change time DODGE RAM 2003 Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2003, Model line: RAM, Model: DODGE RAM 2003Pages: 2895, PDF Size: 83.15 MB
Page 2268 of 2895

by a clutch disc until entire clutch pack is installed
(4 discs and 3 plates are required) (Fig. 220).
(13) Install the reaction plate.
(14) Install selective snap-ring. Be sure snap-ring
is fully seated in retainer groove.
(15) Using a suitable gauge bar and dial indicator,
measure clutch pack clearance (Fig. 222).
(a) Position gauge bar across the clutch drum
with the dial indicator pointer on the pressure
plate (Fig. 222).
(b) Using two small screw drivers, lift the pres-
sure plate and release it.
(c) Zero the dial indicator.
(d) Lift the pressure plate until it contacts the
snap-ring and record the dial indicator reading.
Clearance should be 0.635 - 0.914 mm (0.025 -
0.036 in.). If clearance is incorrect, steel plates, discs,
selective snap ring and pressure plates may have to
be changed.
The selective snap ring thicknesses are:
²0.107 - 0.109 in.
²0.098 - 0.100 in.
²0.095 - 0.097 in.
²0.083 - 0.085 in.
²0.076 - 0.078 in.
²0.071 - 0.073 in.
²0.060 - 0.062 in.
(16) Coat rear clutch thrust washer with petro-
leum jelly and install washer over input shaft and
into clutch retainer (Fig. 223). Use enough petroleum
jelly to hold washer in place.
(17) Set rear clutch aside for installation during
final assembly.
REAR SERVO
DESCRIPTION
The rear (low/reverse) servo consists of a single
stage or diameter piston and a spring loaded plug.
The spring is used to cushion the application of the
rear (low/reverse) band.
OPERATION
While in the de-energized state (no pressure
applied), the piston is held up in its bore by the pis-
ton spring. The plug is held down in its bore, in the
piston, by the plug spring. When pressure is applied
to the top of the piston, the plug is forced down in its
bore, taking up any clearance. As the piston moves, it
causes the plug spring to compress, and the piston
moves down over the plug. The piston continues to
move down until it hits the shoulder of the plug and
fully applies the band. The period of time from the
initial application, until the piston is against the
shoulder of the plug, represents a reduced shocking
of the band that cushions the shift.
Fig. 222 Checking Rear Clutch Pack Clearance
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
2 - PRESSURE PLATE
3 - SNAP-RING
4-STAND
5 - REAR CLUTCH
6 - GAUGE BAR
Fig. 223 Installing Rear Clutch Thrust Washer
1 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER
2 - REAR CLUTCH THRUST WASHER
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 429
REAR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 2497 of 2895

TRANSFER CASE - NV243
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TRANSFER CASE - NV243
DESCRIPTION........................658
OPERATION..........................659
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER
CASE - NV243.......................659
REMOVAL............................660
DISASSEMBLY........................660
CLEANING...........................668
INSPECTION.........................668
ASSEMBLY...........................670
INSTALLATION........................679
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV243.............680
SPECIAL TOOLS
TRANSFER CASE - NV241/NV243........680
EXTENSION HOUSING BUSHING AND SEAL
REMOVAL............................682
INSTALLATION........................682FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID DRAIN AND
REFILL............................682
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL............................683
INSTALLATION........................683
MODE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................684
OPERATION..........................684
SELECTOR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION........................685
OPERATION..........................685
SHIFT MOTOR
DESCRIPTION........................686
OPERATION..........................686
REMOVAL............................686
INSTALLATION........................686
TRANSFER CASE - NV243
DESCRIPTION
The NV243 is an electronically controlled part-time
transfer case with a low range gear reduction system.
The NV243 has three operating ranges plus a NEU-
TRAL position. The low range system provides a gear
reduction ratio for increased low speed torque capa-
bility.
The geartrain is mounted in two aluminum case
halves attached with bolts. The mainshaft front and
rear bearings are mounted in aluminum retainer
housings bolted to the case halves.
OPERATING RANGES
Transfer case operating ranges are:
²2WD (2-wheel drive)
²4HI (4-wheel drive)
²4LO (4-wheel drive low range)
²NEUTRAL
The 2WD range is for use on any road surface at
any time.The 4HI and 4LO ranges are for off road use only.
They are not for use on hard surface roads. The only
exception being when the road surface is wet or slip-
pery or covered by ice and snow.
The low range reduction gear system is operative
in 4LO range only. This range is for extra pulling
power in off road situations. Low range reduction
ratio is 2.72:1.
SHIFT MECHANISM
Operating ranges are selected with a dash
mounted shift selector switch. The shift selector
switch provides a input to the Transfer Case Control
Module (TCCM) to indicate the driver's desire to
change operating ranges. The TCCM uses this input,
along with input from the transfer case mounted
mode sensor and information from the vehicle's bus,
to determine if a shift is permitted. If the TCCM
decides the shift is permitted, the TCCM controls the
shift motor, mounted to the exterior of the transfer
case, to perform the shift.
21 - 658 TRANSFER CASE - NV243DR
Page 2526 of 2895

TRANSFER CASE - NV273
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TRANSFER CASE - NV273
DESCRIPTION........................687
OPERATION..........................688
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER
CASE - NV273.......................688
REMOVAL............................689
DISASSEMBLY........................689
CLEANING...........................698
INSPECTION.........................699
ASSEMBLY...........................701
INSTALLATION........................713
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV273.............713
SPECIAL TOOLS
TRANSFER CASE NV271/NV273.........714
EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL AND DUST BOOT
REMOVAL............................716
INSTALLATION........................716FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID DRAIN AND
REFILL............................716
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL............................717
INSTALLATION........................717
MODE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................718
OPERATION..........................718
SELECTOR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION........................719
OPERATION..........................719
SHIFT MOTOR
DESCRIPTION........................720
OPERATION..........................720
REMOVAL............................720
INSTALLATION........................720
TRANSFER CASE - NV273
DESCRIPTION
The NV273 is an electronically controlled part-time
transfer case with a low range gear reduction system.
The NV273 has three operating ranges plus a NEU-
TRAL position. The low range system provides a gear
reduction ratio for increased low speed torque capa-
bility.
The geartrain is mounted in two aluminum case
halves attached with bolts. The mainshaft front and
rear bearings are mounted in aluminum case halves.
OPERATING RANGES
Transfer case operating ranges are:
²2WD (2-wheel drive)
²4HI (4-wheel drive)
²4LO (4-wheel drive low range)
²NEUTRAL
The 2WD range is for use on any road surface at
any time.The 4HI and 4LO ranges are for off road use only.
They are not for use on hard surface roads. The only
exception being when the road surface is wet or slip-
pery or covered by ice and snow.
The low range reduction gear system is operative
in 4LO range only. This range is for extra pulling
power in off road situations. Low range reduction
ratio is 2.72:1.
SHIFT MECHANISM
Operating ranges are selected with a dash
mounted shift selector switch. The shift selector
switch provides a input to the Transfer Case Control
Module (TCCM) to indicate the driver's desire to
change operating ranges. The TCCM uses this input,
along with input from the transfer case mounted
mode sensor and information from the vehicle's bus,
to determine if a shift is permitted. If the TCCM
decides the shift is permitted, the TCCM controls the
shift motor, mounted to the exterior of the transfer
case, to perform the shift.
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV273 21 - 687
Page 2608 of 2895

(2) Insert a 5/32-inch hex-wrench through hole and
into adjustment screw. Loosen screw.
(3) Operate outside handle several times to release
any restriction because of mis-alignment.
(4) Tighten adjustment screw to 3 N´m (30 in.
lbs.).
(5) Test handle for proper operation.
LATCH STRIKER
REMOVAL
(1) Using a grease pencil or equivalent, mark the
position of the striker.
(2) Remove the bolts and remove the striker.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the striker and install the bolts.
(2) Tighten the bolts to 28 N´m (21 ft. lbs.).
(3) Adjust the striker if needed. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/DOOR - FRONT/LATCH STRIKER - ADJUST-
MENTS)
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT
(1) Using a grease pencil or equivalent, mark the
position of the striker to aid in adjustment.
(2) Loosen the striker bolts.
(3) Change the striker position to adjust the rear
gap and flush measurement. (Refer to 23 - BODY/
BODY STRUCTURE/GAP AND FLUSH - SPECIFI-
CATIONS)
(4) Tighten the bolts to 28 N´m (21 ft. lbs.).
TRIM PANEL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the window crank, if equipped. (Fig.
10)
(2) Remove the interior handle. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/DOORS - REAR/INSIDE HANDLE ACTUA-
TOR - REMOVAL)
(3) Remove the screw near the inside handle. (Fig.
9)
CAUTION: Trim panel is attached to the door using
hooks molded into the panel. Do not pull the trim
panel straight off or damage to the panel and/or
power switch assembly may occur.
(4) Lift the trim panel up off the belt seal and
attachment hooks and separate the panel from the
door slightly.
(5) Disconnect the power window switch electrical
connector, if equipped, and remove the trim panel.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the trim panel onto the lower hooks
and connect the power window switch electrical con-
nector, if equipped.
(2) Position the remaining trim panel attachment
hooks into the door panel and seat the trim panel
into the belt seal fully.
(3) Install the screw near the inside handle.
(4) Install the interior handle. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/DOORS - REAR/INSIDE HANDLE ACTUA-
TOR - INSTALLATION)
(5) Install the window crank, if equipped.
Fig. 8 LATCH ADJUSTMENT SCREW - TYPICAL
1 - DOOR LATCH
2 - MYLAR TAPE
3 - ADJUSTMENT SCREW
Fig. 9 TRIM PANEL
1 - DOOR
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - ATTACHMENT HOOKS
4 - SCREW
5 - TRIM PANEL
DRDOORS - REAR 23 - 33
LATCH (Continued)
Page 2825 of 2895

INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)(Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
CAUTION - REFRIGERANT HOSES/LINES/TUBES
PRECAUTIONS)
(1) Install the accumulator to the bulkhead but do
not tighten yet.
(2) Remove the tape or plugs from the refrigerant
line fittings on the accumulator inlet and the evapo-
rator outlet. Connect the accumulator inlet refriger-
ant line coupler to the evaporator outlet. (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C LINE COUPLERS)
(3) Remove the tape or plugs from the refrigerant
line fittings on the suction line and the accumulator
outlet. Connect the suction line refrigerant line cou-
pler to the accumulator outlet. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C LINE COUPLERS)
(4) Tighten the accumulator fasteners to 4.5 N´m
(40 in. lbs.).
(5) Connect the battery negative cable.
(6) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE)
(7) Charge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
NOTE: If the accumulator is replaced, add 60 milli-
liters (2 fluid ounces) of refrigerant oil to the refrig-
erant system. Use only refrigerant oil of the type
recommended for the compressor in the vehicle.
HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION
The heater core is located in the HVAC housing,
under the instrument panel. It is a heat exchanger
made of rows of tubes and fins.
The heater core is not repairable and if damaged it
must be replaced.
OPERATION
Engine coolant is circulated through heater hoses
to the heater core at all times. As the coolant flowsthrough the heater core, heat removed from the
engine is transferred to the heater core fins and
tubes. Air directed through the heater core picks up
the heat from the heater core fins. The blend door
allows control of the heater output air temperature
by controlling how much of the air flowing through
the HVAC housing is directed through the heater
core. The blower motor speed controls the volume of
air flowing through the HVAC housing.
The heater core cannot be repaired and, if faulty or
damaged, it must be replaced.
REMOVAL
NOTE: Disassembly of the HVAC housing is not
required to remove heater core.
(1) Remove the HVAC housing from the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove the screws and retainers that secure
the heater core to the HVAC housing.
(3) Lift the heater core out of the heater-A/C hous-
ing.
(4) Inspect all seals and repair or replace as
required.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place the heater core into the HVAC housing.
(2) Snap the retainers for the heater core to the
housing. Install and tighten the screws that secure
the heater core to the HVAC housing (if equipped).
Tighten the screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(3) Reinstall the HVAC housing in the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - INSTALLA-
TION)
REFRIGERANT
DESCRIPTION
The refrigerant used in this air conditioning sys-
tem is a HydroFluoroCarbon (HFC), type R-134a.
Unlike R-12, which is a ChloroFluoroCarbon (CFC),
R-134a refrigerant does not contain ozone-depleting
chlorine. R-134a refrigerant is a non-toxic, non-flam-
mable, clear, and colorless liquefied gas.
Even though R-134a does not contain chlorine, it
must be reclaimed and recycled just like CFC-type
refrigerants. This is because R-134a is a greenhouse
gas and can contribute to global warming.
OPERATION
R-134a refrigerant is not compatible with R-12
refrigerant in an air conditioning system. Even a
24 - 50 PLUMBINGDR
ACCUMULATOR (Continued)
Page 2830 of 2895

EMISSIONS CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST
MODE...............................1
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE...............................1
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODES..............................1
DESCRIPTION - TASK MANAGER..........1DESCRIPTION - MONITORED SYSTEMS....1
DESCRIPTION - TRIP DEFINITION.........4
DESCRIPTION - COMPONENT MONITORS . . 4
OPERATION
OPERATION..........................4
OPERATION - TASK MANAGER...........5
OPERATION - NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS . . 8
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS................10
EMISSIONS CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. Connect
the DRB scan tool to the data link connector and
access the state display screen. Then access either
State Display Inputs and Outputs or State Display
Sensors.
DESCRIPTION - CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
MODE
The Circuit Actuation Test Mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) may not internally recognize.
The PCM attempts to activate these outputs and
allow an observer to verify proper operation. Most of
the tests provide an audible or visual indication of
device operation (click of relay contacts, fuel spray,
etc.). Except for intermittent conditions, if a device
functions properly during testing, assume the device,
its associated wiring, and driver circuit work cor-
rectly. Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
connector and access the Actuators screen.
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates the
PCM has recognized an abnormal condition in the
system.Remember that DTC's are the results of a sys-
tem or circuit failure, but do not directly iden-
tify the failed component or components.
BULB CHECK
Each time the ignition key is turned to the ON
position, the malfunction indicator (check engine)
lamp on the instrument panel should illuminate for
approximately 2 seconds then go out. This is done for
a bulb check.
OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Obtain the applicable Powertrain Diagnostic
Manual.
(2) Obtain the DRB Scan Tool.
(3) Connect the DRB Scan Tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(4) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(5) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
(6) To erase DTC's, use the ªErase Trouble Codeº
data screen on the DRB scan tool.Do not erase any
DTC's until problems have been investigated
and repairs have been performed.
DESCRIPTION - TASK MANAGER
The PCM is responsible for efficiently coordinating
the operation of all the emissions-related compo-
nents. The PCM is also responsible for determining if
the diagnostic systems are operating properly. The
software designed to carry out these responsibilities
is call the 'Task Manager'.
DESCRIPTION - MONITORED SYSTEMS
There are new electronic circuit monitors that
check fuel, emission, engine and ignition perfor-
DREMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 1
Page 2831 of 2895

mance. These monitors use information from various
sensor circuits to indicate the overall operation of the
fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems and thus
the emissions performance of the vehicle.
The fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems
monitors do not indicate a specific component prob-
lem. They do indicate that there is an implied prob-
lem within one of the systems and that a specific
problem must be diagnosed.
If any of these monitors detect a problem affecting
vehicle emissions, the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) will be illuminated. These monitors generate
Diagnostic Trouble Codes that can be displayed with
the MIL or a scan tool.
The following is a list of the system monitors:
²Misfire Monitor
²Fuel System Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Leak Detection Pump Monitor (if equipped)
All these system monitors require two consecutive
trips with the malfunction present to set a fault.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnos-
tics Procedures manual for diagnostic proce-
dures.
The following is an operation and description of
each system monitor :
OXYGEN SENSOR (O2S) MONITOR
Effective control of exhaust emissions is achieved
by an oxygen feedback system. The most important
element of the feedback system is the O2S. The O2S
is located in the exhaust path. Once it reaches oper-
ating temperature 300É to 350ÉC (572É to 662ÉF), the
sensor generates a voltage that is inversely propor-
tional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. The
information obtained by the sensor is used to calcu-
late the fuel injector pulse width. This maintains a
14.7 to 1 Air Fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture ratio,
the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons (HC),
carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) from
the exhaust.
The O2S is also the main sensing element for the
Catalyst and Fuel Monitors.
The O2S can fail in any or all of the following
manners:
²slow response rate
²reduced output voltage
²dynamic shift
²shorted or open circuits
Response rate is the time required for the sensor to
switch from lean to rich once it is exposed to a richer
than optimum A/F mixture or vice versa. As the sen-
sor starts malfunctioning, it could take longer todetect the changes in the oxygen content of the
exhaust gas.
The output voltage of the O2S ranges from 0 to 1
volt. A good sensor can easily generate any output
voltage in this range as it is exposed to different con-
centrations of oxygen. To detect a shift in the A/F
mixture (lean or rich), the output voltage has to
change beyond a threshold value. A malfunctioning
sensor could have difficulty changing beyond the
threshold value.
OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER MONITOR
If there is an oxygen sensor (O2S) shorted to volt-
age DTC, as well as a O2S heater DTC, the O2S
fault MUST be repaired first. Before checking the
O2S fault, verify that the heater circuit is operating
correctly.
Effective control of exhaust emissions is achieved
by an oxygen feedback system. The most important
element of the feedback system is the O2S. The O2S
is located in the exhaust path. Once it reaches oper-
ating temperature 300É to 350ÉC (572 É to 662ÉF), the
sensor generates a voltage that is inversely propor-
tional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. The
information obtained by the sensor is used to calcu-
late the fuel injector pulse width. This maintains a
14.7 to 1 Air Fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture ratio,
the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons (HC),
carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) from
the exhaust.
The voltage readings taken from the O2S sensor
are very temperature sensitive. The readings are not
accurate below 300ÉC. Heating of the O2S sensor is
done to allow the engine controller to shift to closed
loop control as soon as possible. The heating element
used to heat the O2S sensor must be tested to ensure
that it is heating the sensor properly.
The O2S sensor circuit is monitored for a drop in
voltage. The sensor output is used to test the heater
by isolating the effect of the heater element on the
O2S sensor output voltage from the other effects.
LEAK DETECTION PUMP MONITOR (IF EQUIPPED)
The leak detection assembly incorporates two pri-
mary functions: it must detect a leak in the evapora-
tive system and seal the evaporative system so the
leak detection test can be run.
The primary components within the assembly are:
A three port solenoid that activates both of the func-
tions listed above; a pump which contains a switch,
two check valves and a spring/diaphragm, a canister
vent valve (CVV) seal which contains a spring loaded
vent seal valve.
Immediately after a cold start, between predeter-
mined temperature thresholds limits, the three port
solenoid is briefly energized. This initializes the
25 - 2 EMISSIONS CONTROLDR
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2835 of 2895

these situations, the effects of another monitor run-
ning could result in an erroneous failure. If thiscon-
flictis present, the monitor is not run until the
conflicting condition passes. Most likely the monitor
will run later after the conflicting monitor has
passed.
For example, if the Fuel System Monitor is in
progress, the Task Manager does not run the EGR
Monitor. Since both tests monitor changes in air/fuel
ratio and adaptive fuel compensation, the monitors
will conflict with each other.
²Suspend
Occasionally the Task Manager may not allow a two
trip fault to mature. The Task Manager willsus-
pendthe maturing of a fault if a condition exists
that may induce an erroneous failure. This prevents
illuminating the MIL for the wrong fault and allows
more precis diagnosis.
For example, if the PCM is storing a one trip fault
for the Oxygen Sensor and the EGR monitor, the
Task Manager may still run the EGR Monitor but
will suspend the results until the Oxygen Sensor
Monitor either passes or fails. At that point the Task
Manager can determine if the EGR system is actu-
ally failing or if an Oxygen Sensor is failing.
MIL Illumination
The PCM Task Manager carries out the illumina-
tion of the MIL. The Task Manager triggers MIL illu-
mination upon test failure, depending on monitor
failure criteria.
The Task Manager Screen shows both a Requested
MIL state and an Actual MIL state. When the MIL is
illuminated upon completion of a test for a third trip,
the Requested MIL state changes to OFF. However,
the MIL remains illuminated until the next key
cycle. (On some vehicles, the MIL will actually turn
OFF during the third key cycle) During the key cycle
for the third good trip, the Requested MIL state is
OFF, while the Actual MILL state is ON. After the
next key cycle, the MIL is not illuminated and both
MIL states read OFF.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
With OBD II, different DTC faults have different
priorities according to regulations. As a result, the
priorities determine MIL illumination and DTC era-
sure. DTCs are entered according to individual prior-
ity. DTCs with a higher priority overwrite lower
priority DTCs.
Priorities
²Priority 0 ÐNon-emissions related trouble codes
²Priority 1 Ð One trip failure of a two trip fault
for non-fuel system and non-misfire.²Priority 2 Ð One trip failure of a two trip fault
for fuel system (rich/lean) or misfire.
²Priority3ÐTwotrip failure for a non-fuel sys-
tem and non-misfire or matured one trip comprehen-
sive component fault.
²Priority4ÐTwotrip failure or matured fault
for fuel system (rich/lean) and misfire or one trip cat-
alyst damaging misfire.
Non-emissions related failures have no priority.
One trip failures of two trip faults have low priority.
Two trip failures or matured faults have higher pri-
ority. One and two trip failures of fuel system and
misfire monitor take precedence over non-fuel system
and non-misfire failures.
DTC Self Erasure
With one trip components or systems, the MIL is
illuminated upon test failure and DTCs are stored.
Two trip monitors are components requiring failure
in two consecutive trips for MIL illumination. Upon
failure of the first test, the Task Manager enters a
maturing code. If the component fails the test for a
second time the code matures and a DTC is set.
After three good trips the MIL is extinguished and
the Task Manager automatically switches the trip
counter to a warm-up cycle counter. DTCs are auto-
matically erased following 40 warm-up cycles if the
component does not fail again.
For misfire and fuel system monitors, the compo-
nent must pass the test under a Similar Conditions
Window in order to record a good trip. A Similar Con-
ditions Window is when engine RPM is within 375
RPM and load is within 10% of when the fault
occurred.
NOTE: It is important to understand that a compo-
nent does not have to fail under a similar window of
operation to mature. It must pass the test under a
Similar Conditions Window when it failed to record
a Good Trip for DTC erasure for misfire and fuel
system monitors.
DTCs can be erased anytime with a DRB III. Eras-
ing the DTC with the DRB III erases all OBD II
information. The DRB III automatically displays a
warning that erasing the DTC will also erase all
OBD II monitor data. This includes all counter infor-
mation for warm-up cycles, trips and Freeze Frame.
Trip Indicator
TheTripis essential for running monitors and
extinguishing the MIL. In OBD II terms, a trip is a
set of vehicle operating conditions that must be met
for a specific monitor to run. All trips begin with a
key cycle.
Good Trip
The Good Trip counters are as follows:
25 - 6 EMISSIONS CONTROLDR
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2841 of 2895
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - EVAP SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
EVAP Canister Mounting
Nuts11 -95
EVAP Canister Mounting
Bracket-to-Frame Bolts14 10125
Leak Detection Pump
Mounting Bolts11 - 9 5
Leak Detection Pump
Filter Mounting Bolt11 - 9 5
CCV HOSE
DESCRIPTION - 8.0L V-10
The 8.0L V-10 engine is equipped with a Crankcase
Ventilation (CCV) system. The CCV system performs
the same function as a conventional PCV system, but
does not use a vacuum controlled valve (PCV valve).
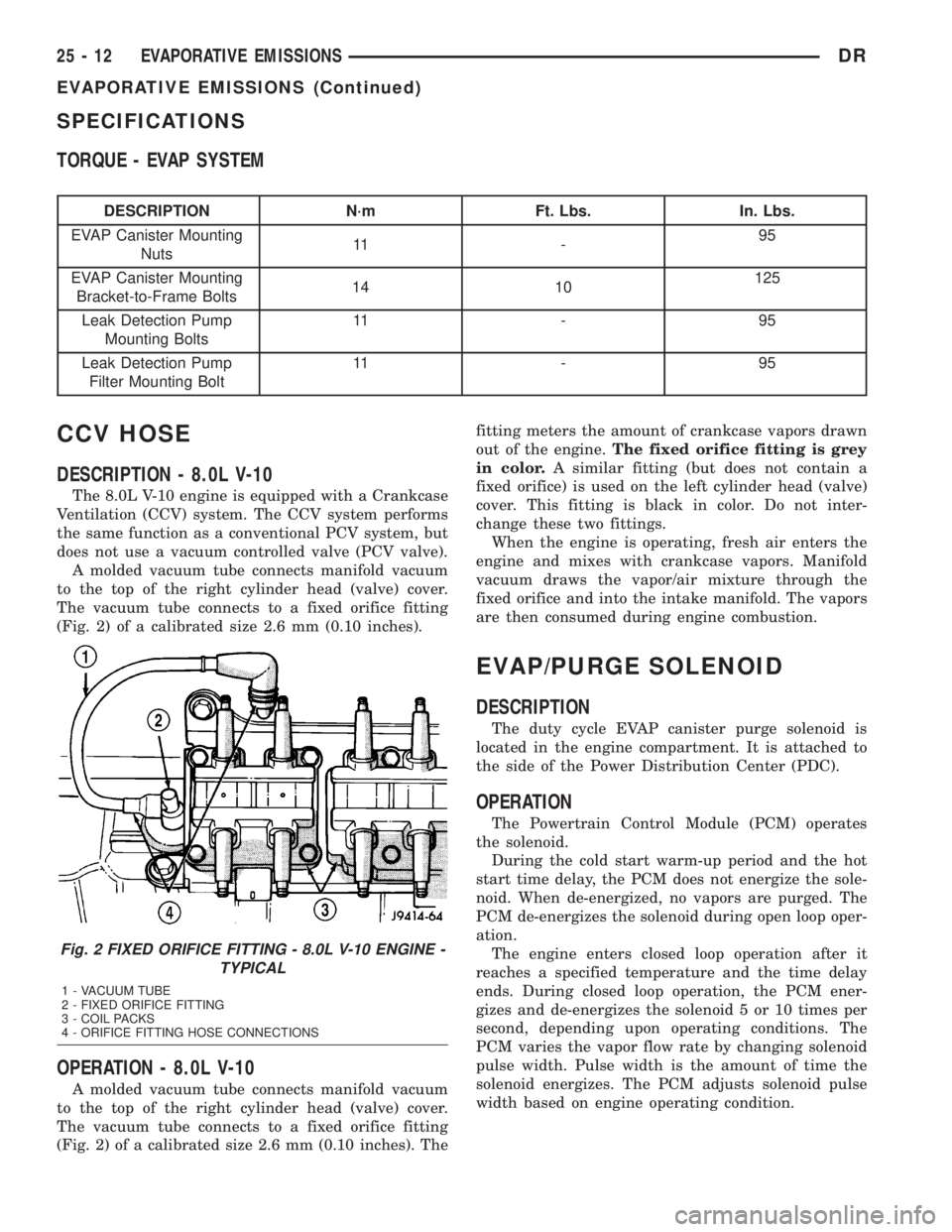
A molded vacuum tube connects manifold vacuum
to the top of the right cylinder head (valve) cover.
The vacuum tube connects to a fixed orifice fitting
(Fig. 2) of a calibrated size 2.6 mm (0.10 inches).
OPERATION - 8.0L V-10
A molded vacuum tube connects manifold vacuum
to the top of the right cylinder head (valve) cover.
The vacuum tube connects to a fixed orifice fitting
(Fig. 2) of a calibrated size 2.6 mm (0.10 inches). Thefitting meters the amount of crankcase vapors drawn
out of the engine.The fixed orifice fitting is grey
in color.A similar fitting (but does not contain a
fixed orifice) is used on the left cylinder head (valve)
cover. This fitting is black in color. Do not inter-
change these two fittings.
When the engine is operating, fresh air enters the
engine and mixes with crankcase vapors. Manifold
vacuum draws the vapor/air mixture through the
fixed orifice and into the intake manifold. The vapors
are then consumed during engine combustion.
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid is
located in the engine compartment. It is attached to
the side of the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
OPERATION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) operates
the solenoid.
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged. The
PCM de-energizes the solenoid during open loop oper-
ation.
The engine enters closed loop operation after it
reaches a specified temperature and the time delay
ends. During closed loop operation, the PCM ener-
gizes and de-energizes the solenoid 5 or 10 times per
second, depending upon operating conditions. The
PCM varies the vapor flow rate by changing solenoid
pulse width. Pulse width is the amount of time the
solenoid energizes. The PCM adjusts solenoid pulse
width based on engine operating condition.
Fig. 2 FIXED ORIFICE FITTING - 8.0L V-10 ENGINE -
TYPICAL
1 - VACUUM TUBE
2 - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING
3 - COIL PACKS
4 - ORIFICE FITTING HOSE CONNECTIONS
25 - 12 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSDR
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS (Continued)
Page 2844 of 2895

the upper pump cavity to atmosphere through the
EVAP air filter. The spring is now able to push the
diaphragm down. The downward movement of the
diaphragm closes the inlet check valve and opens the
outlet check valve pumping air into the evaporative
system. The LDP reed switch turns from open to
closed, allowing the PCM to monitor LDP pumping
(diaphragm up/down) activity (Fig. 8). During the
pumping mode, the diaphragm will not move down
far enough to open the vent valve. The pumping cycle
is repeated as the solenoid is turned on and off.
When the evaporative system begins to pressurize,
the pressure on the bottom of the diaphragm will
begin to oppose the spring pressure, slowing the
pumping action. The PCM watches the time from
when the solenoid is de-energized, until the dia-
phragm drops down far enough for the reed switch to
change from opened to closed. If the reed switch
changes too quickly, a leak may be indicated. The
longer it takes the reed switch to change state, the
tighter the evaporative system is sealed. If the sys-
tem pressurizes too quickly, a restriction somewhere
in the EVAP system may be indicated.
PUMPING ACTION
Action : During portions of this test, the PCM uses
the reed switch to monitor diaphragm movement.
The solenoid is only turned on by the PCM after the
reed switch changes from open to closed, indicating
that the diaphragm has moved down. At other times
during the test, the PCM will rapidly cycle the LDP
solenoid on and off to quickly pressurize the system.
During rapid cycling, the diaphragm will not move
enough to change the reed switch state. In the state
of rapid cycling, the PCM will use a fixed time inter-
val to cycle the solenoid. If the system does not pass
the EVAP Leak Detection Test, the following DTCs
may be set:
²P0442 - EVAP LEAK MONITOR 0.0409LEAK
DETECTED
²P0455 - EVAP LEAK MONITOR LARGE LEAK
DETECTED
²P0456 - EVAP LEAK MONITOR 0.0209LEAK
DETECTED
²P1486 - EVAP LEAK MON PINCHED HOSE
FOUND
²P1494 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP SW OR
MECH FAULT
²P1495 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP SOLENOID
CIRCUIT
Fig. 5 EVAP LEAK DETECTION SYSTEM
COMPONENTS
1 - Reed Switch
2 - Solenoid
3 - Spring
4 - Pump Cavity
5 - Diaphragm
6 - Inlet Check Valve
7 - Vent Valve
8 - From Air Filter
9 - To Canister
10 - Outlet Check Valve
11 - Engine Vacuum
Fig. 6 LDP AT REST
1 - Diaphragm
2 - Inlet Check Valve (Closed)
3 - Vent Valve (Open)
4 - From Air Filter
5 - To Canister
6 - Outlet Check Valve (Closed)
7 - Engine Vacuum (Closed)
DREVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 15
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)