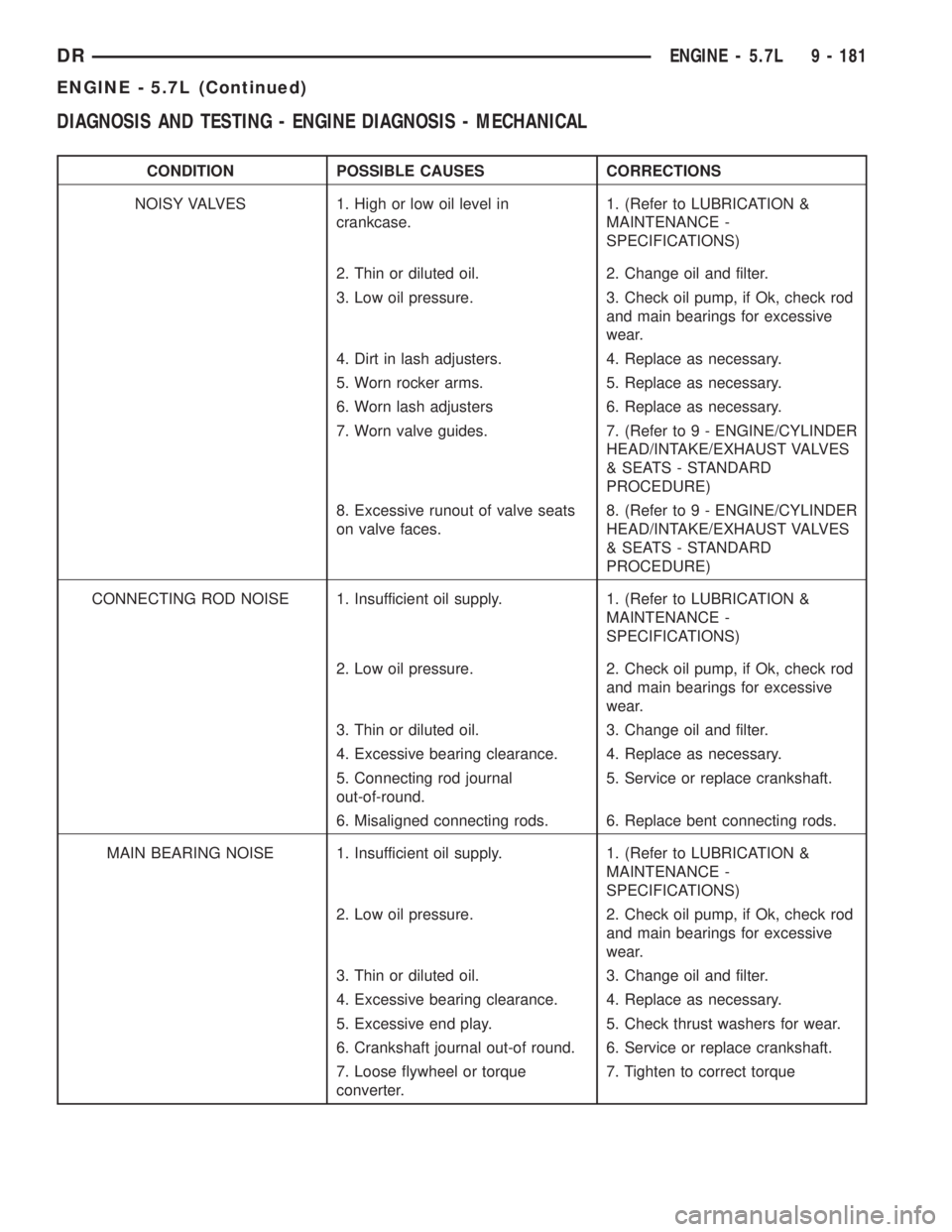
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTIONS
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil and filter.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
4. Dirt in lash adjusters. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Worn rocker arms. 5. Replace as necessary.
6. Worn lash adjusters 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Worn valve guides. 7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
8. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.8. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.5. Service or replace crankshaft.
6. Misaligned connecting rods. 6. Replace bent connecting rods.
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Excessive end play. 5. Check thrust washers for wear.
6. Crankshaft journal out-of round. 6. Service or replace crankshaft.
7. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.7. Tighten to correct torque
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 181
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)
Page 1434 of 2895
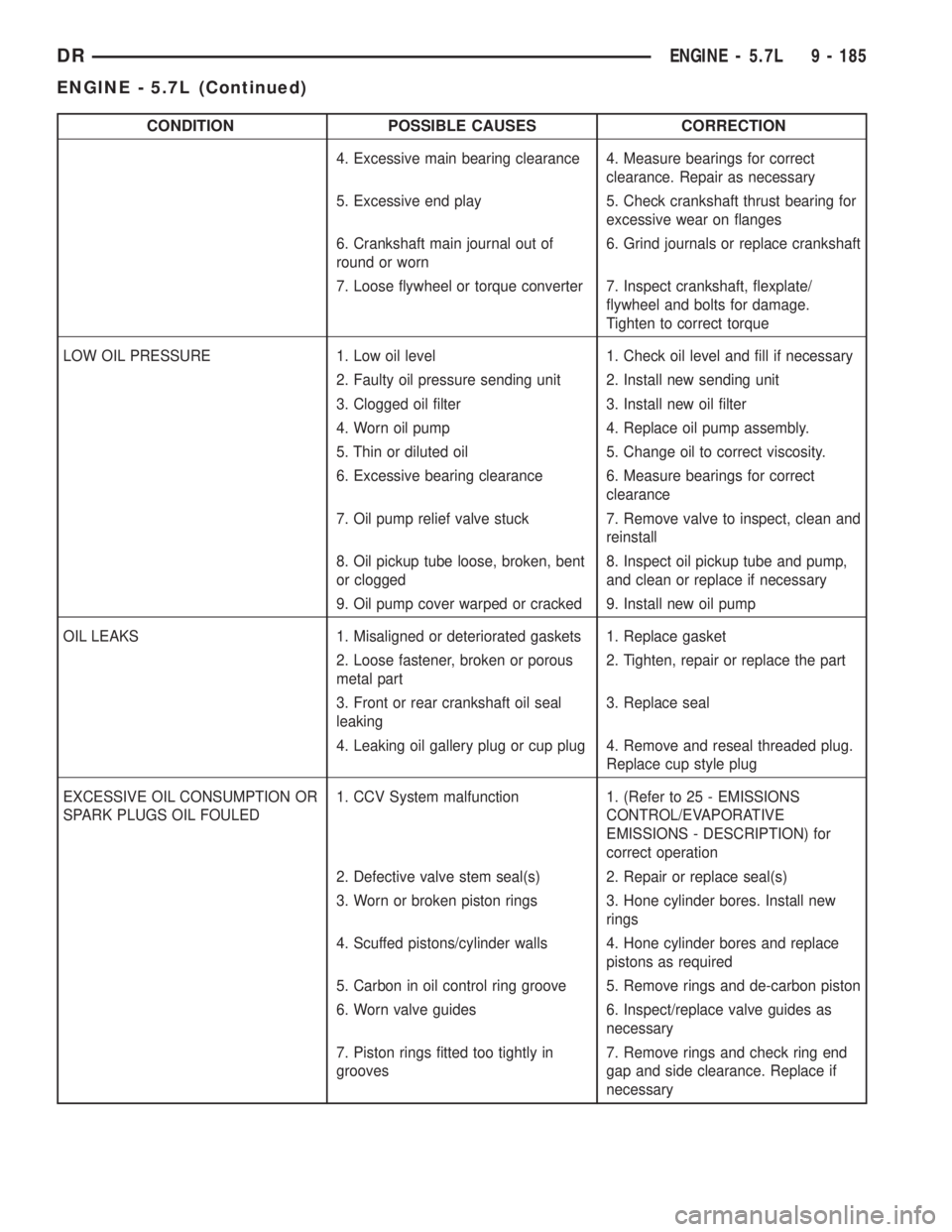
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
4. Excessive main bearing clearance 4. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary
5. Excessive end play 5. Check crankshaft thrust bearing for
excessive wear on flanges
6. Crankshaft main journal out of
round or worn6. Grind journals or replace crankshaft
7. Loose flywheel or torque converter 7. Inspect crankshaft, flexplate/
flywheel and bolts for damage.
Tighten to correct torque
LOW OIL PRESSURE 1. Low oil level 1. Check oil level and fill if necessary
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit 2. Install new sending unit
3. Clogged oil filter 3. Install new oil filter
4. Worn oil pump 4. Replace oil pump assembly.
5. Thin or diluted oil 5. Change oil to correct viscosity.
6. Excessive bearing clearance 6. Measure bearings for correct
clearance
7. Oil pump relief valve stuck 7. Remove valve to inspect, clean and
reinstall
8. Oil pickup tube loose, broken, bent
or clogged8. Inspect oil pickup tube and pump,
and clean or replace if necessary
9. Oil pump cover warped or cracked 9. Install new oil pump
OIL LEAKS 1. Misaligned or deteriorated gaskets 1. Replace gasket
2. Loose fastener, broken or porous
metal part2. Tighten, repair or replace the part
3. Front or rear crankshaft oil seal
leaking3. Replace seal
4. Leaking oil gallery plug or cup plug 4. Remove and reseal threaded plug.
Replace cup style plug
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION OR
SPARK PLUGS OIL FOULED1. CCV System malfunction 1. (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS
CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE
EMISSIONS - DESCRIPTION) for
correct operation
2. Defective valve stem seal(s) 2. Repair or replace seal(s)
3. Worn or broken piston rings 3. Hone cylinder bores. Install new
rings
4. Scuffed pistons/cylinder walls 4. Hone cylinder bores and replace
pistons as required
5. Carbon in oil control ring groove 5. Remove rings and de-carbon piston
6. Worn valve guides 6. Inspect/replace valve guides as
necessary
7. Piston rings fitted too tightly in
grooves7. Remove rings and check ring end
gap and side clearance. Replace if
necessary
DRENGINE - 5.7L 9 - 185
ENGINE - 5.7L (Continued)
Page 1455 of 2895

²Cylinder head(s) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLIN-
DER HEAD - REMOVAL) and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(3) If necessary, remove top ridge of cylinder bores
with a reliable ridge reamer before removing pistons
from cylinder block.Be sure to keep tops of pis-
tons covered during this operation.Pistons and
connecting rods must be removed from top of cylinder
block. When removing piston and connecting rod
assemblies from the engine, rotate crankshaft so the
each connecting rod is centered in cylinder bore.
CAUTION: DO NOT use a number stamp or a punch
to mark connecting rods or caps, as damage to
connecting rods could occur
NOTE: Connecting rods and bearing caps are not
interchangeable and should be marked before
removing to ensure correct reassembly.
(4) Mark connecting rod and bearing cap positions
using a permanent ink marker or scribe tool (Fig.
12).
CAUTION: Care must be taken not to damage the
fractured rod and cap joint face surfaces, as engine
damage may occur.(5) Remove connecting rod cap. Install Special Tool
8507 Connecting Rod Guides into the connecting rod
being removed. Remove piston from cylinder bore.
Repeat this procedure for each piston being removed.
CAUTION: Care must be taken not to nick crank-
shaft journals, as engine damage may occur
(6) Immediately after piston and connecting rod
removal, install bearing cap on the mating connect-
ing rod to prevent damage to the fractured cap and
rod surfaces.
(7) Carefully remove piston rings from piston(s),
starting from the top ring down.
CLEANING
CAUTION: DO NOT use a wire wheel or other abra-
sive cleaning devise to clean the pistons or con-
necting rods. The pistons have a Moly coating, this
coating must not be damaged.
(1) Using a suitable cleaning solvent clean the pis-
tons in warm water and towel dry.
(2) Use a wood or plastic scraper to clean the ring
land grooves.
CAUTION: DO NOT remove the piston pin from the
piston and connecting rod assembly.
INSPECTION
Check the connecting rod journal for excessive
wear, taper and scoring (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Check the connecting rod for signs of twist or bend-
ing.
Check the piston for taper and elliptical shape
before it is fitted into the cylinder bore (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON & CONNECT-
ING ROD - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 11 Bore GaugeÐTypical
1 - FRONT
2 - BORE GAUGE
3 - CYLINDER BORE
4-38MM
(1.5 in)
Fig. 12 Identify Connecting Rod to Cylinder
PositionÐTypical
9 - 206 ENGINE - 5.7LDR
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1478 of 2895
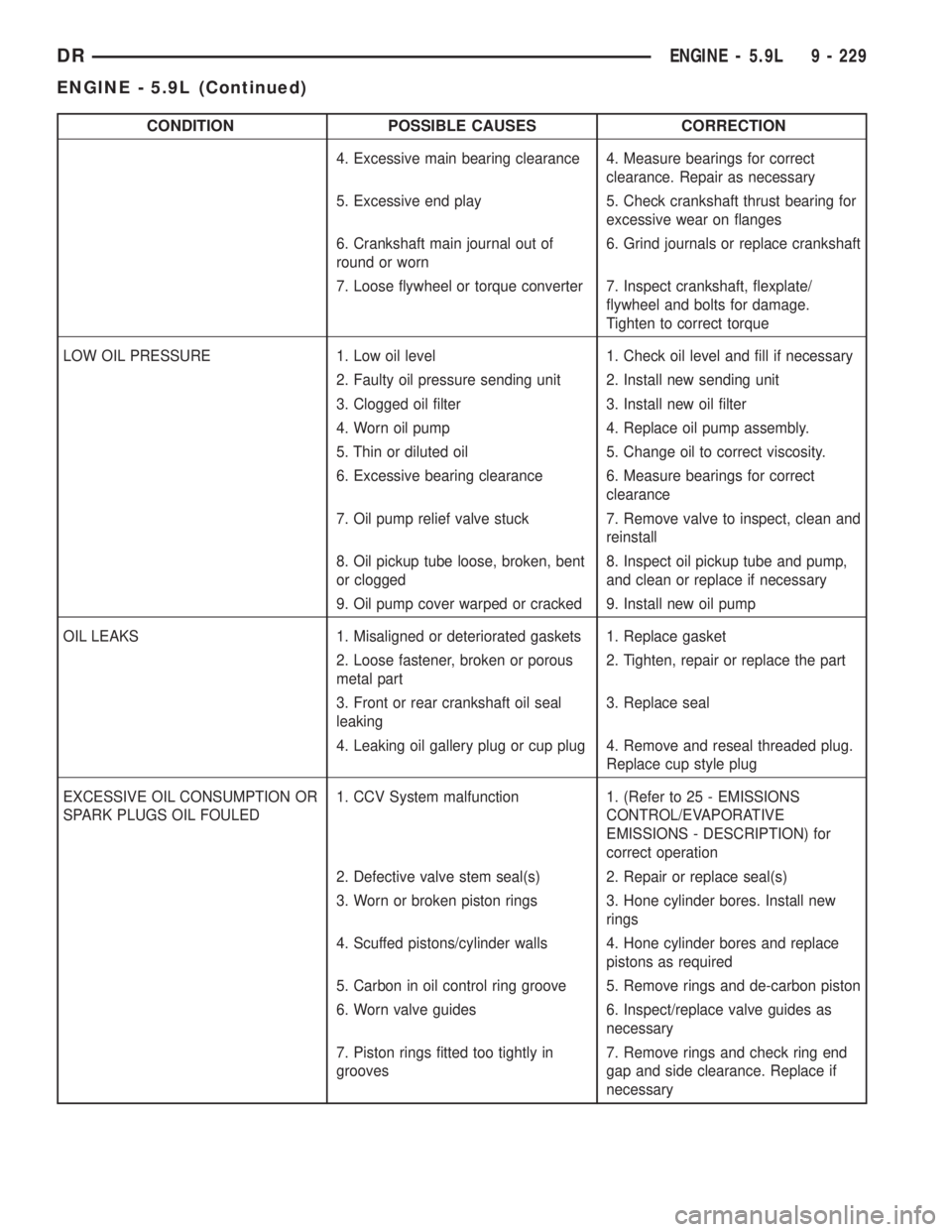
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
4. Excessive main bearing clearance 4. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary
5. Excessive end play 5. Check crankshaft thrust bearing for
excessive wear on flanges
6. Crankshaft main journal out of
round or worn6. Grind journals or replace crankshaft
7. Loose flywheel or torque converter 7. Inspect crankshaft, flexplate/
flywheel and bolts for damage.
Tighten to correct torque
LOW OIL PRESSURE 1. Low oil level 1. Check oil level and fill if necessary
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit 2. Install new sending unit
3. Clogged oil filter 3. Install new oil filter
4. Worn oil pump 4. Replace oil pump assembly.
5. Thin or diluted oil 5. Change oil to correct viscosity.
6. Excessive bearing clearance 6. Measure bearings for correct
clearance
7. Oil pump relief valve stuck 7. Remove valve to inspect, clean and
reinstall
8. Oil pickup tube loose, broken, bent
or clogged8. Inspect oil pickup tube and pump,
and clean or replace if necessary
9. Oil pump cover warped or cracked 9. Install new oil pump
OIL LEAKS 1. Misaligned or deteriorated gaskets 1. Replace gasket
2. Loose fastener, broken or porous
metal part2. Tighten, repair or replace the part
3. Front or rear crankshaft oil seal
leaking3. Replace seal
4. Leaking oil gallery plug or cup plug 4. Remove and reseal threaded plug.
Replace cup style plug
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION OR
SPARK PLUGS OIL FOULED1. CCV System malfunction 1. (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS
CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE
EMISSIONS - DESCRIPTION) for
correct operation
2. Defective valve stem seal(s) 2. Repair or replace seal(s)
3. Worn or broken piston rings 3. Hone cylinder bores. Install new
rings
4. Scuffed pistons/cylinder walls 4. Hone cylinder bores and replace
pistons as required
5. Carbon in oil control ring groove 5. Remove rings and de-carbon piston
6. Worn valve guides 6. Inspect/replace valve guides as
necessary
7. Piston rings fitted too tightly in
grooves7. Remove rings and check ring end
gap and side clearance. Replace if
necessary
DRENGINE - 5.9L 9 - 229
ENGINE - 5.9L (Continued)
Page 1533 of 2895
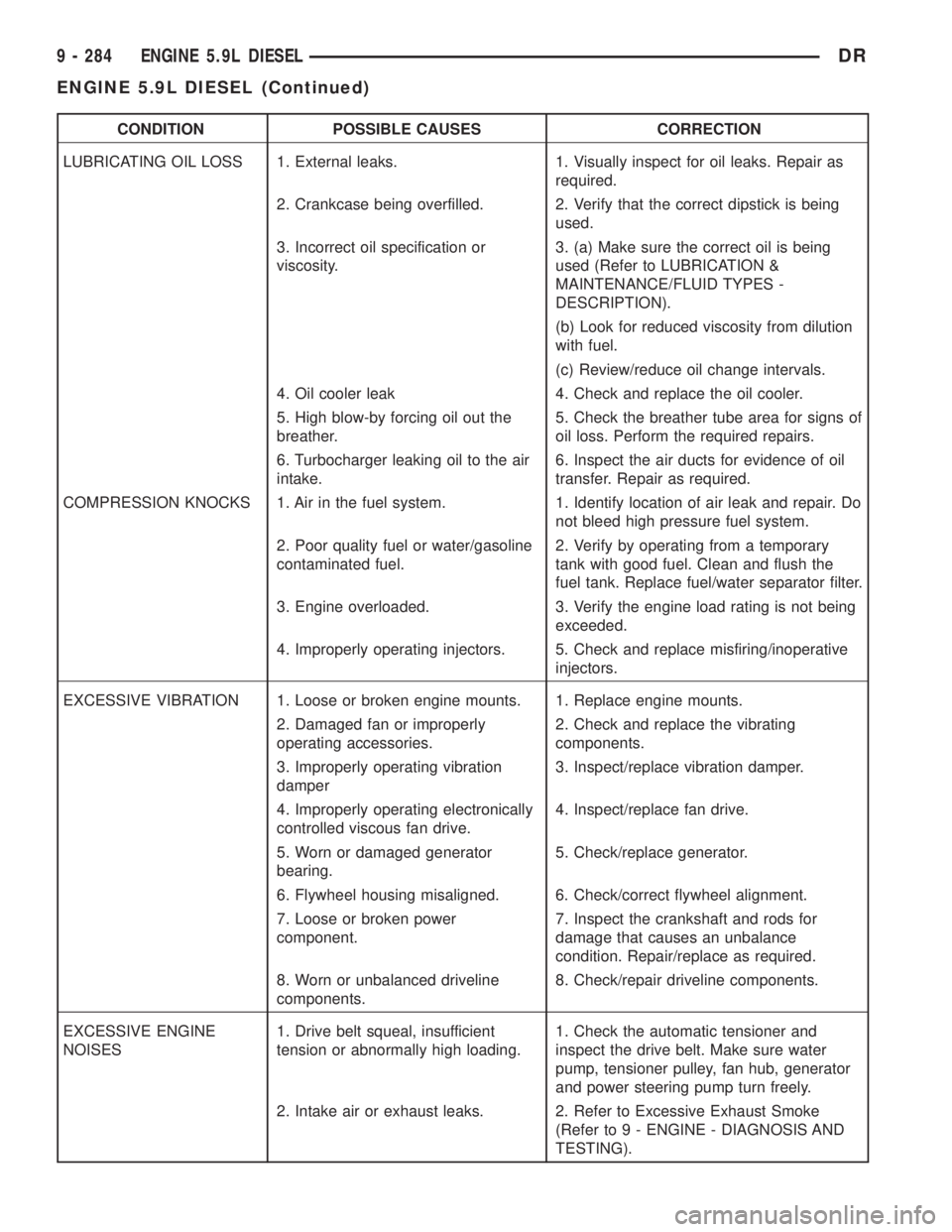
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
LUBRICATING OIL LOSS 1. External leaks. 1. Visually inspect for oil leaks. Repair as
required.
2. Crankcase being overfilled. 2. Verify that the correct dipstick is being
used.
3. Incorrect oil specification or
viscosity.3. (a) Make sure the correct oil is being
used (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION).
(b) Look for reduced viscosity from dilution
with fuel.
(c) Review/reduce oil change intervals.
4. Oil cooler leak 4. Check and replace the oil cooler.
5. High blow-by forcing oil out the
breather.5. Check the breather tube area for signs of
oil loss. Perform the required repairs.
6. Turbocharger leaking oil to the air
intake.6. Inspect the air ducts for evidence of oil
transfer. Repair as required.
COMPRESSION KNOCKS 1. Air in the fuel system. 1. Identify location of air leak and repair. Do
not bleed high pressure fuel system.
2. Poor quality fuel or water/gasoline
contaminated fuel.2. Verify by operating from a temporary
tank with good fuel. Clean and flush the
fuel tank. Replace fuel/water separator filter.
3. Engine overloaded. 3. Verify the engine load rating is not being
exceeded.
4. Improperly operating injectors. 5. Check and replace misfiring/inoperative
injectors.
EXCESSIVE VIBRATION 1. Loose or broken engine mounts. 1. Replace engine mounts.
2. Damaged fan or improperly
operating accessories.2. Check and replace the vibrating
components.
3. Improperly operating vibration
damper3. Inspect/replace vibration damper.
4. Improperly operating electronically
controlled viscous fan drive.4. Inspect/replace fan drive.
5. Worn or damaged generator
bearing.5. Check/replace generator.
6. Flywheel housing misaligned. 6. Check/correct flywheel alignment.
7. Loose or broken power
component.7. Inspect the crankshaft and rods for
damage that causes an unbalance
condition. Repair/replace as required.
8. Worn or unbalanced driveline
components.8. Check/repair driveline components.
EXCESSIVE ENGINE
NOISES1. Drive belt squeal, insufficient
tension or abnormally high loading.1. Check the automatic tensioner and
inspect the drive belt. Make sure water
pump, tensioner pulley, fan hub, generator
and power steering pump turn freely.
2. Intake air or exhaust leaks. 2. Refer to Excessive Exhaust Smoke
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
9 - 284 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1534 of 2895

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
3. Excessive valve lash. 3. Adjust valves. Make sure the push rods
are not bent and rocker arms, adjusting
screws, crossheads, are not severely worn.
Replace bent or severely worn components.
4. Turbocharger noise. 4. Check turbocharger impeller and turbine
wheel for housing contact. Repair/replace
as required.
5. Gear train noise. 5. Visually inspect and measure gear
backlash. Replace gears as required.
6. Power function knock. 6. Check/replace rod and main bearings.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐSMOKE
DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
The following charts include possible causes and
corrections forexcess or abnormalexhaust smoke.Small amounts of exhaust smoke (at certain times)
are to be considered normal for a diesel powered
engine.
EXCESSIVE BLACK SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Air filter dirty or plugged. Check Filter MinderTat air filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER ELEMENT -
REMOVAL).
Air intake system restricted. Check entire air intake system including all hoses and
tubes for restrictions, collapsed parts or damage.
Repair/replace as necessary.
Air Leak in Intake System. Check entire air intake system including all hoses and
tubes for cracks, loose clamps and/or holes in rubber
ducts. Also check intake manifold for loose mounting
hardware.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) active or multiple,
intermittent DTC's.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Engine Control Module (ECM) not calibrated or ECM
has incorrect calibration.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Exhaust system restriction is above specifications. Check exhaust pipes for damage/restrictions. Repair as
necessary.
Fuel grade is not correct or fuel quality is poor. Temporarily change fuel brands and note condition.
Change brand if necessary.
Fuel injection pump malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. If so, refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Fuel injector malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. Perform9Cylinder Cutout
Test9using DRB scan tool to isolate individual
cylinders. Also refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information and, to (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fuel return system restricted. Check fuel return lines for restriction (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Intake manifold restricted. Remove restriction.
DRENGINE 5.9L DIESEL 9 - 285
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1535 of 2895

EXCESSIVE BLACK SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Manifold Air Pressure (Boost) Sensor or sensor circuit
malfunctioning.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Raw fuel in intake manifold. Fuel injectors leaking on engine shutdown. Do Fuel
Injector Test (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Turbocharger air intake restriction. Remove restriction.
Turbocharger damaged. (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - INSPECTION).
Turbocharger has excess build up on compressor
wheel and/or diffuser vanes.(Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - CLEANING).
Turbocharger wheel clearance out of specification. (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - INSPECTION).
EXCESSIVE WHITE SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Air in fuel supply: Possible leak in fuel supply side
(between transfer pump and fuel tank module).(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL
TRANSFER PUMP - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Coolant leaking into combustion chamber. Do pressure test of cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) active or multiple,
intermittent DTC's.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
In very cold ambient temperatures, engine block heater
is malfunctioning (if equipped).(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK
HEATER - REMOVAL).
Engine coolant temperature sensor malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information. Also check
thermostat operation (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Engine Control Module (ECM) not calibrated or has
incorrect calibration.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Fuel filter plugged. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system
testing.
Fuel grade not correct or fuel quality is poor. Temporarily change fuel brands and note condition.
Change brand if necessary.
Fuel heater element or fuel heater temperature sensor
malfunctioning. This will cause wax type build-up in fuel
filter.Refer to Fuel Heater Testing (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL HEATER -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fuel injector malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Perform9Cylinder cutout
Test9using DRB scan tool to isolate individual
cylinders. Also refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information and, (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fuel injector hold-downs loose. Torque to specifications.
9 - 286 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1541 of 2895

(2) Lower engine into the engine compartment and
install the engine the engine mount through bolts
and nuts.
(3) Tighten the mount through bolts and nuts to
88 N-m (65 ft-lbs) torque.
(4) Remove the engine lifting device (Tool 9009).
(5) Check cylinder head capscrew length and
install into cylinder head.
(6) Torque alternately to 70 N-m (52 ft-lbs). Torque
alternately to 105 N-m (77 ft-lbs). Rotate 90 degrees.
(7) Install rocker housing. Torque to 24 N-m (18 ft-
lbs). Refer to Section 9 Rocker Housing Installation
(8) Replace injector o-ring and sealing washer on
injectors #5 and #6. Install injectors and alternately
tighten hold-down capscrews to 10 N-m (89 in-lbs).
(9) Install fuel connector tube and fuel connector
tube nut. Torque to 50 N-m (37 ft-lb). 10.
(10) Install #5 and #6 high pressure fuel lines. Fol-
low correct torque sequence per section 14. Torque
fuel line fittings to 30 N-m (22 ft-lb). Torque brace
capscrew to 24 N-m (18 ft-lb).
(11) Install rear engine lift bracket. Torque to 77
N-m (57 ft-lb).
(12) Install push tubes, rocker arms, and pedestals
for cylinders #4, #5, and #6. Torque the mounting
bolts to 36 N-m (27 ft-lbs).
(13) Reset valve lash on cylinders #4, #5, and #6.
Torque adjusting nuts to 24 N-m (18 ft-lbs).
(14) Install cylinder head cover. Torque to 24 N-m
(18 ft-lbs).(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD -
INSTALLATION).
(15) Connect breather tube and lube oil drain tube
to breather housing. Install breather housing. Torque
capscrews to 24 N-m (18 ft-lbs)
(16) Connect fuel supply and return hoses.
(17) Connect ECM ground to hydroform screw.
Connect ECM power connector.
(18) Install the APPS cable(s) to the APPS. Install
the throttle linkage cover.
(19) Install the power steering pump.
(20) Install the damper and speed indicator ring.
Torque to 40 N-m (30 ft-lb) plus 60 degrees.
(21) Connect the engine block heater connection.
(22) Connect the A/C compressor and pressure sen-
sor connectors
(23) Install the charge air cooler and a/c condenser
(if equipped). Install and tighten the charge air
cooler mounting bolts to 2 N-m (17 in-lbs).
(24) Connect the charge air cooler piping. Torque
all clamps to 8 N-m (72 in-lbs).
(25) Connect the a/c refrigerant lines to the a/c
condenser (if equipped).
(26) Install the radiator upper support panel.
(27) Install radiator.
(28) Connect the transmission quick-connect oil
cooler lines.(29) Raise vehicle.
(30) Connect a/c compressor suction/discharge hose
(if equipped).
(31) Install the radiator lower hose and clamps.
(32) Install the battery negative cables to the
engine block on the driver and passenger side.
(33) Install the transmission adapter with a new
camshaft rectangular ring seal. Torque to 77 N-m (57
ft-lb).
(34) Install the flywheel/flexplate. Torque to 137
N-m (101 ft-lb).
(35) Install the starter motor. Torque to 43 N-m
(32 ft-lb). (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/STARTING/
STARTER MOTOR - INSTALLATION).
(36) Connect engine to vehicle harness connectors.
(37) Install transmission and transfer case (if
equipped).
(38) Connect the exhaust pipe to the turbocharger
elbow.
(39) Connect the transmission auxiliary oil cooler
lines (if equipped).
(40) Lower the vehicle.
(41)
Connect the heater core supply and return hoses.
(42) Install the cooling fan and upper fan shroud
at the same time. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLATION).
(43) Install the coolant recovery bottle.
(44) Install the windshield washer bottle.
(45) Install the upper radiator hose and clamps.
(46) Raise vehicle.
(47) Connect electronically controlled fan drive
wire harness. Install lower radiator fan shroud.
(48) Change oil filter and install new engine oil.
(49) Fill the cooling system with coolant. (Refer to
7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(50) Connect grid heater harness at grid heater
relays.
(51) Connect electrical connections to rear of alter-
nator.
(52) Start the engine and inspect for engine oil,
coolant, and fuel leaks.
INSTALLATIONÐCRANKCASE BREATHER
(1) Install a new o-ring onto the breather element.
(2) Lubricate o-ring and install into cylinder head
cover. Torque capscrews to 10 N´m (89 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect breather tube and lube oil drain tube.
(4) Install breather cover (Fig. 4). Torque to 24
N´m (18 ft. lbs.)
(5) Install oil fill cap.
9 - 292 ENGINE 5.9L DIESELDR
ENGINE 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1606 of 2895
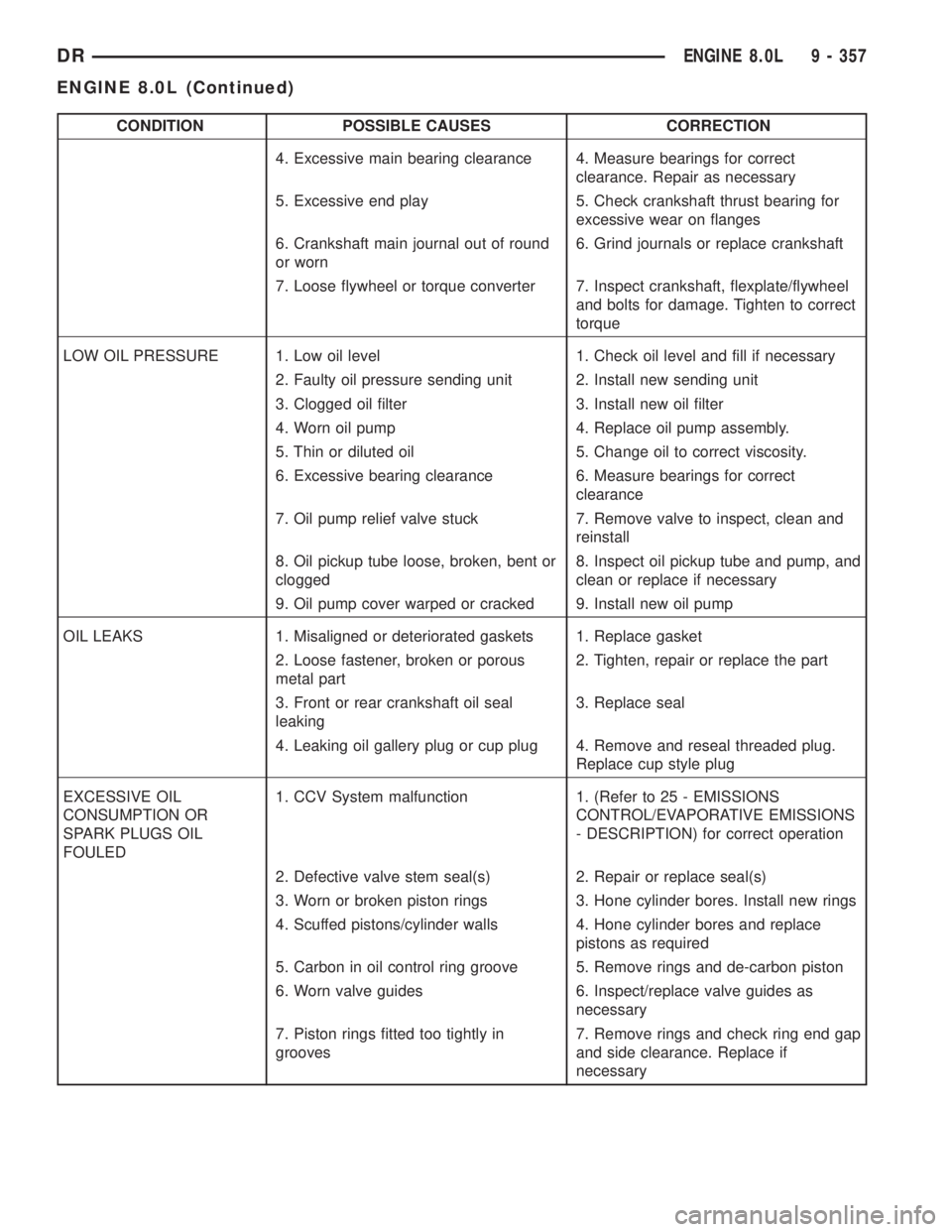
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
4. Excessive main bearing clearance 4. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary
5. Excessive end play 5. Check crankshaft thrust bearing for
excessive wear on flanges
6. Crankshaft main journal out of round
or worn6. Grind journals or replace crankshaft
7. Loose flywheel or torque converter 7. Inspect crankshaft, flexplate/flywheel
and bolts for damage. Tighten to correct
torque
LOW OIL PRESSURE 1. Low oil level 1. Check oil level and fill if necessary
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit 2. Install new sending unit
3. Clogged oil filter 3. Install new oil filter
4. Worn oil pump 4. Replace oil pump assembly.
5. Thin or diluted oil 5. Change oil to correct viscosity.
6. Excessive bearing clearance 6. Measure bearings for correct
clearance
7. Oil pump relief valve stuck 7. Remove valve to inspect, clean and
reinstall
8. Oil pickup tube loose, broken, bent or
clogged8. Inspect oil pickup tube and pump, and
clean or replace if necessary
9. Oil pump cover warped or cracked 9. Install new oil pump
OIL LEAKS 1. Misaligned or deteriorated gaskets 1. Replace gasket
2. Loose fastener, broken or porous
metal part2. Tighten, repair or replace the part
3. Front or rear crankshaft oil seal
leaking3. Replace seal
4. Leaking oil gallery plug or cup plug 4. Remove and reseal threaded plug.
Replace cup style plug
EXCESSIVE OIL
CONSUMPTION OR
SPARK PLUGS OIL
FOULED1. CCV System malfunction 1. (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS
CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
- DESCRIPTION) for correct operation
2. Defective valve stem seal(s) 2. Repair or replace seal(s)
3. Worn or broken piston rings 3. Hone cylinder bores. Install new rings
4. Scuffed pistons/cylinder walls 4. Hone cylinder bores and replace
pistons as required
5. Carbon in oil control ring groove 5. Remove rings and de-carbon piston
6. Worn valve guides 6. Inspect/replace valve guides as
necessary
7. Piston rings fitted too tightly in
grooves7. Remove rings and check ring end gap
and side clearance. Replace if
necessary
DRENGINE 8.0L 9 - 357
ENGINE 8.0L (Continued)
Page 1676 of 2895

CAUTION: Do not reuse damaged fasteners, quality
of repair would be suspect. Failure to use only pro-
duction fasteners or fasteners of equivalent hard-
ness can result in loosening or failure. Do not drill
any holes in the frame that are not specifically out-
lined in this or other, DaimlerChrysler procedure as
frame rail failure can result. When using heat to
straighten frame components do not exceed 566ÉC
(1050ÉF), metal fatigue can result.
NOTE: Procedures for 4X2 and 4X4 are common
except as noted in this procedure.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the front wheelhouse splash shield.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/FRONT WHEEL-
HOUSE SPLASH SHIELD - REMOVAL)
(3) Remove the bolts and position aside the wire
harness and grounds, if required.
(4) Remove the front bumper. (Refer to 13 -
FRAME & BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT BUMPER
- REMOVAL)
(5) Loosen and lower the stabilizer bar mount and
bar. (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/STABI-
LIZER BAR - REMOVAL)
(6) Remove the front cab mount bolt to the Front
End Sheet Metal (FESM) bracket. (Fig. 6)(7) Make a vertical mark on the inside and outside
face of the frame rail 112 mm (4.5 in.) from the for-
ward edge of the PLP hole in the sides of the rail.
(Fig. 8)
(8) Using a straightedge, connect the two lines on
the top and bottom of the rail.
(9) Using the service tip as a guide, re-check your
cut lines to ensure the service tip will fit when the
cut is made.
CAUTION: Do not use any flame or plasma cutting
equipment to cut the frame in this procedure. This
is due to the inaccurate nature of the cut-line and
the fact that the high temperatures achieved during
flame or plasma cutting will change the metal char-
acteristics and may weaken the frame and/or repair
location.
(10) Using a reciprocating saw or equivalent, care-
fully cut and remove the damaged frame rail tip.
(Fig. 7)
Fig. 6 REPLACEMENT FRAME TIP
1 - FRONT END SHEET METAL (FESM) BRACKET
2 - CAB INSULATOR
3 - RING-FILLET WELD/HOLE
4 - PRINCIPLE LOCATING POINT (PLP)
5 - WELD ROOT GAP 4 mm-6mm(0.16 in. - 0.24 in.)
6 - FRONT CAB MOUNT BOLT
7 - REPLACEMENT FRAME TIP
Fig. 7 FRAME CUT LOCATION
1 - REPAIR ROOT OPENING
2 - SERVICE SLEEVE
3 - PRINCIPLE LOCATING POINT (PLP)
4 - SUSPENSION BRACKETS
5 - FRAME
6 - FRAME CUTOFF LOCATION - 112 mm (4.5 in.)
7 - FRAME SERVICE TIP
DRFRAMES & BUMPERS 13 - 5
FRAME (Continued)