DODGE RAM SRT-10 2006 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAM SRT-10, Model: DODGE RAM SRT-10 2006Pages: 5267, PDF Size: 68.7 MB
Page 4171 of 5267

SEAL-FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT
REMOVAL
1. Remove the front propeller shaft (Refer to 3 - DIF-
FERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/
PROPELLER SHAFT - REMOVAL).
2. Install two bolts 180° apart into the front output
shaft companion flange.
3. Place Yoke Holder 6719 (1) over the bolts (2) and
against the companion flange.
4. Remove and discard the front companion flange
nut.
5. Remove the companion flange from the front out-
put shaft. It may be necessary to use Pinion
Flange Remover 8992 to remove the companion
flange.
6. Using a screw and a slide hammer, remove the
front output shaft seal.
INSTALLATION
1. Install the new front output shaft seal with Seal
Installer MB991168A.
2. Install the front companion flange onto the front
output shaft.
3. Install two bolts 180° apart into the front output
shaft companion flange.
4. Place Yoke Holder 6719 (1) over the bolts (2) and
against the companion flange.
5. Install a new front companion flange nut. Tighten
the companion flange nut to 258-312 Nꞏm (190-230
ft.lbs.).
6. Install front propeller shaft (Refer to 3 - DIFFEREN-
TIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PRO-
PELLER SHAFT - INSTALLATION).
Page 4172 of 5267

SENSOR-POSITION
DESCRIPTION
The transfer case position sensor is an electronic device whose output canbe interpreted to indicate the transfer
case’s current operating mode. The sensor consists of a five position, resistive multiplexed circuit which returns a
specific resistance value to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) for eachtransfer case operating mode. The sen-
sor is located on the top of the transfer case, just left of the transfer casecenterline and rides against the sector
plate roostercomb. The PCM supplies 5VDC (+/- 0.5V) to the sensor and monitors the return voltage to determine
the sector plate, and therefore the transfer case, position.
OPERATION
Operating Mode Versus Resistance
SENSOR POSITION OPERATING MODE SENSOR RESISTANCE (ohms)
1 2H 1172-1195
24H677-691
3 NEUTRAL 406-415
44L208-213
5 NOT USED 60-61
During normal vehicle operation, the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM) monitors the transfer case position
sensor return voltage to determine the operating mode
of the transfer case. Refer to the Operating Mode Ver-
sus Resistance table for the correct resistance for
each position.
REMOVAL
1. Raise and support the vehicle.
2. Disengage the transfer case position sensor connector from the positionsensor.
3. Remove the position sensor from the transfer case.
Position Sensor Linear Movement
1 - POSITION 1 - 10mm ±0.5mm
2 - POSITION 2 - 12mm ±0.5mm
3 - POSITION 3 - 14mm ±0.5mm
4 - POSITION 4 - 16mm ±0.5mm
5 - POSITION 5 - 18mm ±0.5mm
6 - POSITION 6 - 20mm±0.5mm - FULL EXTENSION
Page 4173 of 5267

INSTALLATION
1. Inspect the o-ring seal on the transfer case position sensor. Replace the o-ring if necessary.
2. Install the transfer case position sensor into the transfer case. Torque the sensor to 27 Nꞏm (20 ft.lbs.).
3. Engage the transfer case position sensor connector to the position sensor.
4. Lower vehicle.
5. Verify proper sensor operation.
Page 4174 of 5267

LEVER-SHIFT
REMOVAL
1. Shift transfer case into 2H.
2. Raise and support the vehicle.
3. Loosen adjusting trunnion lock bolt and slide shift rod out of trunnion.If rod lacks enough travel to come out of
trunnion, push trunnion out of shift lever.
4. Lower vehicle.
5. Remove transfer case shifter knob cap.
6. Remove nut holding shifter knob (2) to shift lever.
7. Remove shifter knob.
8. Remove the shift boot from the shifter console.
9. Remove the bolts securing the shifter mechanism to the floor pan.
10. Separate shift lever mechanism from the vehicle.
Transfer Case Shifter
1 - SHIFTER BOOT 4 - SHIFTER MECHANISM
2-SHIFTERKNOB 5-ALIGNMENTPIN
3 - SHIFTER CONSOLE 6 - TRANSFER CASE
Page 4175 of 5267

INSTALLATION
1. If the shifter mechanism does not have a adjustment locating pin installed, align the adjustment channel on the
shifter assembly to the locating hole in the lower shift lever and install an appropriately sized pin to retain the
position.
2. Position shift lever in vehicle.
3. Install the bolts to hold the shifter mechanism (4) to the floor pan.
4. Raise vehicle.
5. Verify that the transfer case is still in the 2H position. The 2H detent position on the transfer case shift arm is the
second position from full forward.
6. Install trunnion to shift lever, if necessary.
7. Install shift rod to trunnion, if necessary.
8. Tighten the shift rod lock bolt to 10 Nꞏm (90 in.lbs.).
9. Remove the shifter adjustment locating pin from the adjustment channeland the locating hole.
10. Lower vehicle.
11. Install the transfer case shifter console.
12. Install the shifter boot and the shifter knob onto the shifter lever.
13. Install nut to hold shifter knob to shift lever.
14. Install shifter knob cap.
15. Verify transfer case operation.
Transfer Case Shifter
1 - SHIFTER BOOT 4 - SHIFTER MECHANISM
2-SHIFTERKNOB 5-ALIGNMENTPIN
3 - SHIFTER CONSOLE 6 - TRANSFER CASE
Page 4176 of 5267

ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - SHIFT LEVER
1. Move shift lever into 2H position.
2. Raise vehicle.
3. Loosen shift rod lock bolt at trunnion.
4. Check shift rod fit in trunnion. Be sure rod does not bind in trunnion. Lubricate the shift rod and trunnion if nec-
essary.
5. Verify that transfer case shift lever is in 2H detent position. The 2H detent position on the transfer case shift arm
is the second position from full forward.
6. Align the adjustment locating hole on the lower shifter lever with the adjustment channel on the shifter bracket
assembly.
7. Insert an appropriately sized pin through into the adjustment channel and through the locating hole to hold the
shifter in the correct position.
8. Tighten shift rod lock bolt to 10 Nꞏm (90 in. lbs.) torque.
9. Remove the locating pin from the adjustment channel and locating hole.
10. Check shift linkage operation. Be sure transfer case shifts into and operates properly in all ranges.
Transfer Case Shifter
1 - SHIFTER BOOT 4 - SHIFTER MECHANISM
2-SHIFTERKNOB 5-ALIGNMENTPIN
3 - SHIFTER CONSOLE 6 - TRANSFER CASE
Page 4177 of 5267

page page
TRANSFER CASE - NV243 - SERVICE
INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION ............................. 1657
OPERATION ............................... 1657
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER
CASE - NV243 ............................ 1658
REMOVAL ................................. 1659
DISASSEMBLY ............................. 1659
CLEANING ................................. 1671
INSPECTION ............................... 1671
ASSEMBLY . ............................... 1674
INSTALLATION ............................. 1686
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV243 ................ 1686
SPECIAL TOOLS
TRANSFER CASE - NV243 ................ 1687
SEAL-EXTENSION HOUSING
REMOVAL ................................. 1689
INSTALLATION ............................. 1689
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID DRAIN AND
REFILL ................................... 1690SEAL-FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT
REMOVAL ................................. 1691
INSTALLATION ............................. 1692
SENSOR-MODE
DESCRIPTION ............................. 1693
OPERATION ............................... 1693
SWITCH-SELECTOR
DESCRIPTION ............................. 1695
OPERATION ............................... 1695
MOTOR-SHIFT
DESCRIPTION ............................. 1697
OPERATION ............................... 1697
REMOVAL ................................. 1697
INSTALLATION ............................. 1697
ASSEMBLY-SHIFT MOTOR/MODE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION ............................. 1699
OPERATION ............................... 1699
Page 4178 of 5267

TRANSFER CASE - NV243 - SERVICE INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION
The NV243 is an electronically controlled part-time transfer case with a low range gear reduction system. The
NV243 has three operating ranges plus a NEUTRAL position. The low range system provides a gear reduction ratio
for increased low speed torque capability.
The geartrain is mounted in two aluminum case halves attached with bolts. The mainshaft front and rear bearings
are mounted in aluminum retainer housings bolted to the case halves.
OPERATING RANGES
Transfer case operating ranges are:
2WD (2-wheel drive).
4HI (4-wheel drive).
4LO (4-wheel drive low range).
NEUTRAL.
The 2WD range is for use on any road surface at any time.
The 4HI and 4LO ranges are for off road use only. They are not for use on hard surface roads. The only exception
being when the road surface is wet or slippery or covered by ice and snow.
The low range reduction gear system is operative in 4LO range only. This range is for extra pulling power in off road
situations. Low range reduction ratio is 2.72:1.
SHIFT MECHANISM
Operating ranges are selected with a dash mounted shift selector switch. The shift selector switch provides a input
to the Transfer Case Control Module (TCCM) to indicate the driver’s desireto change operating ranges. The TCCM
uses this input, along with input from the transfer case mounted mode sensor and information from the vehicle’s
bus, to determine if a shift is permitted. If the TCCM decides the shift is permitted, the TCCM controls the shift
motor, mounted to the exterior of the transfer case, to perform the shift.
IDENTIFICATION
A circular ID tag (1) is attached to the rear case of
each transfer case. The ID tag provides the transfer
case model number, assembly number, serial number,
and low range ratio.
The transfer case serial number also represents the
date of build.
OPERATION
The input gear is splined to the transmission output shaft. The input gear drives the mainshaft through the planetary
assembly and range sleeve. The front output shaft is operated by a drive chain that connects the shaft to a drive
sprocket on the mainshaft. The drive sprocket is engaged/disengaged by themodefork,whichoperatesthemode
sleeve and hub. The sleeve and hub are not equipped with a synchronizer mechanism for shifting.
Page 4179 of 5267
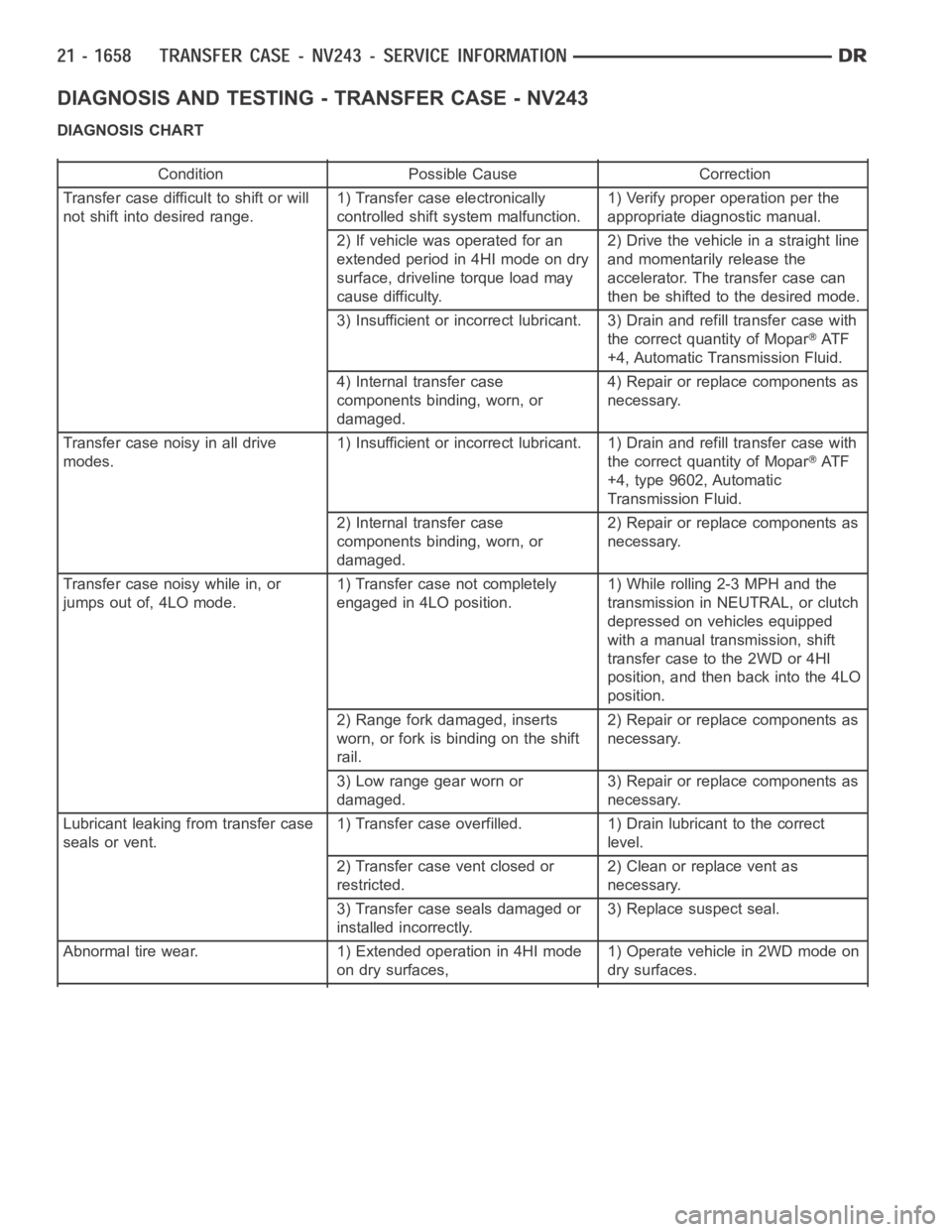
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER CASE - NV243
DIAGNOSIS CHART
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Transfer case difficult to shift or will
not shift into desired range.1) Transfer case electronically
controlled shift system malfunction.1) Verify proper operation per the
appropriate diagnostic manual.
2) If vehicle was operated for an
extended period in 4HI mode on dry
surface, driveline torque load may
cause difficulty.2) Drive the vehicle in a straight line
and momentarily release the
accelerator. The transfer case can
then be shifted to the desired mode.
3) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 3) Drain and refill transfer casewith
the correct quantity of Mopar
AT F
+4, Automatic Transmission Fluid.
4) Internal transfer case
components binding, worn, or
damaged.4) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Transfer case noisy in all drive
modes.1) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 1) Drain and refill transfer casewith
the correct quantity of Mopar
AT F
+4, type 9602, Automatic
Transmission Fluid.
2) Internal transfer case
components binding, worn, or
damaged.2) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Transfer case noisy while in, or
jumps out of, 4LO mode.1) Transfer case not completely
engaged in 4LO position.1) While rolling 2-3 MPH and the
transmission in NEUTRAL, or clutch
depressed on vehicles equipped
with a manual transmission, shift
transfer case to the 2WD or 4HI
position, and then back into the 4LO
position.
2) Range fork damaged, inserts
worn, or fork is binding on the shift
rail.2) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
3) Low range gear worn or
damaged.3) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Lubricant leaking from transfer case
seals or vent.1) Transfer case overfilled. 1) Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2) Transfer case vent closed or
restricted.2) Clean or replace vent as
necessary.
3) Transfer case seals damaged or
installed incorrectly.3) Replace suspect seal.
Abnormal tire wear. 1) Extended operation in 4HI mode
on dry surfaces,1) Operate vehicle in 2WD mode on
dry surfaces.
Page 4180 of 5267

REMOVAL
1. Shift transfer case into 2WD.
2. Raise vehicle.
3. Drain transfer case lubricant.
4. Mark front and rear propeller shafts for alignment
reference.
5. Support transmission with jack stand.
6. Remove the transfer case skid plate, if equipped.
7. Disconnect front and rear propeller shafts at trans-
fer case.
8. Disconnect transfer case shift motor and mode
sensor wire connectors (3).
9. Disconnect transfer case vent hose.
10. Support transfer case with transmission jack.
11. Secure transfer case to jack with chains.
12. Remove nuts attaching transfer case (2) to transmission (1).
13. Pull transfer case and jack rearward to disengage transfer case.
14. Remove transfer case from under vehicle.
DISASSEMBLY
Position transfer case in a shallow drain pan. Remove drain plug and drain any remaining lubricant remaining in
case.
SHIFT MOTOR ASSEMBLY AND FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
1. Remove the bolts (3) which hold the shift motor
and mode sensor assembly (2) to the transfer case
(1).