tail FIAT 500 1957 1.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FIAT, Model Year: 1957, Model line: 500, Model: FIAT 500 1957 1.GPages: 128, PDF Size: 9.01 MB
Page 33 of 128
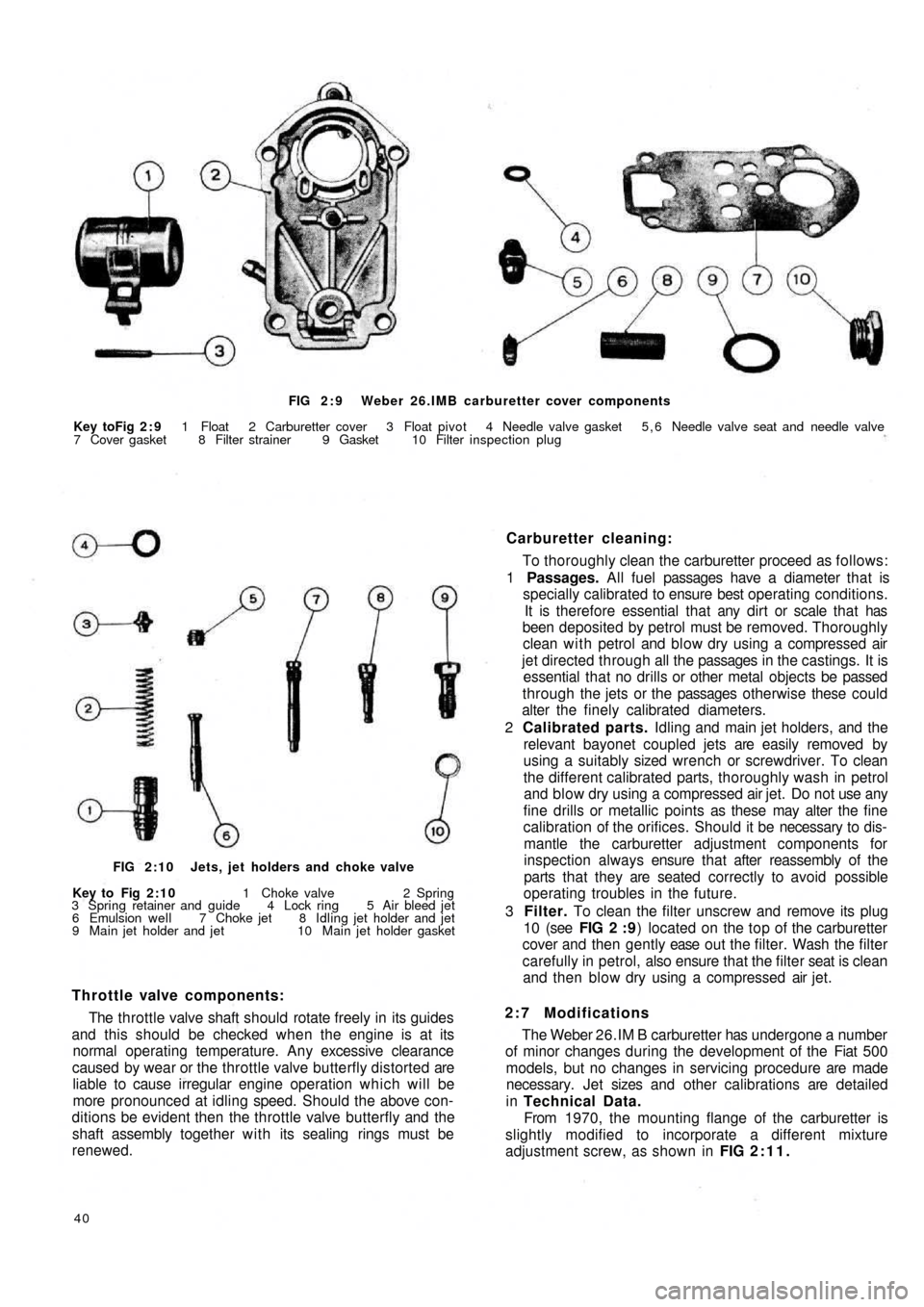
FIG 2 : 9 Weber 26.IMB carburetter cover components
Key toFig 2 : 9 1 Float 2 Carburetter cover 3 Float pivot 4 Needle valve gasket 5 , 6 Needle valve seat and needle valve
7 Cover gasket 8 Filter strainer 9 Gasket 10 Filter inspection plug
Carburetter cleaning:
To thoroughly clean the carburetter proceed as follows:
1 Passages. All fuel passages have a diameter that is
specially calibrated to ensure best operating conditions.
It is therefore essential that any dirt or scale that has
been deposited by petrol must be removed. Thoroughly
clean with petrol and blow dry using a compressed air
jet directed through all the passages in the castings. It is
essential that no drills or other metal objects be passed
through the jets or the passages otherwise these could
alter the finely calibrated diameters.
2 Calibrated parts. Idling and main jet holders, and the
relevant bayonet coupled jets are easily removed by
using a suitably sized wrench or screwdriver. To clean
the different calibrated parts, thoroughly wash in petrol
and blow dry using a compressed air jet. Do not use any
fine drills or metallic points as these may alter the fine
calibration of the orifices. Should it be necessary to dis-
mantle the carburetter adjustment components for
inspection always ensure that after reassembly of the
parts that they are seated correctly to avoid possible
operating troubles in the future.
3 Filter. To clean the filter unscrew and remove its plug
10 (see FIG 2 : 9) located on the top of the carburetter
cover and then gently ease o u t t h e filter. Wash the filter
carefully in petrol, also ensure that the filter seat is clean
and then blow dry using a compressed air jet.
2:7 Modifications
The Weber 26.IM B carburetter has undergone a number
of minor changes during the development of the Fiat 500
models, but no changes in servicing procedure are made
necessary. Jet sizes and other calibrations are detailed
in Technical Data.
From 1970, the mounting flange of the carburetter is
slightly modified to incorporate a different mixture
adjustment screw, as shown in FIG 2:11.
40
Throttle valve components:
The throttle valve shaft should rotate freely in its guides
and this should be checked when the engine is at its
normal operating temperature. Any excessive clearance
caused by wear or the throttle valve butterfly distorted are
liable to cause irregular engine operation which will be
more pronounced at idling speed. Should the above con-
ditions be evident then the throttle valve butterfly and the
shaft assembly together with its sealing rings must be
renewed.
FIG 2:10 Jets, jet holders and choke valve
Key to Fig 2:10 1 Choke valve 2 Spring
3 Spring retainer and guide 4 Lock ring 5 Air bleed jet
6 Emulsion well 7 Choke jet 8 Idling jet holder and jet
9 Main jet holder and jet 10 Main jet holder gasket
Page 34 of 128
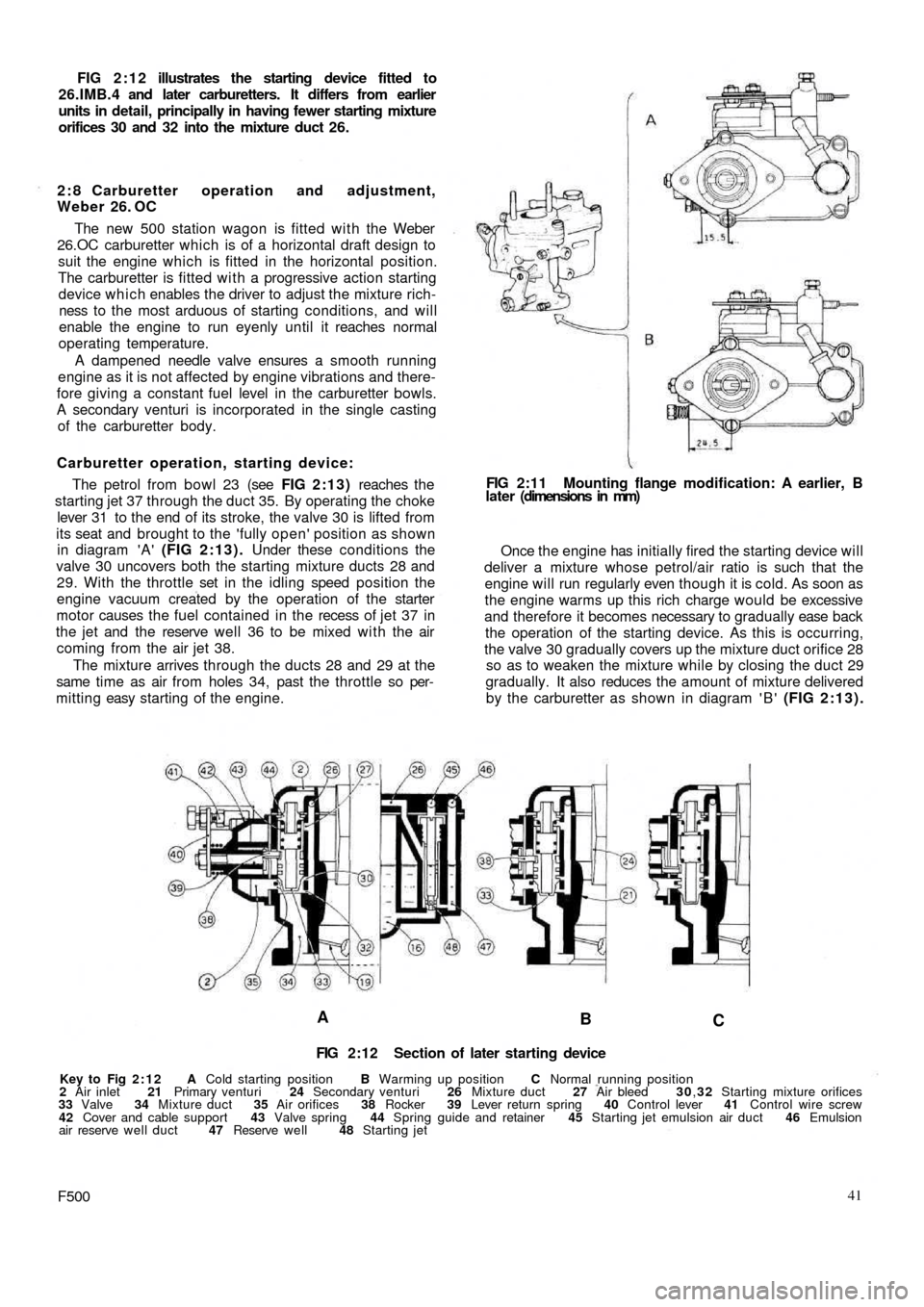
FIG 2:12 illustrates the starting device fitted to
26.IMB.4 and later carburetters. It differs from earlier
units in detail, principally in having fewer starting mixture
orifices 30 and 32 into the mixture duct 26.
2 : 8 Carburetter operation and adjustment,
Weber 26. OC
The new 500 station wagon is fitted with the Weber
26.OC carburetter which is of a horizontal draft design to
suit the engine which is fitted in the horizontal position.
The carburetter is fitted with a progressive action starting
device which enables the driver to adjust the mixture rich-
ness to the most arduous of starting conditions, and will
enable the engine to run eyenly until it reaches normal
operating temperature.
A dampened needle valve ensures a smooth running
engine as it is not affected by engine vibrations and there-
fore giving a constant fuel level in the carburetter bowls.
A secondary venturi is incorporated in the single casting
of the carburetter body.
Carburetter operation, starting device:
The petrol from bowl 23 (see FIG 2:13) reaches the
starting jet 37 through the duct 35. By operating the choke
lever 31 to the end of its stroke, the valve 30 is lifted from
its seat and brought to the 'fully open' position as shown
in diagram 'A' (FIG 2:13). Under these conditions the
valve 30 uncovers both the starting mixture ducts 28 and
29. With the throttle set in the idling speed position the
engine vacuum created by the operation of the starter
motor causes the fuel contained in the recess of j e t 37 in
the jet and the reserve
well 36 to be mixed with the air
coming from the air jet 38.
The mixture arrives through the ducts 28 and 29 at the
same time as air from holes 34, past the throttle so per-
mitting easy starting of the engine.
A
B
C
FIG 2:12 Section of later starting device
Key to Fig 2:12 A Cold starting position B Warming up position C Normal running position
2 Air inlet 21 Primary venturi 24 Secondary venturi 26 Mixture duct 27 Air bleed 30,32 Starting mixture orifices
33 Valve 34 Mixture duct 35 Air orifices 38 Rocker 39 Lever return spring 40 Control lever 41 Control wire screw
42 Cover and cable support 43 Valve spring 44 Spring guide and retainer 45 Starting jet emulsion air duct 46 Emulsion
air reserve well duct 47 Reserve well 48 Starting jet
F50041 Once the engine has initially fired the starting device will
deliver a mixture whose petrol/air ratio is such that the
engine will run regularly even though it is cold. As soon as
the engine warms up this rich charge would be excessive
and therefore it becomes necessary to gradually ease back
the operation of the starting device. As this is occurring,
the valve 30 gradually covers up the mixture duct orifice 28
so as to weaken the mixture while by closing the duct 29
gradually. It also reduces the amount of mixture delivered
by the carburetter as shown in diagram ' B ' (FIG 2:13). FIG 2:11 Mounting flange modification: A earlier, B
later (dimensions in mm)
Page 36 of 128
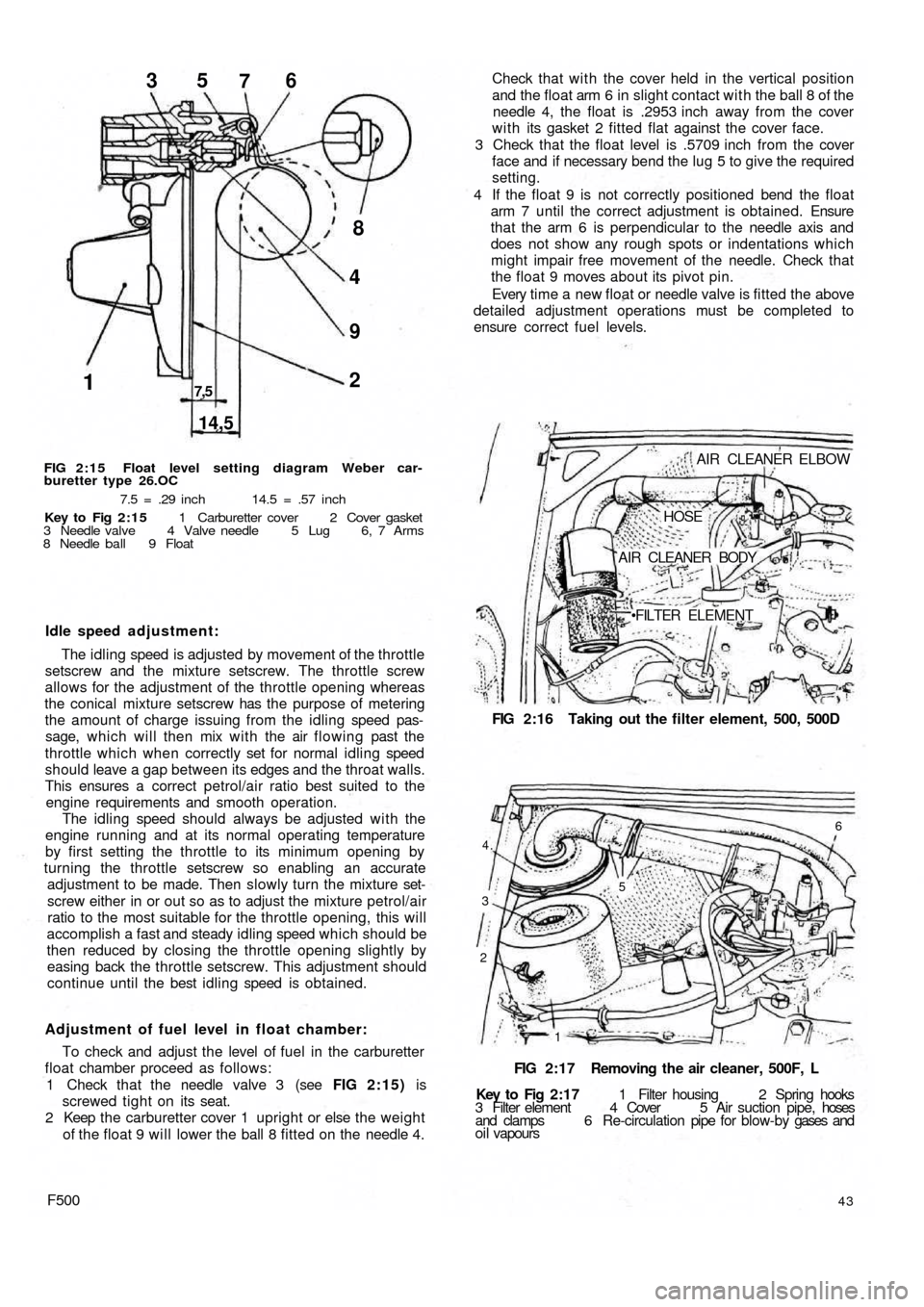
1
14,5
7,52 9 48 35
76
FIG 2:15 Float level setting diagram Weber car-
buretter type 26.OC
7.5 = .29 inch 14.5 = .57 inch
Key to Fig 2:15 1 Carburetter cover 2 Cover gasket
3 Needle valve 4 Valve needle 5 Lug 6, 7 Arms
8 Needle ball 9 Float
Idle speed adjustment:
The idling speed is adjusted by movement of the throttle
setscrew and the mixture setscrew. The throttle screw
allows for the adjustment of the throttle opening whereas
the conical mixture setscrew has the purpose of metering
the amount of charge issuing from the idling speed pas-
sage, which will then mix with the air flowing past the
throttle which when correctly set for normal idling speed
should leave a gap between its edges and the throat walls.
This ensures a correct petrol/air ratio best suited to the
engine requirements and smooth operation.
The idling speed should always be adjusted with the
engine running and at its normal operating temperature
by first setting the throttle to its minimum opening by
turning the throttle setscrew so enabling an accurate
adjustment to be made. Then slowly turn the mixture set-
screw either in or out so as to adjust the mixture petrol/air
ratio to the most suitable for the throttle opening, this will
accomplish a fast and steady idling speed which should be
then reduced by closing the throttle opening slightly by
easing back the throttle setscrew. This adjustment should
continue until the best idling speed is obtained.
Adjustment of fuel level in float chamber:
To check and adjust the level of fuel in the carburetter
float chamber proceed as follows:
1 Check that the needle valve 3 (see FIG 2:15) is
screwed tight on its seat.
2 Keep the carburetter cover 1 upright or else the weight
of the float 9 will lower the ball 8 fitted on the needle 4.
F50043
Key to Fig 2:17 1 Filter housing 2 Spring hooks
3 Filter element 4 Cover 5 Air suction pipe, hoses
and clamps 6 Re-circulation pipe for blow-by gases and
oil vapoursFIG 2:17 Removing the air cleaner, 500F, L
2
1 3
4.
6
5
FIG 2:16 Taking out the filter element, 500, 500D AIR CLEANER ELBOW
HOSE
AIR CLEANER BODY
FILTER ELEMENT Check that with the cover held in the vertical position
and the float arm 6 in slight contact with the ball 8 of the
needle 4, the float is .2953 inch away from the cover
w i t h its gasket 2 fitted flat against the cover face.
3 Check that the float level is .5709 inch from the cover
face and if necessary bend the lug 5 to give the required
setting.
4 If the float 9 is not correctly positioned bend the float
arm 7 until the correct adjustment is obtained. Ensure
that the arm 6 is perpendicular to the needle axis and
does not show any rough spots or indentations which
might impair free movement of the needle. Check that
the float 9 moves about its pivot pin.
Every time a new float or needle valve is fitted the above
detailed adjustment operations must be completed to
ensure correct fuel levels.
Page 37 of 128
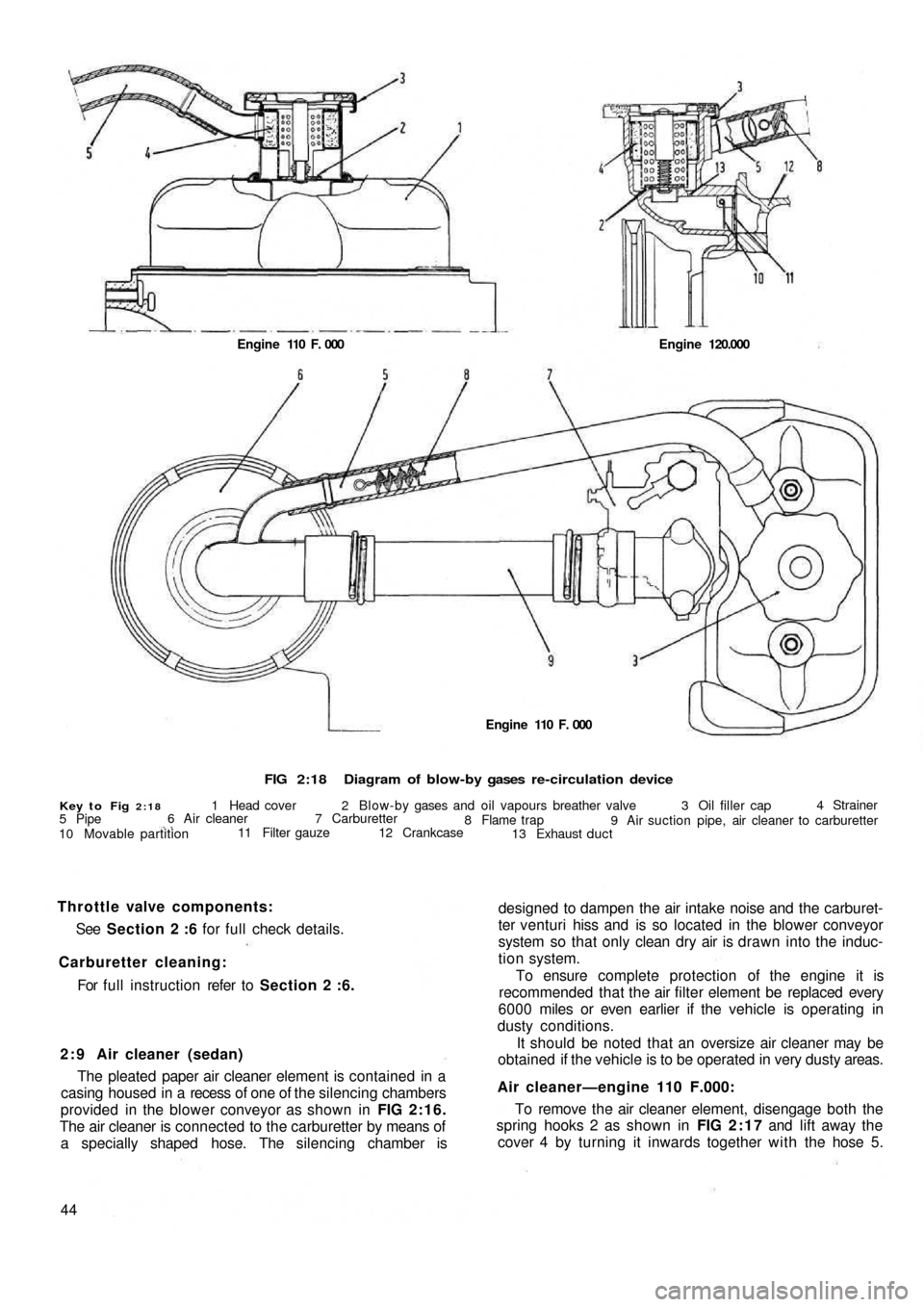
FIG 2:18Diagram of blow-by gases re-circulation device
Key to Fig 2:181 Head cover 2 Blow-by gases and oil vapours breather valve 3 Oil filler cap4 Strainer
9 Air suction pipe, air cleaner to carburetter 8 Flame trap
13 Exhaust duct 12 Crankcase 7 Carburetter 6 Air cleaner
11 Filter gauze
10 Movable partition 5 PipeEngine 110 F. 000 Engine 120.000
designed to dampen the air intake noise and the carburet-
ter venturi hiss and is so located in the blower conveyor
system so that only clean dry air is drawn into the induc-
tion system.
To ensure complete protection of the engine it is
recommended that the air filter element be replaced every
6000 miles or even earlier if the vehicle is operating in
dusty conditions.
It should be noted that an oversize air cleaner may be
obtained if the vehicle is to be operated in very dusty areas.
Air cleaner—engine 110 F.000:
To remove the air cleaner element, disengage both the
spring hooks 2 as shown in FIG 2:17 and lift away the
cover 4 by turning it inwards together with the hose 5. 2 : 9 Air cleaner (sedan)
The pleated paper air cleaner element is contained in a
casing housed in a recess of one of the silencing chambers
provided in the blower conveyor as shown in FIG 2:16.
The air cleaner is connected to the carburetter by means of
a specially shaped hose. The silencing chamber is
44For full instruction refer to Section 2 :6. Carburetter cleaning:See Section 2 :6 for full check details. Throttle valve components:
Engine 110 F. 000
Page 50 of 128

4 : 4 Heating system safety device
110F series sedan engines and later station wagon
engines incorporate a modification to the cylinder head
designed so that in the event of cylinder head gasket
failure exhaust gases are expelled outside the engine and
not leaked into the heating system.
The safety device comprises a square section circular
seat 1 (see FIG 4 :6) which is formed in the upper face of
the cylinder, a special duct in the cylinder head and a
pierced screw 3 for each cylinder.
The system is so designed that the exhaust gases are
released to the atmosphere from the circular seat in the
cylinder via the duct 2 and the pierced screw 3. It should
be noted that the screw 3 is also used for securing the
conveyor.
4 : 5 Maintenance
Due to the simple design of the air cooling system
maintenance has been kept to an absolute minimum and
should consist of the following checks:1 Inspect all the air conveyor system joints and ensure
that all the joint nuts and bolts are tight and that there
is no distortion between two joint faces.
2 Check that the tension of the generator and fan drive
belt is correct: with a hand pressure of approximately
22 Ib the belt should sag 13/32 inch. Adjust if necessary
as detailed in Chapter 1.
3 Ensure that the shutter can swivel freely and that the
spring is in a serviceable condition.
4 : 6 Fault diagnosis
(a) Engine overheating
1 Generator and fan drive belt slipping
2 Shutter control thermostat defective
3 Shutter unable to swivel freely
4 Shutter return spring broken
5 Leaking joints in conveyor system
F50057
Page 60 of 128
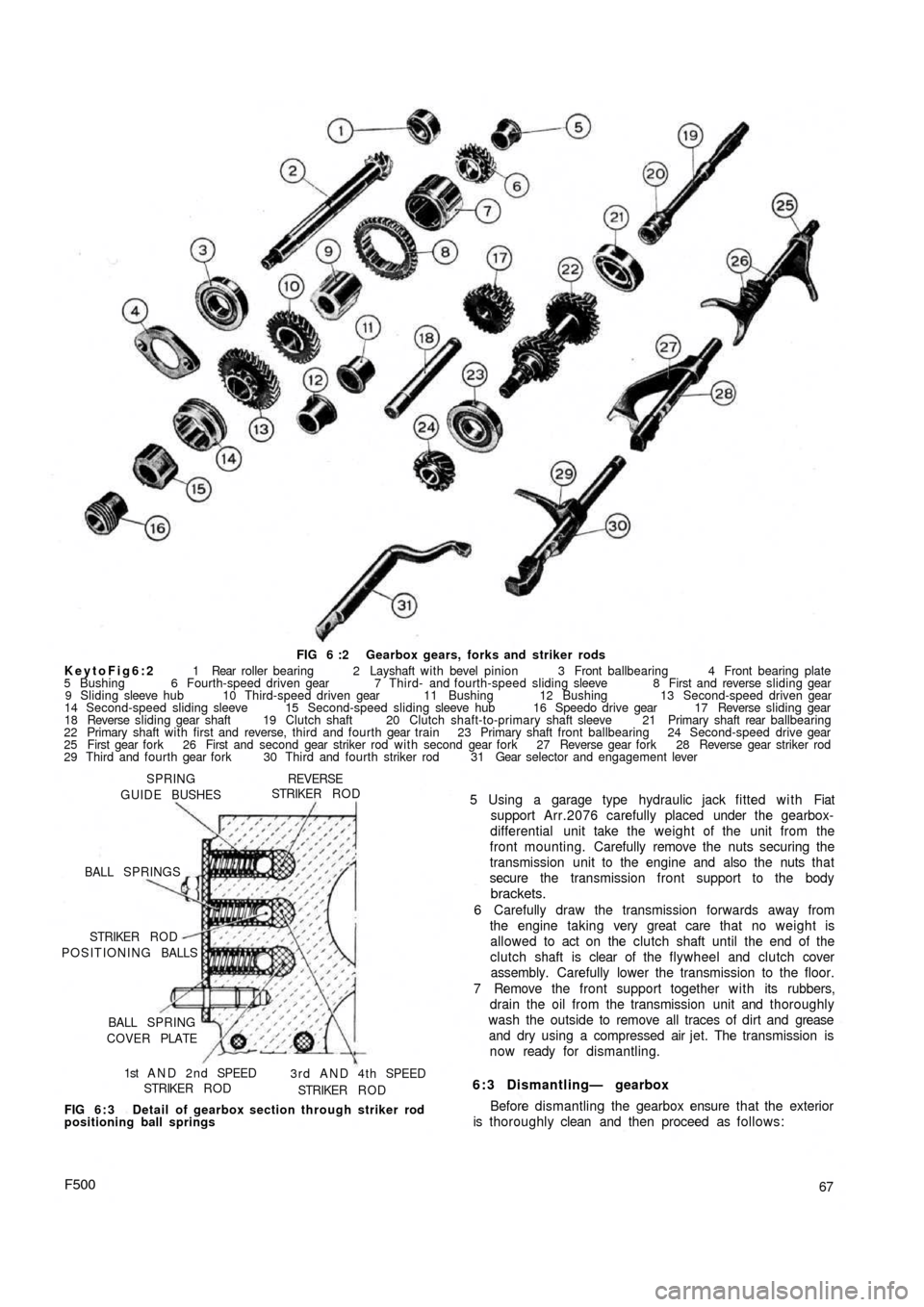
FIG 6 :2 Gearbox gears, forks and striker rods
KeytoFig6:2 1 Rear roller bearing 2 Layshaft with bevel pinion 3 Front ballbearing 4 Front bearing plate
5 Bushing 6 Fourth-speed driven gear 7 Third- and fourth-speed sliding sleeve 8 First and reverse sliding gear
9 Sliding sleeve hub 10 Third-speed driven gear 11 Bushing 12 Bushing 13 Second-speed driven gear
14 Second-speed sliding sleeve 15 Second-speed sliding sleeve hub 16 Speedo drive gear 17 Reverse sliding gear
18 Reverse sliding gear shaft 19 Clutch shaft 20 Clutch shaft-to-primary shaft sleeve 21 Primary shaft rear ballbearing
22 Primary shaft with first and reverse, third and fourth gear train 23 Primary shaft front ballbearing 24 Second-speed drive gear
25 First gear fork 26 First and second gear striker rod with second gear fork 27 Reverse gear fork 28 Reverse gear striker rod
29 Third and fourth gear fork 30 Third and fourth striker rod 31 Gear selector and engagement lever
SPRING
GUIDE BUSHES
REVERSESTRIKER R O D
BALL SPRINGS
POSITIONING BALLS STRIKER R O D
BALL SPRING
COVER PLATE
1st A N D 2 n d SPEED
STRIKER R O D3 r d A N D 4 t h SPEED
STRIKER R O D
FIG 6 : 3 Detail of gearbox section through striker rod
positioning ball springs
F50067 5 Using a garage type hydraulic jack fitted with Fiat
support Arr.2076 carefully placed under the gearbox-
differential unit take the weight of the unit from the
front mounting. Carefully remove the nuts securing the
transmission unit to the engine and also the nuts that
secure the transmission front support to the body
brackets.
6 Carefully draw the transmission forwards away from
the engine taking very great care that no weight is
allowed to act on the clutch shaft until the end of the
clutch shaft is clear of the flywheel and clutch cover
assembly. Carefully lower the transmission to the floor.
7 Remove the front support together with its rubbers,
drain the oil from the transmission unit and thoroughly
wash the outside to remove all traces of dirt and grease
and dry using a compressed air jet. The transmission is
now ready for dismantling.
6:3 Dismantling— gearbox
Before dismantling the gearbox ensure that the exterior
is thoroughly clean and then proceed as follows:
Page 61 of 128
1st A N D 2 n d SPEED
STRIKER R O D LOCK
ROLLER1st A N D 2 n d SPEED
STRIKER R O D 3 r d A N D 4 t h SPEED
STRIKER R O D 3 r d A N D 4 t h SPEED
STRIKER R O D LOCK -
ROLLER REVERSE STRIKER
ROD LOCK ROLLER
REVERSESTRIKER R O D
FIG 6 : 4 Detail of gearbox section through striker rod
lock rollers
2 n d SPEED DRIVENGEAR2 n d SPEED ENGAGEMENT SLIDING SLEEVE 2 n d SPEED FORK 1st A N D 2 n d
SPEED STRIKER R O D REVERSE GEAR3rd AND 4th
SPEED STRIKER R O DREVERSE STRIKER R O D2 n d SPEED DRIVE GEAR SPEED SELECTOR LEVER
FIG 6 : 5 Cross section of gearbox through striker rods
with the indication of the gear selector lever angular
displacement
68
AXLE SHAFT-TO-JOINT SLEEVE
OIL BOOT
RING GEAR
FIG 6:6 Differential unit complete with axle shafts
BEARING CONEADJUSTER LOCK RING BEARING HOUSING DIFFERENTIAL CASE
OIL BOOT RETAINER
AXLE SHAFT
1 Remove the speedometer drive support together with
its gears. Remove the front cover together with its
gasket and the gear selection rod (see FIG 6:2).
2 Remove the lock ring and carefully slide the splined
sleeve from the axle shafts. Remove the t w o roller
bearing housings together with the relevent rubber
boot fastening cover, the rubber boots and the adjuster
ring lock rings.
3 Detach the transmission mounting on engine support
and carefully remove the differential case assembly
complete w i t h the ring gear and axle shafts.
4 Open the fasteners and loosen all the shifter fork lock
bolts.
5 Engage t w o gears at the same time so locking the
input shaft and the mainshaft together. Remove the
cotter pins and the nuts on the front end of the input
shaft and the mainshaft.
6 Remove the retaining cover located on the lefthand
side of the gearbox and carefully take out the shifter
rod positioning balls and springs from their bores.
Remove the upper shifter fork shaft and shifter fork,
the middle shifter fork shaft together with its interlock
pin and also the third and fourth gear shifter fork.
Remove the plain washer and speedometer drive
driving gear from the layshaft.
7 Remove the second gear engagement sliding sleeve
together with the shifter fork, shifter fork shaft, sliding
sleeve hub, second-speed driven gear with relevent
bush and the first gear engagement
fork. Take very
great care not to drop the safety rollers whilst extract-
ing the striker rods.
8 Remove the second-speed driving gear from the input
shaft. Release the reverse shaft retaining screw and
remove the shaft together with the reverse gear cluster.
Remove the layshaft front bearing retaining plate.
9 Push the input shaft forwards until both ballbearing
races are pressed from their seating and the coupling
sleeve located between the input shaft and the clutch
shaft can be reached from above. Carefully remove the
retaining ring and a connection pin at the input shaft
side of the coupling sleeve and carefully withdraw the
clutch shaft and coupling sleeve.
10 Remove the input shaft front bearing race. Tilt the
primary shaft in the casing and remove it from the
gearbox housing. Remove the rear bearing. Carefully
Page 65 of 128
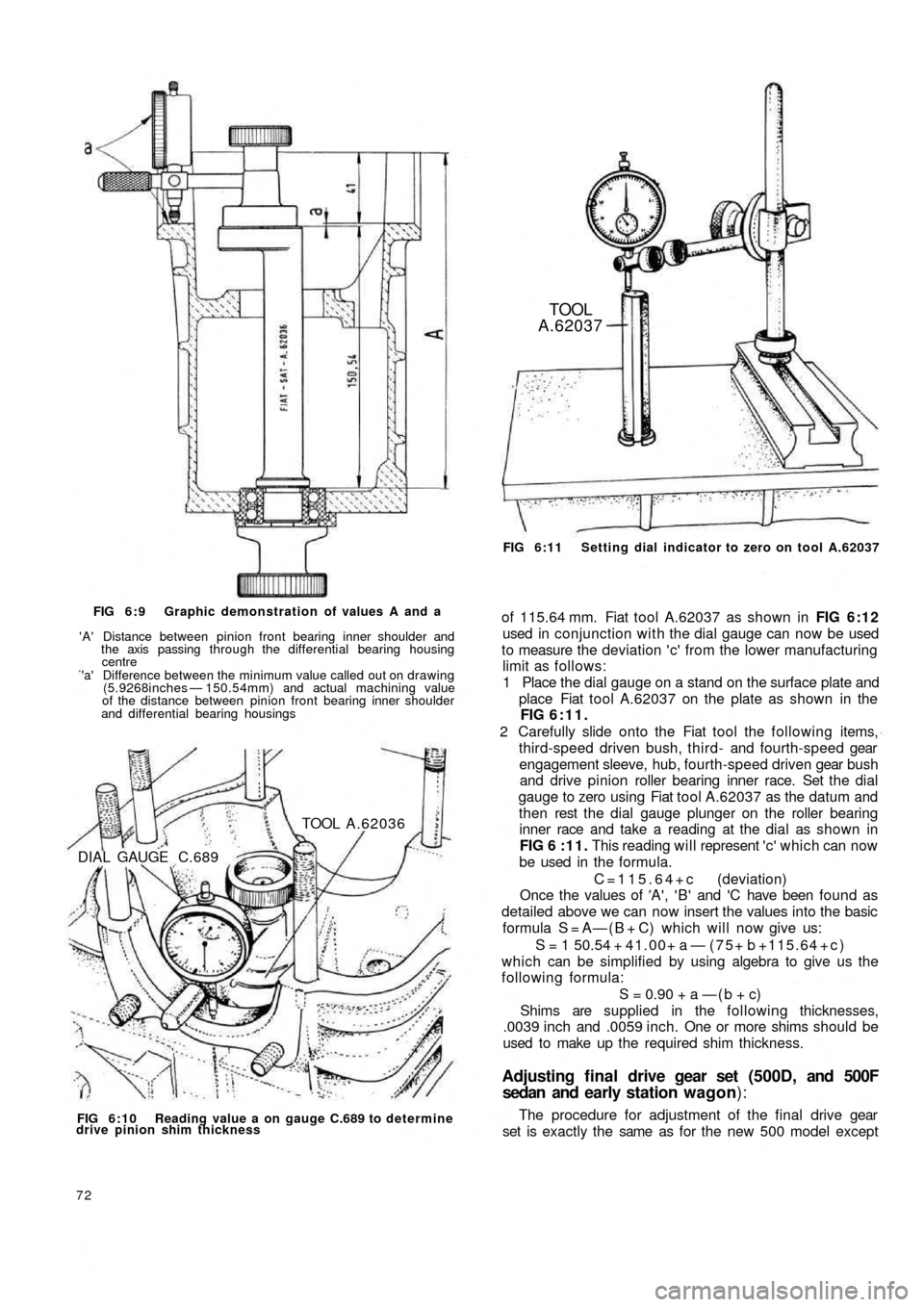
FIG 6:9 Graphic demonstration of values A and a
'A' Distance between pinion front bearing inner shoulder and
the axis passing through the differential bearing housing
centre'a' Difference between the minimum value called out on drawing
(5.9268inches — 150.54mm) and actual machining value
of the distance between pinion front bearing inner shoulder
and differential bearing housings
DIAL GAUGE C.689TOOL A.62036
FIG 6:10 Reading value a on gauge C.689 to determine
drive pinion shim thickness
72The procedure for adjustment of the final drive gear
set is exactly the same as for the new 500 model except of 115.64 mm. Fiat tool A.62037 as shown in FIG 6:12
used in conjunction with the dial gauge can now be used
to measure the deviation 'c' from the lower manufacturing
limit as follows:
1 Place the dial gauge on a stand on the surface plate and
place Fiat tool A.62037 on the plate as shown in the
FIG 6 : 1 1 .
2 Carefully slide onto the Fiat tool the following items,
third-speed driven bush, third- and fourth-speed gear
engagement sleeve, hub, fourth-speed driven gear bush
and drive pinion roller bearing inner race. Set the dial
gauge to zero using Fiat tool A.62037 as the datum and
then rest the dial gauge plunger on the roller bearing
inner race and take a reading at the dial as shown in
FIG 6 :11. This reading will represent 'c' which can now
be used in the formula.
C=115.64+c (deviation)
Once the values of A', ' B ' and 'C have been found as
detailed above we can now insert the values into the basic
formula S = A—(B + C) which will now give us:
S = 1 50.54 + 41.00+ a — (75+ b +115.64 + c )
which can be simplified by using algebra to give us the
following formula:
S = 0.90 + a — ( b + c)
Shims are supplied in the following thicknesses,
.0039 inch and .0059 inch. One or more shims should be
used to make up the
required shim thickness.
Adjusting final drive gear set (500D, and 500F
sedan and early station wagon):
FIG 6:11 Setting dial indicator to zero on tool A.62037
TOOL
A.62037
Page 66 of 128
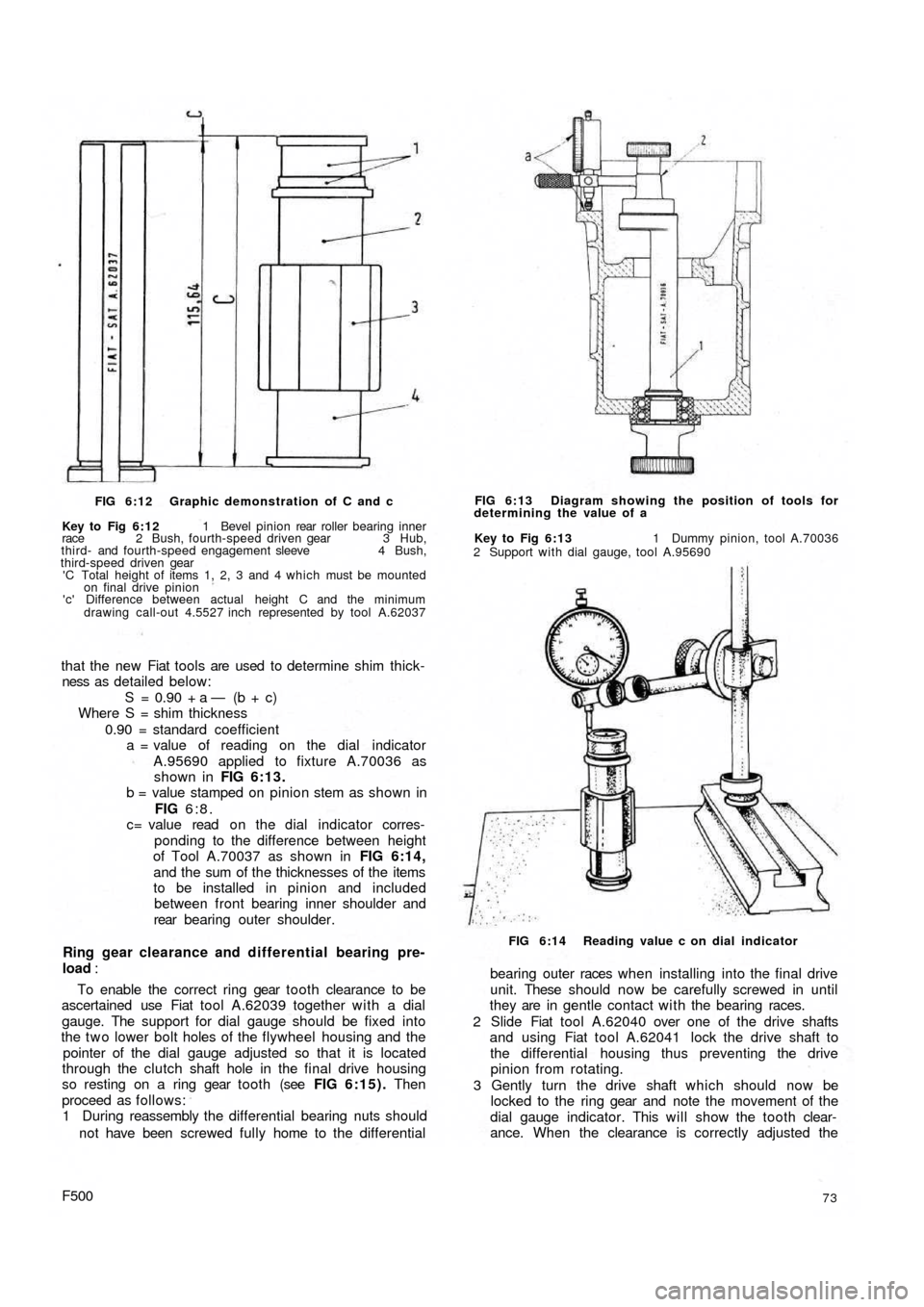
FIG 6:12 Graphic demonstration of C and c
Key to Fig 6:12 1 Bevel pinion rear roller bearing inner
race 2 Bush, fourth-speed driven gear 3 Hub,
third- and fourth-speed engagement sleeve 4 Bush,
third-speed driven gear
'C Total height of items 1, 2, 3 and 4 which must be mounted
on final drive pinion
'c' Difference between actual height C and the minimum
drawing call-out 4.5527 inch represented by tool A.62037
that the new Fiat tools are used to determine shim thick-
ness as detailed below:
S = 0.90 + a — (b + c)
Where S = shim thickness
0.90 = standard coefficient
a = value of reading on the dial indicator
A.95690 applied to fixture A.70036 as
shown in FIG 6:13.
b = value stamped on pinion stem as shown in
FIG 6:8.
c= value read o n the dial indicator corres-
ponding to the difference between height
of Tool A.70037 as shown in FIG 6:14,
and the sum of the thicknesses of the items
to be installed in pinion and included
between front bearing inner shoulder and
rear bearing outer shoulder.
Ring gear clearance and differential bearing pre-
load :
To enable the correct ring gear tooth clearance to be
ascertained use Fiat tool A.62039 together with a dial
gauge. The support for dial gauge should be fixed into
the t w o lower bolt holes of the flywheel housing and the
pointer of the dial gauge adjusted so that it is located
through the clutch shaft hole in the final drive housing
so resting on a ring gear tooth (see FIG 6:15). Then
proceed as follows:
1 During reassembly the differential bearing nuts should
not have been screwed fully home to the differential
F50073
bearing outer races w h e n installing into the f i n a l drive
unit. These should now be carefully screwed in until
they are in gentle contact with the bearing races.
2 Slide Fiat tool A.62040 over one of the drive shafts
and using Fiat tool A.62041 lock the drive shaft to
the differential housing thus preventing the drive
pinion from rotating.
3 Gently turn the drive shaft which should now be
locked to the ring gear and note the movement of the
dial gauge indicator. This will show the tooth clear-
ance. When the clearance is correctly adjusted the
FIG 6:14 Reading value c on dial indicator Key to Fig 6:13 1 Dummy pinion, tool A.70036
2 Support with dial gauge, tool A.95690 FIG 6:13 Diagram showing the position of tools for
determining the value of a
Page 67 of 128

TOOL A 62039
TOOLA. 62040 PIN WRENCH A. 52022
FIG 6:15 Adjusting ring gear-to-pinion backlash and
differential bearing play, using special wrench A.52022
reading on the dial gauge should be between .0031 to
.0047 inch. The actual clearance is adjusted by
screwing in one adjusting nut and screwing out the
other by the equivalent amount using Fiat spanner
A.52022 as shown in FIG 6:15.
4 Remove Fiat tool A.62041 and using Fiat support
A.62040 mount the special dynamometer A.95697 and
adaptor on the axle shaft. Rotate the axle shaft several
turns so seating the bearings and then check using
the dynamometer the rotation torque.
5 If necessary tighten or slacken the adjusters until the
specified torque of 1.01 ± .07 lb ft is obtained. This
operation must be very carefully carried out because if
one adjuster is set differently with respect to the other,
a variation in ring gear to pinion backlash may take
place, resulting in a variation of rotation torque. After
any adjustments always recheck on the ring gear to
pinion backlash and if necessary readjust and then
repeat the rotation torque check.
6 Finally check the tooth contact between the pinion
and ring gear as detailed in the following instructions:
Check and adjustment of tooth contact between
pinion and ring gear:
1 Carefully apply to the ring gear teeth a thin layer of
engineers' blue and gently rotate the differential whilst
holding the axle shaft firmly but allowing them to slip
slightly so as to have the unit working under load
conditions.
2 A contact impression will be left on the ring gear teeth
and the contact will be correct when the drive pinion
tooth contact pattern is evenly distributed on the ring
gear teeth as shown in FIG 6:16. Should the tooth
contact be incorrect the following observations should
be noted.
Excessive contact on tooth flank. Too deep
meshing — move pinion out from ring gear by reducing
thickness of shim.
Excessive contact on tooth heel. Too slight
meshing—move pinion in towards ring gear by
increasing thickness of shim.
74
6 : 8 Replacement of gearbox—differential unit
Installation is the reverse procedure to removal of the
unit from the vehicle as described in Section 6:2.
However, the following points should be noted:
1 Ensure that the clutch driven disc hub is correctly
aligned with the clutch shaft pilot bush.
2 The complete transmission unit should be carefully
pushed towards the engine and the clutch shaft
inserted into the driven disc hub splines and finally
home into the pilot bush. Extreme care must be taken
to ensure that no weight is placed on the clutch shaft
otherwise distortion may take place.
3 Carefully connect the gearbox rear housing to the
engine crankcase by using the studs, t w o of which
have special location dowels fitted. Screw home
finger tight the gearbox/differential to body to front
support mounting screws inserting the fibre washers.
Lower the hydraulic garage jack and pull it away from
underneath the vehicle. Screw in the four lower
mounting nuts and tighten to a torque wrench setting
of between 18.1 to 21.7 Ib f t.Finally tighten the front
support screws.
4 Reconnect the gear shift control rod and the speedo-
meter drive cable. Insert the springs between the axle
shafts and wheel drive shaft and tighten the
three
mounting screws of each splined sleeve on the
flexible joint to a torque wrench setting of 20.3 Ib ft.
5 Refit the flywheel housing cover. Replace the starter
motor together with its relevant cover and tighten the
two mounting nuts to a torque wrench setting of
18.1 to 21.7 Ib ft. Reconnect the starter control rod,
the t w o starter cables, the clutch control tie rod and
hook up the return spring and secure the clutch
control cable retainer bracket to the gearbox casings.
Reconnect the cable to the battery positive terminal
post
6 Lower the vehicle to the floor gently and then give a
thorough road testing.
6 :9 Swing axle shafts and slip joints
Description:
The t w o axle shafts are connected to the differential
unit through specially designed slip joints which allow
the shafts to swing and slide in the splined housing in
the differential side gear. At the other end, the axle shafts
are connected to the wheel drive shaft flexible joints
using a sliding sleeve. Excessive contact on tooth face. Too slight
meshing—move pinion in towards ring gear by in-
creasing thickness of shim.
Excessive contact of tooth toe. Too deep meshing
—move pinion out from ring gear by reducing thickness
of shim.
With all the above detailed cases, to adjust the pinion
by replacing the shim, the differential unit and drive
pinion shaft must be dismantled. This means that when
the unit is reassembled after the necessary adjustments
have been made, the backlash and bearing rotation
torque must be repeated.