instrument panel DODGE RAM SRT-10 2006 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAM SRT-10, Model: DODGE RAM SRT-10 2006Pages: 5267, PDF Size: 68.7 MB
Page 2432 of 5267

2. Install the tilt lever release knob bracket (3) to the
column and install the two new mounting screws
(1). Tighten the two screws to 4.5 Nꞏm (40 in. lbs.).
3. Install the lower shroud.
4. Install the steering column opening cover (Refer to
23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEERING
COLUMN OPENING COVER - INSTALLATION).
5. Install the tilt lever knob (2) and screw (1). Tighten
thescrewto4.5Nꞏm(40in.lbs.).
Page 3968 of 5267

SENSOR-TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE
DESCRIPTION
Transmission fluid temperature readings are supplied
to the transmission control module by the thermistor.
The temperature readings are used to control engage-
ment of the fourth gear overdrive clutch, the converter
clutch, and governor pressure. Normal resistance
value for the thermistor at room temperature is
approximately 2000 ohms.
The thermistor is part of the governor pressure sensor
assembly (2) and is immersed in transmission fluid at
all times.
OPERATION
The PCM prevents engagement of the converter clutch and overdrive clutch,when fluid temperature is below
approximately 10°C (50°F).
If fluid temperature exceeds 126°C (260°F), the PCM causes a 4-3 downshiftand engage the converter clutch.
Engagement is according to the third gear converter clutch engagement schedule.
The Tow/Haul lamp in the instrument panel illuminates when the shift back to third occurs. The transmission will not
allow fourth gear operation until fluid temperature decreases to approximately 110°C (230°F).
Page 4216 of 5267

SWITCH-SELECTOR
DESCRIPTION
The selector switch assembly is mounted in the left
side of the vehicle’s Instrument Panel (IP) and con-
sists of a rotary knob connected to a resistive network
for the mode and range shift selections. Also located
in this assembly is a recessed, normally open momen-
tary switch for making shifts into and out of transfer
case NEUTRAL. A pen, or similar instrument, is used
to make a NEUTRAL shift selection, thus reducing the
likelihood of an inadvertent shift request.
The selector switch also contains four light emitting
diode’s (LED’s) to indicate the transfer case position
and whether a shift is in progress.
OPERATION
As the position of the selector switchvaries, the resistance between the Mode Sensor supply voltage pin and the
Mode Sensor output will vary. Hardware, software, and calibrations within the Transfer Case Control Module
(TCCM) are provided that interpret the selector switch resistance as giveninthetablebelow:SELECTORSWITCH
INTERPRETATION
SELECTOR SWITCH INTERPRETATION
Step Resistance Range (ohms) Required Interpretation
A <200 Shorted
B 400-700 NEUTRAL
C 1050-1450 4LO
D 1850-2300 4HI
E 3050-5950 2WD (Default)
F 9.5-12.5K In between positions
G>15.5KOpen
For resistances between the ranges B-E shown for each valid position (T-Case NEUTRAL, 4LO, 4HI, 2WD), the
TCCM may interpret the resistance as:
either of the neighboring valid positions.
as an invalid fault position.
For resistances between the ranges E and F shown for 2WD and in-between positions, the TCCM may interpret the
resistance as:
the 2WD position.
an invalid fault position.
a valid in-between position.
For resistances between the ranges F and G shown for in-between positions and fault condition (open), the TCCM
may interpret the resistance as:
a valid in-between position.
an invalid fault position.
Page 4260 of 5267

SWITCH-TRANSFER CASE SELECTOR
DESCRIPTION
The selector switch assembly is mounted in the left side of the vehicle’s Instrument Panel (IP) and consists of a
rotary knob connected to a resistive network for the mode and range shift selections. Also located in this assembly
is a recessed, normally open momentary switch for making shifts into and out of transfer case NEUTRAL. A pen, or
similar instrument, is used to make a NEUTRAL shift selection, thus reducing the likelihood of an inadvertent shift
request.
The selector switch also contains light emitting diode’s (LED’s) to indicate the transfer case position and whether a
shift is in progress.
OPERATION
As the position of the selector switchvaries, the resistance between the Mode Sensor supply voltage pin and the
Mode Sensor output will vary. Hardware, software, and calibrations within the Transfer Case Control Module
(TCCM) are provided that interpret the selector switch resistance as giveninthetablebelow:SELECTORSWITCH
INTERPRETATION
SELECTOR SWITCH INTERPRETATION
Step Resistance Range (ohms) Required Interpretation
A <200 Shorted
B 400-700 NEUTRAL
C 1050-1450 4LO
D 1850-2300 4H
E 3050-5950 AWD (Default)
F 9.5-12.5K In between positions
G>15.5KOpen
For resistances between the ranges B-E shown for each valid position (T-Case NEUTRAL, 4LO, 4HI, AWD), the
TCCM may interpret the resistance as:
either of the neighboring valid positions.
as an invalid fault position.
For resistances between the ranges E and F shown for AWD and in-between positions, the TCCM may interpret the
resistance as:
the AWD position.
an invalid fault position.
a valid in-between position.
For resistances between the ranges F and G shown for in-between positions and fault condition (open), the TCCM
may interpret the resistance as:
a valid in-between position.
an invalid fault position.
For resistances between the ranges A and B shown for the fault condition (short) and , T-Case NEUTRAL, the
TCCM may interpret the resistance as:
the T-Case NEUTRAL position.
an invalid fault position.
The LED’s in the selector assembly are illuminated/flashed in the following manner to indicate a particular condition
or state.
A solidly illuminated LED indicates asuccessfully completed shift and the current operating mode of the trans-
fer case. While a shift has been requested but not yet completed, the LED forthe desired transfer case posi-
tion is flashed.
A flashing operating mode LED for the desired gear indicates that a shift tothat position has been requested,
but all of the driver controllable conditions have not been met. This is in an attempt to notify the driver that the
transmission needs to be put into NEUTRAL, the vehicle speed is too great, or some other condition outlined
Page 4310 of 5267

SWITCH-SELECTOR
DESCRIPTION
The selector switch assembly is mounted in the left
side of the vehicle’s Instrument Panel (IP) and con-
sists of a rotary knob connected to a resistive network
for the mode and range shift selections. Also located
in this assembly is a recessed, normally open momen-
tary switch for making shifts into and out of transfer
case NEUTRAL. A pen, or similar instrument, is used
to make a NEUTRAL shift selection, thus reducing the
likelihood of an inadvertent shift request.
The selector switch also contains four light emitting
diode’s (LED’s) to indicate the transfer case position
and whether a shift is in progress.
OPERATION
As the position of the selector switchvaries, the resistance between the Mode Sensor supply voltage pin and the
Mode Sensor output will vary. Hardware, software, and calibrations within the Transfer Case Control Module
(TCCM) are provided that interpret the selector switch resistance as giveninthetablebelow:SELECTORSWITCH
INTERPRETATION
SELECTOR SWITCH INTERPRETATION
Step Resistance Range (ohms) Required Interpretation
A <200 Shorted
B 400-700 NEUTRAL
C 1050-1450 4LO
D 1850-2300 4HI
E 3050-5950 2WD (Default)
F 9.5-12.5K In between positions
G>15.5KOpen
For resistances between the ranges B-E shown for each valid position (T-Case NEUTRAL, 4LO, 4HI, 2WD), the
TCCM may interpret the resistance as:
either of the neighboring valid positions.
as an invalid fault position.
For resistances between the ranges E and F shown for 2WD and in-between positions, the TCCM may interpret the
resistance as:
the 2WD position.
an invalid fault position.
a valid in-between position.
For resistances between the ranges F and G shown for in-between positions and fault condition (open), the TCCM
may interpret the resistance as:
a valid in-between position.
an invalid fault position.
Page 4312 of 5267

MOTOR-SHIFT
DESCRIPTION
The shift motor (1) consists of a permanent magnet
D.C. motor with gear reduction to convert a high
speed-low torque device into a low speed-high torque
device. The output of the device is coupled to a shaft
which internally moves the mode and range forks that
change the transfer case operating ranges. The motor
is rated at 25 amps maximum at (23° C (72° F) with
10 volts at the motor leads.
OPERATION
The transfer case shift motor responds to the Transfer
Case Control Module (TCCM) commands to move the transfer case shift sectorbi-directionally, as required, to
obtain the transfer case operating mode indicated by the instrument panelmounted selector switch.
REMOVAL
NOTE: New shift motor assemblies are shipped in the 2WD/AWD position. If a new shift motor assembly will
be installed, it will be necessary to shift the transfer case to the 2WD/AWDposition prior to motor removal.
1. Raise the vehicle on a suitable hoist.
2. Disengage the wiring connectors from the shift motor and mode sensor.
3. Remove the bolts holding the shift motor and mode sensor assembly onto the transfer case.
4. Separate the shift motor and mode sensor assembly from the transfer case.
INSTALLATION
1. Verify that the shift sector o-ring is clean and properly positioned over the shift sector and against the transfer
case.
NOTE: Verify that the shift motor position and sector shaft orientation are aligned. It may be necessary to
manually shift the transfer case if the shift motor and sector shaft are notaligned.
2. Position the shift motor and mode sensor assembly onto the transfer case.
3. Install the bolts to hold the assembly onto the transfer case. Tighten the bolts to 16-24 Nꞏm (12-18 ft.lbs.).
CAUTION: If the original shift motor and mode sensor assembly bolts are reused, be sure to use Mopar
Lock & Seal or Loctite™ 242 to replenish the lock patch material originallyfound on the bolts
4. Engage the wiring connectors to the shift motor and mode sensor.
5. Refill the transfer case as necessary.
6. Lower vehicle and verify transfer case operation.
Page 4338 of 5267
BODY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BODY
WARNING
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS ..... 2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WATER LEAKS .............................. 2
WIND NOISE ................................ 3
STANDARD PROCEDURE
BODY LUBRICATION ......................... 4
HEAT STAKING .............................. 4
BUZZ, SQUEAK & RATTLE ................... 4
PLASTIC BODY PANEL REPAIR ............... 5
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE ................................... 14
SPECIAL TOOLS
BODY ...................................... 16TA I L G AT E..............................17
DOOR - FRONT.........................28
DOORS - REAR.........................56
EXTERIOR.............................86
HOOD................................126
INSTRUMENT PANEL....................138
INTERIOR.............................176
PA I N T................................215
SEATS...............................221
STATIONARY GLASS....................256
SUNROOF - SERVICE INFORMATION.......270
WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS..................300
WINCH...............................320
BODY STRUCTURE.....................361
Page 4343 of 5267

Rigid Plastics:
Examples of rigid plastic use: Fascias, Hoods, Doors, and other Body Panels, which include SMC, ABS, and Poly-
carbonates.
Semi-Rigid Plastics:
Examples of semi-rigid plastic use: Interior Panels, Under Hood Panels, and other Body Trim Panels.
Flexible Plastics:
Examples of flexible plastic use: Fascias, Body Moldings, and upper and lower Fascia Covers.
Repair Procedure:
The repair procedure for all three categories of plastics is basically thesame. The one difference is the material
used for the repair. The materials must be specific for each substrate, rigid repair material for rigid plastic repair,
semi-rigid repair material for semi-rigid plastic repair and flexible repair material for flexible plastic repair.
Adhesion Promoter/Surface Modifier:
Adhesion Promoters/Surface Modifiers are required for certain plastics. All three categories may have plastics that
require the use of adhesion promoter/surface modifiers. Always follow repair material manufacturer’s plastic identi-
fication and repair procedures.
SAFETY PRECAUTION AND WARNINGS
WARNING:
Eye protection should be used when servicing components. Personal injurycan result.
Use an OSHA approved breathing mask when mixing epoxy, grinding, and spraying paint or solvents in
a confined area. Personal injury can result.
Avoid prolonged skin contact with resin, petroleum, or alcohol based solvents. Personal injury can
result.
Do not venture under a hoisted vehicle that is not properly supported on safety stands. Personal injury
can result.
NOTE:
When holes must be drilled or cut in bodypanels, verify locations of internal body components and elec-
trical wiring. Damage to vehicle can result.
Do not use abrasive chemicals or compounds on undamaged painted surfaces around repair areas. Dam-
age to finish can result.
RIGID, SEMI-RIGID, AND FLEXIBLE PLASTIC PARTS TYPES
CODE FAMILY NAME COMMON TRADE NAME TYPICAL APPLICATION
ASA ACRYLONITRILE STYRENE
ACRYLITELURAN S CONSOLES, GRILLES
ABS ACRYLONITRILE
BUTADIENE STYRENETERLURAN
APILLARS, CONSOLES,
GRILLES
ABS/PC ABS/PC ALLOY PULSE, PROLOY, BAYBLEND DOORS, INSTRUMENT
PA N E L S
ABS/PVC ABS/PV ALLOY PROLOY, PULSE, LUSTRAN,
CYCLOVINDOOR PANELS, GRILLES,
TRIM
BMC BULK MOLDING
COMPOUNDBMC FENDER EXTENSIONS
EMA EHTYLENE METHYL
ACRYLATE/IONOMERSURLYN, EMA, IONOMER BUMPER GUARDS, PADS
Page 4344 of 5267
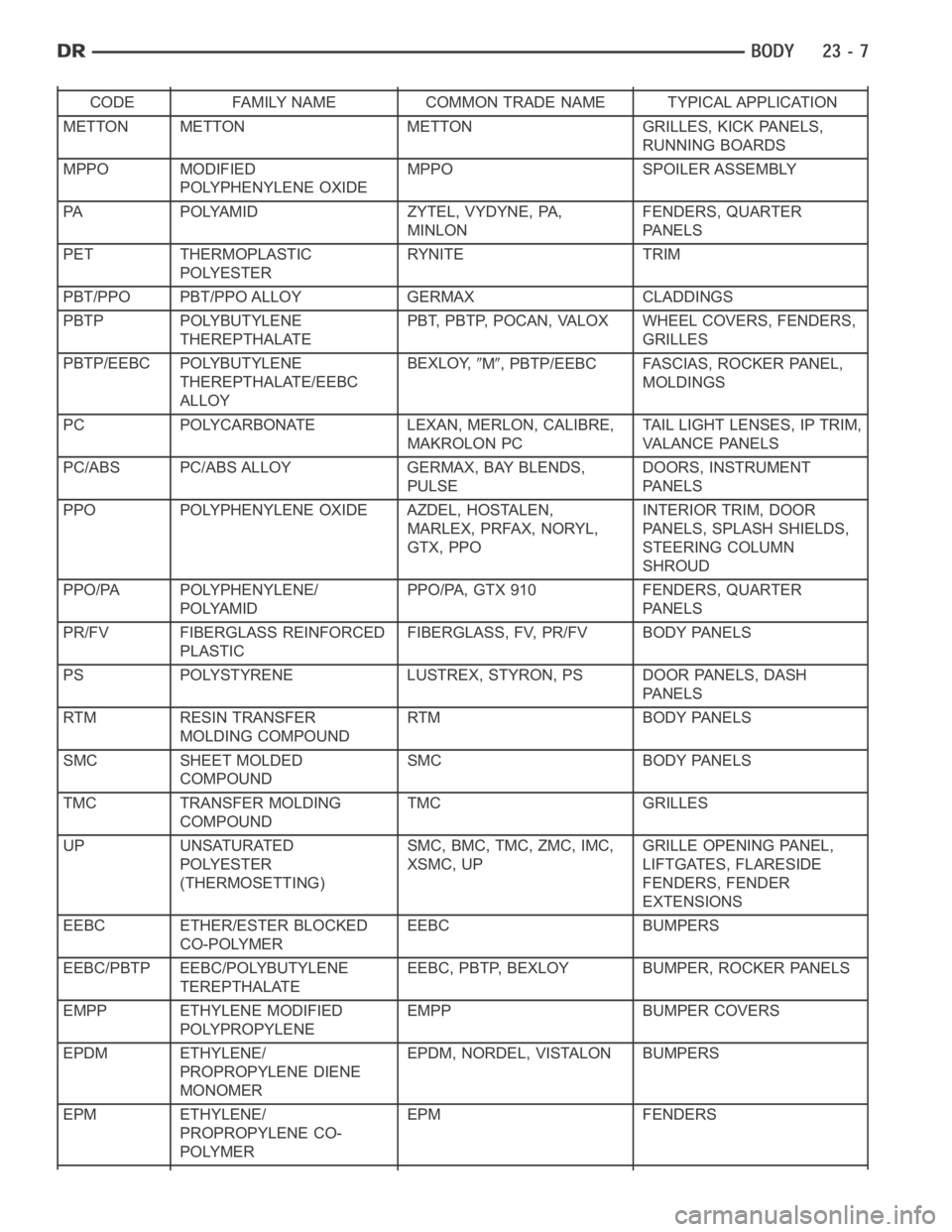
CODE FAMILY NAME COMMON TRADE NAME TYPICAL APPLICATION
METTON METTON METTON GRILLES, KICK PANELS,
RUNNING BOARDS
MPPO MODIFIED
POLYPHENYLENE OXIDEMPPO SPOILER ASSEMBLY
PA POLYAMID ZYTEL, VYDYNE, PA,
MINLONFENDERS, QUARTER
PA N E L S
PET THERMOPLASTIC
POLYESTERRYNITE TRIM
PBT/PPO PBT/PPO ALLOY GERMAX CLADDINGS
PBTP POLYBUTYLENE
THEREPTHALATEPBT, PBTP, POCAN, VALOX WHEEL COVERS, FENDERS,
GRILLES
PBTP/EEBC POLYBUTYLENE
THEREPTHALATE/EEBC
ALLOYBEXLOY,
M, PBTP/EEBC FASCIAS, ROCKER PANEL,
MOLDINGS
PC POLYCARBONATE LEXAN, MERLON, CALIBRE,
MAKROLON PCTAIL LIGHT LENSES, IP TRIM,
VA L A N C E PA N E L S
PC/ABS PC/ABS ALLOY GERMAX, BAY BLENDS,
PULSEDOORS, INSTRUMENT
PA N E L S
PPO POLYPHENYLENE OXIDE AZDEL, HOSTALEN,
MARLEX, PRFAX, NORYL,
GTX, PPOINTERIOR TRIM, DOOR
PANELS, SPLASH SHIELDS,
STEERING COLUMN
SHROUD
PPO/PA POLYPHENYLENE/
POLYAMIDPPO/PA, GTX 910 FENDERS, QUARTER
PA N E L S
PR/FV FIBERGLASS REINFORCED
PLASTICFIBERGLASS, FV, PR/FV BODY PANELS
PS POLYSTYRENE LUSTREX, STYRON, PS DOOR PANELS, DASH
PA N E L S
RTM RESIN TRANSFER
MOLDING COMPOUNDRTM BODY PANELS
SMC SHEET MOLDED
COMPOUNDSMC BODY PANELS
TMC TRANSFER MOLDING
COMPOUNDTMC GRILLES
UP UNSATURATED
POLYESTER
(THERMOSETTING)SMC, BMC, TMC, ZMC, IMC,
XSMC, UPGRILLE OPENING PANEL,
LIFTGATES, FLARESIDE
FENDERS, FENDER
EXTENSIONS
EEBC ETHER/ESTER BLOCKED
CO-POLYMEREEBC BUMPERS
EEBC/PBTP EEBC/POLYBUTYLENE
TEREPTHALATEEEBC, PBTP, BEXLOY BUMPER, ROCKER PANELS
EMPP ETHYLENE MODIFIED
POLYPROPYLENEEMPP BUMPER COVERS
EPDM ETHYLENE/
PROPROPYLENE DIENE
MONOMEREPDM, NORDEL, VISTALON BUMPERS
EPM ETHYLENE/
PROPROPYLENE CO-
POLYMEREPM FENDERS
Page 4351 of 5267
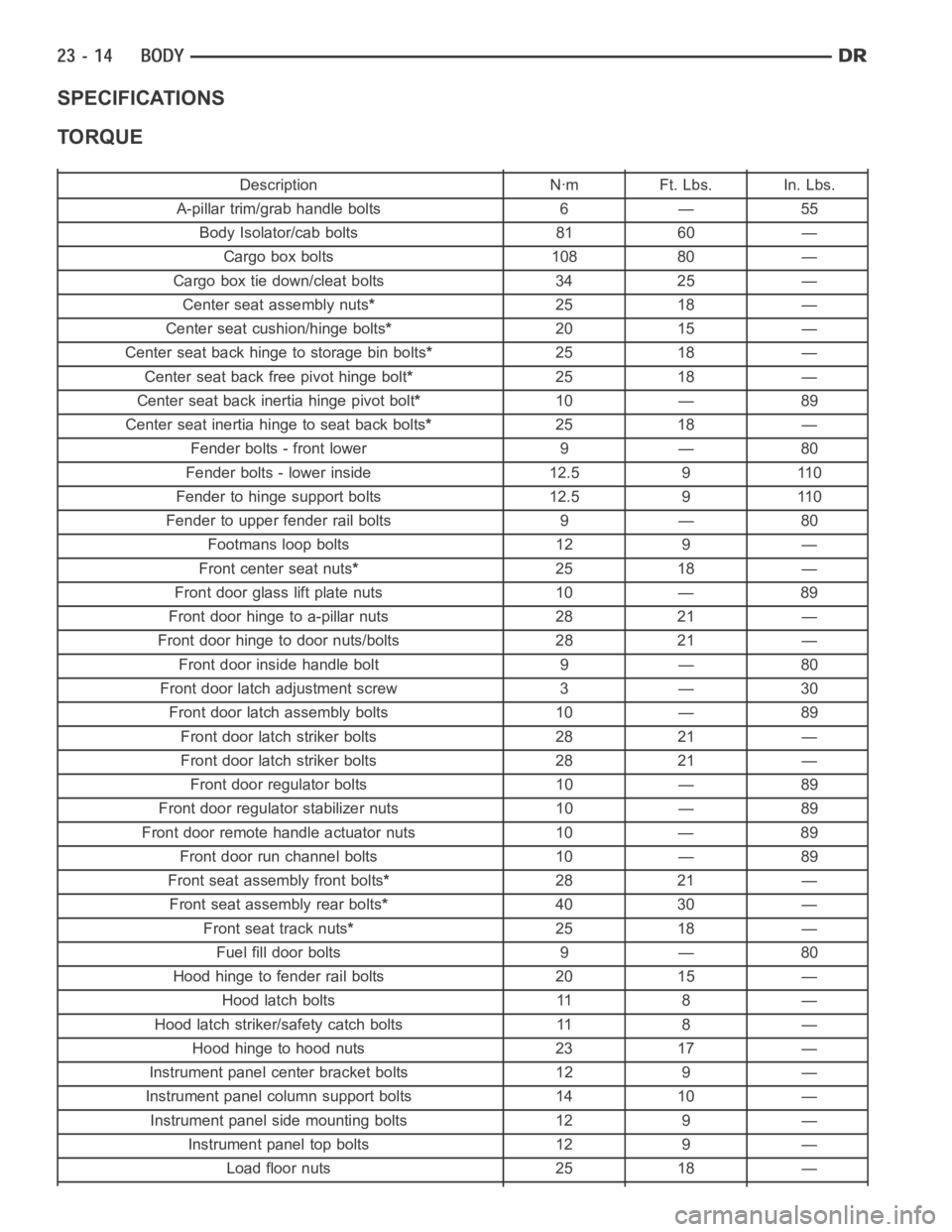
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
Description Nꞏm Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
A-pillar trim/grab handle bolts 6 — 55
Body Isolator/cab bolts 81 60 —
Cargo box bolts 108 80 —
Cargo box tie down/cleat bolts 34 25 —
Center seat assembly nuts*25 18 —
Center seat cushion/hinge bolts*20 15 —
Center seat back hinge to storage bin bolts*25 18 —
Center seat back free pivot hinge bolt*25 18 —
Center seat back inertia hinge pivot bolt*10 — 89
Center seat inertia hinge to seat back bolts*25 18 —
Fender bolts - front lower 9 — 80
Fender bolts - lower inside 12.5 9 110
Fender to hinge support bolts 12.5 9 110
Fender to upper fender rail bolts 9 — 80
Footmans loop bolts 12 9 —
Front center seat nuts*25 18 —
Front door glass lift plate nuts 10 — 89
Front door hinge to a-pillar nuts 28 21 —
Front door hinge to door nuts/bolts 28 21 —
Front door inside handle bolt 9 — 80
Front door latch adjustment screw 3 — 30
Front door latch assembly bolts 10 — 89
Front door latch striker bolts 28 21 —
Front door latch striker bolts 28 21 —
Front door regulator bolts 10 — 89
Front door regulator stabilizer nuts 10 — 89
Front door remote handle actuator nuts 10 — 89
Front door run channel bolts 10 — 89
Front seat assembly front bolts*28 21 —
Front seat assembly rear bolts*40 30 —
Frontseattracknuts*25 18 —
Fuel fill door bolts 9 — 80
Hood hinge to fender rail bolts 20 15 —
Hood latch bolts 11 8 —
Hood latch striker/safety catch bolts 11 8 —
Hood hinge to hood nuts 23 17 —
Instrument panel center bracket bolts 12 9 —
Instrument panel column support bolts 14 10 —
Instrument panel side mounting bolts 12 9 —
Instrument panel top bolts 12 9 —
Load floor nuts 25 18 —